The Gas- and Condensed-Phase Efficacy of Functionalized Phosphorus Flame Retardants for Cotton Fabric: Phenyl vs. Phenoxy Groups
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Coating Procedure
2.3. Vertical Flame Test
2.4. Spectroscopy
2.4.1. FT-IR
2.4.2. Raman Spectroscopy
2.5. TGA
2.6. TG-IR
2.7. MCC
2.8. SEM
2.9. ICP-OES
3. Results
3.1. Characterization and Coating Procedure
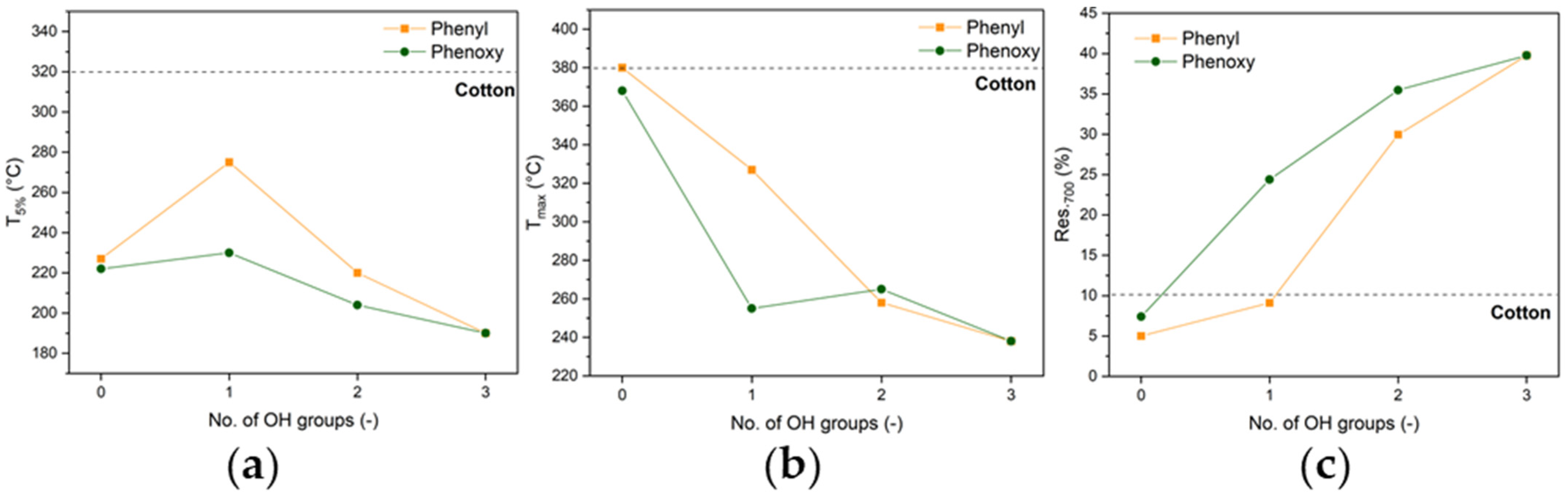
3.2. Thermal Behavior
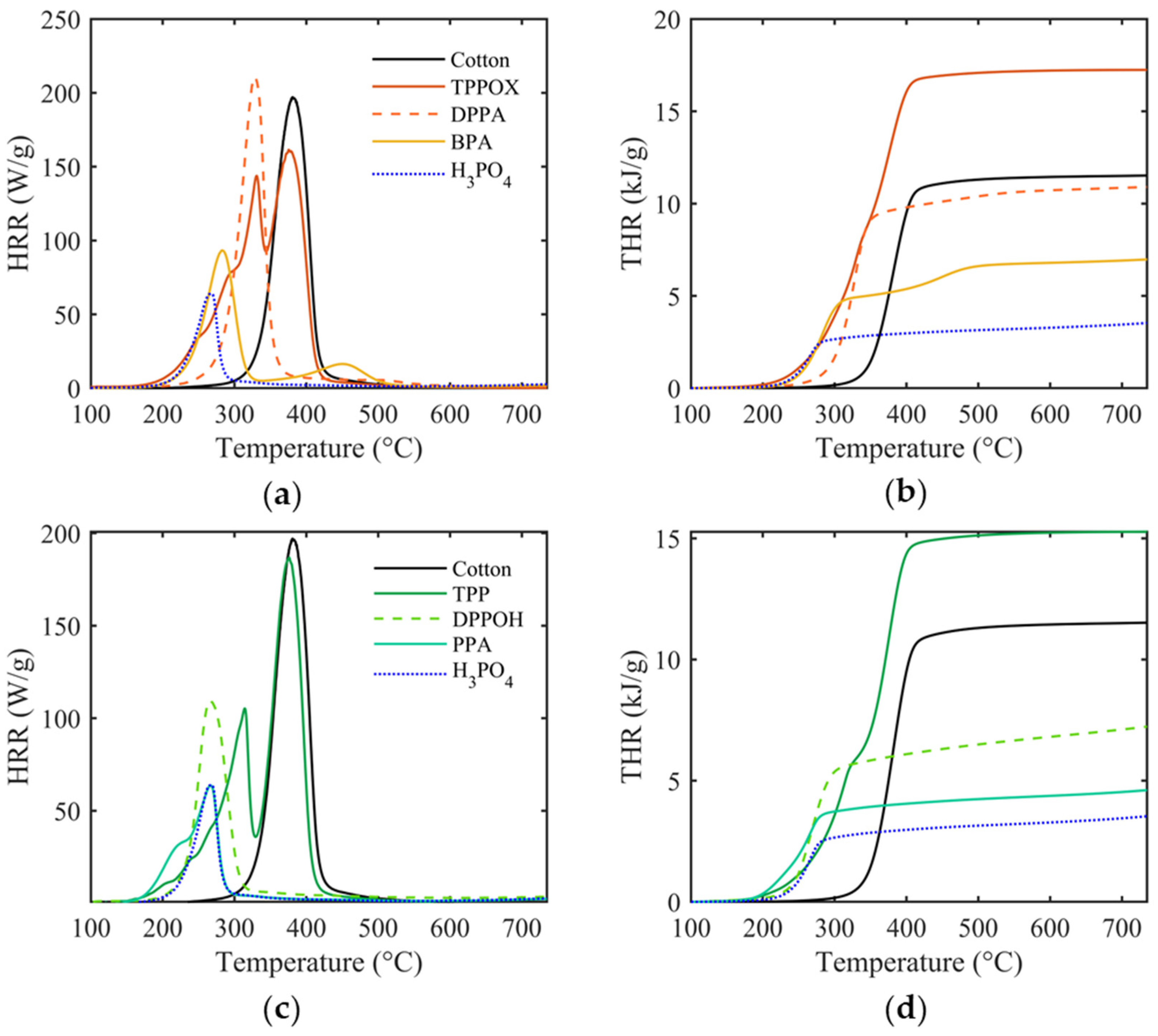
3.3. Combustion Behavior
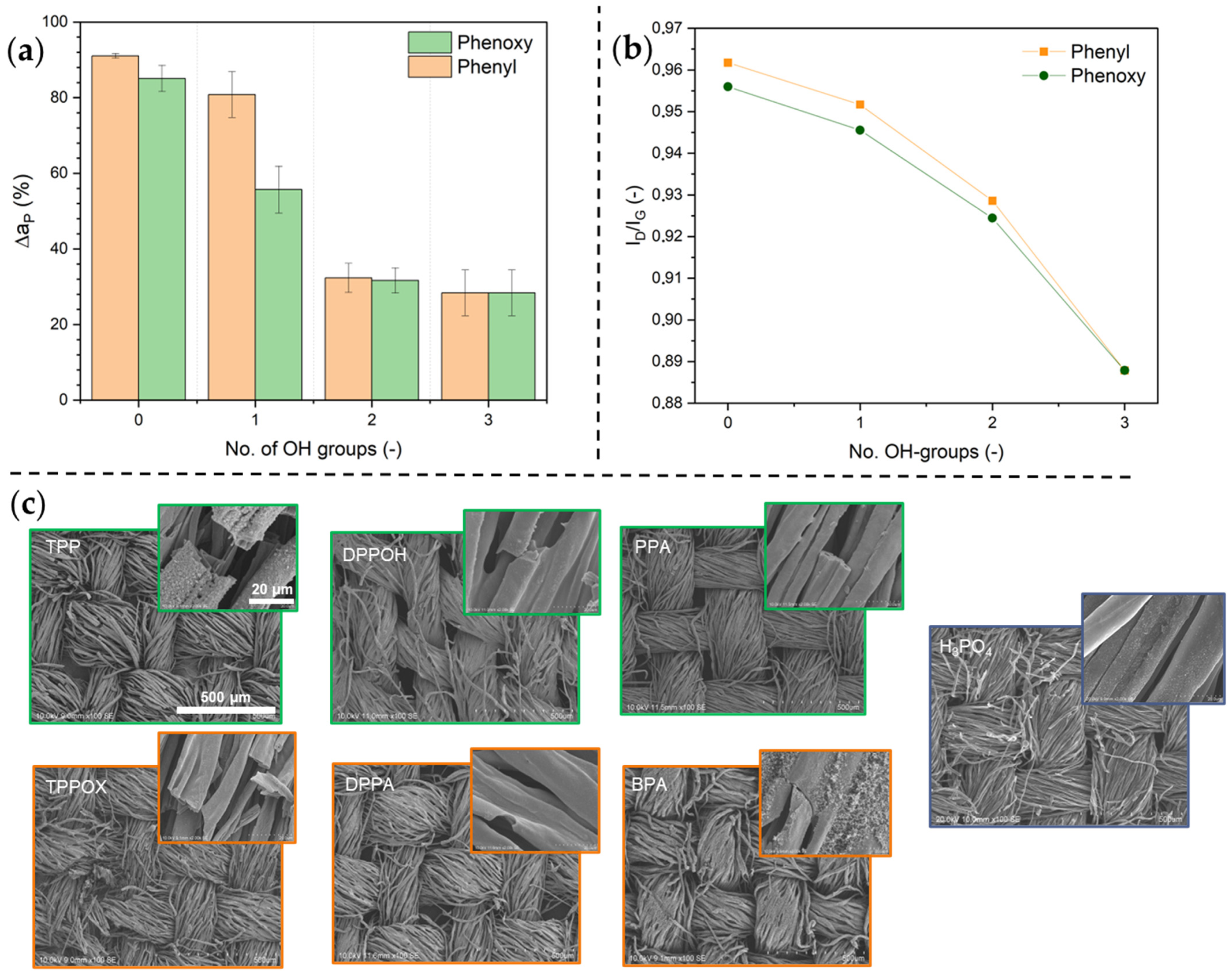
3.4. Flame Test and Condensed-Phase Analysis
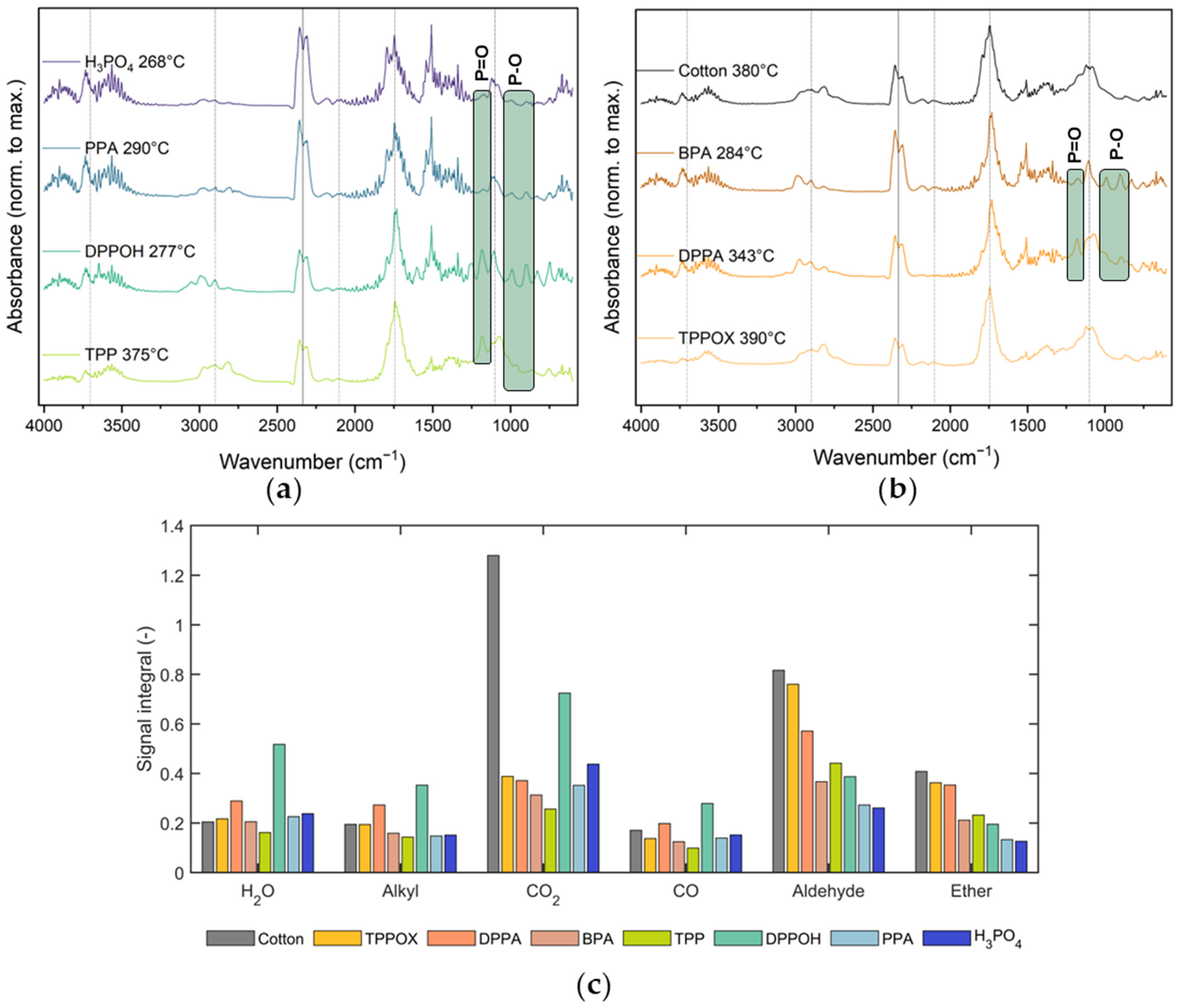
3.5. Gas-Phase Analysis Using TG-IR
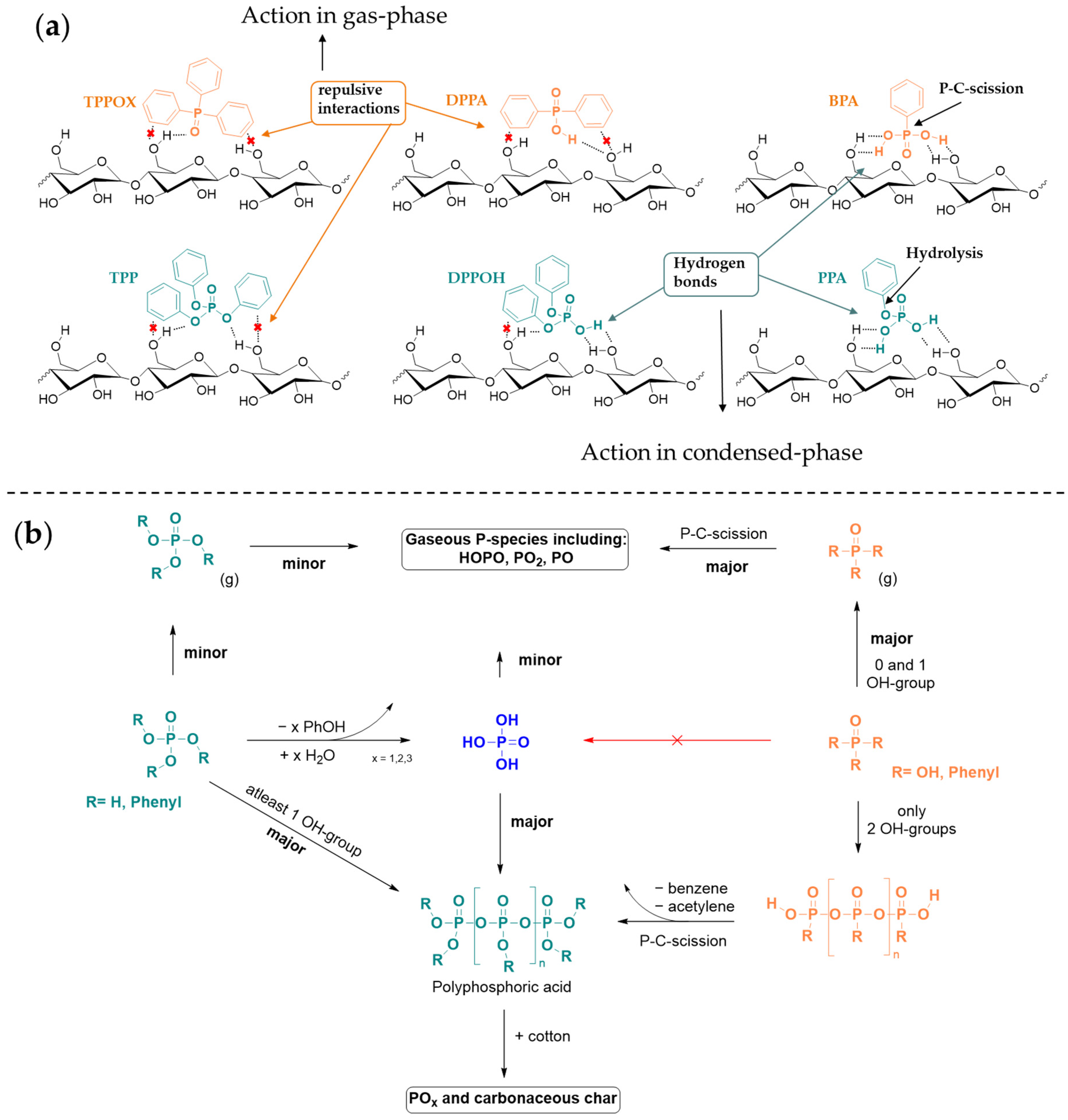
4. Discussion
5. Summary and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trovato, V.; Sfameni, S.; Ben Debabis, R.; Rando, G.; Rosace, G.; Malucelli, G.; Plutino, M.R. How to Address Flame-Retardant Technology on Cotton Fabrics by Using Functional Inorganic Sol–Gel Precursors and Nanofillers: Flammability Insights, Research Advances, and Sustainability Challenges. Inorganics 2023, 11, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velencoso, M.M.; Battig, A.; Markwart, J.C.; Schartel, B.; Wurm, F.R. Molecular Firefighting-How Modern Phosphorus Chemistry Can Help Solve the Challenge of Flame Retardancy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2018, 57, 10450–10467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabani, V.; Ali, W.; Assfour, B.; Otto, R.; Killa, D.; Caglar, S.; Feng, Y.; Shin, E.; Gutmann, J.S.; Mayer-Gall, T. Impact of phosphonate and phosphoramidate in Si/P/triazine hybrid flame retardants on cotton flammability. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2025, 232, 111107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer-Gall, T.; Knittel, D.; Gutmann, J.S.; Opwis, K. Permanent flame retardant finishing of textiles by allyl-functionalized polyphosphazenes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 9349–9363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Kolibaba, T.J.; Lazar, S.; Grunlan, J.C. Facile two-step phosphazine-based network coating for flame retardant cotton. Cellulose 2020, 27, 4123–4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilke, O.; Ali, W.; Kamps, L.; Engels, T.; Schumacher, S.; Danielsiek, D.; Shabani, V.; Salma, A.; Plohl, D.; Wallmeier, R.; et al. Water-Soluble Cyclophosphazenes as Durable Flame-Retardant Finishes for Nylon/Cotton Blend Fabrics. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2022, 4, 8833–8846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Li, H.; He, Y.; Liu, Y.; Dong, C.; Zhu, P. Flame retardancy and thermal behavior of cotton fabrics based on a novel phosphorus-containing siloxane. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 479, 765–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, R.; Gaan, S. Recent developments in P(O/S)–N containing flame retardants. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 47910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmeia, K.A.; Jovic, M.; Ragaisiene, A.; Rukuiziene, Z.; Milasius, R.; Mikucioniene, D.; Gaan, S. Flammability of Cellulose-Based Fibers and the Effect of Structure of Phosphorus Compounds on Their Flame Retardancy. Polymers 2016, 8, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Nguyen, M.; Condon, B.; Smith, J. The comparison of phosphorus-nitrogen and sulfur-phosphorus-nitrogen on the anti-flammability and thermal degradation of cotton fabrics. Fibers Polym. 2017, 18, 666–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymańska, A.; Przybylak, M.; Dutkiewicz, M.; Maciejewski, H. Synthesis of phosphorus, sulfur and silicon-containing flame retardant via thiol-ene click reaction and its use for durable finishing of cotton fabric. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 20132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.; Xie, S.; Zhao, Q.; Guan, J.; Wu, C.; Wang, P. Reactive P/S/N-containing synergistic flame retardant towards eco-friendly durable flame-retardant cotton fabric: Flame-retardant property, durability and mechanism. Polym. Test. 2023, 118, 107918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alongi, J.; Colleoni, C.; Rosace, G.; Malucelli, G. Thermal and fire stability of cotton fabrics coated with hybrid phosphorus-doped silica films. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2012, 110, 1207–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alongi, J.; Colleoni, C.; Rosace, G.; Malucelli, G. Phosphorus- and nitrogen-doped silica coatings for enhancing the flame retardancy of cotton: Synergisms or additive effects? Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deh, S.; Gähr, F.; Buchmeiser, M.R. Synergistic effects in the pyrolysis of phosphorus-based flame-retardants: The role of Si- and N-based compounds. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2016, 130, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappes, R.S.; Urbainczyk, T.; Artz, U.; Textor, T.; Gutmann, J.S. Flame retardants based on amino silanes and phenylphosphonic acid. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2016, 129, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, W.; Zilke, O.; Danielsiek, D.; Salma, A.; Assfour, B.; Shabani, V.; Caglar, S.; Phan, H.M.; Kamps, L.; Wallmeier, R.; et al. Flame-retardant finishing of cotton fabrics using DOPO functionalized alkoxy- and amido alkoxysilane. Cellulose 2023, 30, 2627–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernyy, S.; Ulah, S.; Sørensen, G.; Tordrup, S.W.; Pedersen, P.B.; Almdal, K. DOPO-VTS-based coatings in the realm of fire retardants for cotton textile. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 41955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Hu, Y.; Song, L.; Lu, H. Effect of modified organic–inorganic hybrid materials on thermal properties of cotton fabrics. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2011, 103, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiljević, J.; Jerman, I.; Jakša, G.; Alongi, J.; Malucelli, G.; Zorko, M.; Tomšič, B.; Simončič, B. Functionalization of cellulose fibres with DOPO-polysilsesquioxane flame retardant nanocoating. Cellulose 2015, 22, 1893–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Luo, F.; Li, H.; Chen, D. Synthesis of a graft-functionalized flame retardant based on DOPO and its application on the surface of terylene/cotton fabrics. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2024, 141, e54976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.-M.; Yu, C.-J.; Choe, K.-S.; Choe, C.-H.; Kim, C.-H. Preparation and flame retardant properties of cotton fabrics treated with resorcinol bis(diphenyl phosphate). Cellulose 2021, 28, 4455–4467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Li, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, P. Flame retardant cotton fabrics with anti-UV properties based on tea polyphenol-melamine-phenylphosphonic acid. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 629, 392–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paosawatyanyong, B.; Jermsutjarit, P.; Bhanthumnavin, W. Surface nanomodification of cotton fiber for flame retardant application. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2012, 12, 748–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attia, N.F.; Ameen, H.; El-Sayed, I.E.; Galhoum, A.A.; Xin, J.; Lu, X. Greener tool for synthesis and characterization of textile fabric’s coatings for good flame retardancy, antibacterial and reinforcement properties. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2024, 149, 9131–9143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, L.; Zhu, Z. Fabrication of hydrophobic and flame-retardant cotton fabric via sol–gel method. Cellulose 2023, 30, 11829–11843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Qiu, S.; Xi, J.; Yu, B.; Hu, Y.; Xing, W. Construction of super-hydrophobic, highly effective flame retardant coating for cotton fabric with superior washability and abrasion resistance. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 607, 2019–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alongi, J.; Malucelli, G. Cotton flame retardancy: State of the art and future perspectives. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 24239–24263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, F.; Wang, W.; Peng, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, M.; Wang, W.; Ma, J. Innovative development of green nitrogen-phosphorus-based flame retardant for enhancing fire safety of cotton fabrics. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2025, 231, 111089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Tang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Diao, S.; Zhang, G. Formaldehyde-free durable flame-retardant finishing for polyester/cotton blended fabrics through chemical grafting and cross-linking. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2023, 217, 110531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Xie, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, S.; Li, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, P.; Lu, Z.; et al. A novel P/N-based flame retardant synthesized by one-step method toward cotton materials and its flame-retardant mechanism. Cellulose 2021, 28, 3249–3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, U.; Balabanovich, A.I.; Schartel, B.; Knoll, U.; Artner, J.; Ciesielski, M.; Döring, M.; Perez, R.; Sandler, J.K.; Altstädt, V.; et al. Influence of the oxidation state of phosphorus on the decomposition and fire behaviour of flame-retarded epoxy resin composites. Polymer 2006, 47, 8495–8508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monge, S. Phosphorus-Based Polymers: From Synthesis to Applications, 1st ed.; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2014; ISBN 9781782624523. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, G.; Tao, Y.; Wu, Q.; Shen, H.; Sun, J.; Deng, D.; Liu, X. DOPO-based derivatives with different phosphorous oxidation states as highly efficient flame retardants for epoxy resins. Polym. Bull. 2024, 81, 6131–6148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hergenrother, P.M.; Thompson, C.M.; Smith, J.G.; Connell, J.W.; Hinkley, J.A.; Lyon, R.E.; Moulton, R. Flame retardant aircraft epoxy resins containing phosphorus. Polymer 2005, 46, 5012–5024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Chen, J.; Ruan, S.; Liu, F.; Zhang, L. Theoretical study on the effect of oxidation states of phosphorus flame retardants on their mode of action. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2024, 223, 110735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.-Y.; Song, W.-M.; Wang, B.-H.; Li, P.; Ni, Y.-P.; Liu, Y. Multifunctional polyester-cotton fabrics with excellent flame retardancy, superhydrophobicity, antibacterial property and UV resistance. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2024, 228, 110897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, H.; Guo, Y.; Chen, Z.; Chen, T.; Yu, Y.; He, C.; Zhou, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Bu, Y.; et al. Synergistic effect of phenyl phosphoric acid derivatives and DOPO on multifunctional epoxy resin: Fire safety, mechanical properties, transparency and hydrophobicity. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2023, 216, 110471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN ISO 15025:2016; Protective Clothing—Protection Against Flame—Method of Test for Limited Flame Spread. European Committee for Standardization (CEN): Brussels, Belgium, 2016.
- ISO 11611:2024; Protective Clothing for Use in Welding and Allied Processes. European Committee for Standardization (CEN): Brussels, Belgium, 2024.
- ASTM D7309; Standard Test Method for Determining Flammability Characteristics of Plastics and Other Solid Materials Using Microscale Combustion Calorimetry. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2011.
- Zhu, P.; Sui, S.; Wang, B.; Sun, K.; Sun, G. A study of pyrolysis and pyrolysis products of flame-retardant cotton fabrics by DSC, TGA, and PY–GC–MS. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2004, 71, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.K.; Gu, S. The mechanism for thermal decomposition of cellulose and its main products. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 6496–6504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Neisius, M.; Mispreuve, H.; Naescher, R.; Gaan, S. Flame retardancy and thermal decomposition of flexible polyurethane foams: Structural influence of organophosphorus compounds. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2012, 97, 2428–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Bacon, R. Carbonization of cellulose fibers—I. Low temperature pyrolysis. Carbon 1964, 2, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamadi, A.; Sun, W.; Abid, S.; Chaumeix, N.; Comandini, A. An experimental and kinetic modeling study of benzene pyrolysis with C2−C3 unsaturated hydrocarbons. Combust. Flame 2022, 237, 111858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlowski, K.H.; Schartel, B. Flame retardancy mechanisms of triphenyl phosphate, resorcinol bis(diphenyl phosphate) and bisphenol A bis(diphenyl phosphate) in polycarbonate/acrylonitrile–butadiene–styrene blends. Polym. Int. 2007, 56, 1404–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariappan, T.; Zhou, Y.; Hao, J.; Wilkie, C.A. Influence of oxidation state of phosphorus on the thermal and flammability of polyurea and epoxy resin. Eur. Polym. J. 2013, 49, 3171–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Hu, Y.; Yang, L.; Cai, Y.; Song, L.; Chen, Z.; Fan, W. Fire retardant synergism between melamine and triphenyl phosphate in poly(butylene terephthalate). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2006, 91, 2093–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhena, T.C.; Sadiku, E.R.; Ray, S.S.; Mochane, M.J.; Matabola, K.P.; Motloung, M. Flame retardancy efficacy of phytic acid: An overview. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, e52495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
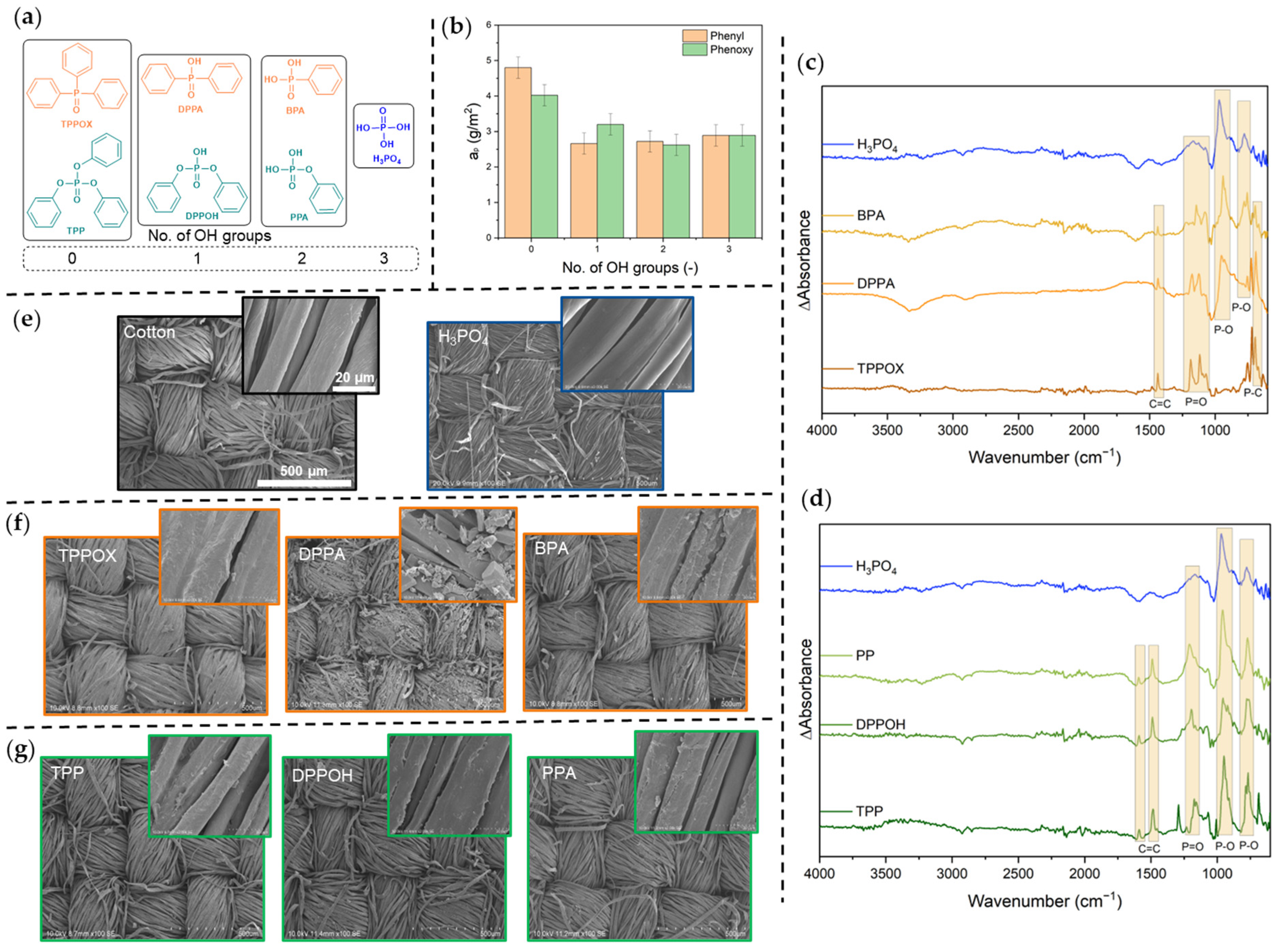



| No. of OH Groups | c (mol/L) | Solvent | Weight Gain Coating (wt. %) | aP (g/m2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 (TPPOX/TPP) | 1.08 | EtOH [t] | 20.5 ± 3.0 | 4.8 ± 0.3 |
| 0.92 | EtOH [t] | 22.0 ± 2.6 | 4.0 ± 0.3 | |
| 1 (DPPA/DPPOH) | 0.18 | EtOH [3p] | 6.6 ± 1.3 | 2.7 ± 0.3 |
| 0.20 | THF [3p] | 6.1 ± 1.9 | 3.2 ± 0.3 | |
| 2 (BPA/PPA) | 0.70 | EtOH [1p] | 3.8 ± 1.3 | 2.7 ± 0.3 |
| 0.57 | EtOH [1p] | 7.2 ± 1.8 | 2.6 ± 0.3 | |
| 3 (H3PO4) | 1.02 | EtOH [t] | 4.7 ± 2.1 | 2.9 ± 0.3 |
| No. of OH Groups | Aft. (s) | Char Yield (wt. %) | aP (g/m2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 (TPPOX/TPP) | 20.8 ± 1.5 | 10.9 ± 0.9 | 0.4 ± 0.2 |
| 17.0 ± 2.2 | 8.1 ± 0.7 | 0.6 ± 0.2 | |
| 1 (DPPA/DPPOH) | 11.3 ± 1.1 | 9.7 ± 1.0 | 0.5 ± 0.2 |
| 4.0 ± 0.8 | 33.3 ± 8.8 | 1.6 ± 0.2 | |
| 2 (BPA/PPA) | 5.5 ± 1.1 | 28.1 ± 3.6 | 1.8 ± 0.3 |
| 0.0 ± 0.0 | 31.7 ± 1.4 | 1.8 ± 0.2 | |
| 3 (H3PO4) | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 40.3 ± 3.5 | 2.1 ± 0.2 |
| T5% (°C) | Tmax (Res. %) (°C) | Res.700 (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cotton | 322 | 380 (42.2) | 10.2 | |||
| No. of OH Groups | Phenyl | Phenoxy | Phenyl | Phenoxy | Phenyl | Phenoxy |
| 0 (TPPOX/TPP) | 227 | 222 | 380 (34.4) | 368 (30.4) | 5.0 | 7.4 |
| 1 (DPPA/DPPOH) | 275 | 230 | 327 (45.8) | 255 (66.4) | 9.1 | 24.4 |
| 2 (BPA/PPA) | 220 | 204 | 258 (66.5) | 265 (69.7) | 30.0 | 35.5 |
| 3 (H3PO4) | 190 | 238 (70.6) | 39.8 | |||
| THR (kJ/g) | pHRR (W/g) | TpHRR (°C) | FGC (J/(g·K)) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cotton | 11.6 ± 0.2 | 200.9 ± 5.6 | 380.3 ± 0.5 | 156.0 ± 0.7 | ||||
| No. of OH Groups | Phenyl | Phenoxy | Phenyl | Phenoxy | Phenyl | Phenoxy | Phenyl | Phenoxy |
| 0 (TPPOX/TPP) | 17.0 ± 0.2 | 15.2 ± 0.1 | 176.6 ± 18.0 | 179.3 ± 9.2 | 349.3 ± 22.7 | 373.7 ± 2.4 | 186.5 ± 2.5 | 162.6 ± 1.4 |
| 1 (DPPA/DPPOH) | 10.8 ± 0.3 | 6.9 ± 0.1 | 210.8 ± 3.6 | 127.1 ± 2.7 | 327.4 ± 0.8 | 261.4 ± 0.7 | 95.4 ± 2.9 | 56.0 ± 1.7 |
| 2 (BPA/PPA) | 7.3 ± 0.4 | 4.5 ± 0.1 | 93.9 ± 0.5 | 64.5 ± 1.0 | 281.7 ± 1.7 | 267.1 ± 0.4 | 62.6 ± 4.0 | 37.9 ± 1.0 |
| 3 (H3PO4) | 3.5 ± 0.1 | 64.7 ± 0.9 | 267.3 ± 1.3 | 26.1 ± 0.4 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Otto, R.; Cardona, A.; Preußner, A.M.; Ali, W.; Gutmann, J.S.; Mayer-Gall, T. The Gas- and Condensed-Phase Efficacy of Functionalized Phosphorus Flame Retardants for Cotton Fabric: Phenyl vs. Phenoxy Groups. Polymers 2025, 17, 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070924
Otto R, Cardona A, Preußner AM, Ali W, Gutmann JS, Mayer-Gall T. The Gas- and Condensed-Phase Efficacy of Functionalized Phosphorus Flame Retardants for Cotton Fabric: Phenyl vs. Phenoxy Groups. Polymers. 2025; 17(7):924. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070924
Chicago/Turabian StyleOtto, Raphael, Ava Cardona, Alexander M. Preußner, Wael Ali, Jochen S. Gutmann, and Thomas Mayer-Gall. 2025. "The Gas- and Condensed-Phase Efficacy of Functionalized Phosphorus Flame Retardants for Cotton Fabric: Phenyl vs. Phenoxy Groups" Polymers 17, no. 7: 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070924
APA StyleOtto, R., Cardona, A., Preußner, A. M., Ali, W., Gutmann, J. S., & Mayer-Gall, T. (2025). The Gas- and Condensed-Phase Efficacy of Functionalized Phosphorus Flame Retardants for Cotton Fabric: Phenyl vs. Phenoxy Groups. Polymers, 17(7), 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070924









