Development of an SA/XLG Composite Hydrogel Film for Customized Facial Mask Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Instrumentation
2.3. Preparation of Hydrogels and Crosslinking Solution
2.3.1. Pre-Screening of SA-Based Hydrogels
2.3.2. Preparation of SA-Based Composite Hydrogels
2.3.3. Preparation of Calcium-Based Facial Mist for Ionic Crosslinking
2.4. Flow Behavior Analysis
2.5. Preparation and Characterization of Dried Hydrogel Films
2.5.1. Film Formation and Drying
2.5.2. Tensile Strength Test
2.5.3. Method of ATR-FTIR Spectral Analysis
2.5.4. Application of SA/XLG Hydrogel on 3D Facial Mold
2.6. Physicochemical Characterization of the SA/XLG Composite Hydrogel Film
2.6.1. Solubility and Swelling Behavior
2.6.2. pH Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical Properties of SA-Based Composite Hydrogels
3.1.1. Flow Behavior and Viscosity Analysis
3.1.2. Mechanical Strength and Extensibility
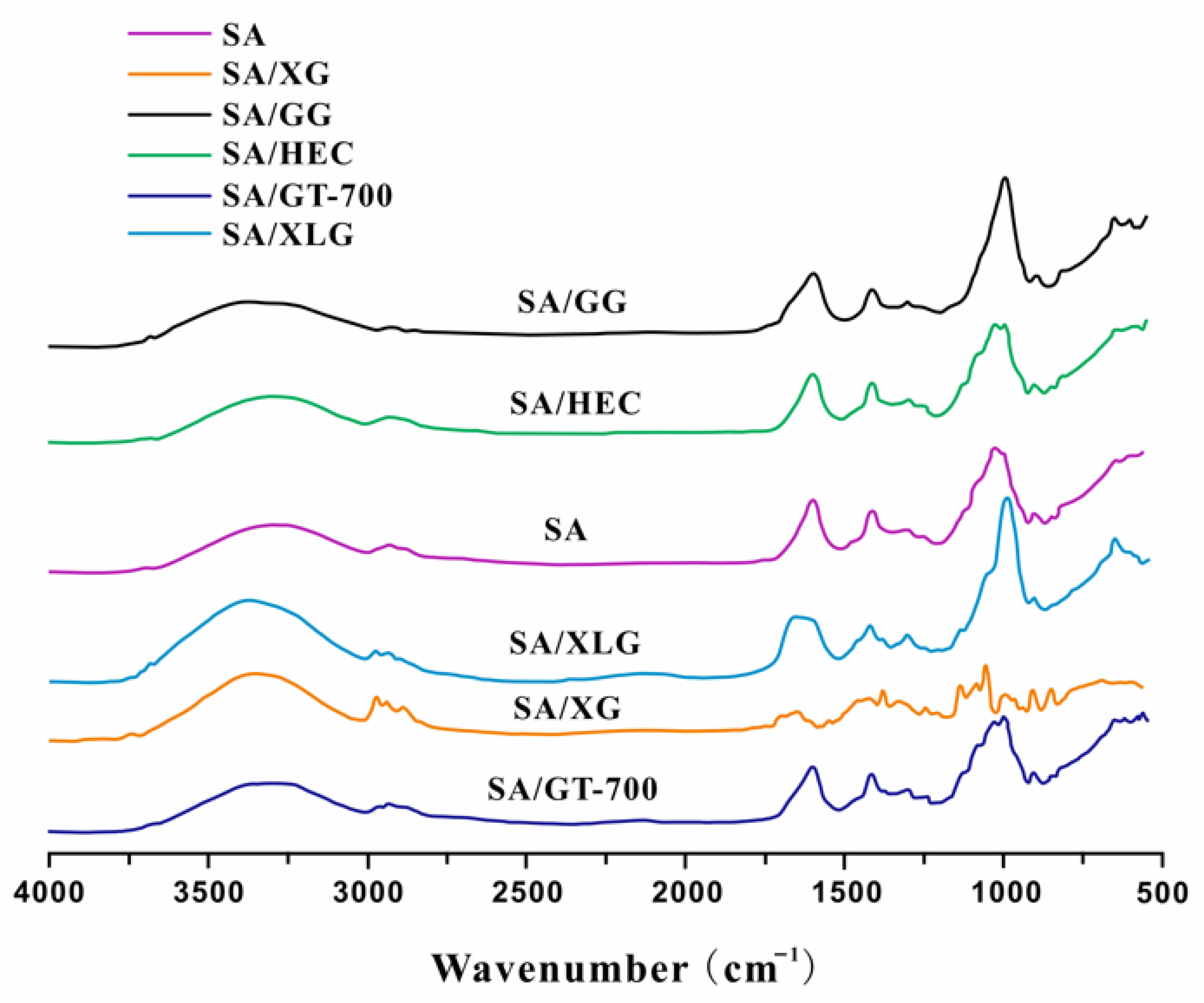
3.1.3. ATR-FTIR Spectral Analysis
3.2. Aqueous Behavior and pH Characteristics of SA/XLG Composite Hydrogel
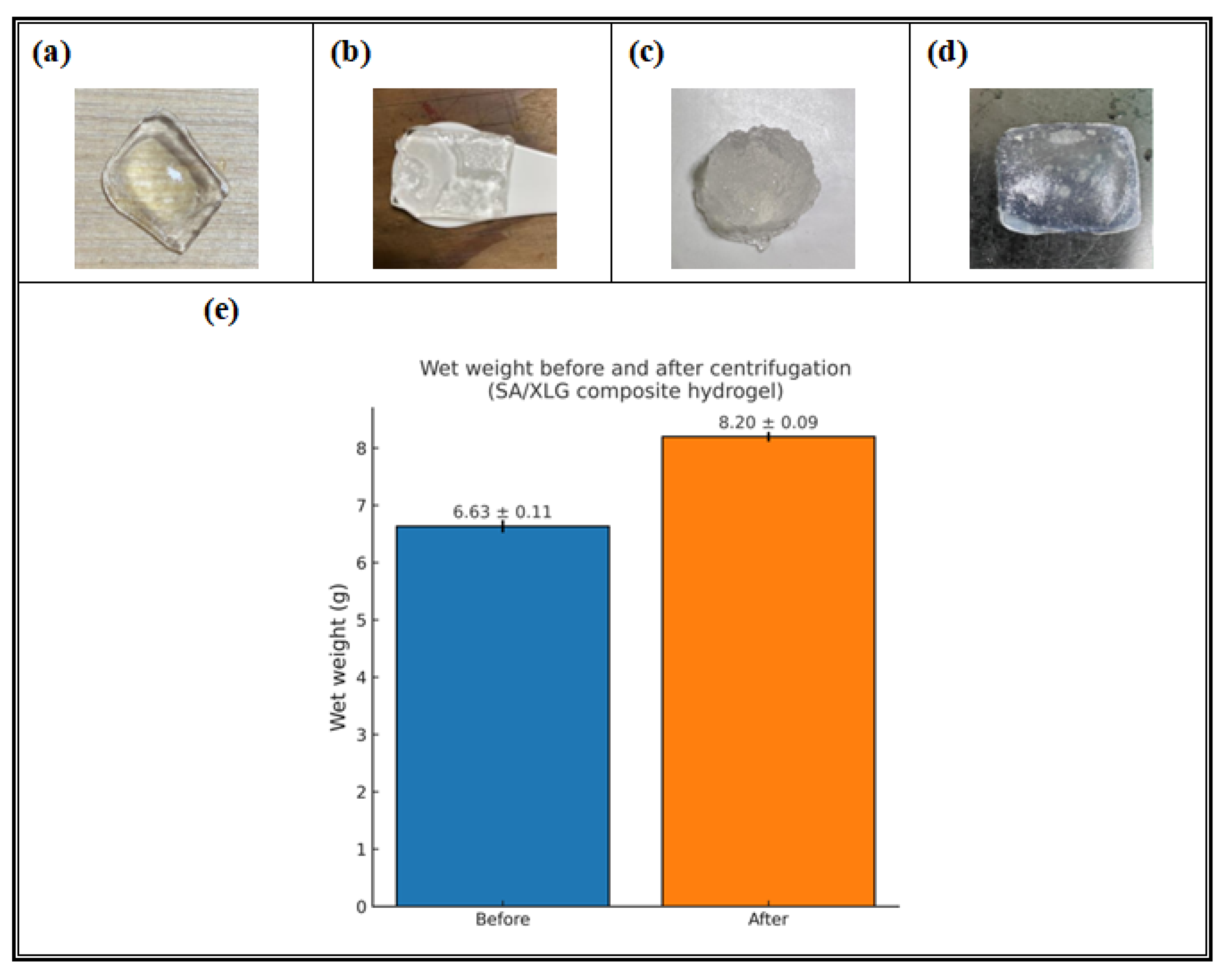
3.2.1. Swelling and Solubility Behavior
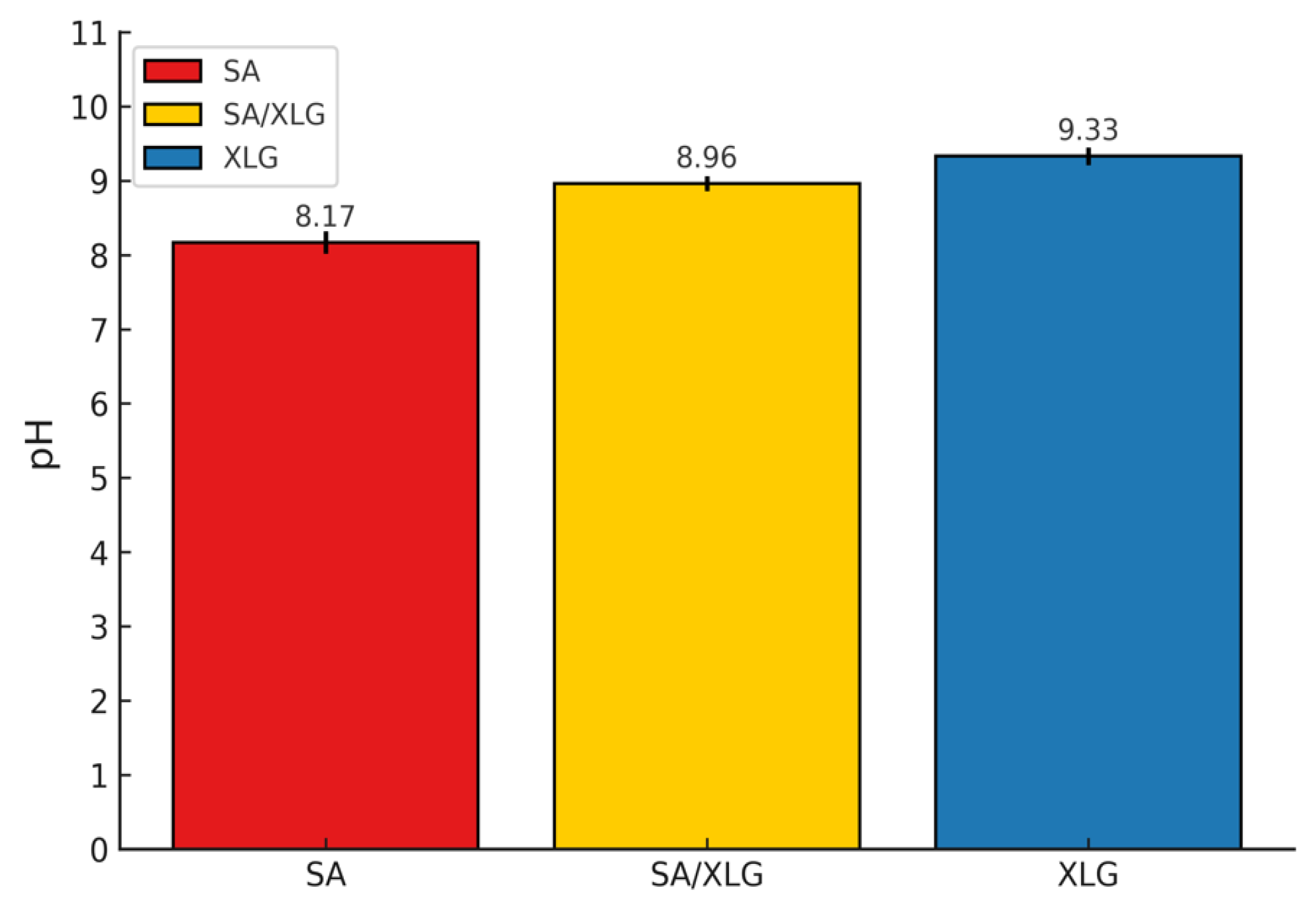
3.2.2. pH Evaluation and Dermatological Implications
3.3. Functional Performance and Application-Oriented Adaptability of SA/XLG Composite Hydrogel
3.3.1. Hydrogel Film Formation and Anatomical Mold Adaptability
3.3.2. Prospective Integration with 3D Printing Technologies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaidi, S.; Bentiss, F.; Jama, C.; Khaya, K.; Belattmania, Z.; Reani, A.; Sabour, B. Isolation and Structural Characterization of Alginates from the Kelp Species Laminaria ochroleuca and Saccorhiza polyschides from the Atlantic Coast of Morocco. Colloids Interfaces 2022, 6, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chèze-Lange, H.; Beunard, D.; Dhulster, P.; Guillochon, D.; Cazé, A.; Morcellet, M.; Saude, N.; Junter, G. Production of microbial alginate in a membrane bioreactor. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2002, 30, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Mooney, D.J. Alginate: Properties and Biomedical Applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 106–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, S.N.; Edgar, K.J. Alginate derivatization: A review of chemistry, properties and applications. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 3279–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemzadeh Pournaki, S.; Santos Aleman, R.; Hasani-Azhdari, S.M.; Marcia Fuentes, J.; Yadav, A.; Moncada, M.L. Current Review: Alginate in the Food Applications. J-Multidiscip. Sci. J. 2024, 7, 281–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Chen, X.; Ji, W.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, W.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Nan, B.; et al. From Lab to Table: Recent Advances in the Application of Sodium Alginate-Based Hydrogel Beads in the Food Industry. Food Res. Int. 2025, 217, 116843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farshidfar, N.; Iravani, S.; Varma, R.S. Alginate-Based Biomaterials in Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Wang, Q.; Xu, W.; Yang, M.; Guo, W.; He, S.; Liu, W. Alginate-Based Hydrogels Mediated Biomedical Applications: A Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 279, 135019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wu, T.; Bu, Y.; Yan, H.; Lin, Q. Fabrication and Biomedical Application of Alginate Composite Hydrogels in Bone Tissue Engineering: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Q.; Cui, Z.; Jiang, F.; Liu, C.-G. Strength and Targeted-Sustained Release Properties of Sodium Alginate–Polyacrylamide Hydrogel for Anti-Wrinkle Eye-Patch. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 100, 106065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łętocha, A.; Miastkowska, M.; Sikora, E. Preparation and characteristics of alginate microparticles for food and cosmetic applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 3834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomić, S.L.; Babić Radić, M.M.; Vuković, J.S.; Filipović, V.V.; Nikodinović-Runić, J.; Vukomanović, M. Alginate-Based Hydrogels and Scaffolds for Biomedical Applications. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bustos-Terrones, Y.A. A review of the strategic use of sodium alginate polymer in the immobilization of microorganisms for water recycling. Polymers 2024, 16, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Lee, C.-S.; Zhang, K.; Alhamzani, A.G.; Hsiao, B.S. Sodium alginate–aldehyde cellulose nanocrystal composite hydrogel for doxycycline and other tetracycline removal. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Wang, K.; Bai, B. A critical review of sodium alginate-based composites in water treatment. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 331, 121850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maloofi, F.; Dadvand Koohi, A. Establishing robust ZnO–sodium alginate nanocomposite for dye wastewater treatment: Characterization, RSM methodology, and mechanism evaluation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2024, 31, 64069–64086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamiak, K.; Sionkowska, A. State of innovation in alginate-based materials. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishfaq, B.; Khan, I.U.; Khalid, S.H.; Asghar, S. Design and evaluation of sodium alginate-based hydrogel dressings containing Betula utilis extract for cutaneous wound healing. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1042077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H. Enhanced Physical and Antimicrobial Properties of Alginate/Chitosan Composite Aerogels Based on Electrostatic Interactions and Noncovalent Crosslinking. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 266, 118102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muangsri, R.; Chuysinuan, P.; Thanyacharoen, T.; Techasakul, S.; Sukhavattanakul, P.; Ummartyotin, S. Utilization of Freeze Thaw Process for Polyvinyl Alcohol/Sodium Alginate (PVA/SA) Hydrogel Composite. J. Met. Mater. Miner. 2022, 32, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malektaj, H.; Drozdov, A.D.; deClaville Christiansen, J. Mechanical properties of alginate hydrogels cross-linked with multivalent cations. Polymers 2023, 15, 3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarova, A.O.; Derkach, S.R.; Khair, T.; Kazantseva, M.A.; Zuev, Y.F.; Zueva, O.S. Ion-induced polysaccharide gelation: Peculiarities of alginate egg-box association with different divalent cations. Polymers 2023, 15, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Song, T.; Chen, H.; Ming, W.; Cheng, Z.; Liu, J.; Liang, B.; Wang, Y.; Wang, G. Bioinspired High-Strength Montmorillonite-Alginate Hybrid Film: The Effect of Different Divalent Metal Cation Crosslinking. Polymers 2022, 14, 2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, A. Synergistic Effect of Palygorskite Nanorods and Ion Crosslinking to Enhance Sodium Alginate–Based Hydrogels. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 147, 110306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonoyama, T.; Gong, J.P. Double-network hydrogel and its potential biomedical application: A review. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. H 2015, 229, 853–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Zhu, D.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, X. Tough double network hydrogels with rapid self-reinforcement and low hysteresis based on highly entangled networks. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syarifuddin, A.; Haliza, N.; Izzah, N.; Tahir, M.M.; Dirpan, A. Physical, mechanical, barrier, and optical properties of sodium alginate/gum arabic/gluten edible films plasticized with glycerol and sorbitol. Foods 2025, 14, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslami, Z.; Elkoun, S.; Robert, M.; Adjallé, K. A review of the effect of plasticizers on the physical and mechanical properties of alginate-based films. Molecules 2023, 28, 6637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cofelice, M.; Messia, M.C.; Marconi, E.; Cuomo, F.; Lopez, F. Effect of the Xanthan Gum on the Rheological Properties of Alginate Hydrogels. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 142, 108768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szulc-Musioł, B.; Siemiradzka, W.; Dolińska, B. Formulation and Evaluation of Hydrogels Based on Sodium Alginate and Cellulose Derivatives with Quercetin for Topical Application. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Song, Q.; Deng, Z.; Ren, J.; Xiang, X. Sodium Alginate Hydrogel Toughened by Guar Gum for Strain Sensors. Polym. Bull. 2024, 81, 8045–8056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manousi, E.; Chatzitaki, A.-T.; Vakirlis, E.; Karavasili, C.; Fatouros, D.G. Development and in Vivo Evaluation of 3D Printed Hydrogel Patches for Personalized Cosmetic Use Based on Skin Type. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 92, 105306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, B. Characterization of Biopolymer-Based Films for Food Packaging Applications. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Guelph, Guelph, ON, Canada, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, S.; Batsh, C.; Gurumayam, S.; Borah, J.C.; Chowdhury, D. Sodium alginate–nanocellulose-based active composite film for edible oils packaging applications. Mater. Adv. 2024, 5, 9314–9329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, M.J.; Figueiredo, M.; Gil, M.H. Rheological Study of Genipin Cross-Linked Chitosan Hydrogels. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 3823–3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gieroba, B.; Kalisz, G.; Krysa, M.; Khalavka, M.; Przekora, A. Application of Vibrational Spectroscopic Techniques in the Study of the Natural Polysaccharides and Their Cross-Linking Process. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plamadiala, I.; Croitoru, C.; Pop, M.A.; Roata, I.C. Enhancing Polylactic Acid (PLA) Performance: A Review of Additives in Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM) Filaments. Polymers 2025, 17, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaňková, E.; Kašparová, P.; Khun, J.; Machková, A.; Julák, J.; Sláma, M.; Hodek, J.; Ulrychová, L.; Weber, J.; Obrová, K.; et al. Polylactic Acid as a Suitable Material for 3D Printing of Protective Masks in Times of COVID-19 Pandemic. PerrJ 2020, 8, 10259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergne, C.; Buchheit, O.; Eddoumy, F.; Sorrenti, E.; Di Martino, J.; Ruch, D. Modifications of the Polylactic Acid Surface Properties by DBD Plasma Treatment at Atmospheric Pressure. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 2011, 133, 030903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q.-H.; Hu, M.-H.; Wang, J.-F.; Hu, J.-J. Enhancing the Flexibility and Hydrophilicity of PLA via Polymer Blends: Electrospinning vs. Solvent Casting. Polymers 2025, 17, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, R.S.; Fantaus, S.S.; Guillot, A.J.; Melero, A.; Beck, R.C.R. 3D-Printed Products for Topical Skin Applications: From Personalized Dressings to Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsegay, F.; Elsherif, M.; Butt, H. Smart 3D Printed Hydrogel Skin Wound Bandages: A Review. Polymers 2022, 14, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Additive | Source | Key Physicochemical Properties | Role in This Study |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Sodium Alginate (SA) | Brown algae/bacteria | Biocompatible, hydrophilic, ionic gelation | Base polymer for hydrogel matrix |
| 2. Xanthan Gum (XG) | Fermentation of Xanthomonas campestris | High viscosity, shear-thinning, stability | Enhances viscosity and membrane uniformity |
| 3. Guar Gum (GG) | Seeds of Cyamopsis tetragonoloba | High hydration capacity, viscoelastic | Improves softness, elasticity, and moisture retention |
| 4. Hydroxyethyl Cellulose (HEC) | Cellulose derivative | Water-soluble, film-forming, stable | Enhances film formation and flexibility |
| 5. GT-700 | PEG-240/HDI copolymer surfactant | Nonionic surfactant, improves spreadability | Improves emulsion stability and handling |
| 6. Laponite® XLG | Synthetic layered silicate | Thixotropic, shear-thinning, colloidal stability | Reinforces structure; increases viscosity and extensibility |
| SA Concentration (w/w, %) | Sodium Alginate (g) | 1,3-Butylene Glycol (g) | Phenoxyethanol (g) | RO Water (g) | Total (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 0.5 | 6.0 | 0.1 | 93.4 | 100 |
| 1.0 | 1.0 | 6.0 | 0.1 | 92.9 | 100 |
| 1.5 | 1.5 | 6.0 | 0.1 | 92.4 | 100 |
| 2.0 | 2.0 | 6.0 | 0.1 | 91.9 | 100 |
| Formulation | Sodium Alginate (g) | Auxiliary Agent (g) | 1,3- Butylene Glycol (g) | pH Regulator (g) | Phenoxyethanol (g) | RO Water (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SA/XG | 1.5 | Xanthan gum (0.3) | 6.0 | – | 0.1 | 92.1 |
| SA/GG | 1.5 | Guar gum (0.3) | 6.0 | Citric acid (0.1) | 0.1 | 92.0 |
| SA/HEC | 1.5 | Hydroxyethyl cellulose (0.3) | 6.0 | Triethanolamine (0.1) | 0.1 | 92.0 |
| SA/GT | 1.5 | GT-700 (0.3) | 6.0 | – | 0.1 | 92.1 |
| SA/XLG | 1.5 | Laponite® XLG (0.3) | 6.0 | – | 0.1 | 92.1 |
| Component | Function | Weight (g) |
|---|---|---|
| Calcium chloride | Ionic crosslinker | 3.0 |
| 1,3-Butylene glycol | Humectant | 6.0 |
| Glycerin | Humectant | 6.0 |
| Trehalose | Moisture retention | 1.0 |
| Sodium pyrrolidone carboxylate (NaPCA) | Moisture retention | 3.0 |
| Reverse osmosis (RO) water | Solvent | 80.9 |
| Phenoxyethanol | Preservative | 0.1 |
| Total | — | 100 |
| Film Formulation | Maximum Extension (mm) | Elongation at Break (%) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elastic Modulus, E (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SA | 2.02 | 2.53 | 0.187 | 20.67 |
| SA/XG | 8.30 | 10.38 | 0.200 | 13.31 |
| SA/GG | 6.08 | 7.60 | 0.170 | 11.34 |
| SA/HEC | 7.36 | 9.20 | 0.173 | 6.91 |
| SA/GT-700 | 7.19 | 8.99 | 0.220 | 11.47 |
| SA/XLG | 11.84 | 14.80 | 0.193 | 11.14 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, S.-M.; Sun, X.-L.; Li, C.-C.; Hwang, J.-J. Development of an SA/XLG Composite Hydrogel Film for Customized Facial Mask Applications. Polymers 2025, 17, 2410. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17172410
Huang S-M, Sun X-L, Li C-C, Hwang J-J. Development of an SA/XLG Composite Hydrogel Film for Customized Facial Mask Applications. Polymers. 2025; 17(17):2410. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17172410
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Su-Mei, Xu-Ling Sun, Chia-Ching Li, and Jiunn-Jer Hwang. 2025. "Development of an SA/XLG Composite Hydrogel Film for Customized Facial Mask Applications" Polymers 17, no. 17: 2410. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17172410
APA StyleHuang, S.-M., Sun, X.-L., Li, C.-C., & Hwang, J.-J. (2025). Development of an SA/XLG Composite Hydrogel Film for Customized Facial Mask Applications. Polymers, 17(17), 2410. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17172410







