Preparation and Adsorption Properties of Maleic Anhydride-Modified Cellulose Nanofibers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
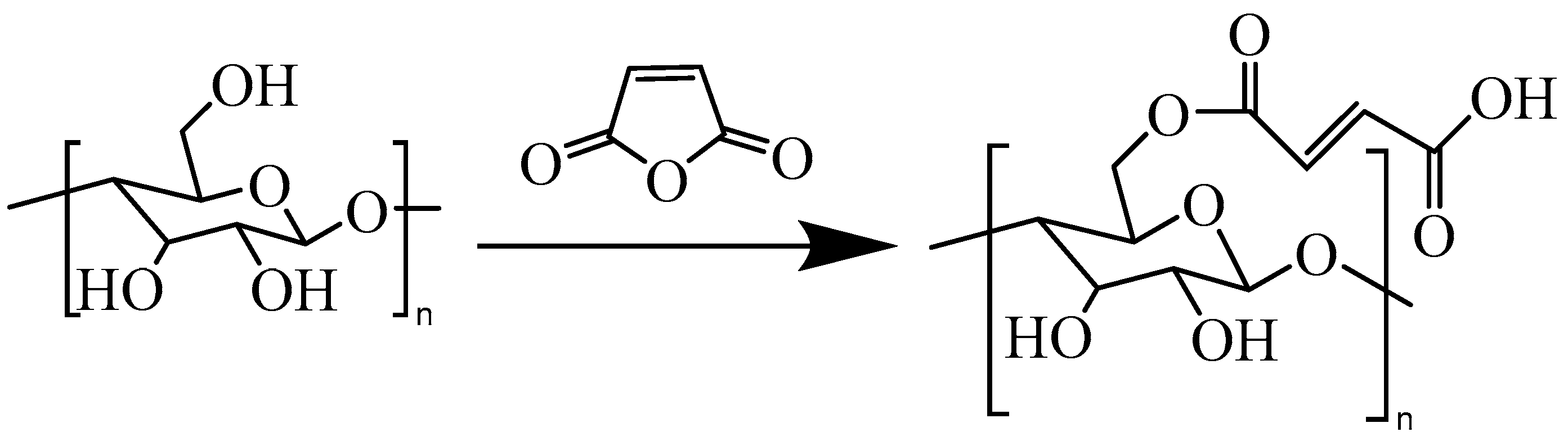
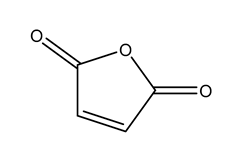
2.2. Esterification Modification of CNF
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Determination of Degree of Substitution
2.5. Determination of Adsorption Performance
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemical Analyses
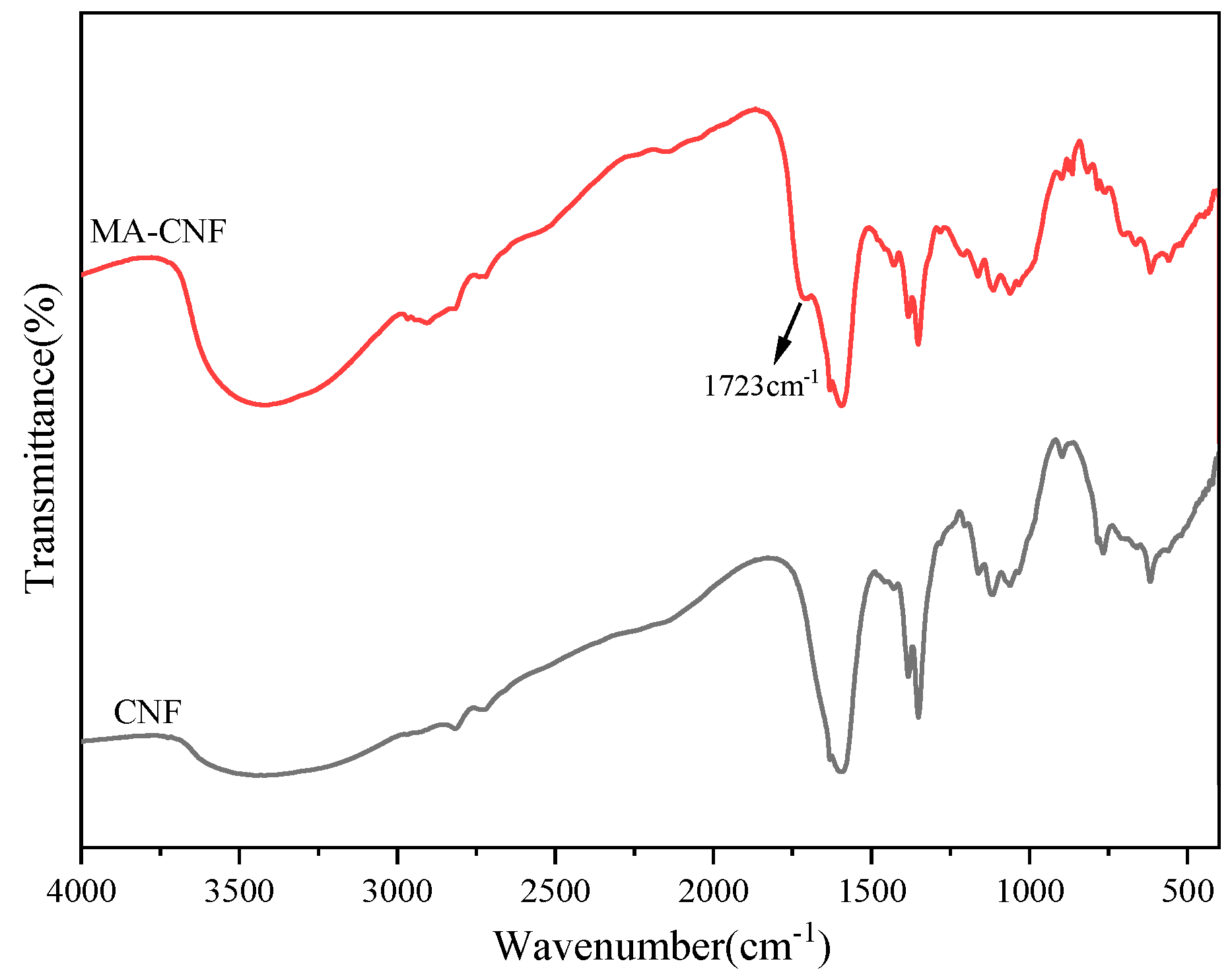
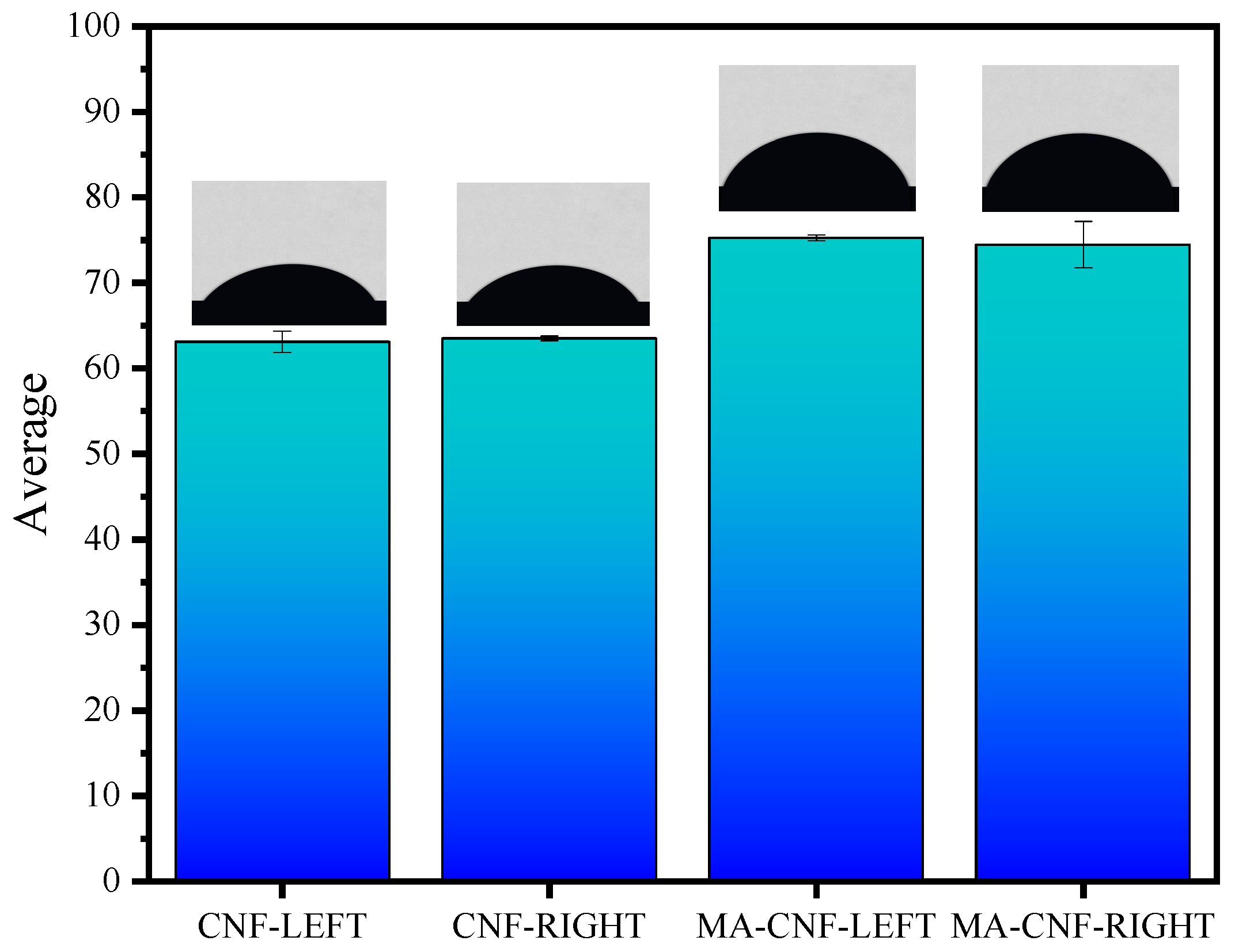
3.2. Characteristics of Structural Properties for MA-CNF
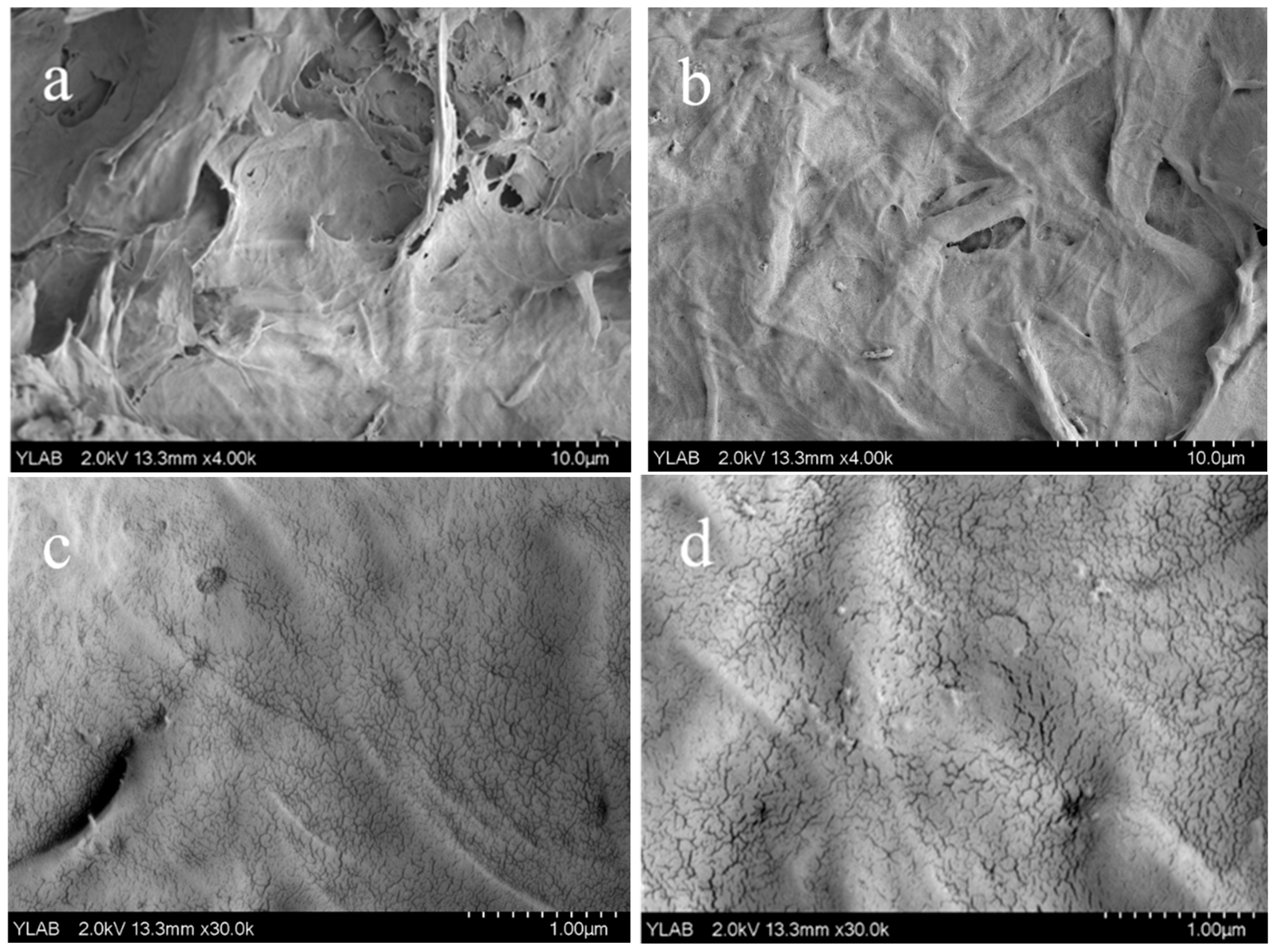
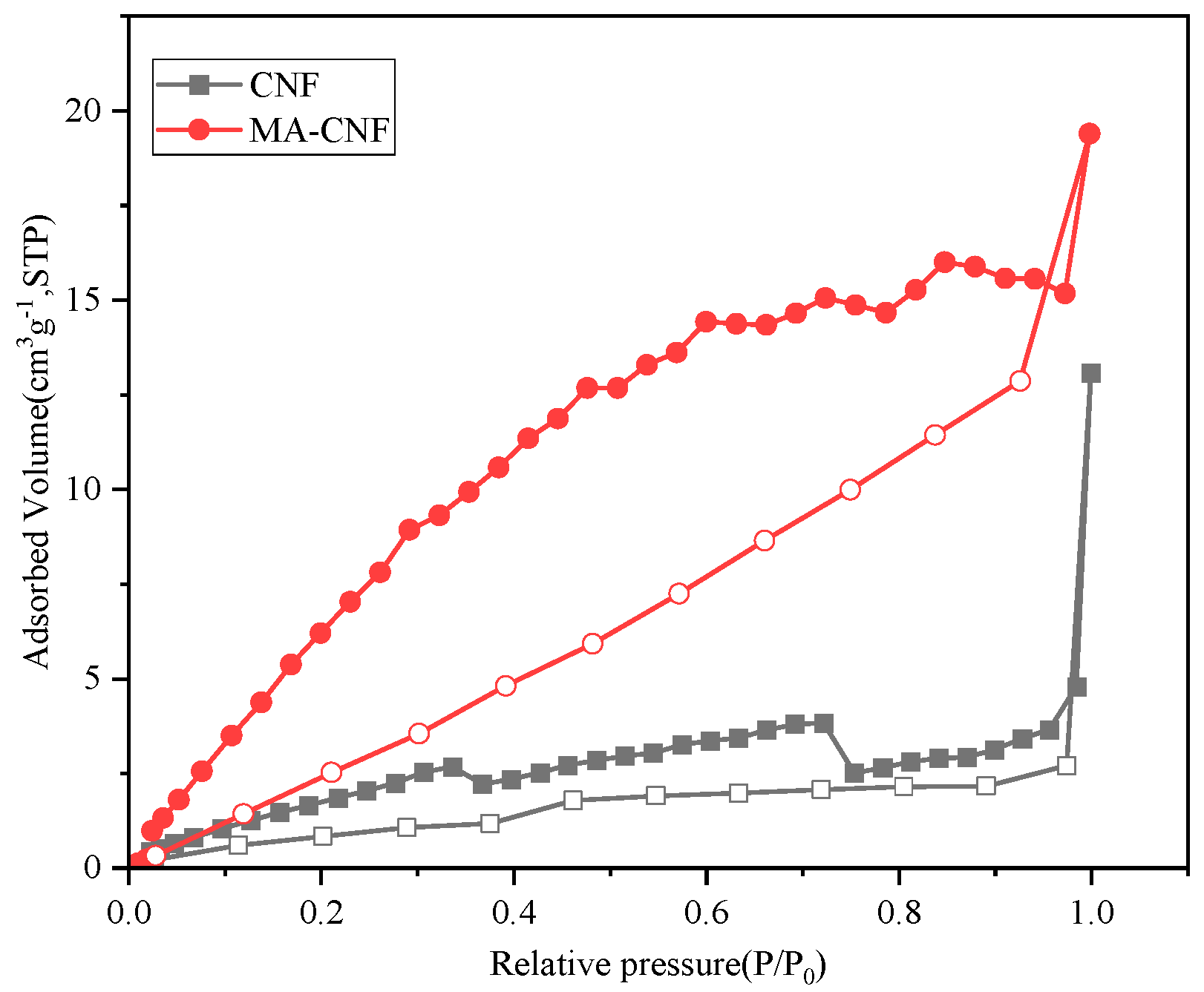
3.3. Characterization and Adsorption Performance Tests
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CNFs | Cellulose nanofibers |
| MA-CNFs | Maleic anhydride-modified cellulose nanofibers |
| MA | Maleic anhydride |
| FA | Folic acid |
| VEA | Vitamin E acetate |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy |
| 1H NMR | Proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
| WCA | Water contact angle |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| BET | Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) method. |
References
- Cho, H.Y.; Lee, T.; Yoon, J.H.; Han, Z.L.; Rabie, H.; Lee, K.B.; Su, W.W.; Choi, J.W. Magnetic Oleosome as a Functional Lipophilic Drug Carrier for Cancer Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 9301–9309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, S.; Thakur, N.; Varshney, N.; Jha, H.C.; Sarma, T.K. Chromatin inspired bio-condensation between biomass DNA and guanosine monophosphate produces all-nucleic hydrogel as a hydrotropic drug carrier. Commun. Chem. 2024, 7, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Hernández, D.; Juárez-Osornio, C.; Izquierdo-Sánchez, V.; Figueroa-Rodríguez, P.A.; Organista-Nava, J.; Gómez-Gómez, Y.; Medina-Lipomics, L.A. A Potential Carrier for the Intravenous Delivery of Lipophilic and Hydrophilic Drugs. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.Q.; Li, R.L.; Parseh, B.; Du, G. Prospects and challenges of anticancer agents’ delivery via chitosan-based drug carriers to combat breast cancer: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 268, 118192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.X.; Teramoto, H. Characterization of Azido-Incorporated Bombyx mori Silk Fibroin as a Drug Carrier Material. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2025, 11, 2783–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.X.; Du, H.S.; Yang, X.G.; Si, C.L. Recent Strategies in Preparation of Cellulose Nanocrystals and Cellulose Nanofibrils Derived from Raw Cellulose Materials. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2018, 2018, 7923068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza Lima, M.M.; Borsali, R. Rodlike cellulose microcrystals: Structure, properties, and applications. Macro Mol. Rapid Commun. 2004, 25, 771–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okubo, H.; Nakae, R.; Iba, D.; Yamada, K.; Hashiba, H.; Nakano, K.; Sato, K.; Sasaki, S. Tribological properties of 100% cellulose nanofiber (CNF) molding under dry- and boundary lubrication-conditions at CNF/steel contacts. Cellulose 2023, 30, 6887–6905. [Google Scholar]
- Kurita, H.; Ishigami, R.; Wu, C.; Narita, F. Mechanical properties of mechanically-defibrated cellulose nanofiber reinforced epoxy resin matrix composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2021, 55, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.Z.; Yashiro, T.; Okubo, K.; Fujii, T. Effect of cellulose nano fiber (CNF) on fatigue performance of carbon fiber fabric composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2015, 76, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, E.; Arrebola, R.I.; Villegas, I.B.; Gutierrez, M.S.; Robles, J.D.; Rodriguez, A. Industrial application of orange tree nanocellulose as papermaking reinforcement agent. Cellulose 2020, 27, 10781–10797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhu, X.Y.; Xu, C.Q.; Yu, J.; Fan, Y.M. A tough, reversible and highly sensitive humidity actuator based on cellulose nanofiber films by intercalation modulated plasticization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 335, 122108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagyu, H.; Saito, T.; Isogai, A.; Koga, H.; Nogi, M. Chemical Modification of Cellulose Nanofibers for the Production of Highly Thermal Resistant and Optically Transparent Nanopaper for Paper Devices. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 22012–22017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloulou, F.; Boufi, S.; Labidi, J. Modified cellulose fibres for adsorption of organic compound in aqueous solution. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 52, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.X.; Odelius, K.; Rajarao, G.K.; Hakkarainen, M. Microwave carbonized cellulose for trace pharmaceutical adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 346, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komal; Gupta, K.; Nidhi; Kaushik, A.; Singhal, S. Amelioration of adsorptive efficacy by synergistic assemblage of functionalized graphene oxide with esterified cellulose nanofibers for mitigation of pharmaceutical waste. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopakumar, D.A.; Pasquini, D.; Henrique, M.A.; de Morais, L.C.; Grohens, Y.; Thomas, S. Meldrum’s Acid Modi highly Cellulose Nano highly Based Polyvinylidene Fluoride Micro highly filtration Membrane for Dye Water Treatment and Nanoparticle Removal. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 2026–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskhan, A.; Banat, F. Removal of Oil from Water by Calcium Alginate Hydrogel Modified with Maleic Anhydride. J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 2901–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.M.; Jin, Q.; Hu, X.Y.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Ma, T. Heavy metal ions and organic dyes removal from water by cellulose modified with maleic anhydride. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 5019–5029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, K.X.; Zhang, D.; Pan, B.Q.; Lim, K.H.; Abitbol, T.; Wang, W.J.; Yang, X. Sustainable route to prepare functional lignin-containing cellulose nanofibrils. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 473, 145189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cichosz, S.; Masek, A.; Wolski, K.; Zaborski, M. Universal approach of cellulose fibres chemical modification result analysis via commonly used techniques. Polym. Bull. 2019, 76, 2147–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.F.; Li, H.; Zhong, X.; Li, X.D.; Gibril, M.E.; Zhang, Y.; Han, K.Q.; Yu, M.H. Study on the chemical modification of Cellulose in Ionic Liquid with Maleic Anhydride. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 581–582, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modupe, O.; Maurras, J.B.; Diosady, L.L. A spectrophotometric method for determining the amount of folic acid in fortified salt. J. Agric. Food Res. 2020, 2, 100060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridrihsone, V.; Zoldners, J.; Skute, M.; Andze, L.; Filipova, I. Cellulose Modification with Maleic Anhydride. Mater. Sci. Forum 2022, 1071, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segal, L.; Creely, J.J.; Martin, A.E., Jr.; Conrad, C.M. An empirical method for estimating the degree of crystallinity of native cellulose using the X-ray diffractometer. Text. Res. J. 1959, 29, 786–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.Y.; Sun, X.; Sun, H.; Zhu, Y.L.; Zhu, J.Y.; Zhu, P.H.; Yu, Z.Y.; Ye, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.H.; Jiang, F. Effect of hornification on the isolation of anionic cellulose nanofibrils from Kraft pulp via maleic anhydride esterification. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 333, 121961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadakkekara, G.J.; Thomas, S.; Nai, C.P.R. Maleic Acid Modified Cellulose for Scavenging Lead from Water. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 129, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.L.; Lang, J.Y.; Lan, P.; Yang, H.Y.; Yang, J.X.; Wu, X.Y.; Zhang, H. Evalution of surface activity of hydrophobic modified nanocrystalline cellulose. Cellulose 2020, 27, 9299–9309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.Z.; Guo, Y.Q.; Niu, Q.Y.; Fang, H.; Zhang, L.S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.Z.; Zhou, L.M. Effects of chitin nanofibers on the microstructure and properties of cellulose nanofibers/chitin nanofibers composite aerogels. Cellulose 2018, 25, 4591–4602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; You, D.S.; Guo, D.Y.; Zhuang, X.C.; Yuan, T.; Qiu, D. Preparation and Properties of Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose Microspheres by Dropping Method. ACS Omega 2025, 10, 4754–4762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.D.; Chen, W.M.; Jiang, F.Y.; Mo, M.M.; Bi, Y.G.; Kong, F.S. Synthesis, characterization and in vitro digestion of folate conjugated chitosan-loaded proanthocyanidins nanoparticles. Food Res. Int. 2023, 163, 112141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudiyanti, D.; Hidayati, S.N.; Siahaan, P.; Ngadiwiyana, N.; Nur, A.; Sari, R.I.; Amalia, I.R.; Christa, S.M.; Patrechia, A.C.; Maharani, A.E. Impact of cholesterol in encapsulated vitamin E acetate within cocoliposomes. Open Chem. 2024, 22, 20240122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marnani, M.B.; Oftadeh, M.; Sohrabi, N. Adsorption of folic acid molecule on diphenylalanine peptide nanohole as a drug delivery in cancer treatment: A molecular dynamics simulation study. J. Mol. Model. 2023, 29, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
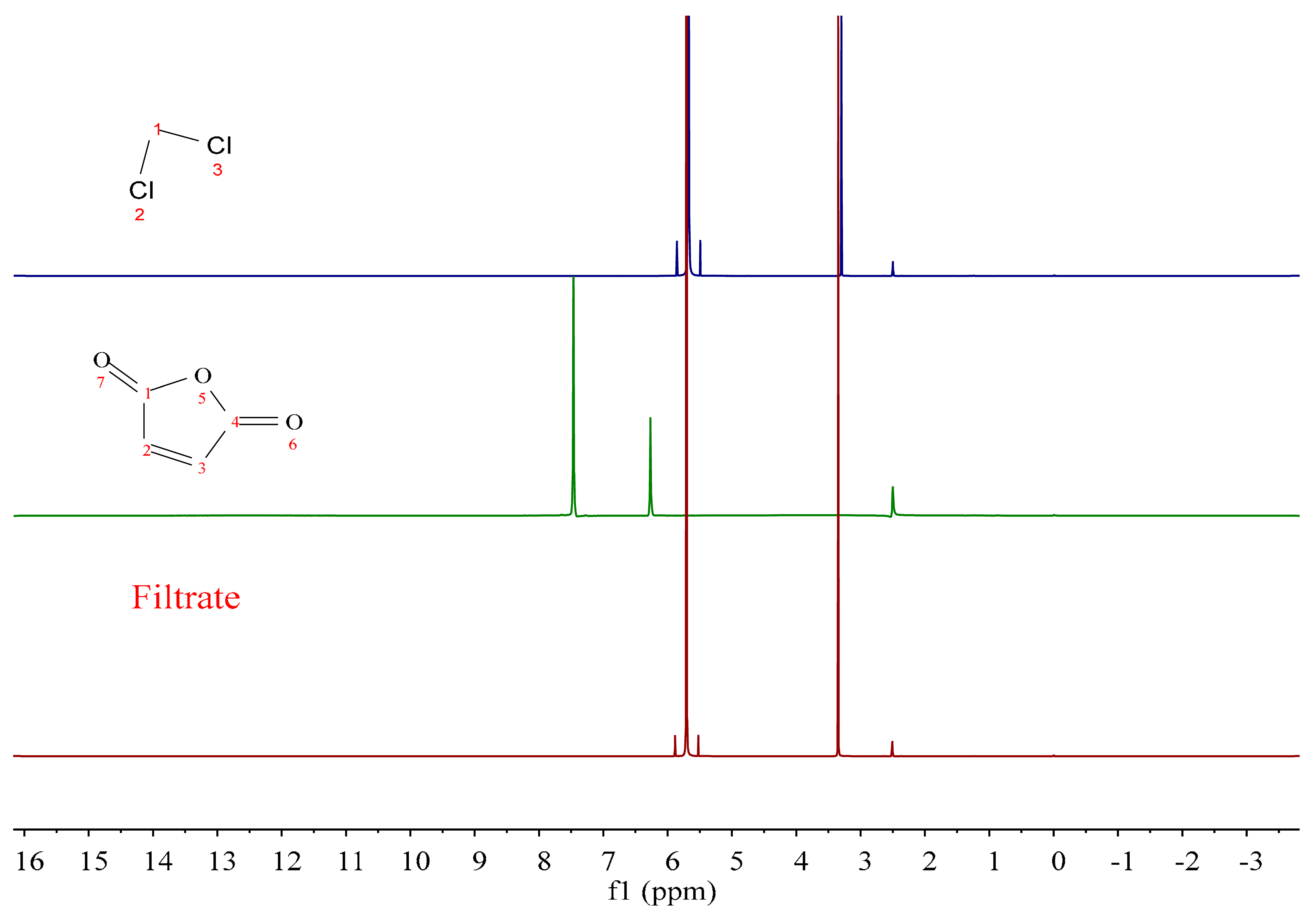





| Substance | Chemical Shift Range (ppm) | Peak Assignment |
|---|---|---|
 | ~2.49–2.51 | DMSO-d6 |
| ~3.70–3.72 | HDO | |
| ~5.3–5.5 | -CH2 | |
 | ~2.50 | DMSO-d6 |
| ~3.30–3.50 ~6.2–6.5 ~7.45–7.66 | HDO -CH=CH- Hydrogens of unsaturated structures in impurities (peak of hydrolysis product maleic acid) |
| Sample | SBET (m2·g−1) | Pore Volume (cm3·g−1) |
|---|---|---|
| CNF | 5.03 | 0.007 |
| MA-CNF | 26.29 | 0.022 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, J.-N.; Qiu, D.; Yuan, T.; Li, Y.; Huang, H.; Wang, L.-H.; Wang, Y.-J.; Wang, R.; Jin, C.-Z. Preparation and Adsorption Properties of Maleic Anhydride-Modified Cellulose Nanofibers. Polymers 2025, 17, 2586. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17192586
Meng J-N, Qiu D, Yuan T, Li Y, Huang H, Wang L-H, Wang Y-J, Wang R, Jin C-Z. Preparation and Adsorption Properties of Maleic Anhydride-Modified Cellulose Nanofibers. Polymers. 2025; 17(19):2586. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17192586
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Jia-Ning, Dan Qiu, Tao Yuan, Ya Li, Huang Huang, Ling-Hui Wang, Ya-Juan Wang, Rui Wang, and Chang-Zi Jin. 2025. "Preparation and Adsorption Properties of Maleic Anhydride-Modified Cellulose Nanofibers" Polymers 17, no. 19: 2586. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17192586
APA StyleMeng, J.-N., Qiu, D., Yuan, T., Li, Y., Huang, H., Wang, L.-H., Wang, Y.-J., Wang, R., & Jin, C.-Z. (2025). Preparation and Adsorption Properties of Maleic Anhydride-Modified Cellulose Nanofibers. Polymers, 17(19), 2586. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17192586







