Magneto-Tunable Surface Roughness and Hydrophobicity of Magnetoactive Elastomers Based on Polymer Networks with Different Architectures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of MAE Samples
2.3. Methods
3. Results
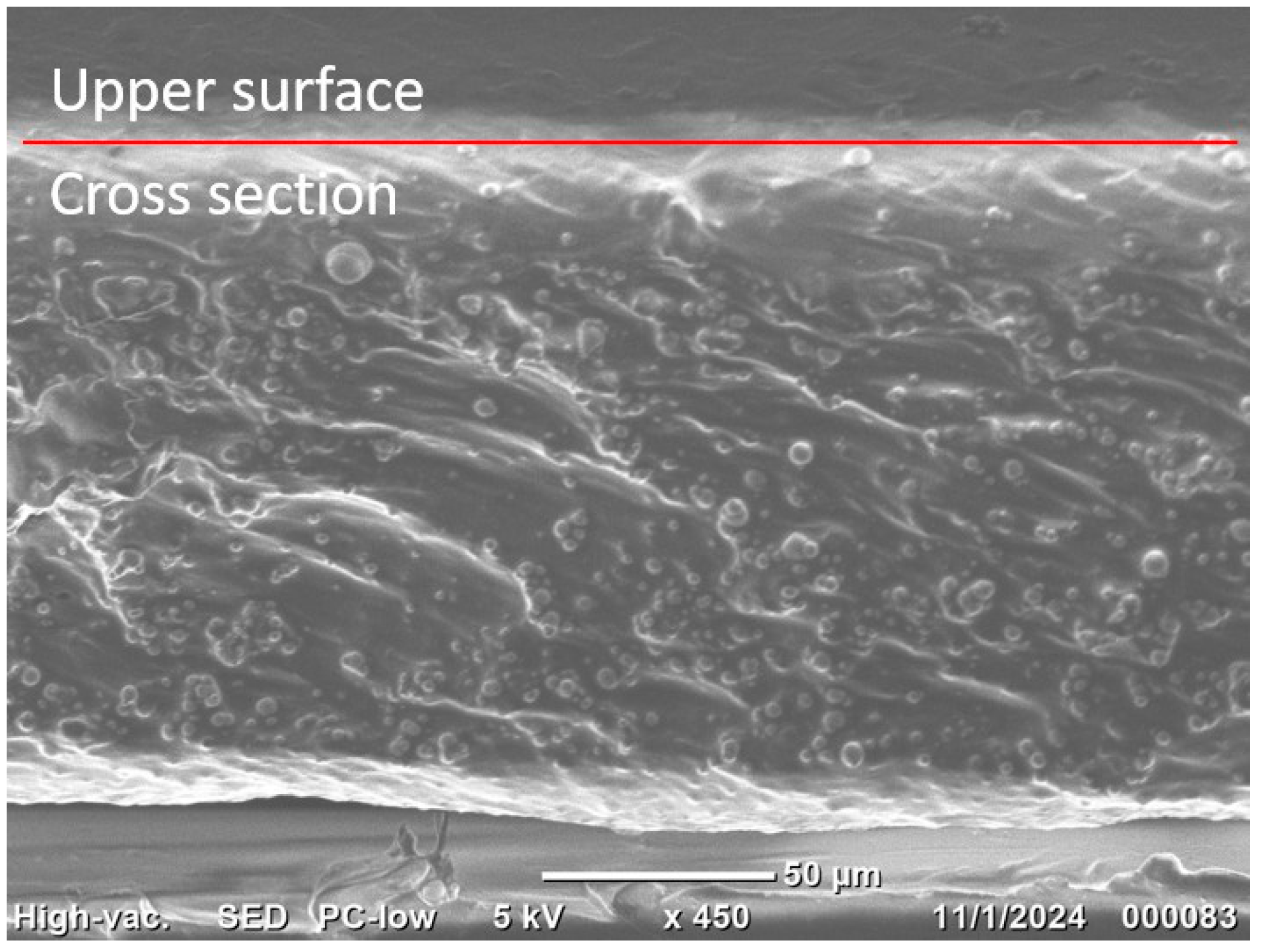
3.1. Characterization of MAE Samples
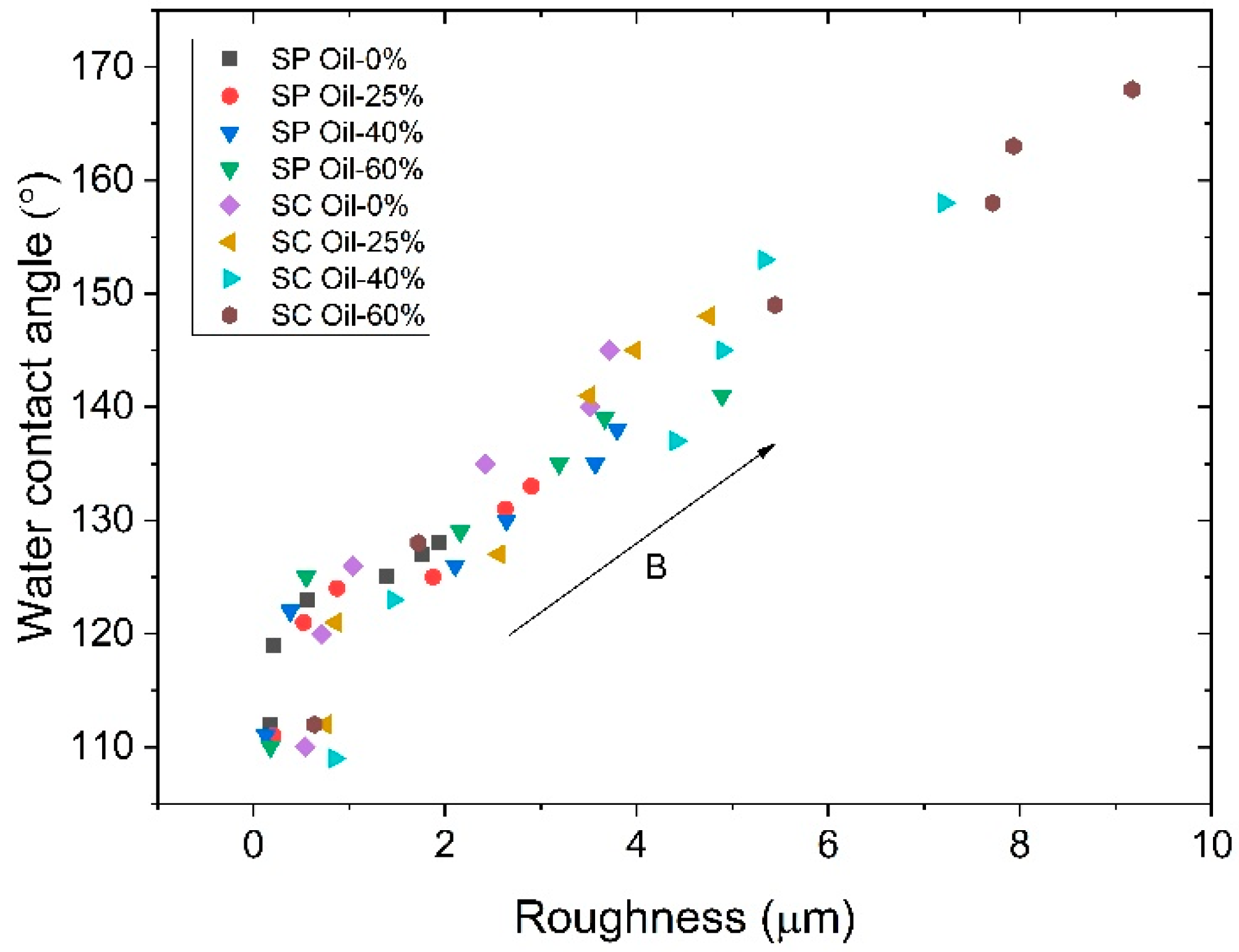
3.2. The Surface Roughness of MAE Samples
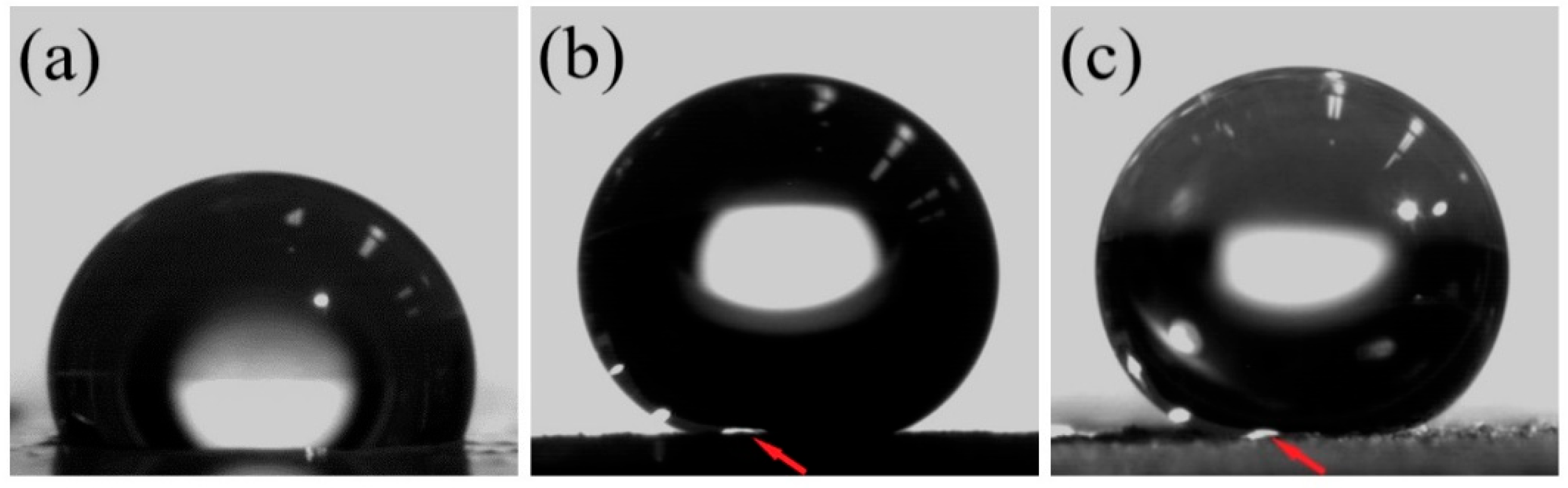
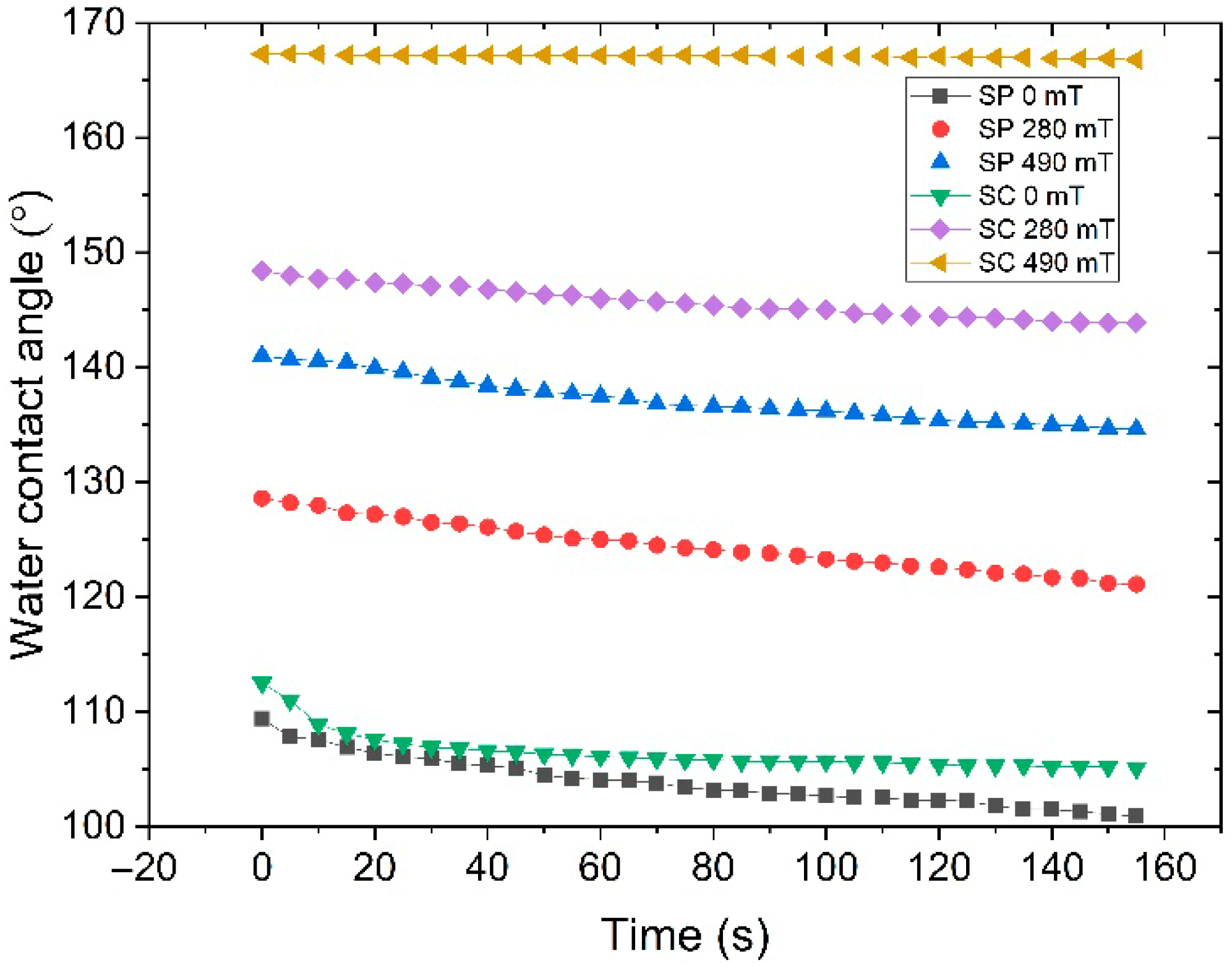
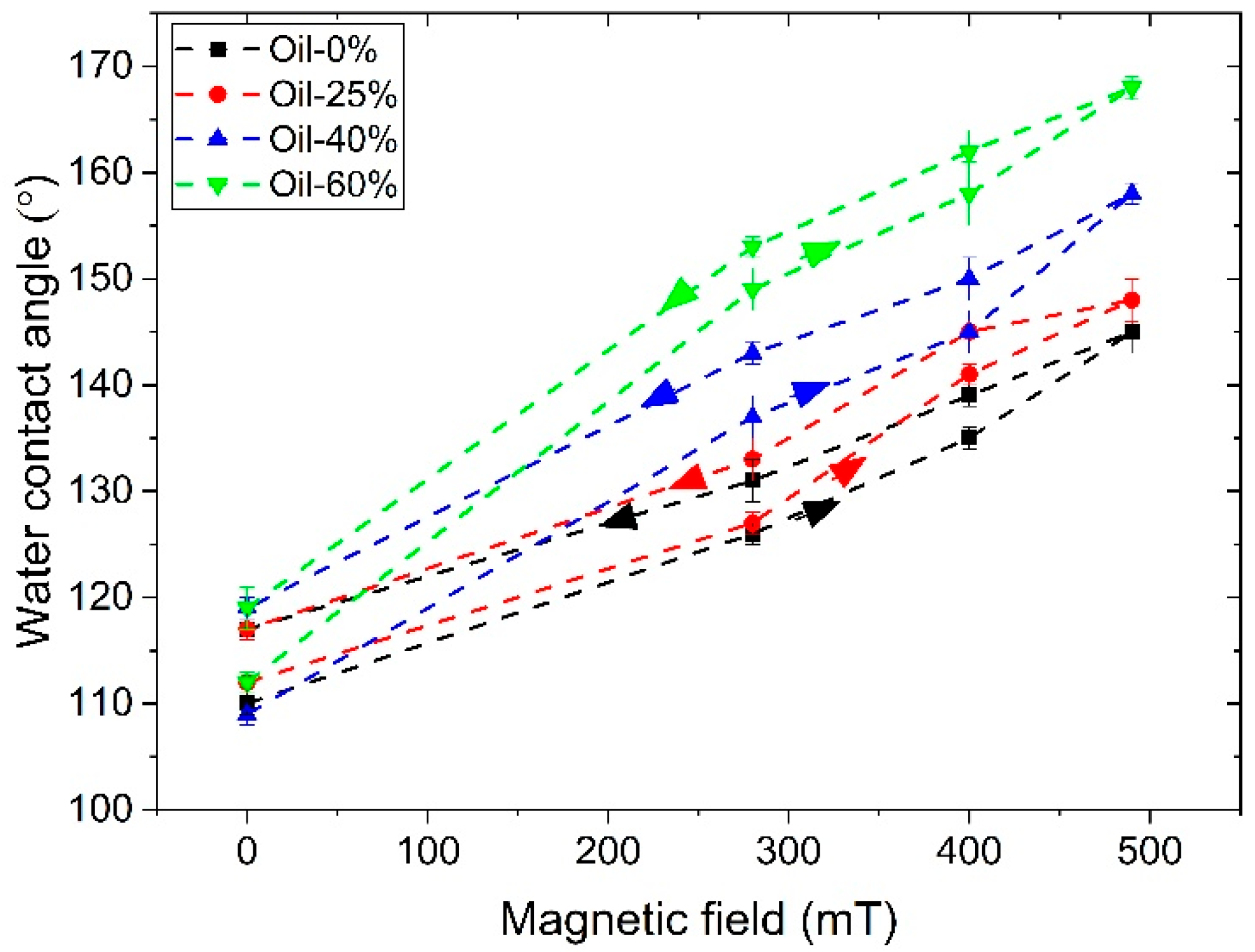
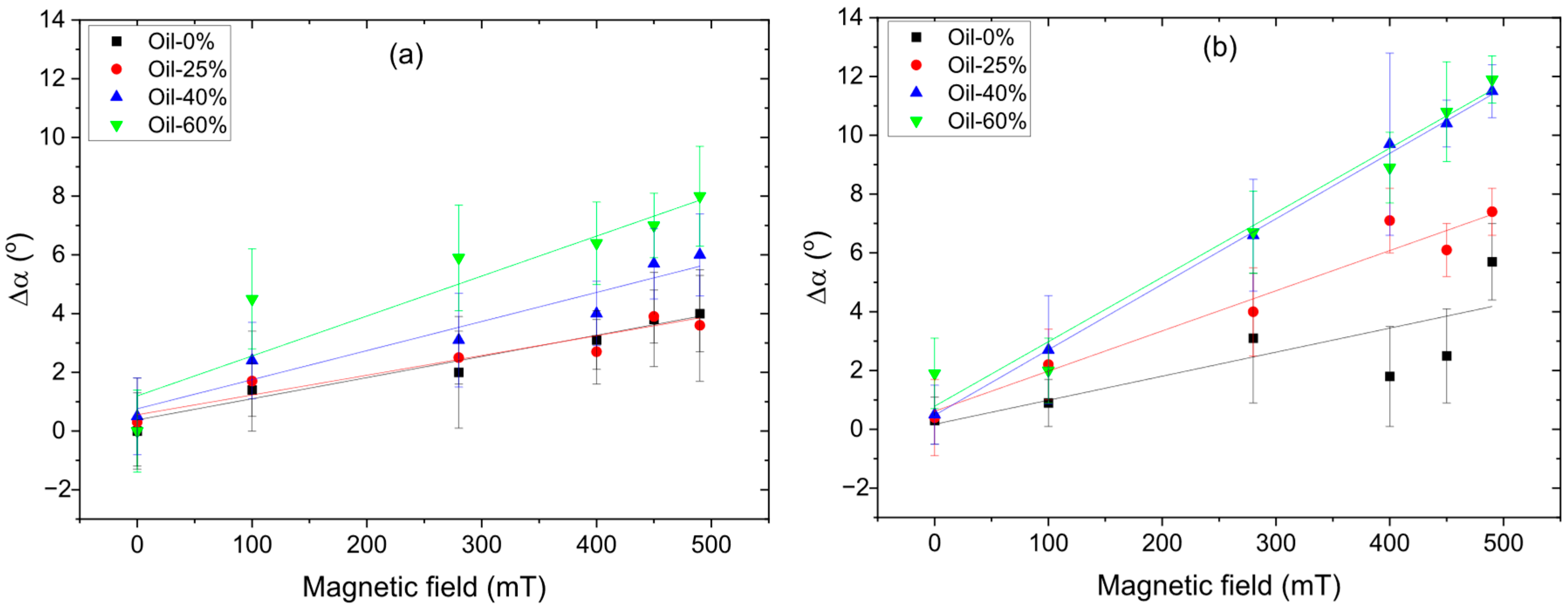
3.3. The Water Contact Angle of MAE Samples
4. Conclusions
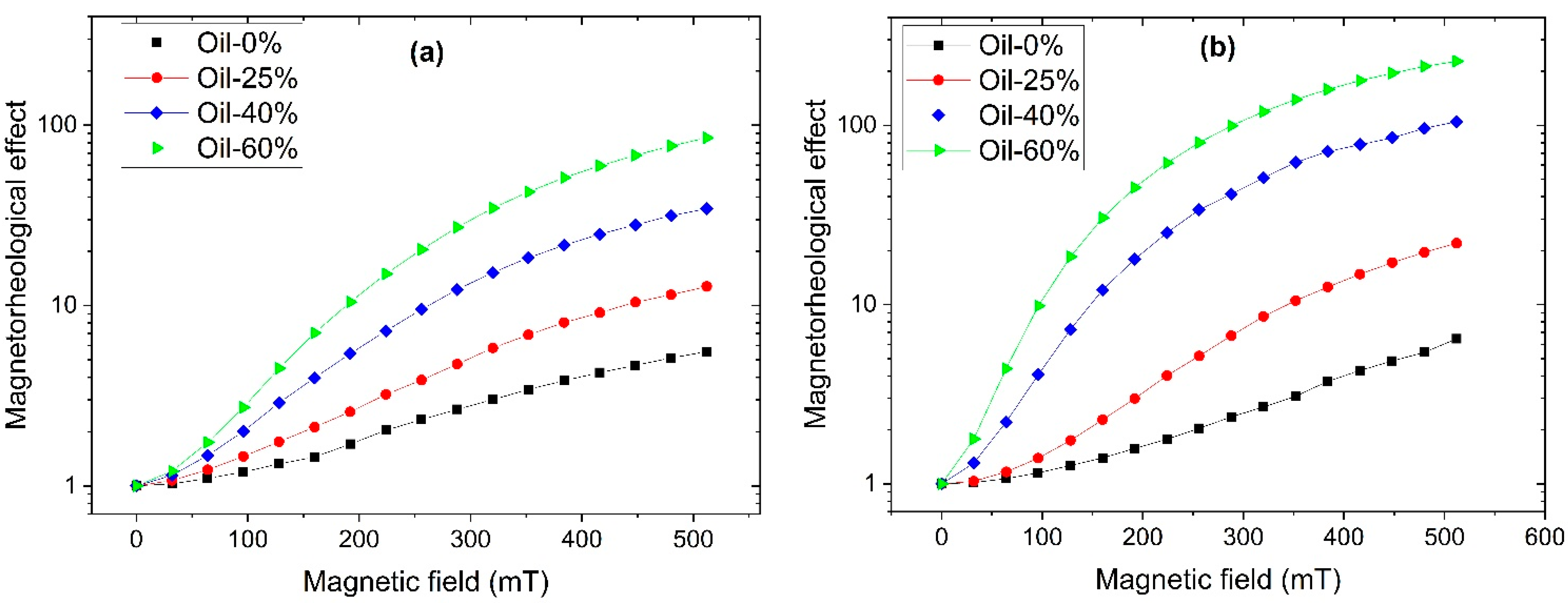
- MAEs exhibit a giant magnetorheological effect, with the elastic modulus increasing by more than two orders of magnitude. SP-based MAEs show a stronger magnetorheological response.
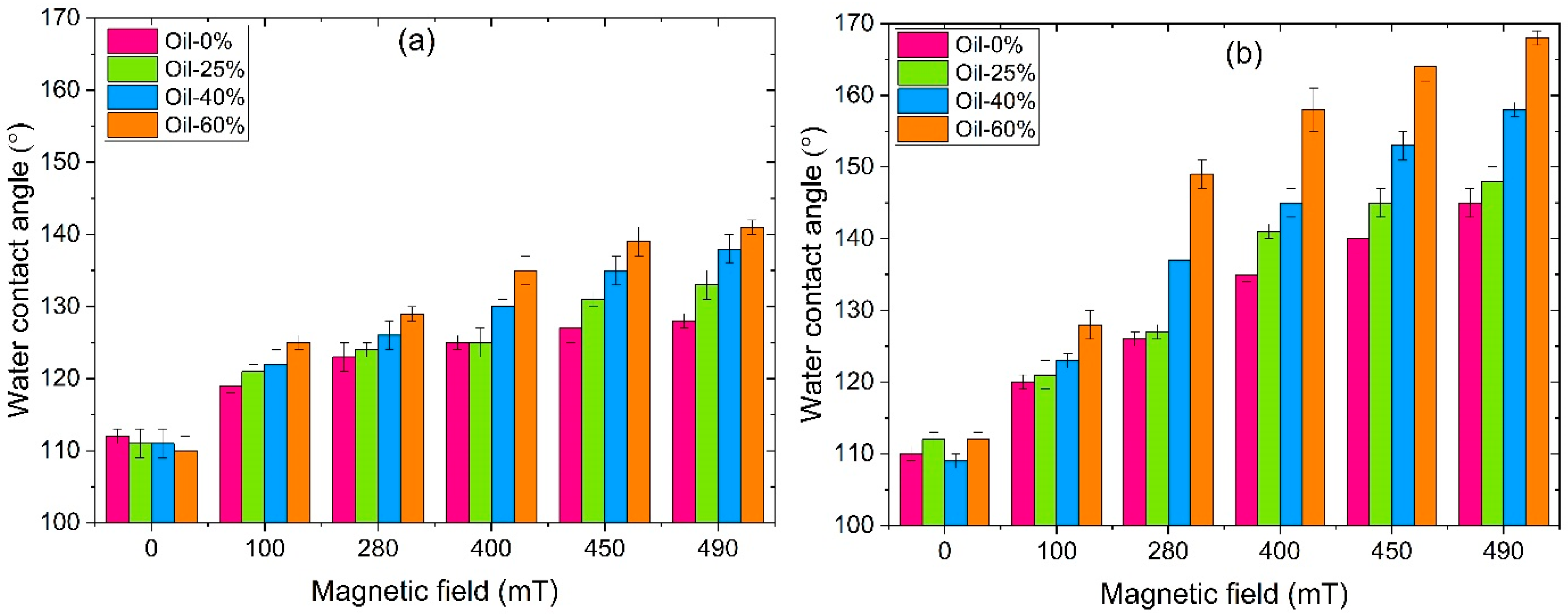
- MAEs display significant magnetic field-induced changes in surface properties. Surface roughness reaches nearly 10 μm, and water contact angles (WCA) reach up to 168°. SC-based MAEs show more pronounced changes in surface properties.
- WCA data for all MAE samples collapse onto a single master curve when plotted as a function of surface roughness, revealing a clear linear relationship.
- WCA exhibits hysteresis during increasing and decreasing magnetic field cycles, indicating memory effects in surface restructuring.
- WCA gradually decreases over time, with this decline being more pronounced for the SC-based MAE series.
- Increasing the thickness of MAE films from 0.2 mm to 0.4 mm reduces the WCA, likely due to a lower effective magnetic field at the surface, farther from the field source. Nevertheless, WCA for SC-based MAEs still reaches values as high as 150°, indicating strong superhydrophobic behavior.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Filipcsei, G.; Csetneki, I.; Szilágyi, A.; Zrínyi, M. Magnetic Field-Responsive Smart Polymer Composites. In Oligomers—Polymer Composites—Molecular Imprinting; Gong, B., Sanford, A.R., Ferguson, J.S., Eds.; Advances in Polymer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 137–189. ISBN 9783540468301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzel, A.M. Tuned, driven, and active soft matter. Phys. Rep. 2015, 554, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubaidillah; Sutrisno, J.; Purwanto, A.; Mazlan, S.A. Recent progress on magnetorheological solids: Materials, fabrication, testing, and applications. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2015, 17, 563–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odenbach, S. Microstructure and rheology of magnetic hybrid materials. Arch. Appl. Mech. 2016, 86, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamonin, M.; Kramarenko, E.Y. Highly Responsive Magnetoactive Elastomers. In Novel Magnetic Nanostructures; Domracheva, N., Caporali, M., Rentschler, E., Eds.; Advanced Nanomaterials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Chapter 7; pp. 221–245. ISBN 9780128135945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramarenko, E.Y.; Stepanov, G.V.; Khokhlov, A.R. Magnetically active silicone elastomers: Twenty years of development. INEOS OPEN 2020, 2, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubaidillah, U.; Lenggana, B.W.; Choi, S.B. Bibliometric Review of Magnetorheological Materials. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadzharyan, T.A.; Shamonin, M.; Kramarenko, E.Y. Theoretical Modeling of Magnetoactive Elastomers on Different Scales: A State-of-the-Art Review. Polymers 2022, 14, 4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanov, G.V.; Abramchuk, S.S.; Grishin, D.A.; Nikitin, L.V.; Kramarenko, E.Y.; Khokhlov, A.R. Effect of a homogeneous magnetic field on the viscoelastic behavior of magnetic elastomers. Polymer 2007, 48, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günther, D.; Borin, D.Y.; Günther, S.; Odenbach, S. X-ray micro-tomographic characterization of field-structured magnetorheologicalelastomers. Smart Mater. Struct. 2012, 21, 105018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubarev, A.Y.; Elkady, A.S. Magnetodeformation and Elastic Properties of Ferrogels and Ferroelastomers. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2014, 413, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeis, D.; Toshchevikov, V.; Saphiannikova, M. Effects of local rearrangement of magnetic particles on deformation in magneto-sensitive elastomers. Soft Matter 2019, 15, 3552–3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semisalova, A.S.; Perov, N.S.; Stepanov, G.V.; Kramarenko, E.Y.; Khokhlov, A.R. Strong magnetodielectric effects in magnetorheological elastomers. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 11318–11324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarova, L.A.; Nadzharyan, T.A.; Alekhina, Y.A.; Stepanov, G.V.; Kazimirova, E.G.; Perov, N.S.; Kramarenko, E.Y. Magnetoactive Elastomer as an Element of a Magnetic Retina Fixator. Smart Mater. Struct. 2017, 26, 095054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Puranam, V.R.; Misra, S.; Venkiteswaran, V.K. A Snake-Inspired Multi-Segmented Magnetic Soft Robot Towards Medical Applications. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 5795–5802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, G.; Jin, Z.; Chen, J. A Review on Magnetic Smart Skin as Human–Machine Interfaces. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2024, 10, 2300677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bira, N.; Dhagat, P.; Davidson, J.R. A Review of Magnetic Elastomers and Their Role in Soft Robotics. Front. Robot. AI 2020, 7, 588391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.; Hu, W.; Dong, X.; Sitti, M. Multi-functional soft-bodied jellyfish-like swimming. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Gao, Y.; Dong, Z.; Han, D.; Gorodov, V.V.; Kramarenko, E.Y.; Zou, J. Sustainable and untethered soft robots created using printable and recyclable ferromagnetic fibers. Bio-Des. Manuf. 2024, 7, 926–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, M.Y.; Arif, Z.U.; Tariq, A.; Hossain, M.; Khan, K.A.; Umer, R. 3D printing of magneto-active smart materials for advanced actuators and soft robotics applications. Eur. Polym. J. 2024, 205, 112718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Pal, A.; Aghakhani, A.; Pena-Francesch, A.; Sitti, M. Soft actuators for real-world applications. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2022, 7, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Li, S.; Shepherd, R.F. Elastomeric Haptic Devices for Virtual and Augmented Reality. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2009364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Yim, C.; Kim, W.; Jeon, S. Magnetorheological elastomer films with tunable wetting and adhesion properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 19853–19856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokin, V.V.; Sokolov, B.O.; Stepanov, G.V.; Kramarenko, E.Y. Controllable hydrophobicity of magnetoactive elastomer coatings. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 459, 268–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glavan, G.; Salamon, P.; Belyaeva, I.A.; Shamonin, M.; Drevenšek-Olenik, I. Tunable surface roughness and wettability of a soft magnetoactive elastomer. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, P.A.; Minina, E.S.; Kantorovich, S.S.; Kramarenko, E.Y. Surface relief of magnetoactive elastomeric films in a homogeneous magnetic field: Molecular dynamics simulations. Soft Matter 2019, 15, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovalev, A.; Belyaeva, I.A.; von Hofen, C.; Gorb, S.; Shamonin, M. Magnetically Switchable Adhesion and Friction of Soft Magnetoactive Elastomers. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2022, 24, 2200372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Murakami, D.; Tanaka, M.; Kawai, M.; Mitsumata, T. Optimal Plasticizer Content for Magnetic Elastomers Used for Cell Culture Substrate. Chem. Lett. 2020, 49, 280–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, S.; Wang, X. Magnetic-Responsive Superhydrophobic Surface of Magnetorheological Elastomers Mimicking from Lotus Leaves to Rose Petals. Langmuir 2021, 37, 2312–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, W.; Ethan, A.; Ylias, S.; Matthew, B.M.; Bobby, P.; Colin, D.W. Amine-Infused Hydrogels with Nonaqueous Solvents: Facile Platforms to Control CO2 Capture Performance. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 14758–14767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, D.; Li, X.; Liao, C.; Yang, P.; Ruan, H.; Shou, M.; Luo, J.; Wang, X. Study on Sliding Friction Characteristics of Magnetorheological Elastomer—Copper Pair Affected by Magnetic-Controlled Surface Roughness and Elastic Modulus. SmartMater. Struct. 2021, 31, 015030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, M.; Ni, Z.; Guan, Q.; Blackman, B.R.K.; Saiz, E. Stimuli-responsive surfaces for switchable wettability and adhesion. J. R. Soc. Interface 2021, 18, 20210162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glavan, G.; Kettl, W.; Brunhuber, A.; Shamonin, M.; Drevenšek-Olenik, I. Effect of Material Composition on Tunable Surface Roughness of Magnetoactive Elastomers. Polymers 2019, 11, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Dong, S.; Wang, X.; Li, W. Magneto-induced surface morphologies in magnetorheological elastomer films: An analytical study. Smart Mater. Struct. 2019, 28, 045016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Li, R.; Li, X.; Wang, X. Magnetic Field Induced Surface Micro-Deformation of Magnetorheological Elastomers for Roughness Control. Front. Mater. 2018, 5, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia, J.A.; Restrepo, J.; Salinas, H.D.; Restrepo, E. Numerical Study on Surface Reconstruction and Roughness of Magnetorheological Elastomers. Polymers 2023, 11, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadzharyan, T.A.; Stolbov, O.V.; Raikher, Y.L.; Kramarenko, E.Y. Field-induced surface deformation of magnetoactive elastomers with anisometric fillers: A single-particle model. Soft Matter 2019, 15, 9507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Pang, T.; Huang, Z.; Wang, J.; Huang, F.; Zhang, L. 3D printing of soft magnetoactive superhydrophobic elastomers for droplet manipulation. Mater. Lett. 2025, 379, 137658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johari, M.A.F.; Mazlan, S.A.; Aziz, S.A.A.; Zain, N.; Nordin, N.A.; Ubaidillah, U.; Upadhyay, R.V.; Yusuf, S.M. Morphological Features of Magnetorheological Elastomer Degradation under a Natural Weathering Environment. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straus, I.; Kravanja, G.; Hribar, L.; Kriegl, R.; Jezeršek, M.; Shamonin, M.; Drevensek-Olenik, I.; Kokot, G. Surface Modification of Magnetoactive Elastomers by Laser Micromachining. Materials 2024, 17, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, W.F.M.; Burdyńska, J.; Vatankhah-Varnoosfaderani, M.V.; Matyjaszewski, K.; Paturej, J.; Rubinstein, M.; Dobrynin, A.D.; Sheiko, S.S. Solvent-free, supersoft and superelastic bottlebrush melts and networks. Nat. Mater. 2015, 15, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatankhah-Varnosfaderani, M.; Daniel, W.F.M.; Erhart, M.H.; Pandya, A.A.; Liang, H.; Matyjaszewski, K.; Dobrynin, A.V.; Sheiko, S.S. Mimicking biological stress–strain behavior with synthetic elastomers. Nature 2017, 549, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keith, A.N.; Vatankhah-Varnosfaderani, M.; Clair, C.; Fahimipour, F.; Dashtimoghadam, E.; Lallam, A.; Sztucki, M.; Ivanov, D.I.; Liang, H.; Dobrynin, A.V.; et al. Bottlebrush bridge between soft gels and firm tissues. ACS Cent. Sci. 2020, 6, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostrov, S.A.; Gorodov, V.V.; Sokolov, B.O.; Muzafarov, A.M.; Kramarenko, E.Y. Low-Modulus Elastomeric Matrices for Magnetoactive Composites with a High Magnetic Field Response. Polym. Sci. Ser. A 2020, 62, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostrov, S.A.; Gorodov, V.V.; Muzafarov, A.M.; Kramarenko, E.Y. Comparative Analysis of Magnetorheological Effect in Soft Isotropic and Anisotropic Magnetoactive Elastomers. Polym. Sci. Ser. B 2022, 64, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostrov, S.A.; Razakov, V.S.; Stepanov, G.V.; Olenich, E.A.; Gorodov, V.V.; Kramarenko, E.Y. Influence of Distribution Anisotropy and Particle Shape on Magnetorheological Properties of Magnetoactive Elastomers. Polym. Sci. Ser. A 2023, 65, 822–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostrov, S.A.; Dashtimoghadam, E.; Keith, A.N.; Sheiko, S.S.; Kramarenko, E.Y. Regulating Tissue-Mimetic Mechanical Properties of Bottlebrush Elastomers by Magnetic Field. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 38783–38791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belyaeva, I.A.; Kramarenko, E.Y.; Stepanov, G.V.; Sorokin, V.V.; Stadler, D.; Shamonin, M. Transient magnetorheological response of magnetoactive elastomers to step and pyramid excitations. Soft Matter. 2016, 12, 2901–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.-N.; Sun, B.; Picken, S.J.; Mendes, E. Long Time Response of Soft Magnetorheological Gels. J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 4702–4711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsumata, T.; Ohori, S. Magnetic polyurethane elastomers with wide range modulation of elasticity. Polym. Chem. 2011, 2, 1063–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Gong, X.; Xuan, S. Soft magnetorheological polymer gels with controllable rheological properties. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 075029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Component | Chemical Formula | Mw | Mw/Mn | m, g |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Matrix 1 | ||||
| α,ω-divinyl-polydimethyl-siloxane | 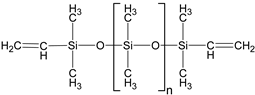 | 37,000 | 1.67 | 5 |
| Polymethyl-hydrosiloxane | 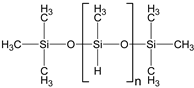 | 3600 | 2.21 | 0.0446 |
| α,ω-dihydride-polydimethyl-siloxane | 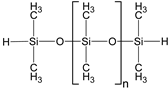 | 1600 | 1.38 | 0.1621 |
| ω-vinyl-polydimethyl-siloxane | 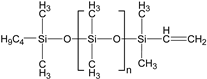 | 3100 | 1.11 | 1.8153 |
| Matrix 2 | ||||
| Vinyl-containing silicone | 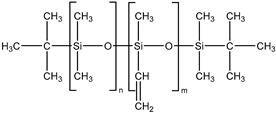 | 100,000 | 1.43 | 3 |
| Vinyl- and hydride-containing silicone | 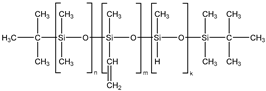 | 100,000 | 1.43 | 3 |
| Magnetic Field, mT | Contact Angle α, ° | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 65 wt.% CIP | 70 wt.% CIP | 75 wt.% CIP | ||||
| 0% Oil | 25% Oil | 0% Oil | 25% Oil | 0% Oil | 25% Oil | |
| 0 | 111 ± 1 | 109 ± 2 | 111 ± 2 | 110 ± 1 | 110 ± 1 | 112 ± 1 |
| 100 | 120 ± 1 | 121 ± 2 | 120 ± 2 | 121 ± 2 | 120 ± 1 | 121 ± 2 |
| 280 | 126 ± 1 | 127 ± 1 | 128 ± 1 | 127 ± 2 | 126 ± 1 | 127 ± 1 |
| 400 | 134 ± 2 | 135 ± 1 | 136 ± 2 | 139 ± 1 | 135 ± 1 | 141 ± 1 |
| 450 | 137 ± 1 | 138 ± 1 | 139 ± 1 | 139 ± 2 | 140 ± 2 | 145 ± 2 |
| 490 | 138 ± 1 | 140 ± 2 | 141 ± 2 | 143 ± 2 | 145 ± 2 | 148 ± 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kirgizov, S.E.; Kostrov, S.A.; Kramarenko, E.Y. Magneto-Tunable Surface Roughness and Hydrophobicity of Magnetoactive Elastomers Based on Polymer Networks with Different Architectures. Polymers 2025, 17, 2411. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17172411
Kirgizov SE, Kostrov SA, Kramarenko EY. Magneto-Tunable Surface Roughness and Hydrophobicity of Magnetoactive Elastomers Based on Polymer Networks with Different Architectures. Polymers. 2025; 17(17):2411. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17172411
Chicago/Turabian StyleKirgizov, Sobit E., Sergey A. Kostrov, and Elena Yu. Kramarenko. 2025. "Magneto-Tunable Surface Roughness and Hydrophobicity of Magnetoactive Elastomers Based on Polymer Networks with Different Architectures" Polymers 17, no. 17: 2411. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17172411
APA StyleKirgizov, S. E., Kostrov, S. A., & Kramarenko, E. Y. (2025). Magneto-Tunable Surface Roughness and Hydrophobicity of Magnetoactive Elastomers Based on Polymer Networks with Different Architectures. Polymers, 17(17), 2411. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17172411







