Multifunctional Electrospun Materials from Poly(Vinyl Alcohol)/Chitosan and Polylactide Incorporating Rosmarinic Acid and Lidocaine with Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of the Electrospun Materials
2.2.1. Preparation of PVA/Ch and RA-Containing PVA/Ch Mats by One-Pot Blend Electrospinning
2.2.2. Preparation of Composite Fibrous Materials by Dual Spinneret Electrospinning
2.3. Characterization
2.4. In Vitro RA and/or LHC Release
2.5. Estimation of the Antioxidant Capacity of the Fibrous Materials
2.6. Assessment of the Antibacterial and Antifungal Activity of the Fibrous Materials
2.7. SEM Observation of the Adhesion of S. aureus Cells to the Surface of Fibrous Materials
2.8. Statistical Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
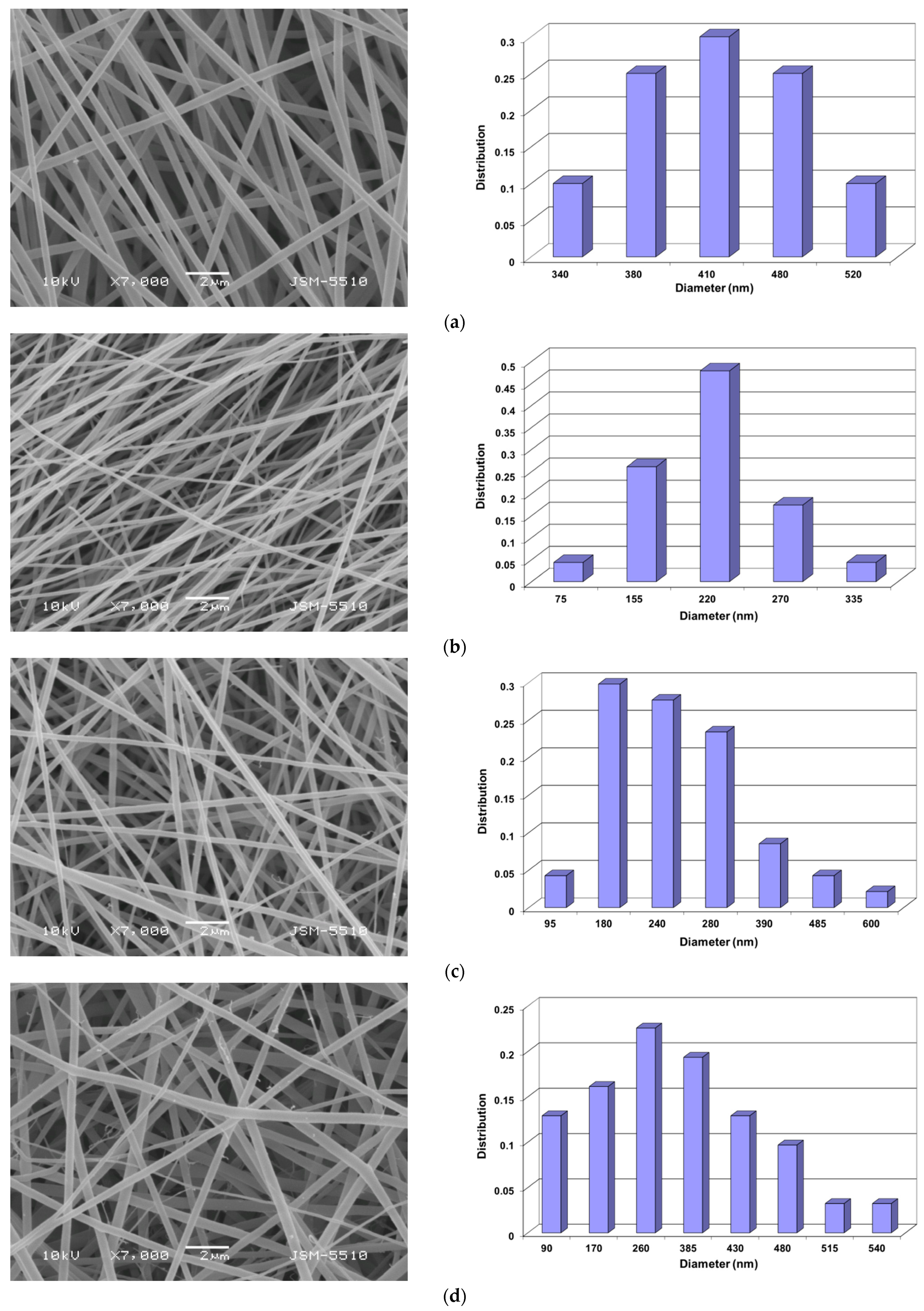
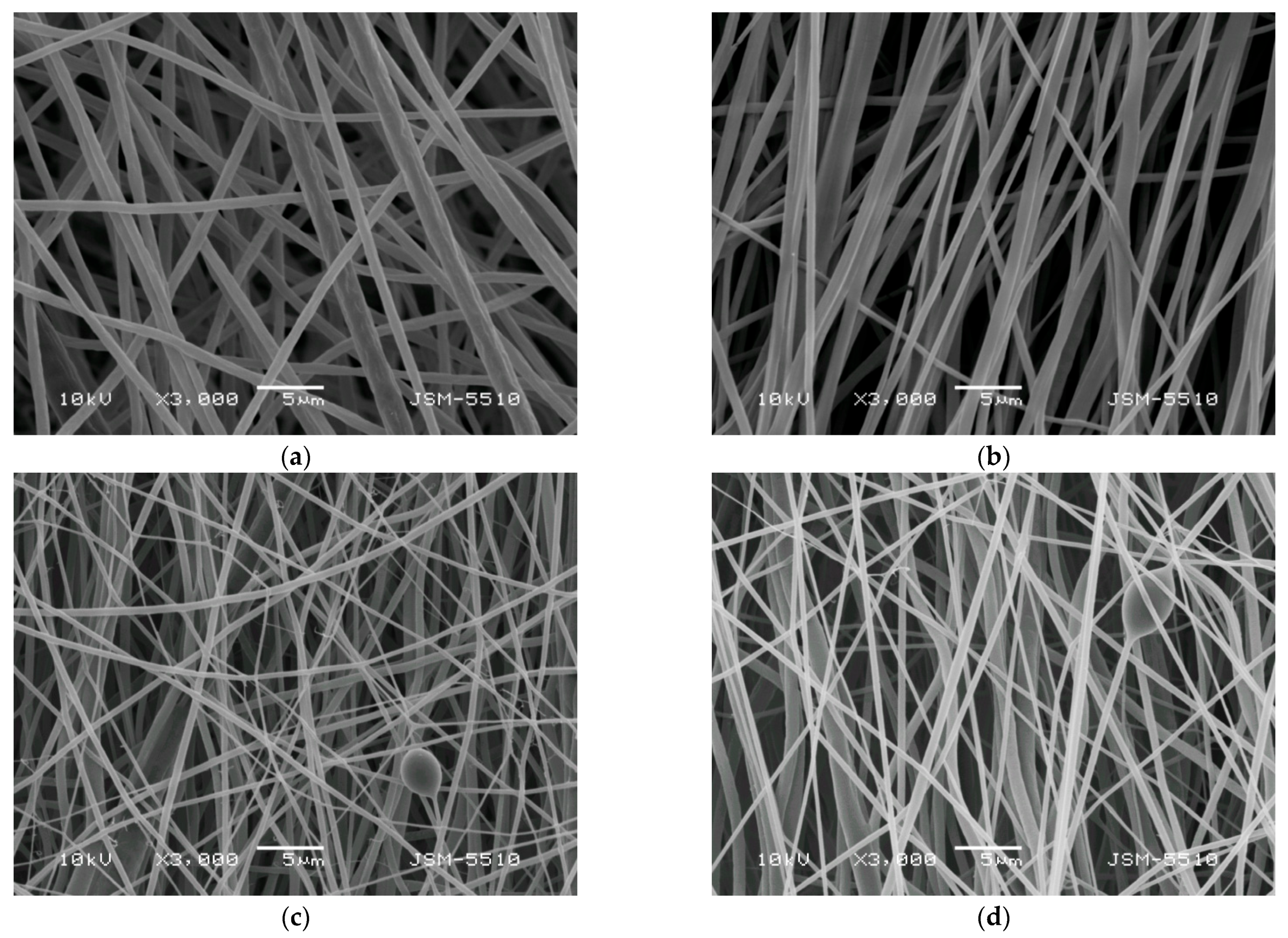
3.1. Preparation of PVA/Ch/RA Fibrous Materials by One-Pot Blend Electrospinning and Characterization of Their Morphology
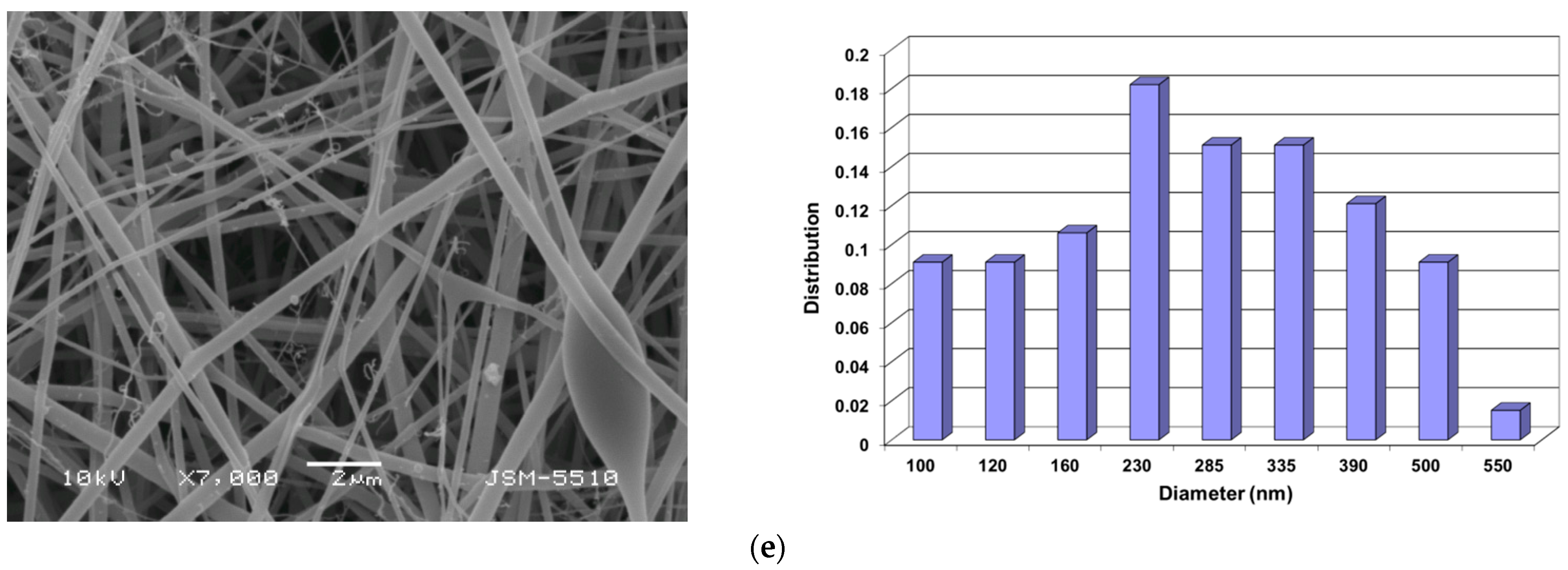
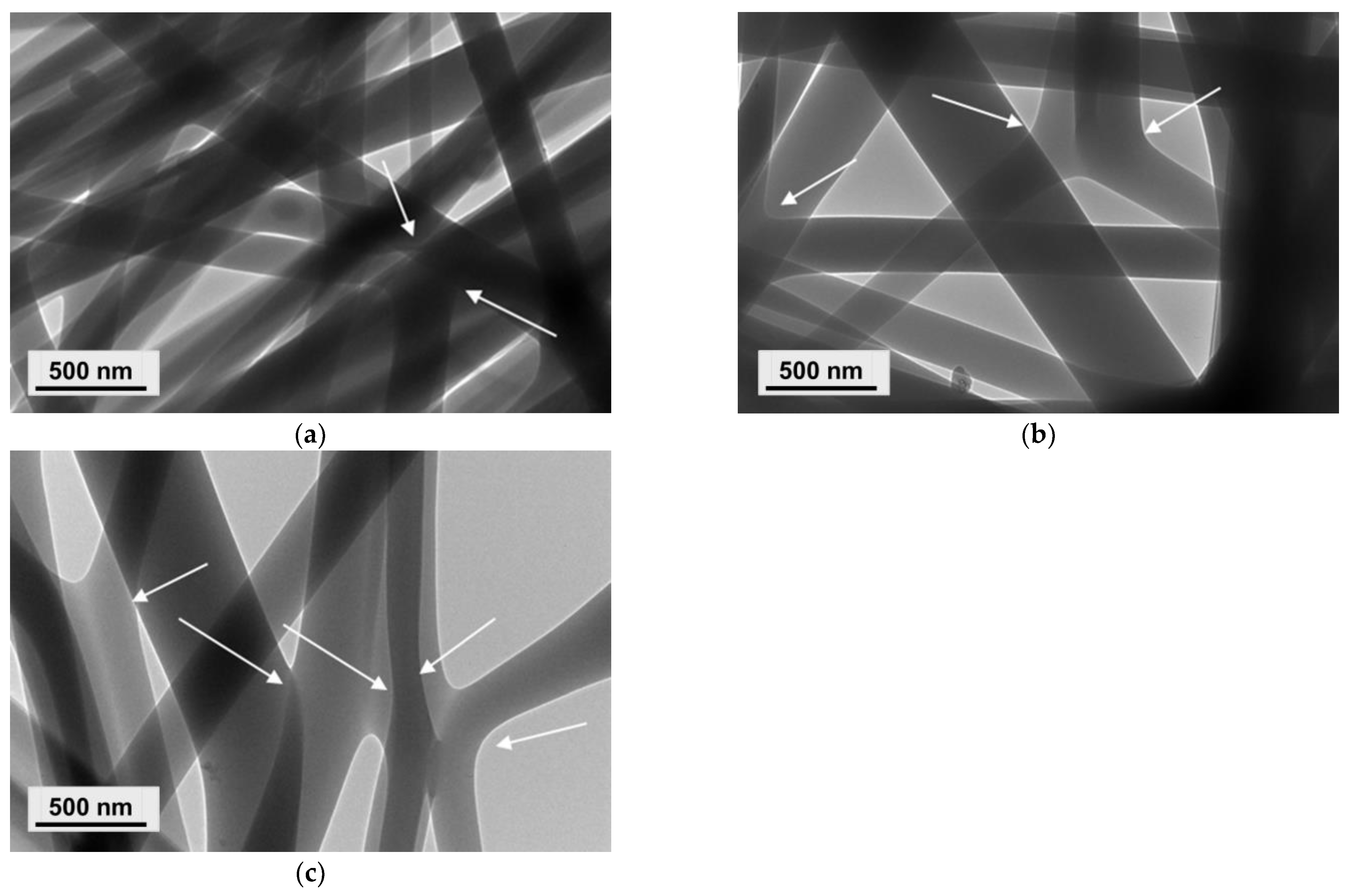
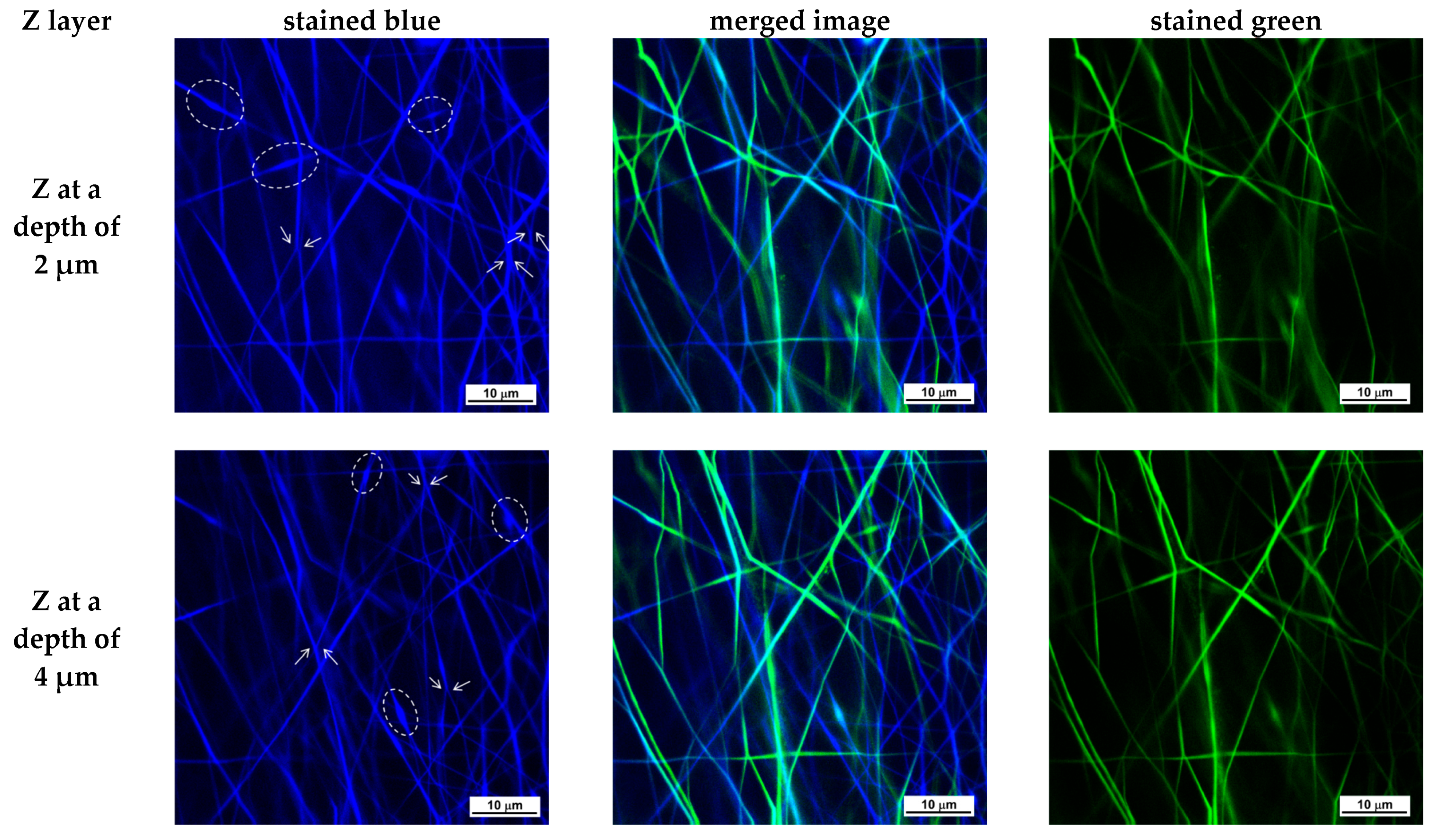
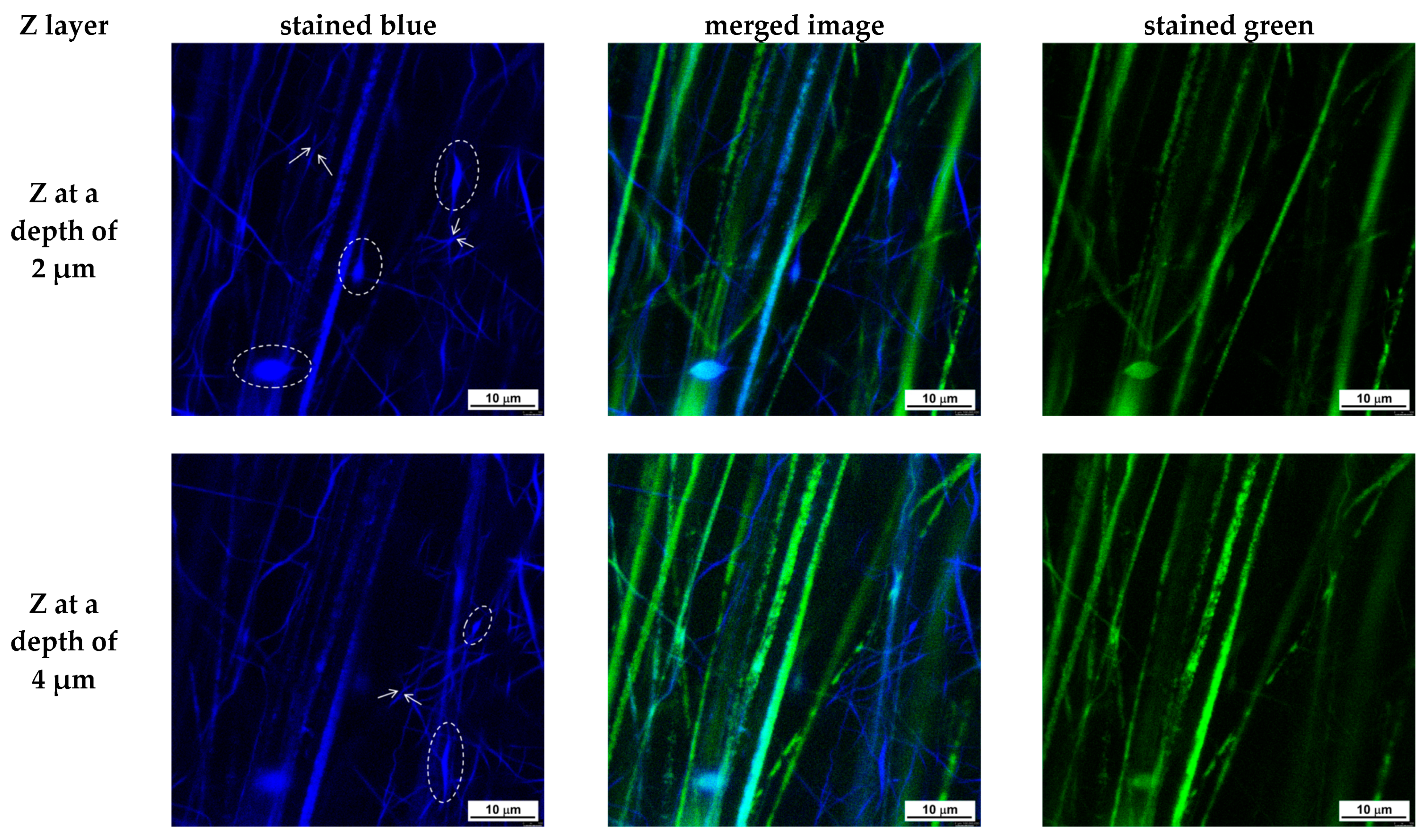
3.2. Preparation of Composite Fibrous Materials from PVA/Ch/RA Fibers and PLA or PLA/LHC Fibers by Dual Spinneret Electrospinning and Characterization of Their Morphology
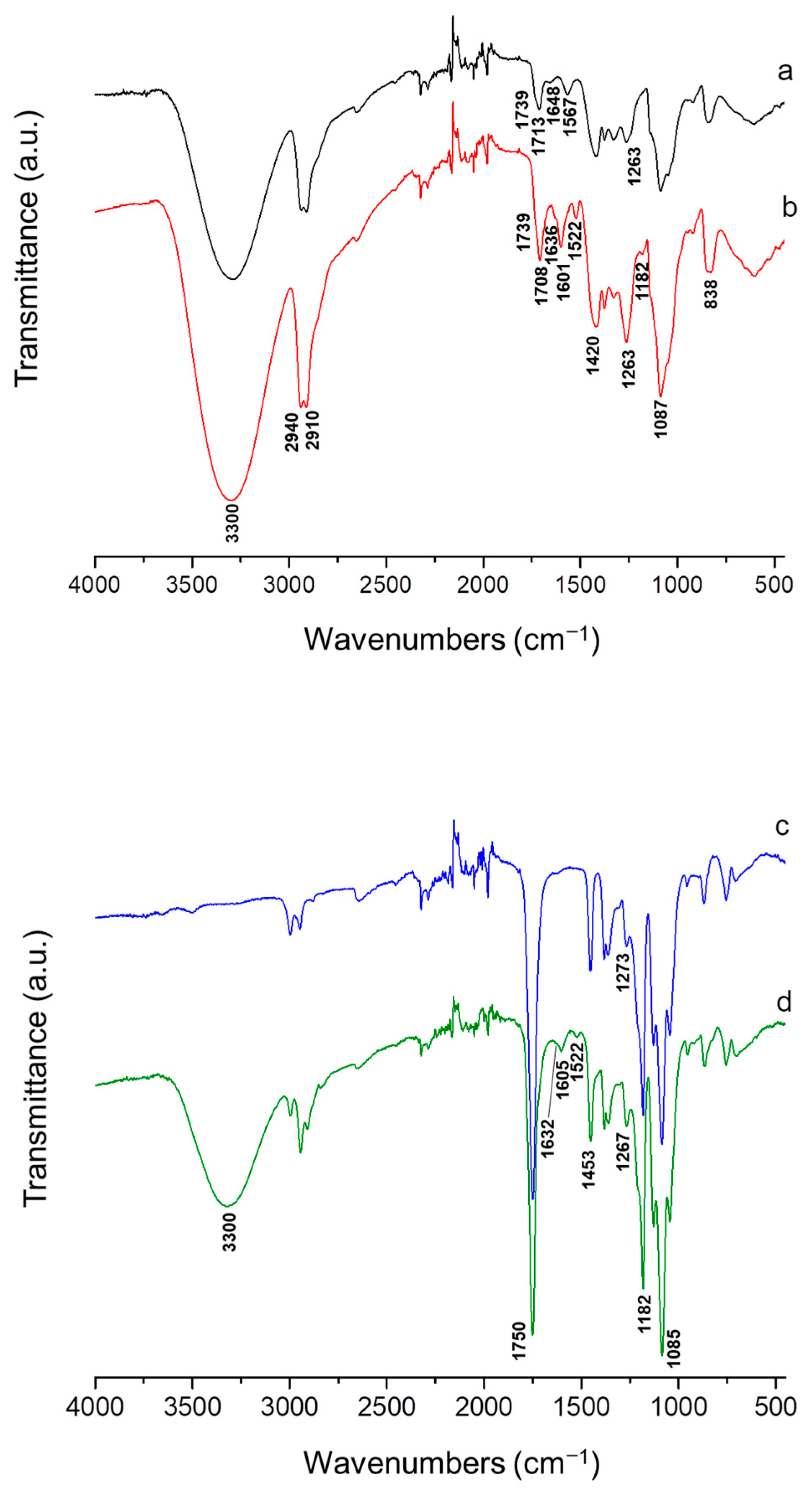
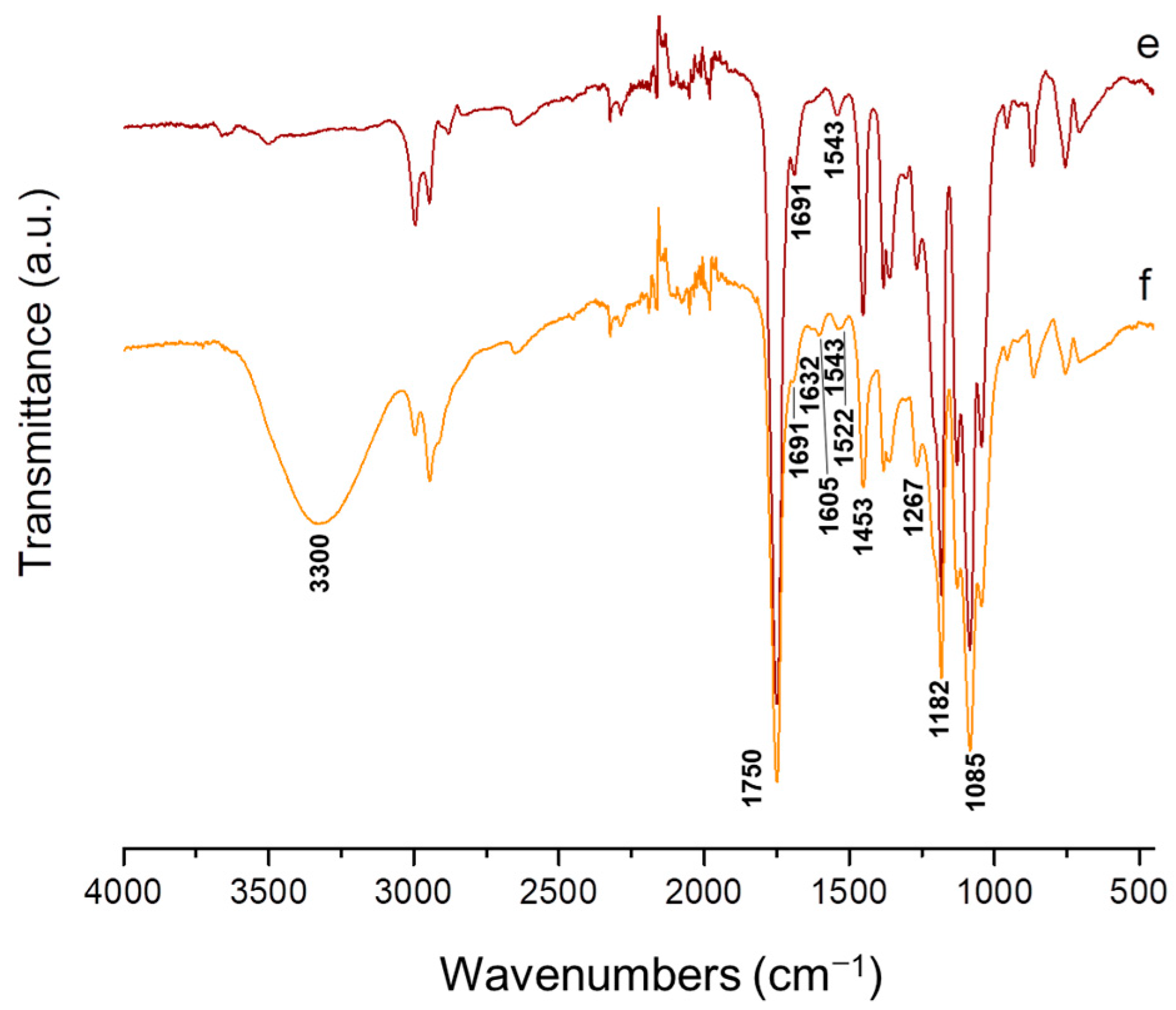
3.3. ATR-FTIR Analysis of the Fibrous Materials
3.4. Thermal Behavior of the Fibrous Materials
3.5. XRD Analysis of the Fibrous Materials
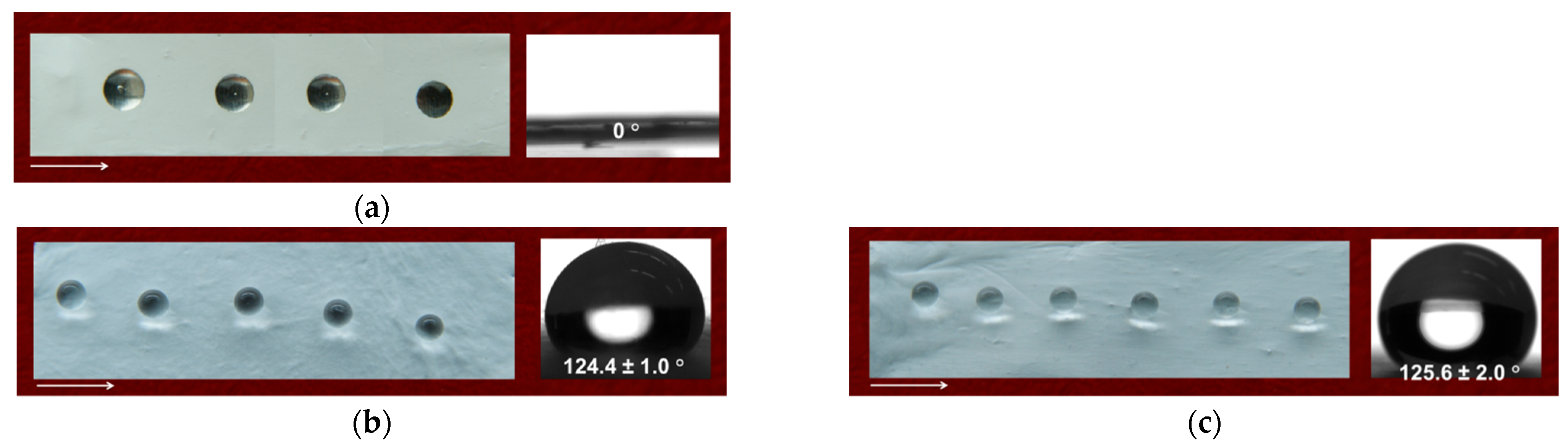
3.6. Water Contact Angle of the Fibrous Materials
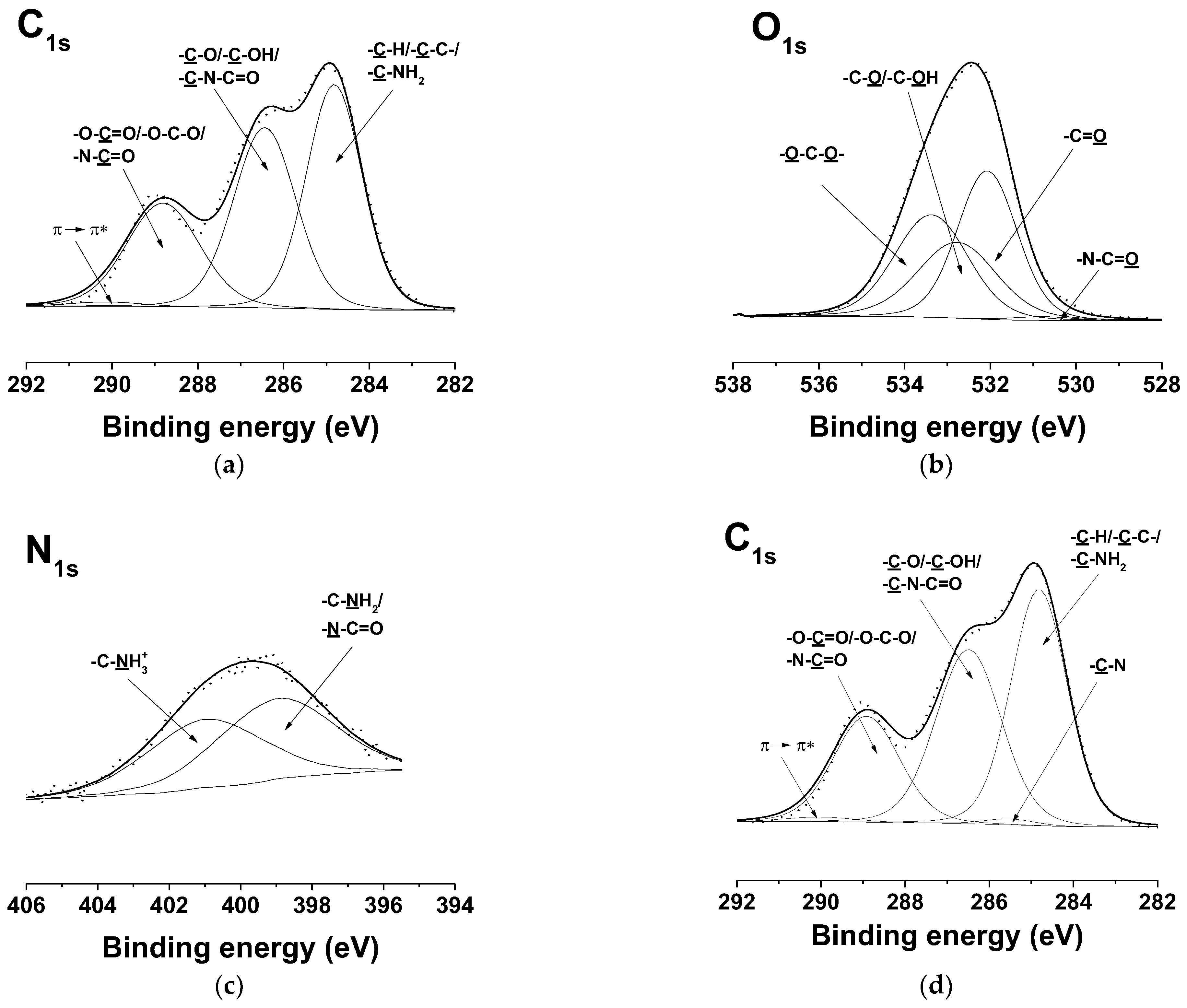
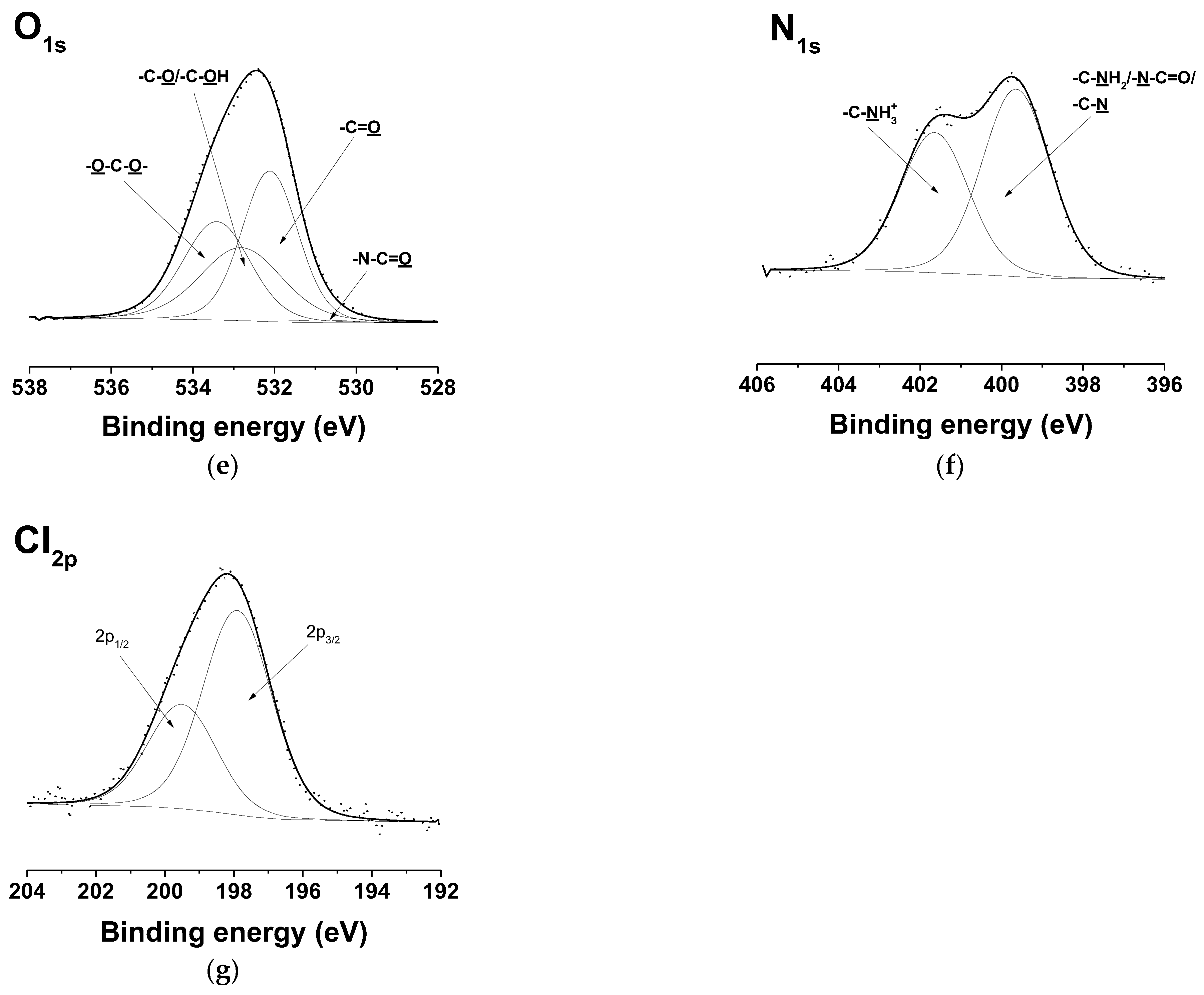
3.7. XPS Analysis of the Fibrous Materials
3.8. Tensile Tests of the Fibrous Materials
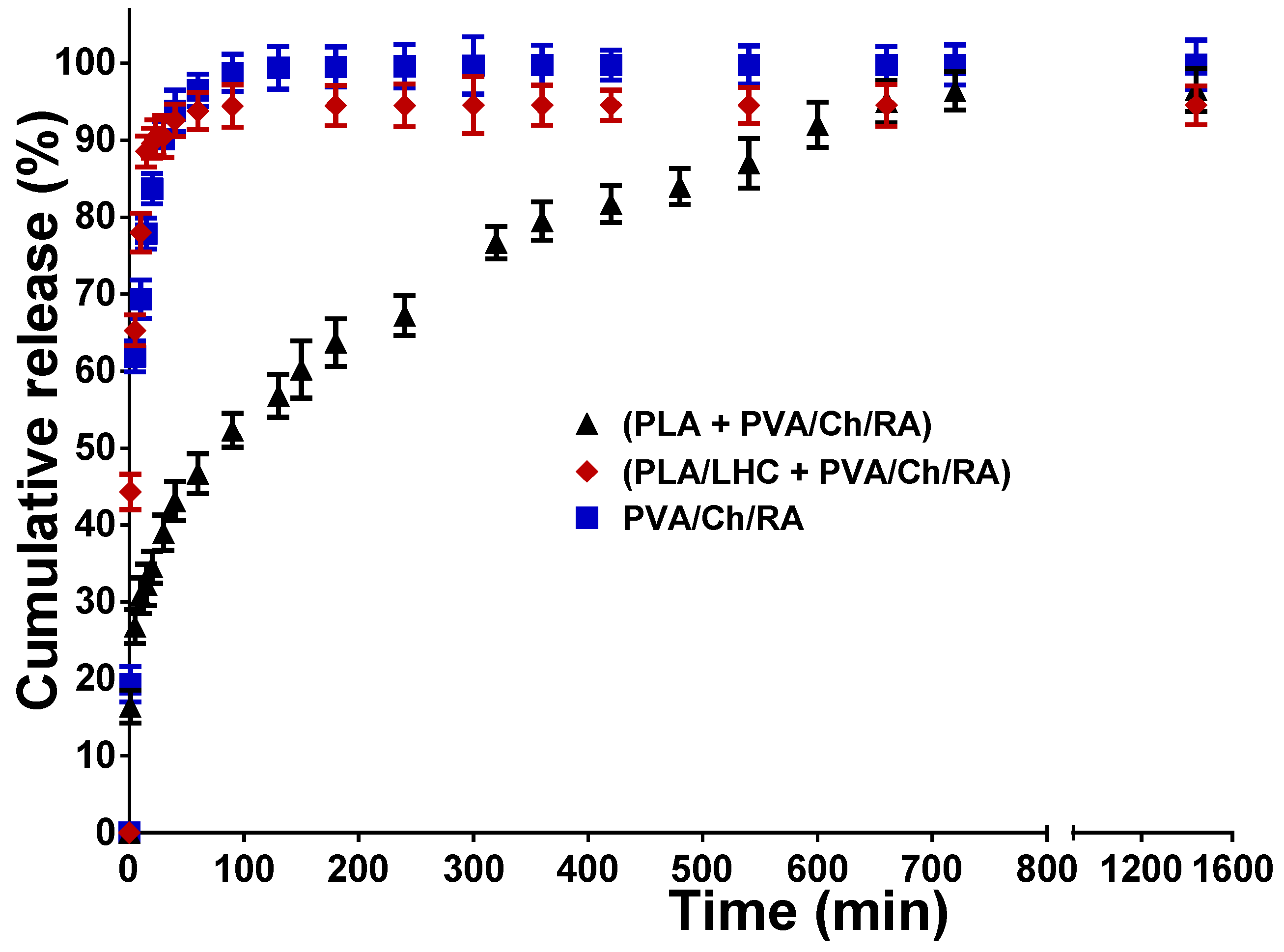
3.9. In Vitro Release Studies
3.10. Antioxidant Activity of Fibrous Materials
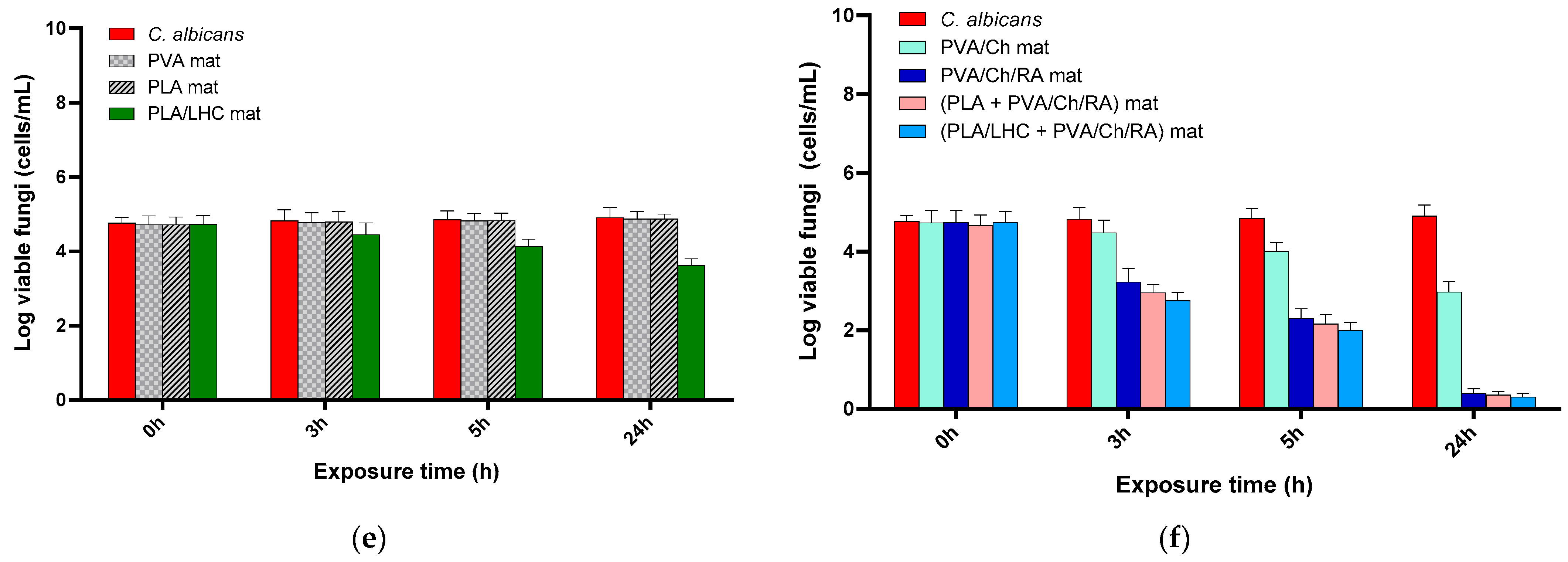
3.11. Evaluation of the Antibacterial and Antifungal Activity of the Fibrous Materials
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dziemidowicz, K.; Sang, Q.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, F.; Lagaron, J.M.; Mo, X.; Parker, G.J.M.; Yu, D.-G.; Zhu, L.-M.; et al. Electrospinning for healthcare: Recent advancements. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 939–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Guan, M.; Bian, Y.; Yin, X. Multifunctional Electrospun Nanofibers for Biosensing and Biomedical Engineering Applications. Biosensors 2024, 14, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, M.H.; Khan, M.M.R.; Zahari, M.A.K.M.; Beg, M.D.H.; Abdullah, N. A review on current trends and future prospectives of electrospun biopolymeric nanofibers for biomedical applications. Eur. Polym. J. 2023, 197, 112352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyuchyuk, S.; Paneva, D.; Manolova, N.; Rashkov, I. Core-Sheath Fibers via Single-Nozzle Spinneret Electrospinning of Emulsions and Homogeneous Blend Solutions. Materials 2024, 17, 5379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, M.M.A.; Khan, S.A.P.M.; Thamer, B.M.; Rajkumar, N.; El-Hamshary, H.; El-Neweh, M. Electrospun nanofibers for drug delivery applications: Methods and mechanism. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2023, 34, 6–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatova, M.; Rashkov, I.; Manolova, N. Drug-loaded electrospun materials in wound-dressing applications and in local cancer treatment. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2013, 10, 469–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ignatova, M.G.; Manolova, N.E.; Rashkov, I.B.; Markova, N.D.; Toshkova, R.A.; Georgieva, A.K.; Nikolova, E.B. Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate)/caffeic acid electrospun fibrous materials coated with polyelectrolyte complex and their antibacterial activity and in vitro antitumor effect against HeLa cells. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 65, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yakub, G.; Ignatova, M.; Manolova, N.; Rashkov, I.; Toshkova, R.; Georgieva, A.; Markova, N. Chitosan/ferulic acid-coated poly(ε-caprolactone) electrospunmaterials with antioxidant, antibacterial and antitumor properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 689–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, P.; Nagarsenker, M. Formulation and Evaluation of Lidocaine Lipid Nanosystems for Dermal Delivery. AAPS PharmSciTech 2009, 10, 985–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madureira, A.R.; Campos, D.A.; Oliveira, A.; Sarmento, B.; Pintado, M.M.; Gomes, A.M. Insights into the protective role of solid lipid nanoparticles on rosmarinic acid bioactivity during exposure to simulated gastrointestinal conditions. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 139, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fachel, F.N.S.; Michels, L.R.; Azambuja, J.H.; Lenz, G.S.; Gelsleichter, N.E.; Endres, M.; Scholl, J.N.; Schuh, R.S.; Barschak, A.G.; Figueiró, F.; et al. Chitosan-coated rosmarinic acid nanoemulsion nasal administration protects against LPS-induced memory deficit, neuroinflammation, and oxidative stress in Wistar rats. Neurochem. Int. 2020, 141, 104875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assaf, S.M.; Maaroof, K.T.; Altaani, B.M.; Ghareeb, M.M.; Alhayyal, A.A.A. Jojoba oil-based microemulsion for transdermal drug delivery. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 16, 326–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaitanya, M.V.N.L.; Ramanunny, A.K.; Babu, M.R.; Gulati, M.; Vishwas, S.; Singh, T.G.; Chellappan, D.K.; Adams, J.; Dua, K.; Singh, S.K. Journey of Rosmarinic Acid as Biomedicine to Nano-Biomedicine for Treating Cancer: Current Strategies and Future Perspectives. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadeem, M.; Imran, M.; Gondal, T.A.; Imran, A.; Shahbaz, M.; Amir, R.M.; Sajid, M.W.; Qaisrani, T.B.; Atif, M.; Hussain, G.; et al. Therapeutic Potential of Rosmarinic Acid: A Comprehensive Review. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Luo, W.; Bao, B.; Cao, Y.; Cheng, F.; Yu, S.; Fan, Q.; Zhang, L.; Wu, Q.; Shan, M.A. Comprehensive Review of Rosmarinic Acid: From Phytochemistry to Pharmacology and Its New Insight. Molecules 2022, 27, 3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harindranath, H.; Susil, A.; Rajeshwari, S.; Sekar, M.; Kumar, B.R.P. Unlocking the potential of Rosmarinic acid: A review on extraction, isolation, quantification, pharmacokinetics and pharmacology. Phytomed. Plus 2025, 5, 100726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatankhah, E. Rosmarinic acid-loaded electrospun nanofibers: In vitro release kinetic study and bioactivity assessment. Eng. Life Sci. 2018, 18, 732–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, E.M.; El Gohary, N.A.; El-Shenawy, B.M.; Handoussa, H.; Klingner, A.; Elwi, M.; Hamed, Y.; Khalil, I.S.M.; El Nashar, R.M.; Mizaikoff, B. Fabrication of Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Beaded Fibers for Rosmarinic Acid. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Du, G.; Guo, Q.; Li, R.; He, H.; Li, C. Synergistic antibacterial performance of rosemarinic acid—Graphene oxide in electrospun polylactic acid membranes for air filtration. J. Polym. Res. 2023, 30, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Du, G.; Guo, Q.; Li, R.; Li, C.; He, H. Fabrication and Characterization of Polylactic Acid Electrospun Wound Dressing Modified with Polyethylene Glycol, Rosmarinic Acid and Graphite Oxide. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spasova, M.; Stoyanova, N.; Stoilova, O. Electrospun Materials Based on Cellulose Acetate Loaded with Rosmarinic Acid with Antioxidant and Antifungal Properties. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelmonem, R.; Bakr, A.; Badawy, I.; Abd El Maksoud, A.I.; Attia, R.T. Quality by Design Approach for the Formulation and Evaluation of Stem Cells Derived Rosmarinic Acid-Loaded Nanofibers as an Anti-Wrinkle Patch: In Vitro and In Vivo Characterizations. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, F.; Mondal, B.; Bairagi, B.; Mandal, S.; Mandal, D.; Nath, D. Fabrication of Chitosan/PEO/Rosmarinic acid based nanofibrous mat for diabetic burn wound healing and its anti-bacterial efficacy in mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 301, 140416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, G.; Qiu, M.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, F.; Yue, X.; Huang, C.; Zhao, S.; Zeng, R.; Zhang, C.; Qu, Y. Fabrication and characterization of PVA@PLA electrospinning nanofibers embedded with Bletilla striata polysaccharide and Rosmarinic acid to promote wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 234, 123693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, H.; Malviya, R.; Kaushik, N. Chitosan in biomedicine: A comprehensive review of recent developments. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2024, 8, 100551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicea, D.; Nicolae-Maranciuc, A. A Review of Chitosan-Based Materials for Biomedical, Food, and Water Treatment Applications. Materials 2024, 17, 5770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türkoğlu, G.C.; Khomarloo, N.; Mohsenzadeh, E.; Gospodinova, D.N.; Neznakomova, M.; Salaun, F. PVA-Based Electrospun Materials—A Promising Route to Designing Nanofiber Mats with Desired Morphological Shape—A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.F.; Guan, Y.L.; Yang, D.Z.; Li, Z.; De Yao, K. Antibacterial action of chitosan and carboxymethylated chitosan. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2000, 79, 1324–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinšová, J.; Vavříková, E. Chitosan Derivatives with Antimicrobial, Antitumour and Antioxidant Activities—A Review. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2011, 17, 3596–3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaudo, M. Chitin and chitosan: Properties and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2006, 31, 603–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña, A.; Sánchez, N.S.; Calahorra, M. Effects of Chitosan on Candida albicans: Conditions for Its Antifungal Activity. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 527549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, L.; Li, J.; Lu, Y.; Li, G.; Li, J. Polylactic acid: A future universal biobased polymer with multifunctional performance—From monomer synthesis, and processing to applications: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2025, 18, 100757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshma, C.S.; Remya, S.; Bindu, J. A review of exploring the synthesis, properties, and diverse applications of poly lactic acid with a focus on food packaging application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 283, 137905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maleki, H.; Azimi, B.; Ismaeilimoghadam, S.; Danti, S. Poly(lactic acid)-Based Electrospun Fibrous Structures for Biomedical Applications. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.; Mourão, J.; Vale, N. A Review of the Lidocaine in the Perioperative Period. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dörfer, C.; Chmiela, K.; Arweiler, N.B.; Petersilka, G.J.; Dommisch, H.; Heckel, R.; Kahl, M.; Kuzmanova, D.; Purucker, P.; Springer, C. Evaluation of acceptance and preference of topical lidocaine application versus articaine injection anesthesia after nonsurgical periodontal treatment: A randomized clinical trial. J. Periodontol. 2024, 95, 821–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatova, M.; Starbova, K.; Markova, N.; Manolova, N.; Rashkov, I. Electrospun nano-fibre mats with antibacterial properties from quaternised chitosan and poly(vinyl alcohol). Carbohydr. Res. 2006, 341, 2098–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henton, D.; Gruber, P.; Lunt, J.; Randall, J. Polylactic acid technology. In Natural Fibers, Biopolymers, and Biocomposites; Mohanty, A.K., Misra, M., Drzal, L.T., Eds.; Taylor and Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; pp. 527–578. [Google Scholar]
- Peppas, N.A.; Merrill, E.W. Differential scanning calorimetry of crystallized PVA hydrogels. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1976, 20, 1457–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyuchyuk, S.; Paneva, D.; Karashanova, D.; Markova, N.; Georgieva, A.; Toshkova, R.; Manolova, N.; Rashkov, I. Core-sheath-like poly(ethylene oxide)/beeswax composite fibers prepared by single-spinneret electrospinning. Antibacterial, antifungal, and antitumor activities. Macromol. Biosci. 2022, 22, 2200015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsmeyer, R.W.; Gurny, R.; Doelker, E.; Buri, P.; Peppas, N.A. Mechanisms of solute release from porous hydrophilic polymers. Int. J. Pharm. 1983, 15, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, T.H.N.; Morozkina, S.N.; Sitnikova, V.E.; Olekhnovich, R.O.; Podshivalov, A.V.; Uspenskaya, M.V. A systematic investigation of solution and technological parameters for the fabrication and characterization of poly(vinyl alcohol–chitosan electrospun nanofibers. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2024, 35, e6423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, T.H.N.; Morozkina, S.N.; Olekhnovich, R.O.; Podshivalov, A.V.; Uspenskaya, M.V. Study on Fabrication and Properties of Polyvinyl Alcohol/Chitosan Nanofibers Created from Aqueous Solution with Acetic Acid and Ethanol by the Electrospinning Method. Polymers 2024, 16, 3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, H.; Singh, S.; Rode, S.; Chaudhary, P.K.; Khan, N.A.; Ramamurthy, P.C.; NathGupta, D.; Kumar, R.; Das, J.; Sharma, A.K. Fabrication and characterization of polyvinyl alcohol-chitosan composite nanofbers for carboxylesterase immobilization to enhance the stability of the enzyme. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 19615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paneva, D.; Ignatova, M.; Manolova, N.; Rashkov, I. Novel chitosan–containing micro- and nanofibrous materials by electrospinning: Preparation and biomedical application. In Nanofibers: Fabrication, Performance, and Applications; Chang, W.N., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 73–151. [Google Scholar]
- Ignatova, M.; Manolova, N.; Rashkov, I.; Markova, N.; Kukeva, R.; Stoyanova, R.; Georgieva, A.; Toshkova, R. 8-Hydroxyquinoline-5-sulfonic acid-containing poly(vinyl alcohol)/chitosan electrospun materials and their Cu2+ and Fe3+ complexes: Preparation, antibacterial, antifungal and antitumor activities. Polymers 2021, 13, 2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohkawa, K.; Cha, D.; Kim, H.; Nishida, A.; Yamamoto, H. Electrospinning of Chitosan. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2004, 25, 1600–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, J.; Gao, W.; Liang, H.; Wang, H.; Li, J. Preparation of chitosan/PLA blend micro/nanofibers by electrospinning. Mater. Lett. 2009, 63, 658–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkawa, K.; Minato, K.-I.; Kumagai, G.; Hayashi, S.; Yamamoto, H. Chitosan nanofiber. Biomacromolecules 2006, 9, 3291–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koombhongse, S.; Liu, W.; Reneker, D.H. Flat polymer ribbons and other shapes by electrospinning. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2001, 39, 2598–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, N.A.M.; Kanjwal, M.A.; Sheikh, F.A.; Kim, H.Y. Spider-net within the N6, PVA and PU electrospun nanofiber mats using salt addition: Novel strategy in the electrospinning process. Polymer 2009, 50, 4389–4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penchev, H.; Paneva, D.; Manolova, N.; Rashkov, I. Hybrid nanofibrous yarns based on N-carboxyethylchitosan and silver nanoparticles with antibacterial activity prepared by self-bundling electrospinning. Carbohydr. Res. 2010, 345, 2374–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyuchyuk, S.; Paneva, D.; Manolova, N.; Rashkov, I.; Karashanova, D.; Markova, N. Core/double-sheath composite fibers from poly(ethylene oxide), poly(L-lactide) and beeswax by single-spinneret electrospinning. Polymers 2022, 14, 5036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahatheeswaran, D.; Mathew, A.; Aswathy, R.G.; Nagaoka, Y.; Venugopal, K.; Yoshida, Y.; Maekawa, T.; Sakthikumar, D. Hybrid fluorescent curcumin loaded zein electrospun nanofibrous scaffold for biomedical applications. Biomed. Mater. 2012, 7, 045001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choong, L.T.; Yi, P.; Rutledge, G.C. Three-dimensional imaging of electrospun fiber mats using confocal laser scanning microscopy and digital image analysis. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 3014–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-M.; Song, C.; Rutledge, G.C. Direct Three-Dimensional Visualization of Membrane Fouling by Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 17001–17008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Lin, L.; Si, J.; Wang, Q.; Peng, X.; Chen, W. Electrospinning and crosslinking of polyvinyl alcohol/chitosan composite nanofiber for transdermal drug delivery. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2017, 37, 1917–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchler, C.G.; Pezzei, C.K.; Beć, K.B.; Henn, R.; Ishigaki, M.; Ozaki, Y.; Huck, C.W. Critical Evaluation of NIR and ATR-IR Spectroscopic Quantifications of Rosmarinic Acid in Rosmarini folium Supported by Quantum Chemical Calculations. Planta Med. 2017, 83, 1076–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonés, A.; Peponi, L.; Lieblich, M.; Benavente, R.; Fiori, S. In Vitro Degradation of Plasticized PLA Electrospun Fiber Mats: Morphological, Thermal and Crystalline Evolution. Polymers 2020, 12, 2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Huwaij, R.; Assaf, S.; Salem, M.; Sallam, A. Mucoadhesive Dosage form of Lidocaine Hydrochloride: I. Mucoadhesive and Physicochemical Characterization. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2007, 33, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olvera Bernal, R.A.; Olekhnovich, R.O.; Uspenskaya, M.V. Chitosan/PVA Nanofibers as Potential Material for the Development of Soft Actuators. Polymers 2023, 15, 2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakane, K.; Yamashita, T.; Iwakura, K.; Suzuki, F. Properties and Structure of Poly(vinyl alcohol)/Silica Composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1999, 74, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.H.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.S.; Chen, L.H.; Zheng, Q.; Chen, T.; Chen, Z.P.; Fu, T.M.; Di, L.Q. Enhanced oral bioavailability and prophylactic effects on oxidative stress and hepatic damage of an oil solution containing a rosmarinic acid-phospholipid complex. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 19, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, R.; Sun, Y.; Lin, D.; Sun, Z.; Pan, W.; Downs, P. Biomimetic nanofiber patterns with controlled wettability. Soft Matter 2008, 4, 2429–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatova, M.; Stoyanova, N.; Manolova, N.; Rashkov, I.; Kukeva, R.; Stoyanova, R.; Toshkova, R.; Georgieva, A. Electrospun materials from polylactide and Schiff base derivative of Jeffamine ED® and 8-hydroxyquinoline-2-carboxaldehyde and its complex with Cu2+: Preparation, antioxidant and antitumor activities. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 116, 111185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toncheva, A.; Paneva, D.; Manolova, N.; Rashkov, I.; Mita, L.; Crispi, S.; Mita, D.G. Dual vs. single spinneret electrospinning for the preparation of dual drug containing non-woven fibrous materials. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2013, 439, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shui, Y.-J.; Yao, W.-H.; Lin, J.-H.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wu, C.-S.; Zhang, X.; Tsou, C.-H. Enhancing Polyvinyl Alcohol Nanocomposites with Carboxy-Functionalized Graphene: An In-Depth Analysis of Mechanical, Barrier, Electrical, Antibacterial, and Chemical Properties. Polymers 2024, 16, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, I.F.; Granja, P.L.; Barbosa, M.A. Chemical modification of chitosan by phosphorylation: An XPS, FT-IR and SEM study. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2005, 16, 1575–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, É.; Bertóti, I.; Vargha-Butler, E.I. XPS and wettability characterization of modified poly(lactic acid) and poly(lactic/glycolic acid) films. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 245, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toncheva, A.; Paneva, D.; Manolova, N.; Rashkov, I. Electrospun Poly(L-lactide) Membranes Containing a Single Drug or Multiple Drug System for Antimicrobial Wound Dressings. Macromol. Res. 2011, 19, 1310–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhimathi, C.; Venugopal, J.; Bhaarathy, V.; Ramakrishna, S.; Kumar, S. Biocomposite nanofibrous strategies for the controlled release of biomolecules for skin tissue regeneration. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 4709–4722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakub, G.; Toncheva, A.; Manolova, N.; Rashkov, I.; Danchev, D.; Kussovski, V. Electrospun polylactide-based materials for curcumin release: Photostability, antimicrobial activity, and anticoagulant effect. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 133, 42940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, J.R.; Granja, P.L.; Bártolo, P.J. Advances in electrospun skin substitutes. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2016, 84, 314–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherman, S.P.; Biliuță, G.; Bele, A.; Ipate, A.M.; Baron, R.I.; Ochiuz, L.; Șpac, A.F.; Zavastin, D.E. Biomaterials Based on Chitosan and Polyvinyl Alcohol as a Drug Delivery System with Wound-Healing Effects. Gels 2023, 9, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mwiiri, F.K.; Daniels, R. Influence of PVA Molecular Weight and Concentration on Electrospinnability of Birch Bark Extract-Loaded Nanofibrous Scaffolds Intended for Enhanced Wound Healing. Molecules 2020, 25, 4799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadilah, N.I.M.; Phang, S.J.; Kamaruzaman, N.; Salleh, A.; Zawani, M.; Sanyal, A.; Maarof, M.; Fauzi, M.B. Antioxidant Biomaterials in Cutaneous Wound Healing and Tissue Regeneration: A Critical Review. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukaegbu, K.; Allen, E.; Svoboda, K.K.H. Reactive Oxygen Species and Antioxidants in Wound Healing: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential. Int. Wound J. 2025, 22, e70330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, A.; Xu, Q.; Sun, Y.; Li, H. Antioxidant activity of high molecular weight chitosan and N,O-quaternized chitosans. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 6921–6928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adomako-Bonsu, A.G.; Chan, S.L.F.; Pratten, M.; Fry, J.R. Antioxidant activity of rosmarinic acid and its principal metabolites in chemical and cellular systems: Importance of physico-chemical characteristics. Toxicol. In Vitro 2017, 40, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavčič, H.; Jug, U.; Mavri, J.; Umek, N. Antioxidant activity of lidocaine, bupivacaine, and ropivacaine in aqueous and lipophilic environments: An experimental and computational study. Front. Chem. 2023, 11, 1208843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





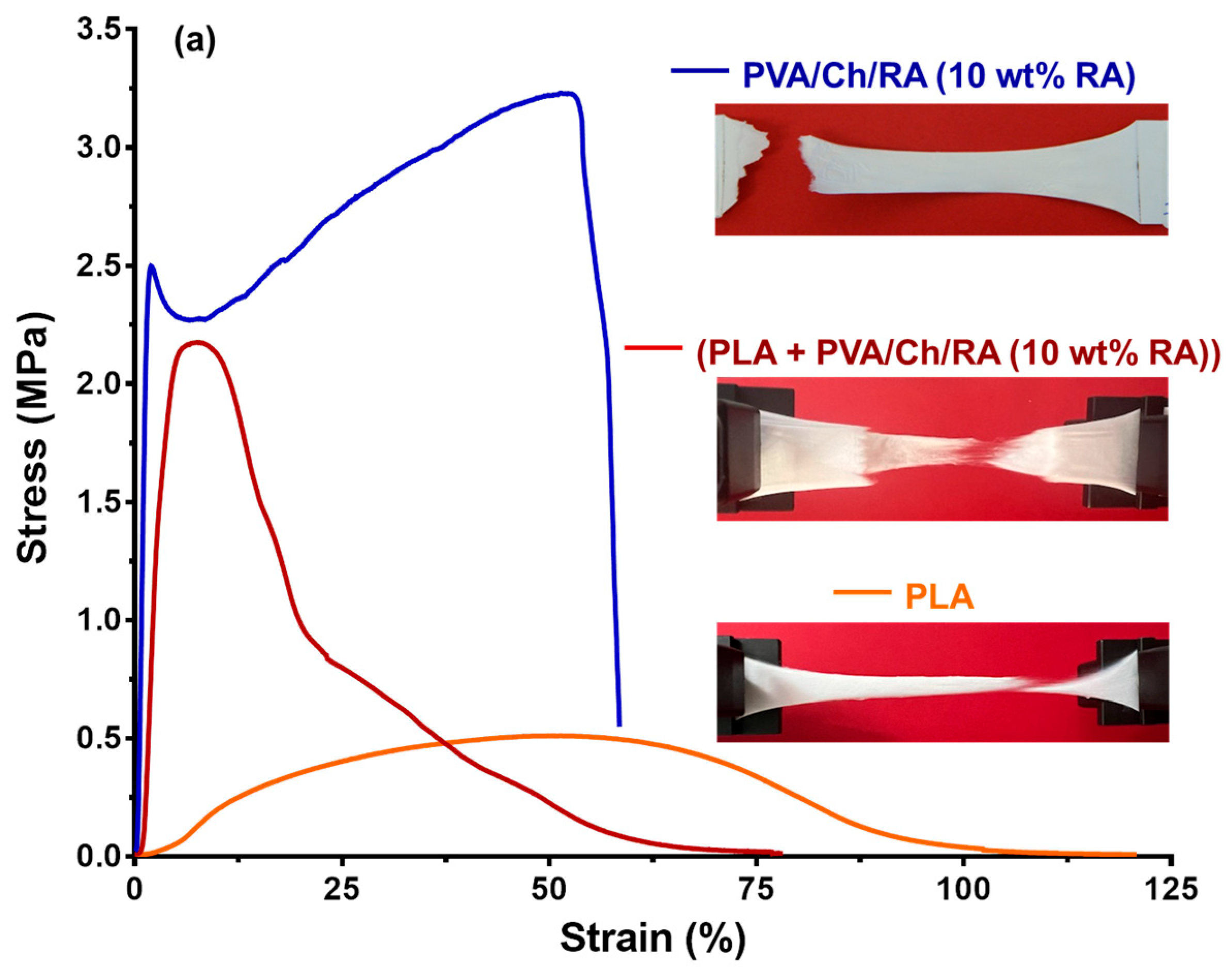
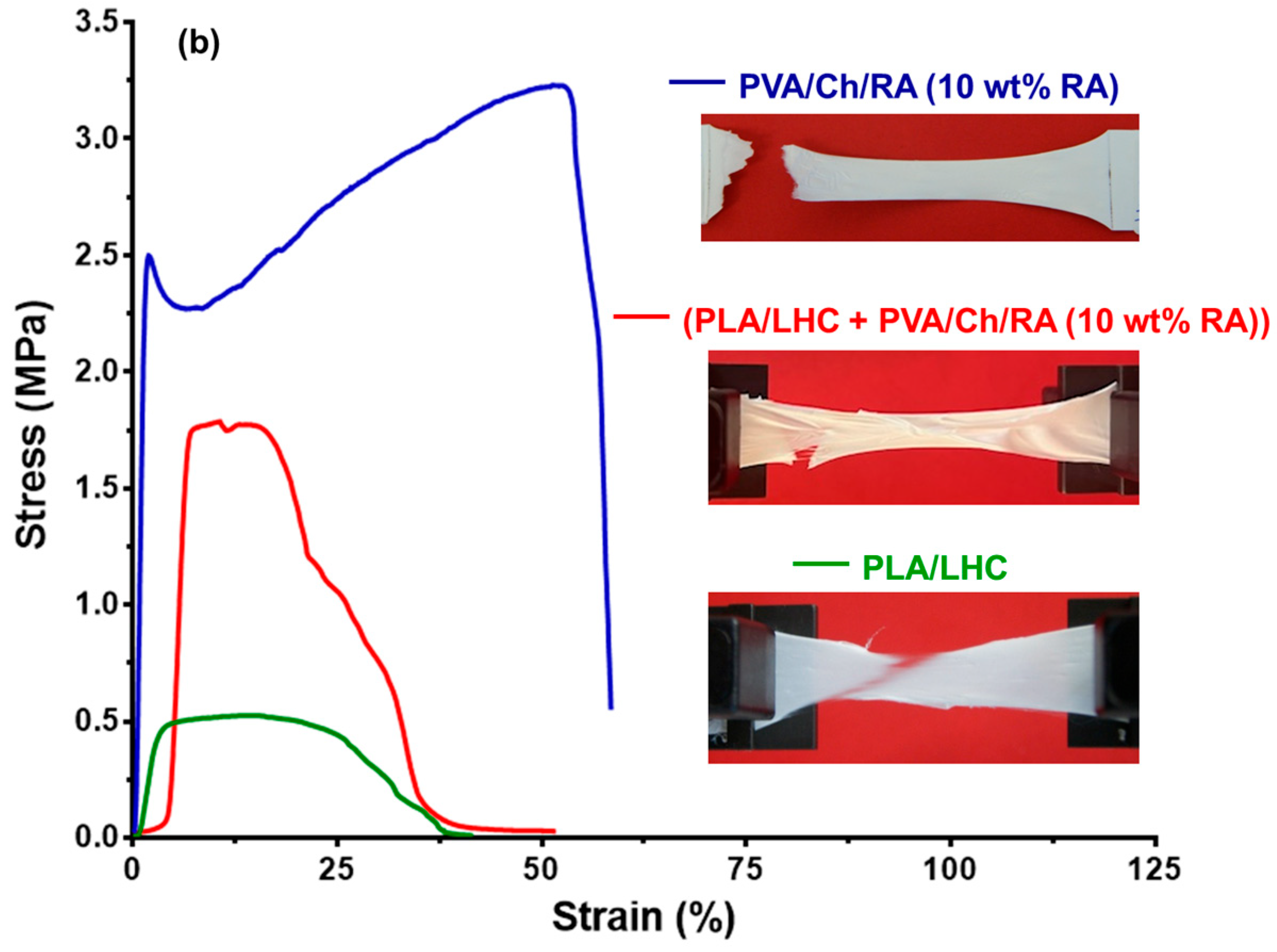


| Fibrous Materials | Tensile Strength, MPa | Young’s Modulus, MPa | Elongation at Break, % |
|---|---|---|---|
| PVA/Ch | 7.30 ± 0.60 | 112.90 ± 27.40 | 40.40 ± 3.50 |
| PVA/Ch/RA (10 wt% RA) | 3.20 ± 0.03 | 246.40 ± 2.10 | 58.60 ± 0.20 |
| (PLA + PVA/Ch/RA (10 wt% RA)) | 2.20 ± 0.18 | 121.00 ± 28.90 | 81.50 ± 6.90 |
| (PLA/LHC + PVA/Ch/RA (10 wt% RA)) | 1.80 ± 0.40 | 86.00 ± 28.90 | 51.80 ± 25.20 |
| PLA/LHC | 0.53 ± 0.05 | 26.70 ± 9.30 | 39.80 ± 2.60 |
| PLA | 0.52 ± 0.07 | 3.60 ± 0.60 | 115.60 ± 11.70 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ignatova, M.; Paneva, D.; Kyuchyuk, S.; Manolova, N.; Rashkov, I.; Mourdjeva, M.; Markova, N. Multifunctional Electrospun Materials from Poly(Vinyl Alcohol)/Chitosan and Polylactide Incorporating Rosmarinic Acid and Lidocaine with Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Properties. Polymers 2025, 17, 2657. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17192657
Ignatova M, Paneva D, Kyuchyuk S, Manolova N, Rashkov I, Mourdjeva M, Markova N. Multifunctional Electrospun Materials from Poly(Vinyl Alcohol)/Chitosan and Polylactide Incorporating Rosmarinic Acid and Lidocaine with Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Properties. Polymers. 2025; 17(19):2657. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17192657
Chicago/Turabian StyleIgnatova, Milena, Dilyana Paneva, Selin Kyuchyuk, Nevena Manolova, Iliya Rashkov, Milena Mourdjeva, and Nadya Markova. 2025. "Multifunctional Electrospun Materials from Poly(Vinyl Alcohol)/Chitosan and Polylactide Incorporating Rosmarinic Acid and Lidocaine with Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Properties" Polymers 17, no. 19: 2657. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17192657
APA StyleIgnatova, M., Paneva, D., Kyuchyuk, S., Manolova, N., Rashkov, I., Mourdjeva, M., & Markova, N. (2025). Multifunctional Electrospun Materials from Poly(Vinyl Alcohol)/Chitosan and Polylactide Incorporating Rosmarinic Acid and Lidocaine with Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Properties. Polymers, 17(19), 2657. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17192657








