Flexible, Stretchable, and Self-Healing MXene-Based Conductive Hydrogels for Human Health Monitoring
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methodology
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of MXene
2.3. Preparation of PVA/PAM/LiCl/MXene Hydrogel
2.4. Characterization
2.5. Mechanical Property Tests
2.6. Multimodal Sensing Tests
2.7. Application Tests
3. Results and Discussion
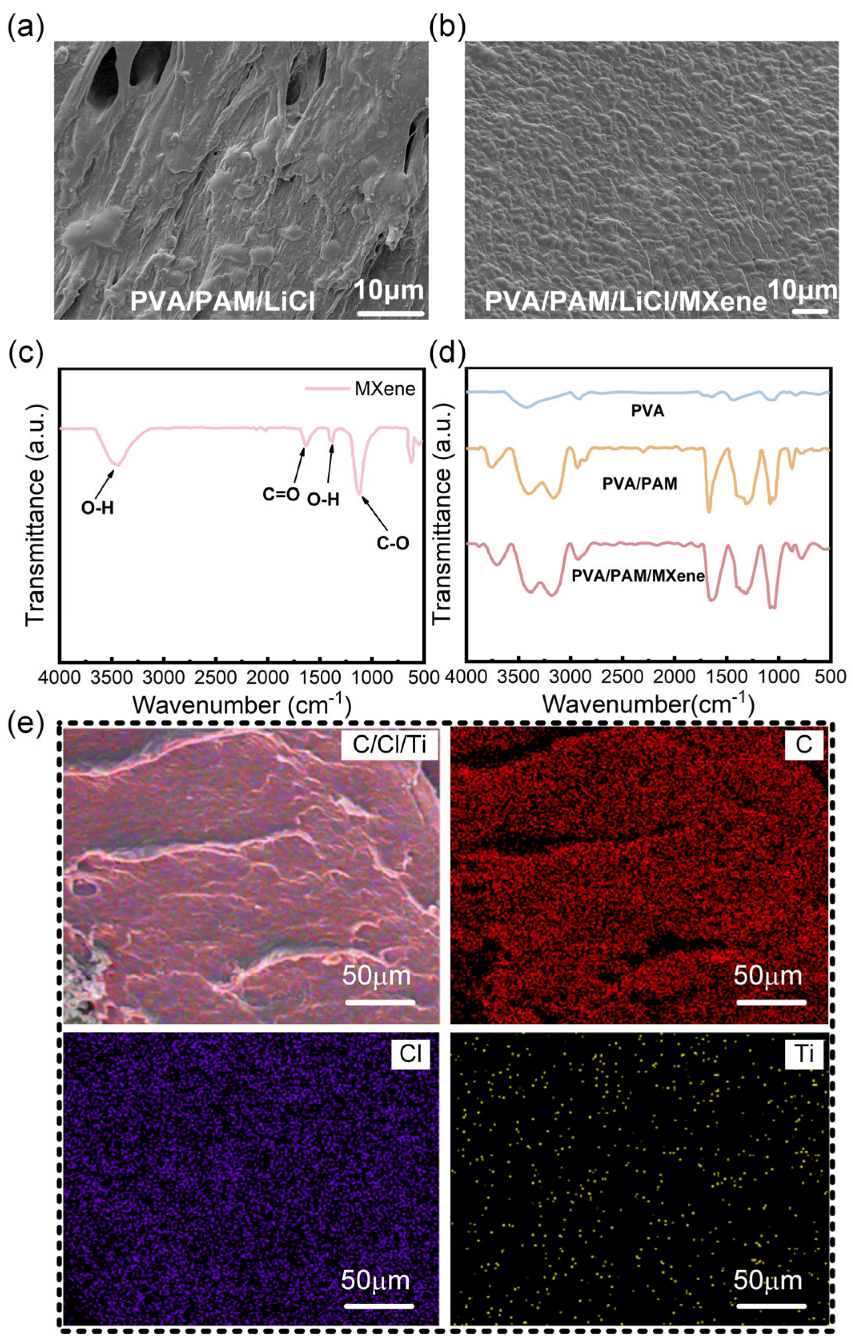
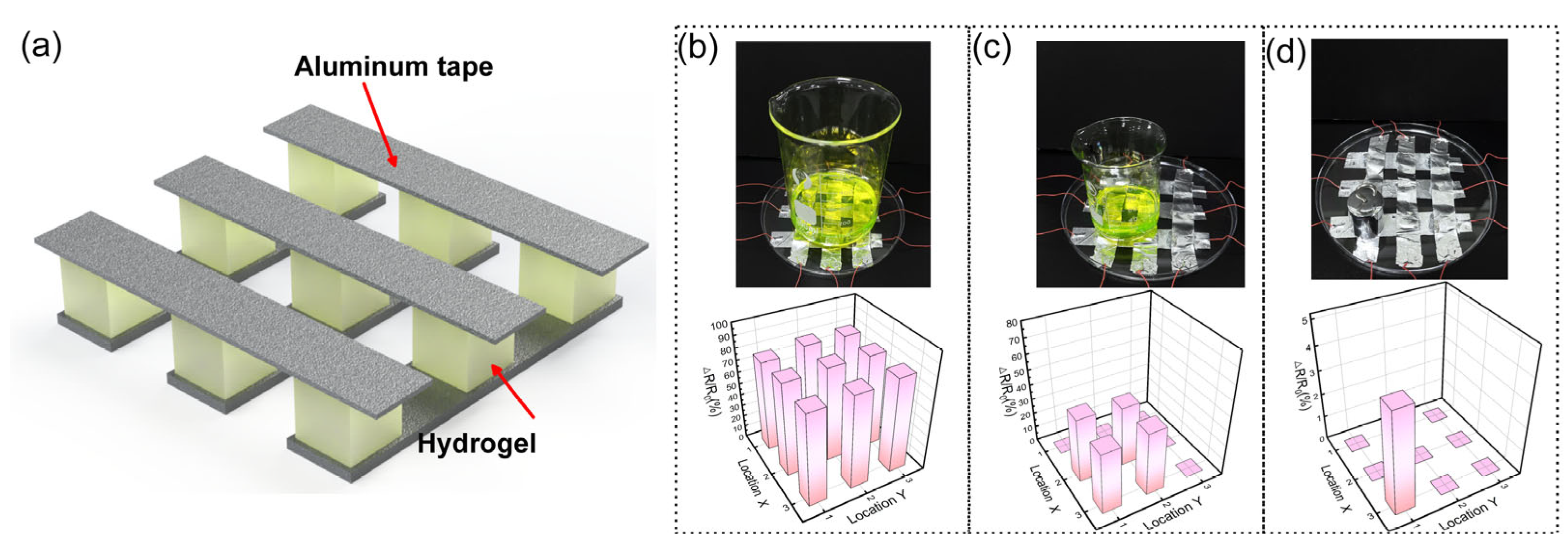
3.1. Fabrication and Characterization of PVA/PAM/LiCl/MXene Hydrogel
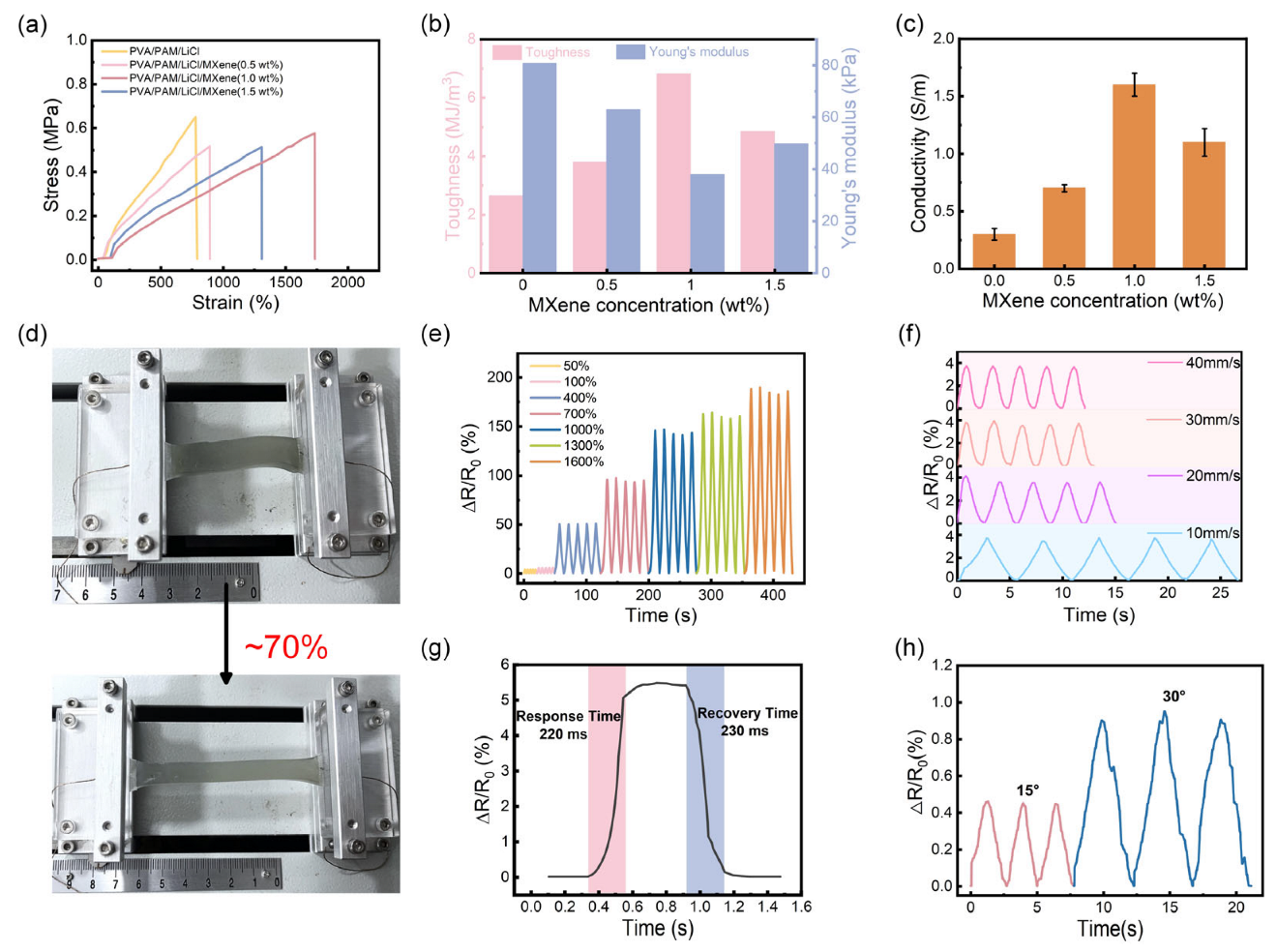
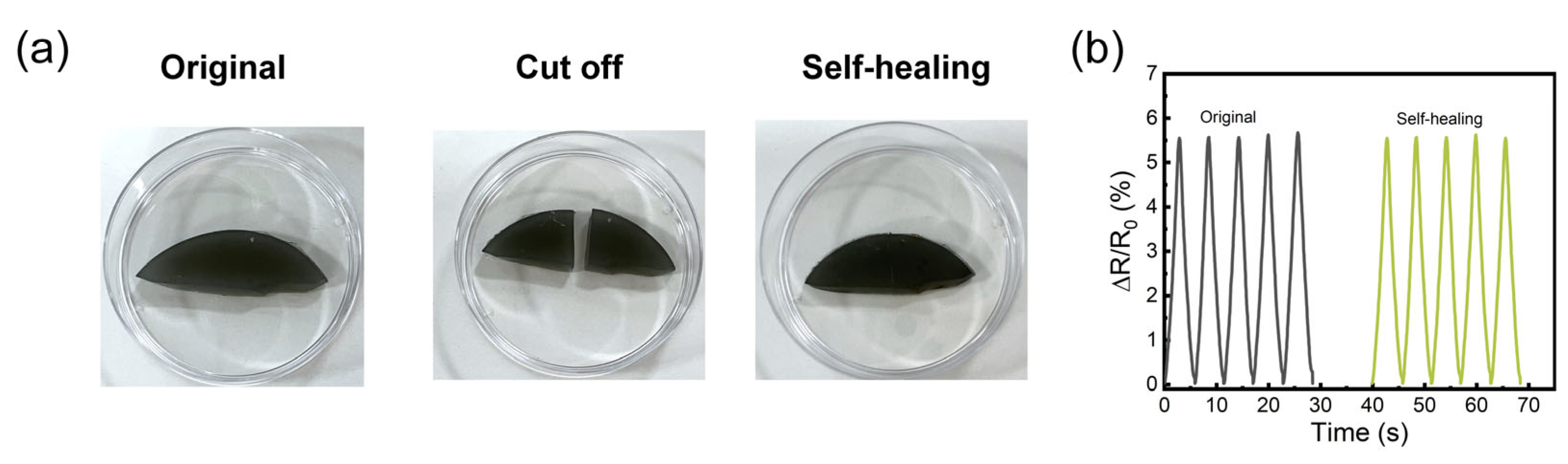
3.2. Mechanical Properties and Self-Healing Performance
3.3. Temperature and Humidity Performance
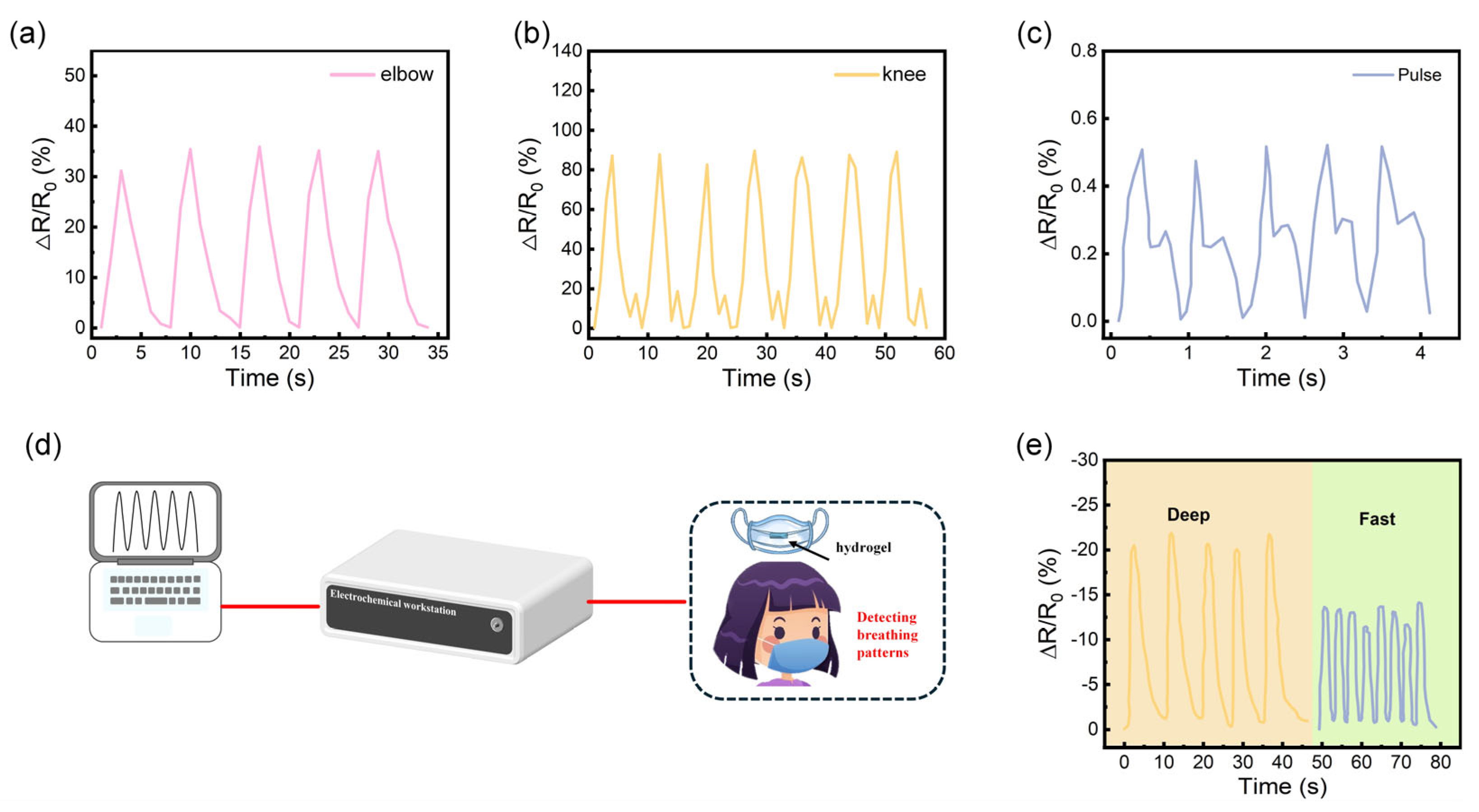
3.4. PVA/PAM/LiCl/MXene Sensor for Detection of Human Motion and Physiological Activities
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tomo, T.P.; Schmitz, A.; Wong, W.K.; Kristanto, H.; Somlor, S.; Hwang, J.; Jamone, L.; Sugano, S. Covering a robot fingertip with uSkin: A soft electronic skin with distributed 3-axis force sensitive elements for robot hands. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2017, 3, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Liang, K.; Liu, H.; Liu, R.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, S.; Tian, Y. Skin-inspired ultra-tough supramolecular multifunctional hydrogel electronic skin for human–machine interaction. Nano-Micro Lett. 2023, 15, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, G.H.; Tseng, W.M. PZT and PNIPAM film-based flexible and stretchable electronics for knee health monitoring and enhanced drug delivery. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 9736–9743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, U. Electronic skin: From flexibility to a sense of touch. Nature 2021, 591, 685–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei, M.; Lee, G.; Lee, S.G.; Cho, K. Advances in biodegradable electronic skin: Material progress and recent applications in sensing, robotics, and human–machine interfaces. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2203193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, N.; Yin, J.; Wang, X.; Xu, L.; Jiao, T.; Qin, Z. Interface interaction-mediated design of tough and conductive MXene-composited polymer hydrogel with high stretchability and low hysteresis for high-performance multiple sensing. Sci. China Mater. 2023, 66, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Shen, J.; Wan, S.; Han, L.; Dou, G.; Sun, L. Wet-adhesive multifunctional hydrogel with anti-swelling and a skin-seamless interface for underwater electrophysiological monitoring and communication. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 11549–11562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Han, X.; Jiang, F. Cellulose nanofibrils enhanced, strong, stretchable, freezing-tolerant ionic conductive organohydrogel for multi-functional sensors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2003430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhu, W.; Guan, L.; Yang, X.; Zvyagin, A.V.; Zhao, Y.; Shen, C.; Yang, B.; Lin, Q. Muscle-inspired MXene conductive hydrogels with anisotropy and low-temperature tolerance for wearable flexible sensors and arrays. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2105264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Zang, X.; Chen, J.; Zhu, T.; Yang, Y.; Huang, J.; Cai, W.; Lai, Y. Flexible MXene-based hydrogel enables wearable human–computer interaction for intelligent underwater communication and sensing rescue. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2301127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, A.; Murali, G.; Lee, S.-Y.; Gwak, J.; Kim, S.J.; Jeong, Y.J.; Kang, H.; Park, S.; Lee, A.S.; Koh, D.-Y.; et al. Highly oxidation-resistant and self-healable MXene-based hydrogels for wearable strain sensor. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2213382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirumalai, D.; Santhamoorthy, M.; Kim, S.-C.; Lim, H.-R. Conductive polymer-based hydrogels for wearable electrochemical biosensors. Gels 2024, 10, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, F.; Wang, J.; Zeng, H.; Yu, J. Functional Conductive Hydrogels for Bioelectronics. ACS Mater. Lett. 2020, 2, 1287–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-Z.; El-Demellawi, J.K.; Jiang, Q.; Ge, G.; Liang, H.; Lee, K.; Dong, X.; Alshareef, H.N. MXene hydrogels: Fundamentals and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 7229–7251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Du, C.; Liao, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, W.; Ren, T.; Sun, Z.; Lu, Y.; Nie, Z.; et al. Approaching intrinsic dynamics of MXenes hybrid hydrogel for 3D printed multimodal intelligent devices with ultrahigh superelasticity and temperature sensitivity. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xia, K.; Wang, H.; Liang, X.; Yin, Z.; Zhang, Y. Advanced carbon for flexible and wearable electronics. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1801072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Lee, J.-H.; Shen, X.; Chen, X.; Kim, J.-K. Graphene-based wearable piezoresistive physical sensors. Mater. Today 2020, 36, 158–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Xiang, L.; Ou, H.; Li, F.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, Y.; Hao, L.; Diao, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, P.; et al. MXene-based conductive organohydrogels with long-term environmental stability and multifunctionality. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2005135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Li, C.; Li, G.; Yu, D.; Song, Z.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Liu, H.; Liu, W. Development of conductive hydrogels for fabricating flexible strain sensors. Small 2022, 18, 2101518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Mathis, T.S.; Li, K.; Lin, Z.; Vlcek, L.; Torita, T.; Osti, N.C.; Hatter, C.; Urbankowski, P.; Sarycheva, A.; et al. Influences from solvents on charge storage in titanium carbide MXenes. In MXenes; Jenny Stanford Publishing: Singapore, 2023; pp. 783–810. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.; Zhou, M.; Gao, Y.; Wang, J.; Cao, Y.; Wang, W.; Wu, D.; Yang, Y. A mechanically robust all-solid-state supercapacitor based on a highly conductive double-network hydrogel electrolyte and Ti3C2Tx MXene electrode with anti-freezing property. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 25073–25085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, R.; Kiran, P.S.; Kumar, K.V.; Pandit, N.; Satish, C.; Keshri, S.; Keshri, A.K. MXene/Biomass-derived activated carbon composite for supercapacitor applications. Carbon 2025, 236, 120101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Z.; Xi, G.; Mao, R.; Ma, Y.; Wang, D.; Tang, M.; Xu, Z.; Luan, H. Ultrastretchable, self-healing conductive hydrogel-based triboelectric nanogenerators for human–computer interaction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 5128–5138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christina, X.J.; Vinodhini, S.P.; Anitha, G.; Xavier, J.R. Exploring the multifunctional potential of MXenes for high-performance supercapacitor energy storage applications. J. Mater. Sci. 2025, 60, 10632–10669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Jin, S.; Wang, S.; Xiao, H.; Zhao, Y. Injectable, adhesive, self-healing and conductive hydrogels based on MXene nanosheets for spinal cord injury repair. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 452, 139252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pati, A.R.; Ko, Y.-S.; Bae, C.; Choi, I.; Heo, Y.J.; Lee, C. Highly porous hydrogels for efficient solar water evaporation. Soft Matter 2024, 20, 4988–4997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, N.; Xu, L.; Wang, H.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, L.; Wang, C.; Zhao, J.; Rong, J. Dual physically cross-linked double network hydrogels with high mechanical strength, fatigue resistance, notch-insensitivity, and self-healing properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 34034–34044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, A.; Maity, S.; Das, R.K. A highly stretchable, tough, self-healing, and thermoprocessable polyacrylamide–chitosan supramolecular hydrogel. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2018, 303, 1800322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chee, B.S.; de Lima, G.G.; Devine, D.M.; Nugent, M.J. Investigation of the effects of orientation on freeze/thawed Polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel properties. Mater. Today Commun. 2018, 17, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.-Y.; Gao, S.; Zhou, R.-B.; Wang, R.-D.; Zhou, F. Dual-crosslinked networks of superior stretchability and toughness polyacrylamide-carboxymethylcellulose hydrogel for delivery of alendronate. Mater. Des. 2022, 217, 110627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zameer, A.; Qin, Y.; Xu, H.; Liang, Q.; Zhang, Q. Functional Hydrogels for Wearable Electronics. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2025, 226, 2400491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Li, M.; Chen, R.; Gao, D.; Wang, Z.; Qin, C.; Yang, W.; Liu, H.; Zhang, P. Enhanced mechanical strength of metal ion-doped MXene-based double-network hydrogels for highly sensitive and durable flexible sensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 51774–51784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Shang, Z.; Yao, M.; Ke, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, P. Molecular insights on the mechanical properties of double-network hydrogels reinforced by covalently compositing with silica-nanoparticles. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 368, 120611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-Z.; Lee, K.H.; Anjum, D.H.; Sougrat, R.; Jiang, Q.; Kim, H.; Alshareef, H.N. MXenes stretch hydrogel sensor performance to new limits. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaat0098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Xu, D.; Peng, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, F.; Fan, X. Ti2C3Tx nanosheets as photothermal agents for near-infrared responsive hydrogels. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 15387–15392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Cao, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, W. Multifunctional MXene-Based Fireproof Electromagnetic Shielding Films with Exceptional Anisotropic Heat Dissipation Capability and Joule Heating Performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 27350–27360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Z.; Peng, K.; Lin, L.; Yang, J.; Cheng, Z.; Gan, Q.; Chen, Y.; Feng, C. A conductive hydrogel based on nature polymer agar with self-healing ability and stretchability for flexible sensors. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 454, 139843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zhang, J.; Fan, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, M.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Li, G. A mechanically strong and highly conductive MXene/polyacrylamide–alginate composite hydrogel with a double-network structure for a flexible wearable sensor. New J. Chem. 2025, 49, 9283–9294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, H.; Zhang, D.; Xu, Z.; Zhao, W.; Yang, C.; Chen, X. MXene-based composite double-network multifunctional hydrogels as highly sensitive strain sensors. J. Mater. Chem. C 2022, 10, 7604–7613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, D.; Ding, Y.; Lv, X.; Huang, T.; Yuan, B.; Jiang, L.; Sun, X.; Yao, Y.; Tang, J. A conductive polyacrylamide hydrogel enabled by dispersion-enhanced MXene@chitosan assembly for highly stretchable and sensitive wearable skin. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 8862–8870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Feng, H.; Gui, Y.; Chen, T.; Xu, H.; Huang, X.; Ma, X. Flexible stretchable, dry-resistant MXene nanocomposite conductive hydrogel for human motion monitoring. Polymers 2023, 15, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Hydrogel System | MXene Loading | Maximum Strain | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| MXene–sodium alginate–PAM-Ca2+/Li+ composite hydrogel | 1 wt% | 224.2% | [38] |
| PAM/sodium alginate/MXene double-network hydrogel | 3.5 wt% | 1400% | [32] |
| PAM/sodium alginate/MXene hydrogel | 4 g | 1500% | [39] |
| Dispersion-enhanced MXene hydrogel | 0.76 wt% | 800% | [40] |
| polyvinyl alcohol/polyacrylamide/MXene hydrogel | 0.3 wt% | 1033% | [41] |
| PVA/PAM/LiCl/MXene hydrogel | 1 wt% | 1700% | Our work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, R.; Chang, S.; Bi, J.; Guo, H.; Yi, J.; Chu, C. Flexible, Stretchable, and Self-Healing MXene-Based Conductive Hydrogels for Human Health Monitoring. Polymers 2025, 17, 2683. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17192683
Li R, Chang S, Bi J, Guo H, Yi J, Chu C. Flexible, Stretchable, and Self-Healing MXene-Based Conductive Hydrogels for Human Health Monitoring. Polymers. 2025; 17(19):2683. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17192683
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ruirui, Sijia Chang, Jiaheng Bi, Haotian Guo, Jianya Yi, and Chengqun Chu. 2025. "Flexible, Stretchable, and Self-Healing MXene-Based Conductive Hydrogels for Human Health Monitoring" Polymers 17, no. 19: 2683. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17192683
APA StyleLi, R., Chang, S., Bi, J., Guo, H., Yi, J., & Chu, C. (2025). Flexible, Stretchable, and Self-Healing MXene-Based Conductive Hydrogels for Human Health Monitoring. Polymers, 17(19), 2683. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17192683






