Hybrid Devulcanized/Vulcanized Crumb Rubber Strategy for High-Performance Asphalt with over 40% Recycled Tire Rubber Content
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Rubber-Modified Asphalt
2.3. Characterization
- (1)
- Physical properties
- (2)
- Rheological test
- (3)
- Phase separation of CRMA and calculation of particle effect (PE)/interaction effect (IE)
- (4)
- Multiple stress creep recovery (MSCR) test
- (5)
- Gel permeation chromatography
- (6)
- Atomic force microscopy (AFM)
- (7)
- Solubility test
3. Results and Discussion
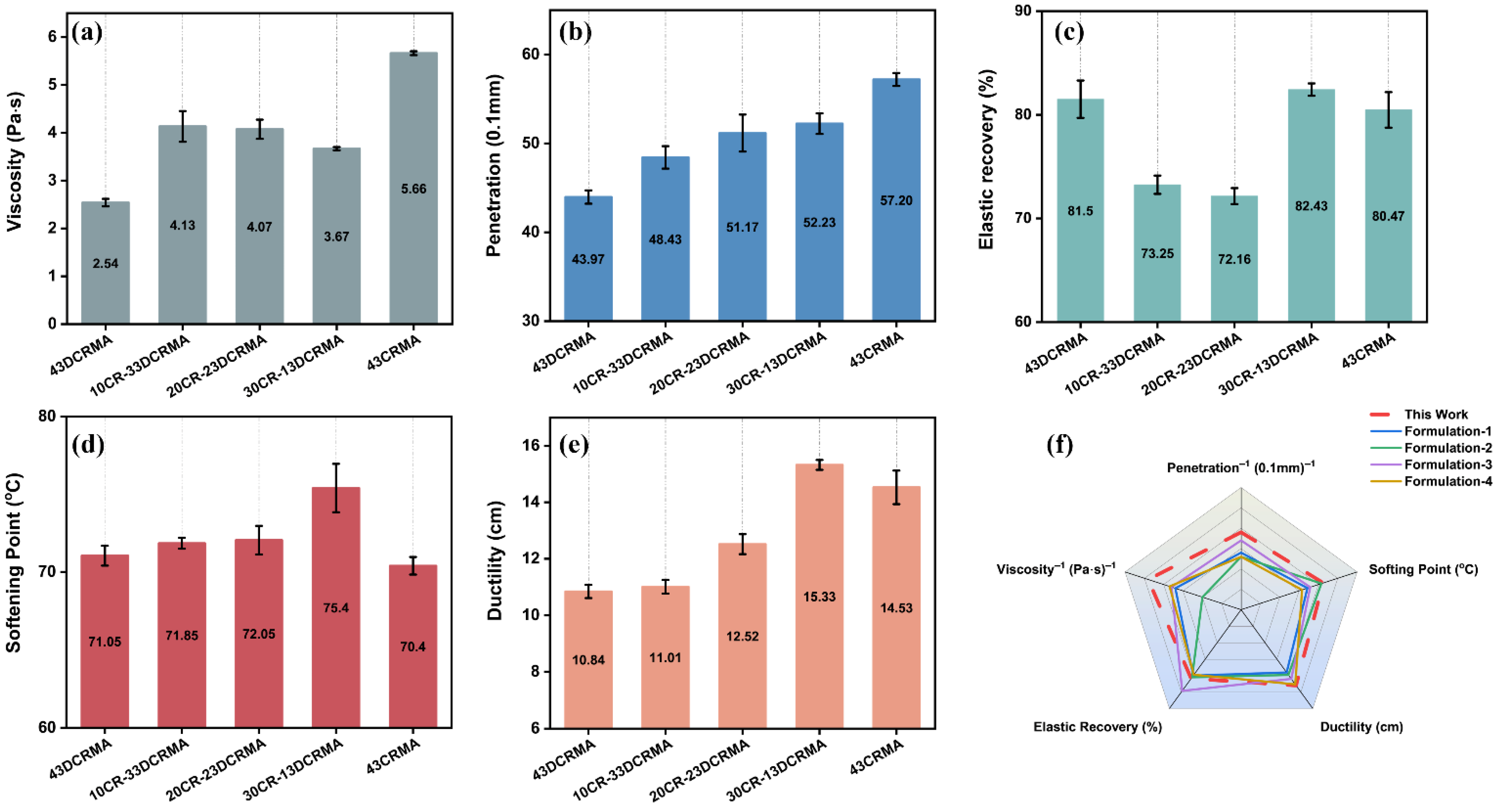
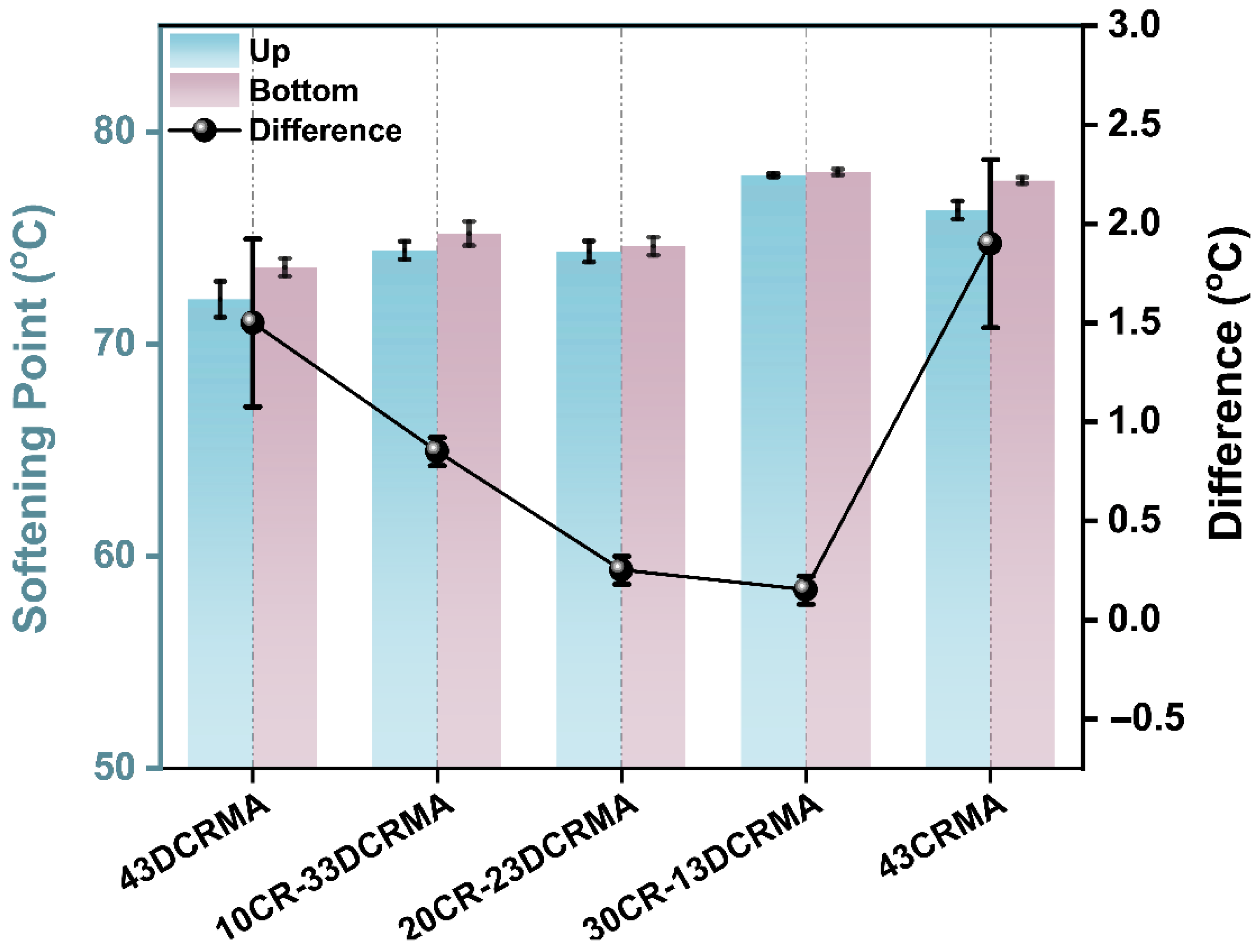
3.1. Effect of High-Content Hybrid Rubber on Fundamental Properties of Asphalt
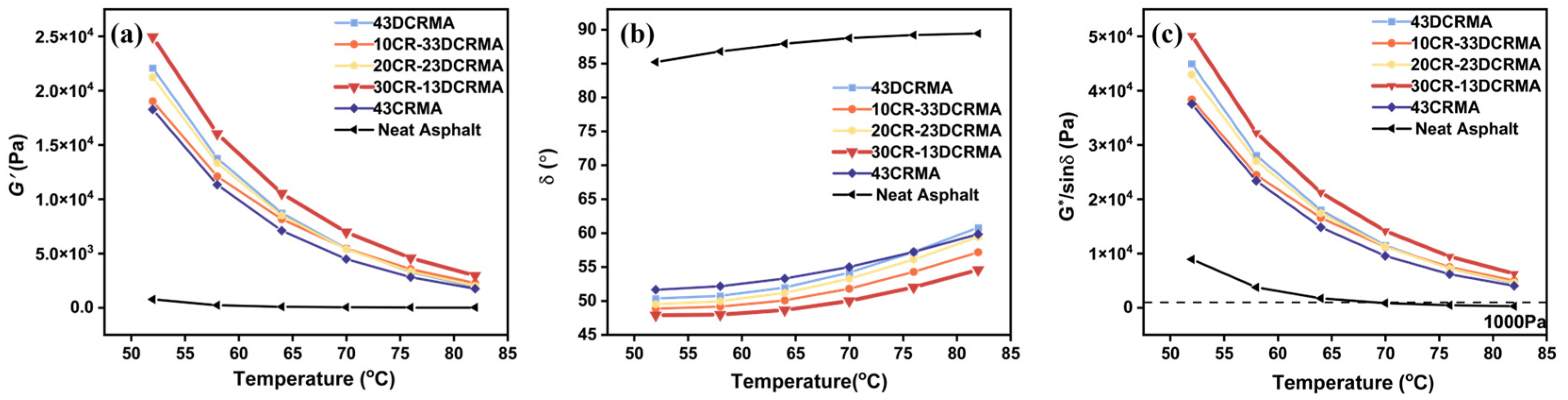
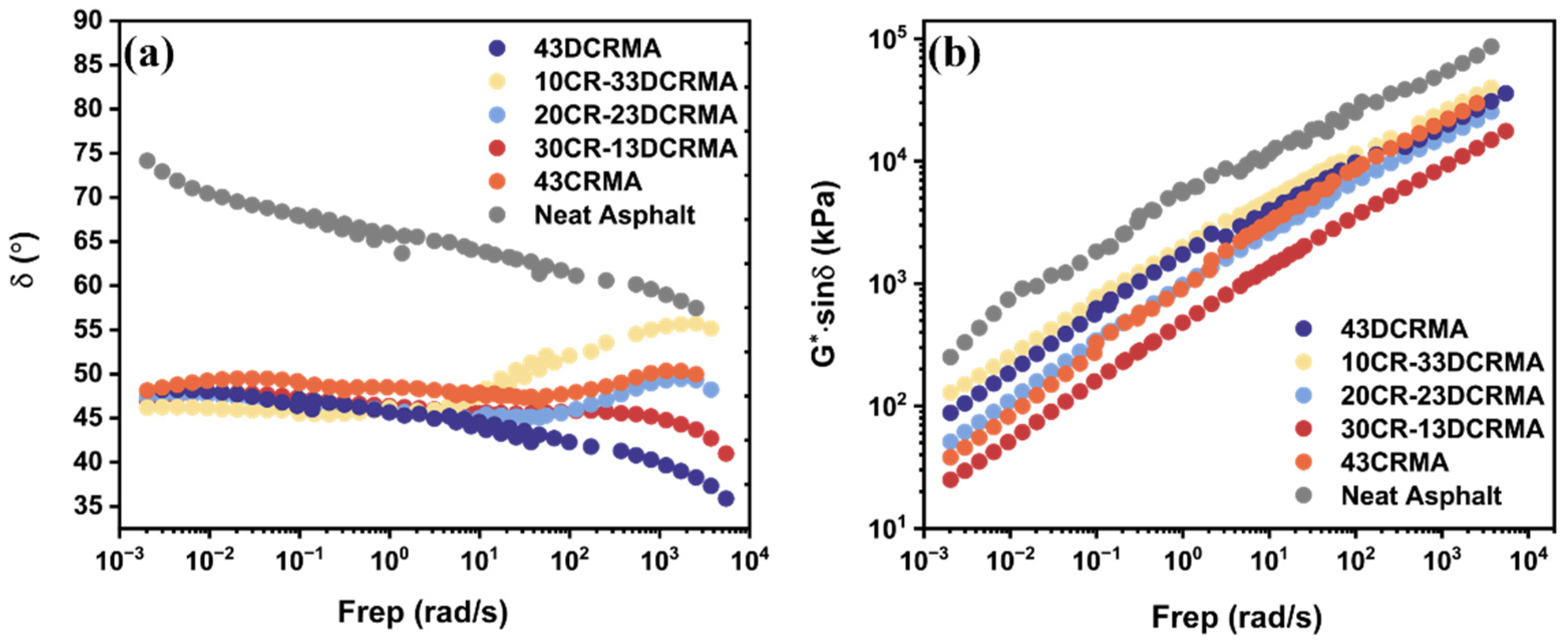
3.2. Rheological Properties and Rutting Resistance
3.3. 10 °C Frequency Scan Analysis
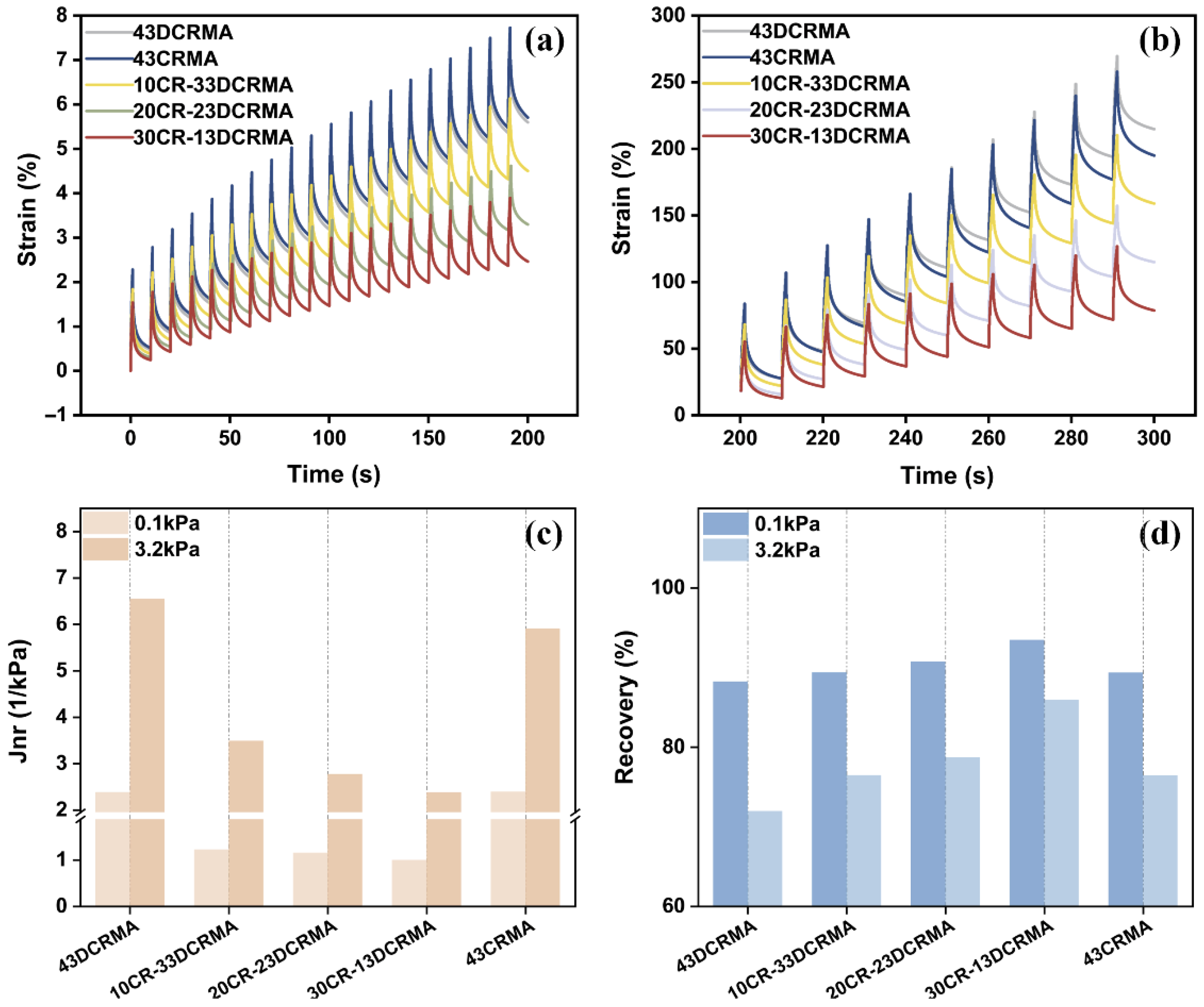
3.4. Multiple Stress Creep Recovery (MSCR) Analysis
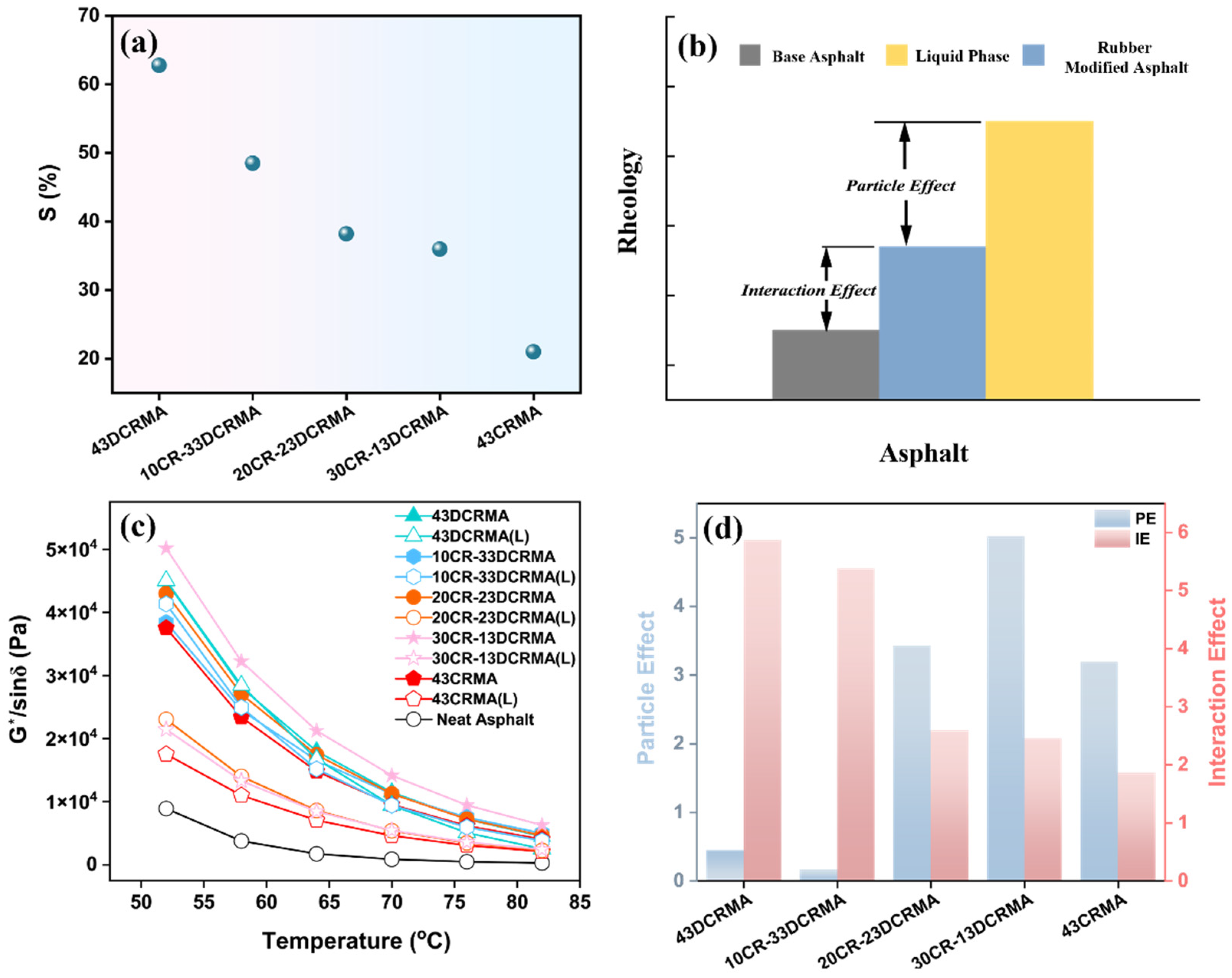
3.5. Solubility Test and PE-IE Analysis
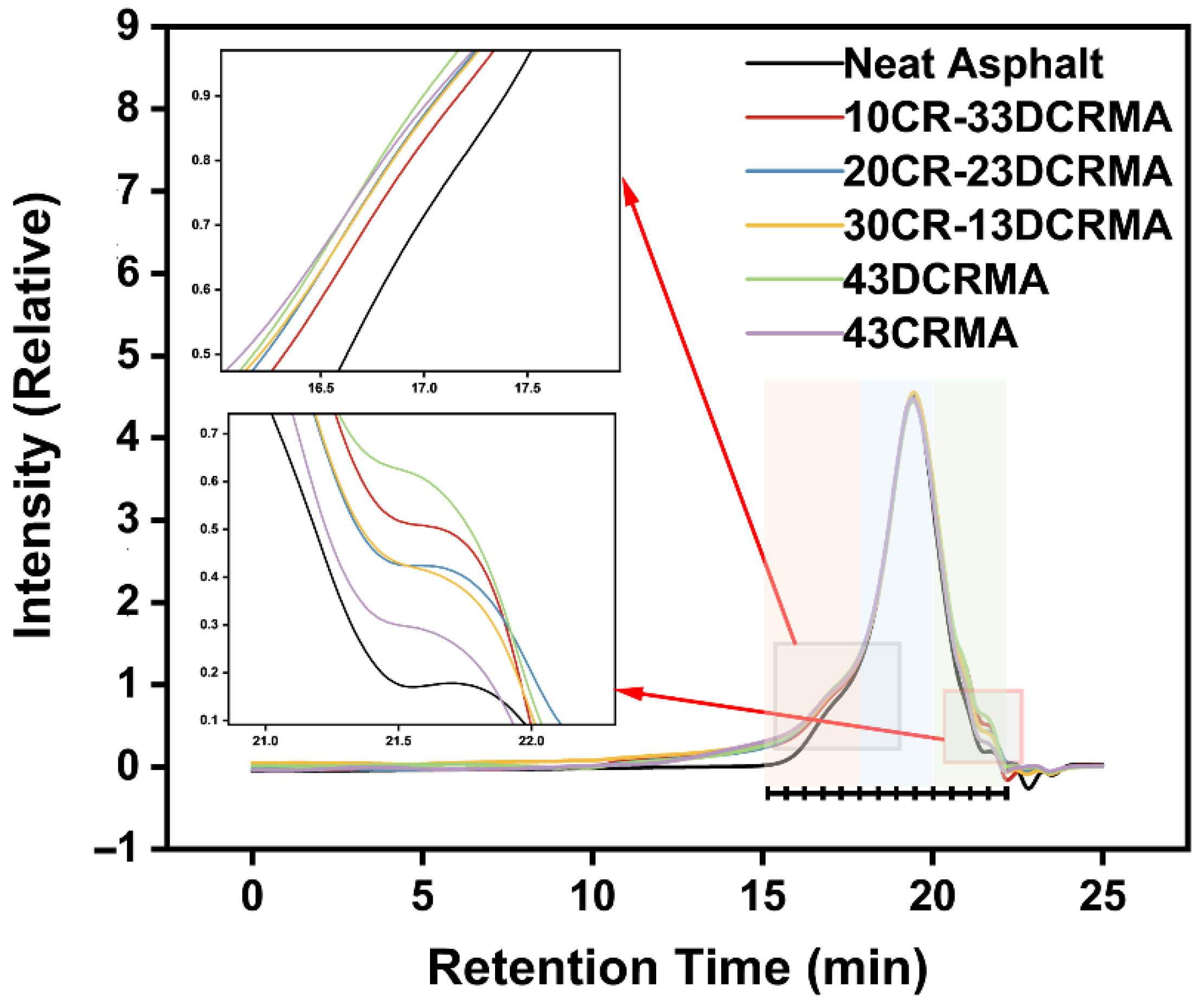
3.6. Gpc Test Analysis
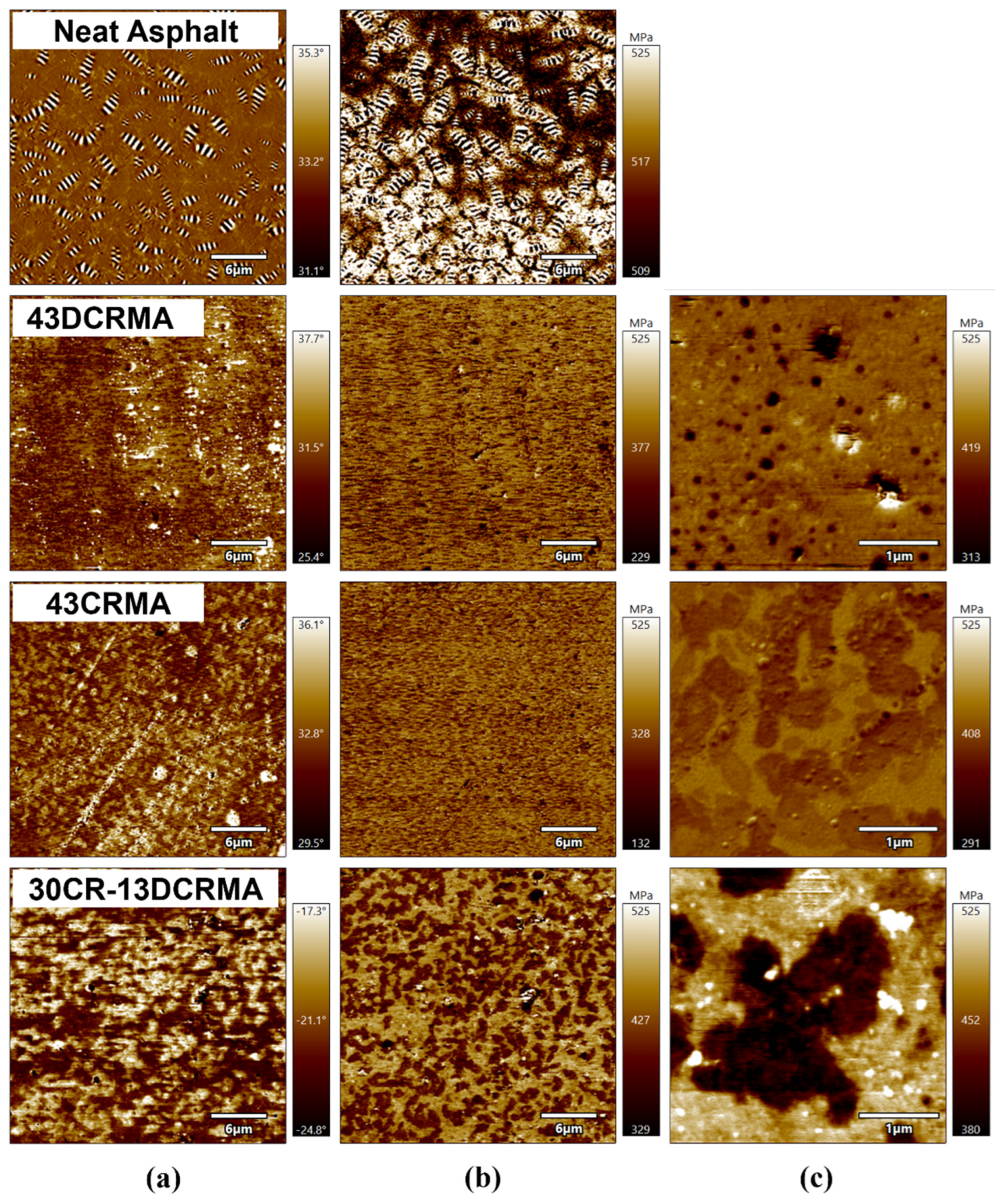
3.7. AFM Analysis
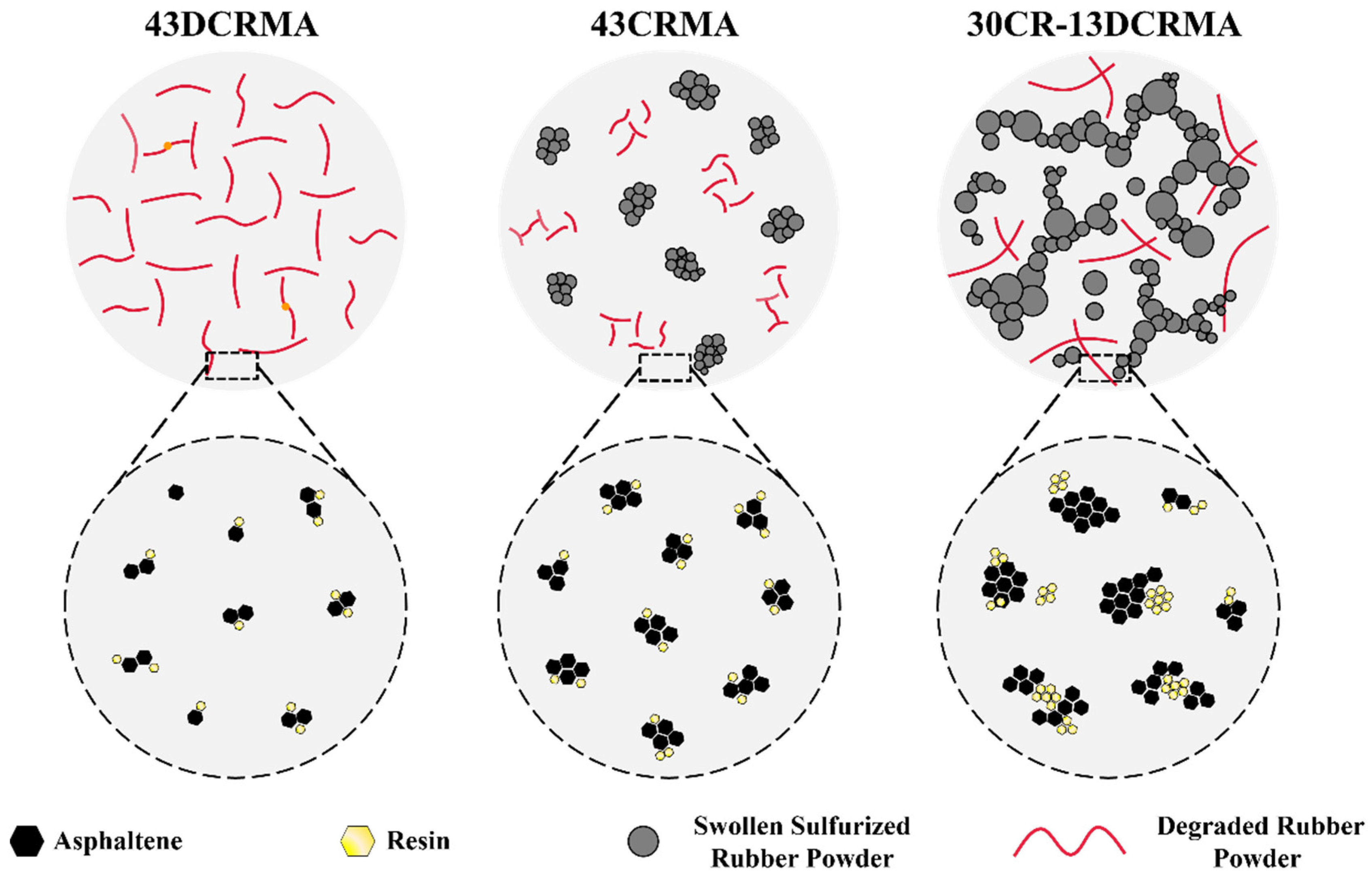
3.8. Mechanism of the CR/DCR Hybridization’s Improved Performance
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Hybrid-rubber-modified asphalt demonstrated superior fundamental properties over single-type counterparts. The optimal performance was achieved in the 30CR-13DCRMA formulation, which exhibited a softening point of 78.4 °C, enhanced ductility of 15.33 cm, and a reduced softening point difference of only 0.15 °C.
- (2)
- Compared with neat DCR- or CR-modified asphalt, 30CR-13DCRMA exhibited enhanced high-temperature rutting resistance and fatigue tolerance. Its non-recoverable creep compliance of under 0.1 kPa and 3.2 kPa decreased to 0.99 and 2.37 kPa−1, respectively, while maintaining excellent elastic recovery performance.
- (3)
- Based on rheological analysis, solubility tests, GPC and AFM characterization, the underlying mechanism responsible for the improved physical properties of high-content rubber-modified asphalt can be explained as follows: The hybrid strategy enables maximized absorption capabilities of rubber particles to enable their full swelling, while altering the microstructure of the asphalt matrix with resin/asphaltene-enriched domains.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akkenzheyeva, A.; Haritonovs, V.; Bussurmanova, A.; Merijs-Meri, R.; Imanbayev, Y.; Serikbayeva, A.; Sydykov, S.; Ayapbergenov, Y.; Jankauskas, M.; Trumpels, A.; et al. The Use of Rubber-Polymer Composites in Bitumen Modification for the Disposal of Rubber and Polymer Waste. Polymers 2024, 16, 3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Muttaqin, F.; Zhang, Y.Q. Investigating non-petroleum-based biodegradable polymers as eco-friendly and sustainable materials in asphalt modification: A review on natural rubbers and natural oils. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 436, 140483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W. The Status of Biological Research and Prospect Analysis of Asphalt. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2015, 744–746, 1547–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.J.; Yao, Y.S.; Ma, T.; Hao, S.W.; Ni, B. Experimental study and molecular simulation on regeneration feasibility of high-content waste tire crumb rubber modified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 369, 130570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Q.D.; Xia, L.; Tang, J.Q.; Zhang, M.M.; Wang, D.; Cao, D.W. From waste tires to long-life asphalt pavement: Evaluation of rheological and fatigue properties of high-content rubber/SBS composite modified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 495, 143671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Li, C.; Wang, Q. Thermosetting Polymer Modified Asphalts: Current Status and Challenges. Polym. Rev. 2024, 64, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, A.F.; Battistelle, R.A.; Bezerra, B.S.; de Castro, R. Use of scrap tire rubber in place of SBS in modified asphalt as an environmentally correct alternative for Brazil. J. Clean. Prod. 2012, 33, 236–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.C. Rubber concentrations on rheology of aged asphalt binders. J. Mater. Civil. Eng. 2008, 20, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.C.; Pauli, A.T. Particle Size Effect of Crumb Rubber on Rheology and Morphology of Asphalt Binders with Long-term Aging. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2008, 9, 73–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Boateng, K.A.; Yin, L.; Liu, Z.D.; You, Z.P.; Jin, D.Z. High-content crumb rubber modified asphalt mixture via wet process: Laboratory evaluation and field application. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 494, 143438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.; Coree, B.J.; Lovell, C.W. Evaluation of Pyrolized Carbon Black from Scrap Tires as Additive in Hot Mix Asphalt. Transp. Res. Rec. 1996, 1530, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.S.; Cao, Z.; Xu, X.; Xiao, F.; Abdel-Wahed, T. Bonding, rheological, and physiochemical characteristics of reclaimed asphalt rejuvenated by crumb rubber modified binder. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 373, 133896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.H.; Zhu, C.Z.; Li, Y.Q.; Zhang, H.L.; Zhang, S.; Xiao, F.P.; Amirkhanian, S. Effect of crumb rubber percentages and bitumen sources on high-temperature rheological properties of less smell crumb rubber modified bitumen. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 277, 122248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, K.X.; Wang, C.H.; Liu, J.K.; Song, L.; Chen, Q.; Chen, Y.Z. Research progress and performance evaluation of crumb-rubber-modified asphalts and their mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 361, 129687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.T.; Cao, W.D.; Fang, J.G.; Shang, S.J. Variance analysis and performance evaluation of different crumb rubber modified (CRM) asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 2701–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.P.; Liu, X.Y.; Apostolidis, P.; Erkens, S.; Scarpas, T. Numerical investigation of rubber swelling in bitumen. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 214, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Li, H.; Wei, Y.Z.; Zhang, X.J.; Wei, D.B.; Li, J. Microscopic Properties of Hydrogen Peroxide Activated Crumb Rubber and Its Influence on the Rheological Properties of Crumb Rubber Modified Asphalt. Materials 2019, 12, 1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Yu, F.; Fini, D.E.H. Swelling-degradation dynamic evolution behaviors of bio-modified rubberized asphalt under thermal conditions. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 426, 139061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Kong, P.P.; Yu, Y.H.; Yang, J.Y.; Zhu, M.H.; Chen, X.H. Rheological properties of rubber modified asphalt as function of waste tire rubber reclaiming degree. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 332, 130113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.S.; Wang, H.B.; Yao, H.R.; ul Haq, Z.; Wang, S.F. Self-healing behavior of rubberized asphalt modulated by the degradation of crumb tire rubber. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 440, 137403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, P.P.; Xu, G.; Yang, J.Y.; Chen, X.H.; Zhu, Y.Q. Study on Storage Stability of Activated Reclaimed Rubber Powder Modified Asphalt. Materials 2021, 14, 4684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.G.; Zhang, Y.P.; Chen, J.; Liu, W.C.; Wang, W.S. Effect of Desulfurization Process Variables on the Properties of Crumb Rubber Modified Asphalt. Polymers 2022, 14, 1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farina, A.; Kutay, M.E.; Anctil, A. Environmental assessment of asphalt mixtures modified with polymer coated rubber from scrap tires. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 418, 138090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, P.P.; Chen, X.H.; Xu, G.; Wei, W. Preparation and characterization of maleic anhydride-grafted desulfurization rubber powder by free-radical polymerization. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2021, 61, 2567–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.J.; Guo, X.H.; Luo, Y.F.; Jia, Z.X.; Chen, Y.J.; Jia, D.M. Inorganic and Organic Hybrid Nanoparticles as Multifunctional Crosslinkers for Rubber Vulcanization with High-Filler Rubber Interaction. Polymers 2018, 10, 1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.B.; Sun, J.M.; Hao, G.X.; Zhao, Q.Y.; Hu, Y.H.; Zou, X.L.; Li, Z.G. Effect of styrene butadiene styrene and desulfurized rubber powder on asphalt modification: Preparation, performance enhancement, mechanism analysis. Sci. Total. Environ. 2024, 912, 169077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Wan, C.Y.; Xie, Y.L.; Formela, K.; Wang, S.F. Vegetable derived-oil facilitating carbon black migration from waste tire rubbers and its reinforcement effect. Waste Manag. 2018, 78, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.L.; Hassan, A.A.; Song, P.; Zhan, Z.; Wang, S.F. High scission of butadiene rubber vulcanizate under thermo-oxidation. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2019, 167, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saputra, R.; Walvekar, R.; Khalid, M.; Mubarak, N.M.; Sillanpää, M. Current progress in waste tire rubber devulcanization. Chemosphere 2021, 265, 129033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Sousa, F.D.B.; Scuracchio, C.H.; Hu, G.H.; Hoppe, S. Devulcanization of waste tire rubber by microwaves. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2017, 138, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Highway Science Research Institute of Ministry of Transport. Standard Test Methods of Bitumen and Bituminous Mixtures for Highway Engineering: JTG E20-2011; People’s Communications Press: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- AASHTO T 315-2016; Standard Method of Test for Determining the Rheological Properties of Asphalt Binder Using a Dynamic Shear Rheometer (DSR). American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials: Washington, DC, USA, 2016.
- Qian, C.D.; Fan, W.Y.; Yang, G.M.; Han, L.; Xing, B.D.; Lv, X.B. Influence of crumb rubber particle size and SBS structure on properties of CR/SBS composite modified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 235, 117517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, T.; Pei, J.; Amirkhanian, S.; Fan, Z. Low temperature and fatigue characteristics of treated crumb rubber modified asphalt after a long term aging procedure. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 234, 1262–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.; Sun, L.J.; Liu, L.P.; Li, M.C.; Li, J.H.; Yuan, J.; Yang, R.K.; Cheng, H.L. Development of dynamic shear-rheology-based method to improve evaluation of swelling degree of recycled crumb rubber in asphalt rubber. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 449, 141851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Ashish, P.K.; Jagadeesh, A. Influence of Particle and Interaction Effects of Different Sizes of Crumb Rubber on Rheological Performance Parameters of Binders. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2018, 30, 04018066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AASHTO T 350-19; Standard Method of Test for Multiple Stress Creep Recovery (MSCR) Test of Asphalt Binder Using a Dynamic Shear Rheometer (DSR). American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials: Washington, DC, USA, 2023.
- Xing, B.D.; Feng, Y.L.; Sun, S.W.; Qian, C.D.; Fang, C.; Lv, X.B.; Song, A.M.; Lyu, Y. Investigations on the rheological and swelling-degradation behavior of crumb rubber within the bituminous matrix. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 367, 130262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Liu, Q.; Chen, L.; Pei, J.; Li, R. Review and comparison of methods to assess the storage stability of terminal blend rubberized asphalt binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 258, 119586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Gao, J.P.; Pei, J.Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, J.P.; Li, R. Research on highly dissolved rubber asphalt prepared using a composite waste engine oil addition and microwave desulfurization method. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 282, 122641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.L.; Jiang, X.M.; Ding, Z.; Zhao, J.K.; Shen, M.H. Analysis of viscosity and composition properties for crumb rubber modified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 169, 638–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, K.; Tang, N.; Yuan, C.; Li, R.; Zhu, H.; Wang, L.; Qin, F. Rheological properties and storage stability of high content rubber modified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 489, 142129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, B.H.; Domingues, D.; Rato, M.J. Towards the decarbonization: Integration of recycled crumb rubber Rapid Digestion Process and reclaimed asphalt on asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 500, 144039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.L. Research on High Dosage of Crumb Rubber Modified Asphalt. Master’s Thesis, College of Civil Engineering of Chongqing University, Chongqing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G. The Performance of High Content Asphalt Rubber Based on Activation Technique. Master’s Thesis, College of Civil Engineering of Chongqing University, Chongqing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, J.; Zhao, X.C.; Liu, Y.N.; Ge, D.D.; Wang, S.F.; Ding, Z.Y.; Lv, S.T. Microbial treatment of waste crumb rubber: Reducing energy consumption and harmful emissions during asphalt production process. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 464, 142778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.L.; Ning, Z.K.; Feng, X.W.; He, X.Y.; Tan, S.R. Methods for improving storage stability of rubber bitumen: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 449, 141595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.P.; Liu, X.Y.; Erkens, S.; Skarpas, A. Experimental characterization of storage stability of crumb rubber modified bitumen with warm-mix additives. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 249, 118840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Deng, X.K.; Xiao, P.; Qian, P.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, A.H. Properties and interaction evolution mechanism of CR modified asphalt. Fuel 2024, 371, 131886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Li, X.; Lv, Y.; Xie, A.; Li, X.; Sun, T.; Zhu, Y.; Tao, H.; Wang, L. Preparation and characterizations of Fe3O4/n-OD@SiO2@C composite microcapsule for electromagnetic wave absorption and heat storage dual-functional cement-based composite material. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 489, 142307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.R.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Li, Z.L. Performance Evaluation of Desulfurized Rubber Asphalt Based on Rheological and Environmental Effects. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2020, 32, 04019330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.P.; Zhang, Y.F.; Zhao, Z.J.; Xie, J.; Wu, S.P. Performance Evaluation of Vulcanized Rubber Asphalt and Desulfurized Rubber Asphalt. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. 2024, 48, 771–775. [Google Scholar]
- Putman, B.J.; Amirkhanian, S.N. Crumb rubber modification of binders: Interaction and particle effects. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2006, 6, 655–677. [Google Scholar]
- Putman, B.J.; Amirkhanian, S.N. Characterization of the Interaction Effect of Crumb Rubber Modified Binders Using HP-GPC. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2010, 22, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, M.Z.; Li, C.; Aljarmouzi, A. Secondary degradation of bio-oil degraded crumb rubber and preparation of stable degraded crumb rubber modified asphalt. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 20, e03254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.B.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.Y.; Zou, Y.X.; Chen, A.Q.; Wang, F.; Liu, L.R.; Gu, D.J.; Zhou, S.Y. Swelled Mechanism of Crumb Rubber and Technical Properties of Crumb Rubber Modified Bitumen. Materials 2022, 15, 7987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, A.M.; Fini, E.H. AFM study of asphalt binder “bee” structures: Origin, mechanical fracture, topological evolution, and experimental artifacts. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 96972–96982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, L.; Mikhailenko, P.; Piao, Z.Y.; Fini, E.H.; Pei, J.Z.; Poulikakos, L.D. Unraveling the modification mechanisms of waste bio-oils and crumb rubber on asphalt binder based on microscopy and chemo-rheology. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 185, 106447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, D.K.; Topal, A.; McNally, T. Relationship between microstructure and phase morphology of SBS modified bitumen with processing parameters studied using atomic force microscopy. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 268, 121061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.H.; Wang, Z.K.; Ma, Q.Y.; Yu, W.W.; Zhu, F.B.; He, H.W.; Du, H.Y.; Liao, L.; Fan, Y.H.; Zhang, B.; et al. Microstructure of modified asphalt with high desulfurized crumb rubber (DCR) contents and its impact on viscoelastic properties. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2025, 37, 3230–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wang, Z.; Cui, C.; Yu, W.; Zhu, F.; He, H.; Du, H.; Liao, L.; Duan, D.; Zhang, B.; et al. Secondary relaxation-driven self-healing optimization in desulfurized crumb rubber-modified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 489, 142370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
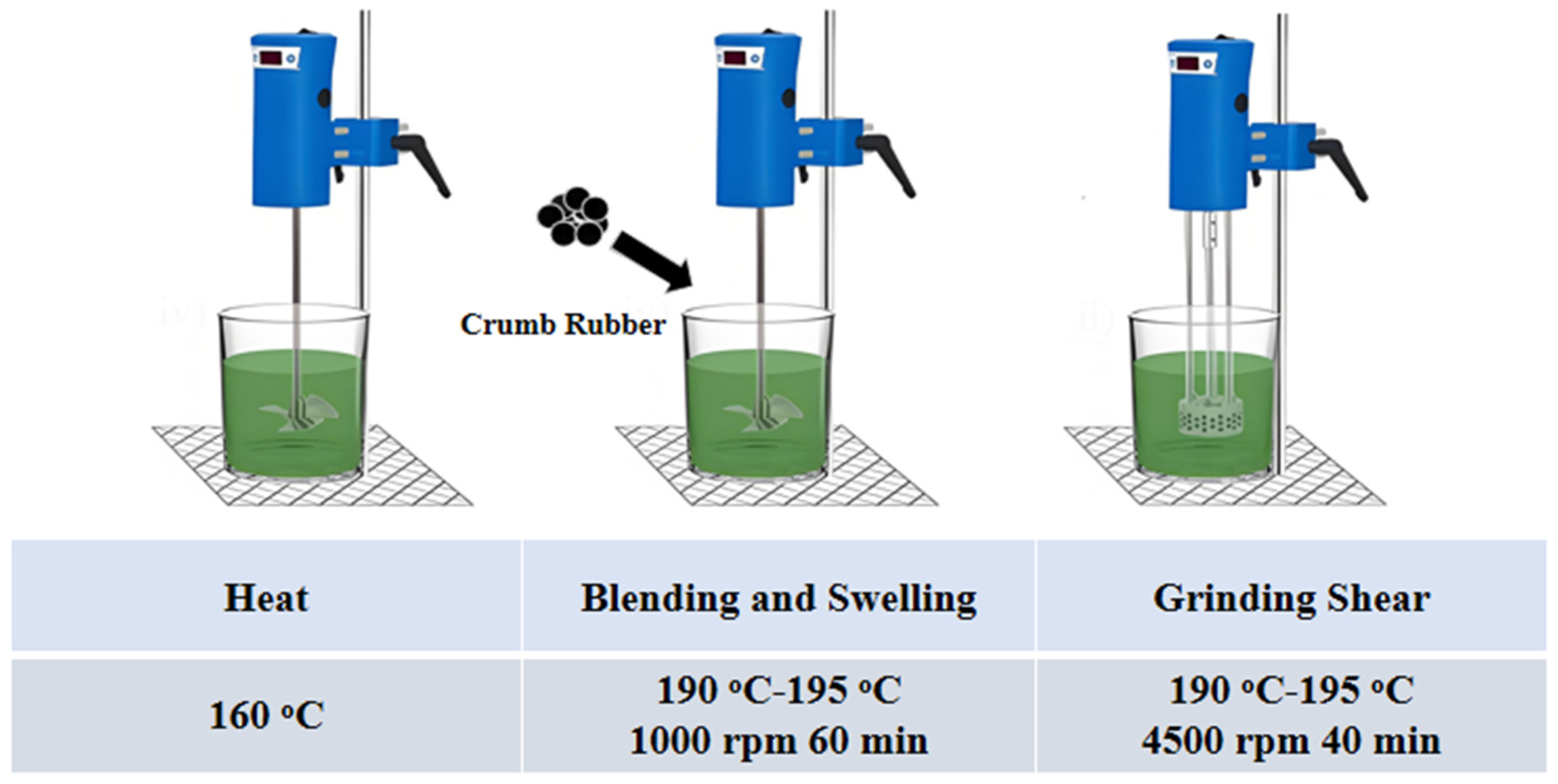
| Properties | Test Values |
|---|---|
| Penetration (25 °C, 0.1 mm) | 73 |
| Softening point (°C) | 45.4 |
| Ductility (5 °C, cm) | 0 |
| Brook Viscosity (180 °C, Pa·s) | 0.12 |
| Components | DCR | CR |
|---|---|---|
| Rubber hydrocarbon (wt%) | 55.51 | 57.13 |
| Carbon-black (wt%) | 27.18 | 27.37 |
| Ash (wt%) | 9.58 | 6.88 |
| Oil (wt%) | 7.68 | 8.6 |
| Sol (%) | 32 | — |
| Samples | CR Content (wt%) | DCR Content (wt%) | Total Content (wt%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 43 wt% DCR Modified Asphalt | 0 | 43 | 43 wt% |
| 10 wt% CR/33wt% DCR Modified Asphalt | 10 | 33 | |
| 20 wt% CR/23wt% DCR Modified Asphalt | 20 | 23 | |
| 30 wt% CR/13wt% DCR Modified Asphalt | 30 | 13 | |
| 43 wt% CR Modified Asphalt | 43 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Wang, R.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, B.; Fan, Y.; Yu, W.; Zheng, Q.; Zhu, F. Hybrid Devulcanized/Vulcanized Crumb Rubber Strategy for High-Performance Asphalt with over 40% Recycled Tire Rubber Content. Polymers 2025, 17, 2987. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17222987
Wang Z, Wang R, Zhang H, Zhang B, Fan Y, Yu W, Zheng Q, Zhu F. Hybrid Devulcanized/Vulcanized Crumb Rubber Strategy for High-Performance Asphalt with over 40% Recycled Tire Rubber Content. Polymers. 2025; 17(22):2987. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17222987
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhengkun, Ruihuan Wang, Heng Zhang, Bo Zhang, Yinghua Fan, Wenwen Yu, Qiang Zheng, and Fengbo Zhu. 2025. "Hybrid Devulcanized/Vulcanized Crumb Rubber Strategy for High-Performance Asphalt with over 40% Recycled Tire Rubber Content" Polymers 17, no. 22: 2987. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17222987
APA StyleWang, Z., Wang, R., Zhang, H., Zhang, B., Fan, Y., Yu, W., Zheng, Q., & Zhu, F. (2025). Hybrid Devulcanized/Vulcanized Crumb Rubber Strategy for High-Performance Asphalt with over 40% Recycled Tire Rubber Content. Polymers, 17(22), 2987. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17222987






