Impact of Printing Angle and Layer Height on the Mechanical Strength of PLA Reinforced with Chopped Carbon Fibres Using FDM 3D Printing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Print Settings
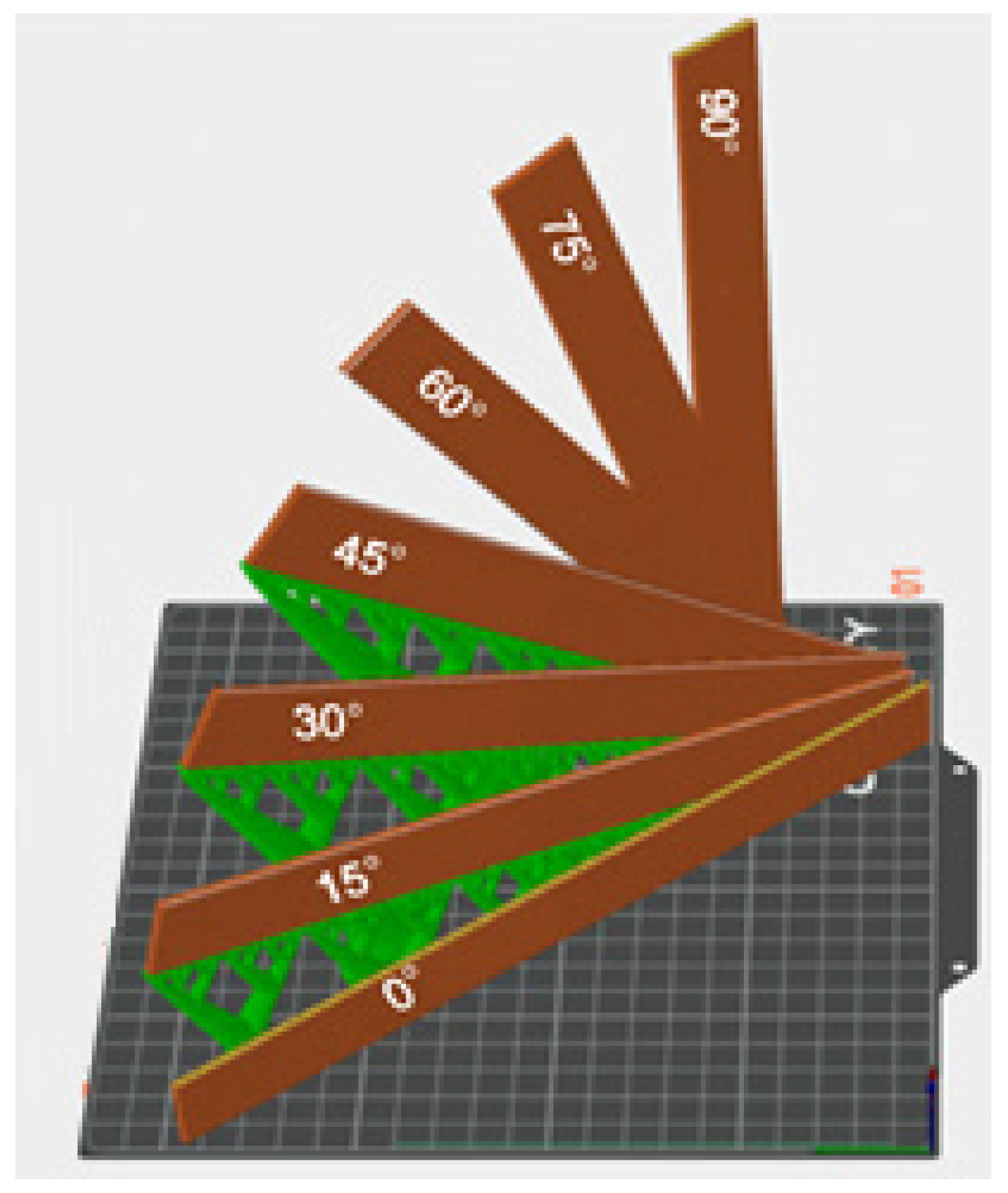
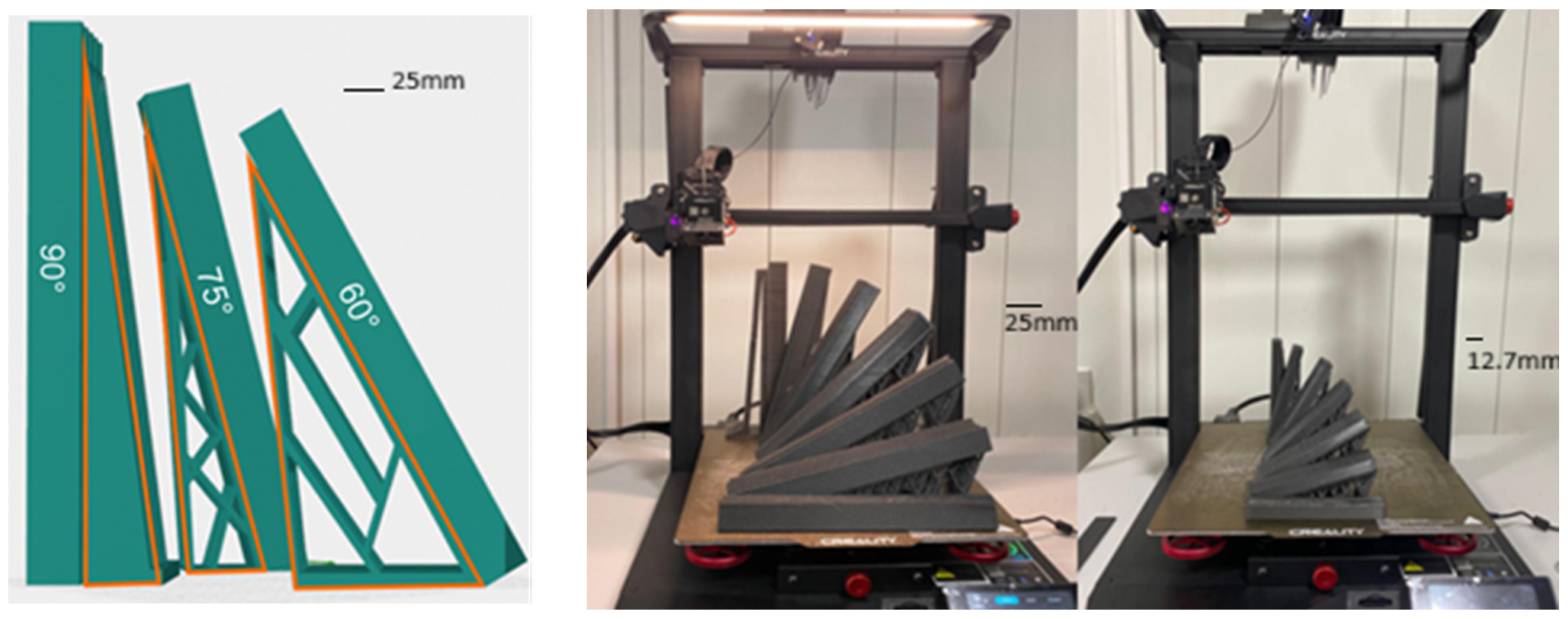
2.2. Experimental Design
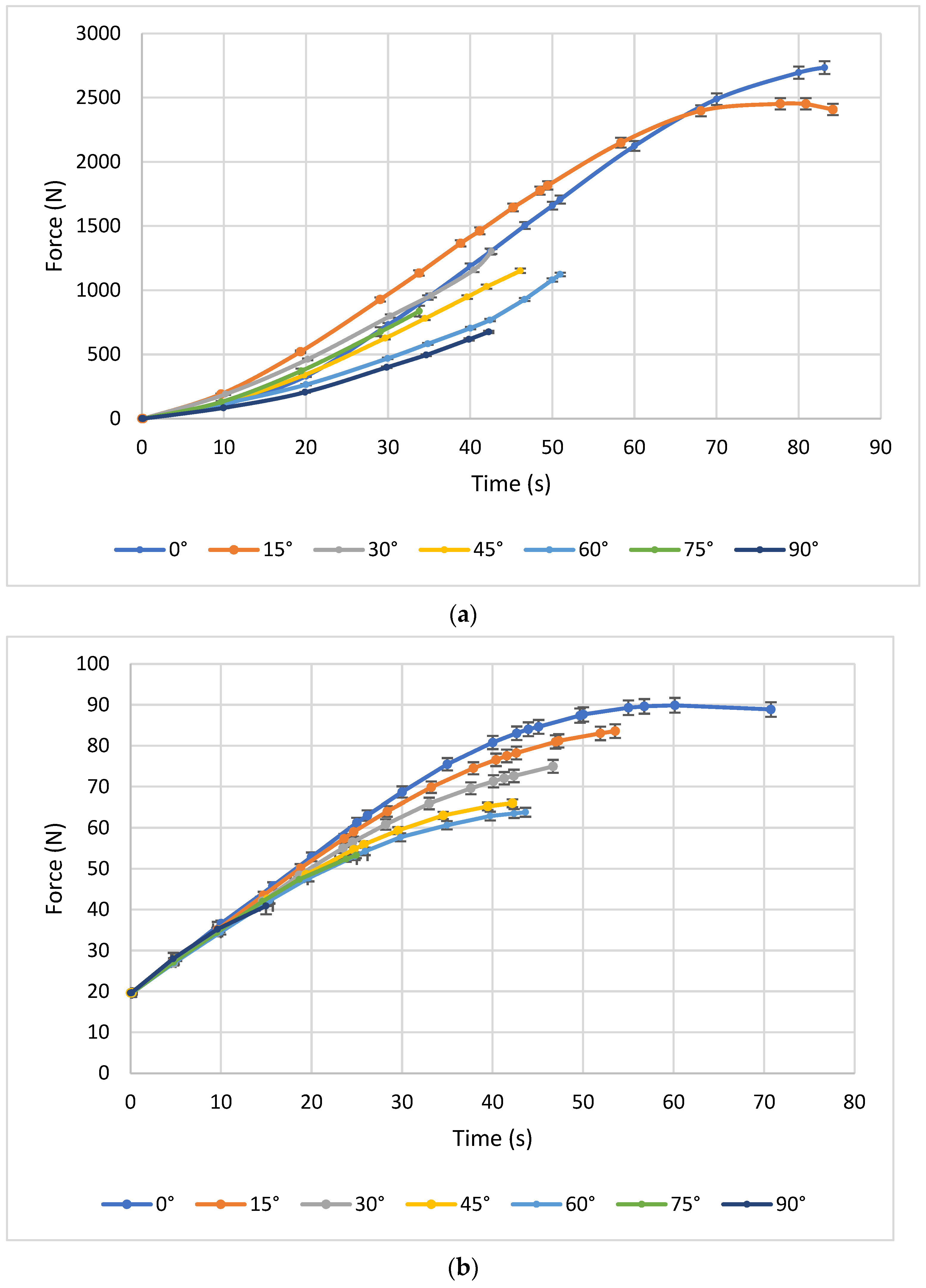
2.3. Uniaxial Tensile Experiment
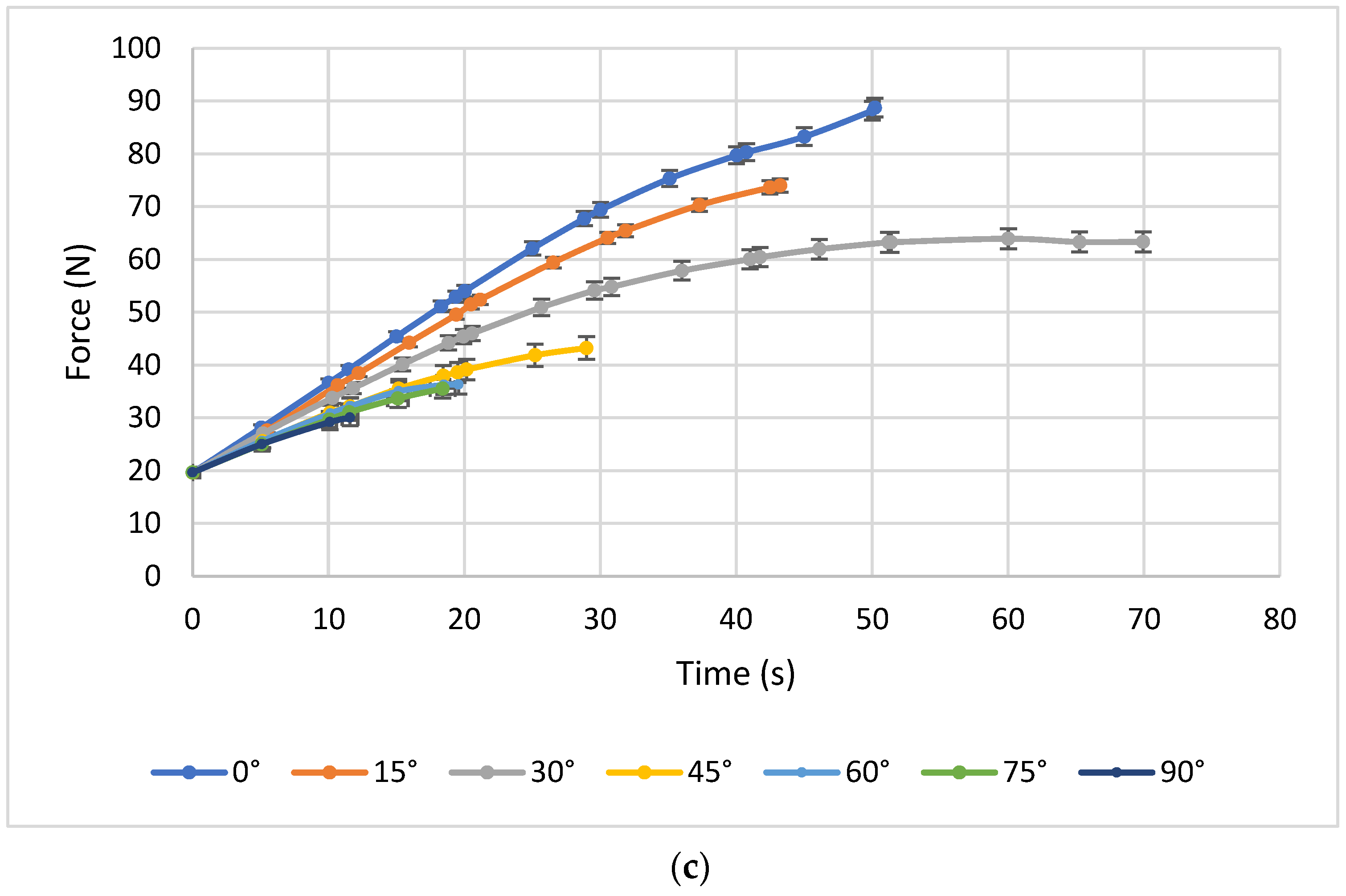
2.4. Three-Point Bending Test
2.5. Statistical Analysis
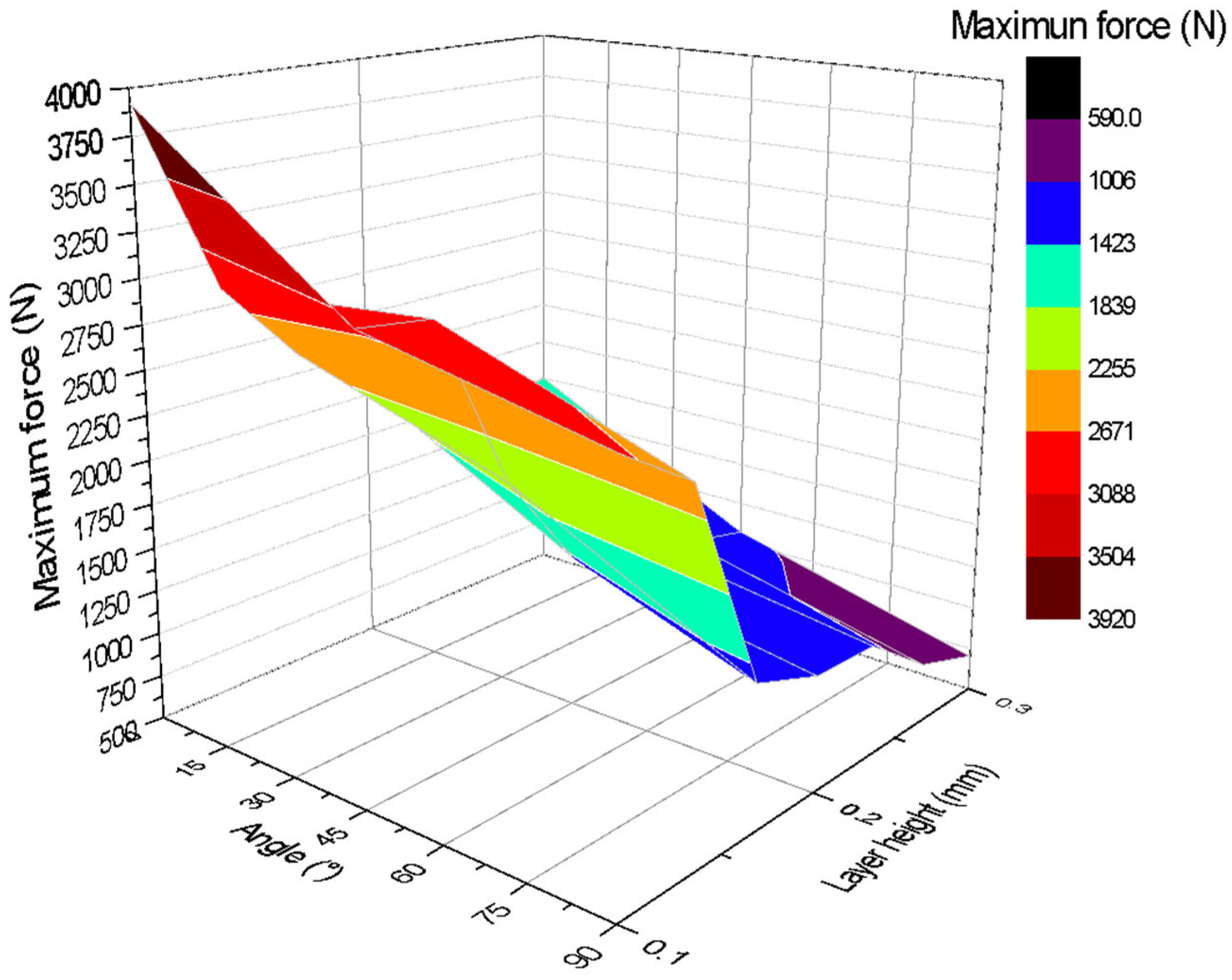
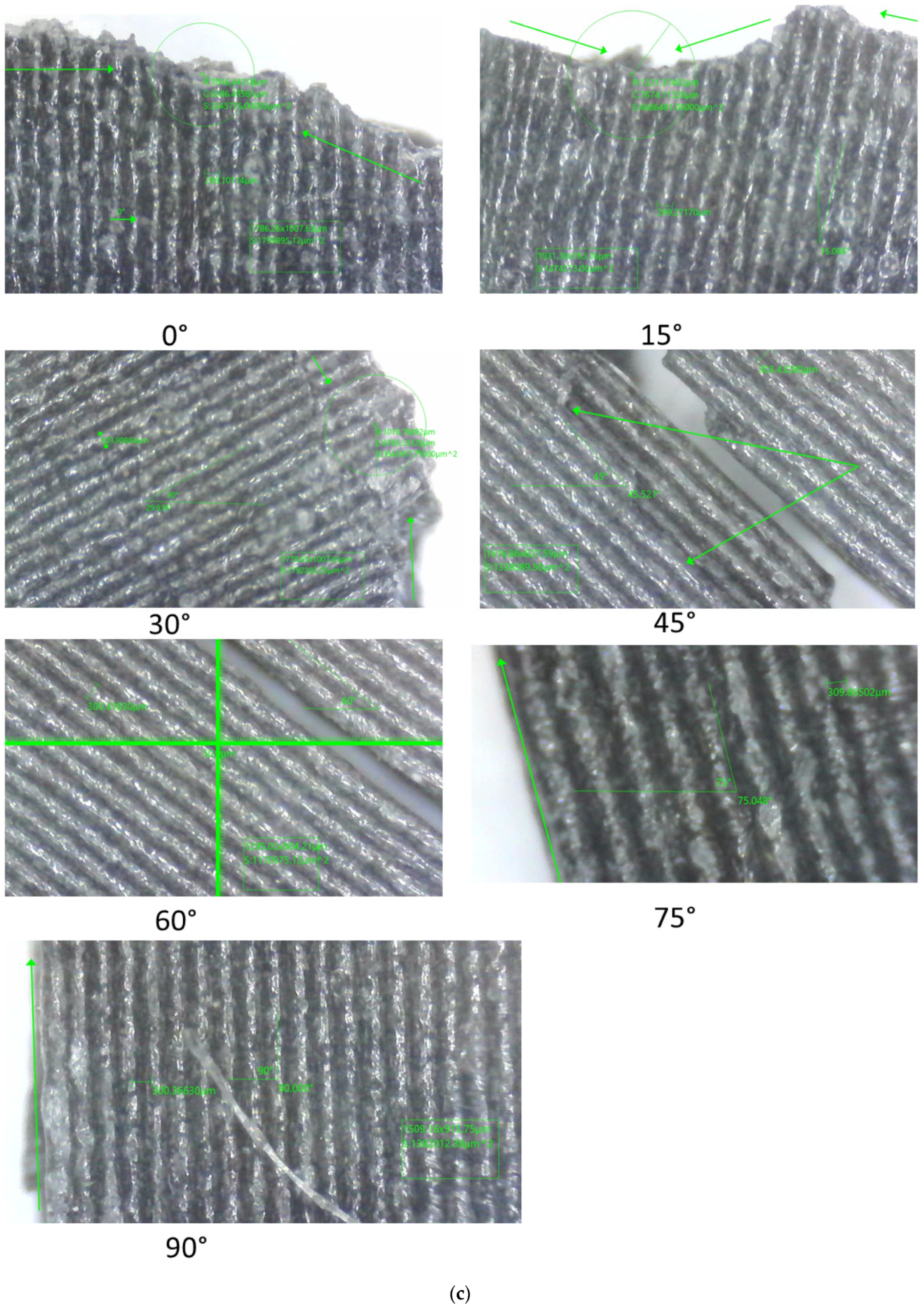
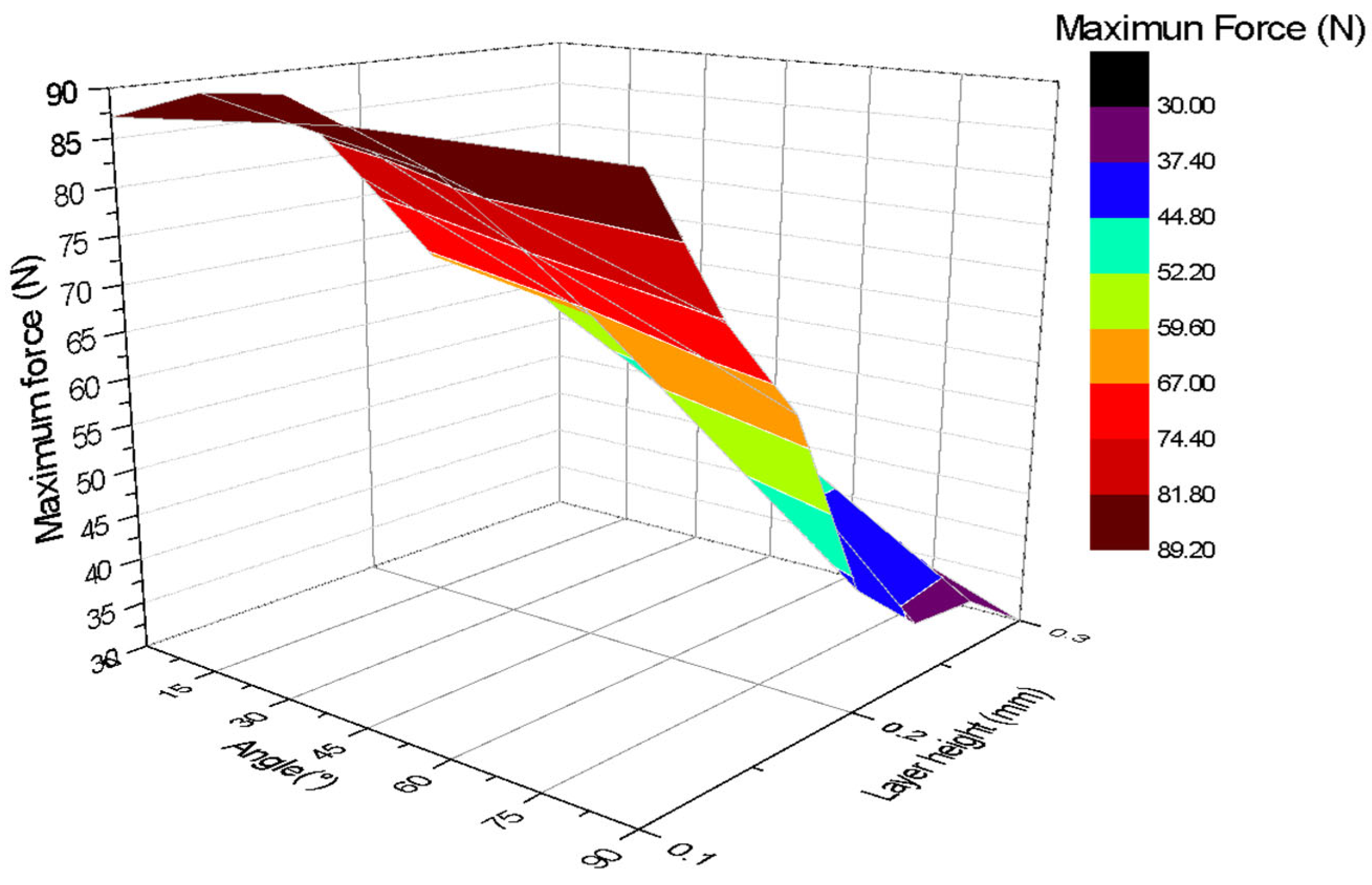
3. Results
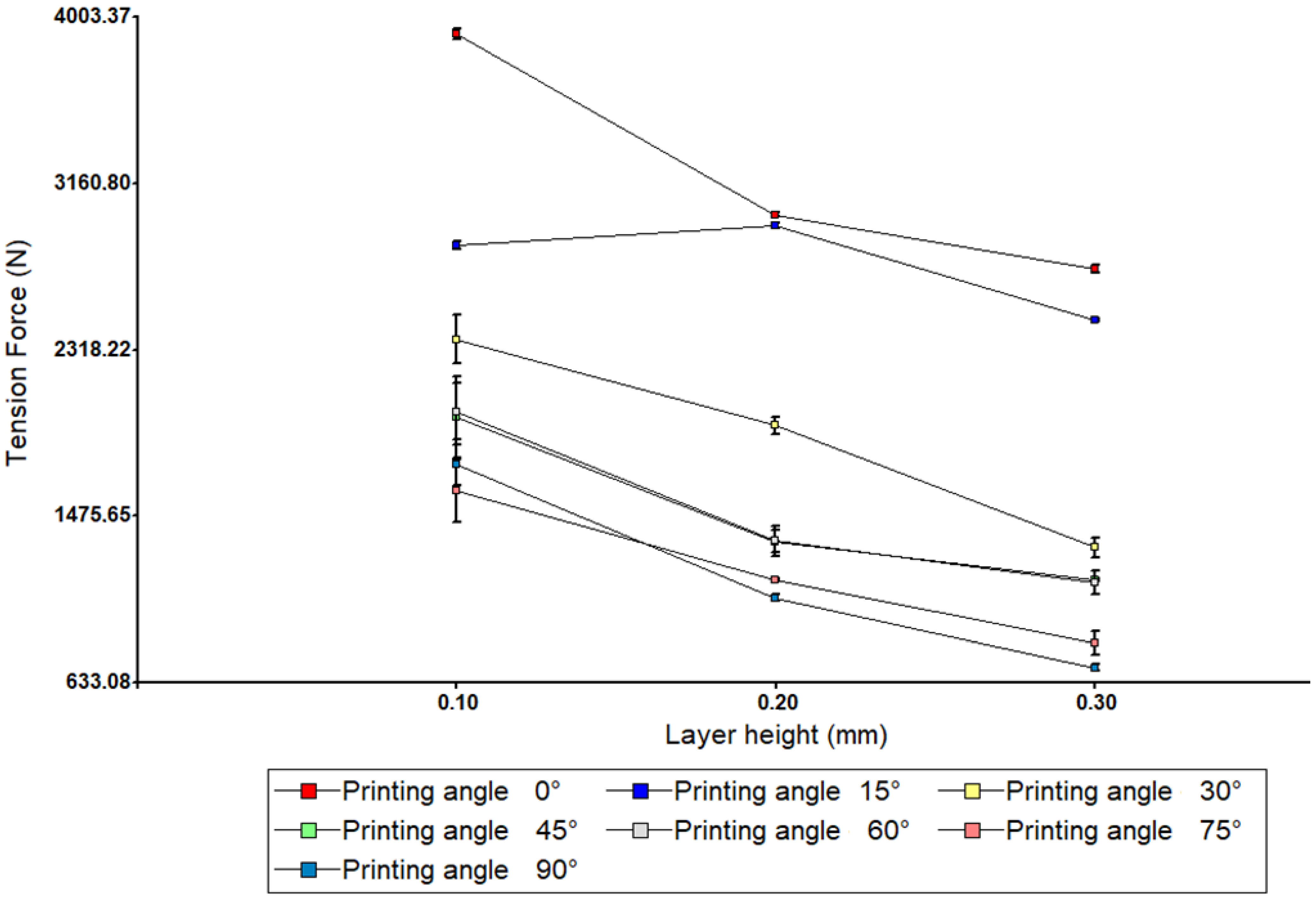
3.1. Uniaxial Tensile Tests
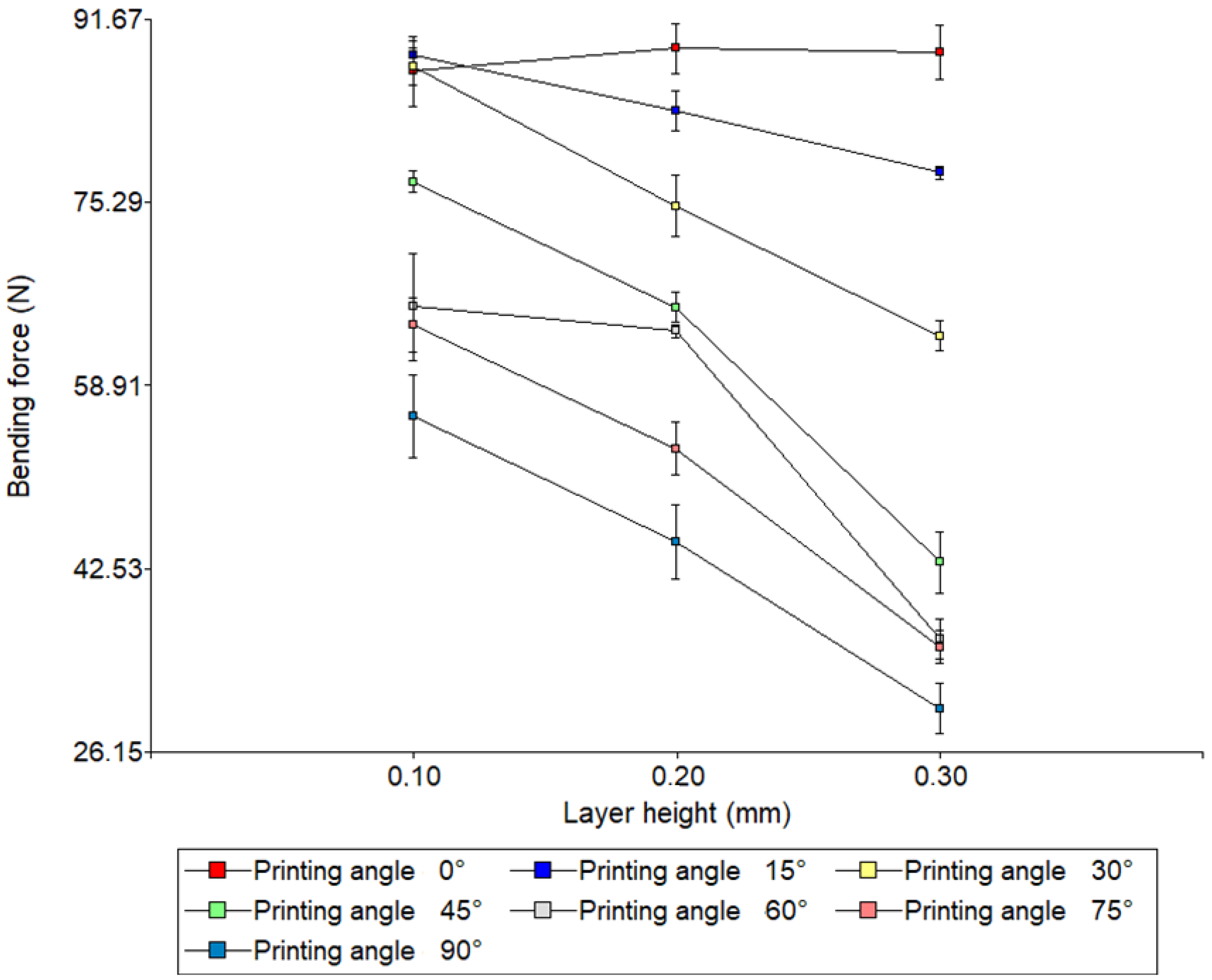
3.2. Three-Point Bending Tests
4. Discussion
4.1. Analysis of Uniaxial Tensile Tests
4.2. Analysis of Three-Point Bending Tests
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferreira, R.T.L.; Amatte, I.C.; Dutra, T.A.; Bürger, D. Experimental characterization and micrography of 3D printed PLA and PLA reinforced with short carbon fibers. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 124, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Chen, K.; Pan, M.; Wang, M.; Song, Z. An Augmentation Strategy for Medical Image Processing Based on Statistical Shape Model and 3D Thin Plate Spline for Deep Learning. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 133111–133121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari-Rarani, M.; Rafiee-Afarani, M.; Zahedi, A.M. Mechanical characterization of FDM 3D printing of continuous carbon fiber reinforced PLA composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 175, 107147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covallane, K.; Johan, D.; Singh, R.K.; Sinha, R.; Boodala, D.; Jaiswal, K.K.; Kumar, K.S. Experimental and Numerical Investigation of Jute Fibre-Reinforced Composite, a Sustainable Material for Green Energy. Eng. Proc. 2025, 95, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida, J.H.S., Jr.; Miettinen, A.; Léonard, F.; Falzon, B.G.; Withers, P.J. Microstructure and damage evolution in short carbon fibre 3D-printed composites during tensile straining. Compos. Part B Eng. 2025, 292, 112073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sam-Daliri, O.; Flanagan, T.; Modi, V.; Finnegan, W.; Harrison, N.; Ghabezi, P. Composite upcycling: An experimental study on mechanical behaviour of injection moulded parts prepared from recycled material extrusion printed parts, previously prepared using glass fibre polypropylene composite industry waste. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 499, 145280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghabezi, P.; Sam-Daliri, O.; Flanagan, T.; Walls, M.; Harrison, N.M. Mechanical and microstructural analysis of glass Fibre-Reinforced high density polyethylene thermoplastic waste composites manufactured by material extrusion 3D printing technology. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2025, 194, 108930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çakan, B.G. Effects of raster angle on tensile and surface roughness properties of various FDM filaments. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2021, 35, 3347–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, S.; Lopez-Anido, R.A.; Gardner, D.J. Enhancing the interlayer tensile strength of 3D printed short carbon fiber reinforced PETG and PLA composites via annealing. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 30, 100922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeStefano, V.; Khan, S.; Tabada, A. Applications of PLA in modern medicine. Eng. Regen. 2020, 1, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mehtedi, M.; Buonadonna, P.; El Mohtadi, R.; Loi, G.; Aymerich, F.; Carta, M. Optimizing milling parameters for enhanced machinability of 3D-printed materials: An analysis of PLA, PETG, and carbon-fiber-reinforced PETG. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2024, 8, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, S.A.; Muthukumaran, E.; Jayakrishna, K. A case study of 3D printed PLA and its mechanical properties. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 11219–11226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenhalgh, S. The effects of 3D printing in design thinking and design education. J. Eng. Des. Technol. 2016, 14, 752–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cercenelli, L.; De Stefano, A.; Billi, A.M.; Ruggeri, A.; Marcelli, E.; Marchetti, C.; Manzoli, L.; Ratti, S.; Badiali, G. AEducaAR, anatomical education in augmented reality: A pilot experience of an innovative educational tool combining AR technology and 3D printing. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blake, B.; Mendenhall, R.; Eslami, B. Balancing Strength and Flexibility: Mechanical Characterization of Carbon Fiber-Reinforced PLA Composites in FDM 3D Printing. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2025, 9, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atakok, G.; Kam, M.; Koc, H.B. Tensile, three-point bending and impact strength of 3D printed parts using PLA and recycled PLA filaments: A statistical investigation. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 18, 1542–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Werken, N.; Tekinalp, H.; Khanbolouki, P.; Ozcan, S.; Williams, A.; Tehrani, M. Additively manufactured carbon fiber-reinforced composites: State of the art and perspective. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 31, 100962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D-3039; Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Polymer Matrix Composite Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2014.
- Maqsood, N.; Rimašauskas, M. Characterization of carbon fiber reinforced PLA composites manufactured by fused deposition modeling. Compos. Part C Open Access 2021, 4, 100112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, H.; Cheng, Y.; Ye, W.; Zhang, D.; Li, J.; Miao, Z.; Rudykh, S. Effect of process parameters on tensile mechanical properties of 3D printing continuous carbon fiber-reinforced PLA composites. Materials 2020, 13, 3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochnia, J.; Blasiak, M.; Kozior, T. A comparative study of the mechanical properties of FDM 3D prints made of PLA and carbon fiber-reinforced PLA for thin-walled applications. Materials 2021, 14, 7062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D-790; Standard Test Methods for Flexural Properties of Unreinforced and Reinforced Plastics and Electrical Insulating Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017.
- Liang, L.; Huang, T.; Yu, S.; Cao, W.; Xu, T. Study on 3D printed graphene/carbon fiber multi-scale reinforced PLA composites. Mater. Lett. 2021, 300, 130173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Deng, Z.; Zhang, K.; Li, S. A method to predict the ultimate tensile strength of 3D printing polylactic acid (PLA) materials with different printing orientations. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 163, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugroho, A.W.; Budiantoro, C. Improving the tensile properties of 3D printed PLA by optimizing the processing parameter. J. Energy Mech. Mater. Manuf. Eng. 2019, 4, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Ye, J.; Deng, Z.; Zhang, K.; Ma, Y.; Ouyang, H. Tensile failure strength and separation angle of FDM 3D printing PLA material: Experimental and theoretical analyses. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 188, 107894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D. Enhanced buckling strength of the thin-walled continuous carbon fiber–reinforced thermoplastic composite through dual coaxial nozzles material extrusion process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 128, 1305–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Liu, T.; Yang, C.; Wang, Q.; Li, D. Interface and performance of 3D printed continuous carbon fiber reinforced PLA composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2016, 88, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, C.-H.; Park, J.-M.; Kim, J.-H.; Kang, Y.-J.; Kim, J.-H. Assessment of compatibility between various intraoral scanners and 3D printers through an accuracy analysis of 3D printed models. Materials 2020, 13, 4419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budziński, B.; Federowicz, K. Evaluation of PLA and PETG as 3D-Printed Reference Materials for Compressive Strength Testing. Materials 2025, 18, 3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enemuoh, E.U.; Duginski, S.; Feyen, C.; Menta, V.G. Effect of process parameters on energy consumption, physical, and mechanical properties of fused deposition modeling. Polymers 2021, 13, 2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garofalo, E.; Di Maio, L.; Incarnato, L. PLA/PBS Biocomposites for 3D FDM Manufacturing: Effect of Hemp Shive Content and Process Parameters on Printing Quality and Performances. Polymers 2025, 17, 2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desole, M.P.; Gisario, A.; Barletta, M. Evaluation of Bending Stress and Shape Recovery Behavior Under Cyclic Loading in PLA 4D-Printed Lattice Structures. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 8540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivan, A.M.; Cristoiu, C.A.; Parpala, L.F. CAD Analysis of 3D Printed Parts for Material Extrusion—Pre-Processing Optimization Method. Technologies 2025, 13, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 4D Lab. PLA-CF. Available online: https://4dlab.co/products/pla?gad_source=1&gad_campaignid=20668639833&gbraid=0AAAAAo3Z-sS67b_7k4YN4mUJbqfHxvPCP&gclid=CjwKCAiAz_DIBhBJEiwAVH2XwLURz3hZAIUdPjNRCEeNvpEIiXBWaj6NI0JCClm-KtTaJ0JKOSa0ERoCBXkQAvD_BwE (accessed on 12 January 2025).
- Vanaei, S.; Rastak, M.; El Magri, A.; Vanaei, H.R.; Raissi, K.; Tcharkhtchi, A. Orientation-Dependent Mechanical Behavior of 3D Printed Polylactic Acid Parts: An Experimental–Numerical Study. Machines 2023, 11, 1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobov, E.; Vindokurov, I.; Tashkinov, M. Mechanical properties and performance of 3D-printed acrylonitrile butadiene styrene reinforced with carbon, glass and basalt short fibers. Polymers 2024, 16, 1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Chen, H.; Yao, K.; Lei, H.; Pei, Y.; Fang, D. Experimental and theoretical studies on inter-fiber failure of unidirectional polymer-matrix composites under different strain rates. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2017, 113, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogaili, A.A.F.; Basem, A.; Kadhim, M.S.; Al-Sharify, Z.T.; Jaber, A.A.; Njim, E.K.; Al-Haddad, L.A.; Hamzah, M.N.; Al-Ameen, E.S. The effect of chopped carbon fibers on the mechanical properties and fracture toughness of 3D-printed PLA parts: An experimental and simulation study. J. Compos. Sci. 2024, 8, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Property | PLA Carbon (PLA-CF) |
|---|---|
| Base Material | PLA with chopped carbon fibre |
| Colour | Black |
| % Deformation at failure | 8% (estimated) |
| Carbon Fibre Content | ~15–20 wt% |
| Density (typical) | ~1.24 g/cm3 |
| Carbon Fibre Length | ~100–150 μm (chopped) |
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Layer height | 0.1 mm, 0.2 mm, 0.3 mm |
| Fill density | 100% |
| Fill pattern | Lineal |
| Print temperature (used) | 220° C |
| Bed temperature (used) | 60 °C |
| Filament diameter | 1.75 mm |
| Print speed | 40 mm/s |
| Print sequence | 5 units |
| Flow | 100% |
| Layer ventilation | 50% |
| Material Fluid % | 95% |
| Printing Angle (°) | ||||||
| 0° | 15° | 30° | 45° | 60° | 75° | 90° |
| Layer height = 0.1 mm | ||||||
| Uniaxial tensile tests | ||||||
| 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Three-point bending test | ||||||
| 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Layer height = 0.2 mm | ||||||
| Uniaxial tensile tests | ||||||
| 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Three-point bending test | ||||||
| 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Layer height = 0.3 mm | ||||||
| Uniaxial tensile tests | ||||||
| 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Three-point bending test | ||||||
| 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Tensile Test | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Layer Height | Printing Angle (°) | Tensile Strength (Mpa) | Average Value (N) | Stand. Desv. | CV (%) |
| 0.1 | 0° | 62.68 | 3917.49 L | 24.23 | 0.62 |
| 15° | 45.58 | 2848.74 J | 20.22 | 0.71 | |
| 30° | 37.92 | 2370.13 H | 123.05 | 5.19 | |
| 45° | 31.58 | 1973.9 G | 207.51 | 10.51 | |
| 60° | 32.09 | 2005.38 G | 143.56 | 7.16 | |
| 75° | 25.69 | 1605.43 E | 163.78 | 10.20 | |
| 90° | 27.74 | 1733.82 F | 105.28 | 6.07 | |
| 0.2 | 0° | 48.04 | 3002.72 K | 11.41 | 0.38 |
| 15° | 47.16 | 2947.39 J,K | 15.27 | 0.52 | |
| 30° | 30.95 | 1934.36 G | 42.92 | 2.22 | |
| 45° | 21.55 | 1346.98 D | 55.86 | 4.15 | |
| 60° | 21.56 | 1347.74 D | 74.08 | 5.50 | |
| 75° | 18.40 | 1150 C | 7.91 | 0.69 | |
| 90° | 16.95 | 1059.34 C | 17.11 | 1.61 | |
| 0.3 | 0° | 43.63 | 2727.16 I | 18.38 | 0.67 |
| 15° | 39.46 | 2466.37 H | 6.07 | 0.25 | |
| 30° | 21.04 | 1314.99 D | 47.68 | 3.63 | |
| 45° | 18.40 | 1150 C | 7.91 | 0.69 | |
| 60° | 18.24 | 1140.09 C | 58.78 | 5.16 | |
| 75° | 13.32 | 832.49 B | 57.09 | 6.86 | |
| 90° | 11.32 | 707.78 A | 17.26 | 2.44 | |
| Three-Point Bending Tests | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Layer Height | Printing Angle (°) | Flexural Strength (Mpa) | Average Value (N) | Stand. Desv. | CV (%) |
| 0.1 | 0° | 120.43 | 87.01 H | 3.15 | 3.62 |
| 15° | 122.55 | 88.54 H | 1.24 | 1.40 | |
| 30° | 121.04 | 87.45 H | 1.61 | 1.84 | |
| 45° | 106.80 | 77.16 F | 0.93 | 1.21 | |
| 60° | 91.30 | 65.96 E | 4.79 | 7.27 | |
| 75° | 89.08 | 64.36 E | 2.45 | 3.81 | |
| 90° | 77.79 | 56.2 D | 3.68 | 6.55 | |
| 0.2 | 0° | 123.27 | 89.06 H | 2.24 | 2.51 |
| 15° | 115.56 | 83.49 G | 1.74 | 2.08 | |
| 30° | 103.81 | 75 F | 2.71 | 3.61 | |
| 45° | 91.18 | 65.88 E | 1.34 | 2.03 | |
| 60° | 88.29 | 63.79 E | 0.55 | 0.87 | |
| 75° | 73.73 | 53.27 D | 2.35 | 4.41 | |
| 90° | 62.12 | 44.88 C | 3.33 | 7.41 | |
| 0.3 | 0° | 122.77 | 88.7 H | 2.41 | 2.72 |
| 15° | 107.89 | 77.95 F | 0.54 | 0.70 | |
| 30° | 87.72 | 63.38 E | 1.30 | 2.06 | |
| 45° | 59.67 | 43.11 C | 2.76 | 6.40 | |
| 60° | 50.22 | 36.28 B | 1.80 | 4.97 | |
| 75° | 49.15 | 35.51 B | 1.47 | 4.15 | |
| 90° | 41.55 | 30.02 A | 2.26 | 7.54 | |
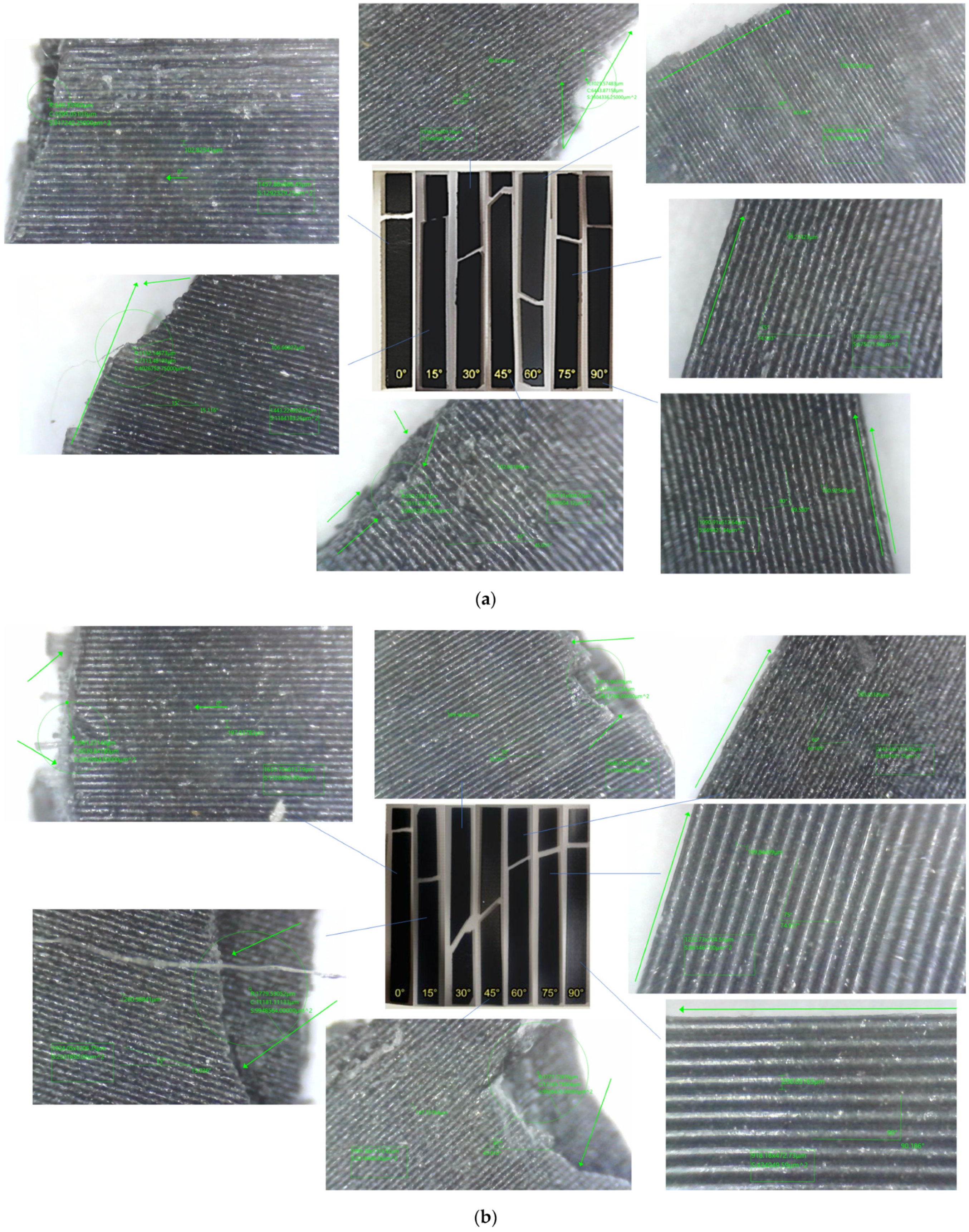
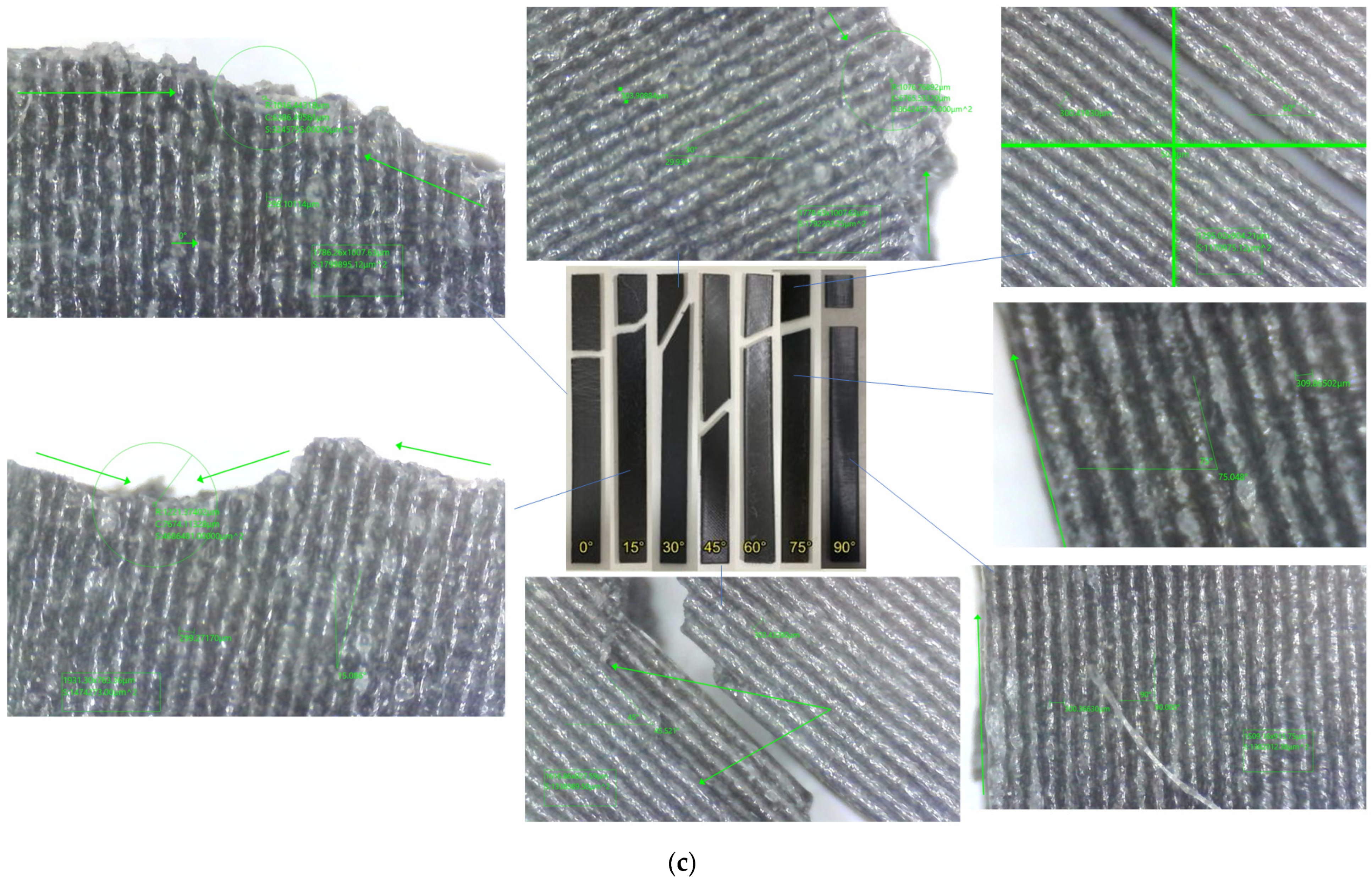
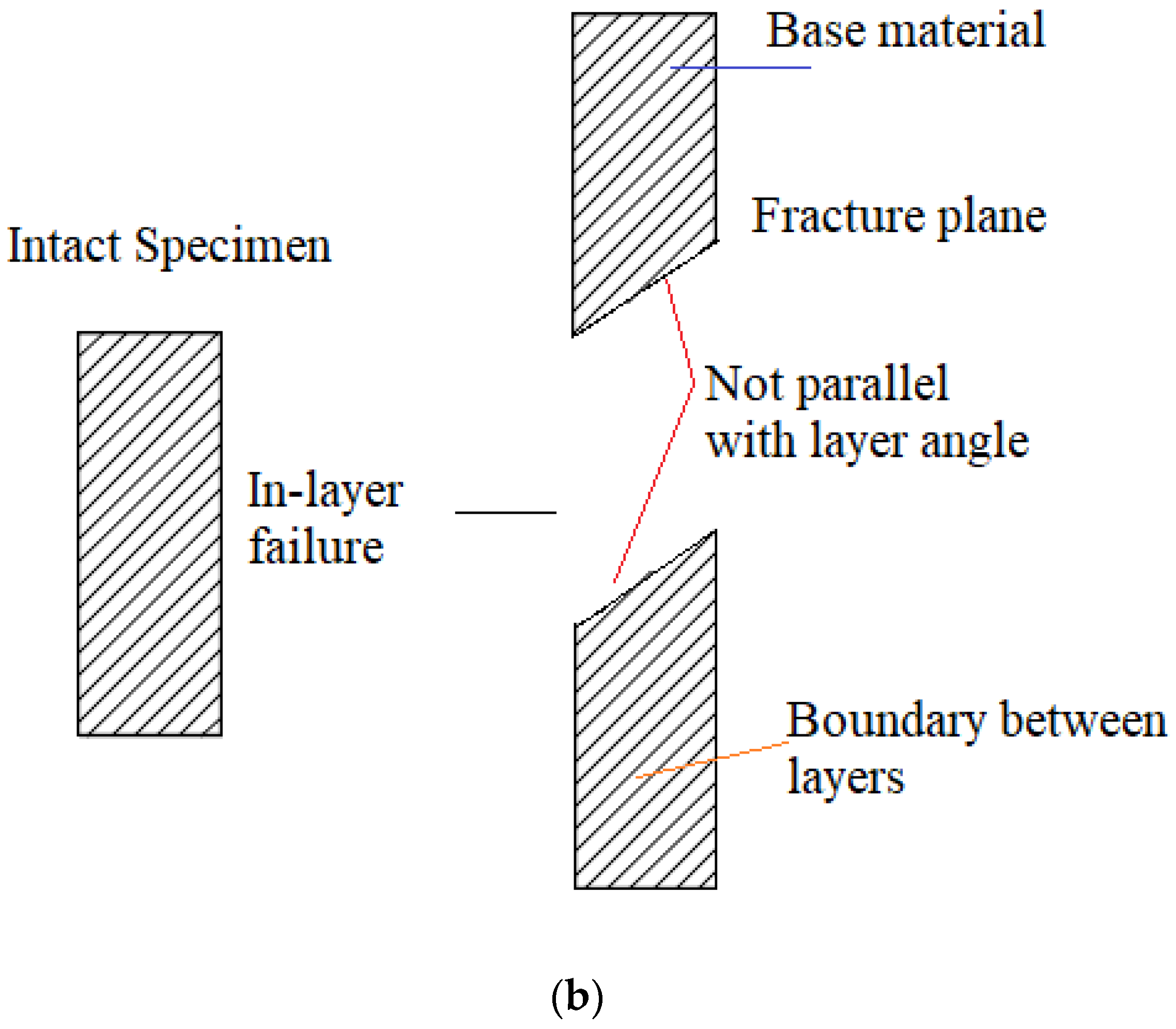
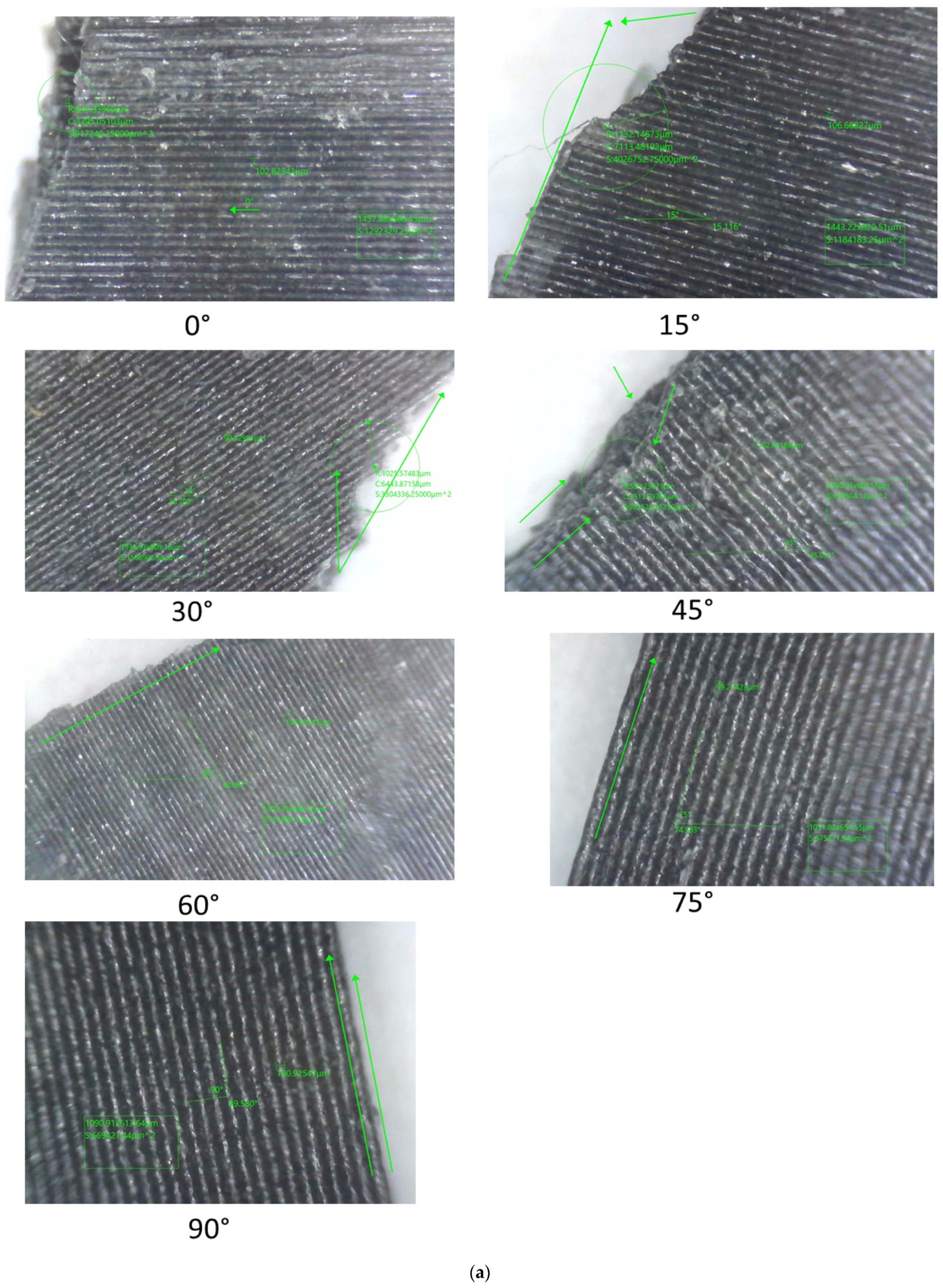
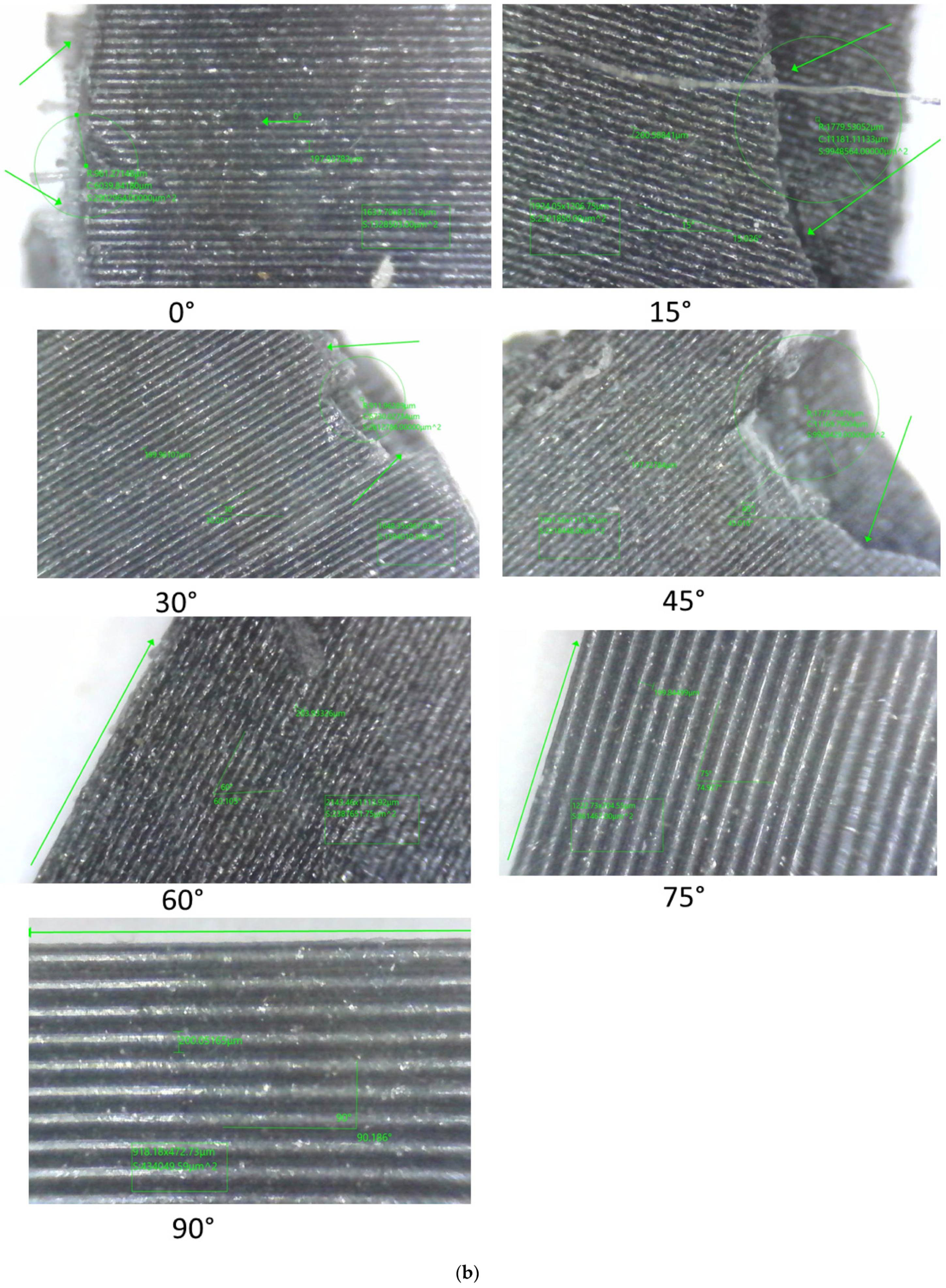
| Layer Height (mm) | Failure Modes | |
|---|---|---|
| In-Layer Failure | Inter-Layer Failure | |
| 0.1 | 0° 15° 30° 45° | 60° 75° 90° |
| 0.2 | 0° 15° 30° 45° | 60° 75° 90° |
| 0.3 | 0° 15° 30° 45° | 60° 75° 90° |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Araque, O.; Sánchez-Echeverri, L.A.; Cerón, I.X. Impact of Printing Angle and Layer Height on the Mechanical Strength of PLA Reinforced with Chopped Carbon Fibres Using FDM 3D Printing. Polymers 2025, 17, 3069. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17223069
Araque O, Sánchez-Echeverri LA, Cerón IX. Impact of Printing Angle and Layer Height on the Mechanical Strength of PLA Reinforced with Chopped Carbon Fibres Using FDM 3D Printing. Polymers. 2025; 17(22):3069. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17223069
Chicago/Turabian StyleAraque, Oscar, Luz Adriana Sánchez-Echeverri, and Ivonne X. Cerón. 2025. "Impact of Printing Angle and Layer Height on the Mechanical Strength of PLA Reinforced with Chopped Carbon Fibres Using FDM 3D Printing" Polymers 17, no. 22: 3069. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17223069
APA StyleAraque, O., Sánchez-Echeverri, L. A., & Cerón, I. X. (2025). Impact of Printing Angle and Layer Height on the Mechanical Strength of PLA Reinforced with Chopped Carbon Fibres Using FDM 3D Printing. Polymers, 17(22), 3069. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17223069







