Photodegradation Behavior of Nanosilica-Filled PMMA Composite: Cooperative Effect of Mixed Solvents and Interfacial Functional Groups
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Preparation
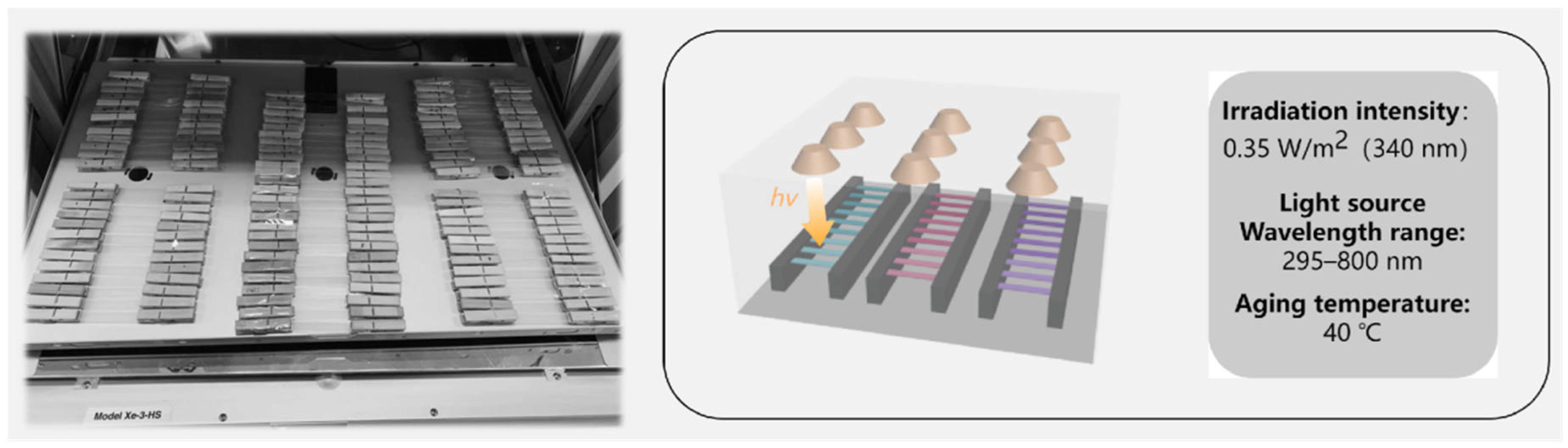
2.2. Photooxidative Aging
2.3. Characterization Methods
3. Results
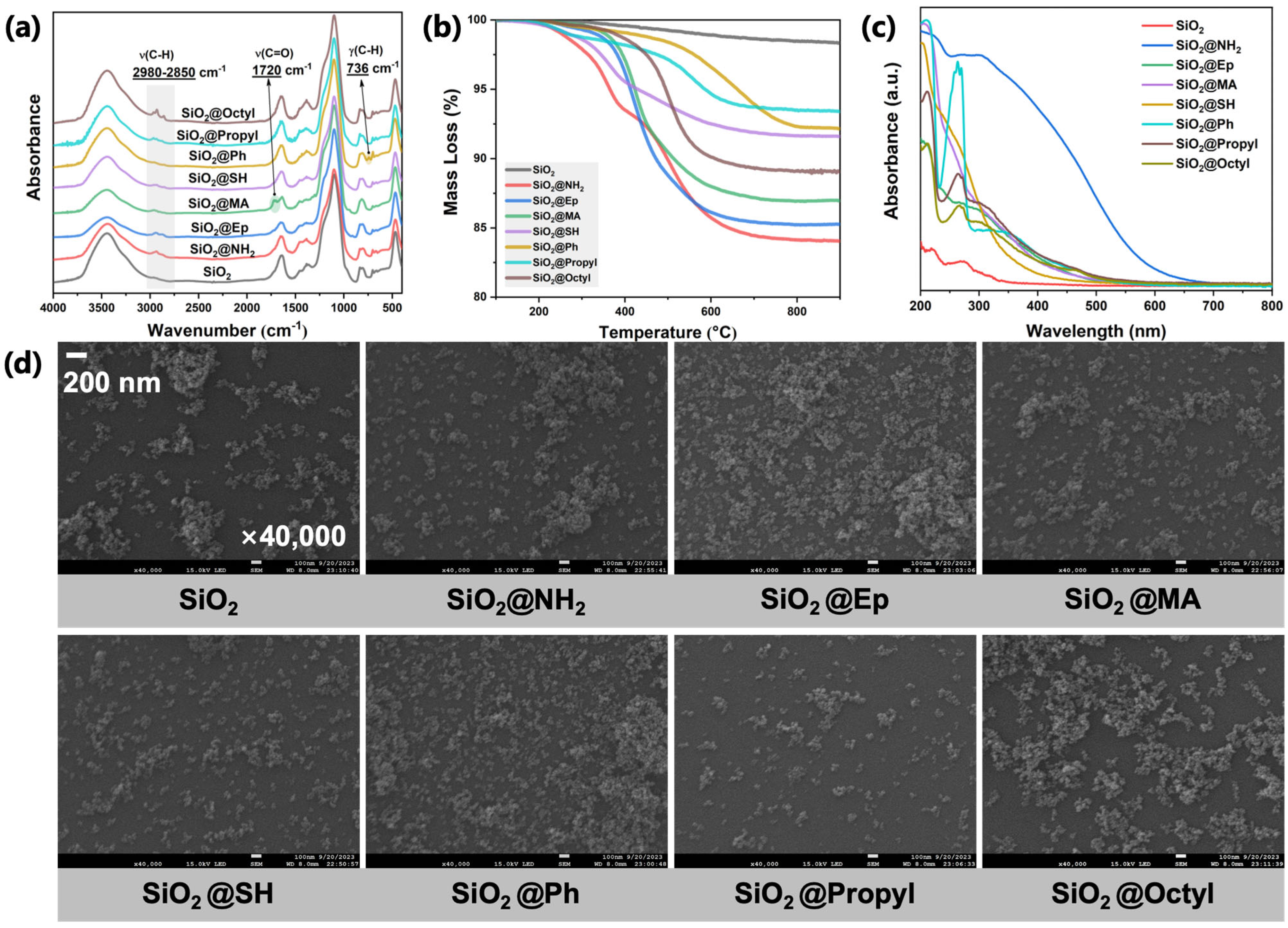
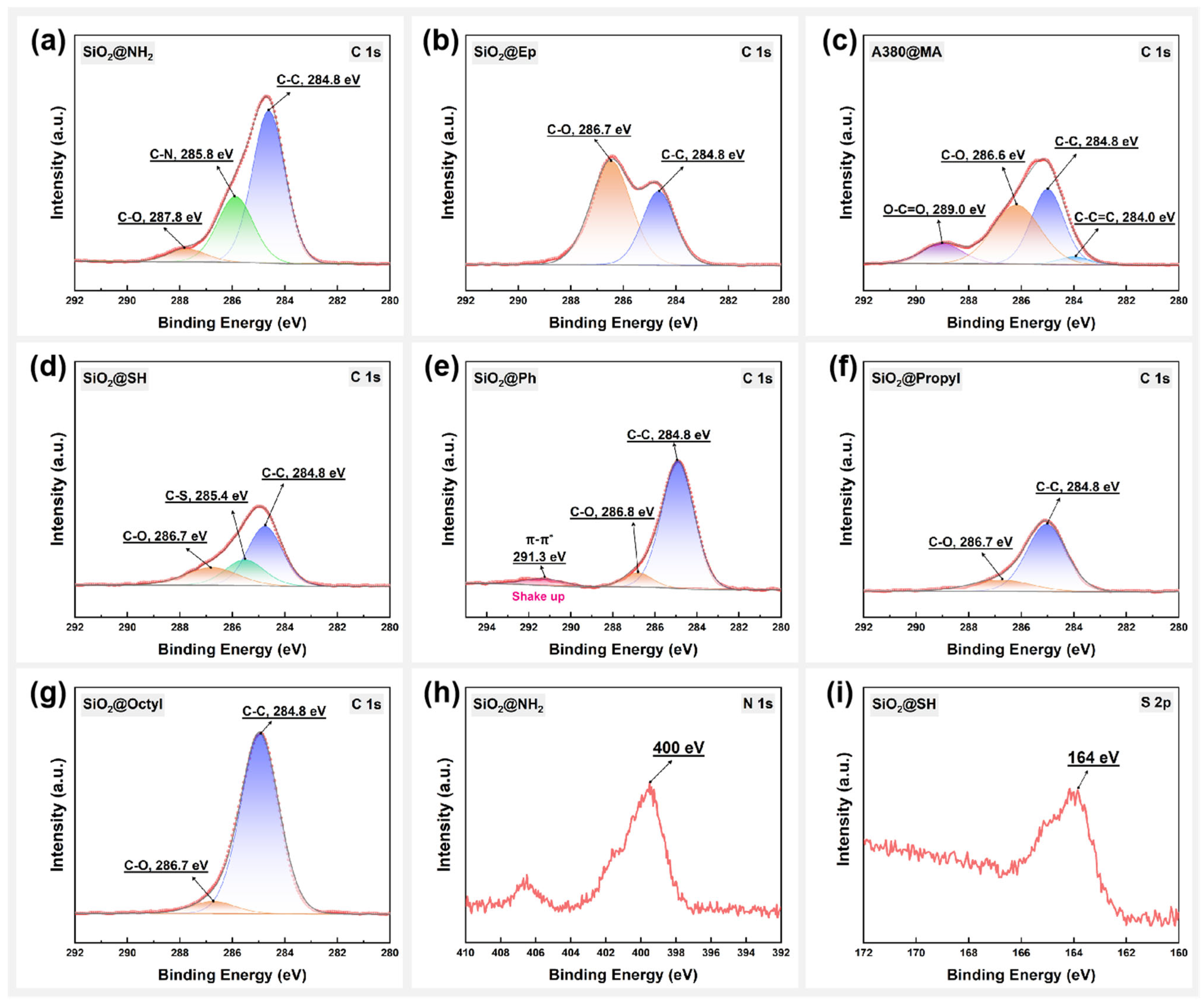
3.1. Surface Structure Analysis of Modified SiO2
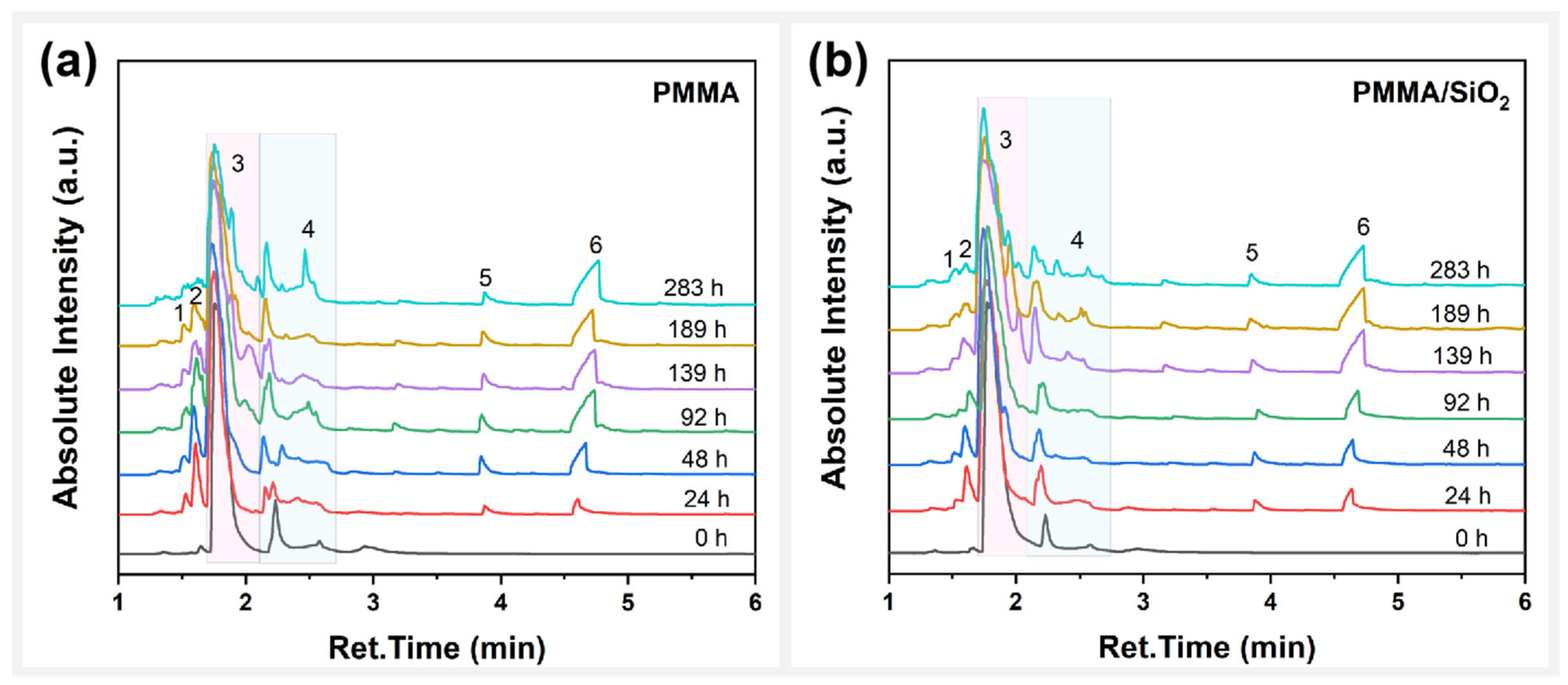
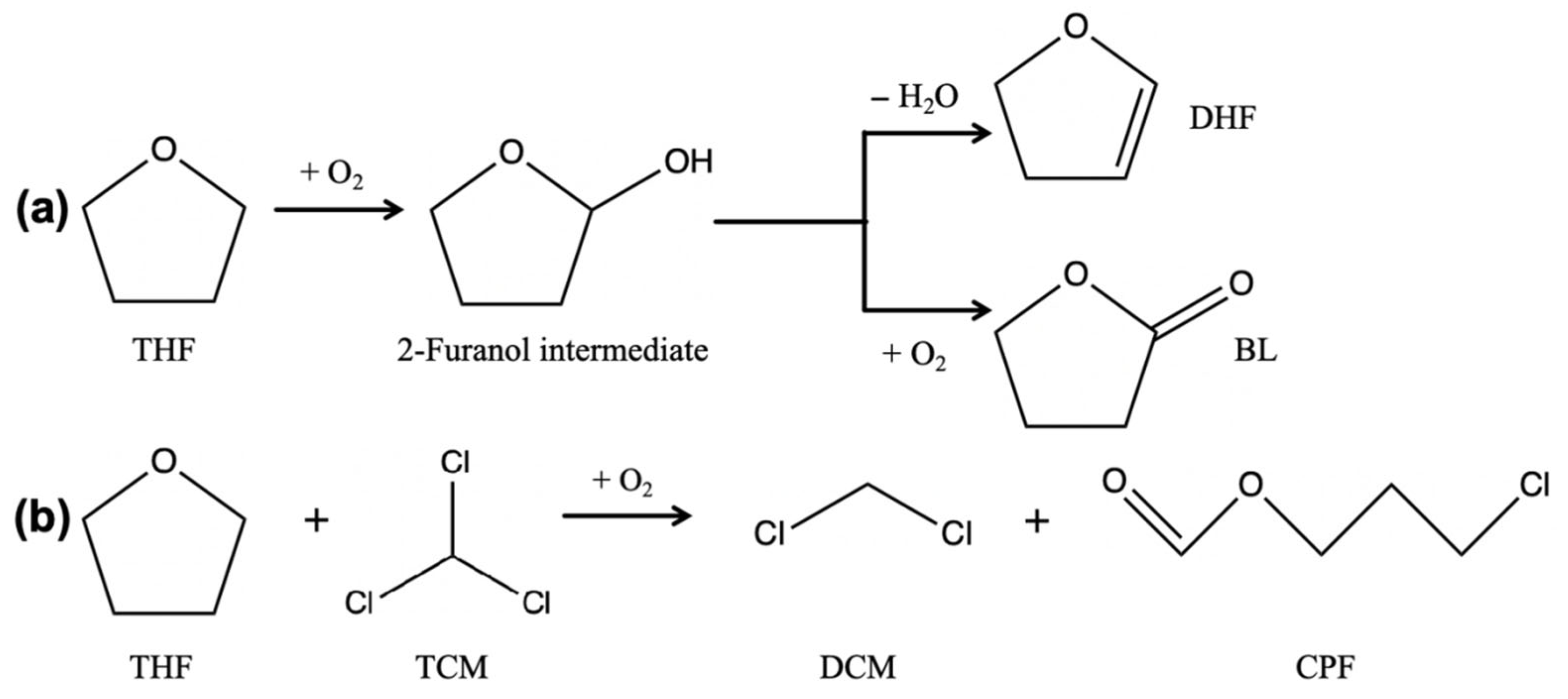
3.2. Analysis of Photodegradation Products
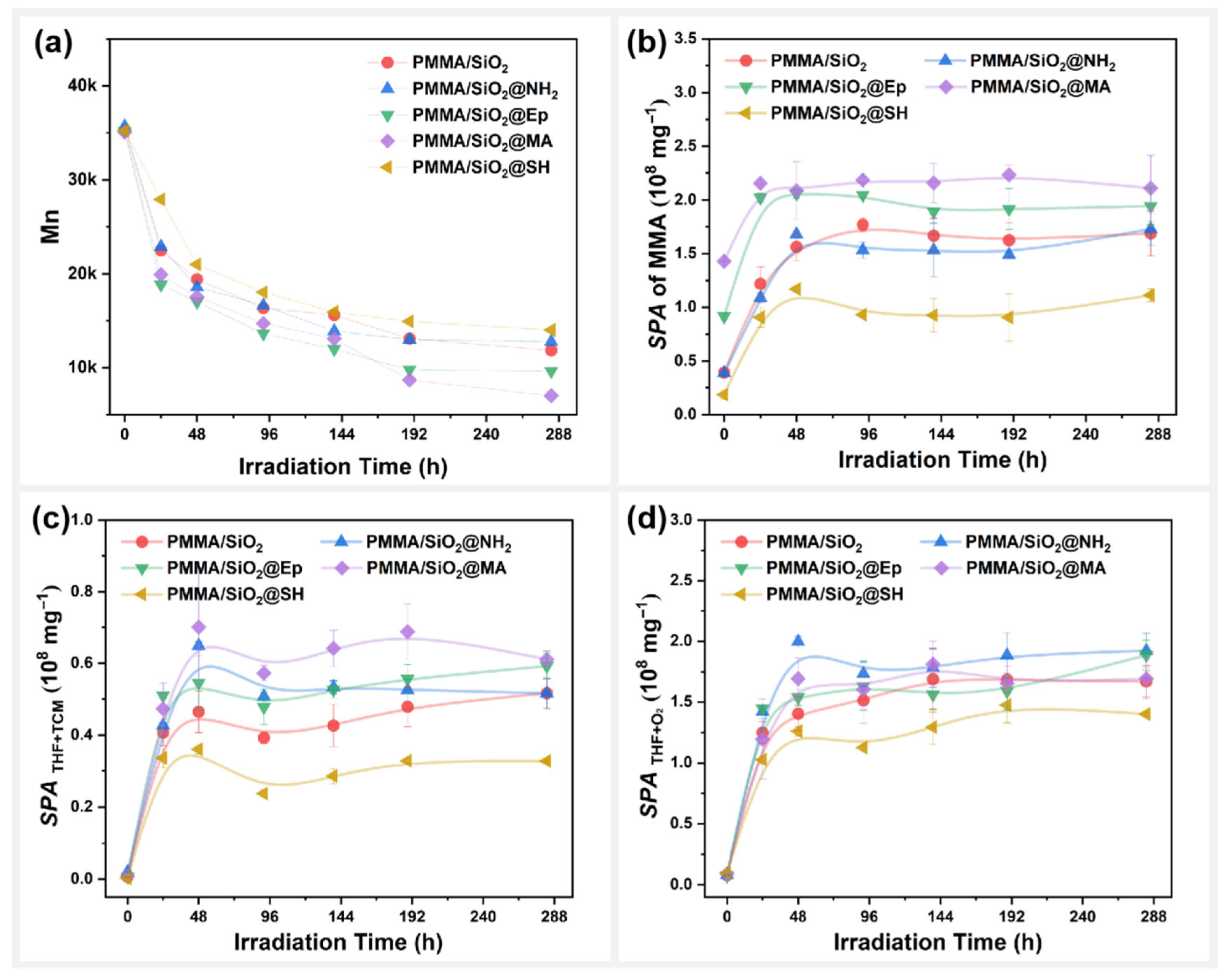
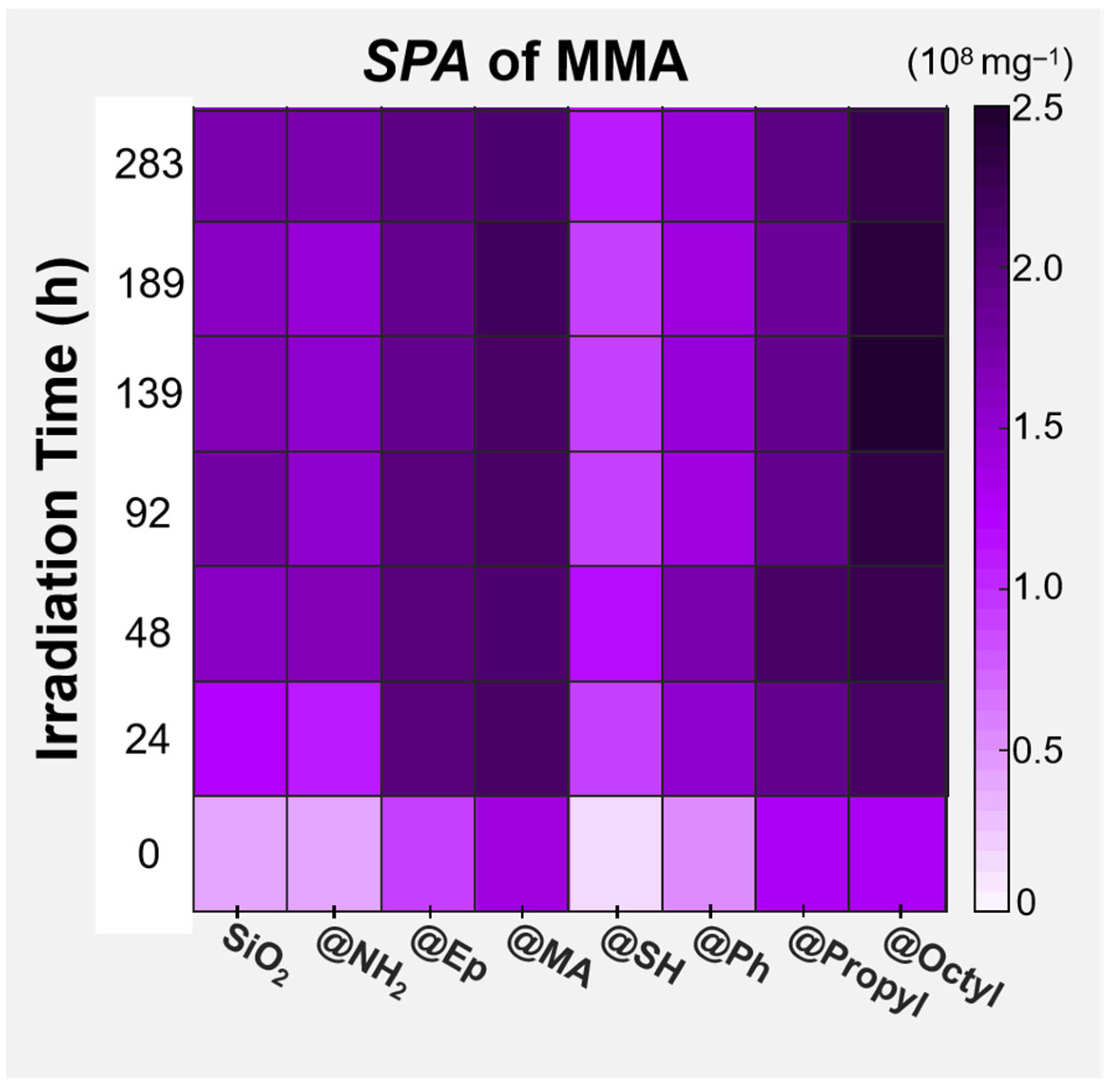
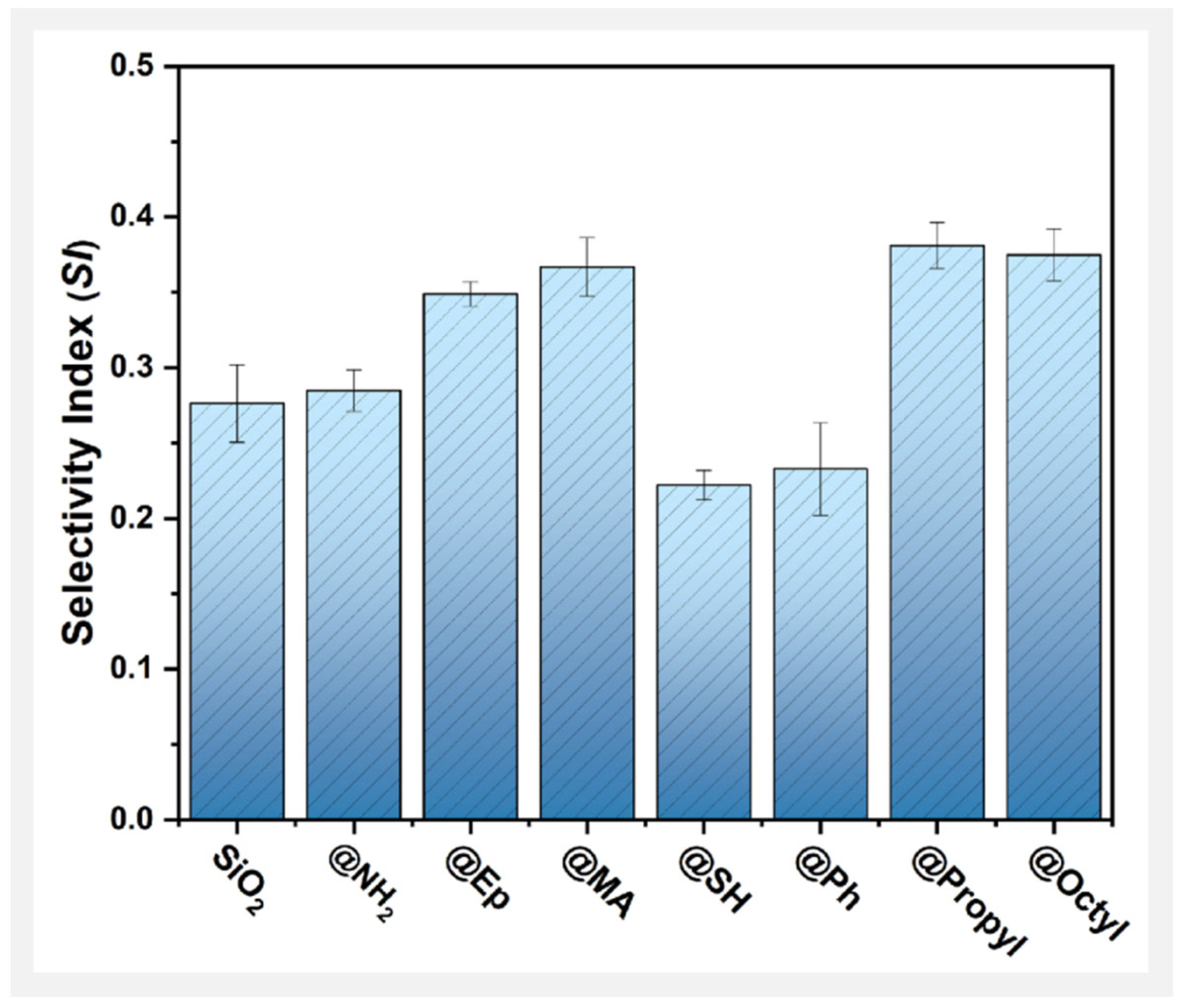
3.3. Effect of Surface Polar Functionalization Modification on the Photodegradation Behavior of PMMA/SiO2
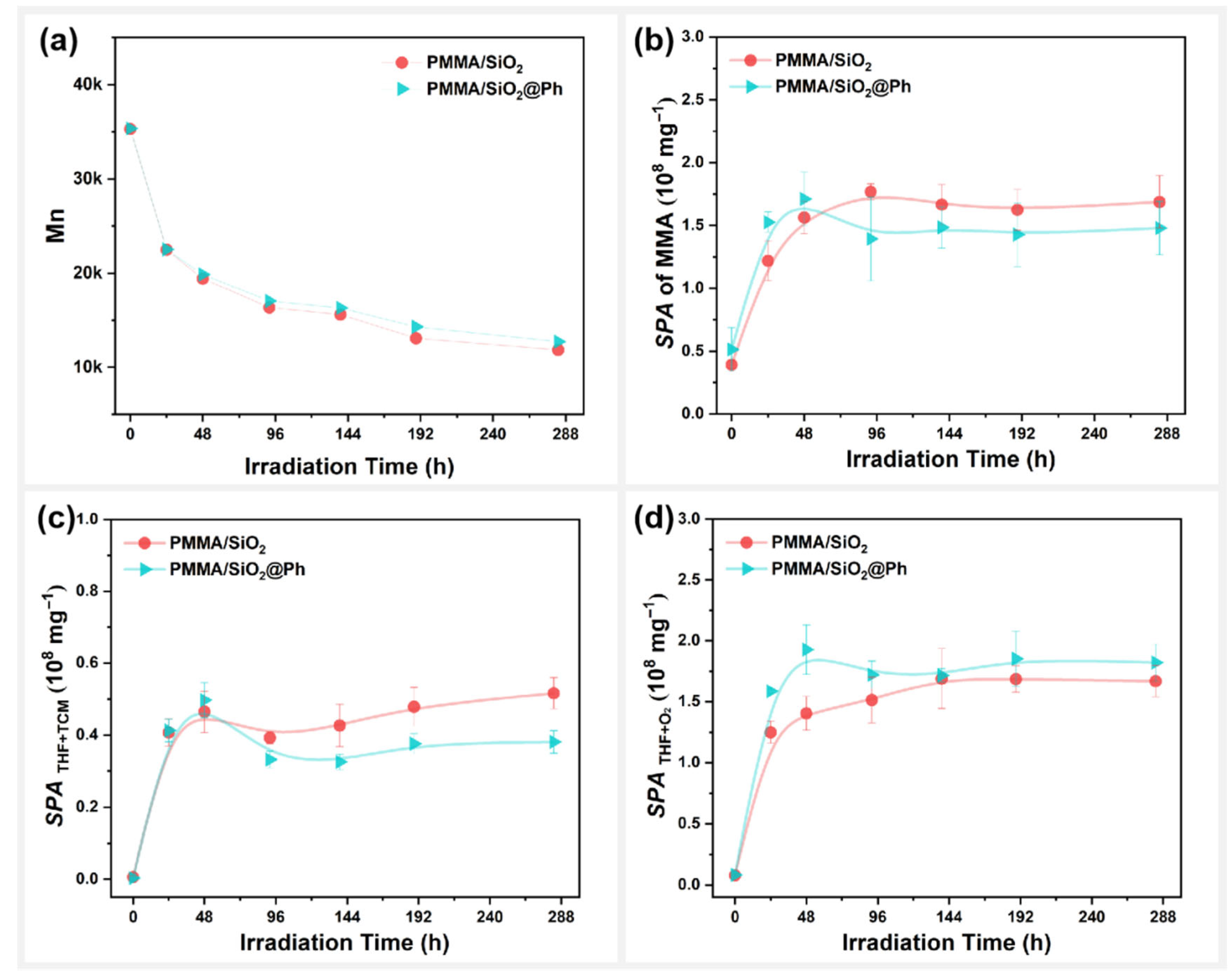
3.4. Effect of Surface Arylation Modification on the Photodegradation Behavior of PMMA/SiO2
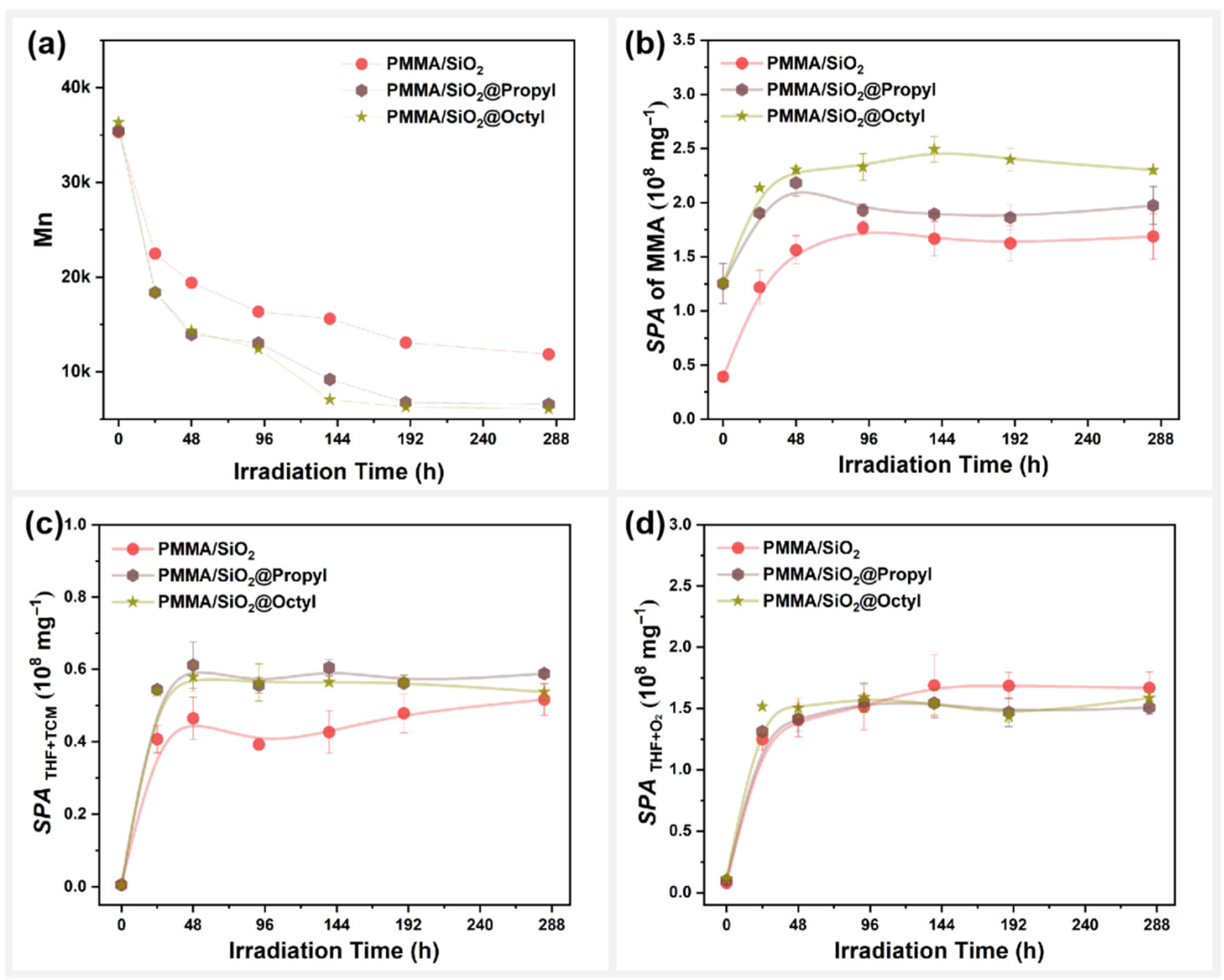
3.5. Effect of Surface Alkylation Modification on the Photodegradation Behavior of PMMA/SiO2
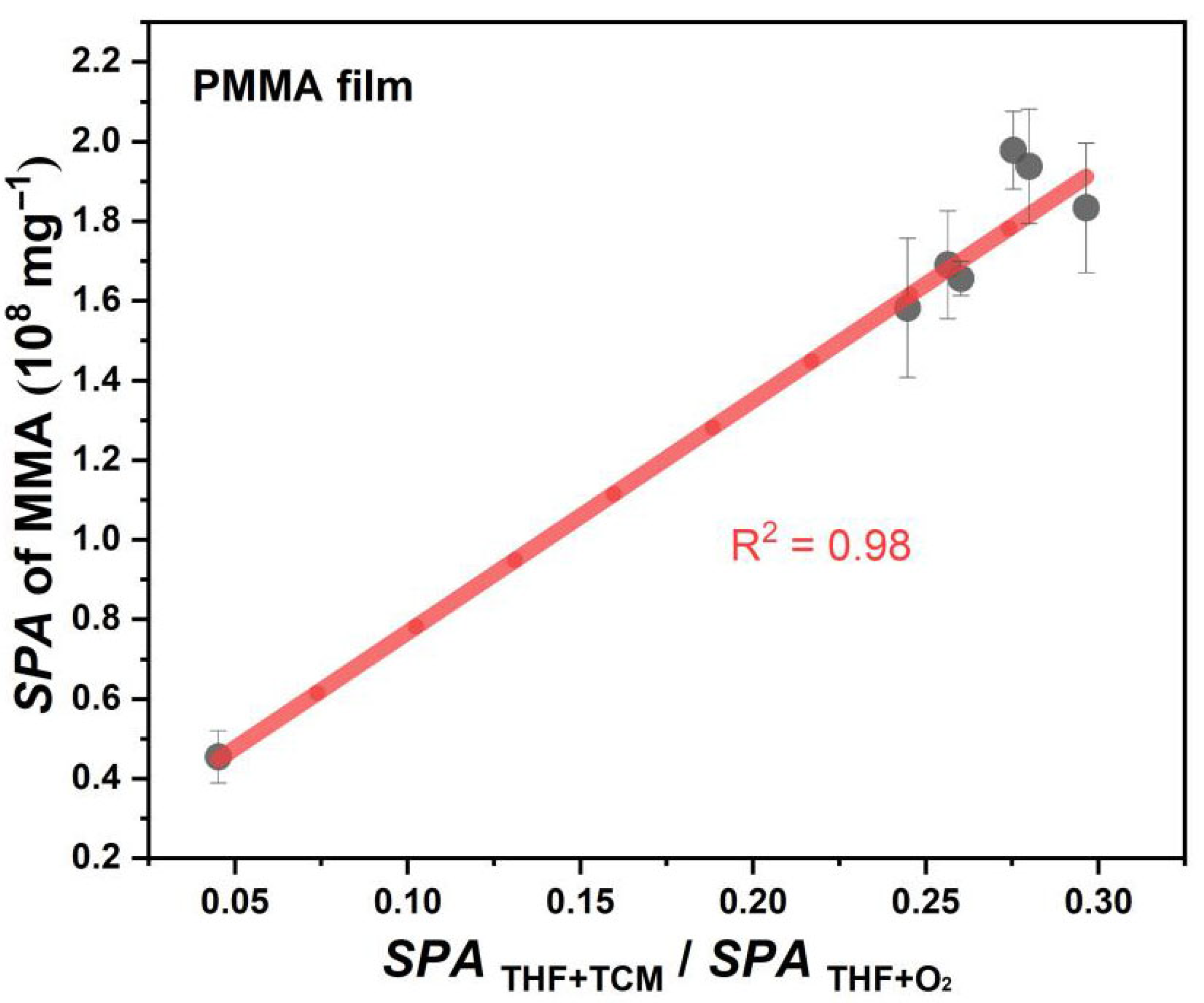
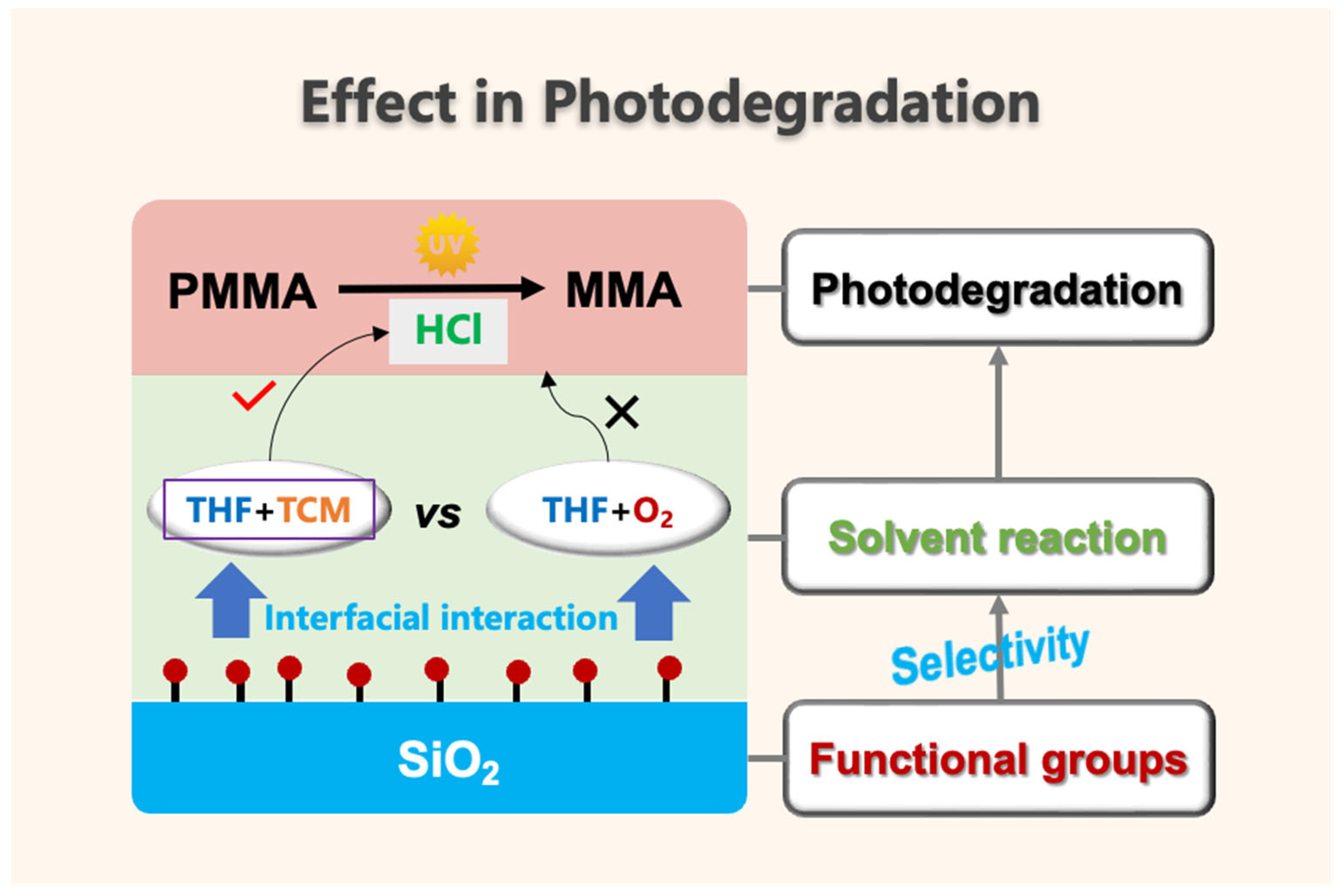
3.6. Interfacial Effect in Photodegradation
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Polar modification, arylation modification, and alkylation modification on the surface of SiO2 significantly affected the photodegradation behavior of the SiO2-filled PMMA composite films with residual mixed solvents. Among them, @Octyl, @Propyl, @MA, and @Ep modifications promoted the photodegradation of the PMMA composite films; @SH and @Ph modifications inhibited the photodegradation of the PMMA composite films; and @NH2 modifications had no effect on the photodegradation rate of the PMMA composite films.
- (2)
- The effects of surface groups on SiO2 on solvent reactivity were the main reason for the different photodegradation behavior of PMMA composite films with residual mixed solvents.
- (3)
- We proposed a cooperative effect in the photodegradation of PMMA/SiO2 composite films with residual mixed solvents. The photodegradation of PMMA composite films was accelerated only when the surface group of SiO2 exhibited a selective promotion effect on the reaction between THF and TCM.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zafar, M.S. Prosthodontic Applications of Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA): An Update. Polymers 2020, 12, 2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, M.-Y.; Choi, T.G. Research trends in polymer materials for use in lightweight vehicles. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2015, 16, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, A.; Patel, A.; Purohit, R. An overview of polymeric materials for automotive applications. Mater. Today Proc. 2017, 4, 3807–3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsulami, Q.A.; Rajeh, A. Structural, thermal, optical characterizations of polyaniline/polymethyl methacrylate composite doped by titanium dioxide nanoparticles as an application in optoelectronic devices. Opt. Mater. 2022, 123, 111820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wei, W.; Zhang, P.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Lv, K.; Liu, X.; Gao, Y. Cs0.32WO3/PMMA nanocomposite via in-situ polymerization for energy saving windows. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2020, 215, 110656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedel, M.; Rosati, A.; Bertasini, M.; Rossi, S. Cu doped YInO3-ZnO green colored NIR reflective pigments: Synthesis and application in PMMA based cool-roof coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2023, 182, 107708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soumya, S.; Sheemol, V.; Amba, P.; Mohamed, A.P.; Ananthakumar, S. Sn and Ag doped ZnO quantum dots with PMMA by in situ polymerization for UV/IR protective, photochromic multifunctional hybrid coatings. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2018, 174, 554–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashiwagi, T.; Morgan, A.B.; Antonucci, J.M.; VanLandingham, M.R.; Harris, R.H., Jr.; Awad, W.H.; Shields, J.R. Thermal and flammability properties of a silica–poly (methylmethacrylate) nanocomposite. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 89, 2072–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinthamanipeta, P.S.; Kobukata, S.; Nakata, H.; Shipp, D.A. Synthesis of poly (methyl methacrylate)–silica nanocomposites using methacrylate-functionalized silica nanoparticles and RAFT polymerization. Polymer 2008, 49, 5636–5642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, G.; Srivastava, S.; Soni, P.; Kalotra, P.; Vijay, Y. Optical, mechanical and structural properties of PMMA/SiO2 nanocomposite thin films. Mater. Res. Express 2018, 5, 015302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Acosta, M.; Quevedo-Lopez, M.; Gnade, B.E.; Ramírez-Bon, R. PMMA-SiO2 organic–inorganic hybrid films: Determination of dielectric characteristics. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2011, 58, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, I.; Vejayakumaran, P.; Sipaut, C.; Ismail, J.; Chee, C. Size-dependent physicochemical and optical properties of silica nanoparticles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2009, 114, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaccaro, L.; Morana, A.; Radzig, V.; Cannas, M. Bright visible luminescence in silica nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 19476–19481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mammeri, F.; Rozes, L.; Le Bourhis, E.; Sanchez, C. Elaboration and mechanical characterization of nanocomposites thin films: Part II. Correlation between structure and mechanical properties of SiO2-PMMA hybrid materials. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2006, 26, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celina, M.C. Review of polymer oxidation and its relationship with materials performance and lifetime prediction. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 2419–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.C.; Carloni, J.D.; Johnson, D.K.; Pankow, J.W.; Gjersing, E.L.; To, B.; Packard, C.E.; Kennedy, C.E.; Kurtz, S.R. An investigation of the changes in poly (methyl methacrylate) specimens after exposure to ultra-violet light, heat, and humidity. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2013, 111, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferriol, M.; Gentilhomme, A.; Cochez, M.; Oget, N.; Mieloszynski, J. Thermal degradation of poly (methyl methacrylate)(PMMA): Modelling of DTG and TG curves. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2003, 79, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, B.; Hay, J.N. The kinetics and mechanisms of the thermal degradation of poly (methyl methacrylate) studied by thermal analysis-Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Polymer 2001, 42, 4825–4835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.-H.; Chen, C.-Y.; Wang, C.-C. Viscoelastic properties and thermal degradation kinetics of silica/PMMA nanocomposites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2004, 84, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laachachi, A.; Ruch, D.; Addiego, F.; Ferriol, M.; Cochez, M.; Cuesta, J.-M.L. Effect of ZnO and organo-modified montmorillonite on thermal degradation of poly (methyl methacrylate) nanocomposites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2009, 94, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laachachi, A.; Leroy, E.; Cochez, M.; Ferriol, M.; Cuesta, J.L. Use of oxide nanoparticles and organoclays to improve thermal stability and fire retardancy of poly (methyl methacrylate). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2005, 89, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzi-Nshuti, C.; Wang, D.; Hossenlopp, J.M.; Wilkie, C.A. The role of the trivalent metal in an LDH: Synthesis, characterization and fire properties of thermally stable PMMA/LDH systems. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2009, 94, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzi-Nshuti, C.; Wang, D.; Hossenlopp, J.M.; Wilkie, C.A. Aluminum-containing layered double hydroxides: The thermal, mechanical, and fire properties of (nano) composites of poly(methyl methacrylate). J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 3091–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Watson, S.S.; Sung, L.-P. Surface degradation process affected by heterogeneity in nano-titanium dioxide filled acrylic urethane coatings under accelerated UV exposure. Polymer 2014, 55, 6594–6603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raad, R.; Abdallh, M.; Yousif, E.; Ahmed, A.; Bofaroosha, M. Study of the photochemical behaver of poly (methyl methacrylate) nanocomposite modified by sulfadiazine. J. Polym. Res. 2022, 29, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laachachi, A.; Cochez, M.; Ferriol, M.; Lopez-Cuesta, J.; Leroy, E. Influence of TiO2 and Fe2O3 fillers on the thermal properties of poly (methyl methacrylate)(PMMA). Mater. Lett. 2005, 59, 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinausero, N.; Azema, N.; Cochez, M.; Ferriol, M.; Essahli, M.; Ganachaud, F.; Lopez-Cuesta, J.-M. Influence of the surface modification of alumina nanoparticles on the thermal stability and fire reaction of PMMA composites. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2008, 19, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grohens, Y.; Schultz, J.; Prud’Homme, R. PMMA conformational changes on γ-alumina powder: Influence of the polymer tacticity on the configuration of the adsorbed layer. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 1997, 17, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Japić, D.; Marinšek, M.; Orel, Z.C. Effect of ZnO on the Thermal Degradation Behavior of Poly (Methyl Methacrylate) Nanocomposites. Acta Chim. Slov. 2016, 63, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Chen, M.; Wei, C.; Tao, J.; Huang, N.; Qi, Z.; Li, L. Synthesis at the nanoscale of ZnO into poly (methyl methacrylate) and its characterization. Appl. Phys. A 2014, 117, 1085–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laachachi, A.; Cochez, M.; Ferriol, M.; Leroy, E.; Cuesta, J.L.; Oget, N. Influence of Sb2O3 particles as filler on the thermal stability and flammability properties of poly (methyl methacrylate)(PMMA). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2004, 85, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, A.; Dubey, K.; Bhardwaj, Y.; Jain, D.; Choudhury, S.; Tyagi, A. UV-shielding transparent PMMA/In2O3 nanocomposite films based on In2O3 nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 20913–20921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, E.; Shin, K. Radiation resistant polymer–carbon nanotube nanocomaposite thin films. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2005, 257, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, R.; Ali, S.; Ahmed, F.; Ullah, S.; Grant, J.T. Thermal and thermomechanical behavior of amino functionalized and metal decorated MWCNTs/PMMA nanocomposite films. Polym. Compos. 2014, 35, 1807–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.S.; Agrachev, M.; Kim, H.; Truong, N.P.; Choi, T.-L.; Jeschke, G.; Anastasaki, A. Visible light–triggered depolymerization of commercial polymethacrylates. Science 2025, 387, 874–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Meng, X.; Liu, Y.; Yang, R. Accelerated photodegradation of PMMA films: Synergistic effect of mixed solvents. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2025, 189, 107106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuravlev, L.T. The surface chemistry of amorphous silica. Zhuravlev model. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2000, 173, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Reagents | Features | Abbreviations | Company |
|---|---|---|---|
| Xylene | AR, ≥99.7% | Greagent, Shanghai, China | |
| Anhydrous ethanol | AR, ≥99.7% | Greagent, Shanghai, China | |
| Octyltrimethoxysilane | Purity: 98% ρ = 0.91 g/mL Boiling point: 191.5 ± 8.0 °C | OTMS | Heowns Biochem Technologies. Llc. Tianjin, China |
| Propyltriethoxysilane | Purity: 98% ρ = 0.89 g/mL Boiling point: 168.4 ± 8.0 °C | PTES | Bide Pharmatech Co., Ltd. Shanghai, China |
| γ-(2,3-epoxypropoxy) propyltrimethoxysilane | Purity: 98% ρ = 1.07 g/mL Boiling point: 299.4 °C | EPPTMS | Energy Chemical, Anhui Senrise Technologies Co., Ltd., Hefei, China |
| 3-mercaptopropyltri- methoxysilane | Purity: 98% ρ = 1.06 g/mL Boiling point: 198.0 °C | MPTMS | Energy Chemical, Anhui Senrise Technologies Co., Ltd. |
| 3-aminopropyltriethoxy-silane | Purity: 99.5% ρ = 0.95 g/mL Boiling point: 222.1 ± 13.0 °C | APTES | Energy Chemical, Anhui Senrise Technologies Co., Ltd. |
| γ-methacryloxypropyltri-methoxysilane | Purity: 98% ρ = 1.04 g/mL Boiling point: 190 °C | MAPTMS | Shanghai Dibai Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China |
| Phenyltrimethoxysilane | Purity: 99.5% ρ = 1.06 g/mL Boiling point: 185.7 ± 9.0 °C | PhTMS | Energy Chemical, Anhui Senrise Technologies Co., Ltd. |
| Peaks | Ret. Time | Volatile Products | Molecular Structure |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.6 | Dichloromethane (DCM) | 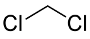 |
| 2 | 1.7 | 2,3-dihydrofuran (DHF) | 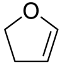 |
| 3 | 1.7–2.2 | Solvents | 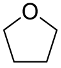 or or 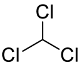 |
| 4 | 2.2–2.8 | Methyl methacrylate (MMA) |  |
| 5 | 4.2 | 3-Chloropropyl formate (CPF) | 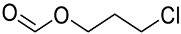 |
| 6 | 4.8 | γ-butyrolactone (BL) | 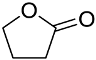 |
| Modified SiO2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2@NH2 | ↑ | ↑ | - |
| SiO2@Ep | ↑ | - | ↑ |
| SiO2@MA | ↑↑ | - | ↑↑ |
| SiO2@SH | ↓↓ | ↓ | ↓ |
| SiO2@Ph | ↓ | ↑ | ↓ |
| SiO2@Propyl | ↑↑ | - | ↑ |
| SiO2@Octyl | ↑↑ | - | ↑↑↑ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Z.; Li, L.; Liu, Y.; Yang, R. Photodegradation Behavior of Nanosilica-Filled PMMA Composite: Cooperative Effect of Mixed Solvents and Interfacial Functional Groups. Polymers 2025, 17, 2241. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17162241
Xu Z, Li L, Liu Y, Yang R. Photodegradation Behavior of Nanosilica-Filled PMMA Composite: Cooperative Effect of Mixed Solvents and Interfacial Functional Groups. Polymers. 2025; 17(16):2241. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17162241
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Zhiping, Liangchen Li, Ying Liu, and Rui Yang. 2025. "Photodegradation Behavior of Nanosilica-Filled PMMA Composite: Cooperative Effect of Mixed Solvents and Interfacial Functional Groups" Polymers 17, no. 16: 2241. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17162241
APA StyleXu, Z., Li, L., Liu, Y., & Yang, R. (2025). Photodegradation Behavior of Nanosilica-Filled PMMA Composite: Cooperative Effect of Mixed Solvents and Interfacial Functional Groups. Polymers, 17(16), 2241. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17162241







