Influence of Molecular Structure of POM on Processability Within Metal Injection Molding
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
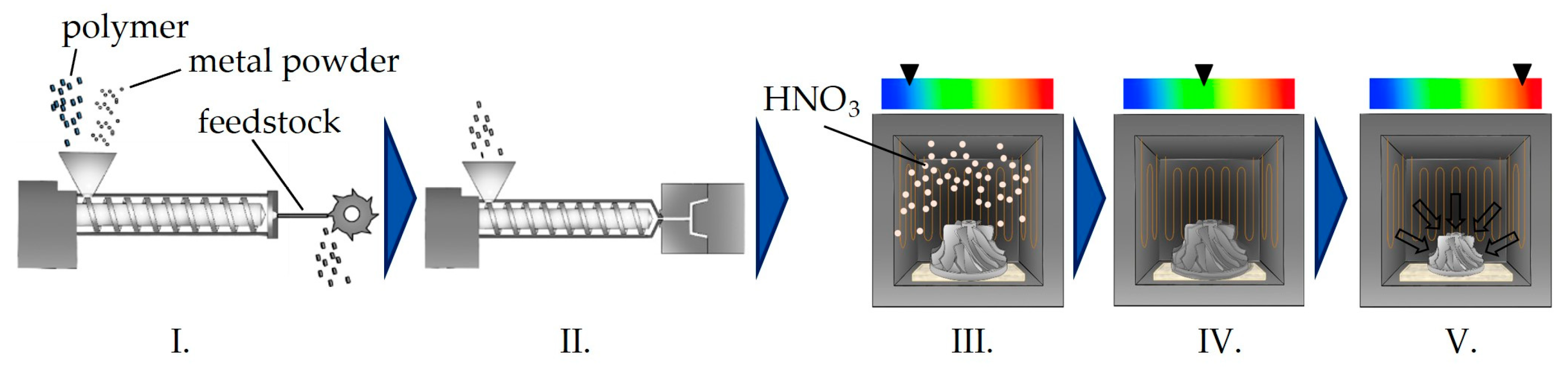
2.2. Processing
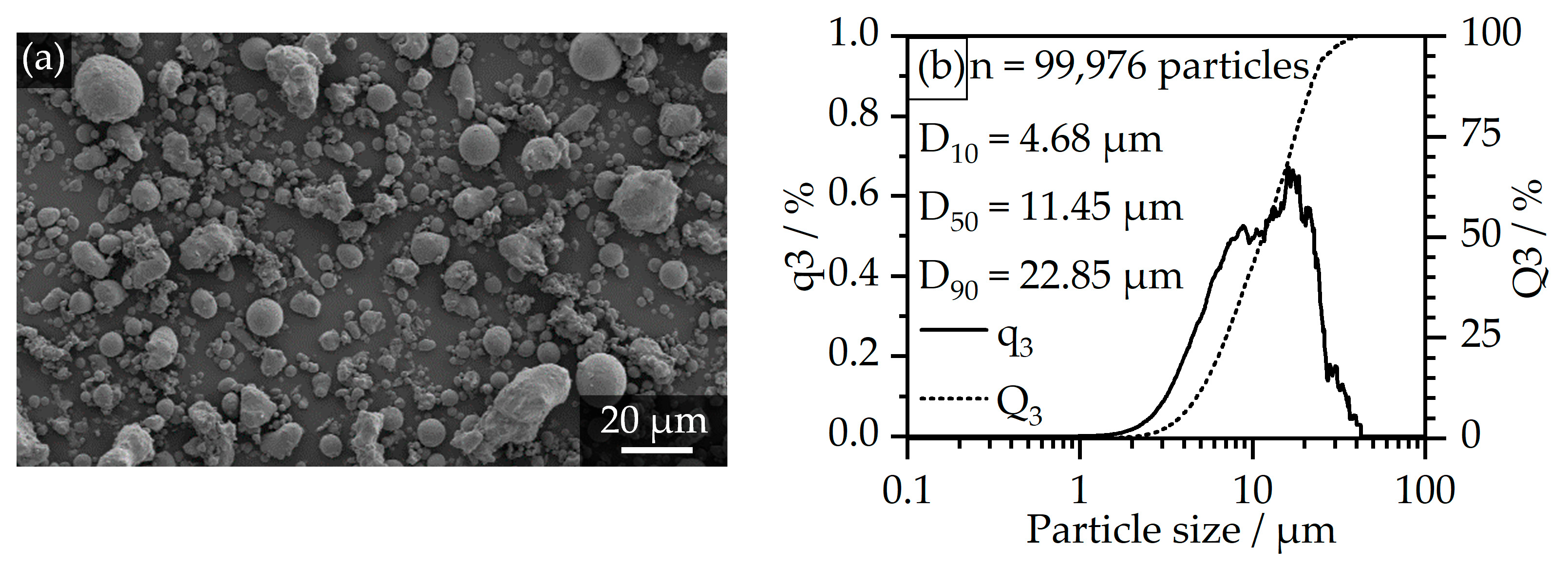
2.3. Methods
3. Results and Discussion
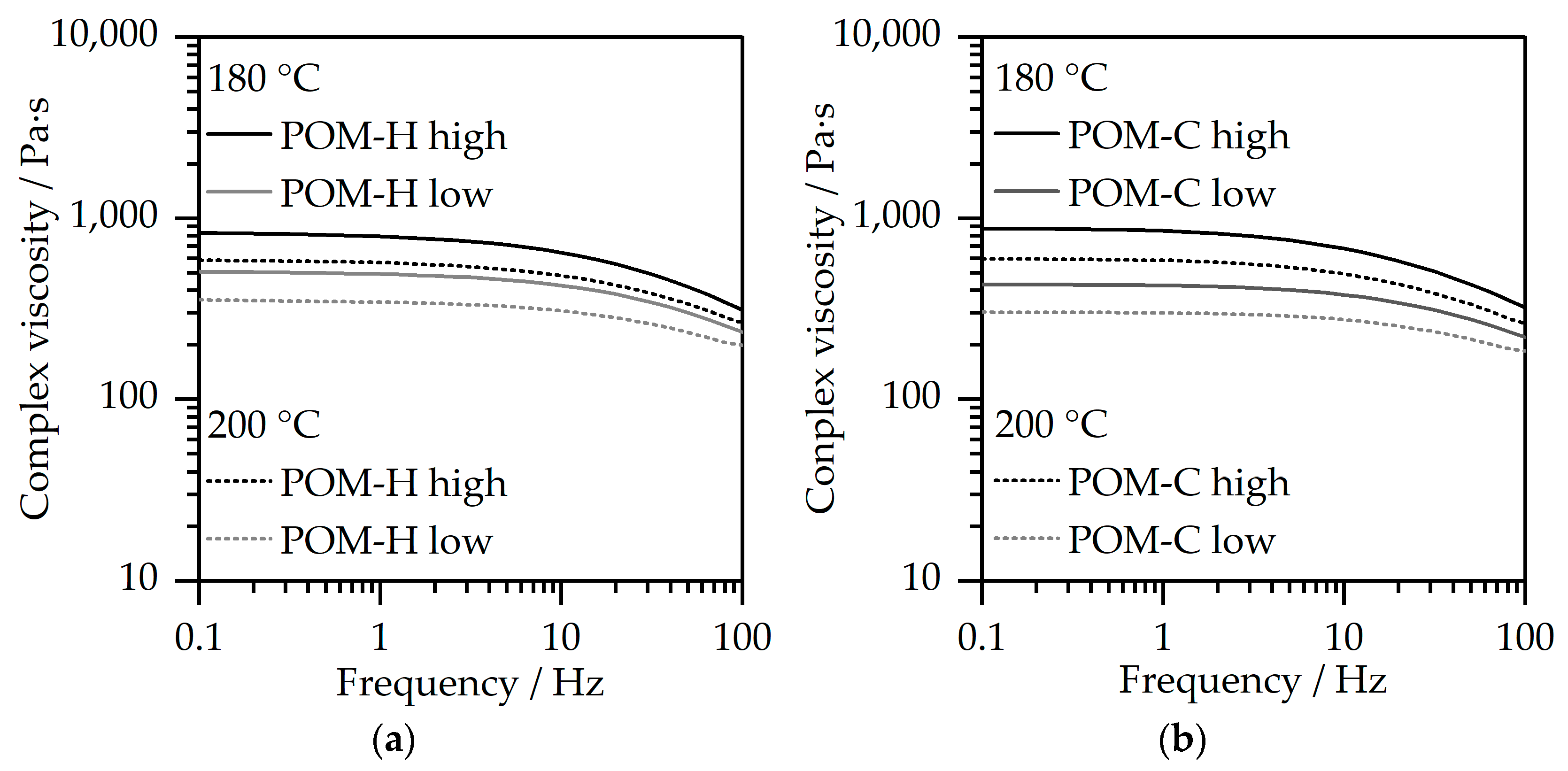
3.1. Rheological Characterization
3.2. Thermal Stability
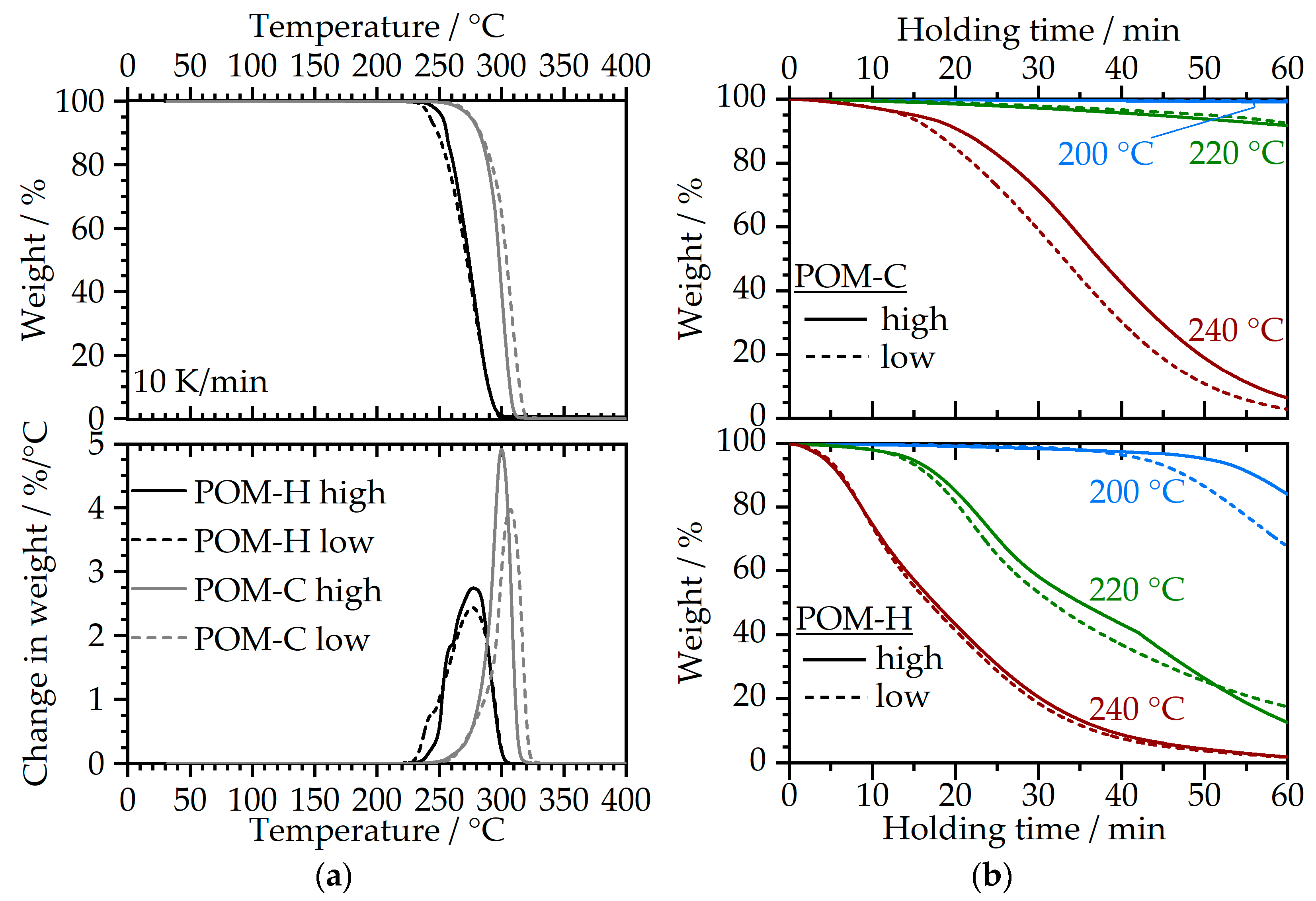
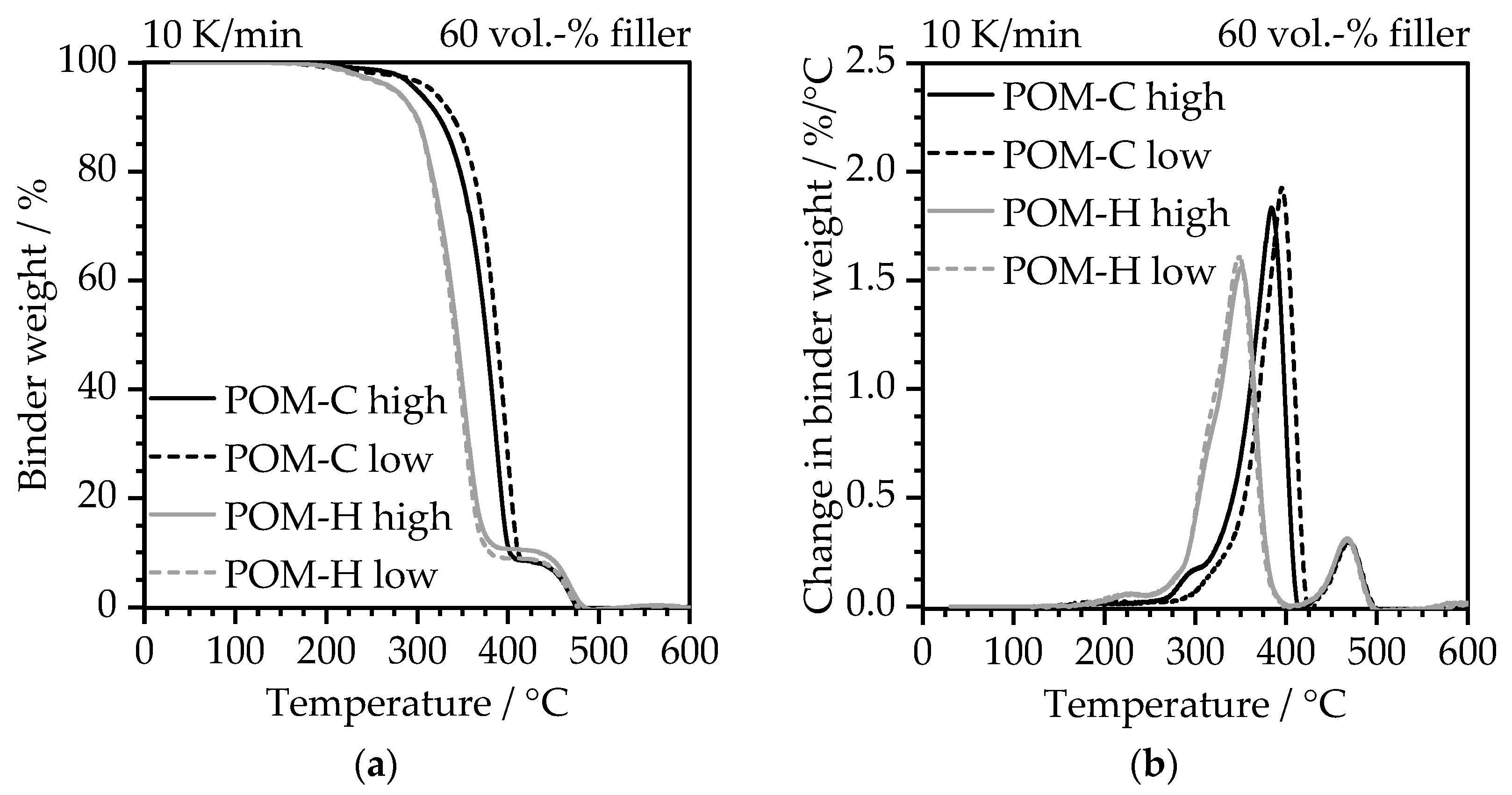
3.2.1. Thermogravimetrical Analysis (TGA)
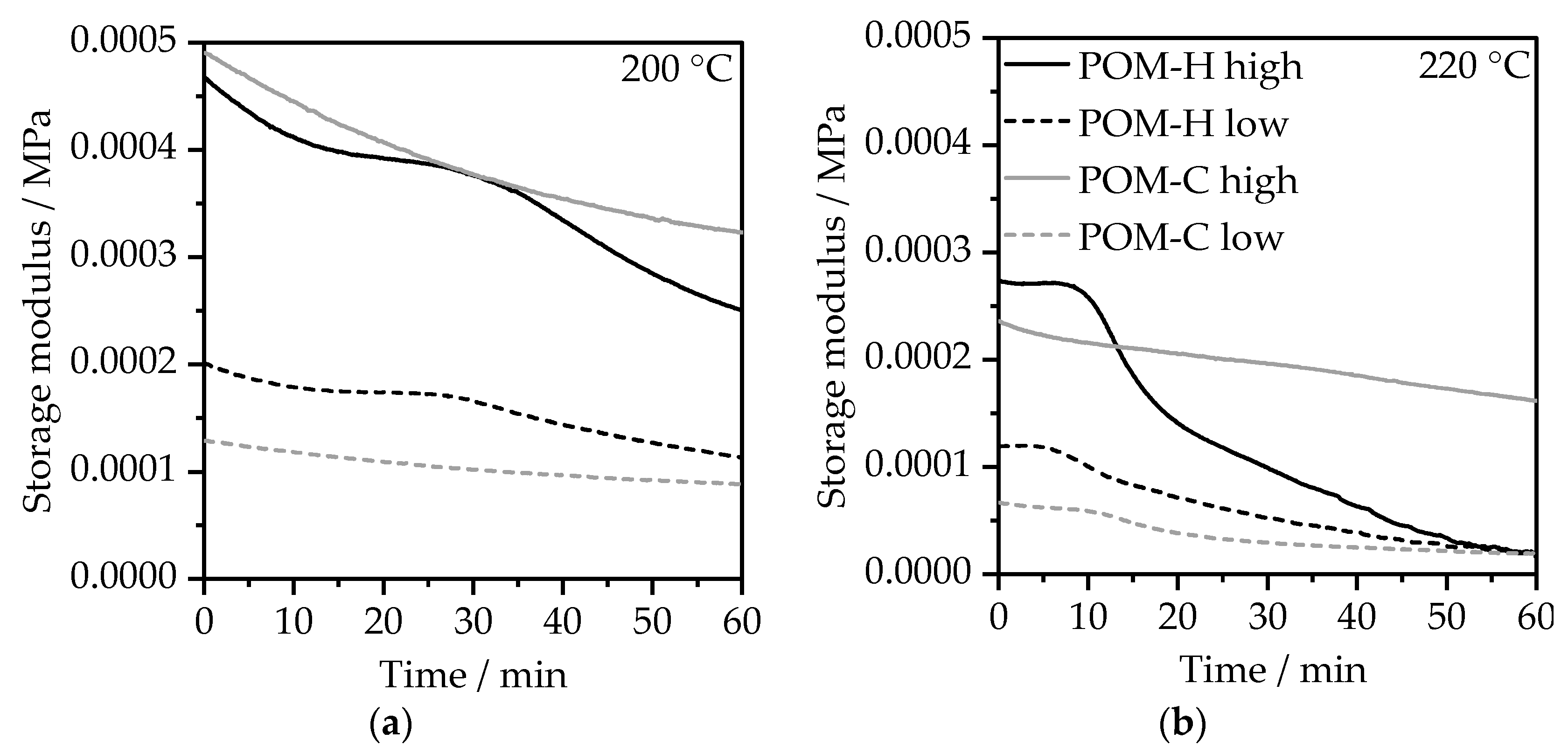
3.2.2. Rotational Rheometry—Time-Sweep Experiments
3.3. Feedstock Properties
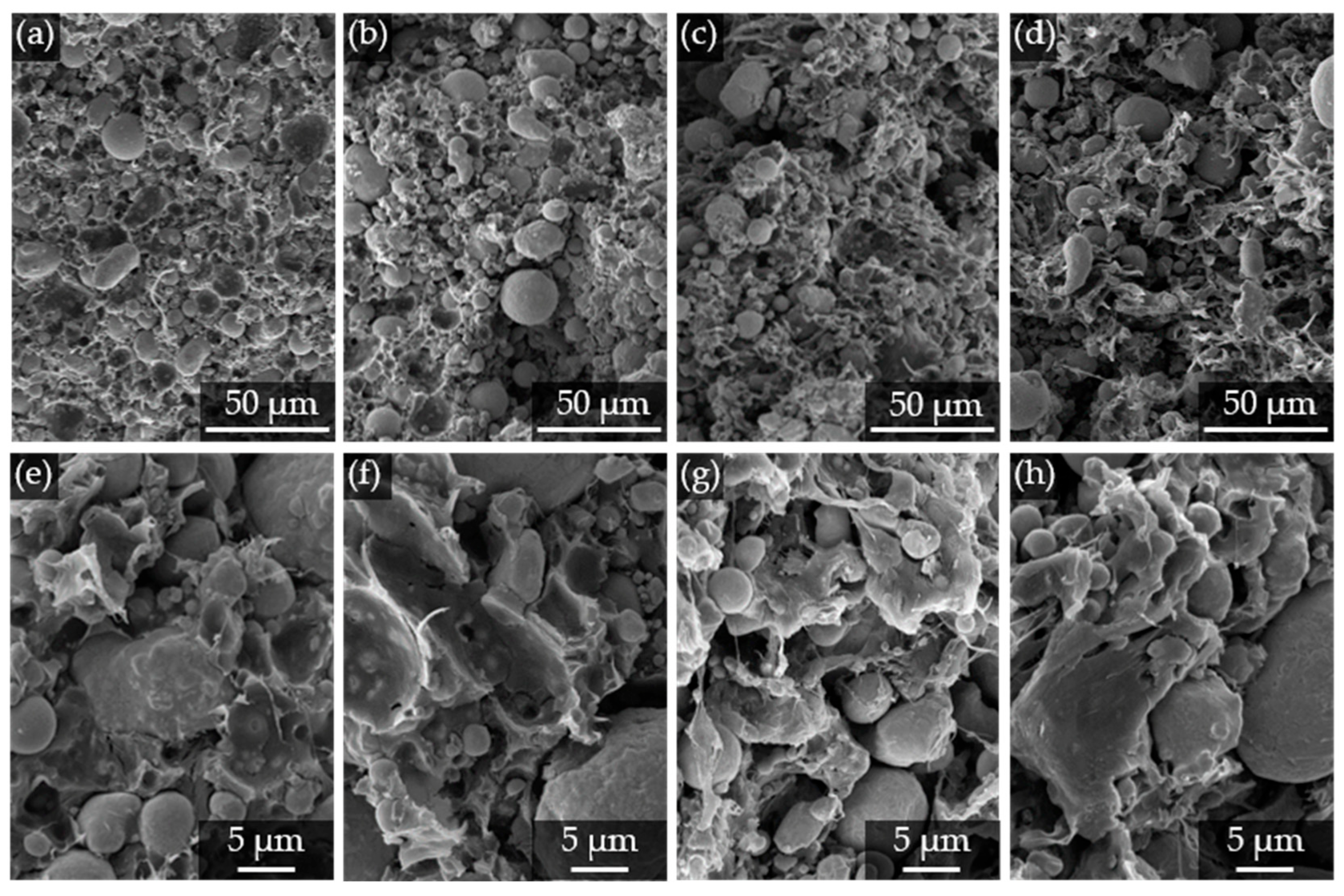
3.3.1. Filler–Matrix Interaction
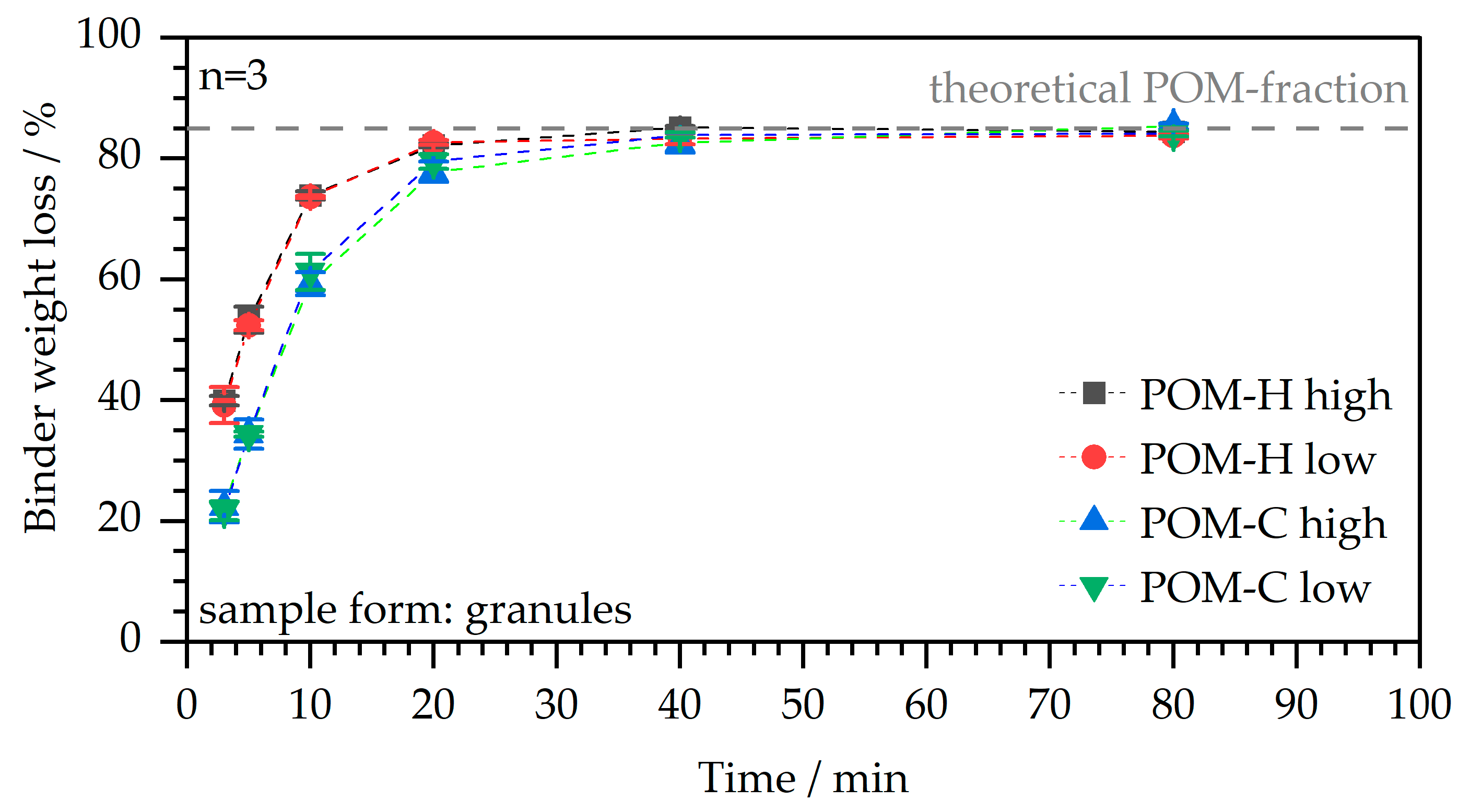
3.3.2. Catalytic Debinding Behavior
3.3.3. Thermal Debinding Behavior
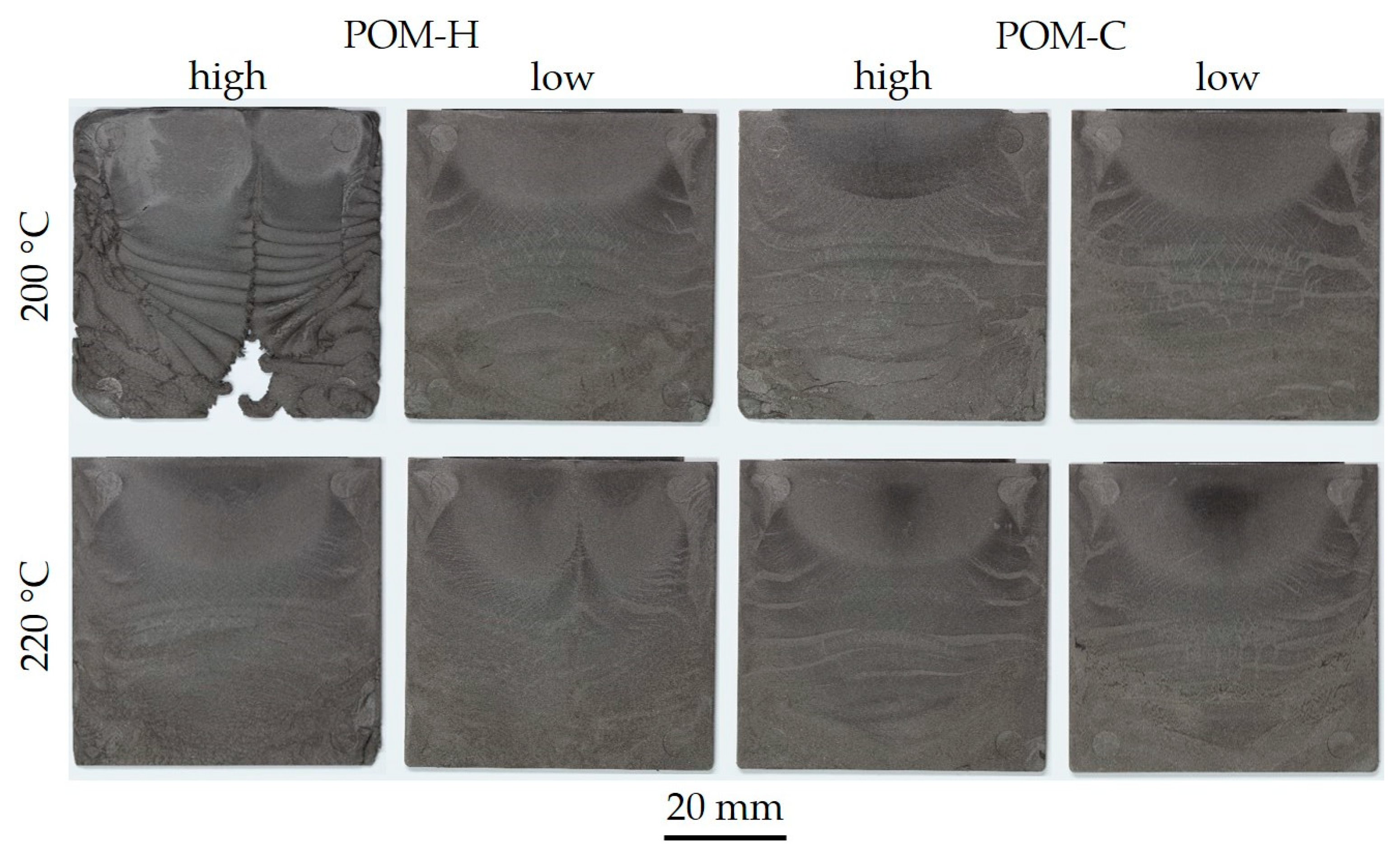
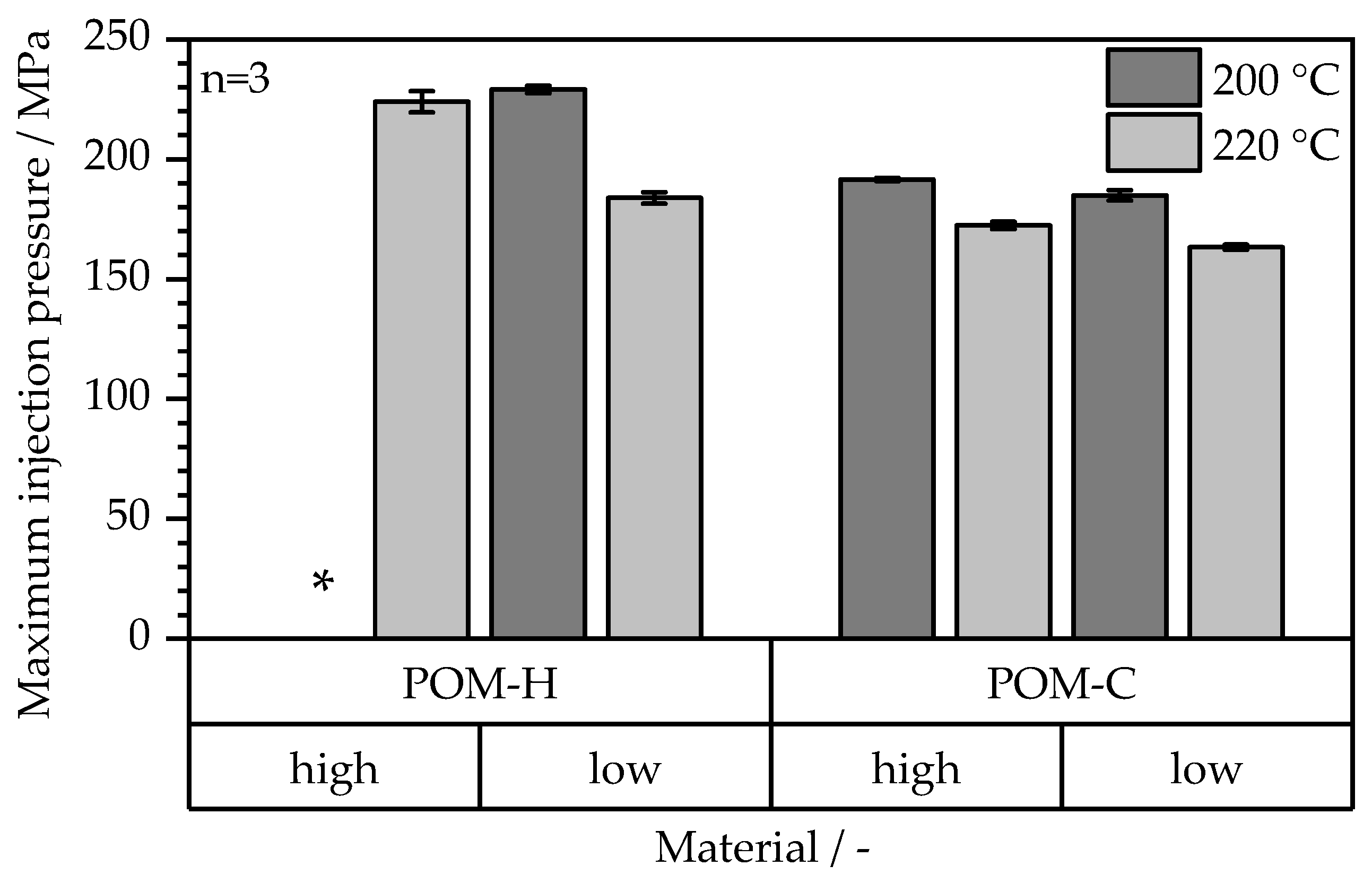
3.4. Processability in MIM
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gonzalez-Gutierrez, J.; Cano, S.; Schuschnigg, S.; Kukla, C.; Sapkota, J.; Holzer, C. Additive Manufacturing of Metallic and Ceramic Components by the Material Extrusion of Highly-Filled Polymers: A Review and Future Perspectives. Materials 2018, 11, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bankapalli, N.K.; Gupta, V.; Saxena, P.; Bajpai, A.; Lahoda, C.; Polte, J. Filament fabrication and subsequent additive manufacturing, debinding, and sintering for extrusion-based metal additive manufacturing and their applications: A review. Compos. Part B Eng. 2023, 264, 110915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schüßler, P.; Franke, J.; Czink, S.; Antusch, S.; Mayer, D.; Laube, S.; Hanemann, T.; Schulze, V.; Dietrich, S. Characterization of the Metal Fused Filament Fabrication Process for Manufacturing of Pure Copper Inductors. Materials 2023, 16, 6678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, R.M. Powder Injection Molding; Metal Powder Industries Federation: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1990; ISBN 0-918404-95-9. [Google Scholar]
- German, R.M. Metal powder injection molding (MIM): Key trends and markets. In Handbook of Metal Injection Molding; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 1–21. ISBN 9780081021521. [Google Scholar]
- Clemens, F. Thermoplastic Extrusion for Ceramic Bodies. In Extrusion in Ceramics; Derby, B., Händle, F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 295–312. ISBN 978-3-540-27100-0. [Google Scholar]
- Salehi, M.; Pfaff, E.M.; Kaletsch, A.; Graule, T.; Clemens, F.; Grobéty, B. Manufacturing of Tubular Dead-End Membranes by Continuous Thermoplastic Extrusion. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2015, 12, E13–E18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Torre-Gamarra, C.d.; Sotomayor, M.E.; Sanchez, J.-Y.; Levenfeld, B.; Várez, A.; Laïk, B.; Pereira-Ramos, J.-P. High mass loading additive-free LiFePO4 cathodes with 500 μm thickness for high areal capacity Li-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2020, 458, 228033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.-W.; Huang, Z.-K.; Tseng, C.-F.; Hwang, K.-S. Microstructures, mechanical properties, and fracture behaviors of metal-injection molded 17-4PH stainless steel. Met. Mater. Int. 2015, 21, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Gutierrez, J.; Duretek, I.; Kukla, C.; Poljšak, A.; Bek, M.; Emri, I.; Holzer, C. Models to Predict the Viscosity of Metal Injection Molding Feedstock Materials as Function of Their Formulation. Metals 2016, 6, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitri, C.; Mohamed, S.; Thierry, B.; Jean-Claude, G. Influence of particle-size distribution and temperature on the rheological properties of highly concentrated Inconel feedstock alloy 718. Powder Technol. 2017, 322, 273–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausnerova, B.; Mukund, B.N.; Sanetrnik, D. Rheological properties of gas and water atomized 17-4PH stainless steel MIM feedstocks: Effect of powder shape and size. Powder Technol. 2017, 312, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukund, B.N.; Hausnerova, B. Variation in particle size fraction to optimize metal injection molding of water atomized 17–4PH stainless steel feedstocks. Powder Technol. 2020, 368, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langlais, D.; Demers, V.; Brailovski, V. Rheology of dry powders and metal injection molding feedstocks formulated on their base. Powder Technol. 2022, 396, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thavanayagam, G.; Swan, J.E. Aqueous debinding of polyvinyl butyral based binder system for titanium metal injection moulding. Powder Technol. 2018, 326, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivashankar, T.S.; Enneti, R.K.; Park, S.-J.; German, R.M.; Atre, S.V. The effects of material attributes on powder–binder separation phenomena in powder injection molding. Powder Technol. 2013, 243, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, K.C.; Lin, C.C.; Lo, G.M. The Effect of Wax Composition on the Injection Molding of Carbonyl Iron Powder with LDPE. Can. Metall. Q. 1996, 35, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supriadi, S.; Baek, E.R.; Choi, C.J.; Lee, B.T. Binder system for STS 316 nanopowder feedstocks in micro-metal injection molding. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2007, 187–188, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Li, D.; Lu, R.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Z. Study of hyperbranched polymer on POM-based binder in metal injection molding. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 125377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berges, C.; Hidalgo, J.; Herranz, G. Exploring the Elemental Interactions of Melamine with Binder–Metal Powder Mixtures: A Pathway to Enhanced Catalytic Debinding and Rheological Control. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfizarei, Z.; Mostafapour, A.; Barari, A.; Jalili, A.; Patterson, A.E. Overview of debinding methods for parts manufactured using powder material extrusion. Addit. Manuf. 2023, 61, 103335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maat, T.; Hendrik, J.H.; Schütte, W.; Sterzel, H.-J. Verfahren zur Herstellung Eines Organischen Sinterformteils. AT507836B1, 15 January 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Trübenbach, P. Method of Producing Sintered Articles. WO 94/25205, 10 November 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Kern, W.; Cherdron, H. Der Abbau von polyoxymethylenen. Poloxymethylene. 14. Mitteilung. Makromol. Chem. 1960, 40, 101–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassie, N.; Roche, R.S. The thermal degradation of polyoxymethylene. Makromol. Chem. 1968, 112, 16–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archodoulaki, V.-M.; Lüftl, S.; Seidler, S. Thermal degradation behaviour of poly(oxymethylene): 1. Degradation and stabilizer consumption. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2004, 86, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archodoulaki, V.-M.; Lüftl, S.; Koch, T.; Seidler, S. Property changes in polyoxymethylene (POM) resulting from processing, ageing and recycling. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2007, 92, 2181–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archodoulaki, V.-M.; Lüftl, S.; Seidler, S. Oxidation induction time studies on the thermal degradation behaviour of polyoxymethylene. Polym. Test. 2006, 25, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardinelli, F.M.; Dolce, T.J.; Walling, C. Degradation and stabilization of polyacetal copolymers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1965, 9, 1419–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Gutierrez, J.; Stringari, G.B.; Megen, Z.M.; Oblak, P.; Bernstorff, B.S.v.; Emri, I. Selection of appropriate polyoxymethylene based binder for feedstock material used in powder injection moulding. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2015, 602, 12001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stringari, G.B.; Zupančič, B.; Kubyshkina, G.; Bernstorff, B.v.; Emri, I. Time-dependent properties of bimodal POM—Application in powder injection molding. Powder Technol. 2011, 208, 590–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorjan, L.; Galusca, C.; Sami, M.; Sebastian, T.; Clemens, F. Effect of stearic acid on rheological properties and printability of ethylene vinyl acetate based feedstocks for fused filament fabrication of alumina. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 36, 101391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forstner, T.; Cholewa, S.; Drummer, D. Influence of wax addition on feedstock processing behavior in additive manufacturing of metals by material extrusion. Prog. Addit. Manuf. 2024, 9, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pielichowska, K. The influence of polyoxymethylene molar mass on the oxidative thermal degradation of its nanocomposites with hydroxyapatite. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2016, 124, 751–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, M.; Wagner, M.H. Time-resolved rheometry of poly(ethylene terephthalate) during thermal and thermo-oxidative degradation. Rheol. Acta 2016, 55, 789–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, M. Crystallization and melting of copolymers of polyoxymethylene. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1964, 8, 2225–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahangaran, F.; Navarchian, A.H. Recent advances in chemical surface modification of metal oxide nanoparticles with silane coupling agents: A review. Adv. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2020, 286, 102298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.-M.; Wu, J.-J.; Tan, C.-M. Processing Optimization for Metal Injection Molding of Orthodontic Braces Considering Powder Concentration Distribution of Feedstock. Polymers 2020, 12, 2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Parameter/Unit | Value |
|---|---|
| Mold temperature/°C | 100 |
| Mass temperature/°C | 200/220 |
| Injection speed/mm·s−1 | 20 |
| Holding pressure/bar | 900 |
| Time of holding pressure/s | 10 |
| Residual cooling time/s | 30 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Forstner, T.; Cholewa, S.; Früh, T.; Drummer, D. Influence of Molecular Structure of POM on Processability Within Metal Injection Molding. Polymers 2025, 17, 2621. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17192621
Forstner T, Cholewa S, Früh T, Drummer D. Influence of Molecular Structure of POM on Processability Within Metal Injection Molding. Polymers. 2025; 17(19):2621. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17192621
Chicago/Turabian StyleForstner, Thomas, Simon Cholewa, Tobias Früh, and Dietmar Drummer. 2025. "Influence of Molecular Structure of POM on Processability Within Metal Injection Molding" Polymers 17, no. 19: 2621. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17192621
APA StyleForstner, T., Cholewa, S., Früh, T., & Drummer, D. (2025). Influence of Molecular Structure of POM on Processability Within Metal Injection Molding. Polymers, 17(19), 2621. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17192621






