Moisture-Driven Morphology Changes in the Thermal and Dielectric Properties of TPU-Based Syntactic Foams
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Manufacturing and Conditioning
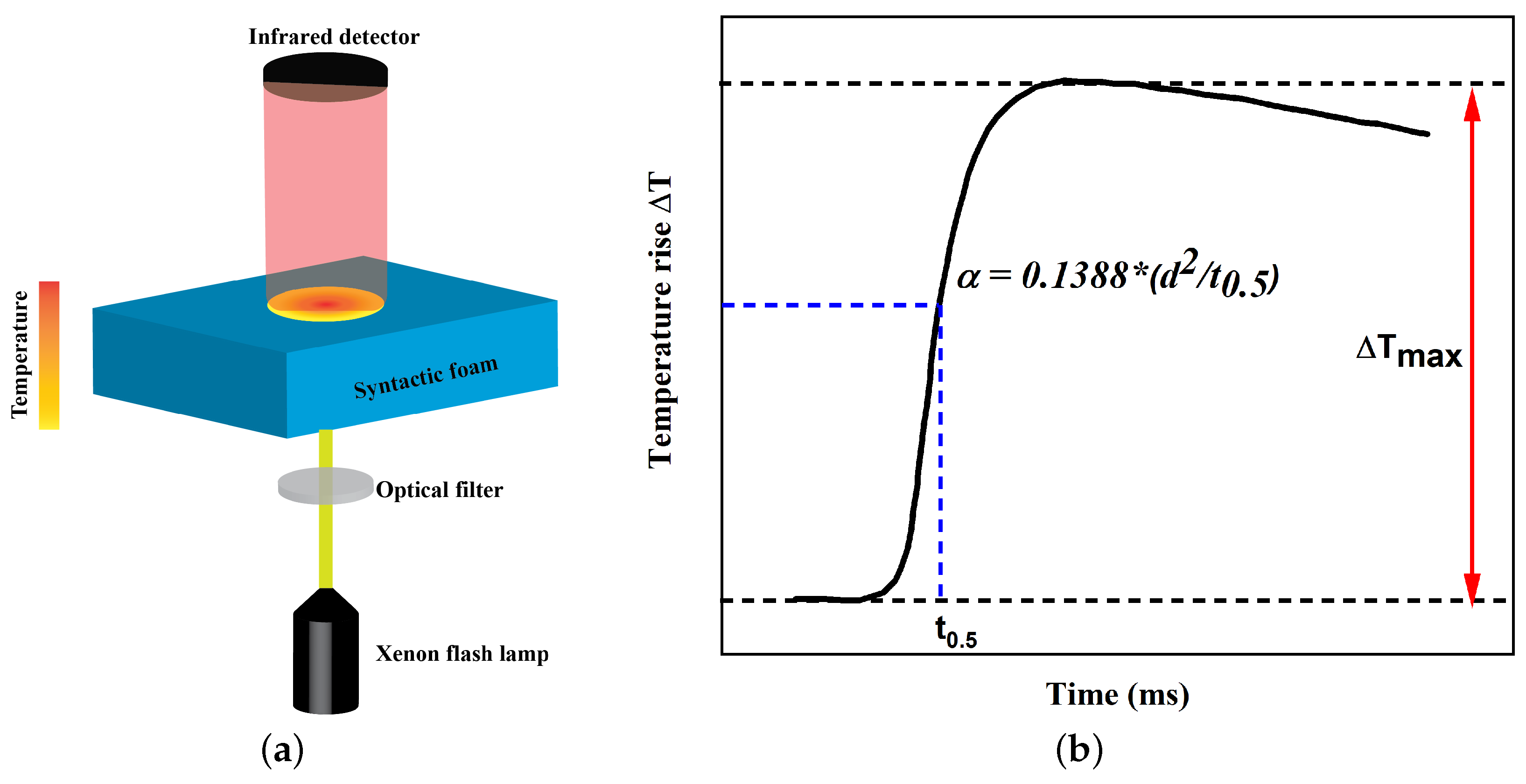
2.2. Thermal Transport Characterization
2.3. Dielectric Characterization
3. Results
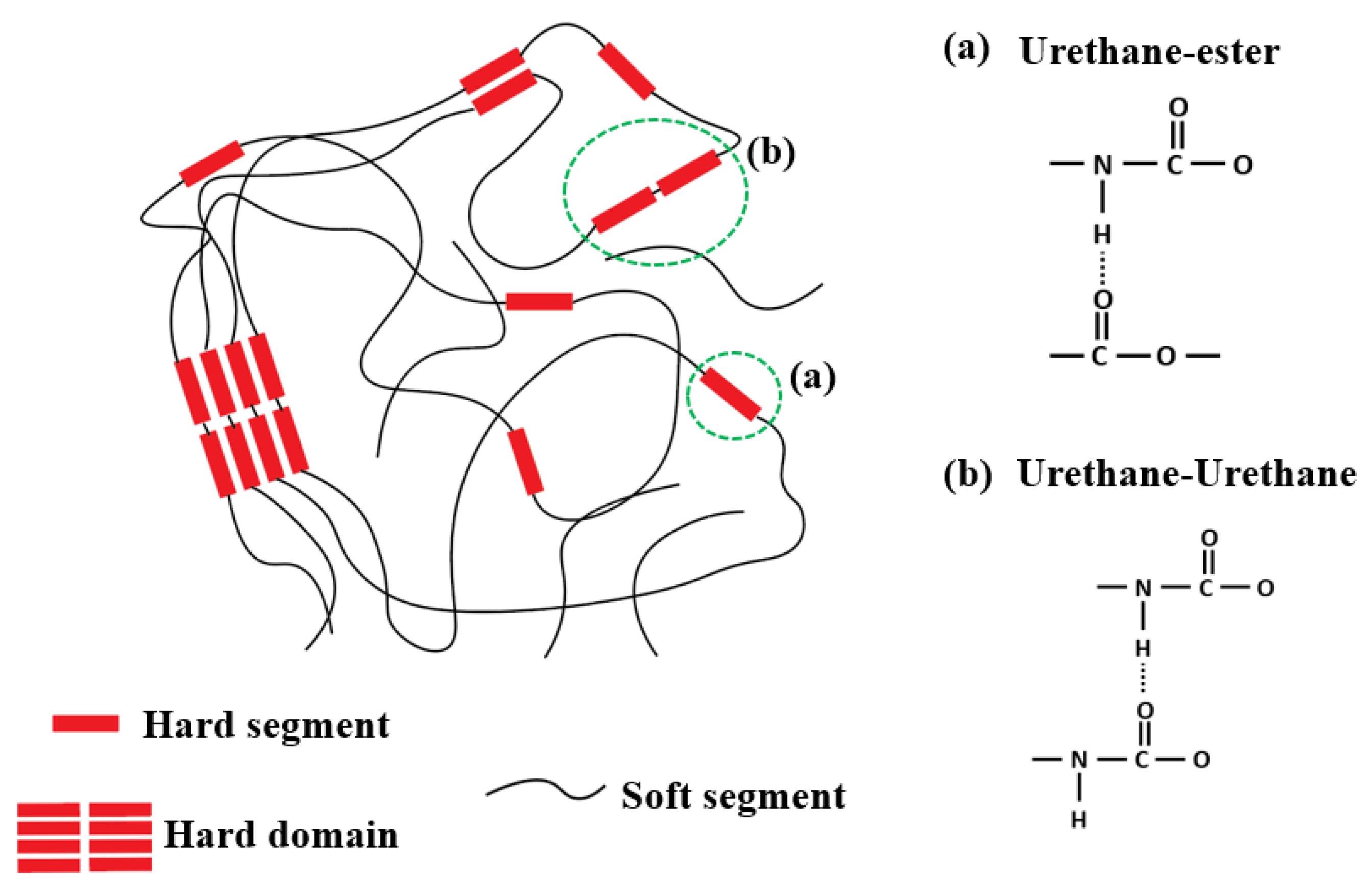
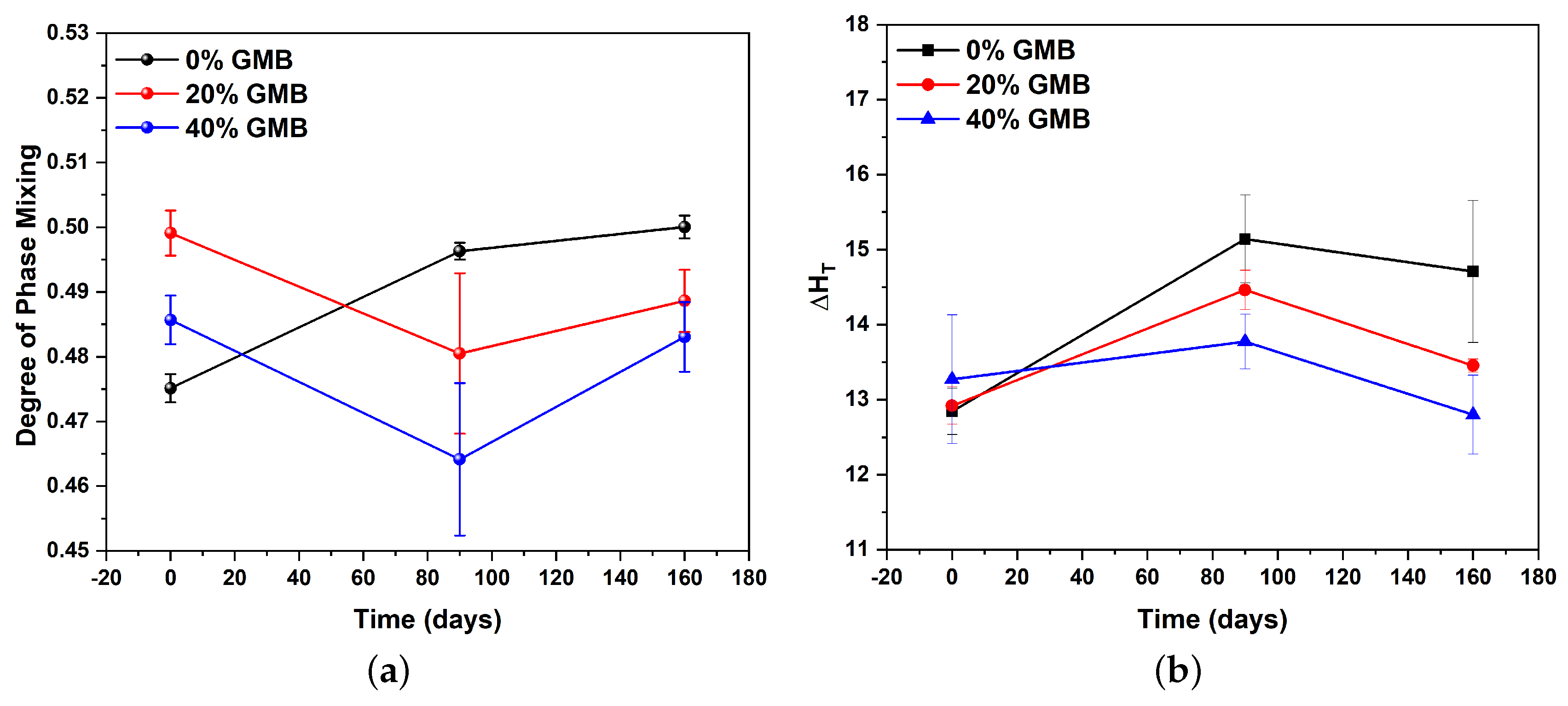
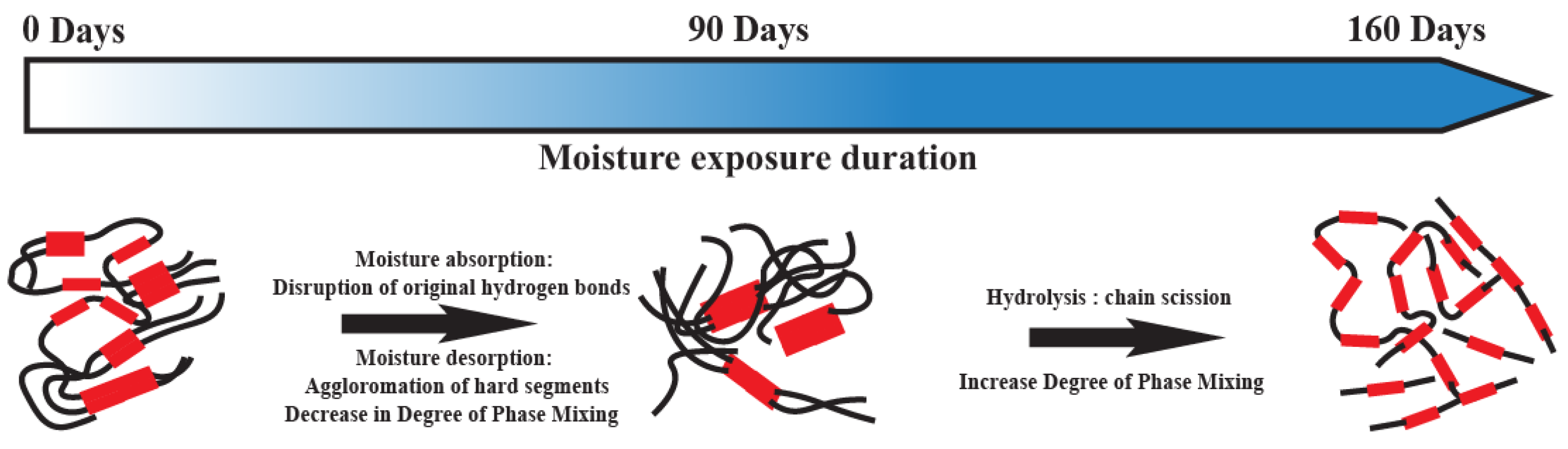
3.1. Microphase Morphological Characterization of TPU-Based Syntactic Foam
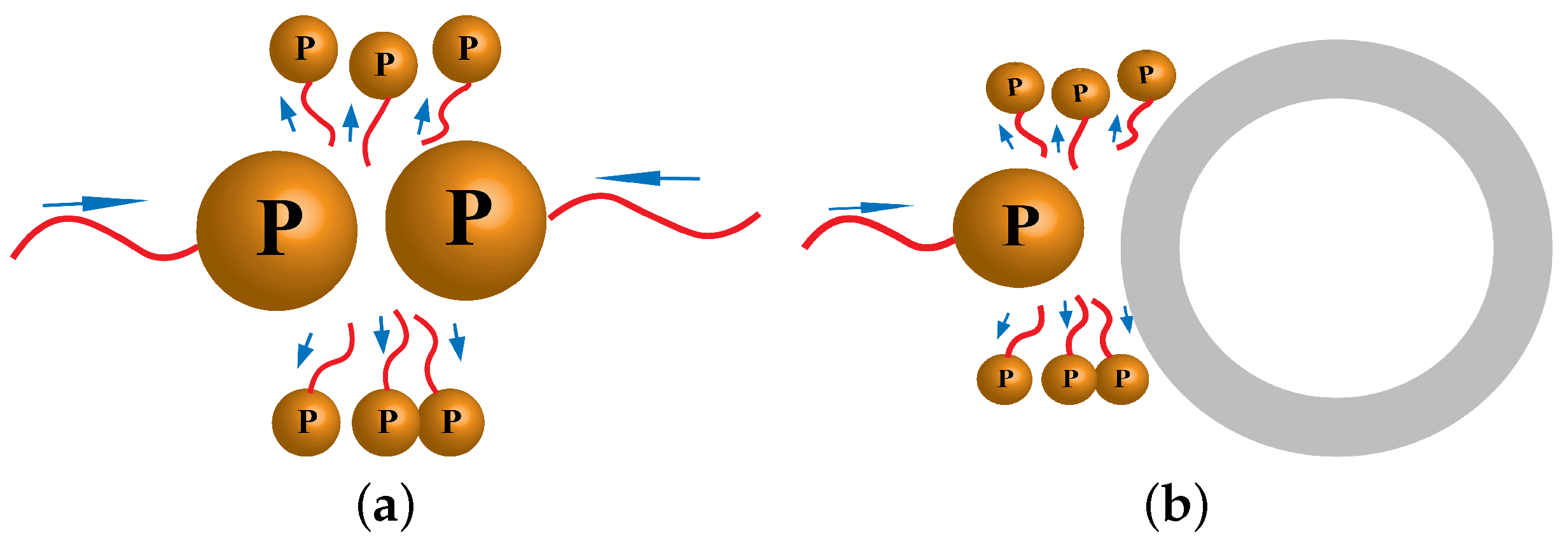
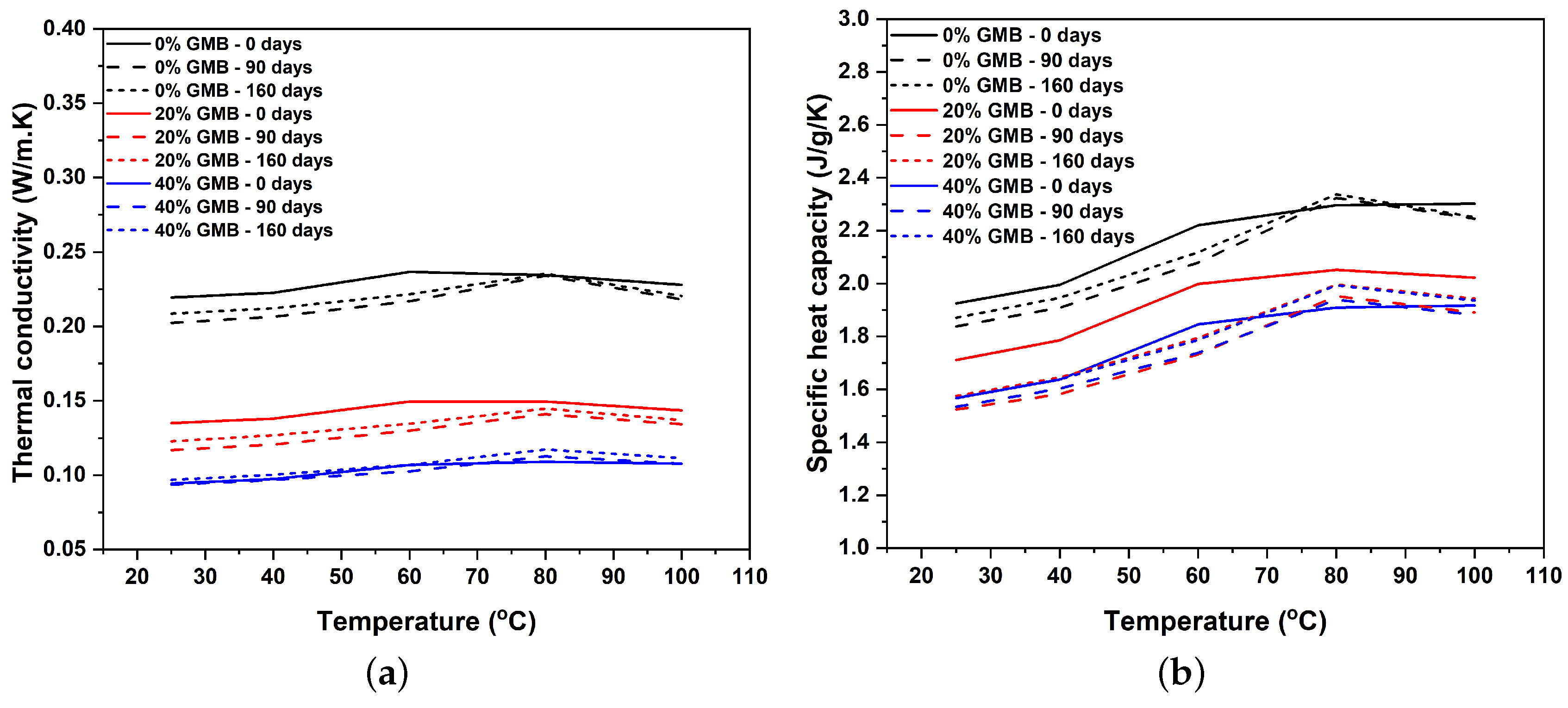
3.2. Influence of Moisture and GMB Volume Fraction on Thermal Transport Properties of Syntactic Foam
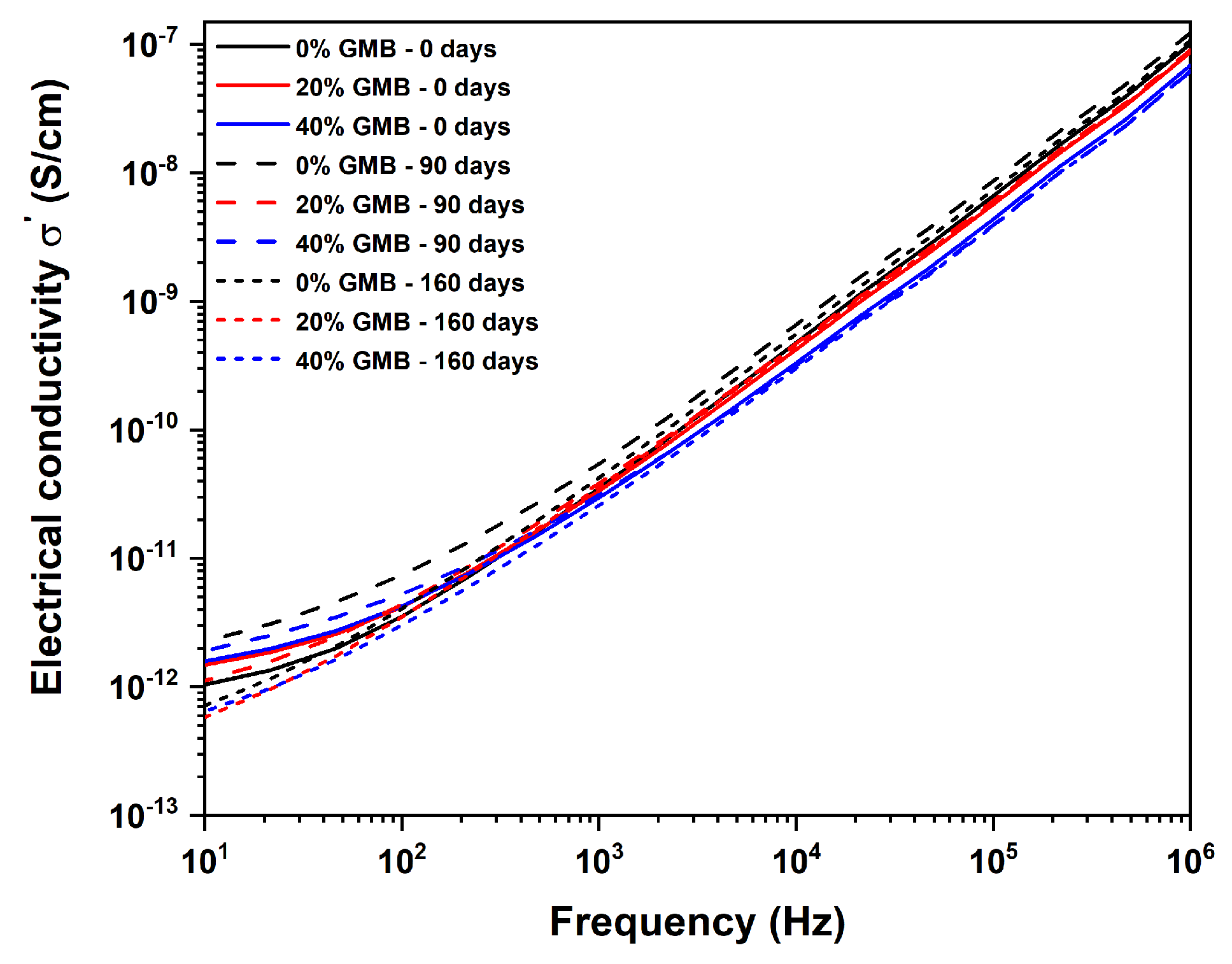
3.3. Influence of Moisture and GMB Volume Fraction on Dielectric Properties of Syntactic Foam
4. Conclusions
4.1. Thermal Transport
4.2. Dielectric Properties
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Dielectric Study

References
- Yilgör, I.; Yilgör, E.; Wilkes, G.L. Critical parameters in designing segmented polyurethanes and their effect on morphology and properties: A comprehensive review. Polymer 2015, 58, A1–A36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Gao, W.; Ren, X.; Ouyang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, H.; Wu, W.; Huang, C.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; et al. A review of microphase separation of polyurethane: Characterization and applications. Polym. Test. 2022, 107, 107489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurilia, M.; Piscitelli, F.; Sorrentino, L.; Lavorgna, M.; Iannace, S. Detailed analysis of dynamic mechanical properties of TPU nanocomposite: The role of the interfaces. Eur. Polym. J. 2011, 47, 925–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruckmoser, K.; Resch, K. Investigation of ageing mechanisms in thermoplastic polyurethanes by means of IR and Raman spectroscopy. Macromol. Symp. 2014, 339, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.W.; Yu, T.L.; Ho, C.H. Effect of aging under strain on the physical properties of polyester–urethane elastomer. Polym. J. 1994, 26, 1368–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osswald, T.A.; Menges, G. Material Science of Polymers for Engineers, 3rd ed.; Carl Hanser Verlag GmbH & Co. KG: Munich, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.; Liu, F.; Pan, G.; Zhao, Z.G.; Yang, X.; Shi, H.C.; Luan, S.F. Softening and hardening of thermal plastic polyurethane blends by water absorbed. Polymer 2021, 218, 123498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, D.; Ying, S.; Li, J. Hydrogen bonding and crystallization behaviour of segmented polyurethaneurea: Effects of hard segment concentration. Polymer 1992, 33, 1335–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, D.; Liu, L.; Liang, Y. Effect of hard segment content on structure, dielectric and mechanical properties of hydroxyl-terminated butadiene-acrylonitrile copolymer-based polyurethane elastomers. Polymer 2017, 132, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walo, M.; Przybytniak, G.; Łyczko, K.; Piatek-Hnat, M. The effect of hard/soft segment composition on radiation stability of poly(ester-urethane)s. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2014, 94, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petcharoen, K.; Sirivat, A. Electrostrictive properties of thermoplastic polyurethane elastomer: Effects of urethane type and soft-hard segment composition. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2013, 13, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Ton Loontjens, J.A.; Shan, Z. The varying mass ratios of soft and hard segments in waterborne polyurethane films: Performances of thermal conductivity and adhesive properties. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 112, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jomaa, M.H.; Seveyrat, L.; Lebrun, L.; Masenelli-Varlot, K.; Cavaille, J.Y. Dielectric properties of segmented polyurethanes for electromechanical applications. Polymer 2015, 63, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Huang, W.M.; Li, C.; Li, L. Effects of moisture on the thermomechanical properties of a polyurethane shape memory polymer. Polymer 2006, 47, 1348–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boubakri, A.; Elleuch, K.; Guermazi, N.; Ayedi, H.F. Investigations on hygrothermal aging of thermoplastic polyurethane material. Mater. Des. 2009, 30, 3958–3965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boubakri, A.; Haddar, N.; Elleuch, K.; Bienvenu, Y. Impact of aging conditions on mechanical properties of thermoplastic polyurethane. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 4194–4201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puentes-Parodi, A.; Santoro, L.A.; Ferreira, I.; Leuteritz, A.; Kuehnert, I. Influence of annealing on the permeation properties of a thermoplastic elastomer. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2019, 59, 1810–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardin, A.; Le Gac, P.; Cérantola, S.; Simon, G.; Bindi, H.; Fayolle, B. Hydrolytic kinetic model predicting embrittlement in thermoplastic elastomers. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2020, 171, 109002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Seethamraju, K.; Delaney, J.; Willoughby, P.; Faust, R. Long-term in vitro hydrolytic stability of thermoplastic polyurethanes. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2015, 103, 3798–3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.Y.; Kim, C.K. Degradation and lifetime prediction of thermoplastic polyurethane encapsulants in seawater for underwater acoustic sensor applications. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2023, 209, 110281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Zeltmann, S.E.; Shunmugasamy, V.C.; Pinisetty, D. Applications of polymer matrix syntactic foams. JOM 2014, 66, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afolabi, L.O.; Ariff, Z.M.; Hashim, S.; Alomayri, T.; Mahzan, S.; Kamarudin, K.; Muhammad, I. Syntactic foams formulations, production techniques, and industry applications: A review. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 10698–10718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahapurkar, K.; Garcia, C.D.; Doddamani, M.; Mohan Kumar, G.C.; Prabhakar, P. Compressive behavior of cenosphere/epoxy syntactic foams in arctic conditions. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 135, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, C.; Shahapurkar, K.; Doddamani, M.; Kumar, G.; Prabhakar, P. Effect of arctic environment on flexural behavior of fly ash cenosphere reinforced epoxy syntactic foams. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 151, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakar, P.; Feng, H.; P. Subramaniyan, S.; Doddamani, M. Densification mechanics of polymeric syntactic foams. Compos. Part B Eng. 2022, 232, 109597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amos, S.E.; Yalcin, B. Hollow Glass Microspheres for Plastics, Elastomers, and Adhesives Compounds; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Tripathi, M.; Parthasarathy, S.; Yadav, R.; Roy, P.K. Flexible silicone-hollow glass microballoon syntactic foams for application in fire protective clothing. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, 52101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniyan, S.P.; Prabhakar, P. Moisture-Driven Degradation Mechanisms in the Viscoelastic Properties of TPU-Based Syntactic Foams. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2023, 218, 110547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewani, H.; Hinaus, M.; Talukdar, M.; Sone, H.; Prabhakar, P. Architected syntactic foams: A tale of additive manufacturing and reinforcement parameters. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2211.00955. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, M.; Zhu, W.; Yu, S.; Tian, Y.; Zhou, K. Selective laser sintering of carbon nanotube–coated thermoplastic polyurethane: Mechanical, electrical, and piezoresistive properties. Compos. Part C Open Access 2022, 7, 100212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, W.; Hu, H.; Rui, Z.; Du, X.; Zhao, T.; Li, J. Multi-dimensional fillers synergistically enhanced thermal conductivity of TPU composites in selective laser sintering technology. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 33, 104012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Lavorgna, M.; Ronca, A.; Fei, G.; Xia, H. Simultaneous realization of conductive segregation network microstructure and minimal surface porous macrostructure by SLS 3D printing. Mater. Des. 2019, 178, 107874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Zheng, Y.; Chua, C.K.; Yan, Q.; Zhou, K. Electrical and thermal conductivities of MWCNT/polymer composites fabricated by selective laser sintering. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2018, 105, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, Z.; Gan, X.; Fu, D.; Fei, G.; Xia, H. Selective Laser Sintering 3D Printing: A Way to Construct 3D Electrically Conductive Segregated Network in Polymer Matrix. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2017, 302, 1700211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Wu, W.; Hu, H.; Rui, Z.; Ye, J.; Zhang, C. Preparation of carbon black/graphene nanosheets/PP composites with 3D separated conductive networks based on selective laser sintering. Polym. Compos. 2023, 44, 3522–3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, W.; Zhao, T.; Li, J. The combination of AlN and h-BN for enhancing the thermal conductivity of thermoplastic polyurethane composites prepared by selective laser sintering. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, e53051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raihan, M.R. Dielectric Properties of Composite Materials During Damage Accumulation and Fracture. Ph.D. Thesis, University of South Carolina, Columbia, SC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Brett, J.K.; Celina, M.C. Hydrolysis of poly(ester urethane): In-depth mechanistic pathways through FTIR 2D-COS spectroscopy. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2025, 231, 111094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahebi Jouibari, I.; Haddadi-Asl, V.; Mirhosseini, M. A novel investigation on micro-phase separation of thermoplastic polyurethanes: Simulation, theoretical, and experimental approaches. Iran. Polym. J. 2019, 28, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehra, N.; Mu, L.; Ji, T.; Yang, X.; Kong, J.; Gu, J.; Zhu, J. Thermal transport in polymeric materials and across composite interfaces. Appl. Mater. Today 2018, 12, 92–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Ruan, K.; Shi, X.; Yang, X.; Gu, J. Factors affecting thermal conductivities of the polymers and polymer composites: A review. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 193, 108134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashora, P.; Gupta, G. On the temperature dependence of the thermal conductivity of linear amorphous polymers. Polymer 1996, 37, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Ma, J.; Wang, J.; Wu, J.; Peng, D. Thermal, dielectric and compressive properties of hollow glass microsphere filled epoxy-matrix composites. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2012, 31, 1311–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.L.; Zheng, H.; Wang, J.; Ma, J.; Wu, J.; Wu, R. Tailoring of thermal and dielectric properties of LDPE-matrix composites by the volume fraction, density, and surface modification of hollow glass microsphere filler. Compos. Part B Eng. 2014, 58, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Priya, S.; Islam, R.; Ricci, W. Characterization of mechanical and electrical properties of epoxy-glass microballoon syntactic composites. Ferroelectrics 2006, 345, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, J.C. A Treatise on Electricity and Magnetism; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1873; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, K.W. The after effect in dielectrics. Arch. Electrotech. 1914, 2, e394. [Google Scholar]
- Sillars, R.W. The properties of a dielectric containing semiconducting particles of various shapes. J. Inst. Electr. Eng. 1937, 80, 378–394. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Zhou, J.; Jin, L.; Long, X.; Wu, H.; Xu, L.; Gong, Y.; Zhou, W. Improved dielectric properties of thermoplastic polyurethane elastomer filled with core-shell structured PDA@TiC particles. Materials 2020, 13, 3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, P.P.; Vadlamudi, V.; Raihan, R. Dielectric state variables as qualitative indicators of moisture absorption-caused mechanical property degradation in GFRP composite structures. Compos. Part C Open Access 2022, 9, 100295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Note, A.A. Agilent Basics of Measuring the Dielectric Properties of Materials; Agilent Literature Number; Agilent Technologies: Santa Clara, CA, USA, 2006; pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pushparaj Subramaniyan, S.; Das, P.P.; Raihan, R.; Prabhakar, P. Moisture-Driven Morphology Changes in the Thermal and Dielectric Properties of TPU-Based Syntactic Foams. Polymers 2025, 17, 691. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17050691
Pushparaj Subramaniyan S, Das PP, Raihan R, Prabhakar P. Moisture-Driven Morphology Changes in the Thermal and Dielectric Properties of TPU-Based Syntactic Foams. Polymers. 2025; 17(5):691. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17050691
Chicago/Turabian StylePushparaj Subramaniyan, Sabarinathan, Partha Pratim Das, Rassel Raihan, and Pavana Prabhakar. 2025. "Moisture-Driven Morphology Changes in the Thermal and Dielectric Properties of TPU-Based Syntactic Foams" Polymers 17, no. 5: 691. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17050691
APA StylePushparaj Subramaniyan, S., Das, P. P., Raihan, R., & Prabhakar, P. (2025). Moisture-Driven Morphology Changes in the Thermal and Dielectric Properties of TPU-Based Syntactic Foams. Polymers, 17(5), 691. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17050691





