Machinability of Vitrified Semi-Finished Products: Chip Formation and Heat Development at the Cutting Edge
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Machining of Fibre Reinforced Plastics (FRP) and Vitrimers
1.2. Chip Formation and Recyclability
2. Vitrimer Specimen Preparation
2.1. Vitrimeric Materials
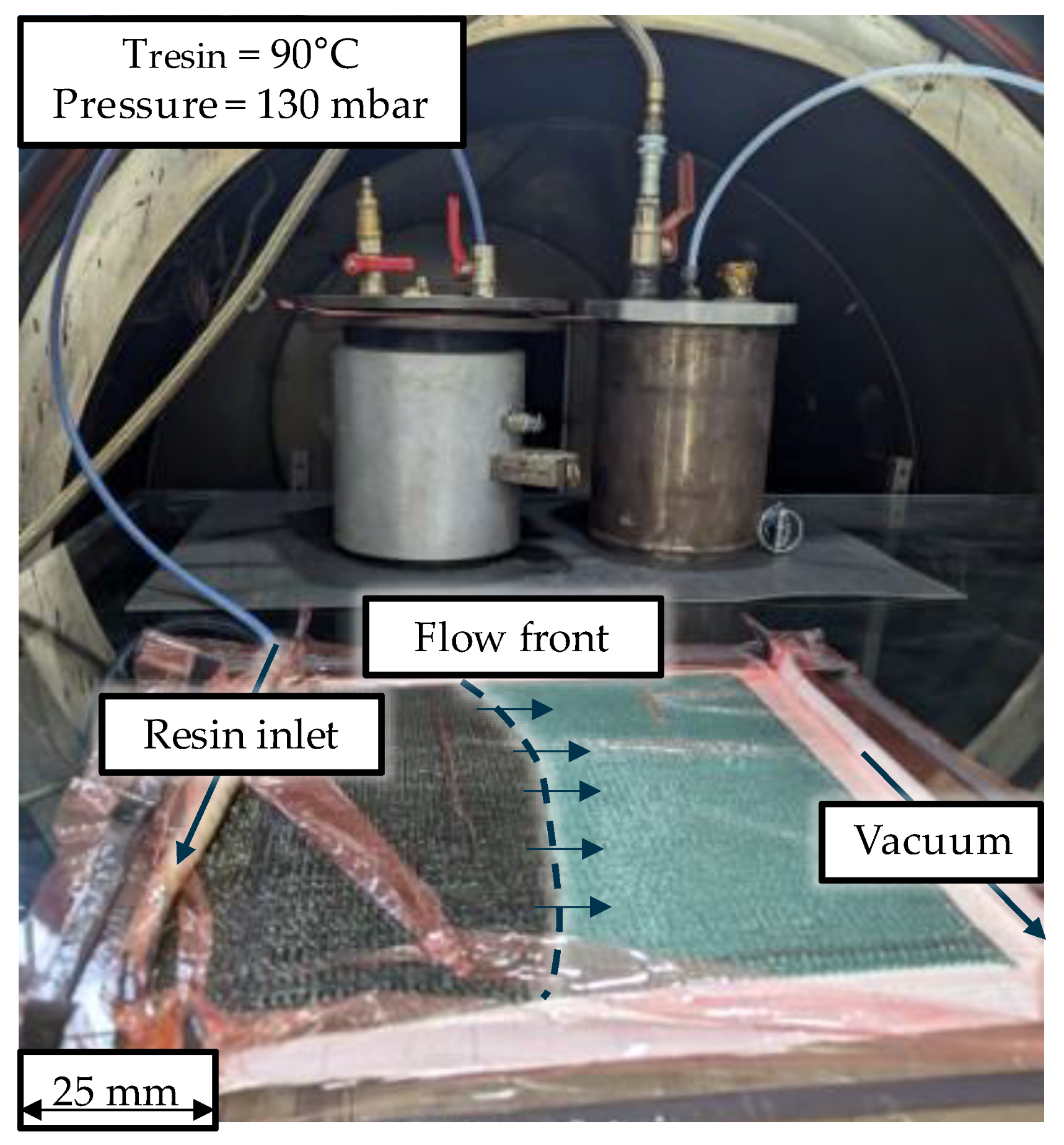
2.2. Infusion Process of Carbon Fibre Reinforced Fabrics
2.3. Quality Analysis of Fibre Reinforced Vitrimeric Specimens
2.4. Specimen Preparation for Orthogonal Cutting
3. Orthogonal Cutting of Fibre Reinforced Vitrimeric Specimens
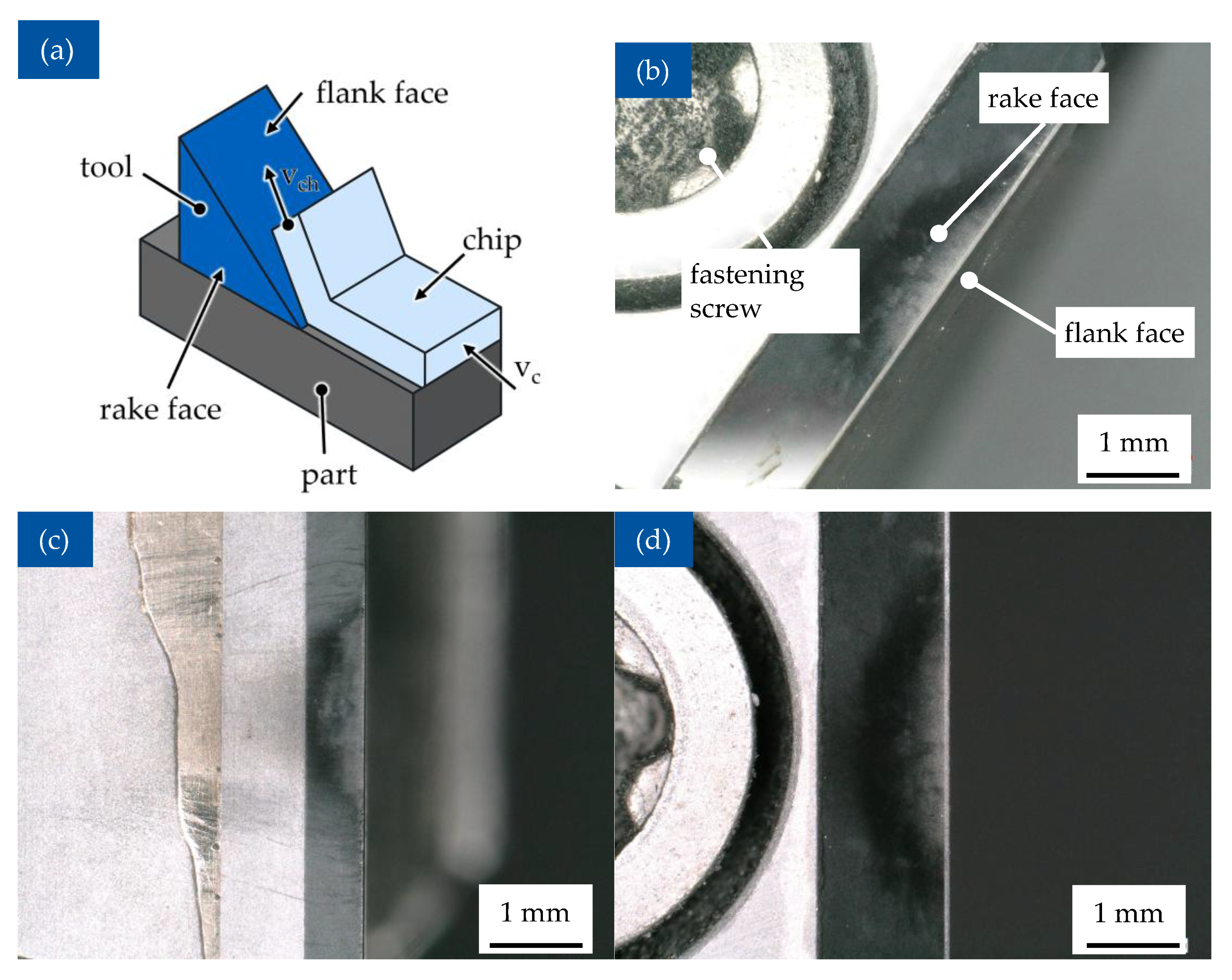
3.1. Orthogonal Cutting of Fibre Reinforced Vitrimeric Specimen
3.2. Cutting Force Measurements
3.3. Temperature Measurements
3.4. Chip Formation During Machining
3.5. Tool Wear
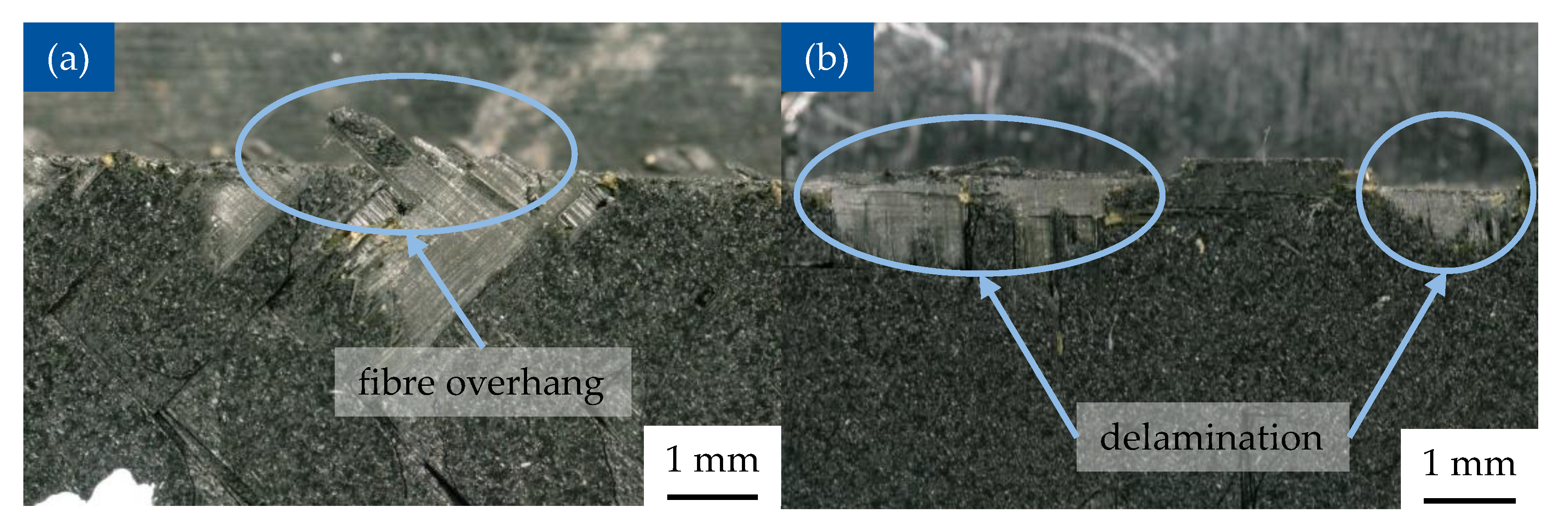
3.6. Microscopic Analysis of Machined Surface
4. Conclusions and Outlook
- Cutting forces are lower with diagonal fibre orientation, increasing with cutting depth, but remaining largely independent of cutting speed. Periodic fluctuations occur with stronger signal noise for diagonal fibres. The change of force indicates the different chip forming mechanisms.
- At higher cutting speeds, the chip temperature exceeds 235 °C, while the sample surface remains below 80 °C. Most heat is removed with the chips. Measurements may be affected by the emission from dust particles and need to be considered during the later studies.
- Chip formation depends strongly on cutting speed: large fibre–matrix chips occur at low speeds, while finer particles and dust appear at higher speeds. Colour changes of the removed material may indicate debonding of disulfide cross-links.
- No significant tool wear was observed. Only slight discolouration without geometric changes occurred.
- Surface quality is more affected with diagonal fibre orientation. Damage depth increases with cutting depth due to the increased mechanical loads. For 0°/90° orientation, the damage becomes stable above 50 m/min, whereas with diagonal orientation it increases up to 100 m/min and then decreases sharply at 150 m/min. Fibre overhang is consistently lower than damage depth and mainly increases with cutting depth which affects the bending of the fibres.
- To minimize the surface damage of machined vitrimeric CFRP parts and preserve the recyclability of waste materials, the cutting speed must be set in range of 25–50 m/min with the cutting depth not greater than 0.2 mm
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weng, M.; Huang, Z.; Yuan, Q.; Liu, Z.; Qu, J. Ultrawide sensing-range, super durable and high-strength epoxy/carbon fiber composites sensor based on stress-induced structure. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2024, 250, 110522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, B. Leichtbau-Konstruktion; Springer Fachmedien Wiesbaden: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2013; ISBN 978-3-658-02271-6. [Google Scholar]
- Pascault, J.-P.; Williams, R.J.J. Thermosetting Polymers. In Handbook of Polymer Synthesis, Characterization, and Processing; Saldívar-Guerra, E., Vivaldo-Lima, E., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 519–533. ISBN 9780470630327. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, C.; Wang, Y.; Mushtaq, R.T.; Zhang, K.; Li, X.; Chen, X. Preparation, characterization, and curing kinetics of elevated and cryogenic temperature-resistant epoxy resin composites. Polym. Test. 2022, 116, 107783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Ma, C.; Gu, J.; Guo, J.; Yan, X.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, Z. An overview of multifunctional epoxy nanocomposites. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 5890–5906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Ji, Y.; Wei, Y. Functional epoxy vitrimers and composites. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2021, 120, 100710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utekar, S.; Suriya, V.K.; More, N.; Rao, A. Comprehensive study of recycling of thermosetting polymer composites—Driving force, challenges and methods. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 207, 108596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morici, E.; Dintcheva, N.T. Recycling of Thermoset Materials and Thermoset-Based Composites: Challenge and Opportunity. Polymers 2022, 14, 4153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, P.R.; Brackenridge, J.A.; Advincula, A.A.; Taussig, L.A.; Nepal, D. Reformable and sustainable thermosetting carbon fiber composites from epoxy vitrimer. Compos. Part B Eng. 2024, 274, 111270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.-I.; Hu, J.-Y.; Shiu, J.-W.; Rwei, S.-P.; Chen, C.-W. Sustainability and repeatedly recycled epoxy-based vitrimer electromagnetic shielding composite material. Polym. Test. 2023, 127, 108200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, B.; Xiao, M.; Dong, X.; Yang, X.; Zheng, M.-S.; Dang, Z.-M.; Chen, G.; Zha, J.-W. Dynamic Covalent Adaptable Polyimide Hybrid Dielectric Films with Superior Recyclability. Adv. Mater. 2023, 36, e2304175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, A.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Z.; Qin, R.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, X.; Ye, D.; Liu, Z. Recyclable Carbon Fiber Reinforced Vanillin-Based Polyimine Vitrimers: Degradation and Mechanical Properties Study. Macro Mater. Eng. 2022, 307, 2100893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Jia, S.; Xie, R.; Chen, L.; Xiong, Y. Furan-derived Schiff base covalent adaptable thermosets with recyclability and anti-flammability. Green Chem. Eng. 2024, 5, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capelot, M.; Montarnal, D.; Tournilhac, F.; Leibler, L. Metal-catalyzed transesterification for healing and assembling of thermosets. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 7664–7667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capelot, M.; Unterlass, M.M.; Tournilhac, F.; Leibler, L. Catalytic Control of the Vitrimer Glass Transition. ACS Macro Lett. 2012, 1, 789–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montarnal, D.; Capelot, M.; Tournilhac, F.; Leibler, L. Silica-like malleable materials from permanent organic networks. Science 2011, 334, 965–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenz, N.; Dyer, W.E.; Kumru, B. Exploring the Cure State Dependence of Relaxation and the Vitrimer Transition Phenomena of a Disulfide-Based Epoxy Vitrimer. J. Polym. Sci. 2025, 63, 3739–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloxin, C.J.; Bowman, C.N. Covalent adaptable networks: Smart, reconfigurable and responsive network systems. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 7161–7173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kloxin, C.J.; Scott, T.F.; Adzima, B.J.; Bowman, C.N. Covalent Adaptable Networks (CANs): A Unique Paradigm in Crosslinked Polymers. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 2643–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenk, V.; Labastie, K.; Destarac, M.; Olivier, P.; Guerre, M. Vitrimer composites: Current status and future challenges. Mater. Adv. 2022, 3, 8012–8029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrin, H.; Vaudemont, R.; Del Frari, D.; Verge, P.; Puchot, L.; Bodaghi, M. On the cyclic delamination-healing capacity of vitrimer-based composite laminates. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2024, 177, 107899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, G.; Prasad, V.; Yasar, M.; Cicala, G.; Ivankovic, A.; Murphy, N.; Latteri, A. Investigation of mechanical properties and self-healing efficiency of carbon fibers composites infused with unsaturated polyester vitrimer. Polym. Compos. 2024, 45, 10404–10417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Biswal, A.K.; Nandi, A.; Frost, K.; Smith, J.A.; Nguyen, B.H.; Patel, S.; Vashisth, A.; Iyer, V. Recyclable vitrimer-based printed circuit boards for sustainable electronics. Nat. Sustain. 2024, 7, 616–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lessard, J.J.; Scheutz, G.M.; Hughes, R.W.; Sumerlin, B.S. Polystyrene-Based Vitrimers: Inexpensive and Recyclable Thermosets. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 2, 3044–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandemir, A.; Longana, M.L.; Hamerton, I.; Eichhorn, S.J. Developing aligned discontinuous flax fibre composites: Sustainable matrix selection and repair performance of vitrimers. Compos. Part B Eng. 2022, 243, 110139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, E.; Liu, J.; Qin, J.; Wu, M.; Yang, C.; Liang, L. Self-healing, reprocessable, degradable, thermadapt shape memory multifunctional polymers based on dynamic imine bonds and their application in nondestructively recyclable carbon fiber composites. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 454, 139992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, Z.; Ma, Y.; Shang, Q.; Hu, Y.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, M.; Jia, P.; Zhou, Y. Tung Oil-Based Degradable Vitrimer for Reprocessable and Recyclable Vitrimer–MWCNT Composites with Self-Healing Ability Triggered by Multiple Stimuli. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2023, 5, 9203–9212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdugo, P.; Santiago, D.; La Flor, S.; Serra, À. A Biobased Epoxy Vitrimer with Dual Relaxation Mechanism: A Promising Material for Renewable, Reusable, and Recyclable Adhesives and Composites. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 5965–5978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H.; Bijalwan, V.; Mourad, A.-H.I.; Kumar, A.; Schlögl, S.; Rana, S. Self-healable epoxy/graphene oxide vitrimers and their recyclable glass fiber reinforced composites. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2024, 07316844241295848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, N.; Zawadzki, T.; Keller, L.; Fuchs, J.; Fischer, K.; Hopmann, C. Characterization and modeling of an epoxy vitrimer based on disulfide exchange for wet filament winding applications. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2024, 64, 3682–3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Diaz, D.; Cortés, A.; Jiménez-Suárez, A.; Prolongo, S.G. Hardener Isomerism and Content of Dynamic Disulfide Bond Effect on Chemical Recycling of Epoxy Networks. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2022, 4, 5068–5076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guggari, S.; Magliozzi, F.; Malburet, S.; Graillot, A.; Destarac, M.; Guerre, M. Vanillin-Based Epoxy Vitrimers: Looking at the Cystamine Hardener from a Different Perspective. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 6021–6031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, I.; Greco, L.; Mignanelli, C.; Simoncini, M.; Vita, A. Environmental Sustainability of vitrimer-based composite materials. Procedia CIRP 2024, 122, 1059–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benazzo, F.; Sodano, H.A. Evaluation of Interfacial Shear Strength Healing Efficiency between Dynamic Covalent Bond-Based Epoxy and Functionalized Fiberglass. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2022, 4, 2925–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alms, J.; Sambale, A.K.; Fuchs, J.; Lorenz, N.; den Berg, N.v.; Conen, T.; Çelik, H.; Dahlmann, R.; Hopmann, C.; Stommel, M. Qualification of the Vitrimeric Matrices in Industrial-Scale Wet Filament Winding Processes for Type-4 Pressure Vessels. Polymers 2025, 17, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Chen, Y.-H.; An, Q.-L.; Cai, X.-J.; Ming, W.-W.; Chen, M. Drilling temperature and hole quality in drilling of CFRP/aluminum stacks using diamond coated drill. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2015, 16, 1689–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, A.; Forbes, A. Spanende Bearbeitung von Leichtbauwerkstoffen: Einführung und Überblick; e-mobil BW GmbH, Fraunhofer IPA; e-mobil BW GmbH: Stuttgart, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hintze, W. CFK-Bearbeitung: Trenntechnologien für Faserverbundkunststoffe und den Hybriden Leichtbau; Springer Vieweg: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Weidmann, S.; Volk, P.; Mitschang, P.; Markaide, N. Investigations on thermoforming of carbon fiber reinforced epoxy vitrimer composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2022, 154, 106791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geier, N.; Davim, J.P.; Szalay, T. Advanced cutting tools and technologies for drilling carbon fibre reinforced polymer (CFRP) composites: A review. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2019, 125, 105552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisol de Melo, E.; dos Santos Silva, J.C.; Klein, T.B.; Polte, J.; Uhlmann, E.; de Oliveira Gomes, J. Evaluation of carbon fiber reinforced polymer—CFRP—Machining by applying industrial robots. Sci. Eng. Compos. Mater. 2021, 28, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, R.; Krishnaraj, V.; Zitoune, R.; Sheikh-Ahmad, J. High-Speed Edge Trimming of CFRP and Online Monitoring of Performance of Router Tools Using Acoustic Emission. Materials 2016, 9, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Png, Z.M.; Ng, S.H.; Tham, G.X.; Ye, E.; Goh, S.S.; Loh, X.J.; Li, Z. Vitrimers: Current research trends and their emerging applications. Mater. Today 2021, 51, 586–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poór, D.I.; Tobey, M.; Taynton, P.; Pomázi, Á.; Toldy, A.; Geier, N. A comparative machinability analysis of polyimine vitrimer, epoxy and polycarbonate polymers through orthogonal machining experiments. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 131, 1361–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Arwadi, O.; Raut, A.; Meyer, J.L.; Polycarpou, A.; Naraghi, M. Time and temperature-dependent fracture mechanics of self-healing vitrimers. Polymer 2025, 322, 128148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xu, K.; Lin, Z.; Fu, J. A unified geometrical modeling and analysis method for evaluating CFRP machining performance: Cutting geometry space. Compos. Part B Eng. 2024, 283, 111649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassouna, A.; Mzali, S.; Zemzemi, F.; Mezlini, S. Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering: Orthogonal Cutting of UD-CFRP Using Micromechanical Modeling. In Advances in Integrated Desing and Production II; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Castro, G. Drilling Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastic and Titanius Stacks. Master’s Thesis, Washington State University, Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Santiuste, C.; Díaz-Álvarez, J.; Soldani, X.; Miguélez, H. Modelling thermal effects in machining of carbon fiber reinforced polymer composites. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2014, 33, 758–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.; Jia, Z.; Wang, F.; Jin, Y.; Sun, D.; Yang, L.; Cheng, D. Drill-exit temperature characteristics in drilling of UD and MD CFRP composites based on infrared thermography. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2018, 135, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinert, K.; Kempmann, C. Cutting Temperatures and Their Effects on the Machining Behaviour in Drilling Reinforced Plastic Composites. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 684–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.J.; Kim, K.B.; Yang, J.K.; Cho, M.W. Influence of cutting temperature on carbon fiber-reinforced plastic composites in high-speed machining. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2017, 31, 1861–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldosari, S.M.; AlOtaibi, B.M.; Alblalaihid, K.S.; Aldoihi, S.A.; AlOgab, K.A.; Alsaleh, S.S.; Alshamary, D.O.; Alanazi, T.H.; Aldrees, S.D.; Alshammari, B.A. Mechanical Recycling of Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Polymer in a Circular Economy. Polymers 2024, 16, 1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Franco, E.; Gomez Culebro, V.A.; Franco-Urquiza, E.A. Technologies for Mechanical Recycling of Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Polymers (CFRP) Composites: End Mill, High-Energy Ball Milling, and Ultrasonication. Polymers 2024, 16, 2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naqvi, S.R.; Prabhakara, H.M.; Bramer, E.A.; Dierkes, W.; Akkerman, R.; Brem, G. A critical review on recycling of end-of-life carbon fibre/glass fibre reinforced composites waste using pyrolysis towards a circular economy. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 136, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-W.; Lee, H.-M.; An, J.-H.; Chung, D.-C.; An, K.-H.; Kim, B.-J. Recycling and characterization of carbon fibers from carbon fiber reinforced epoxy matrix composites by a novel super-heated-steam method. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 203, 872–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Olivetti, E.A.; Zhao, Y.; Chang, J.C.; Pickering, S.J.; McKechnie, J. Comparing Life Cycle Energy and Global Warming Potential of Carbon Fiber Composite Recycling Technologies and Waste Management Options. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 9854–9865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, L.; Amirkhosravi, M.; Gong, X.; Gray, T.G.; Manas-Zloczower, I. Recycling Epoxy by Vitrimerization: Influence of an Initial Thermoset Chemical Structure. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 12706–12712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Cui, J.; Hu, G.; Zhang, B. Recycling strategies for vitrimers. Int. J. Smart Nano Mater. 2022, 13, 367–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlmann, E.; Meier, P. Carbon Fibre Recycling from Milling Dust for the Application in Short Fibre Reinforced Thermoplastics. Procedia CIRP 2017, 66, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, J.R.; Almeida, N.M.; Figueira, J.R. Recycling of FRP composites: Reusing fine GFRP waste in concrete mixtures. J. Clean. Prod. 2011, 19, 1745–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hintze, W. CFK-Bearbeitung; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; ISBN 978-3-662-63264-2. [Google Scholar]
- Ghafarizadeh, S.; Lebrun, G.; Chatelain, J.-F. Experimental investigation of the cutting temperature and surface quality during milling of unidirectional carbon fiber reinforced plastic. J. Compos. Mater. 2016, 50, 1059–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Q.; Chen, J.; Cai, X.; Peng, T.; Chen, M. Thermal characteristics of unidirectional carbon fiber reinforced polymer laminates during orthogonal cutting. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2018, 37, 905–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashworth, S.; Fairclough, J.P.A.; Meredith, J.; Takikawa, Y.; Kerrigan, K. Effects of tool coating and tool wear on the surface quality and flexural strength of slotted CFRP. Wear 2022, 498–499, 204340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, K.; Witt, M.; Putz, M. Influence of cutting edge radius on process forces in orthogonal machining of carbon fibre reinforced plastics (CFRP). Procedia CIRP 2019, 85, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klocke, F. Fertigungsverfahren 1: Zerspanung Mit Geometrisch Bestimmter Schneide, 9th ed.; Springer Vieweg: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; ISBN 978-3-662-54206-4. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.H.; Ramulu, M.; Arola, D. Orthogonal cutting mechanisms of graphite/epoxy composite. Part I: Unidirectional laminate. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 1995, 35, 1623–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abena, A.; Soo, S.L.; Ataya, S.; Hassanin, H.; El-Sayed, M.A.; Ahmadein, M.; Alsaleh, N.A.; Ahmed, M.M.Z.; Essa, K. Chip Formation and Orthogonal Cutting Optimisation of Unidirectional Carbon Fibre Composites. Polymers 2023, 15, 1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amfilochiou, V.; Debsharma, T.; Baere, I.d.; Du Prez, F.; van Paepegem, W. Interlaminar fracture toughness behaviour of a repairable glass-fibre-reinforced vitrimer for wind-energy applications. Compos. Part B Eng. 2025, 291, 112023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benazzo, F.; Rigamonti, D.; Bettini, P.; Sala, G.; Grande, A.M. Interlaminar fracture of structural fibre/epoxy composites integrating damage sensing and healing. Compos. Part B Eng. 2022, 244, 110137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Process Parameter | Unit | Variation |
|---|---|---|
| Orientation of fibres to the direction of the cut θ | ° | 0°/90°/45°/135° |
| Undeformed chip thickness h | mm | 0.1/0.2/0.3 |
| Cutting speed vc | m/min | 10, 25, 50, 100, 150 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fuchs, J.; Kozlovets, Y.; Alms, J.; Meurer, M.; Hopmann, C.; Bergs, T.; Abouridouane, M. Machinability of Vitrified Semi-Finished Products: Chip Formation and Heat Development at the Cutting Edge. Polymers 2025, 17, 2681. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17192681
Fuchs J, Kozlovets Y, Alms J, Meurer M, Hopmann C, Bergs T, Abouridouane M. Machinability of Vitrified Semi-Finished Products: Chip Formation and Heat Development at the Cutting Edge. Polymers. 2025; 17(19):2681. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17192681
Chicago/Turabian StyleFuchs, Jannick, Yehor Kozlovets, Jonathan Alms, Markus Meurer, Christian Hopmann, Thomas Bergs, and Mustapha Abouridouane. 2025. "Machinability of Vitrified Semi-Finished Products: Chip Formation and Heat Development at the Cutting Edge" Polymers 17, no. 19: 2681. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17192681
APA StyleFuchs, J., Kozlovets, Y., Alms, J., Meurer, M., Hopmann, C., Bergs, T., & Abouridouane, M. (2025). Machinability of Vitrified Semi-Finished Products: Chip Formation and Heat Development at the Cutting Edge. Polymers, 17(19), 2681. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17192681







