Dual-Responsive Hybrid Microgels Enabling Phase Inversion in Pickering Emulsions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of P(NIPAM-co-MAA) Microgels
2.3. Synthesis of H-SiO2@P(NIPAM-co-MAA) Hybrid Microgels
2.4. Preparation of Pickering Emulsions
2.5. In Situ Reversible Phase Inversion
2.6. Characterization
2.6.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.6.2. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
2.6.3. Zeta Potential
2.6.4. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
2.6.5. Contact Angle Measurements
2.6.6. Dynamic Interfacial Tension (IFT) Measurements
2.6.7. Optical Microscopy
2.6.8. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM)
2.6.9. Droplet Size and Shape Analysis
- Equivalent circular diameter (ECD, μm): calculated from the projected droplet area,
- Aspect ratio (AR): obtained from ellipse fitting, defined as major/minor axis length;
- Standard deviation (SD): statistical spread of ECD and AR within each sample set;
- Coefficient of variation (CV): defined as SD/mean, a dimensionless measure of polydispersity.
3. Results and Discussion
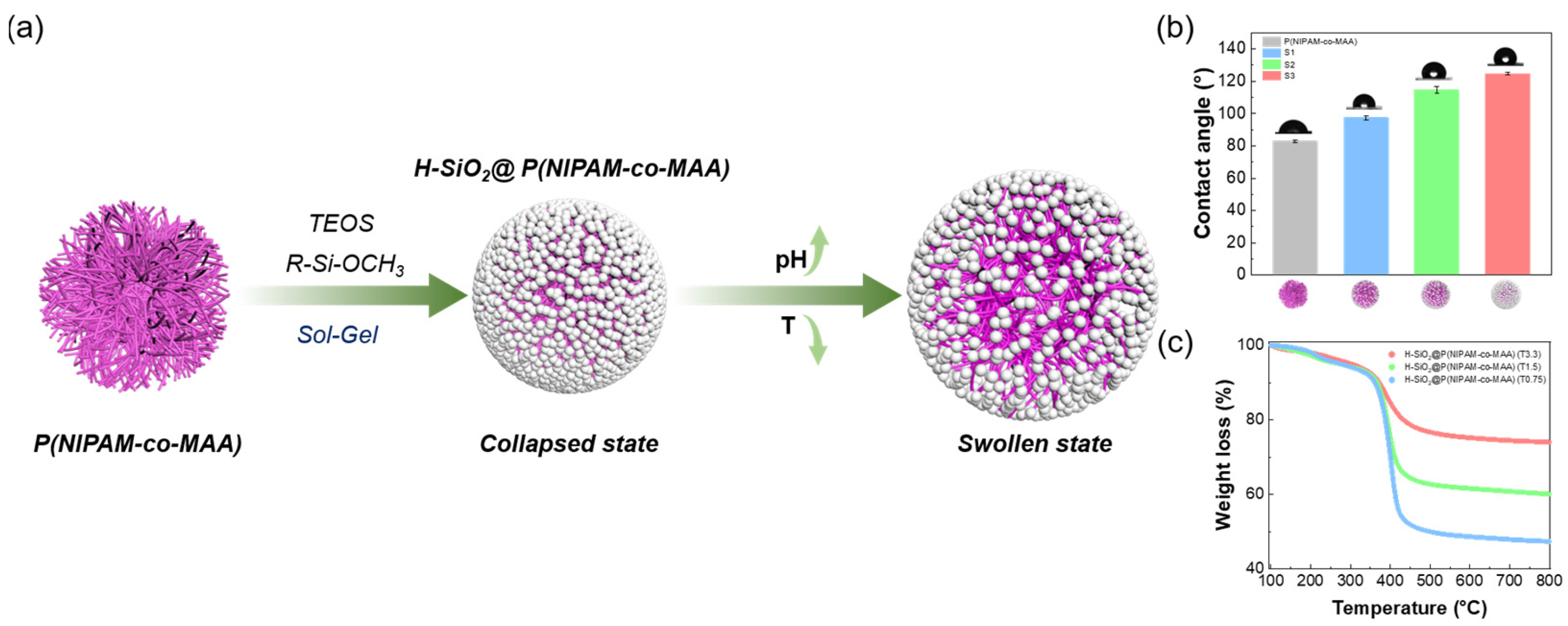
3.1. Structure and Characterization of H-SiO2@P(NIPAM-co-MAA) Hybrid Microgels
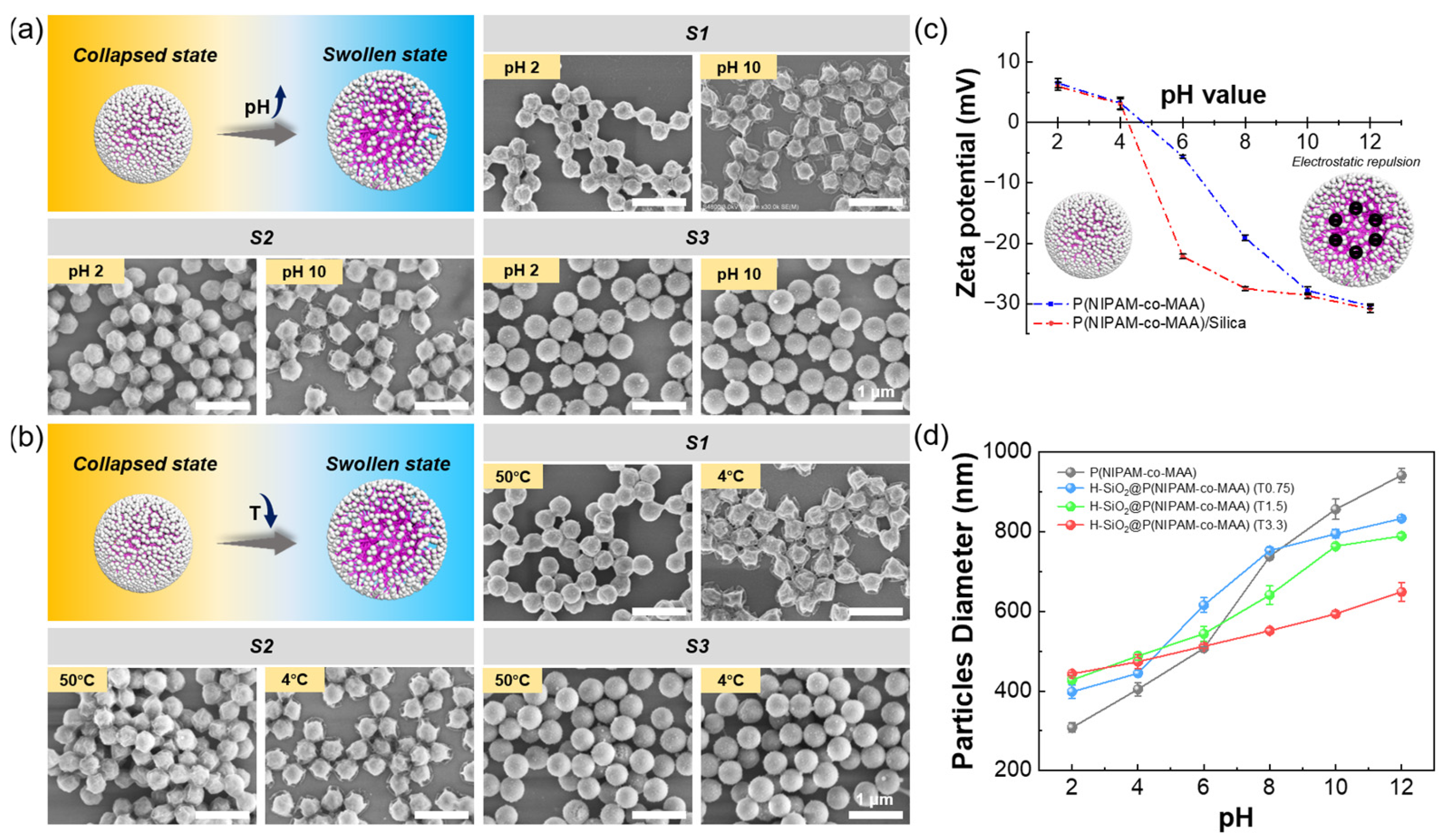
3.2. pH and Temperature Responsiveness of H-SiO2@P(NIPAM-co-MAA) Hybrid Microgels
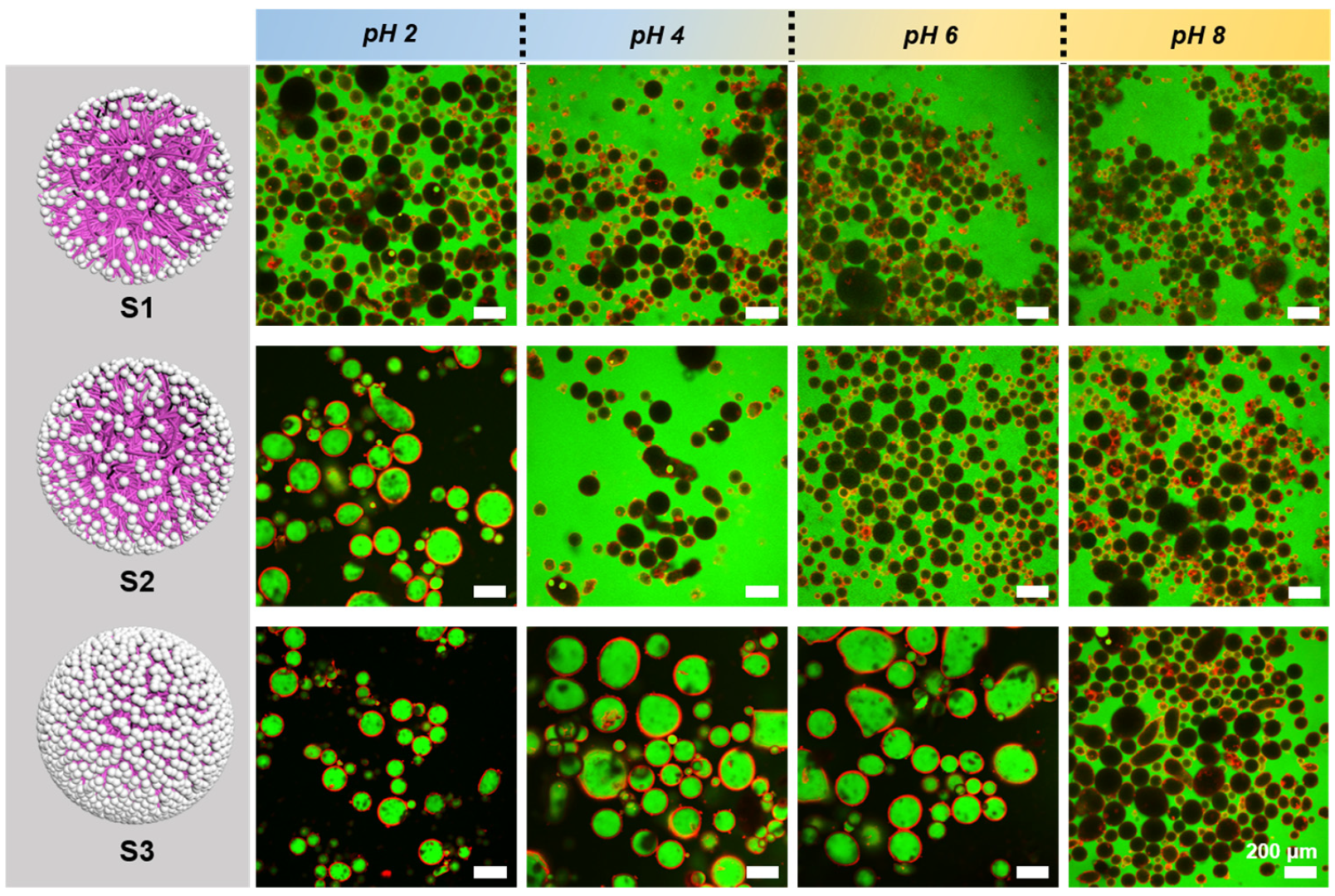
3.3. Responsive Behavior of Pickering Emulsions Stabilized by H-SiO2@P(NIPAM-co-MAA) Hybrid Microgels
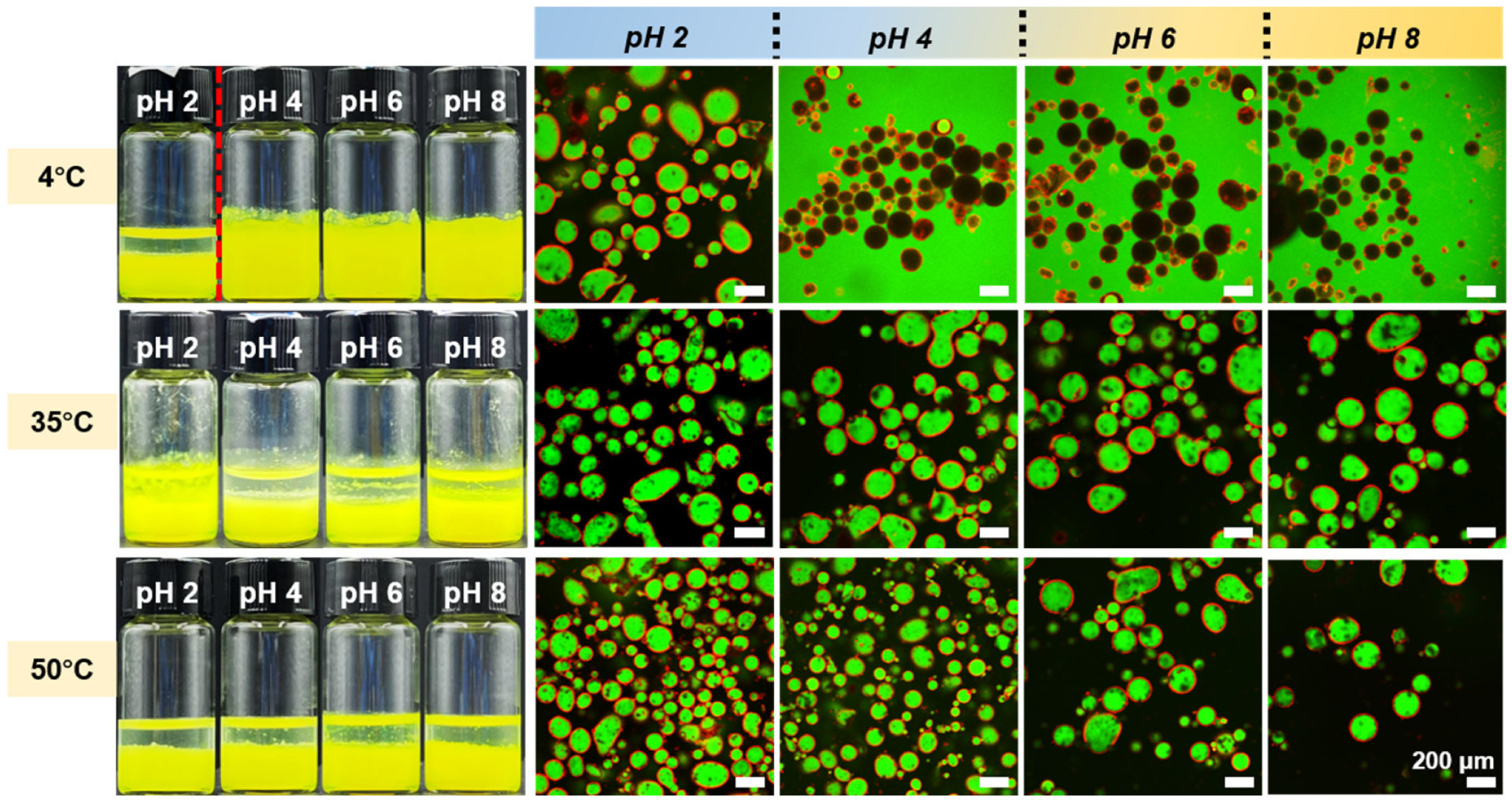
3.4. In Situ Reversible Phase Inversion of Pickering Emulsions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramsden, W. Separation of Solids in the Surface-Layers of Solutions and “Suspensions” (Observations on Surface-Membranes, Bubbles, Emulsions, and Mechanical Coagulation)-Preliminary Account. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1903, 72, 156–164. [Google Scholar]
- Pickering, S.U. CXCVI.—Emulsions. J. Chem. Soc. Trans. 1907, 91, 2001–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binks, B.P.; Lumsdon, S.O. Influence of Particle Wettability on the Type and Stability of Surfactant-Free Emulsions. Langmuir 2000, 16, 8622–8631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, M.; Kolker, J.; Richards, J.A.; Malhotra, I.; Glen, T.S.; Li, N.Y.D.; Laidlaw, F.H.J.; Renggli, D.; Vermant, J.; Schofield, A.B.; et al. Interactions between Interfaces Dictate Stimuli-Responsive Emulsion Behaviour. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanzawa, M.; Kanai, N.; Sakai, T.; Yamada, K.; Kumagai, S.; Mijiddorj, B.; Kawamura, I. Enhancing Emulsion Stability and Adsorption of Pickering Emulsions Using Alkylated Cellulose Nanofibers. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2024, 8, 100574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Jiang, H.; Lin, J.; Ngai, T. Pickering Emulsions: Microgels as Alternative Surfactants. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 73, 101827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, B.; Liu, H.; Zhang, K. Recent Progress on Pickering Emulsions Stabilized by Polysaccharides-Based Micro/Nanoparticles. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 296, 102522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Hu, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, C.; Ngai, T. Engineering Proteinaceous Colloidosomes as Enzyme Carriers for Efficient and Recyclable Pickering Interfacial Biocatalysis. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 12463–12467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, C.; Zou, S.; Wei, Z.; Tong, Z. Simple, Reversible Emulsion System Switched by pH on the Basis of Chitosan without Any Hydrophobic Modification. Langmuir 2012, 28, 11017–11024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Sun, X.; Fan, X.; Li, M.; He, G. Pickering Emulsions Stabilized by Hydrophobically Modified Alginate Nanoparticles: Preparation and pH-Responsive Performance in Vitro. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2018, 39, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y.; Liu, B.; Wang, S.; Wei, S.; Yin, S.; Ngai, T.; Yang, X. CO2 -Responsive Pickering Emulsions Stabilized by Soft Protein Particles for Interfacial Biocatalysis. Chem. Sci. 2022, 13, 2884–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuji, S.; Kawaguchi, H. Thermosensitive Pickering Emulsion Stabilized by Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide)-Carrying Particles. Langmuir 2008, 24, 3300–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirksen, M.; Fandrich, P.; Goett-Zink, L.; Cremer, J.; Anselmetti, D.; Hellweg, T. Thermoresponsive Microgel-Based Free-Standing Membranes: Influence of Different Microgel Cross-Linkers on Membrane Function. Langmuir 2022, 38, 638–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, M.; Li, Z.; Ngai, T. Controlling the Synthesis and Characterization of Micrometer-Sized PNIPAM Microgels with Tailored Morphologies. Langmuir 2013, 29, 9581–9591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, G.; Agrawal, R. Stimuli-Responsive Microgels and Microgel-Based Systems: Advances in the Exploitation of Microgel Colloidal Properties and Their Interfacial Activity. Polymers 2018, 10, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.J.; Rajendran, R.R.; Mohanto, S.; Agarwal, U.; Panda, K.; Dhotre, K.; Manne, R.; Deepak, A.; Zafar, A.; Yasir, M.; et al. Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide)-Based Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications: A Review of the State-of-the-Art. Gels 2022, 8, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Babu, A.; Chakraborty, S.; Van Guyse, J.F.R.; Hoogenboom, R.; Maji, S. Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) and Its Copolymers: A Review on Recent Advances in the Areas of Sensing and Biosensing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2402432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brugger, B.; Richtering, W. Emulsions Stabilized by Stimuli-Sensitive Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide)-Co-Methacrylic Acid Polymers: Microgels versus Low Molecular Weight Polymers. Langmuir 2008, 24, 7769–7777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brugger, B.; Rosen, B.A.; Richtering, W. Microgels as Stimuli-Responsive Stabilizers for Emulsions. Langmuir 2008, 24, 12202–12208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngai, T.; Behrens, S.H.; Auweter, H. Novel Emulsions Stabilized by pH and Temperature Sensitive Microgels. Chem. Commun. 2005, 3, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Rodriguez, M.A.; Martín-Molina, A.; Maldonado-Valderrama, J. Microgels at Interfaces, from Mickering Emulsions to Flat Interfaces and Back. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 288, 102350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, R.; Ickler, M.; Markovina, A.; Kanwal, S.; Vogel, N.; Klinger, D. Amphiphilic Nanogels as Versatile Stabilizers for Pickering Emulsions. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 25499–25511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Qi, L.; Li, Y.; Zhao, B.; Guan, X.; Ma, P.; Liu, W.; Yang, C.; Jiang, J.; Binks, B.P.; et al. Localizing Anaerobic Microbial Cultivation and Recovery Through Intelligent Pickering Emulsion Phase Inversion. CCS Chem. 2025, 7, 2137–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelton, R. Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAM) Is Never Hydrophobic. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 348, 673–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stock, S.; Jakob, F.; Röhl, S.; Gräff, K.; Kühnhammer, M.; Hondow, N.; Micklethwaite, S.; Kraume, M.; von Klitzing, R. Exploring Water in Oil Emulsions Simultaneously Stabilized by Solid Hydrophobic Silica Nanospheres and Hydrophilic Soft PNIPAM Microgel. Soft Matter 2021, 17, 8258–8268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, S.; Röhl, S.; Mirau, L.; Kraume, M.; Von Klitzing, R. Maximum Incorporation of Soft Microgel at Interfaces of Water in Oil Emulsion Droplets Stabilized by Solid Silica Spheres. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belthle, T.; Pich, A. Aqueous Microgels with Engineered Hydrophobic Nano-Domains. Mol. Syst. Des. Eng. 2022, 7, 1207–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhou, H.; Ren, J.; Gao, G.; Zhao, G.; Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, J. Polymer@SiO2 Core–Shell Composite Particles: Preparation and Application. Coatings 2023, 13, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Liu, Y.; Xia, Y.; Steve Tse, Y.-L.; Ngai, T. Assembly and Jamming of Polar Additive-Swollen Microgels at Liquid–Liquid Interfaces: From Inverse Pickering Emulsions to Functional Materials. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2025, 679, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Wen, H.; Ou, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, L.; Zhou, H.; Di, B.; Yu, Z.; Hu, C. A New Design for Living Cell-Based Biosensors: Microgels with a Selectively Permeable Shell That Can Harbor Bacterial Species. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 334, 129648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, M. A Tutorial Review on Composites of Silica and Smart Microgels. JOM 2024, 76, 1203–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Fang, E.; Qi, L.; Guan, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, W.; Ngai, T. Dual-Responsive Colloidosome-like Microgels as the Building Blocks for Phase Inversion of Pickering Emulsions. Soft Matter 2023, 19, 8240–8246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Jiang, H.; Liu, W.; Guan, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, C.; Ngai, T. Pickering Emulsion Templated Proteinaceous Microsphere with Bio-Stimuli Responsiveness. Acta Phys. Chim. Sin. 2023, 39, 2301041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Takizawa, M.; Jiang, H.; Ngai, T.; Suzuki, D. Hydrophobized Nanocomposite Hydrogel Microspheres as Particulate Stabilizers for Water-in-Oil Emulsions. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 5990–5993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pich, A.; Richtering, W. Microgels by Precipitation Polymerization: Synthesis, Characterization, and Functionalization. In Chemical Design of Responsive Microgels; Pich, A., Richtering, W., Eds.; Advances in Polymer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Volume 234, pp. 1–37. ISBN 978-3-642-16378-4. [Google Scholar]
- Farooqi, Z.H.; Khan, H.U.; Shah, S.M.; Siddiq, M. Stability of Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide-Co-Acrylic Acid) Polymer Microgels under Various Conditions of Temperature, pH and Salt Concentration. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brugger, B.; Vermant, J.; Richtering, W. Interfacial Layers of Stimuli-Responsive Poly-(N-Isopropylacrylamide-Co-Methacrylicacid) (PNIPAM-Co-MAA) Microgels Characterized by Interfacial Rheology and Compression Isotherms. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 14573–14578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, H. On Going to a New Era of Microgel Exhibiting Volume Phase Transition. Gels 2020, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Style, R.W.; Isa, L.; Dufresne, E.R. Adsorption of Soft Particles at Fluid Interfaces. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 7412–7419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vialetto, J.; Nussbaum, N.; Bergfreund, J.; Fischer, P.; Isa, L. Influence of the Interfacial Tension on the Microstructural and Mechanical Properties of Microgels at Fluid Interfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 608, 2584–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Ngai, T. One-Step Formation of Double Emulsions Stabilized by PNIPAM-Based Microgels: The Role of Co-Monomer. Langmuir 2021, 37, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro Arrebola, I.; Billon, L.; Aguirre, G. Microgels Self-Assembly at Liquid/Liquid Interface as Stabilizers of Emulsion: Past, Present & Future. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 287, 102333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Sample ID | TEOS/mL | IBTMS/mL | Molar Ratio (TEOS:IBTMS) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 0.75 | 0.225 | 2.87:1 |
| S2 | 1.50 | 0.45 | 2.86:1 |
| S3 | 3.30 | 1.00 | 2.83:1 |
| Sample ID | pH | Mean ECD ± SD (μm) | CV | Mean AR ± SD | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 2 | 103.3 ± 35.9 | 0.35 | 1.28 ± 0.42 | O/W |
| 4 | 101.8 ± 32.7 | 0.32 | 1.21 ± 0.37 | O/W | |
| 6 | 93.4 ± 32.5 | 0.35 | 1.28 ± 0.36 | O/W | |
| 8 | 82.1 ± 27.0 | 0.33 | 1.22 ± 0.30 | O/W | |
| S2 | 2 | 129.3 ± 45.4 | 0.35 | 1.42 ± 0.54 | W/O |
| 8 | 104.2 ± 36.2 | 0.35 | 1.21 ± 0.22 | O/W | |
| 4 | 83.2 ± 25.4 | 0.31 | 1.13 ± 0.21 | O/W | |
| 6 | 87.2 ± 32.9 | 0.38 | 1.19 ± 0.34 | O/W | |
| S3 | 2 | 103.7± 38.4 | 0.37 | 1.28 ± 0.40 | W/O |
| 4 | 141.7 ± 65.5 | 0.46 | 1.29 ± 0.26 | W/O | |
| 6 | 160.2 ± 73.3 | 0.46 | 1.32 ± 0.44 | W/O | |
| 8 | 99.2 ± 32.5 | 0.33 | 1.26 ± 0.34 | O/W |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, M.; Qi, L.; Zhang, L.; Ma, P.; Liu, W.; Ngai, T.; Jiang, H. Dual-Responsive Hybrid Microgels Enabling Phase Inversion in Pickering Emulsions. Polymers 2025, 17, 2762. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17202762
Shen M, Qi L, Zhang L, Ma P, Liu W, Ngai T, Jiang H. Dual-Responsive Hybrid Microgels Enabling Phase Inversion in Pickering Emulsions. Polymers. 2025; 17(20):2762. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17202762
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Minyue, Lin Qi, Li Zhang, Panfei Ma, Wei Liu, To Ngai, and Hang Jiang. 2025. "Dual-Responsive Hybrid Microgels Enabling Phase Inversion in Pickering Emulsions" Polymers 17, no. 20: 2762. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17202762
APA StyleShen, M., Qi, L., Zhang, L., Ma, P., Liu, W., Ngai, T., & Jiang, H. (2025). Dual-Responsive Hybrid Microgels Enabling Phase Inversion in Pickering Emulsions. Polymers, 17(20), 2762. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17202762








