A Programmable Soft Electrothermal Actuator Based on a Functionally Graded Structure for Multiple Deformations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Characterization
2.3. Preparation of MWCNTs Dispersion
2.4. Preparation of PDMS/MWCNTs Composite Materials
2.5. Rheological Testing of PDMS/MWCNTs Composite Materials
2.6. Stress–Strain Tests of PDMS/MWCNTs Composite Materials
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Design and Fabrication Process of the Electrothermal Actuator
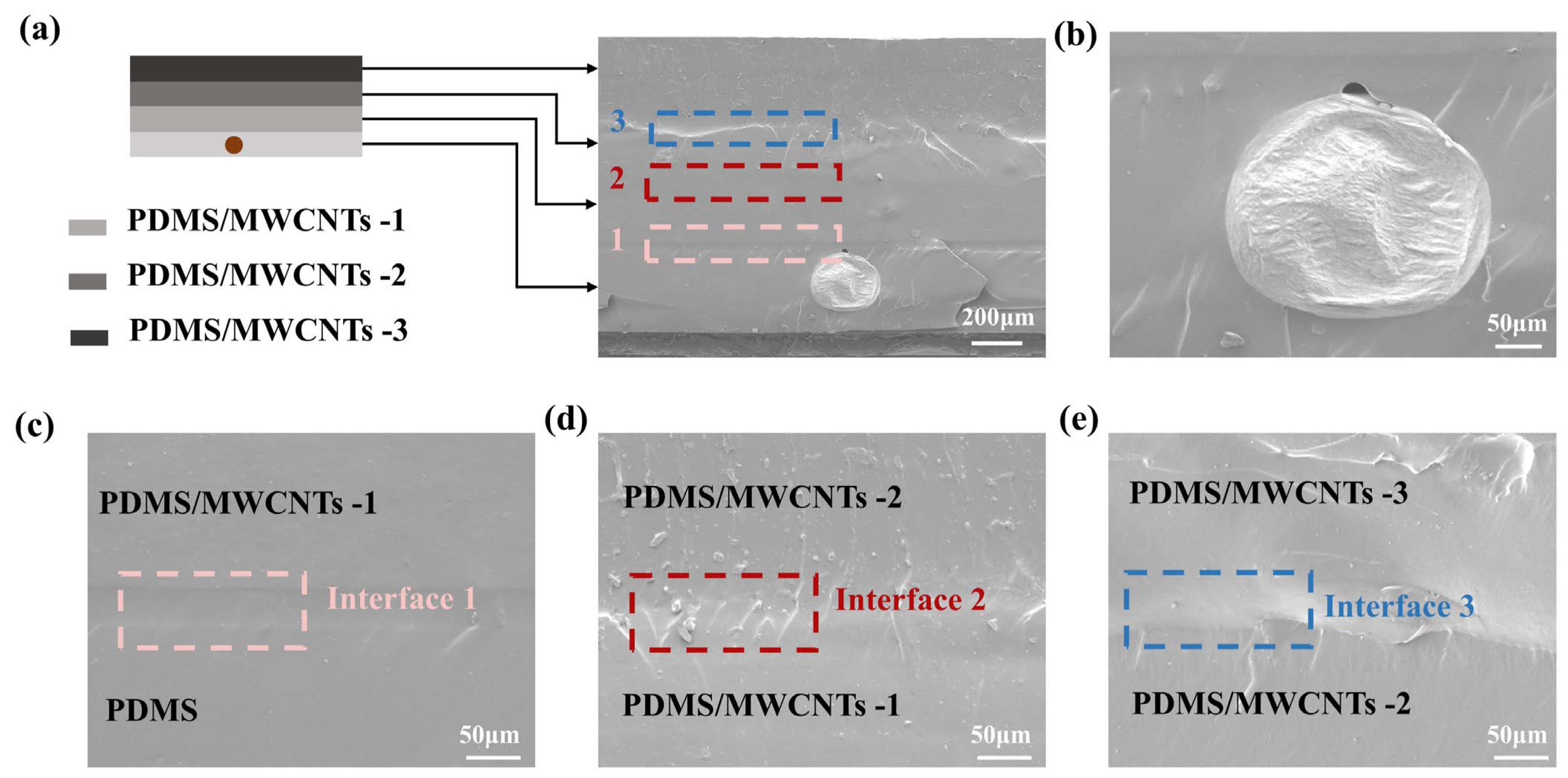
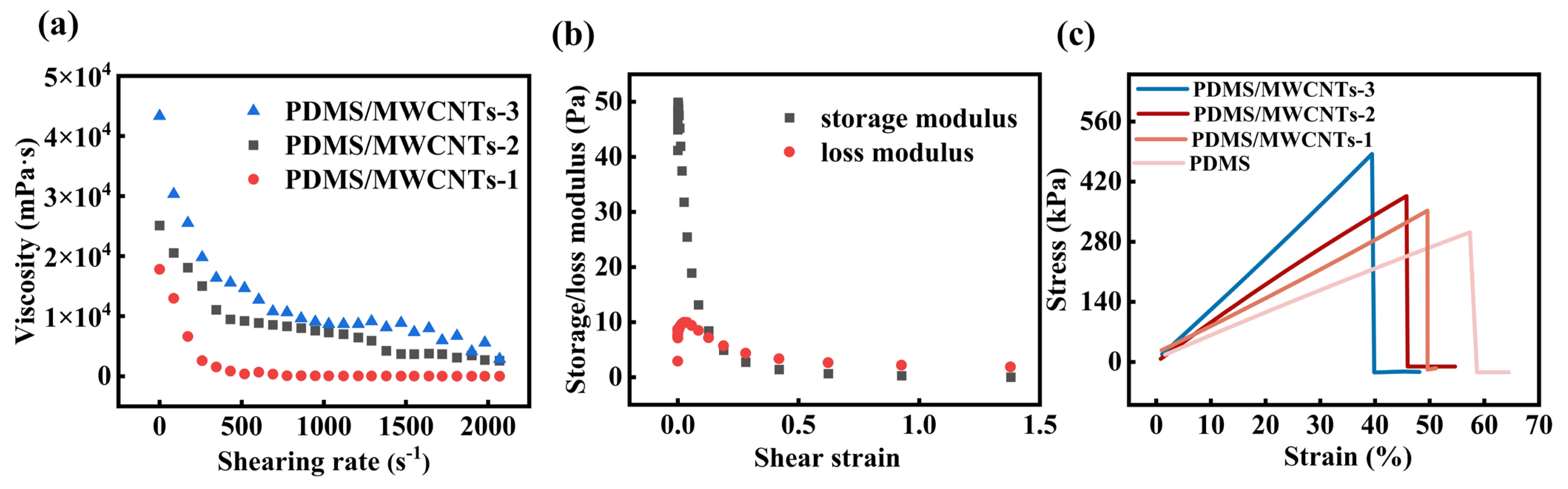
3.2. Characterization of PDMS/MWCNTs Composite Materials
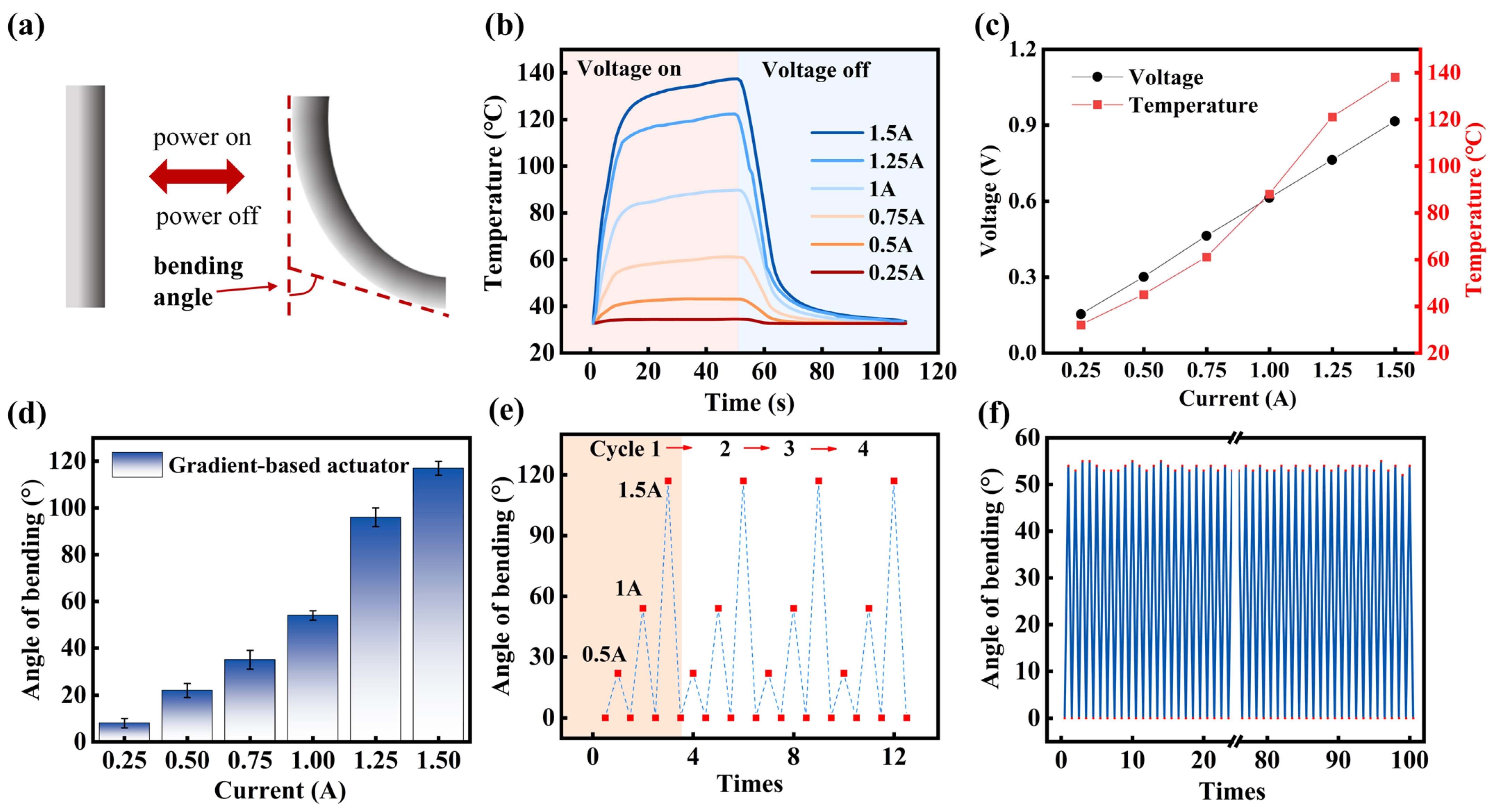
3.3. Performance of Programmable Soft Electrothermal Actuator
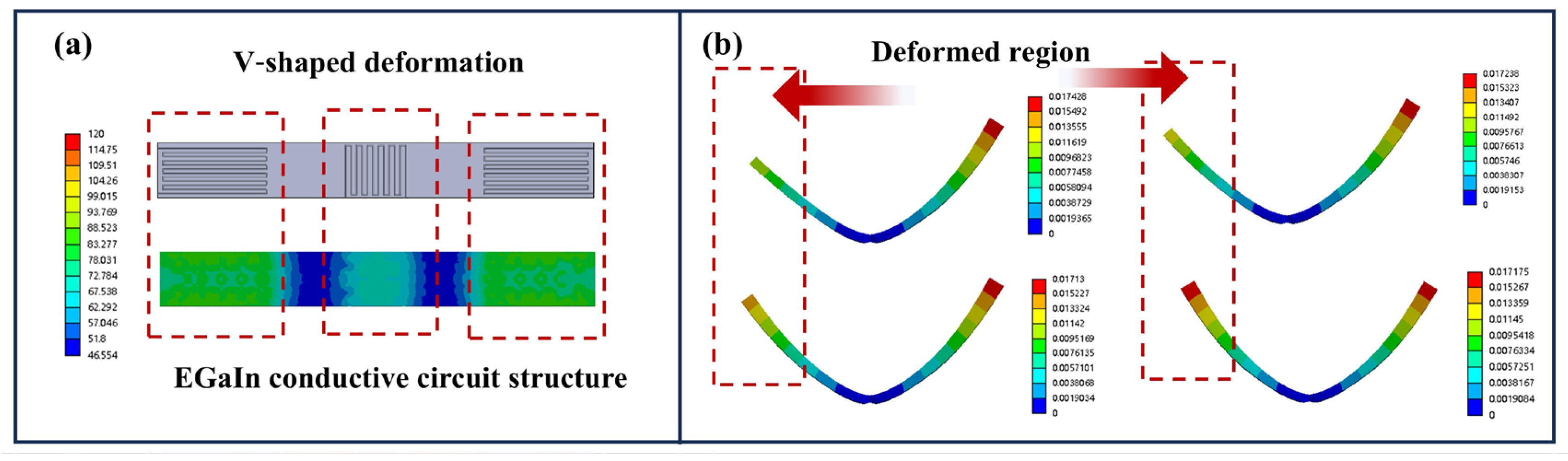
3.4. The Programmable Deformation of the Soft Electrothermal Actuator
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, X.W.; Lee, A.; Yang, B.; Gao, L.X.; Ning, H.M.; Huang, K.Y.; Luo, X.L.; Zhang, L.D.; Zhang, J.F.; Yang, C.; et al. A 3D cross-linked hierarchical hydrogel E-skin with sensing of touch position and pressure. Carbon 2024, 216, 118514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.Q.; Sameoto, D. A review of electrically driven soft actuators for soft robotics. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.F.; Zhang, S.X.; Fang, B.; Sun, F.C.; Liu, H.P.; Li, H.Y. A review of smart materials for the boost of soft actuators, soft sensors, and robotics applications. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2022, 35, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.F.; Ke, J.W.; Xiao, R.K.; Jiang, X.T.; Li, M.; Xiao, X.H.; Guo, Z. Bioinspired bidirectional stiffening soft actuators enable versatile and robust grasping. Soft Robot. 2024, 11, 494–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.X.; Ai, W.F.; Long, Y.; Song, K. MXene-based soft humidity-driven aActuator with high sensitivity and fast response. Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 27650–27656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.D.; Hu, W.; Li, Z.H. A physically intelligent, multimodal universal soft gripper using granular materials. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 35, 202418549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.K.; Han, G.M.; Jin, H.; Xu, M.; Dong, E. Design and force/angle independent control of a bionic mechanical ankle based on an artificial muscle matrix. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akashi, N.; Kuniyoshi, Y.; Jo, T.; Nishida, M.; Sakurai, R.; Wakao, Y.; Nakajima, K. Embedding bifurcations into pneumatic artificial muscle. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2304402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.X.; Luo, Y.; Plamthottam, R.; Pei, S.Y.; Wei, C.; Han, Z.Q.; Fan, J.C.; Possinger, M.; Liu, K.D.; Zhu, Y.K.; et al. Haptic artificial muscle skin for extended reality. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, EADR1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, W.; Ren, Z.; Chang, L.F.; Xu, X.Y.; Hu, Y. Endowing actuators with sensing capability: Recent progress on perceptive soft actuators. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 479, 147550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Dong, J.Y. Fabrication, modeling, and characterization of soft twisting electrothermal actuators with directly printed oblique heater. J. Micromechan. Microeng. 2022, 32, 035001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandeya, S.P.; Zou, S.; Roh, B.-M.; Xiao, X. Programmable Thermo-Responsive Self-Morphing Structures Design and Performance. Materials 2022, 15, 8775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.L.; Yu, Q.H.; Su, C.L.; Jiang, J.H.; Chen, N.L.; Shao, H.Q. Light-responsive soft actuators: Mechanism, materials, fabrication, and applications. Actuators 2021, 10, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.Y.; Lu, Y.; Jiang, L.X.; Yu, Y.L. Liquid crystal soft actuators and robots toward mixed reality. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2009835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.X.; Gao, D.; Lee, P.S. Recent progress in artificial muscles for interactive soft robotics. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2003088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.X.; Yin, X.F.; Zhang, C.; Chen, B.H.; Sun, P.; Xu, Y. Weaving liquid crystal elastomer fiber actuators for multifunctional soft robotics. Sci. Adv. 2025, 11, eads3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.H.; Yang, Y.; Qian, X.J.; Chen, Q.M.; Wei, Y.; Ji, Y. Liquid-crystalline soft actuators with switchable thermal reprogrammability. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 4778–4784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalulu, M.; Chilikwazi, B.; Hu, J.; Fu, G.D. Soft actuators and actuation: Design, synthesis, and applications. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2025, 46, 2400282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Li, L.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Y.F.; Wu, M.S.; Gu, G.Y.; Ge, Q. Effect of temperature on the programmable helical deformation of a reconfigurable anisotropic soft actuator. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2020, 199, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Dong, J.Y. High-performance low-voltage soft electrothermal actuator with directly printed micro-heater. Sens. Actuators A-Phys. 2019, 297, 111546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.W.; Lee, A.; Yang, B.; Ning, H.M.; Liu, H.W.; An, K.X.; Liao, H.S.; Huang, K.Y.; Wen, J.; Luo, X.L.; et al. Machine learning assisted electronic/Ionic skin recognition of thermal stimuli and mechanical dDeformation for soft robots. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2401123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilami, M.; Bagheri, H.; Ahmed, R.; Skowronek, E.O.; Marvi, H. Materials, actuators, and sensors for soft bioinspired robots. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2003139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Qiu, M.F.; Dai, K.; Zheng, G.Q.; Liu, C.T.; Shen, C.Y. Tendril-inspired programmable soft actuator based on bilayer thermoplastic film. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 503, 158524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.T.; Hu, R.; Li, P.; Gao, A.Z.; Sun, X.T.; Zhang, X.H.; Qi, X.J.; Fan, Q.; Liu, Y.D.; Liu, X.Q.; et al. Soft bimorph actuator with real-time multiplex motion perception. Nano Energy 2020, 76, 104926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, S.N.; Melvin, A.A.; Choi, J.W. Stimuli-responsive polymer actuator for softr Robotics. Polymers 2024, 16, 2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, P.; Kim, K.K.; Kim, H.; Park, J.J.; Ha, I.; Shin, J.; Jung, J.; Cho, H.; Kwon, J.; Lee, H.; et al. Transparent soft actuators/sensors and camouflage skins for imperceptible soft robotics. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2002397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.M.; Wei, K.; Yang, R.H. Untethered soft pneumatic actuators with embedded multiple sensing capabilities. Soft Robot. 2024, 11, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.W.; Zhang, L.D.; Cheng, L.J.; Xiang, C.X.; Lee, A.; Ning, H.M.; Huang, K.Y.; Liu, H.W.; Liao, H.S.; An, K.X.; et al. Multilayer self-sensing hydrogel soft robot prepared via stereolithography for on-demand drug delivery. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 519, 164352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Guo, Y.C.; Bu, F.; Wei, S.J.; Cheng, E. Wireless flexible actuator photoelectric synergistically driven for environment adaptability crawling robots. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2025, 17, 8036–8046. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, M.; Li, S.T.; Hu, X.Y.; Leng, X.Q.; Wang, R.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Z.F. Progresses in tensile, torsional, and multifunctional soft actuators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2007437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.; Kwon, K.; Lee, J.; Ko, S.H. Untethered soft actuators for soft standalone robotics. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 3510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Peng, Q.Y.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Z.L.; Zhao, X.; Li, P.Y.; Xu, L.L.; Zheng, H.W.; Xue, F.H.; Ding, R.J.; et al. Dried bonito flakes-inspired moisture-responsive actuator with a gradient structure for smart devices. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 167, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, X.C.; Zheng, Z.H.; Ding, X.B. A dynamic self-regulation actuator combined double network gel with gradient structure driven by chemical oscillating reaction. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 13168–13172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, A.; Wang, C.L.; Wang, Y.L.; He, H.Y.; Deng, W.T.; Stiernet, P.; Bergstrom, L.; Yuan, J.Y.; Zhang, M. MXene-based solvent-responsive actuators with a polymer-intercalated gradient structure. Chem. Sci. 2025, 16, 2191–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalulu, M.; Munyati, O.; Oderinde, O.; Hu, J.; Ogungbesan, S.O.; Fu, G.D. Robust fabrication of anisotropic bilayer hydrogel embedded with a gradient structure in one layer: Enhanced temperature-responsive bending, shape programmability, and actuator and sensor applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2025, 142, e56707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Z.; Bu, F.; Cheng, E.; Yang, C.; Zhang, Z.S.; Hu, N. Lower-voltage-driven deformable soft electrothermal actuators with embedded liquid metal EGaIn. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2023, 25, 2300253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Gui, X.P.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Wang, Z.Q.; Gao, N.N.; Zhang, T.Q.; Luo, J.W.; Zhai, X.X.; Chen, J.F.; Geng, L.; et al. Overcoming strength-ductility trade-off by building a micro-nano laminated structure based on an ultralow amount of single-dispersed carbon nanotubes. Int. J. Plast. 2023, 171, 103805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bu, F.; Zhu, F.; Zhang, Z.; Xiao, H. A Programmable Soft Electrothermal Actuator Based on a Functionally Graded Structure for Multiple Deformations. Polymers 2025, 17, 2288. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17172288
Bu F, Zhu F, Zhang Z, Xiao H. A Programmable Soft Electrothermal Actuator Based on a Functionally Graded Structure for Multiple Deformations. Polymers. 2025; 17(17):2288. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17172288
Chicago/Turabian StyleBu, Fan, Feng Zhu, Zhengyan Zhang, and Hanbin Xiao. 2025. "A Programmable Soft Electrothermal Actuator Based on a Functionally Graded Structure for Multiple Deformations" Polymers 17, no. 17: 2288. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17172288
APA StyleBu, F., Zhu, F., Zhang, Z., & Xiao, H. (2025). A Programmable Soft Electrothermal Actuator Based on a Functionally Graded Structure for Multiple Deformations. Polymers, 17(17), 2288. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17172288




