Study on the Influence of Hygrothermal Aging on the Mechanical Properties of Carbon Fabric/Polyetheretherketone Composites
Abstract
1. Instruction
2. Materials and Methods
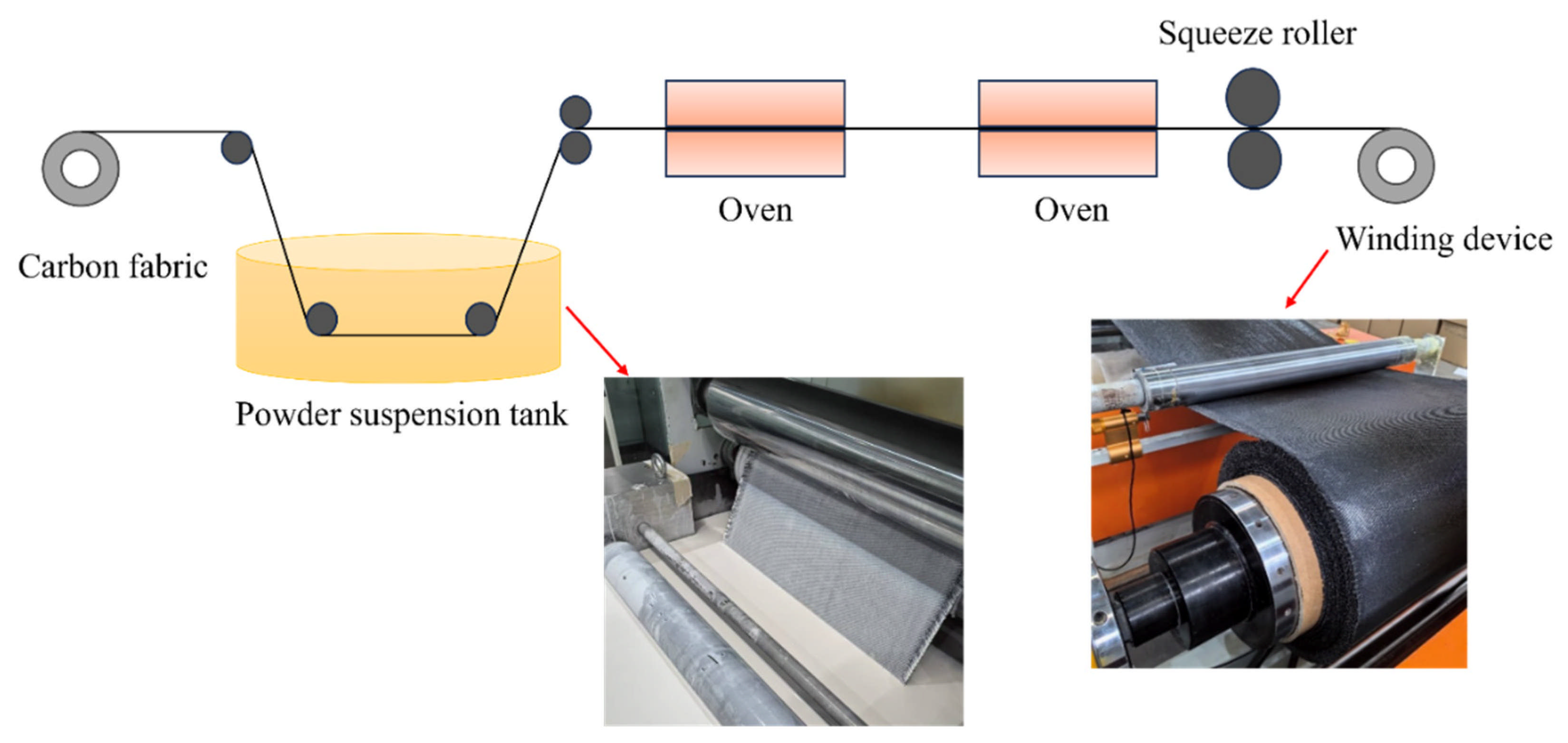
2.1. Raw Materials and Sample Preparation
2.2. Hygrothermal Treatment
2.3. Mechanics Performance Testing
2.4. Morphological Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
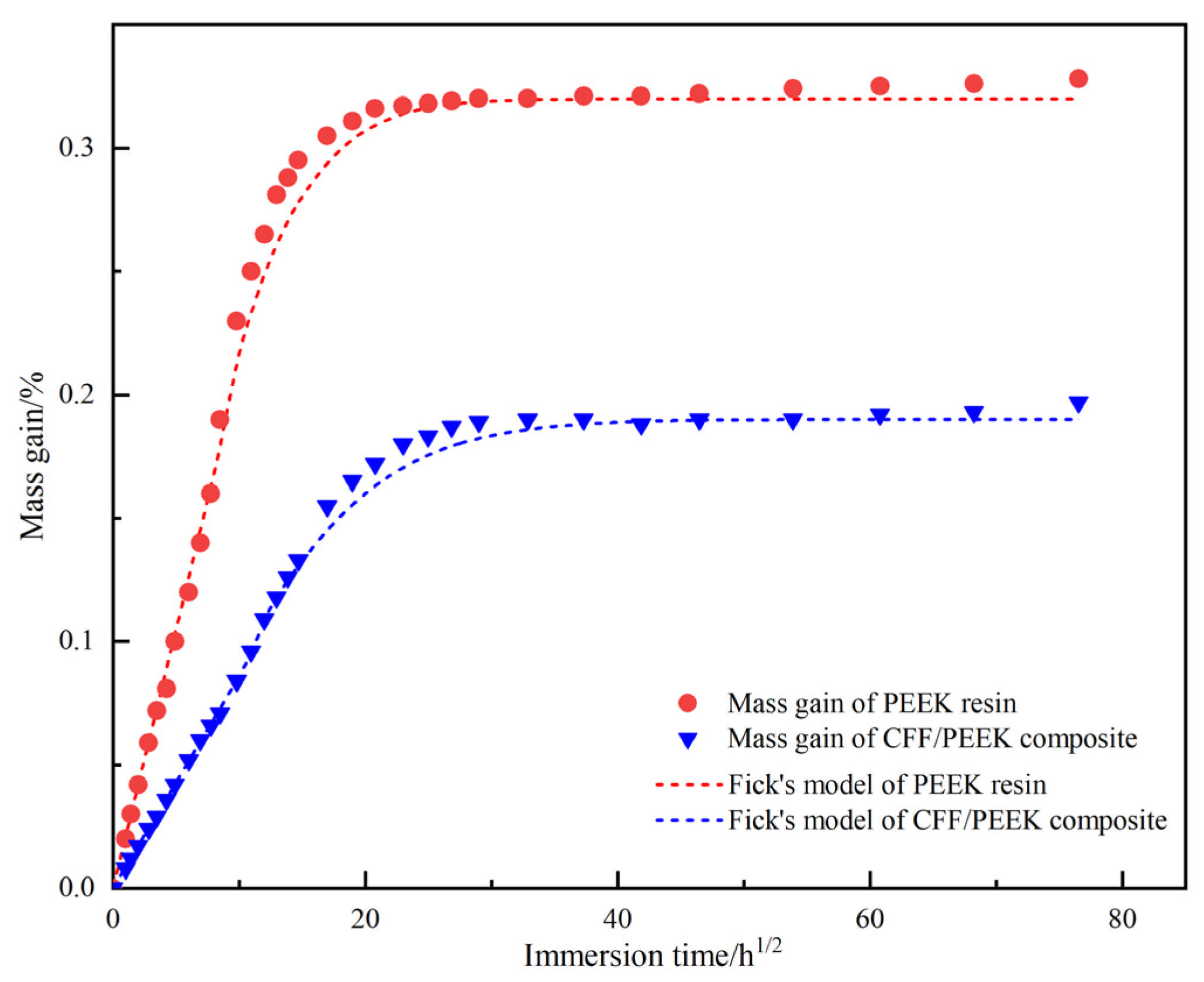
3.1. Moisture Absorption Characteristics
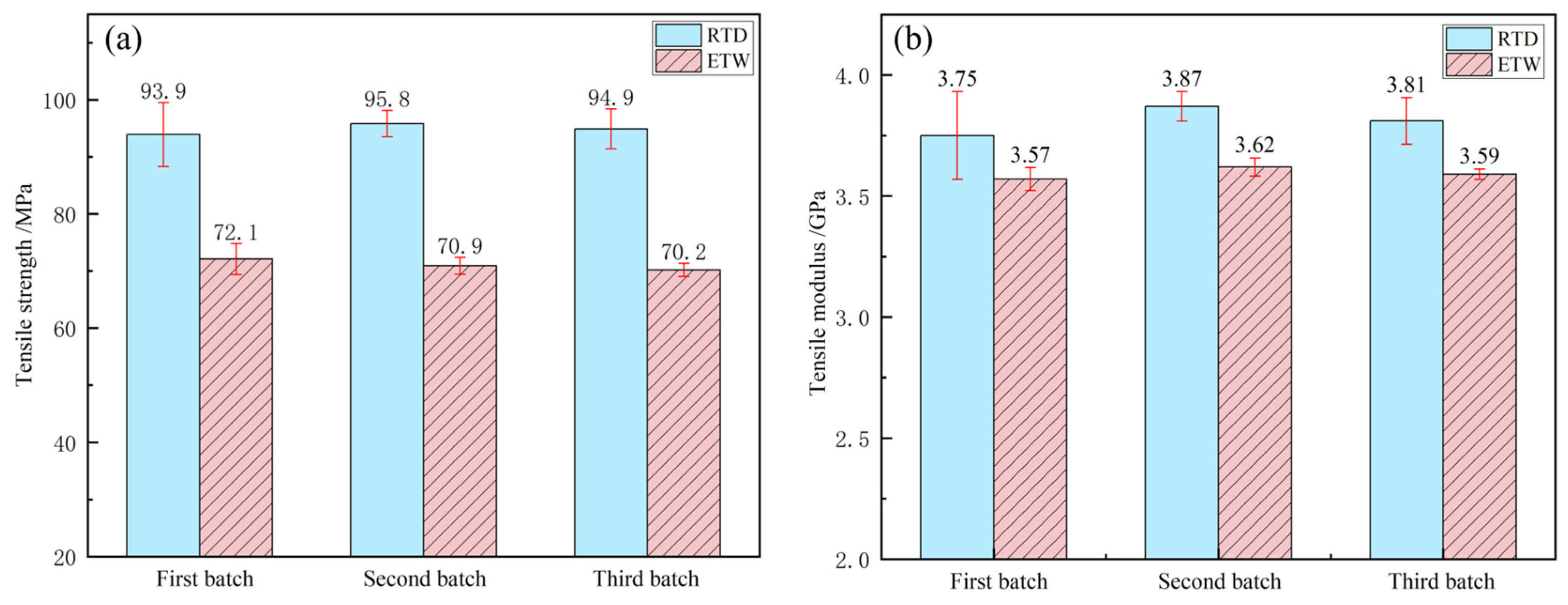
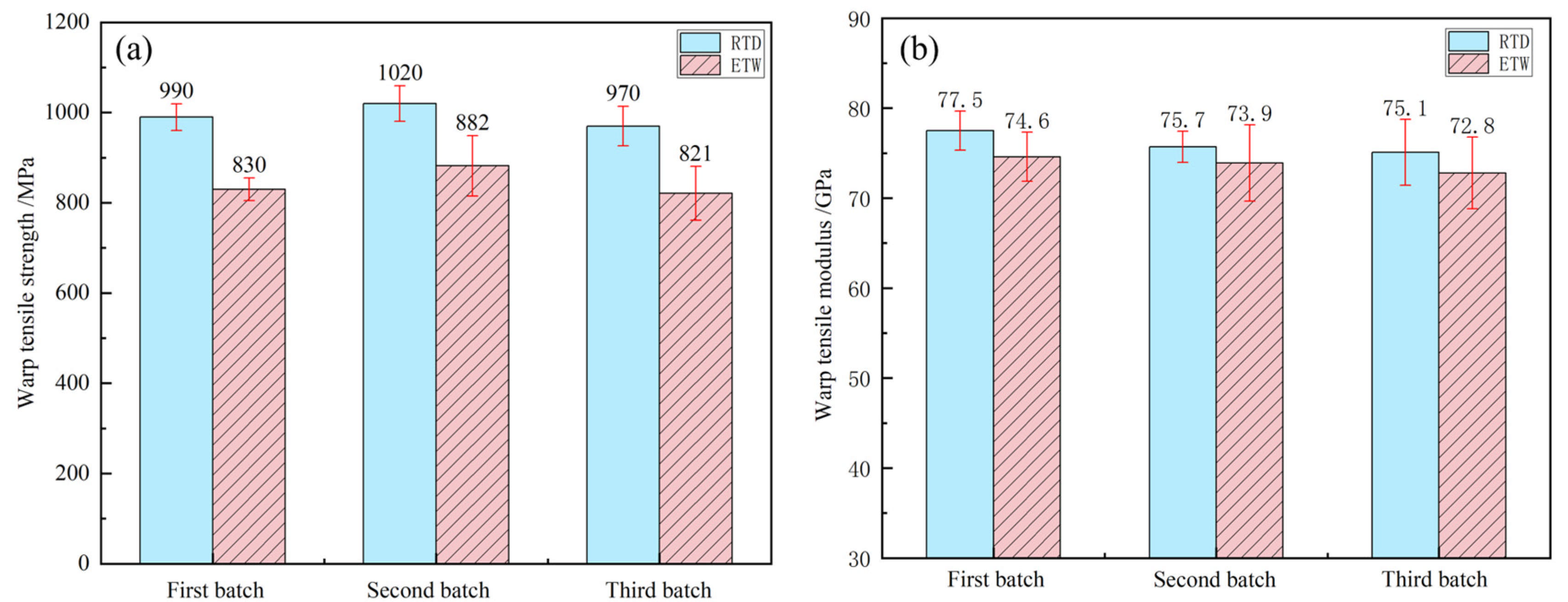
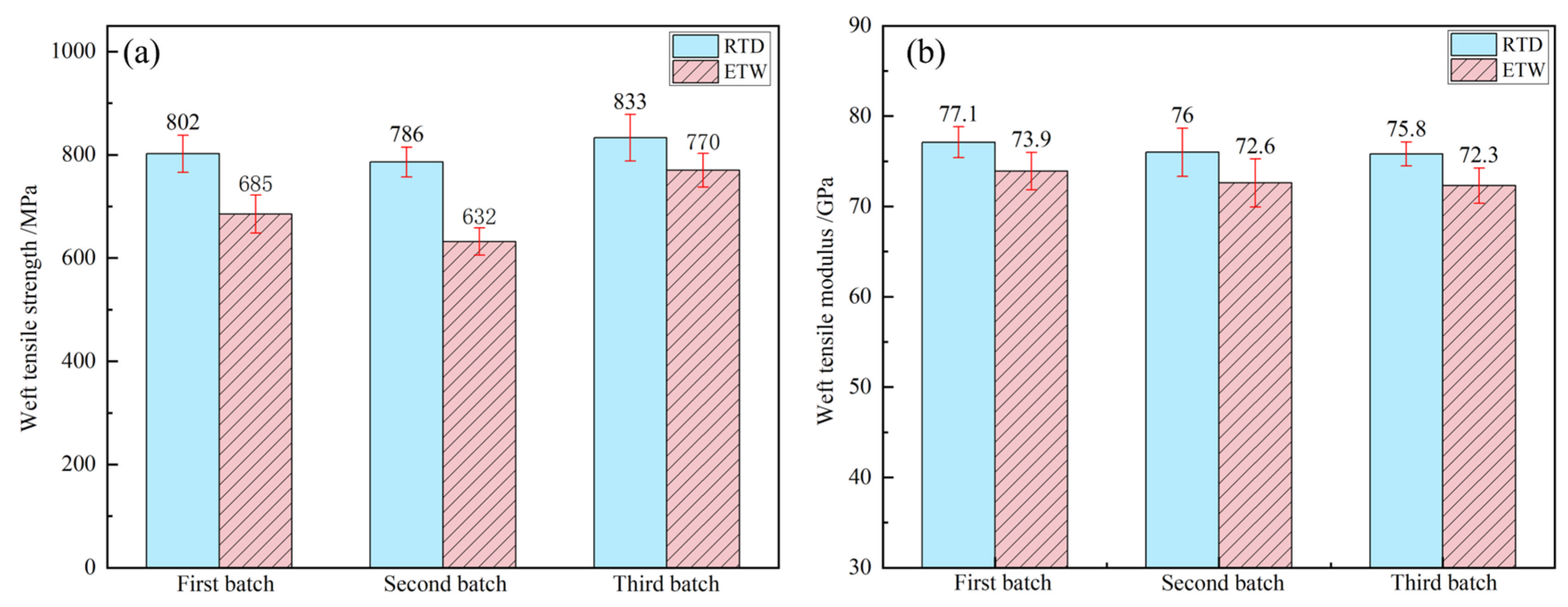
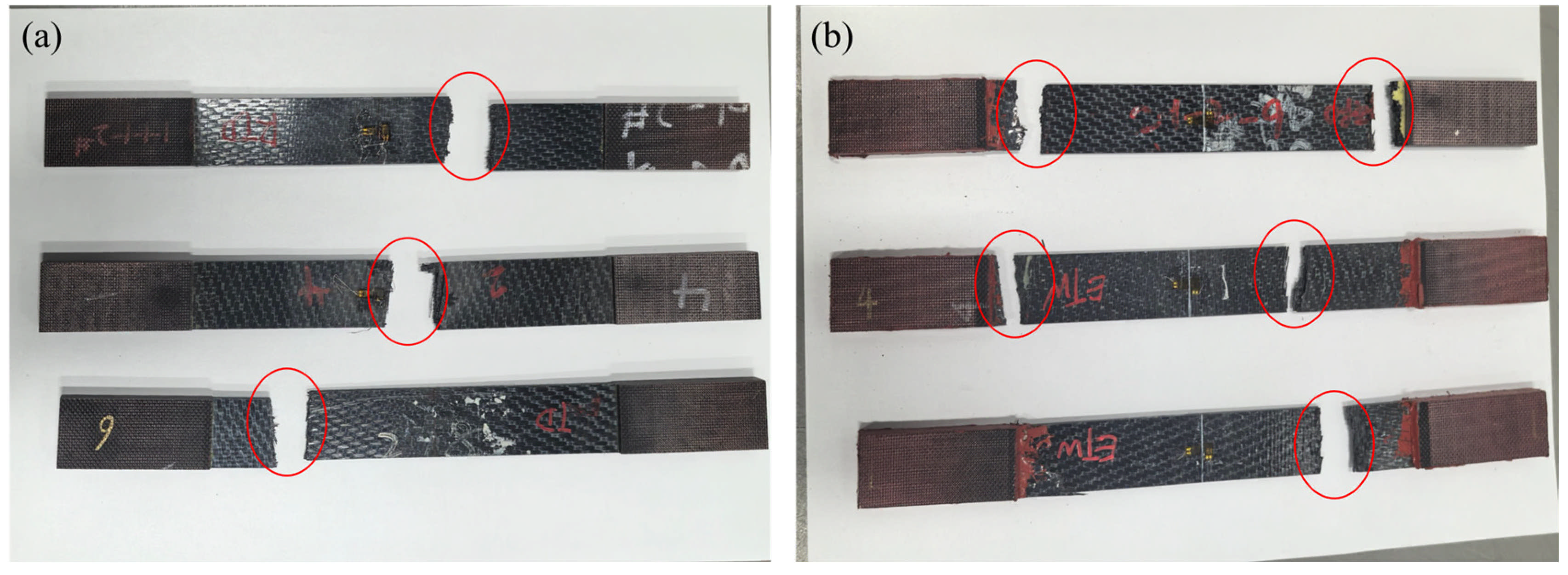
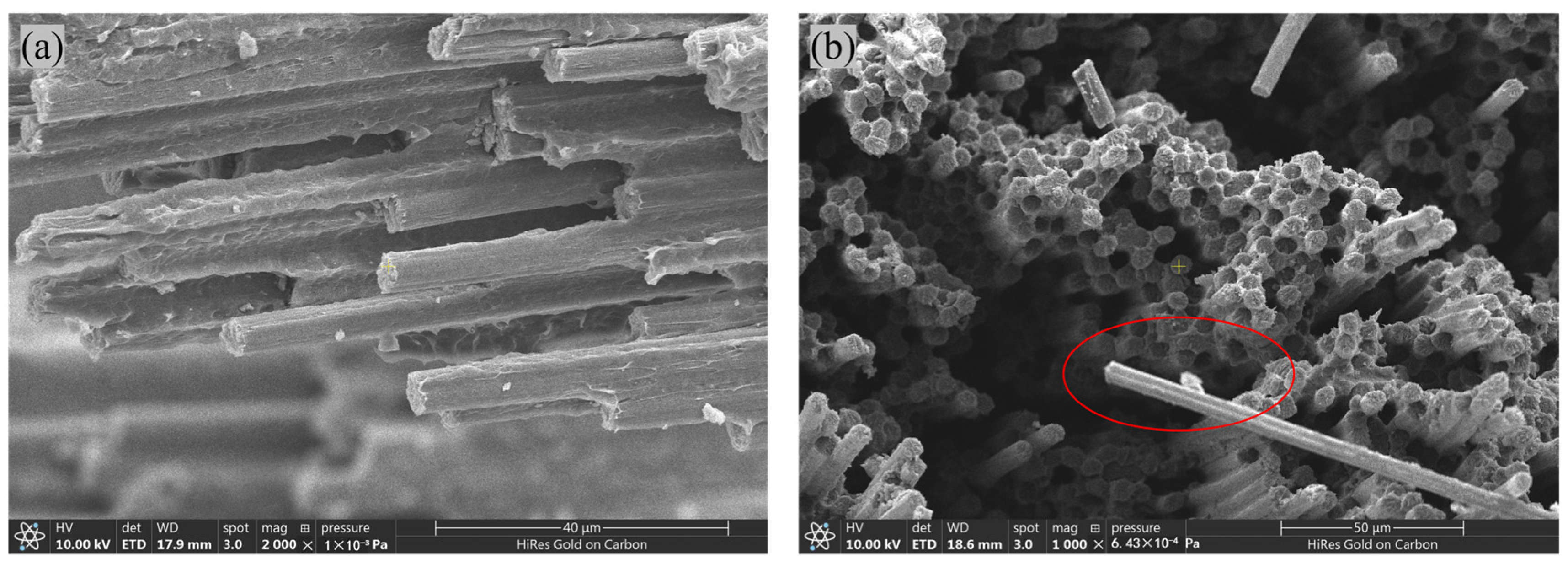
3.2. Influence of the Hygrothermal Environment on the Tensile Properties
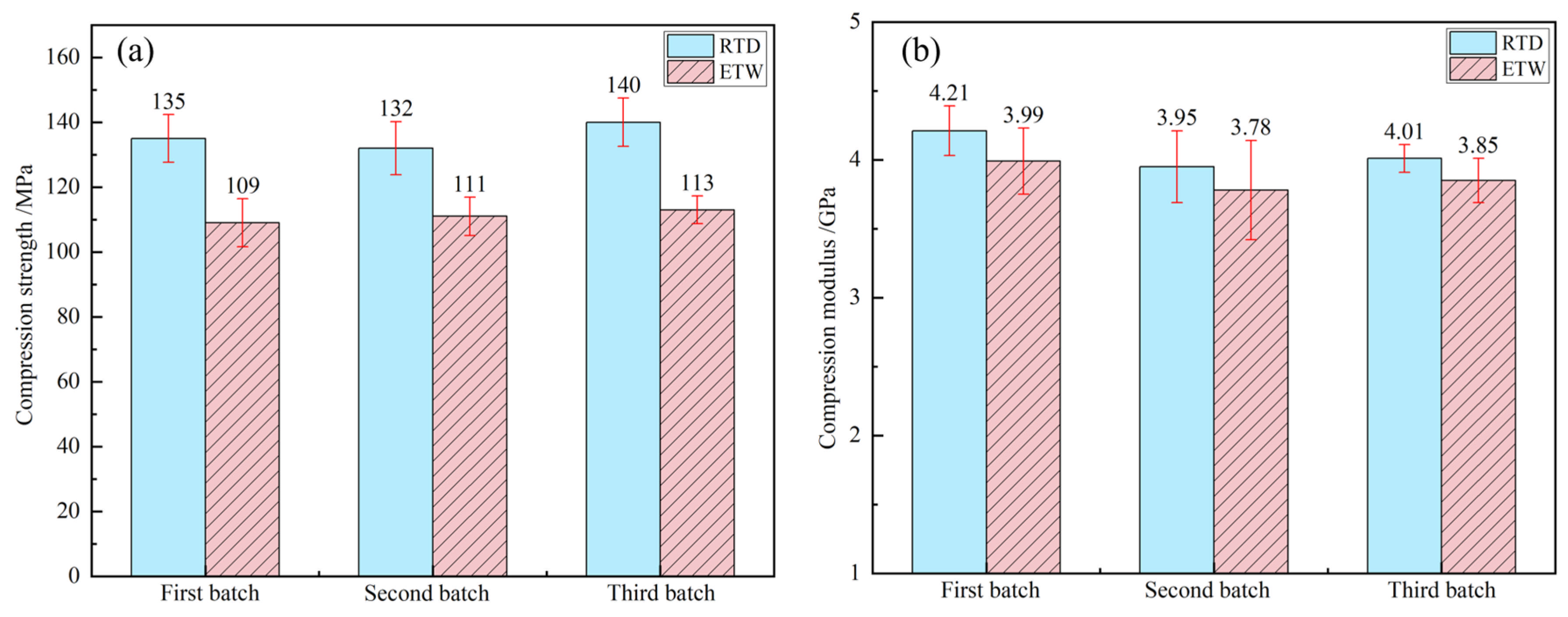
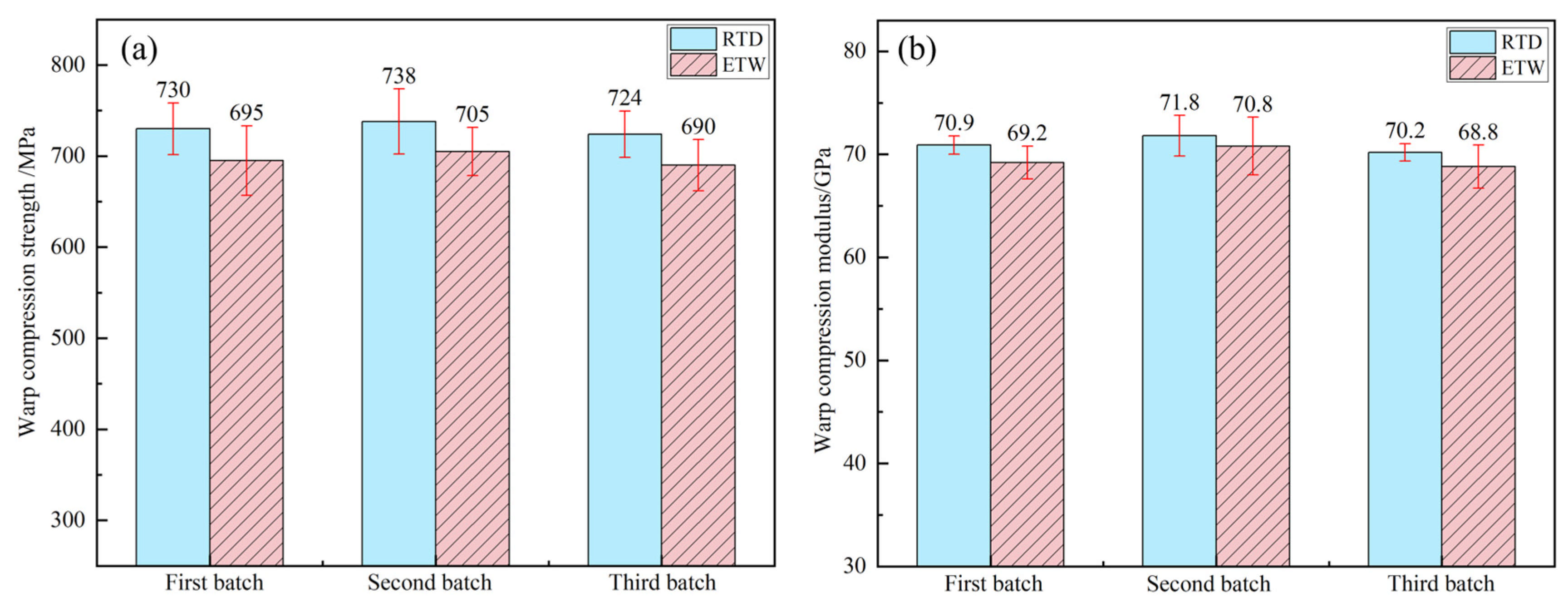
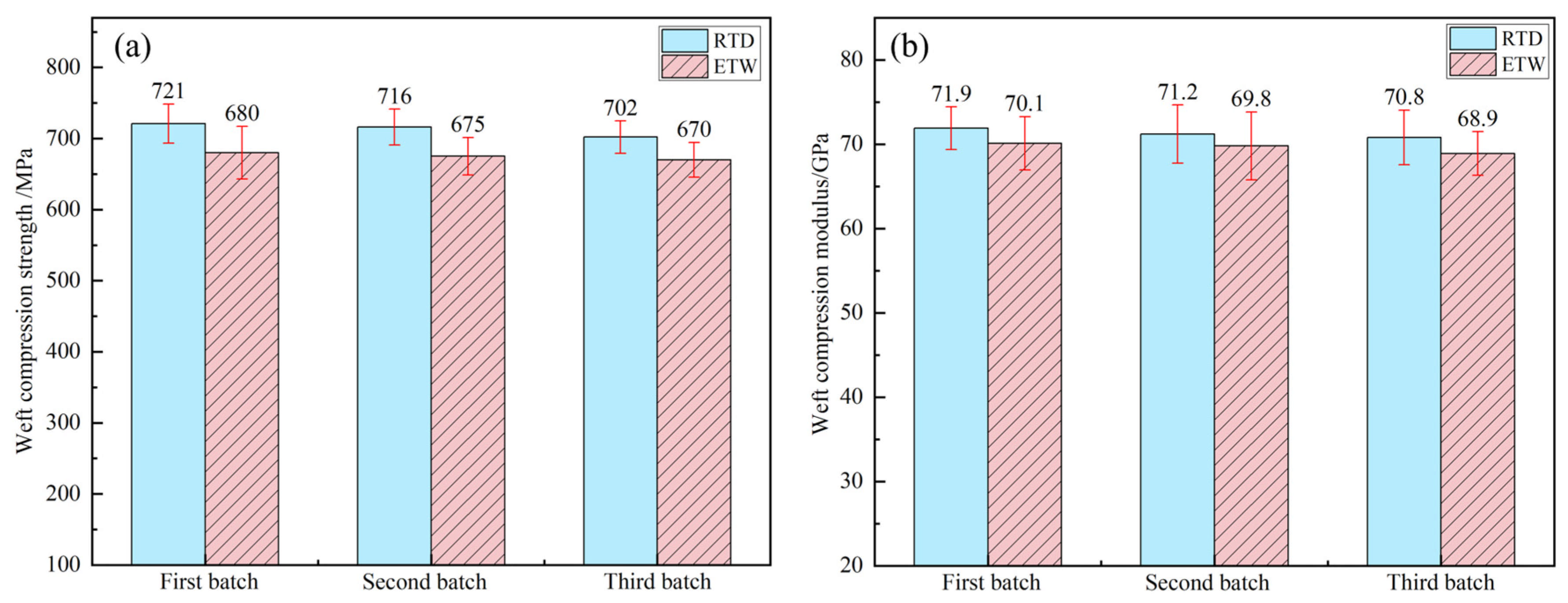
3.3. Influence of Hygrothermal Environment on Compression Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Y.; Lu, F.; Xu, N.; Wang, B.; Yang, L.; Huang, Y.; Hu, Z. Mechanically robust, hydrothermal aging resistant, imine-containing epoxy thermoset for recyclable carbon fiber reinforced composites. Mater. Des. 2022, 224, 111357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, G.; Shen, Y.; Blackie, E.; He, L. Mode-II fracture toughness of carbon fiber reinforced polymer composites interleaved with polyethersulfone (PES)/carbon nanotubes (CNTs). Compos. Struct. 2023, 320, 117214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Li, X.; Ye, J.; Liu, K.; Xu, X.; Liu, Z. Semi-destructive methods for evaluating the micro-scale residual stresses of carbon fiber reinforced polymers, Semi-destructive methods for evaluating the micro-scale residual stresses of carbon fiber reinforced polymers. Compos. Part B Eng 2024, 284, 111722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Catalanotti, G.; Falzon, B.; Higgins, C.; McClory, C.; Thiebot, J.-A.; Zhang, L.; He, M.; Jin, Y.; Sun, D. Process characteristics, damage mechanisms and challenges in machining of fibre reinforced thermoplastic polymer (FRTP) composites: A review. Compos. Part B Eng. 2024, 273, 111247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, K.; Zhao, Y. Enhanced interfacial interactions of carbon fiber reinforced PEEK composites by regulating PEI and graphene oxide complex sizing at the interface. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 154, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Chen, D.; Zhu, G.; Li, Q. Lightweight hybrid materials and structures for energy absorption: A state-of-the-art review and outlook. Thin-Walled Struct. 2022, 172, 108760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avic, R.; Çakıcı, U.G.; Çetinkaya, B.; Öktem, M.F. Effect of atmospheric plasma treatment and wet blast on adhesion characteristics of carbon fiber reinforced LM-PAEK thermoplastic composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2024, 278, 111394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgi, C.; Demir, B.; Aydın, H.; Üstün, B.; Kurtan, Ü. Effect of functionalized graphene nanoplatelet dispersion on thermal and electrical properties of hybrid carbon fiber reinforced aviation epoxy laminated composite. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2024, 325, 129702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harussani, M.M.; Sapuan, S.M.; Nadeem, G.; Rafin, T.; Kirubaanand, W. Recent applications of carbon-based composites in defence industry: A review. Def. Technol. 2022, 18, 1281–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toro, S.A.; Gonzálezb, C.; Fernández-Blázquezc, J.P.; Ridruejob, A. Fabrication and mechanical properties of a high-performance PEEK-PEI hybrid multilayered thermoplastic matrix composite reinforced with carbon fiber. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2024, 185, 108308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Peng, G.; Zhang, B.; Shi, F.; Gao, L.; Gao, J. Material performance, manufacturing methods, and engineering applications in aviation of carbon fiber reinforced polymers: A comprehensive review. Thin-Walled Struct. 2025, 209, 112899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Fring, L.D.; Pallaka, M.R.; Simmons, K.L. A review of the fabrication methods and mechanical behavior of continuous thermoplastic polymer fiber-thermoplastic polymer matrix composites. Polym. Compos. 2023, 44, 694–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Ma, Z.; Pu, Y.; Liu, L.; Huang, Y. Soluble semi-aliphatic polyimide sizing in CF/PEI composites for improving mechanical performance and hydrothermal aging resistance. Compos. Commun. 2021, 28, 100982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabees, S.; Wickramasingha, Y.A.; Akhavan, B.; Hayne, D.J.; Dharmasiri, B.; Henderson, L.C. Tribological behaviour of surface modified carbon-fibre-reinforced polyphenylene sulphide under dry condition. Tribol. Int. 2024, 194, 109528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoeffler, K.; Andjelic, S.; Legros, N.; Roberge, J.; Schougaard, S.B. Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) composites reinforced with recycled carbon fiber. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2013, 84, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matus-Aguirre, M.; Cosson, B.; Garnier, C.; Schmidt, F.; Akué-Asséko, A.C.; Chabert, F. Characterization and modeling of laser transmission welded polyetherketoneketone (PEKK) joints: Influence of process parameters and annealing on weld properties. J. Adv. Join. Process. 2024, 10, 100252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.-J.; Kim, D.-K.; Han, W.; Choi, S.-H.; Chung, D.-C.; Kim, K.-W.; Kim, B.-J. Facile enhancement of mechanical interfacial strength of recycled carbon fiber web-reinforced polypropylene composites via a single-step silane modification process. Polymers 2025, 17, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.G.; Johansson, C.; Tavares, J.R.; Dubé, M. CF/PEEK skins assembly by induction welding for thermoplastic composite sandwich panels. Compos. Part B Eng. 2024, 284, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhou, K.; Jing, B.; Zhu, K.; Shi, J.; Li, C. Effects of hygrothermal condition on water diffusion and flexural properties of carbon–glass hybrid fiber-reinforced epoxy polymer winding pipes. Polymers 2024, 16, 3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Yu, T. Quasi-static compression and hygrothermal stability of BMI/CE co-cured composite lattice cylindrical shell. Compos. Struct. 2021, 257, 113130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanpour, B.; Karbhari, V.M. Characteristics and models of moisture uptake in fiber-reinforced composites: A topical review. Polymers 2024, 16, 2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.C.M.; Lee, C.L.; Chang, M.J.; Tai, N.H. Hygrothermal behavior of carbon fiber-reinforced poly(ether ether ketone) and poly(phenylene sulfide) composites. Polym. Compos. 1992, 13, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Li, Y.; Yu, T. Comparative study on the hygrothermal durability of different fiber reinforced composites. Acta Mater. 2022, 39, 4406–4419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, Y. Effects of cyclic hygrothermal environments on interfacial behavior and properties of CF/EP composites. Compos. Commun. 2025, 53, 102229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Mou, H.; Xie, J.; Gong, T. Hygrothermal environment effects on mechanical properties of T700/3228 CFRP laminates. Mater. Test. 2019, 61, 857–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, A.; Shi, J. Hygrothermal aging effect on static and fatigue behavior of three-dimensional five-directional hybrid braided composites under tension. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 40, 109843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micelli, F.; Nanni, A. Durability of FRP rods for concrete structures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2004, 18, 491–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 3855-2005; Test Method for Resin Content of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastics. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2005.
- GB/T 1463-2005; Test Method for Density and relative Density of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastics. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2005.
- ASTM D3171; Standard Test Methods for Constituent Content of Composite Materials. American Society of Testing Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022.
- ASTM D7028; Glass Transition Temperature (DMA Tg) of Polymer Matrix Composites by Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA). American Society of Testing Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022.
- ASTM D5229; Standard Test Method for Moisture Absorption Properties and Equilibrium Conditioning of Polymer Matrix Composite Materials. American Society of Testing Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- GB/T 1040-2018; Plastics-Determination of Tensile Properties-Part 1: General Principles. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2018.
- GB/T 1040-2008; Plastics-Determination of Compressive Properties. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2008.
- ASTM D3039; Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Polymer Matrix Composite Materials. American Society of Testing Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017.
- ASTM D6641; Standard Test Method for Compressive Properties of Polymer Matrix Composite Materials Using a Combined Loading Compression (GLC) Test Fixture. American Society of Testing Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2016.
- Scida, D.; Assarar, M.; Poilâne, C.; Ayad, R. Influence of hygrothermal ageing on the damage mechanisms of flax-fibre reinforced epoxy composite. Compos. Part B Eng. 2013, 48, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F. Carbon Fibre and Graphite Fibre[M]; Chemical industry press: Beijing, China, 2010; pp. 364–368. [Google Scholar]
- Falkenreck, C.K.; Zarges, J.-C.; Heim, H.-P. Hygrothermal aging behavior of regenerated cellulose fiber-reinforced polyamide 5.10 composites. Polym. Test. 2025, 143, 108717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Kiran, R.; Zafar, S.; Pathak, H. Effect of hygrothermal ageing on the mechanical properties of glass fiber reinforced polymer composite: Experimental and numerical approaches. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 41, 111060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbhari, V.M. Influence of Montmorillonite Organoclay Fillers on Hygrothermal Response of Pultruded E-Glass/Vinylester Composites. Polymers 2024, 16, 2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Wang, X.; Guan, Y.; Du, C.; Fan, T.; Li, H.; Zhai, J. An Experimental Investigation of the Mechanism of Hygrothermal Aging and Low-Velocity Impact Performance of Resin Matrix Composites. Polymers 2024, 16, 1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Type | Ply Count | Layup | Nominal Lamina Thickness/mm | Size/mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Warp Tensile Test | 8 | [0f]8 | 2.4 | 250 × 25 |
| Weft Tensile Test | 8 | [90f]8 | 2.4 | 250 × 25 |
| Warp Compression Test | 8 | [0f]8 | 2.4 | 140 × 12 |
| Weft Compression Test | 8 | [90f]8 | 2.4 | 140 × 12 |
| Properties | Resin Content | Density | Fiber Volume Fraction | Glass Transition Temperature |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 38 wt% | 1.57 g/cm3 | 55 vol% | 146 °C |
| Test Method | GB/T 3855 [28] | GB/T 1463 [29] | ASTM D3171 [30] | ASTM D 7028 [31] |
| Material | n | k/h−n | Mm/% | k′ | D/(10−3 mm2/h−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEEK | 0.455 | 0.057 | 0.32 | 0.008 | 2.317 |
| CFF/PEEK composite | 0.526 | 0.063 | 0.18 | 0.021 | 1.353 |
| Material | Performance | First Batch | Second Batch | Third Batch | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEEK resin | Tensile strength (%) | 76.78 | 74.01 | 73.97 | 74.92 |
| Tensile modulus (%) | 95.20 | 93.54 | 94.23 | 94.32 | |
| CFF/PEEK composite | Warp tensile strength (%) | 83.84 | 86.47 | 84.64 | 84.98 |
| Warp tensile modulus (%) | 96.26 | 97.62 | 96.94 | 96.94 | |
| Weft tensile strength (%) | 85.41 | 80.41 | 92.44 | 86.08 | |
| Weft tensile modulus (%) | 95.85 | 95.53 | 95.38 | 95.59 |
| Material | Performance | First Batch | Second Batch | Third Batch | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEEK resin | Compression strength (%) | 80.74 | 84.09 | 80.71 | 81.85 |
| Compression modulus (%) | 94.77 | 95.70 | 96.01 | 95.49 | |
| CFF/PEEK composite | Warp compression strength (%) | 95.21 | 95.53 | 95.30 | 95.35 |
| Warp compression modulus (%) | 97.60 | 98.61 | 98.01 | 98.07 | |
| Weft compression strength (%) | 94.31 | 94.27 | 95.44 | 94.67 | |
| Weft compression modulus (%) | 97.50 | 98.03 | 97.32 | 97.62 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, X.; Zhang, B.; Shi, F.; Liu, K.; Peng, G.; Gao, L.; Gao, J.; Du, Y. Study on the Influence of Hygrothermal Aging on the Mechanical Properties of Carbon Fabric/Polyetheretherketone Composites. Polymers 2025, 17, 724. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17060724
Xu X, Zhang B, Shi F, Liu K, Peng G, Gao L, Gao J, Du Y. Study on the Influence of Hygrothermal Aging on the Mechanical Properties of Carbon Fabric/Polyetheretherketone Composites. Polymers. 2025; 17(6):724. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17060724
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Xiangyu, Baoyan Zhang, Fenghui Shi, Kai Liu, Gongqiu Peng, Liang Gao, Junpeng Gao, and Yu Du. 2025. "Study on the Influence of Hygrothermal Aging on the Mechanical Properties of Carbon Fabric/Polyetheretherketone Composites" Polymers 17, no. 6: 724. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17060724
APA StyleXu, X., Zhang, B., Shi, F., Liu, K., Peng, G., Gao, L., Gao, J., & Du, Y. (2025). Study on the Influence of Hygrothermal Aging on the Mechanical Properties of Carbon Fabric/Polyetheretherketone Composites. Polymers, 17(6), 724. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17060724






