Synthetic Electrospun Fiber Matrix in the Management of Acute Wounds Following Excision of Hidradenitis Suppurativa Lesions: A Prospective Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
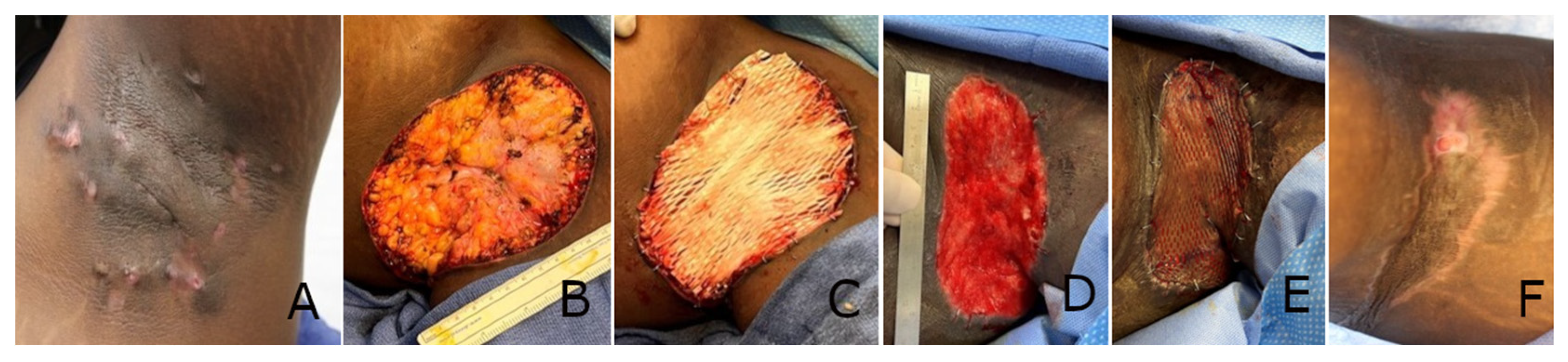
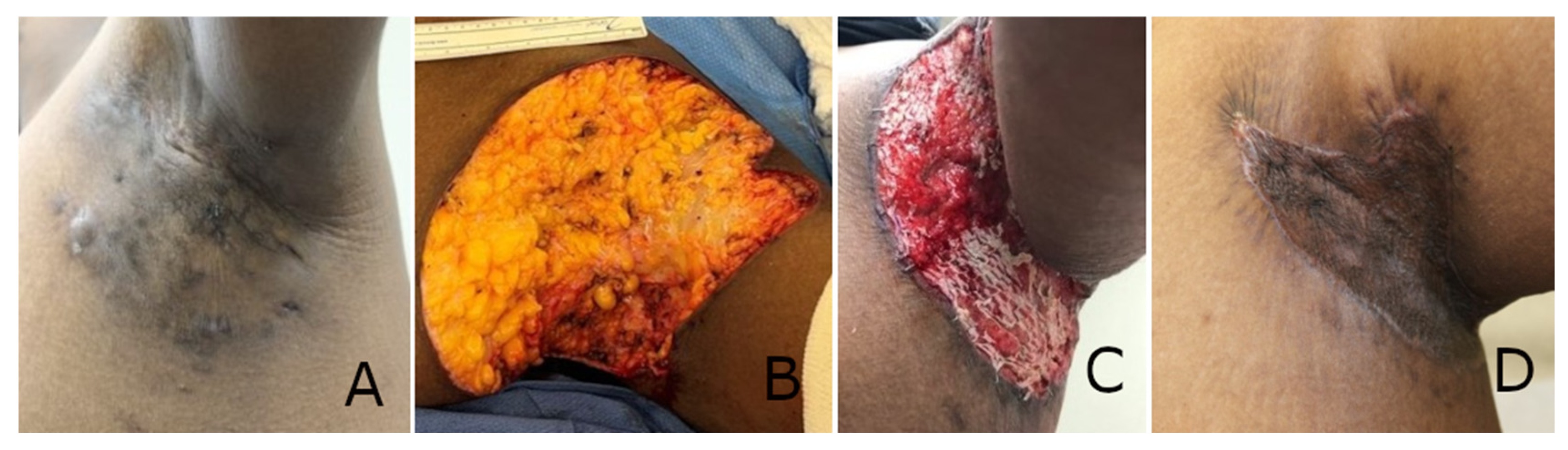
3. Results
3.1. Patient Demographics
3.2. Clinical Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| ECM | Extracellular Matrix |
| HIPPA | Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act |
| HS | Hidradenitis Suppurativa |
| IRB | Institutional Review Board |
| NPWT | Negative Pressure Wound Therapy |
| OR | Operating Room |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| SEFM | Synthetic Electrospun Fiber Matrix |
| STSG | Split-Thickness Skin Graft |
| USP | United States Pharmacopeia |
References
- Beshara, M.A. Hidradenitis suppurativa: A clinician’s tool for early diagnosis and treatment. Adv. Skin Wound Care 2010, 23, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amat-Samaranch, V.; Agut-Busquet, E.; Vilarrasa, E.; Puig, L. New perspectives on the treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa. Thera. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2021, 12, 20406223211055920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelucci, A.; Janowska, A.; Granieri, G.; Margiotta, F.M.; Morganti, R.; Romanelli, M.; Dini, V. Advanced wound management approaches in Hidradenitis Suppurativa postsurgical lesions. Health Sci. Rep. 2023, 6, e1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovadja, Z.N.; Schuit, M.M.; van der Horst, C.M.A.M.; Lapid, O. Inter- and intrarater reliability of Hurley staging for hidradenitis suppurativa. Br. J. Dermatol. 2019, 181, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, R.; Karagaiah, P.; Patil, A.; Farnbach, K.; Ortega-Loayza, A.G.; Tzellos, T.; Szepietowski, J.C.; Giulini, M.; Schepler, H.; Grabbe, S.; et al. Surgical treatment in hidradenitis suppurativa. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vellaichamy, G.; Braunberger, T.L.; Nahhas, A.F.; Hamzavi, I.H. Surgical procedures for hidradenitis suppurativa. Cutis 2018, 102, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Burney, R.E. 35-year experience with surgical treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa. World J. Surg. 2017, 41, 2723–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngaage, L.M.; Wu, Y.; Ge, S.; Gebran, S.; Liang, F.; Rada, E.M.; Nam, A.J.; Silverman, R.P.; Rasko, Y.M. Factors influencing the local cure rate of hidradenitis suppurativa following wide local excision. Int. Wound J. 2019, 17, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.K.; Kapoor, K.M.; Singh, G. Reconstruction in extensive axillary Hidradenitis suppurativa with local fasciocutaneous V-Y advancement flaps. Indian J. Plast. Surg. 2020, 39, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshammary, R.H.; Allaha, E.H.H.; Fakhruddin, M.S.; Bakhiet, M. Use of multiple fasciocutaneous flaps for the management of extensive hidradenitis suppurativa. BMJ Case Rep. 2023, 16, e255037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredini, M.; Garbarino, F.; Bigi, L.; Pallacani, G.; Magnoni, C. Hidradenitis suppurativa: Surgical and postsurgical managment. Skin Appendage Disord. 2021, 6, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groka, R. Preparation for a successful skin grafting. In Skin Grafts for Successful Wound Closure; Gore, M., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, D.K.; Louis, M.R.; Gimenez, A.; Reece, E.M. The basics of Integra dermal regeneration template and its expanding clinical applications. Semin. Plast. Surg. 2019, 33, 18–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, S.A.; Pham, T.N. Use of dermal regenerative templates for burns. J. Burn. Care Res. 2023, 44, S19–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taupin, P.; Gandhi, A.; Saini, S. Integra dermal regeneration template: From design to clinical use. Cureus 2023, 15, e38608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajaram, R.; Zhang, M.; Premaratne, G.; Ng, S. Novosorb BTM—History, production and application in challenging wounds. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2024, 12, 1450973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, S.R.; Wolter, K.G.; Yeun, J.C. Infectious complications associated with the use of Integra: A systematic review of the literature. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2020, 8, e2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martini, C.J.; Burgess, B.; Ghodasra, J.H. Treatment of traumatic crush injury using a synthetic hybrid-scale fiber matrix in conjunction with split-thickness skin graft. Foot Ankle Surg. 2022, 2, 100112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, L.; Orsi, C.; Okeoke, B.; Moudy, P.; Critelli, P.; Norwood, S.; Matthews, M.; Kim, P.; MacEwan, M.; Sallade, E. Synergistic clinical application of synthetic electrospun fiber wound matrix in the management of a complex traumatic wound: Degloving left groin and thigh auger injury. Wounds 2024, 36, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herron, K. Treatment of a complex pressure ulcer using a synthetic hybrid-scale fiber matrix. Cureus 2021, 13, e14515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacEwan, M.R.; MacEwan, S.; Kovacs, T.R.; Batts, J. What makes the optimal wound healing material? A review of current science and introduction of a synthetic nanofabricated wound care scaffold. Cureus 2017, 9, e1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacEwan, M.; Jeng, L.; Kovács, T.; Sallade, E. Clinical application of bioresorbable, synthetic, electrospun matrix in wound healing. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regulski, M.J.; MacEwan, M.R. Implantable nanomedical scaffold facilitates healing of chronic lower extremity wounds. Wounds 2018, 30, E77–E80. [Google Scholar]
- Husain, K.; Malik, A.; Kirchens, J.; Choi, G. A prospective, blinded, randomized controlled clinical trial evaluating the effect of the synthetic electrospun fiber matrix in the treatment of chronic diabetic foot ulcers. Foot Ankle Surg. 2024, 4, 100362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieczorek, M.; Walecka, I. Hidradenitis suppurativa—Known and unknown disease. Reumatologia 2018, 56, 337–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohorst, J.J.; Baum, C.R.; Otley, C.C.; Roenigk, R.K.; Schenck, L.A.; Pemberton, J.H.; Dozois, E.J.; Tran, N.V.; Senchenkov, A.; Davis, M.D.P. Surgical management of hidradenitis suppurativa: Outcomes of 590 consecutive patients. Dermatol. Surg. 2016, 42, 1030–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chawla, S.; Toale, C.; Morris, M.; Tobin, A.M.; Kavanagh, D. Surgical management of hidradenitis suppurativa: A narrative review. J. Clin. Aesthet. Dermatol. 2022, 15, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Torabi, R.; Hui, A.; Barton, J.; Lau, F. Tumescent-based radical excision of hidradenitis suppurativa: Safe, fast, and efficacious. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2018, 227, e144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkin, K.; Daveluy, S.; Avanaki, K.M. Hidradenitis suppurativa: Current understanding, diagnostic and surgical challenges, and developments in ultrasound application. Skin Res. Technol. 2020, 26, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, J.; Chai, K.; Rosa, N.; Feffell, L.; Jemec, B. Hidradenitis suppurativa: A review of post-operative outcomes. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2021, 74, 644–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallade, E.; Grimes, D.; Jeng, L.; MacEwan, M.R. Antimicrobial effectiveness testing of resorbable electrospun fiber matrix per United States Pharmacopeia (USP) <51>. Cureus 2023, 15, e50055. [Google Scholar]
- Enoch, S.; Leaper, D.J. Basic science of wound healing. Surgery 2008, 26, 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Kandiyali, R.; Thom, H.; Young, A.E.; Greenwood, R.; Welton, N.J. Cost-effectiveness and value of information analysis of a low-friction environment following skin graft in patients with burn injury. Pilot Feasibility Stud. 2020, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabdulkareem, M.; Berkane, Y.; Le Bras, E.; Rousson, E.; Chrelias, T.; Beaufils, T.; Leclere, F.-M.; Watier, E.; Bertheuil, N. Axillary hidradenitis suppurativa: A comparison between two perforator flap reconstructive approaches after radical surgical management. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2023, 11, e5301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, L.; Schar, A.; Matthews, M.; Kim, P.J.; Thompson, C.; Williams, N.; Stutsman, M. Synthetic hybrid-scale fiber matrix in the trauma and acute care surgical practice. Wounds 2021, 33, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Chen, B.P.; Soleas, I.M.; Ferko, N.C.; Caeron, C.G.; Hinoul, P. Prolonged operative duration increases risk of surgical site infections: A systematic review. Surg. Infect. 2017, 18, 722–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madsen, H.J.; Gillette, R.A.; Colborn, K.L.; Henderson, W.G.; Dyas, A.R.; Bronsert, M.R.; Lambert-Kerzner, A.; Meguid, R.A. The association between obesity and postoperative outcomes in a broad surgical population: A 7-year American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement analysis. Surgery 2023, 173, 1213–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barillo, D.J.; Barillo, A.R.; Korn, S.; Lam, K.; Attar, P.S. The antimicrobial spectrum of Xeroform®. Burns 2017, 43, 1189–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Lim, P.; Stanley, E.; Lee, G.; Lin, S.; Neoh, D.; Liew, J.; Ng, S.K. Experience with Novosorb® Biodegradable Temporizing Matrix in reconstruction of complex wounds. ANZ J. Surg. 2021, 91, 1744–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.S.; Wells, M.; Ascha, M.; Gatherwright, J.; Chepla, K. Performance of biodegradable temporizing matrix vs collage-chondroitin silicone bilayer dermal regeneration substitutes in soft tissue wound healing: A retrospective analysis. Wounds 2022, 34, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, L.; Matthews, M.; Kim, P.J. A synthetic hybrid-scale fiber matrix for complex surgical wounds: Consensus guidelines. Wounds 2023, 35, E160–E168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Patient Demographic Information | |
|---|---|
| Gender (n, %) | |
| Male | 4 (50%) |
| Female | 4 (50%) |
| Patient age, years (mean ± SD 1) | |
| 32.6 ± 7.9 | |
| Race (n, %) | |
| African American | 8 (100%) |
| Body Mass Index (mean ± SD 1) | |
| 34.6 ± 3.8 | |
| Post-excision wound surface area, cm2 | |
| Mean ± SD 1 | 174.8 ± 139.6 |
| Range | 18–551 |
| Wound location (n, %) | |
| Axillary | 6 (28%) |
| Vulvar | 4 (19%) |
| Inguinal | 3 (14%) |
| Perianal | 3 (14%) |
| Scrotal | 1 (5%) |
| Perineal | 1 (5%) |
| Abdomincal | 1 (5%) |
| Mons | 1 (5%) |
| Scalp | 1 (5%) |
| Primary Outcome | |
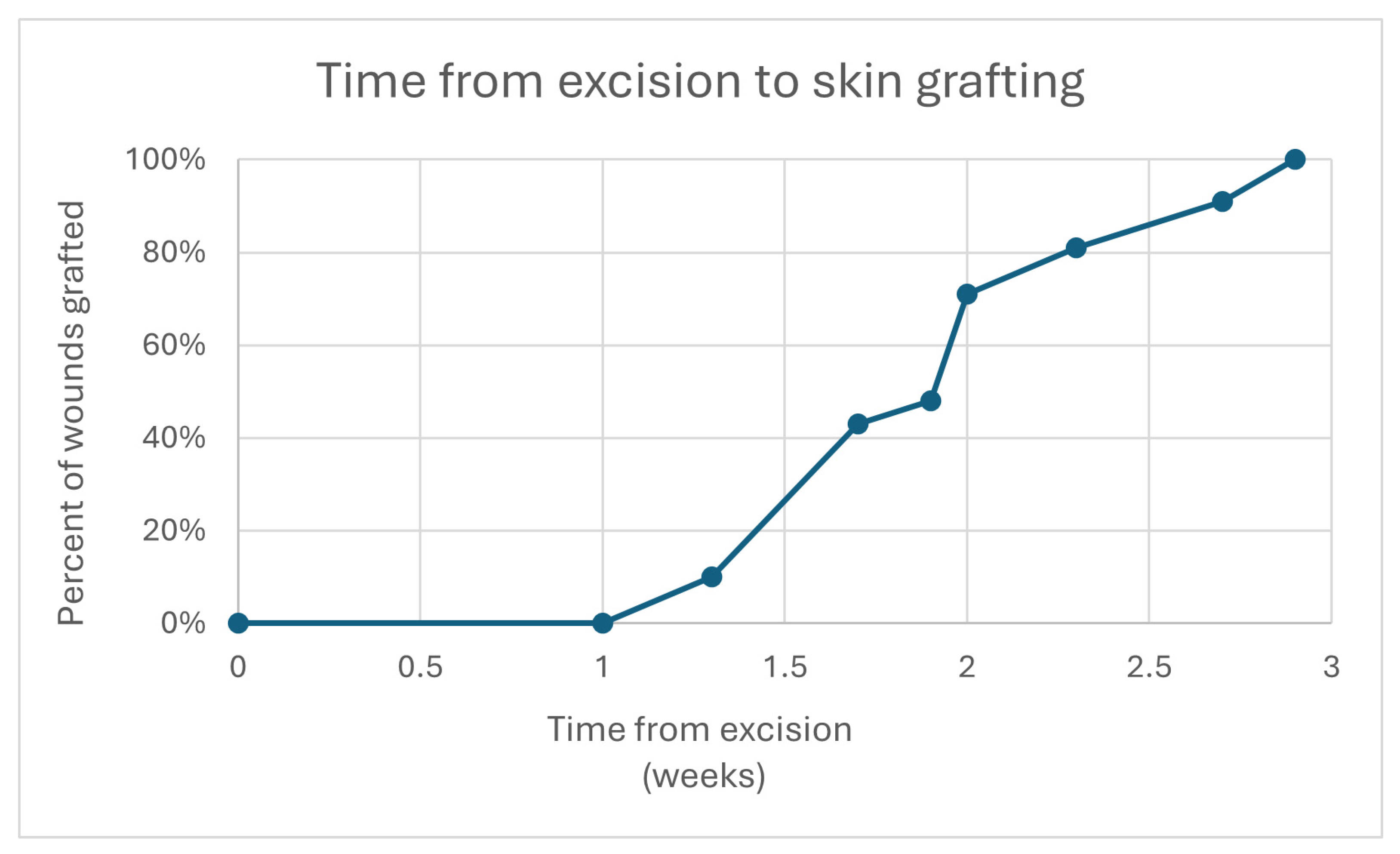
| Time to STSG 1 (days) (mean ± SD 2) | |
| 14 ± 3.2 | |
| Secondary Outcomes | |
| Percent STSG 1 incoporation (mean ± SD 2) | |
| 71% ± 28% | |
| Follow-up time (weeks) | |
| Mean ± SD 2 | 3.3 ± 3.0 |
| Range | 0.7–8.0 |
| Percent STSG 1 incoporation by wound location (mean ± SD 2) | |
| Axillary | 95% ± 11% |
| Vulvar | 76% ± 12% |
| Inguinal | 63% ± 6% |
| Perianal 3 | 40% ± 33% |
| Other 4,5 | 62% ± 33% |
| Complications (infection, bleeding, hematoma) (n, %) | |
| Complications | 0 (0%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Madueke, M.; Lau, F. Synthetic Electrospun Fiber Matrix in the Management of Acute Wounds Following Excision of Hidradenitis Suppurativa Lesions: A Prospective Pilot Study. Polymers 2025, 17, 2563. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17192563
Madueke M, Lau F. Synthetic Electrospun Fiber Matrix in the Management of Acute Wounds Following Excision of Hidradenitis Suppurativa Lesions: A Prospective Pilot Study. Polymers. 2025; 17(19):2563. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17192563
Chicago/Turabian StyleMadueke, Michael, and Frank Lau. 2025. "Synthetic Electrospun Fiber Matrix in the Management of Acute Wounds Following Excision of Hidradenitis Suppurativa Lesions: A Prospective Pilot Study" Polymers 17, no. 19: 2563. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17192563
APA StyleMadueke, M., & Lau, F. (2025). Synthetic Electrospun Fiber Matrix in the Management of Acute Wounds Following Excision of Hidradenitis Suppurativa Lesions: A Prospective Pilot Study. Polymers, 17(19), 2563. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17192563






