Development of Photoresponsive Water-Soluble Superhydrophobic Coatings and Properties of the Modified Paper
Abstract
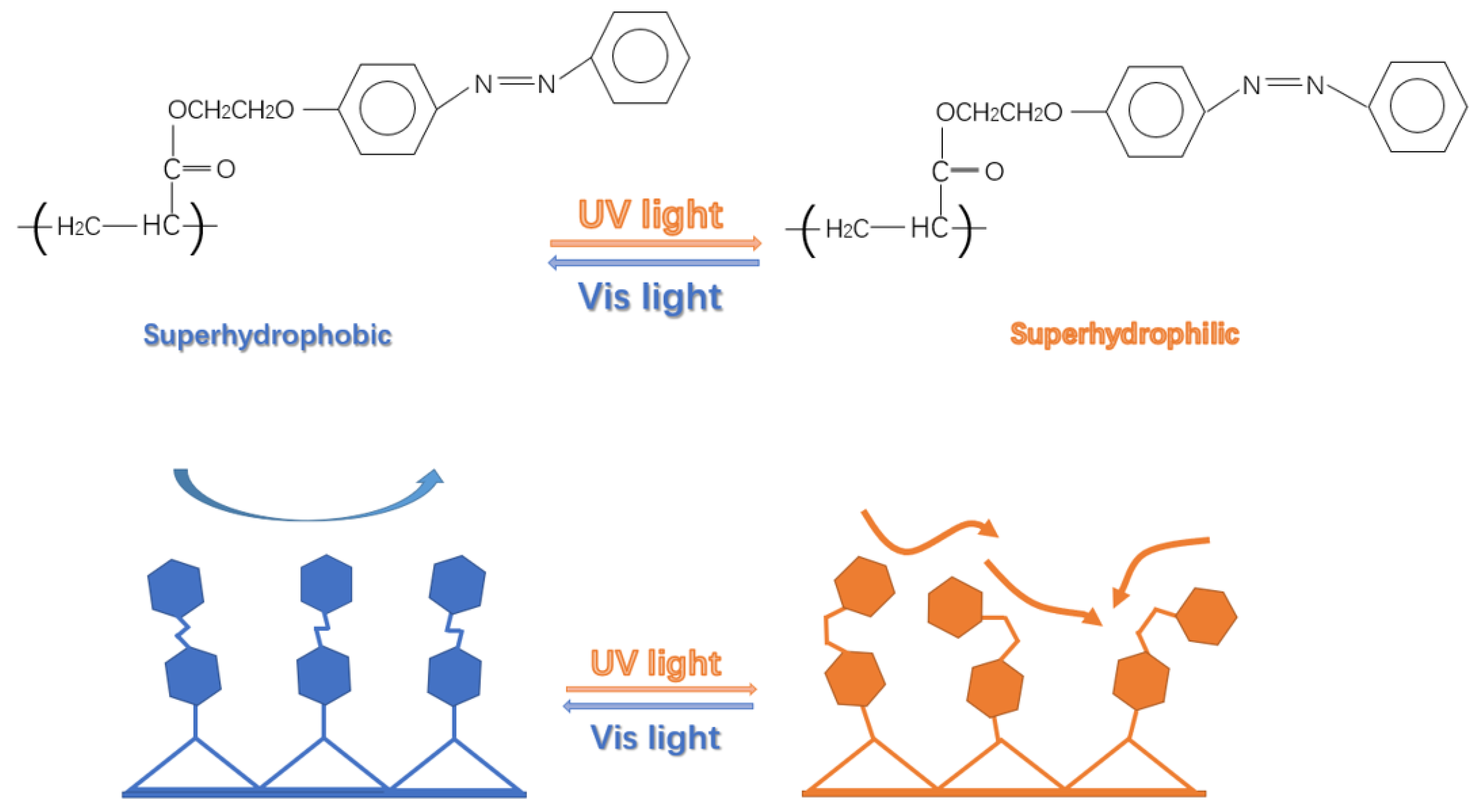
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
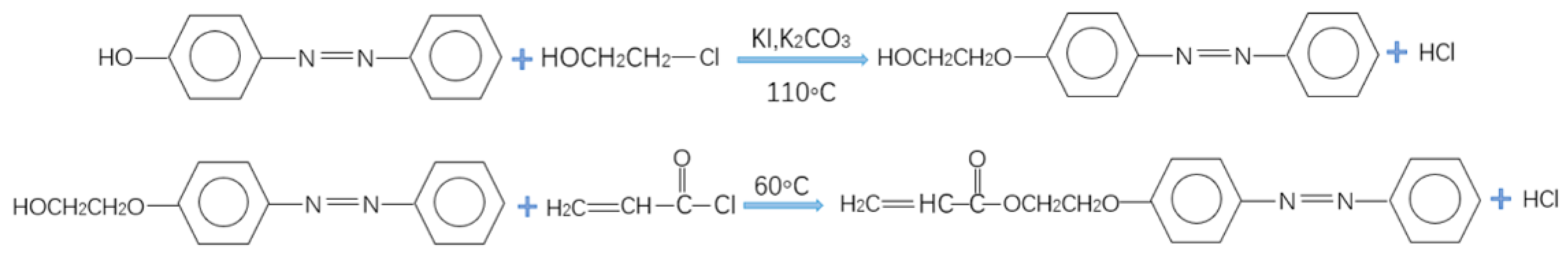
2.2. Preparation of the Light-Responsive Monomer PAPAE
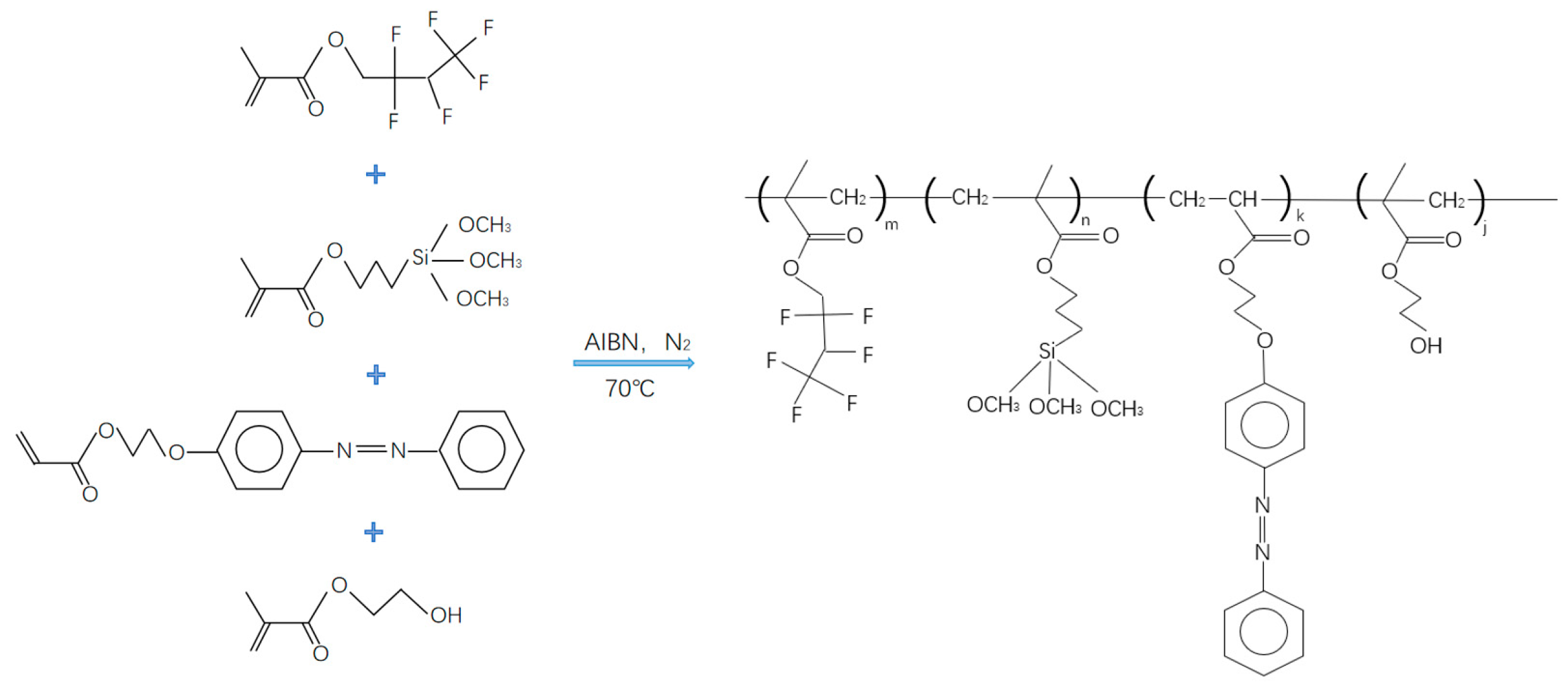
2.3. Preparation of Water-Soluble Light-Responsive Polymer
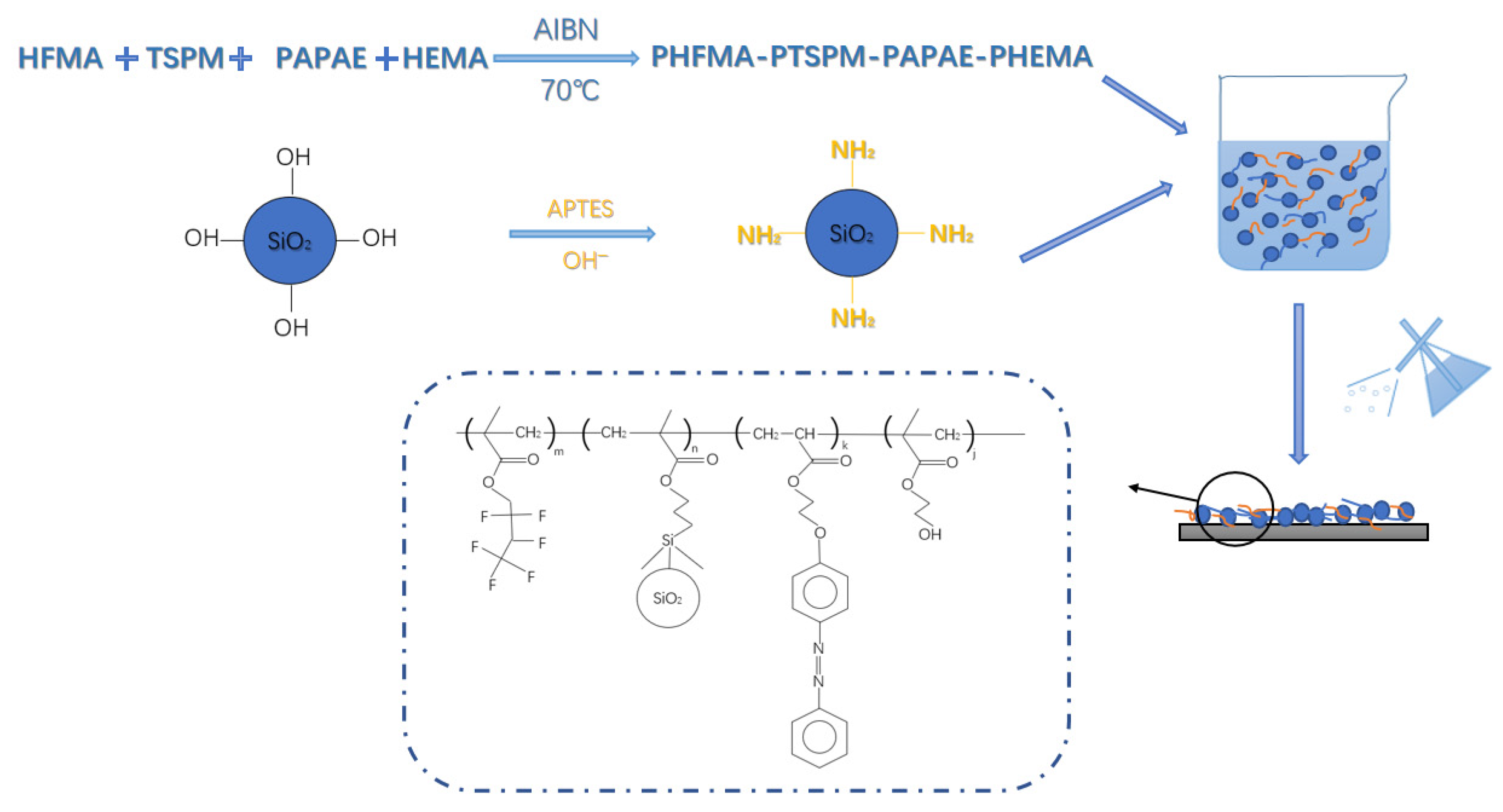
2.4. Preparation of Amino Modified SiO2
2.5. Preparation of Light-Responsive Superhydrophobic Paper
2.6. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
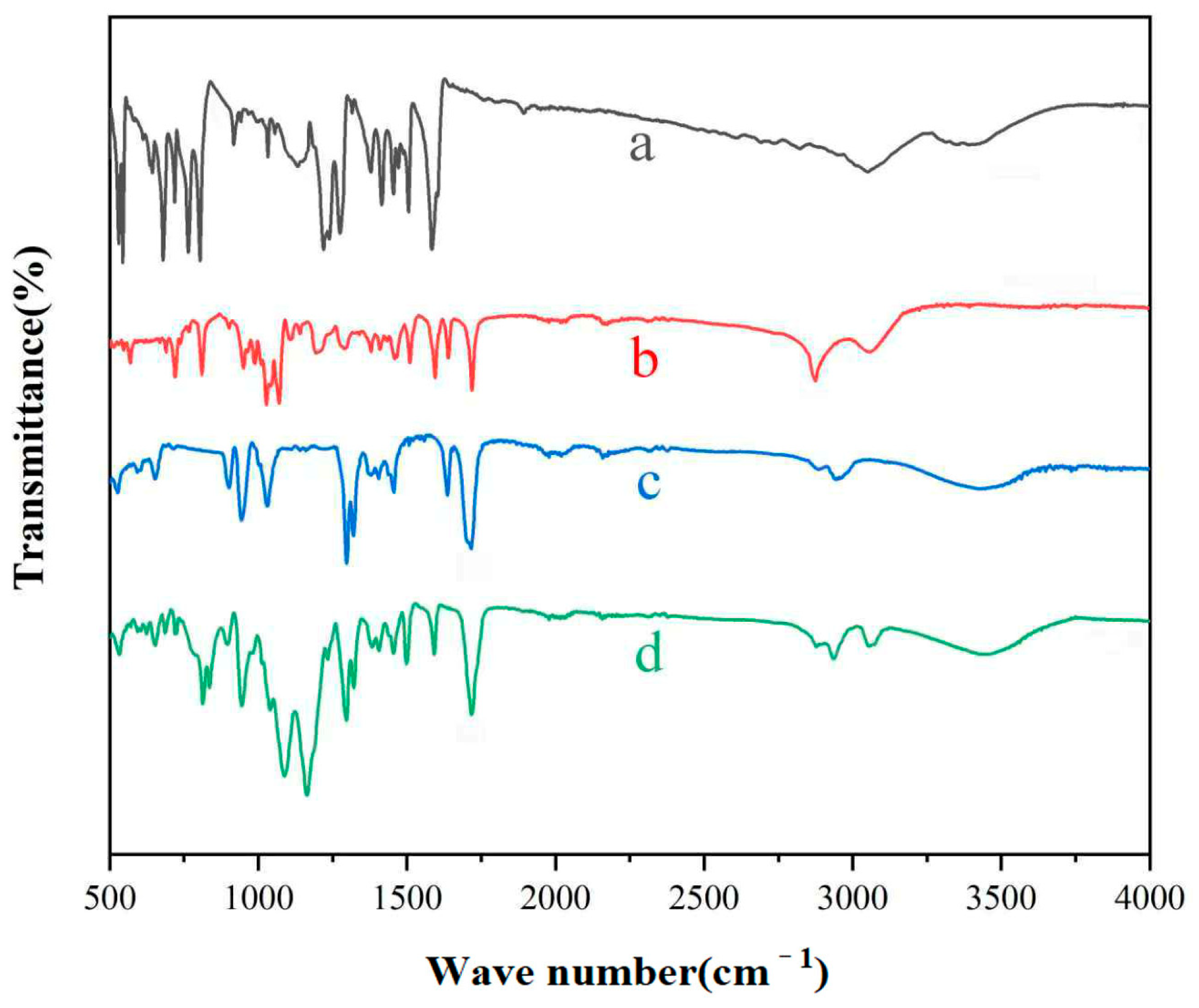
3.1. Infrared Characterization of Polymers
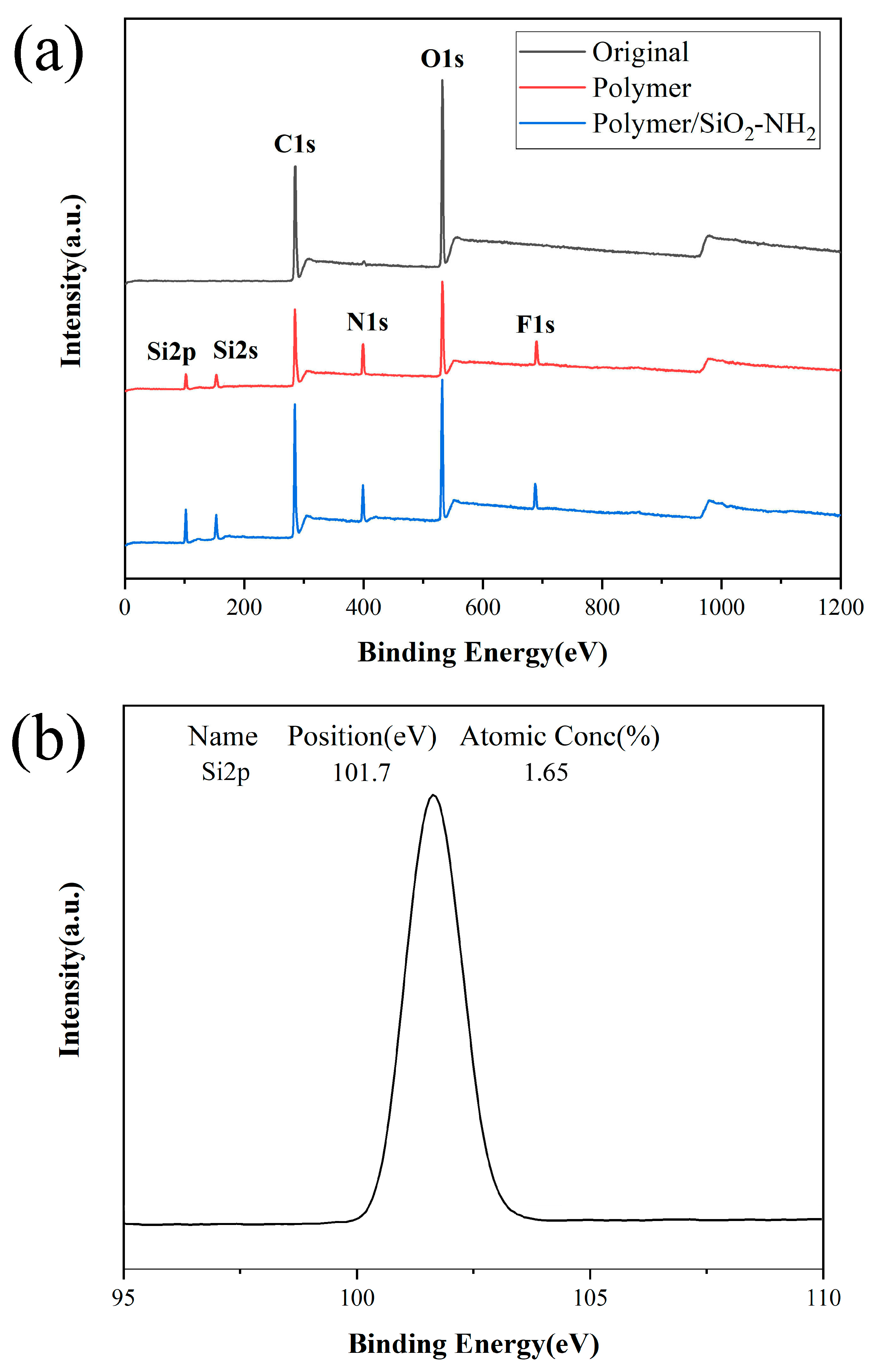
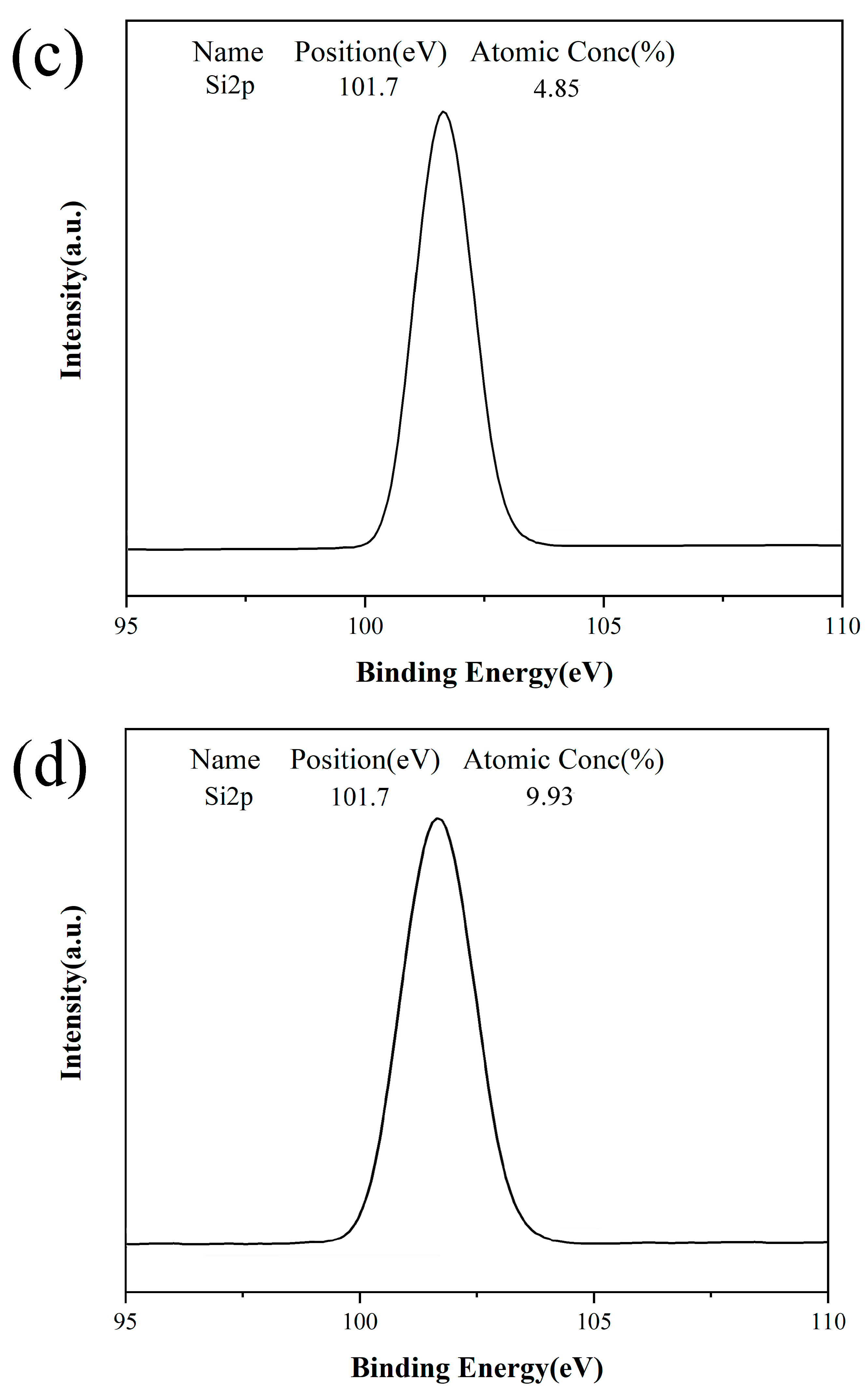
3.2. XPS Test on Different Papers
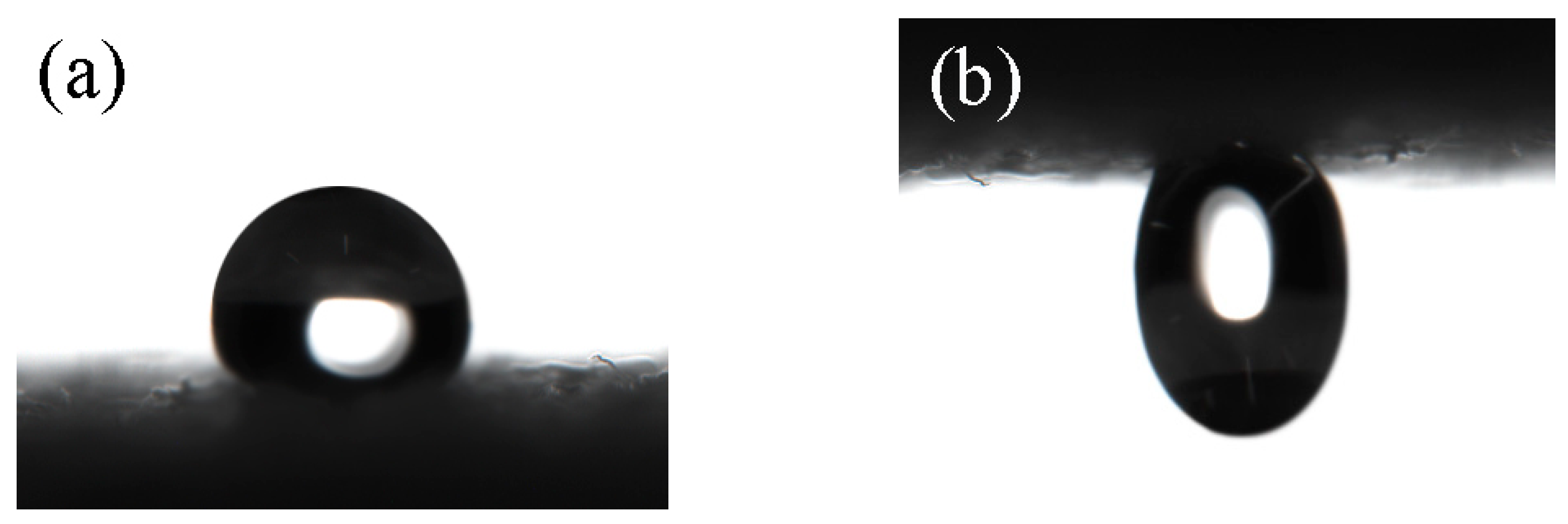
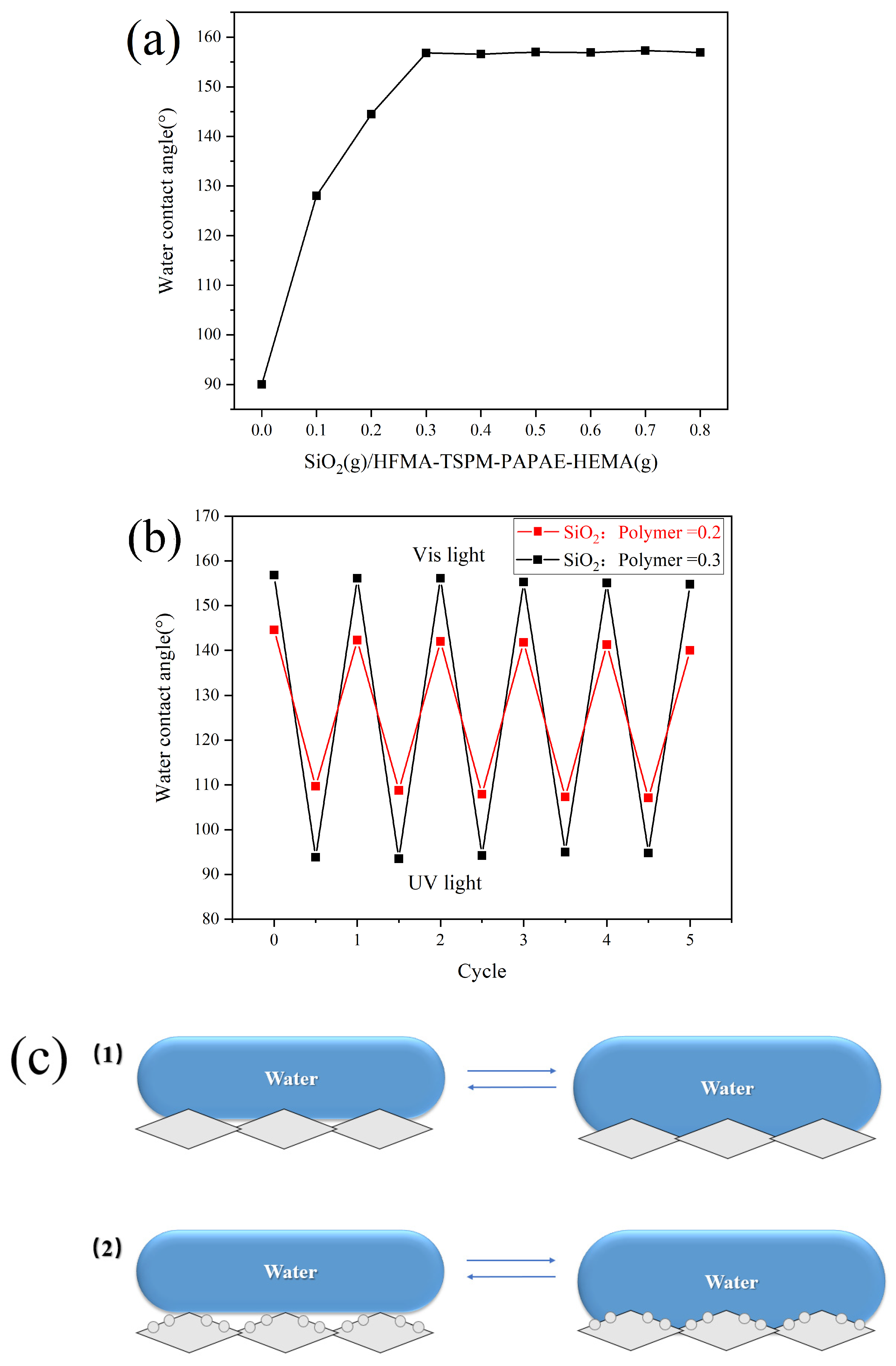
3.3. Effect of Monomer Addition on the Properties of Modified Paper
3.4. Effect of Paper Surface Roughness on Light-Induced Wettability
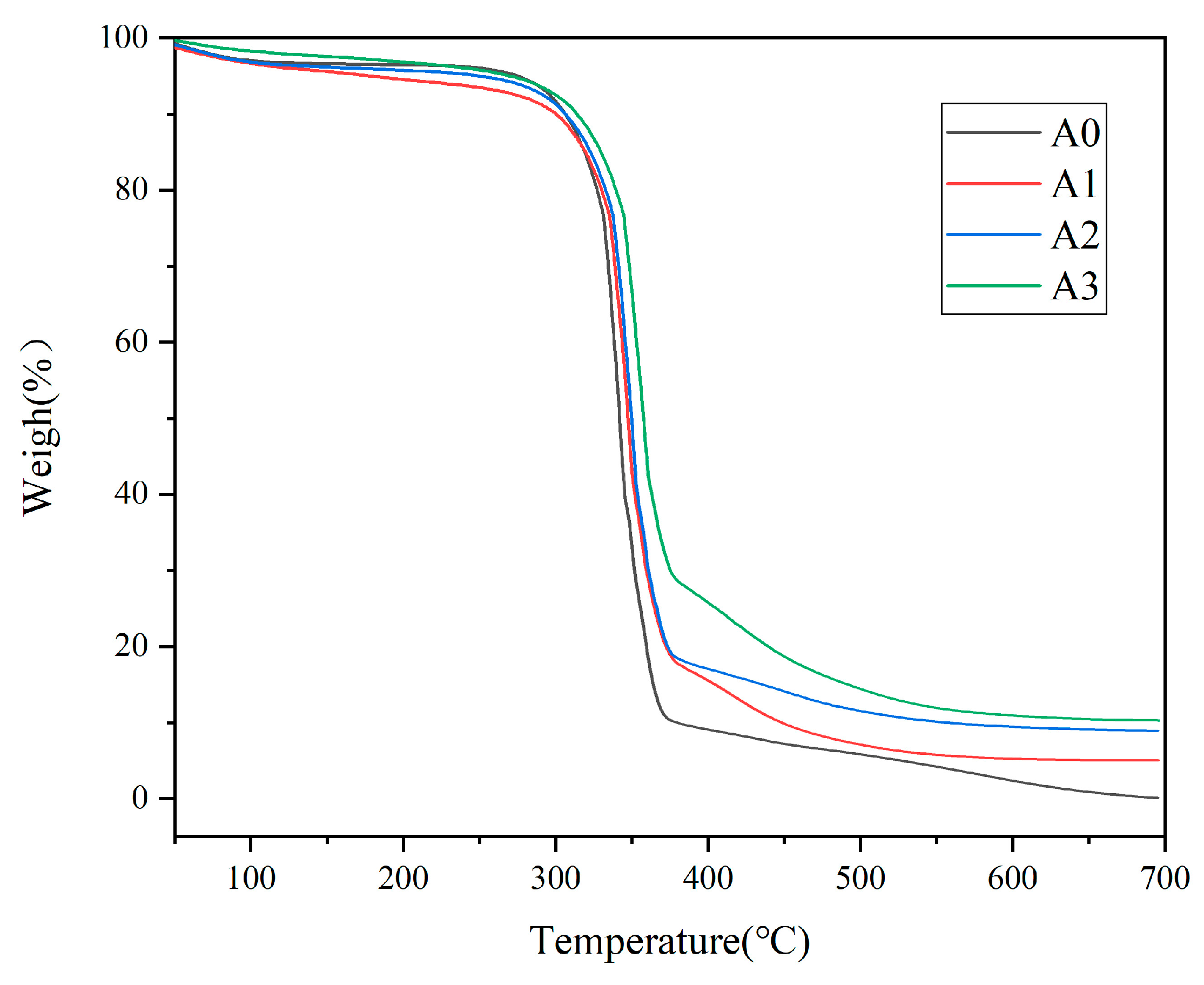
3.5. Thermogravimetric Analysis
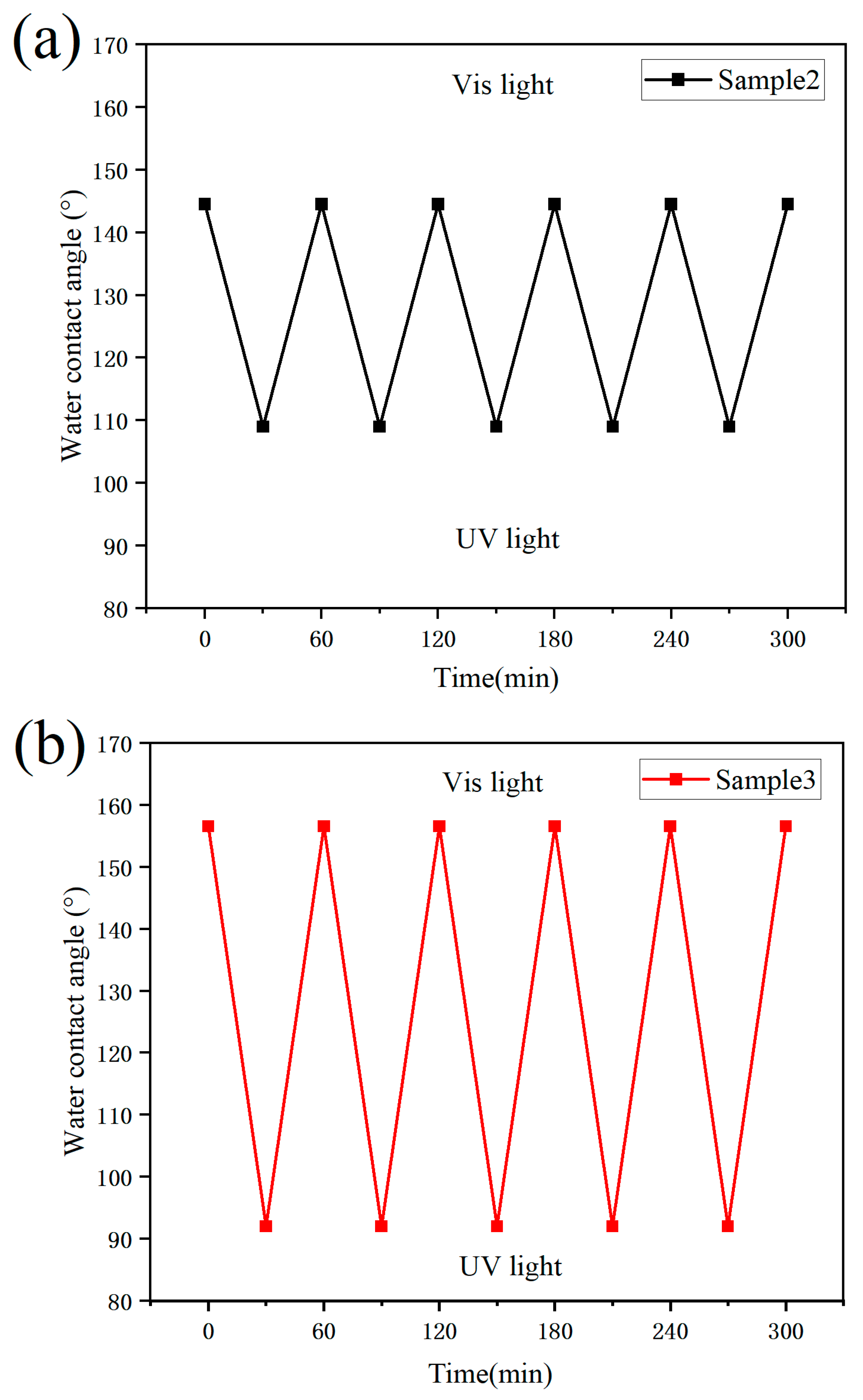
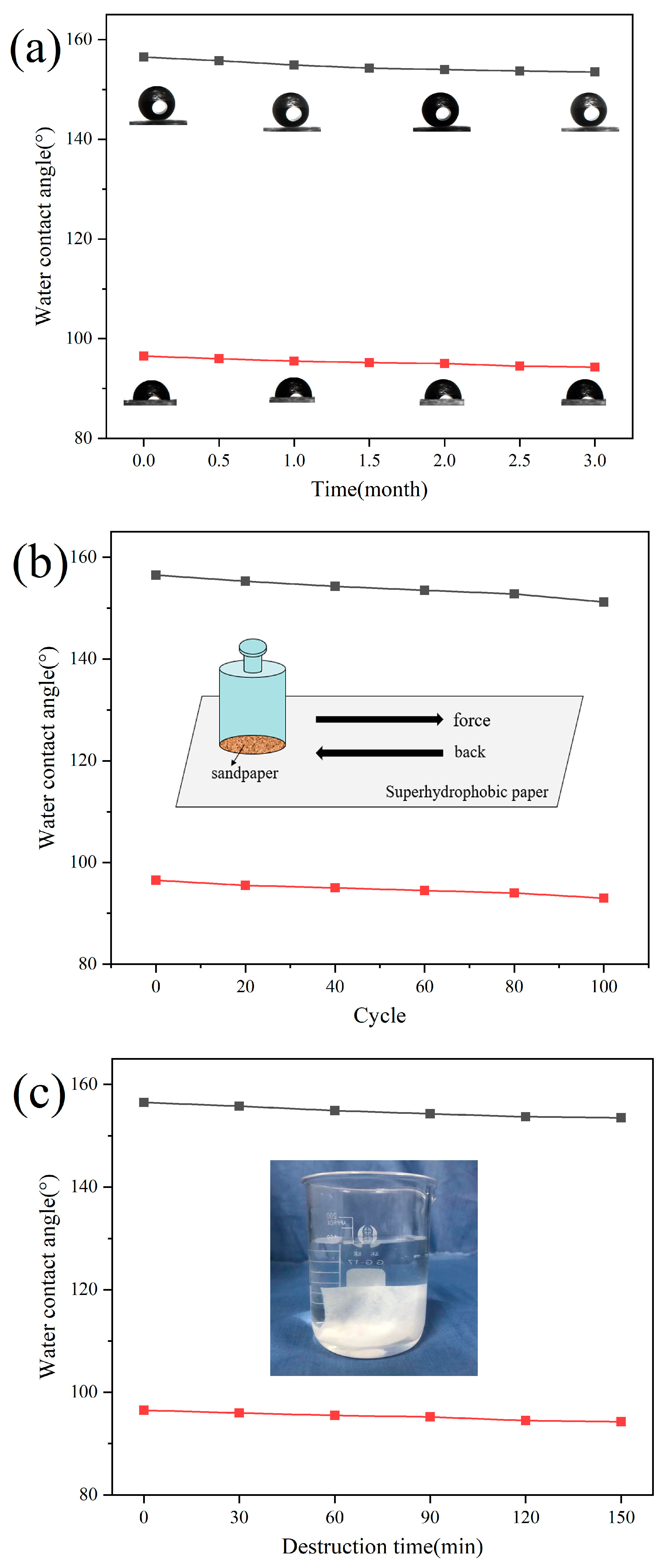
3.6. Stability Test
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fatriasari, W.; Rizky Safina Daulay, I.; Fitria; Syahidah; Rajamanickam, R.; Selvasembian, R.; Farobie, O.; Hartulistiyoso, E.; Solihat, N.N.; Hua, L.S. Recent advances in superhydrophobic paper derived from nonwood fibers. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2024, 27, 101900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Ye, L. Facile construction of durable superhydrophobic cellulose paper for oil-water separation. Cellulose 2023, 30, 5074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shi, B.; Chen, Y. Facile preparation of economical, eco-friendly superhydrophobic surface on paper substrate with excellent mechanical durability. Prog. Org. Coat. 2020, 147, 105877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, M.; He, G.; Sun, Z. Facile fabrication of a low adhesion, stable and superhydrophobic filter paper modified with ZnO microclusters. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 496, 143743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Pang, Z.; Tan, G. Optically/thermally dual-responsive shape memory superhydrophobic surfaces with advanced multi-functionalities. Compos. Part A 2025, 192, 108812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, T.; Li, X.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, Y. Randomly heterogeneous oleophobic/pH-responsive polymer coatings with reversible wettability transition for multifunctional fabrics and controllable oil–water separation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 594, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Fang, W.; Chen, F.; Zhong, M. Preparation and properties of a pH-responsive PDMS platform. AIP Conf. Proc. 2019, 2065, 040004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Zhou, S. A method for preparing the pH-responsive superhydrophobic paper with high stability. Mater. Res. Express 2021, 8, 065306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Xu, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, A. Hydrophobic/superhydrophobic reversible smart materials via photo/thermo dual-response dynamic wrinkled structure. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 127679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.; Zhang, C.; Sun, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Wei, Y.; Jiang, Y. Magnetically superamphiphobic nanoparticles for magnetic response surface preparation. Langmuir 2020, 36, 14318–14323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, L.; Wei, X.; Lei, F.; Cheng, H. Stable ZnO/ionic liquid hybrid materials: Novel dual-responsive superhydrophobic layers to light and anions. Sci. China Chem. 2014, 57, 1002–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, R.; Zhang, W.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Shih, T.; Wei, Y.; Feng, L. A smart nano-V2O5/ODA-coated mesh for a co-responsive photo-induced wettability transition and ROS generation for in situ water purification. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 18003–18009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Ni, X.; Zhang, X.; Lei, Y.; Guo, J.; Jin, J.; You, B. UV−NIR dual-responsive nanocomposite coatings with healable, superhydrophobic, and contaminant-resistant properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 48101–48108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pant, R.; Singha, S.; Bandyopadhyay, A.; Khare, K. Investigation of static and dynamic wetting transitions of UV responsive tunable wetting surfaces. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 292, 777–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Zhou, S.; Yang, S.; Wu, L. Fabrication of all-water-based self-repairing superhydrophobic coatings based on UV-responsive microcapsules. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 25, 1035–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Yang, S.; Chen, D.; Li, N.; Xu, Q.; Li, H.; He, J.; Lu, J. A robust absorbent material based on light-responsive superhydrophobic melamine sponge for oil recovery. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 3, 1500683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosario, R.; Gust, D.; Garcia, A.; Hayes, M.; Taraci, J.; Clement, T.; Dailey, J.; Picraux, S. Lotus effect amplifies light-induced contact angle switching. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 12640–12642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Liu, D.; Ma, X.; Fang, X.; Jiang, L. Enthalpy-driven three-state switching of a superhydrophilic/superhydrophobic surface. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 3989–3991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Jia, J.; Zhao, Y.; Lv, K.; Wang, C. Transparent smart surface with pH-induced wettability transition between superhydrophobicity and underwater superoleophobicity. Mater. Des. 2017, 135, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, L.; Li, J.; Guo, Z. Advances in the theory of superhydrophobic surfaces. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 20112–20127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassie, A.; Baxter, S. Wettability of porous surfaces. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1944, 40, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescher, D.; Thiele, T.; Ruhmann, R.; Schulz, G. Synthesis of liquid-crystalline poly(meth)acrylates with 4-trifluoromethoxy-azobenzene mesogenic side-groups. J. Fluor. Chem. 1995, 74, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Zhou, S.; Du, B.; Luo, R. Preparation of the temperature-responsive superhydrophobic paper with high stability. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 16016–16028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, B.; Chen, F.; Luo, R.; Li, H.; Zhou, S.; Liu, S.; Hu, J. Superhydrophobic surfaces with pH-induced switchable wettability for oil−water separation. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 16508–16516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Zhou, S.; Du, B.; Luo, R. Preparation of superhydrophobic paper with double-size silica particles modified by amino and epoxy groups. AIP Adv. 2021, 11, 025127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Serizawa, T.; Komiyama, M. Binding analysis of peptides that recognize preferentially cis-azobenzene groups of synthetic polymers. J. Pept. Sci. 2011, 17, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, G.; Pichardo, J.; Chen, G. Reversible photo/thermo responsive structured polymer surfaces modified with a spirobenzopyran-containing copolymer for tunable wettability. Analyst 2010, 135, 2303–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Zhou, S.; Du, B.; Luo, R. A study on the stability of superhydrophobic paper reinforced by amino-assisted modified PHFMA-PTSPM polymer. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 105301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Jia, S.; Zhang, J.; Tian, L.; Chen, H.; Wang, M. Preparation of superhydrophobic surfaces on cotton textiles. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2008, 9, 035008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| HFMA | TSPM | PAPAE | HEMA | Water Contact Angle | Responsiveness | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample 1 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 135.5 ± 2.8° | × |
| Sample 2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 140.6 ± 1.9° | √ |
| Sample 3 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 156.6 ± 2.1° | √ |
| Sample 4 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 156.8 ± 2.3° | √ |
| HFMA | TSPM | PAPAE | HEMA | Water Contact Angle | Water Solubility | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample 1 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 158.5 ± 1.6° | × |
| Sample 2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 156.3 ± 1.7° | √ |
| Sample 4 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 139 ± 2.6° | √ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, S.; Zuo, Y. Development of Photoresponsive Water-Soluble Superhydrophobic Coatings and Properties of the Modified Paper. Polymers 2025, 17, 2615. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17192615
Jiang S, Zuo Y. Development of Photoresponsive Water-Soluble Superhydrophobic Coatings and Properties of the Modified Paper. Polymers. 2025; 17(19):2615. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17192615
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Shangjie, and Yonghui Zuo. 2025. "Development of Photoresponsive Water-Soluble Superhydrophobic Coatings and Properties of the Modified Paper" Polymers 17, no. 19: 2615. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17192615
APA StyleJiang, S., & Zuo, Y. (2025). Development of Photoresponsive Water-Soluble Superhydrophobic Coatings and Properties of the Modified Paper. Polymers, 17(19), 2615. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17192615







