A Light-Steered Self-Rowing Liquid Crystal Elastomer-Based Boat
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Model and Formulation
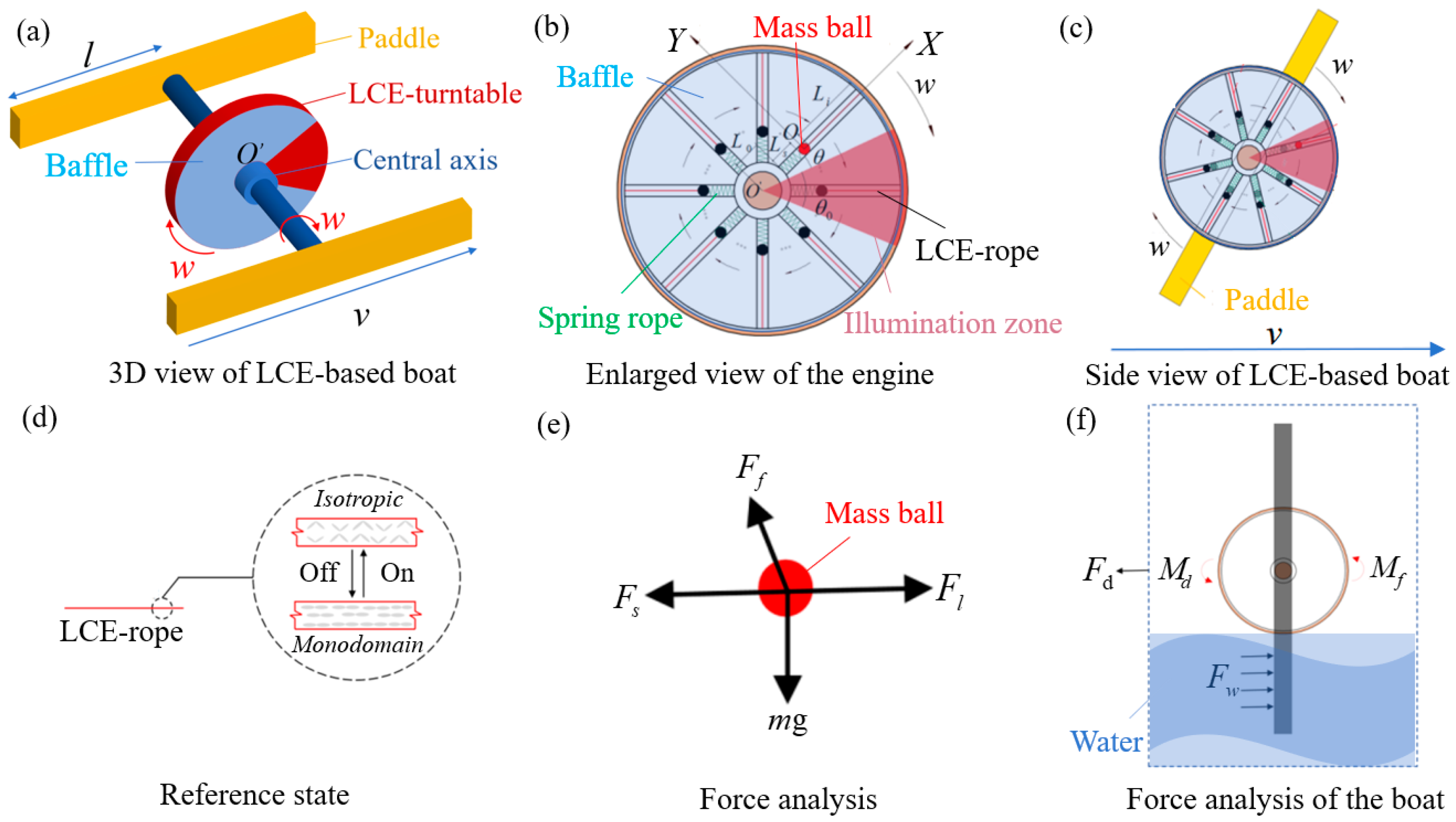
2.1. Dynamics of the Self-Rowing LCE-Based Boat
2.2. Photothermally Responsive LCE Model
2.3. Nondimensionalization and Solution Method
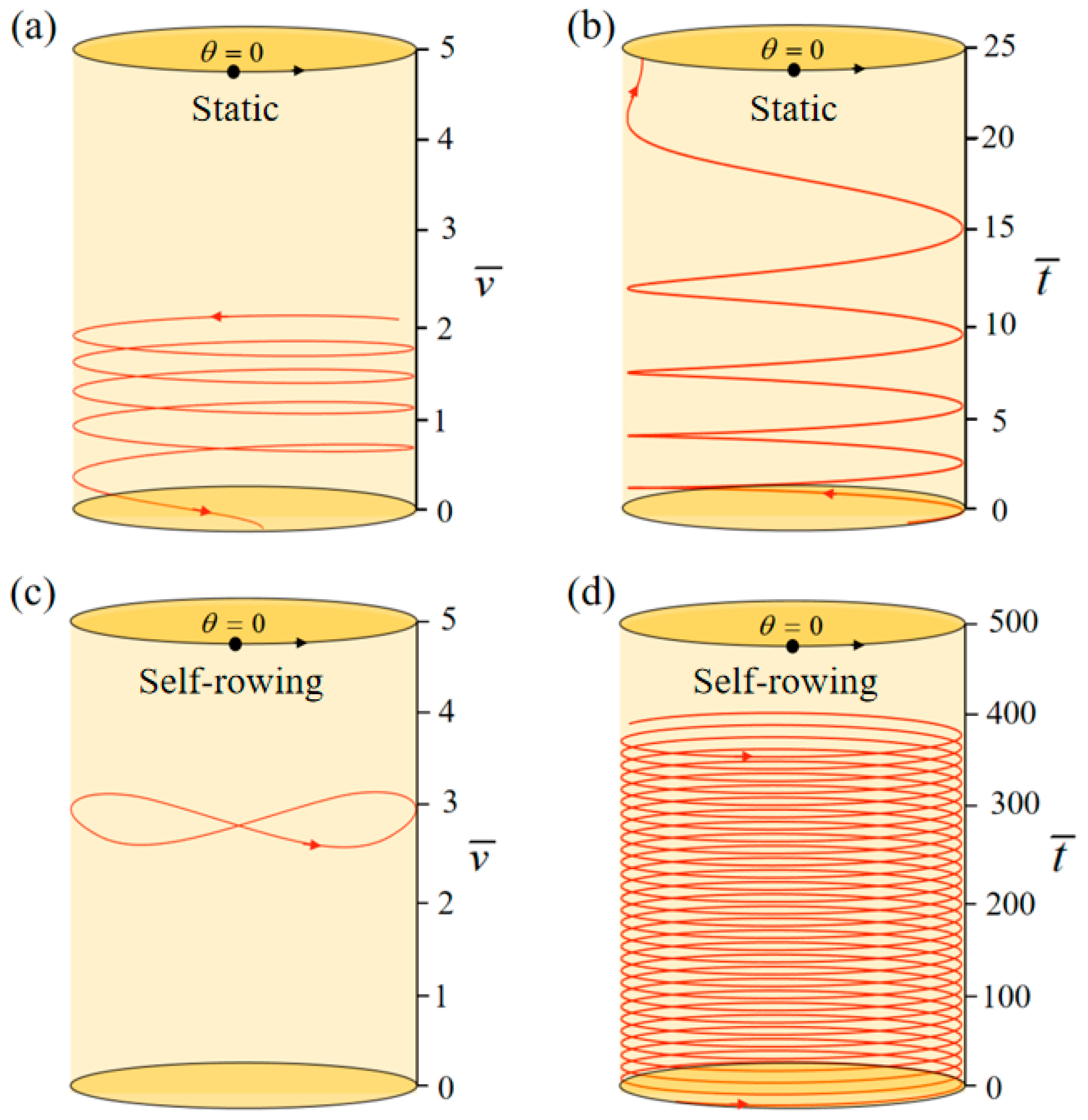
3. Two Motion Patterns and Mechanism of Self-Excited Motion
3.1. Two Motion Patterns
3.2. Mechanism of the Self−Rowing
4. Parametric Study
4.1. Influence of the Maximum Frictional Torque
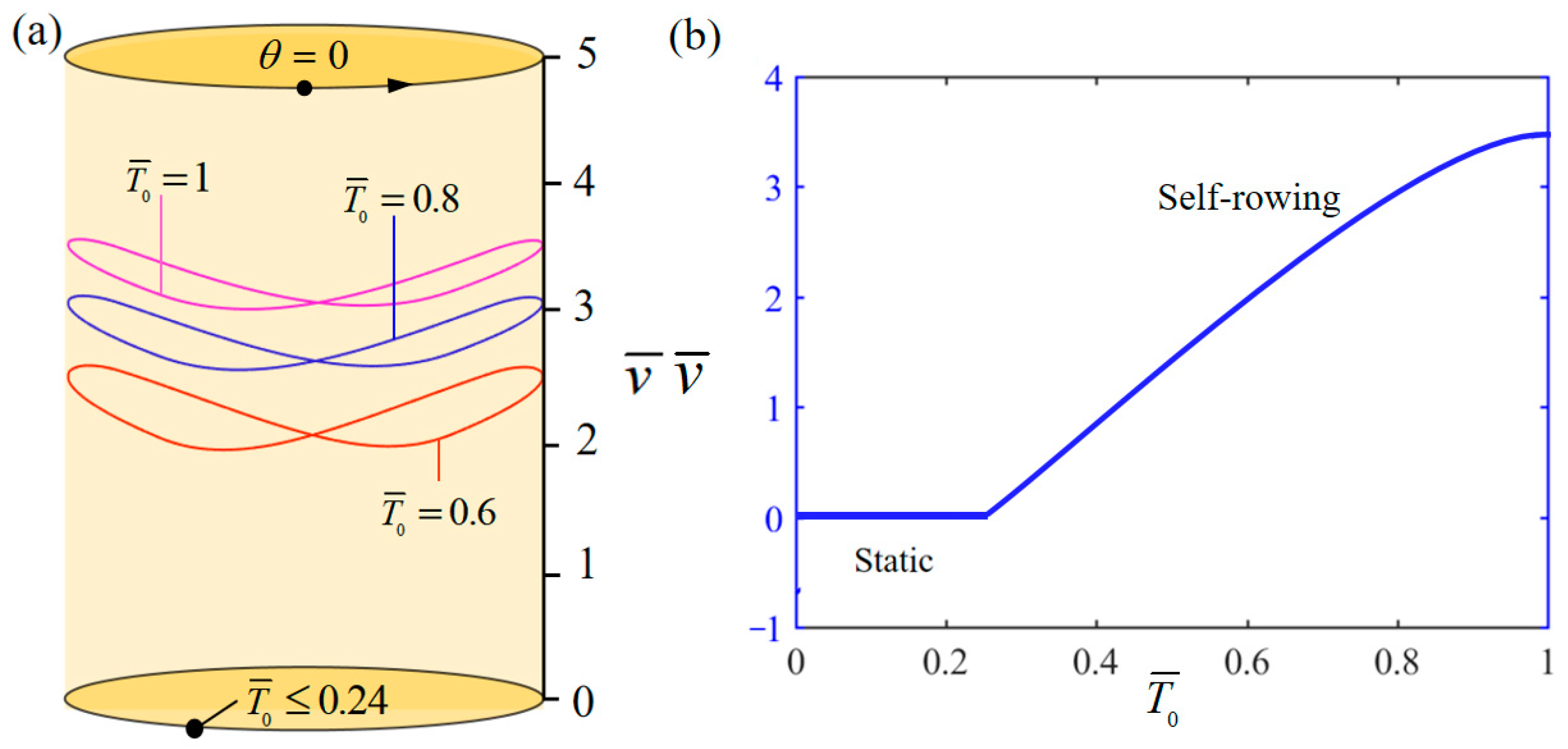
4.2. Influence of the Limit Temperature
4.3. Influence of the Gravitational Acceleration
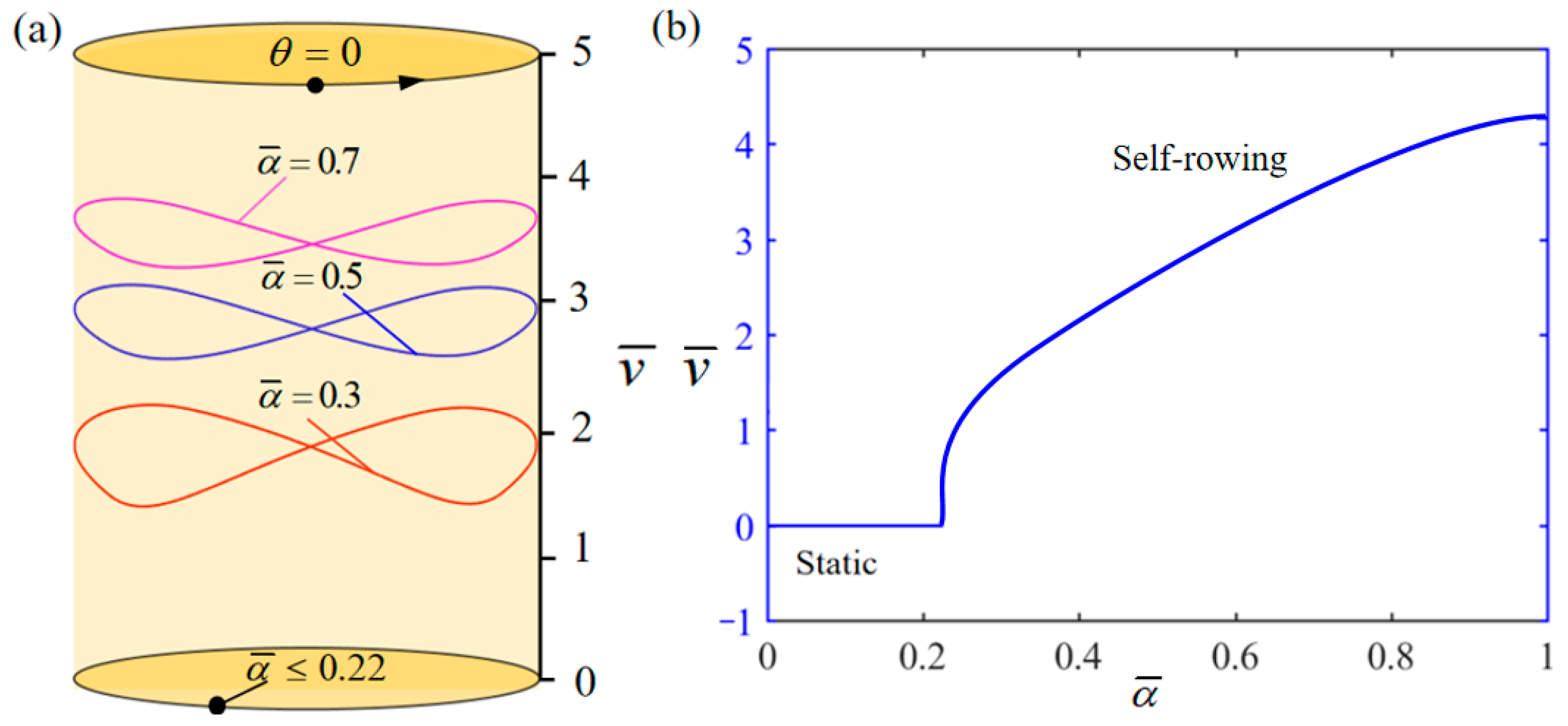
4.4. Influence of the Thermal Shrinkage Coefficient
4.5. Influence of the Initial Position of the Mass Ball
4.6. Influence of the Length of Paddle
4.7. Influence of the Damping Factor
4.8. Influence of the Rolling Resistance Coefficient
4.9. Influence of the Elastic Stiffness of LCE−Rope
4.10. Influence of the Elastic Stiffness of Spring
4.11. Influence of the Illumination Zone Angle
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ding, W.J. Self−Excited Vibration; Tsing−Hua University Press: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Xu, L.; Ji, Q.; Chang, L.; Hu, Y.; Peng, Q.; He, X. A MXene-Based Light-Driven Actuator and Motor with Self-Sustained Oscillation for Versatile Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2310955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Qi, M.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, D.; Yan, X. Mechanical response of the isolated cantilever with a floating potential in steady electrostatic field. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2019, 161, 105066. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, W.; Lum, G.Z.; Mastrangeli, M.; Sitti, M. Small−scale soft−bodied robot with multimodal locomotion. Nature 2018, 554, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iliuk, I.; Balthazar, J.M.; Tusset, A.M.; Piqueira, J.R.; Pontes, D.B.R.; Felix, J.L.; Bueno, A.M. Application of passive control to energy harvester efficiency using a nonideal portal frame structural support system. J. Int. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2014, 25, 417–429. [Google Scholar]
- Korner, K.; Kuenstler, A.S.; Hayward, R.C.; Audoly, B.; Bhattacharya, K. A nonlinear beam model of photomotile structures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 9762–9770. [Google Scholar]
- Martella, D.; Nocentini, S.C.; Parmeggiani, C.; Wiersma, D.S. Self−regulating capabilities in photonic robotics. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1800571. [Google Scholar]
- Sangwan, V.; Taneja, A.; Mukherjee, S. Design of a robust self−excited biped walking mechanism. Mech. Theory 2004, 39, 1385–1397. [Google Scholar]
- Erturk, A.; Inman, D.J. Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting; John Wiley Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Rosso, M. Intentional and Inherent Nonlinearities in Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Briand, D.; Yeatman, E.; Roundy, S.; Brand, O.; Fedder, G.K.; Hierold, C.; Tabata, O. Micro Energy Harvesting; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH Company KGaA: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mohsen, S.; Henry, A.S.; Steven, R.A. A review of energy harvesting using piezoelectric materials: State-of-the-art a decade later (2008–2018). Smart Mater. Struct. 2019, 28, 113001. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.-L.; Kyung, C.-M.; Hiroto, Y.; Liu, Y. Smart Sensors and Systems; Springer Nature Switzerland AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ambaye, G.; Boldsaikhan, E.; Krishnan, K. Soft Robot Design, Manufacturing, and Operation Challenges: A Review. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2024, 8, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Yin, R.; Hua, Y.; Jiao, W.; Mo, C.; Shu, H.; Raney, J.R. A modular strategy for distributed, embodied control of electronics-free soft robots. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eade9247. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z. Advanced MEMS/NEMS Fabrication and Sensors; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Corigliano, A.; Ardito, R.; Comi, C.; Frangi, A.; Ghisi, A.; Mariani, S. Mechanics of Microsystems; John Wiley Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, R. Self−oscillating gels driven by the Belousov−Zhabotinsky reaction as novel smart materials. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 3463–3483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, L.; Xu, J.; Xiao, R. Modeling the Stimulus-Responsive Behaviors of Fiber-Reinforced Soft Materials. Int. J. Appl. Mech. 2024, 16, 2450041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boissonade, J.; Kepper, P.D. Multiple types of spatio−temporal oscillations induced by differential diffusion in the Landolt reaction. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 4132–4137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, C.; Annapooranan, R.; Cai, S. Electrospun liquid crystal elastomer microfiber actuator. Sci. Robot. 2021, 6, eabi9704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Lou, J.; Wang, J.; Chuang, K.C.; Wu, H.M.; Huang, Z.L. A self-excited bistable oscillator with a light-powered liquid crystal elastomer. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2024, 271, 109124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dang, A.; Zhang, Z.; Yin, R.; Gao, Y.; Feng, L.; Yang, S. Repeatable and reprogrammable shape morphing from photoresponsive gold nanorod/liquid crystal elastomers. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2004270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Li, Y.; Lv, J. Phototunable self−oscillating system driven by a self−winding fiber actuator. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Liu, H.; Luo, J.; Li, N.; Zhang, Z.; Gan, J.; Yang, Z. Liquid Crystal Elastomer Actuators Enhanced by Tapered Optical Fibers for Controllable Bending Directions and Amplitudes. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2024, 9, 2400073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chi, Y.; Hong, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, S.; Yin, J. Twisting for soft intelligent autonomous robot in unstructured environments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2200265119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graeber, G.; Regulagadda, K.; Hodel, P.; Küttel, C.; Landolf, D.; Schutzius, T.; Poulikakos, D. Leidenfrost droplet trampolining. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, A.; Choi, G.P.T.; Mahadevan, L. Self−Excited Motions of Volatile Drops on Swellable Sheets. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2020, 124, 258002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Li, K.; Yu, X.; Yang, J.; Wang, Z. A Multimodal Self-Propelling Tensegrity Structure. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2314093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Yao, S.; Zhang, H.; Man, W.; Bai, Z.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Y. Liquid crystal elastomer metamaterials with giant biaxial thermal shrinkage for enhancing skin regeneration. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2106175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Ge, D.; Qiu, Y.; Li, K.; Xu, P. Mechanics of light-fueled bidirectional self-rolling in a liquid crystal elastomer rod on a track. Chaos Soliton Fract. 2025, 191, 115901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, D.; Dai, Y.; Liang, H.; Li, K. Self-rolling and circling of a conical liquid crystal elastomer rod on a hot surface. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2024, 263, 108780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Qian, G.; Dai, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Song, W.; Li, K. Nonlinear dynamics modeling of a light-powered liquid crystal elastomer-based perpetual motion machine. Chaos Soliton Fract. 2024, 184, 114957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Ge, D.; Wu, H.; Li, K.; Xu, P. Self-rotation of a liquid crystal elastomer rod under constant illumination. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2024, 283, 109665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Zhao, C.; Qiu, Y.; Dai, Y. Light-powered self-rolling of a liquid crystal elastomer-based dicycle. Appl. Math. Mech. 2025, 46, 253–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.; Kang, J.; Wang, Y.Q. Light-induced motion of three-dimensional pendulum with liquid crystal elastomeric fiber. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2024, 266, 108911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, D.; Liang, H.; Li, K. Self-oscillation of a liquid crystal elastomer string-mass system under constant gradient temperature. J. Appl. Mech. 2024, 91, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhou, L.; Li, K. Self-oscillation of a liquid crystal elastomer fiber-shading laminate system under line illumination. Chaos Soliton Fract. 2025, 192, 115957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Qiu, Y.; Li, K. Modeling of a light-fueled liquid crystal elastomer-steered self-wobbling tumbler. Chaos Soliton Fract. 2025, 191, 115941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Qiu, Y.; Dai, Y.; Yu, Y. Modeling the dynamic response of a light-powered self-rotating liquid crystal elastomer-based system. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2024, 263, 108794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Li, K.; Priimagi, A.; Zeng, H. Light-steerable locomotion using zero-energy modes. Nat. Mater. 2024, 23, 1728–1735. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Nie, Z.; Wang, M.; Liu, Z.; Huang, S.; Yang, H. Springtail-inspired Light-driven Soft Jumping Robots Based on Liquid Crystal Elastomers with Monolithic Three-leaf Panel Fold Structure. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2023, 62, e202218227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Liu, Y.; Dai, Y.; Yu, Y. Light-powered self-oscillation of a liquid crystal elastomer bow. J. Sound. Vib. 2024, 570, 118142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Li, K. Self-rotation-eversion of an anisotropic-friction-surface torus. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2024, 281, 109584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Dai, Y.; Li, K. Self-spinning of liquid crystal elastomer tubes under constant light intensity. Commun. Nonlinear. Sci. 2024, 139, 108296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Chen, Y.; Sun, X.; Dai, Y.; Li, K. Light-powered self-sustained chaotic motion of a liquid crystal elastomer-based pendulum. Chaos Soliton Fract. 2024, 184, 115027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Ge, D.; Li, K.; Xu, P. Chaotic self-oscillation of liquid crystal elastomer double-line pendulum under a linear temperature field. Chaos Soliton Fract. 2024, 189, 115653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhou, K.; Xu, P. Chaotic self-beating of left ventricle modeled by liquid crystal elastomer. Thin. Wall. Struct. 2024, 205, 112540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Qian, P.; Hu, H.; Dai, Y.; Ge, D. A light-powered liquid crystal elastomer semi-rotary motor. Int. J. Solids. Struct. 2023, 284, 112509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Chen, H.; Li, K. Optically-responsive liquid crystal elastomer thin film motors in linear/nonlinear optical fields. Thin. Wall. Struct. 2024, 202, 112082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Ge, D.; Chen, J.; Xu, P.; Li, K. A light-fueled self-rolling unicycle with a liquid crystal elastomer rod engine. Chaos Soliton. Fract. 2024, 186, 115327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Dai, Y.; Li, K. Multimodal self-operation of a liquid crystal elastomer spring-linkage mechanism under constant light. Int. J. Solids. Struct. 2024, 302, 112998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, X.; Zuo, W.; Li, K. Multi-modal self-sustained motions of a silicone oil paper disc on a surface driven by hot steam. Chaos Soliton Fract. 2025, 191, 115898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhao, C.; Dai, Y.; Li, K. Light-fueled self-fluttering aircraft with a liquid crystal elastomer-based engine. Commun. Nonlinear. Sci. 2024, 132, 107942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, M.; Peeketi, A.R.; Ramgopal, A.; Annabattula, R.K.; Schenning, A. Light−driven continual oscillatory rocking of a polymer film. Chem. Open 2020, 9, 1149–1152. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Lu, H.; Lee, X.; Zeng, H.; Priimagi, A. Kirigami−based light−induced shape−morphing and locomotion. Adv. Mater. 2019, 32, 1906233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelebart, A.H.; Mulder, D.J.; Varga, M.; Konya, A.; Vantomme, G.; Meijer, E.W.; Selinger, R.S.; Broer, D.J. Making waves in a photoactive polymer film. Nature 2017, 546, 632–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Zhang, C.; Su, J.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, C.; Lin, J. Bioinspired multi−responsive soft actuators controlled by laser tailored graphene structures. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 5415–5423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Zhang, C.; Chen, B.; Wang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Xiao, R. Bioinspired design of stimuli-responsive artificial muscles with multiple actuation modes. Smart Mater. Struct. 2023, 32, 085023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wang, Y.; Liao, W.; Yang, Z. Ultrafast, High-Contractile Electrothermal-Driven Liquid Crystal Elastomer Fibers towards Artificial Muscles. Small. 2021, 17, 2103700. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Liu, C.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, R. Modeling the thermo-responsive behaviors of polydomain and monodomain nematic liquid crystal elastomers. Mech. Mater. 2024, 188, 104838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisoyi, H.K.; Urbas, A.M.; Li, Q. Soft materials driven by photo thermal effect and their applications. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2018, 6, 1800458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Wang, L.; Chen, B.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, R. Shape memory behaviors of 3D printed liquid crystal elastomers. Soft. Sci. 2023, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wei, Z.; Xu, Z.; Yu, Q.; Wu, Z.L.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, R. Shape Morphing of 3D Printed Liquid Crystal Elastomer Structures with Precuts. ACS. Appl. Polym. Mater. 2023, 5, 7477–7484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yin, R.; Jin, L.; Liu, M.; Gao, Y.; Raney, J.; Yang, S. 3D-Printed Photoresponsive Liquid Crystal Elastomer Composites for Free-Form Actuation. Adv. Func. Mater. 2023, 33, 2210614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Du, C.; Zhu, F.; Dai, Y.; Ge, D.; Li, K. Self-galloping of a liquid crystal elastomer catenary cable under a steady temperature field. Thin Wall. Struct. 2024, 202, 112071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Dai, C.; Dai, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, K. Self-oscillation of cantilevered silicone oil paper sheet system driven by steam. Thin Wall. Struct. 2024, 203, 112270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, B.; Zang, H.; Chen, M.; Wang, Y.; Lang, X.; Zhu, N.; Yang, Z.; Yi, Y. Soft rod−climbing robot inspired by winding locomotion of snake. Soft Robot. 2020, 7, 500–511. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Haberl, J.M.; Sanchez-Ferrer, A.; Mihut, A.M.; Dietsch, H.; Hirt, A.M.; Mezzenga, R. Liquid−crystalline elastomer−nanoparticle hybrids with reversible switch of magnetic memory. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 1787–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.H.; Keller, P.; Li, B.; Wang, X.; Brunet, M. Light−driven side−on nematic elastomer actuators. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 569–572. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, X.; Chen, Q.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Wei, Y.; Ji, Y. Untethered recyclable tubular actuators with versatile locomotion for soft continuum robots. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1801103. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, W.; Yang, Z. The integration of sensing and actuating based on a simple design fiber actuator towards intelligent soft robots. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2023, 7, 2101260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotikian, A.; Watkins, A.A.; Bordiga, G.; Spielberg, A.; Davidson, Z.S.; Bertoldi, K.; Lewis, J.A. Liquid Crystal Elastomer Lattices with Thermally Programmable Deformation via Multi-Material 3D Printing. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2310743. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y. Light-driven soft microrobots based on hydrogels and LCEs: Development and prospects. RSC. Adv. 2024, 14, 14278–14288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strogatz, S.H. Nonlinear Dynamics and Chaos: With Applications to Physics, Biology, Chemistry, and Engineering; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Z.; Liu, J.; Qian, G.; Dai, Y.; Li, K. Self-Rotation of Electrothermally Responsive Liquid Crystal Elastomer-Based Turntable in Steady-State Circuits. Polymers 2023, 15, 4598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanackovic, T.M.; Guran, A.; Atanackovic, T.M. Hooke’s law. In Theory of Elasticity for Scientists and Engineers; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; pp. 85–111. [Google Scholar]
- Camacho-Lopez, M.; Finkelmann, H.; Palffy-Muhoray, P.; Shelley, M. Fast liquid-crystal elastomer swims into the dark. Nat. Mater. 2004, 3, 307. [Google Scholar]
- Hogan, P.M.; Tajbakhsh, A.R.; Terentjev, E.M. UV manipulation of order and macroscopic shape in nematic elastomers. Phys. Rev. 2002, 65, 041720. [Google Scholar]
- Baumann, A.; Sánchez-Ferrer, A.; Jacomine, L.; Martinoty, P.; Houerou, V.; Ziebert, F.; Kuli´c, I. Motorizing fibers with geometric zero-energy modes. Nat. Mater. 2018, 17, 523. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]






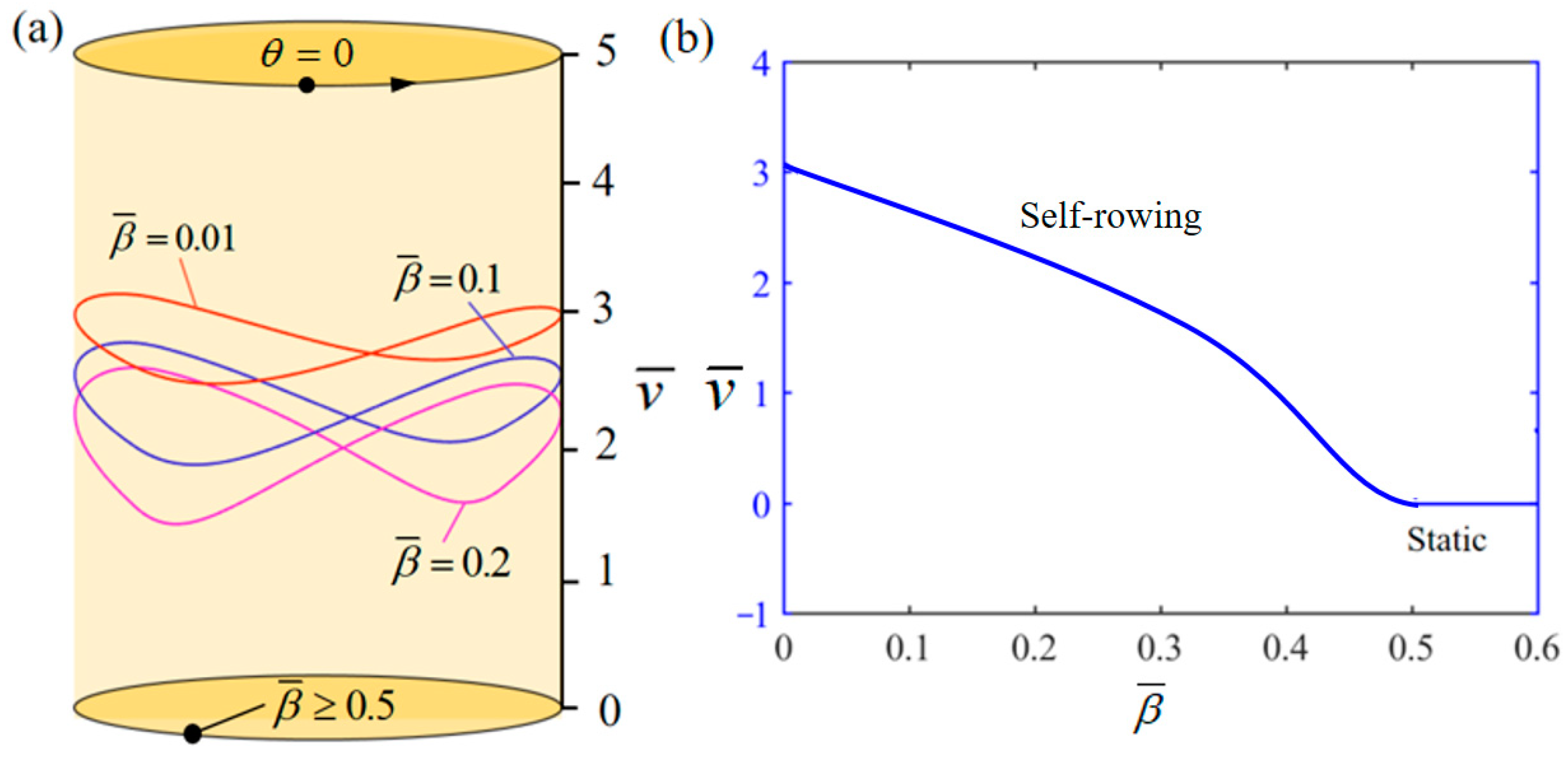
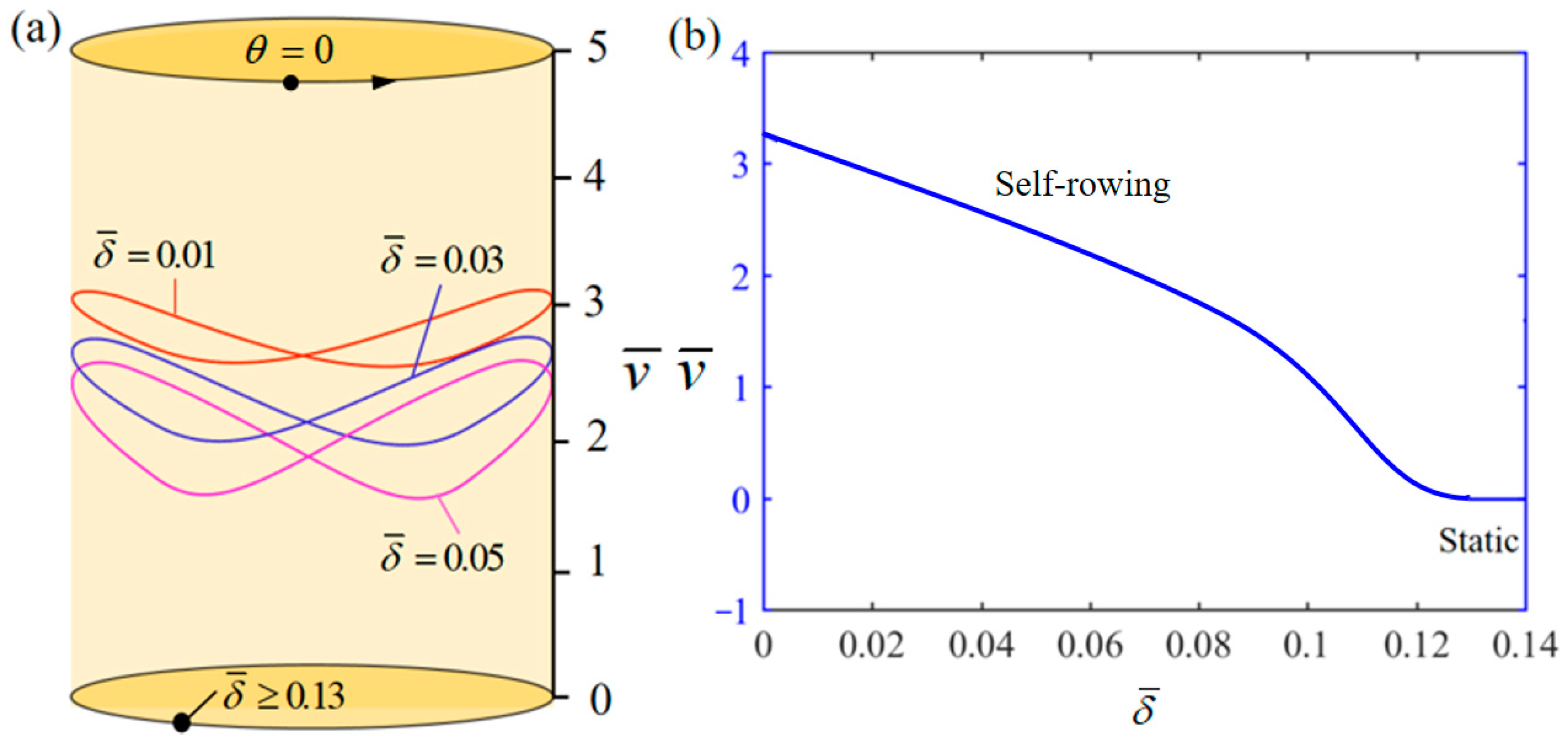
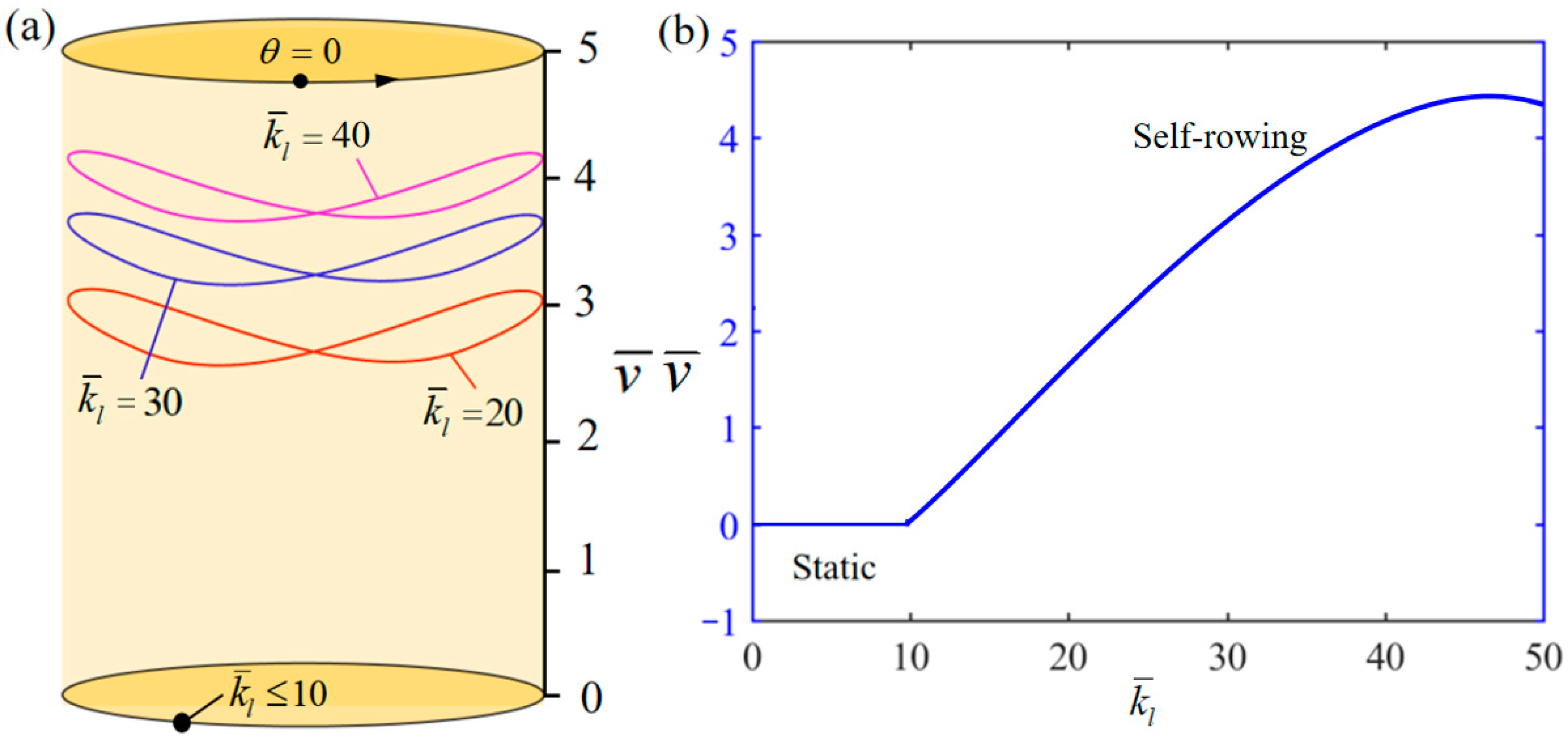


| Parameter | Definition | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thermal shrinkage coefficient of the LCE material [21,78] | 0–0.5 | / | |
| Gravitational acceleration | 10 | ||
| Damping factor | 0.001~0.01 | ||
| illumination zone angle | 0.4π~0.8π | / | |
| Initial angle of the mass ball | 0~2π | / | |
| Initial angular velocity | 0.4~2 | ||
| Elastic stiffness of the spring | 0.005~50 | ||
| Elastic stiffness of the LCE rope | 0.005~50 | ||
| Distance from mass ball to turntable center | 0.04~0.16 | ||
| Initial length of spring | 1.6~20 | ||
| Thermal characteristic time [79] | 0.001~0.1 | ||
| Limit temperature difference in LCE-rope | 0–20 | °C | |
| Specific heat capacity of LCE material | 1000~4500 | ||
| Heat flux [79] | 0~0.02 | ||
| Heat transfer coefficient [80] | 1 |
| Parameter | |||||||||||
| Value | 0–0.8 | 0.24–1 | 5–20 | 0.22–0.8 | 1–5 | 1–7 | 0–0.5 | 0–0.13 | 10–50 | 10–40 |
| Parameter | |
|---|---|
| decreases with increasing | |
| increases with increasing | |
| increases with increasing | |
| increases with increasing | |
| first increases and then decreases with increasing | |
| decreases with increasing | |
| decreases with increasing | |
| decreases with increasing | |
| increases with increasing | |
| decreases with increasing | |
| first increases and then decreases with increasing |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, Z.; Zha, J.; Liu, J. A Light-Steered Self-Rowing Liquid Crystal Elastomer-Based Boat. Polymers 2025, 17, 711. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17060711
Yuan Z, Zha J, Liu J. A Light-Steered Self-Rowing Liquid Crystal Elastomer-Based Boat. Polymers. 2025; 17(6):711. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17060711
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Zongsong, Jinze Zha, and Junxiu Liu. 2025. "A Light-Steered Self-Rowing Liquid Crystal Elastomer-Based Boat" Polymers 17, no. 6: 711. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17060711
APA StyleYuan, Z., Zha, J., & Liu, J. (2025). A Light-Steered Self-Rowing Liquid Crystal Elastomer-Based Boat. Polymers, 17(6), 711. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17060711





