Study on an Injectable Chitosan–Lignin/Poloxamer Hydrogel Loaded with Platelet-Rich Plasma for Intrauterine Adhesion Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Preparations
2.2. Preparation of the CL-PF127@PRP Hydrogel
2.3. Structural Characterization
2.4. In Vitro Soaking of Hydrogels
2.5. In Vitro PRP Release of CL-PF127@PRP Hydrogels
2.6. Preparation of the Hydrogel Extract
2.7. Cell Culture
2.8. Biocompatibility
2.9. RT-qPCR Testing
2.10. Western Blot
2.11. Construction of a Cellular Inflammation Model
2.12. Angiogenesis Experiment
2.13. Animal Experiment
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of the CL-PF127@PRP Hydrogel
3.1.1. FT-IR Analysis
3.1.2. SEM Observation
3.1.3. Rheological Analysis
3.1.4. Injectability Test
3.2. In Vitro Soaking of the Poloxamer–Chitosan/Lignin/PRP Hydrogel
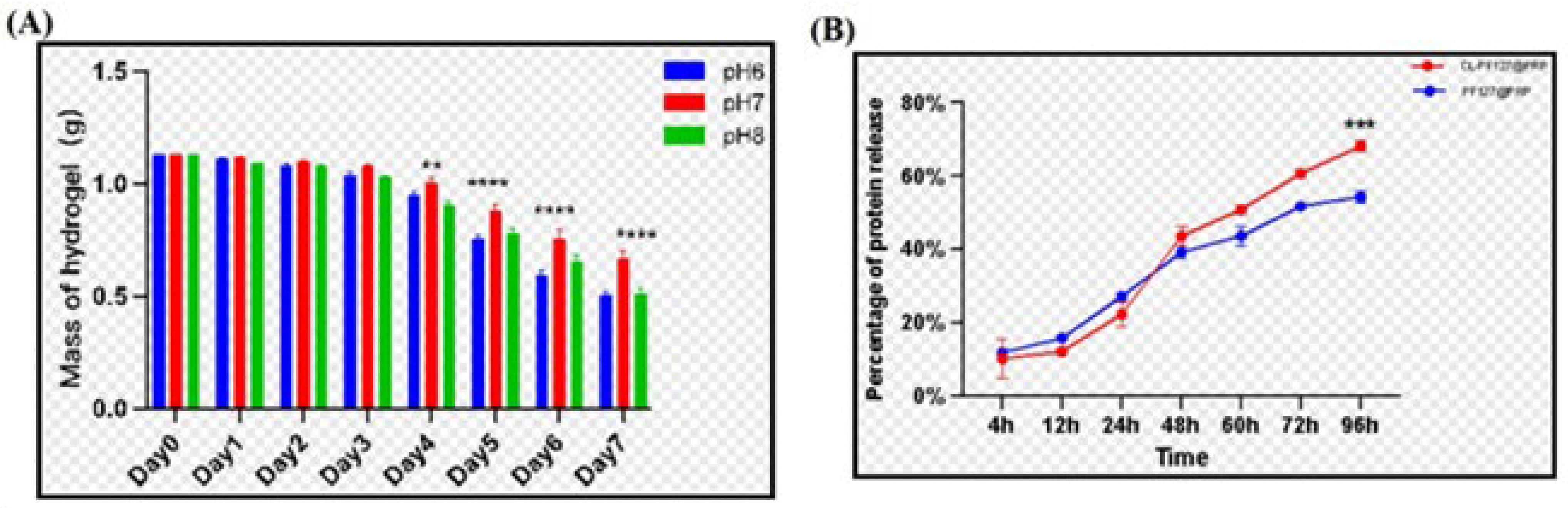
3.2.1. Weight Loss of Samples After Degradation
3.2.2. Release of PRP of the Poloxamer–Chitosan/Lignin/PRP Hydrogel
3.3. Biocompatibility of Hydrogels
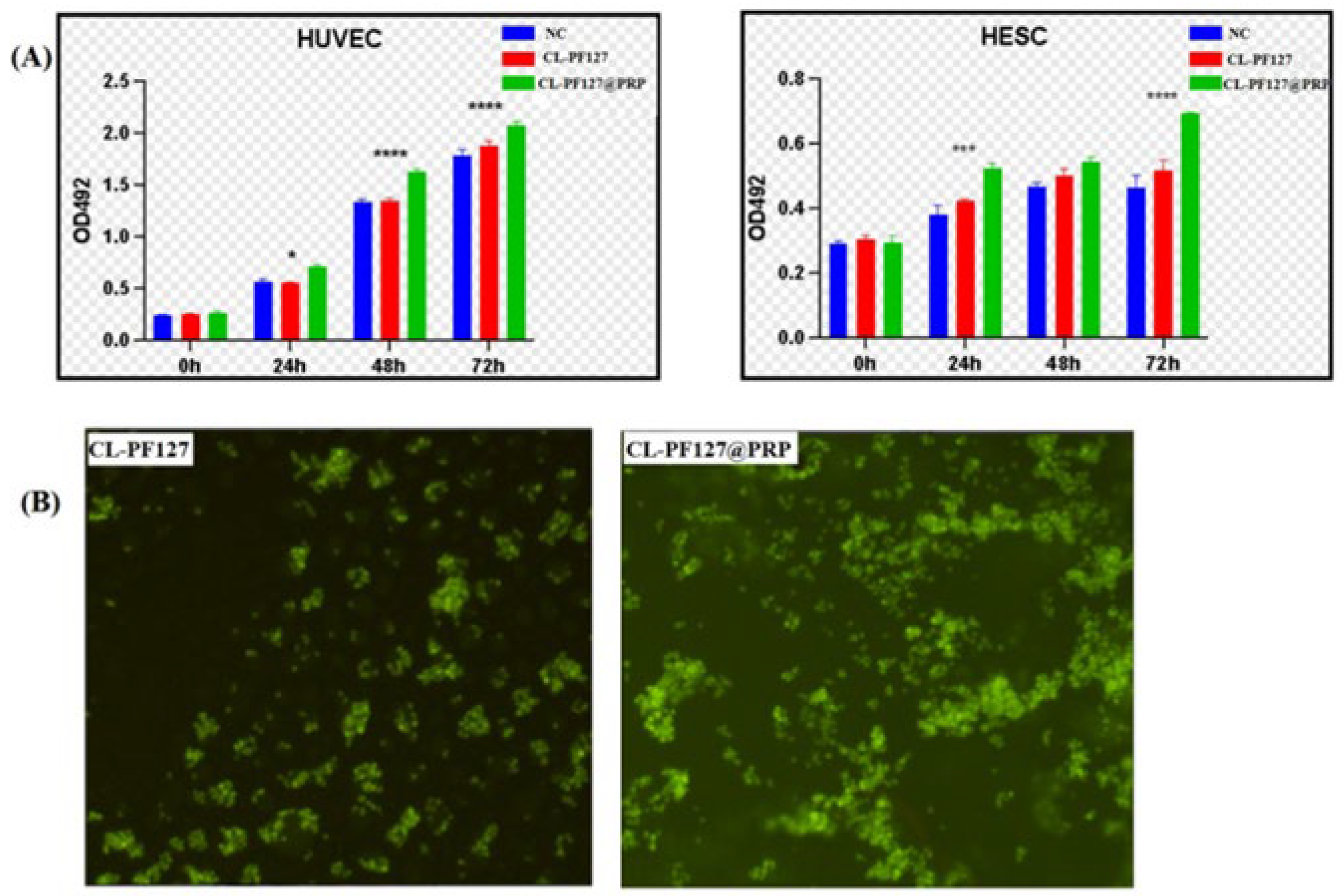
3.3.1. MTT Test
3.3.2. AO Fluorescence Staining
3.4. Anti-Inflammatory
3.5. Angiogenesis Promotion
3.6. Animal Experiment
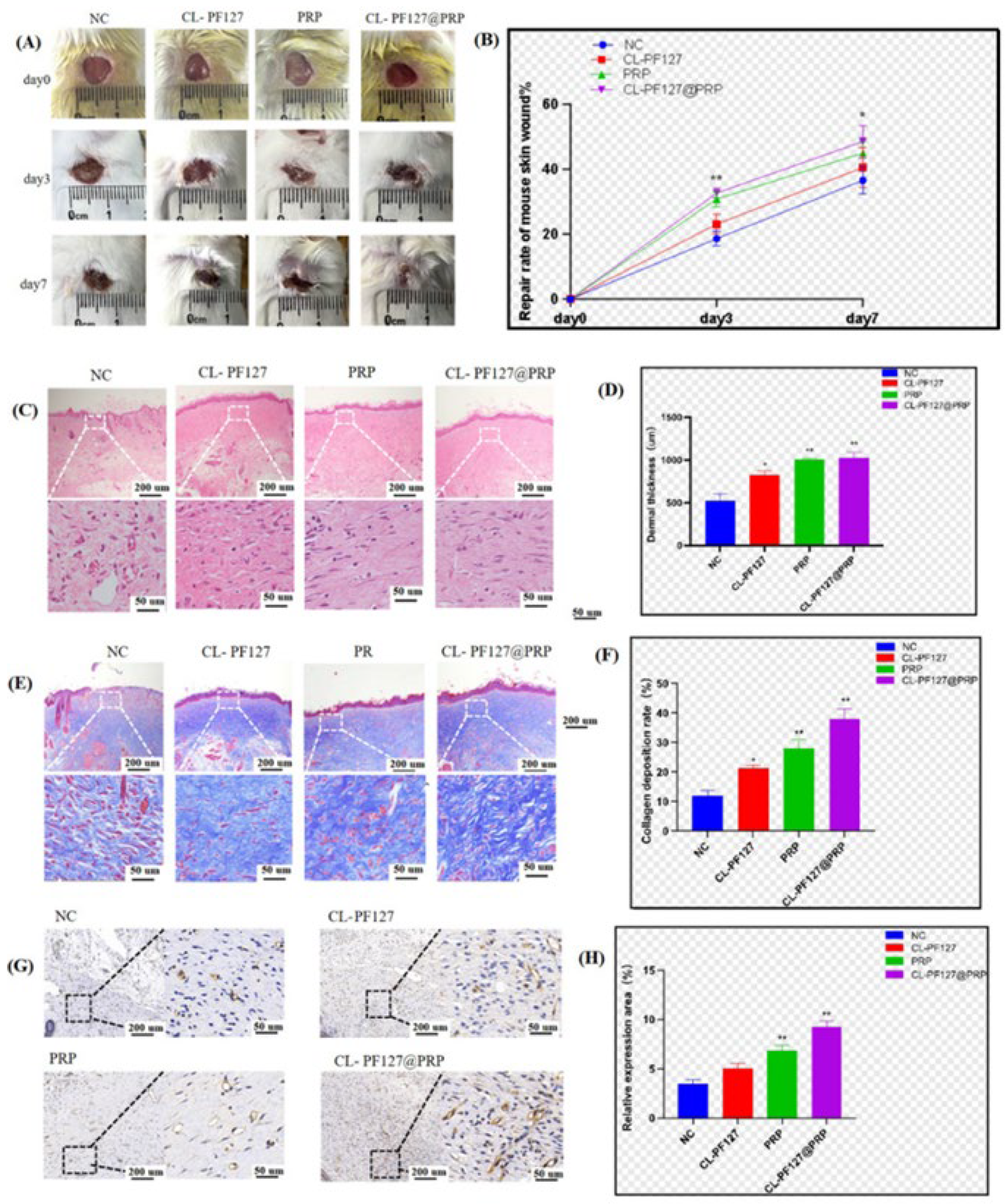
3.6.1. Skin Injury Repair in Mice
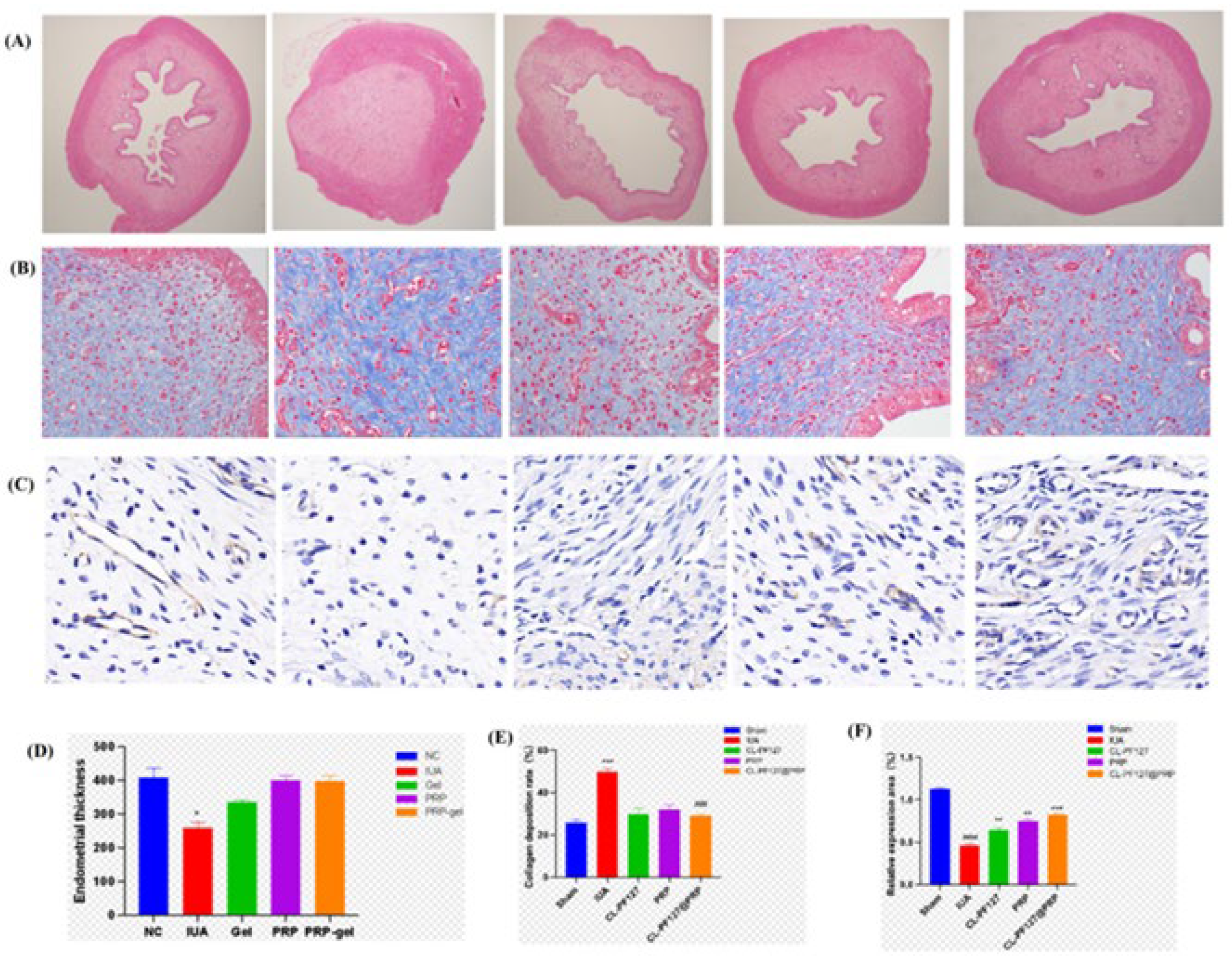
3.6.2. Intrauterine Adhesion Repair in SD Rats
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, H.H.; Chen, W.J.; Liu, Y.H.; Zhu, Y.C.; Huang, Y.N.; Lu, Z.X. Janus adhesive microneedle patch loaded with exosomes for intrauterine adhesion treatment. J. Mater. Chem. B 2024, 12, 3543–3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.S.; Lai, J.H.; Chen, J.Z.; Zheng, L.W.; Wang, M. 3D printed gelatin/PTMC core/shell scaffolds with NIR laser-tuned drug/biomolecule release for cancer therapy and uterine regeneration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 283, 137193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Z.X.; Wang, H.; Ma, P.X.; Guo, B.L. Self-healing conductive hydrogels: Preparation, properties and applications. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 1224–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, H.Y.; Wu, B.B.; Song, J.Y.; Wu, W.; Cai, W.Y.; Xu, J. Hydrogel, a novel therapeutic and delivery strategy, in the treatment of intrauterine adhesions. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 6536–6552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.Y.; Wang, L.Q.; Ma, Y.; Duan, W.L.; Martin-Saldaña, S.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, B.; Li, C.; Hu, S.; et al. Engineering self-healing adhesive hydrogels with antioxidant properties for intrauterine adhesion prevention. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 27, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, N.A.; Dai, C.Y.; Mao, X.R.; Lv, X.; Gu, Y.; Lee, E.S.; Jiang, H.B.; Sun, Y. Poloxamer-Based Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering Applications: A Review. Gels 2022, 8, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliano, E.; Paolino, D.; Fresta, M.; Cosco, D. Mucosal Applications of Poloxamer 407-Based Hydrogels: An Overview. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.H.; Deng, Y.F.; Zhang, Y.C.; Feng, P.; Xu, C.H.; Fu, L.H.; Lin, B. Study on long-term pest control and stability of double-layer pesticide carrier in indoor and outdoor environment. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 403, 126342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.Z.; Wang, Y.S.; Wang, Z.J.; He, Y.F.; Song, P.F.; Wang, R.M. Preparation and Properties of Hydrogels Based on Lignosulfonate and Its Efficiency of Drug Delivery. Chemistryselect 2021, 6, 8213–8218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culebras, M.; Barrett, A.; Pishnamazi, M.; Walker, G.M.; Collins, M.N. Wood-Derived Hydrogels as a Platform for Drug-Release Systems. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 2515–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craciun, A.M.; Morariu, S.; Marin, L. Self-Healing Chitosan Hydrogels: Preparation and Rheological Characterization. Polymers 2022, 14, 2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, B.R.; Hua, S.Y.; Tian, Y.; Liu, J.Y. Chemical and physical chitosan hydrogels as prospective carriers for drug delivery: A review. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 10050–10064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enoch, K.; Rakavi, C.S.; Somasundaram, A.A. Thixotropic chitosan hydrogels for biomedical applications: Unravelling the effect of chitosan concentration on the mechanical behaviour. Surf. Interfaces 2024, 50, 104475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Yang, F.C.; Guo, Z.G. The chitosan hydrogels: From structure to function. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 17162–17180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.L.; Zhang, T.; Li, N.; Cong, H.P.; Yu, S.H. Anisotropic and self-healing hydrogels withmulti-responsiveactuating capability. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Jiang, L.Y.; Ma, B.L.; Tang, C.Y.; Wen, Y.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Su, S.P. Preparation and characterization of bamboo fiber/chitosan/nano-hydroxyapatite composite membrane by ionic crosslinking. Cellulose 2020, 27, 5089–5100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Jiang, L.Y.; Jiang, Z.H.; Ma, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.; Su, S.P. Preparation and Characterization of a Novel Tragacanth Gum/Chitosan/Sr-Nano-Hydroxyapatite Composite Membrane. Polymers 2023, 15, 2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohman, G.; Langueh, C.; Ramtani, S.; Lataillade, J.J.; Lutomski, D.; Senni, K.; Changotade, S. The Use of Platelet-Rich Plasma to Promote Cell Recruitment into Low-Molecular-Weight Fucoidan-Functionalized Poly(Ester-Urea-Urethane) Scaffolds for Soft-Tissue Engineering. Polymers 2019, 11, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, M.; Daneshpajooh, A.; Farsinezhad, A.; Jafarian, Z.; Ebadzadeh, M.R.; Saberi, N.; Teimorian, M. The Therapeutic Effect of Intravesical Instillation of Platelet Rich Plasma on Recurrent Bacterial Cystitis in Women: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Urol. J. 2019, 16, 609–613. [Google Scholar]
- Pincelli, T.; Zawawi, S.; Shapiro, S.; Heckman, M.G.; Hochwald, A.P.; Desmond, C.; Arthurs, J.; Tolaymat, L.; Forte, A.; Bruce, A. A Pilot, Randomized, Single-Blind, Controlled Study Evaluating the Use of Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) for Hand Skin Rejuvenation. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2024, 154, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seker, S.; Elçin, A.E.; Elçin, Y.M. Current trends in the design and fabrication of PRP-based scaffolds for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Biomed. Mater. 2025, 20, 022001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Z.; Wang, H.; Bai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tao, L.; Wei, Y.; Fan, Y.; Guo, X.; Liu, H. Improving Chronic Diabetic Wound Healing through an Injectable and Self-Healing Hydrogel with Platelet-Rich Plasma Release. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 55659–55674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; Deng, S.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, W.; Chen, W.; Huang, L.; Zhang, C.; Li, M.; Ao, L.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Platelet Rich Plasma Loaded Multifunctional Hydrogel Accelerates Diabetic Wound Healing via Regulating the Continuously Abnormal Microenvironments. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 12, 202301370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, G.; Sharma, G.; Raheja, A.; Sarkar, P. The effect of subendometrial injection of autologous platelet rich plasma (PRP) guided by hysteroscopy in recurrent implantation failure patients-A pilot study. Hum. Reprod. 2023, 38, 931100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.T.; Li, M.Z.; Zeng, H.T.; Zeng, Z.; Huang, J.A.; Liang, X.Y. Intrauterine infusion of platelet-rich plasma is a treatment method for patients with intrauterine adhesions after hysteroscopy. Int. J. Gynecol. Obstet. 2020, 151, 362–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehraninejad, E.S.; Kashani, N.G.; Hosseini, A.; Tarafdari, A. Autologous platelet-rich plasma infusion does not improve pregnancy outcomes in frozen embryo transfer cycles in women with history of repeated implantation failure without thin endometrium. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2021, 147, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari, L.; Salehpour, S.; Hoseini, S.; Zadehmodarres, S.; Azargashb, E. Effects of autologous platelet-rich plasma on endometrial expansion in patients undergoing frozen-thawed embryo transfer: A double-blind RCT. Int. J. Reprod. Biomed. 2019, 17, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.-Y.; Myoung, S.M.; Choe, J.M.; Kim, T.; Cheon, Y.-P.; Kim, Y.M.; Park, H. Effects of Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma on Regeneration of Damaged Endometrium in Female Rats. Yonsei Med. J. 2017, 58, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Park, M.; Paek, J.Y.; Lee, W.S.; Song, H.; Lyu, S.W. Intrauterine Infusion of Human Platelet-Rich Plasma Improves Endometrial Regeneration and Pregnancy Outcomes in a Murine Model of Asherman’s Syndrome. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 103389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apakupakul, J.; Sattasathuchana, P.; Chanloinapha, P.; Thengchaisri, N. Optimization of a rapid one-step platelet-rich plasma preparation method using syringe centrifugation with and without carprofen. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Liang, Y.; Sun, L.; Yang, Z.; Xu, J.; Dong, D.; Liu, H. Degradation Characteristics of Cellulose Acetate in Different Aqueous Conditions. Polymers 2023, 15, 4505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.P.; Tang, E.N.; Zhao, H.J. An Environmentally Sensitive Silk Fibroin/Chitosan Hydrogel and Its Drug Release Behaviors. Polymers 2019, 11, 1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasemali, S.; Barzegar, A.; Farajnia, S.; Rahmati, M.; Negahdari, B.; Etemadi, A.; Nazari, A. VEGFR2 Mimicking Peptide Inhibits the Proliferation of Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells (Huvecs) by Blocking VEGF. Anti-Cancer Agent. Me 2023, 23, 1678–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slyusarenko, M.; Nikiforova, N.; Sidina, E.; Nazarova, I.; Egorov, V.; Garmay, Y.; Merdalimova, A.; Yevlampieva, N.; Gorin, D.; Malek, A. Formation and Evaluation of a Two-Phase Polymer System in Human Plasma as a Method for Extracellular Nanovesicle Isolation. Polymers. 2021, 13, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, K.A.; Miller, A.F.; Oceandy, D.; Saiani, A. Western blot analysis of cells encapsulated in self-assembling peptide hydrogels. Biotechniques 2017, 63, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Z.Y.; Ding, N.; Lin, S.; Zhang, S.; Xiao, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, S. Polysaccharide Based Self-Driven Tubular Micro/Nanomotors as a Comprehensive Platform for Quercetin Loading and Anti-inflammatory Function. Biomacromolecules. 2024, 25, 6840–6854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.B.; Balikov, D.A.; Yang, J.W.; Kim, K.S.; Park, H.K.; Kim, J.K.; Kwon, I.K.; Bellan, L.M.; Sung, H.-J. Cationic Nanocylinders Promote Angiogenic Activities of Endothelial Cells. Polymers 2016, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlevanneshan, Z.; Deypour, M.; Kefayat, A.; Rafienia, M.; Sajkiewicz, P.; Neisiany, R.E. Polyurethane-Nanolignin Composite Foam Coated with Propolis as a Platform for Wound Dressing: Synthesis and Characterization. Polymers 2021, 13, 3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Li, X.; Cao, Y.; Long, Y.; Lai, J.; Yao, Y.; Meng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.-D.; Vankelecom, H.; et al. Locationally activated PRP via an injectable dual-network hydrogel for endometrial regeneration. Biomaterials 2024, 309, 122615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yu, L.; Wu, F.; Jiang, J.; Yang, H.; Bi, R.; Yu, Y. Novel Ca-SLS-LDH nanocomposites obtained via lignosulfonate modification for corrosion protection of steel bars in simulated concrete pore solution. Appl. Clay Sci. 2021, 211, 106195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, Z.; Min, Y.; Ouyang, Q.; Fu, Y.; Mao, Y.; Xiang, S.; Hu, X.; Jiang, L. Study on an Injectable Chitosan–Lignin/Poloxamer Hydrogel Loaded with Platelet-Rich Plasma for Intrauterine Adhesion Treatment. Polymers 2025, 17, 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17040474
Yu Z, Min Y, Ouyang Q, Fu Y, Mao Y, Xiang S, Hu X, Jiang L. Study on an Injectable Chitosan–Lignin/Poloxamer Hydrogel Loaded with Platelet-Rich Plasma for Intrauterine Adhesion Treatment. Polymers. 2025; 17(4):474. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17040474
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Zhipeng, Yang Min, Qi Ouyang, Yuting Fu, Ying Mao, Shuanglin Xiang, Xiang Hu, and Liuyun Jiang. 2025. "Study on an Injectable Chitosan–Lignin/Poloxamer Hydrogel Loaded with Platelet-Rich Plasma for Intrauterine Adhesion Treatment" Polymers 17, no. 4: 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17040474
APA StyleYu, Z., Min, Y., Ouyang, Q., Fu, Y., Mao, Y., Xiang, S., Hu, X., & Jiang, L. (2025). Study on an Injectable Chitosan–Lignin/Poloxamer Hydrogel Loaded with Platelet-Rich Plasma for Intrauterine Adhesion Treatment. Polymers, 17(4), 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17040474





