Preparation of pH-Responsive PET TeMs by Controlled Graft Block Copolymerisation of Styrene and Methacrylic Acid for the Separation of Water–Oil Emulsions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
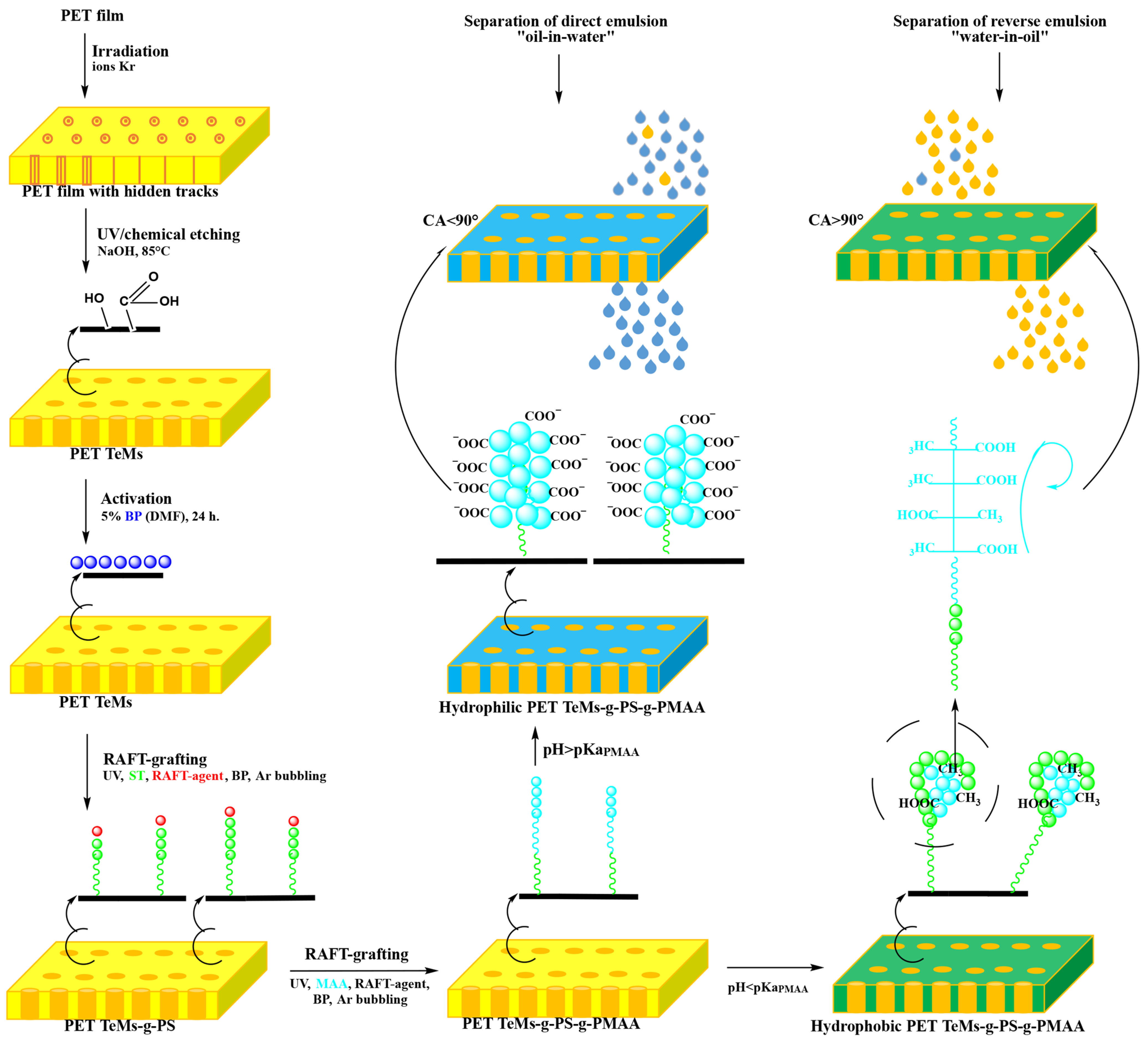
2.2. Preparation and Modification of Track-Etched Membranes
2.2.1. Track-Etched Membranes Base Preparation: Irradiation and Etching of PET Films
2.2.2. UV-Initiated RAFT Graft Polymerization for PET TeMs Modification
2.3. PET TeMs-g-PS-g-PMAA Characterization
2.3.1. Contact Angle (CA) Measurement and pH-Responsivity Evaluation
2.3.2. Degree of Grafting (DG) Determination
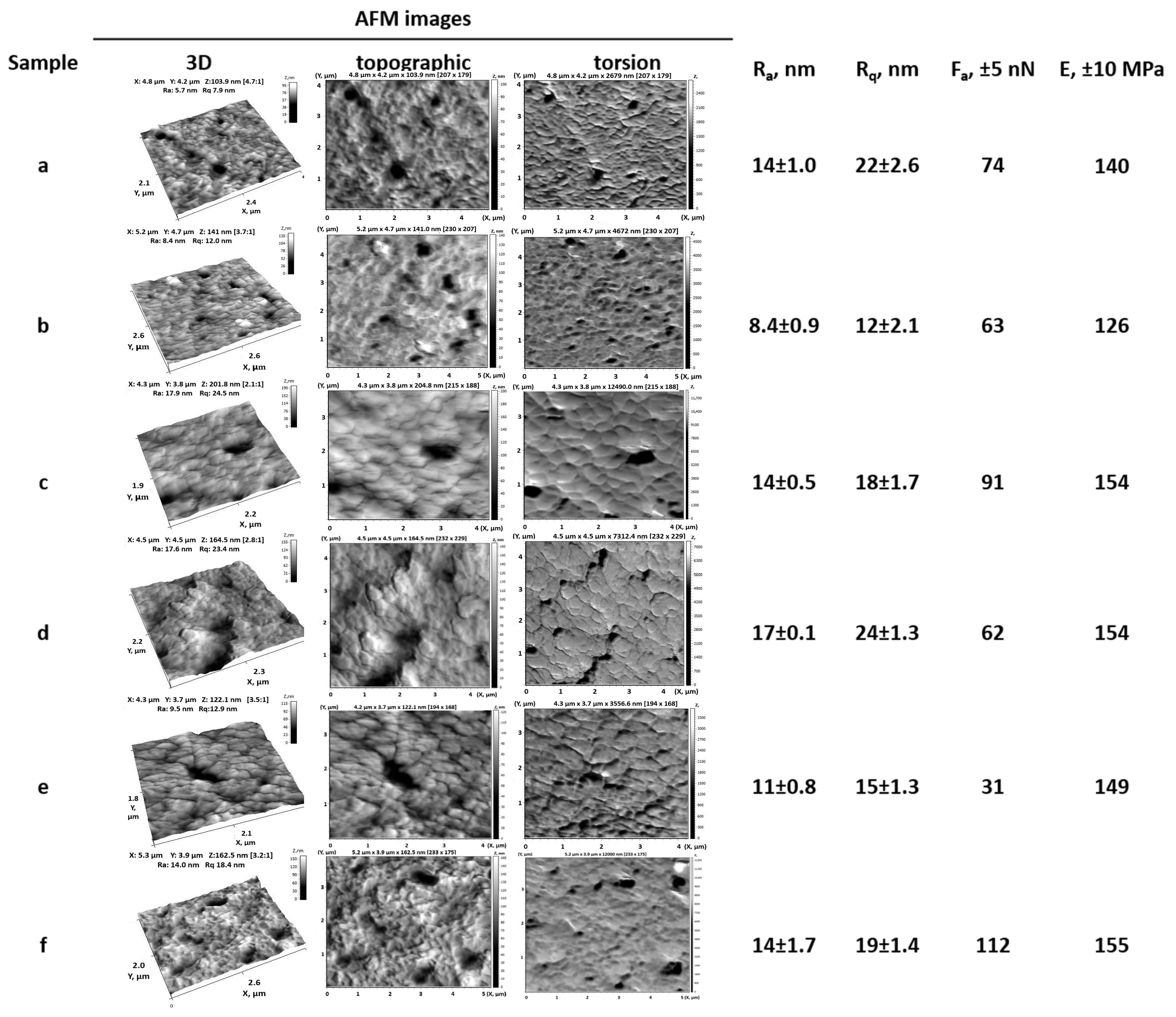
2.3.3. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
2.3.4. UV-Vis Spectroscopy
2.3.5. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
2.3.6. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.3.7. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.4. Performance Assessment of PET TeMs-g-PS-g-PMAA in Water-Oil Emulsion Separation
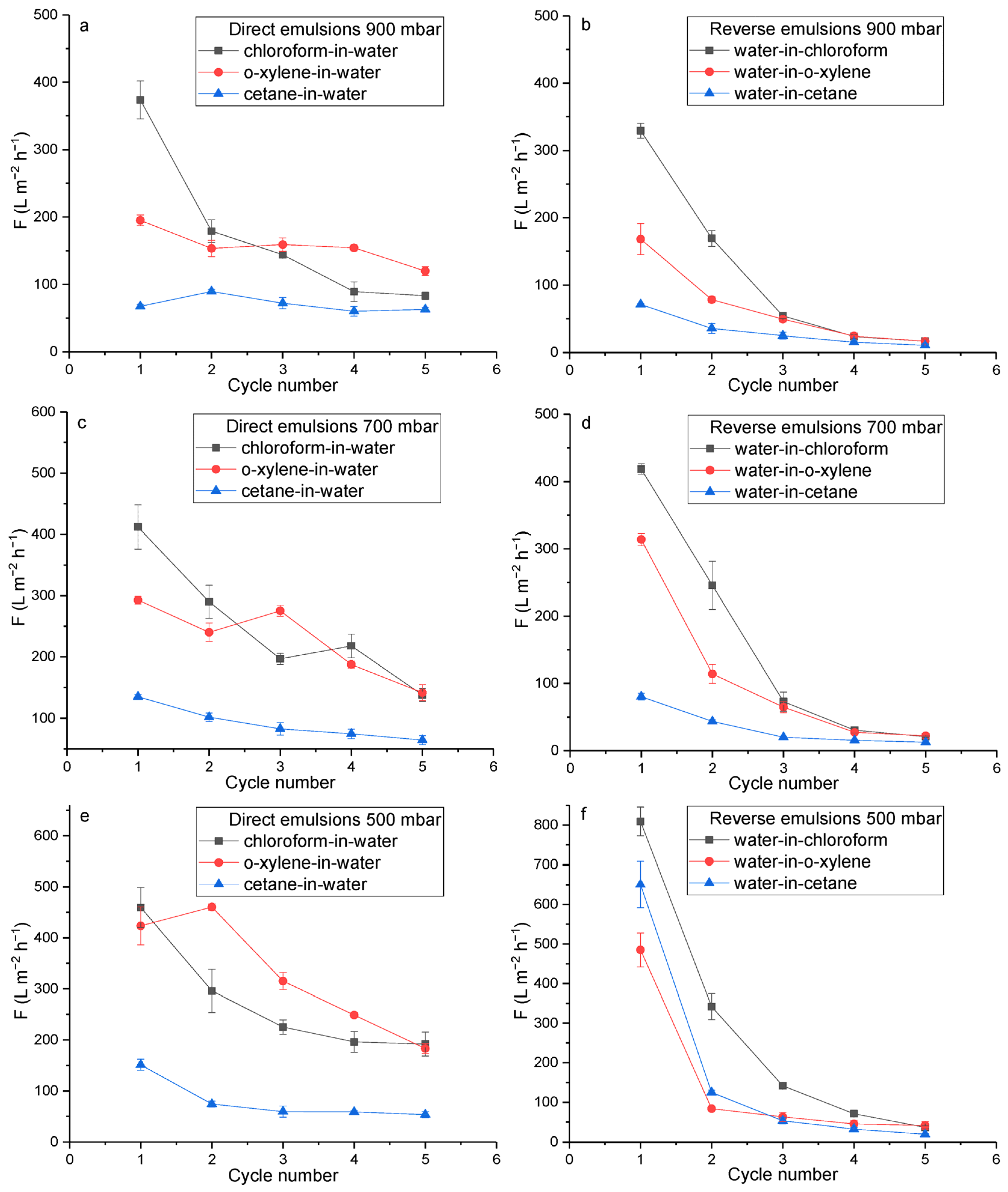
2.4.1. Evaluation of PET TeMs-g-PS-g-PMAA Fouling and Flux Recovery in Water-Oil Separation
2.4.2. Analytical Techniques for Emulsion and Permeate Characterization
3. Results and Discussions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, N.; Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, J.; Cui, P.; Jiang, W. A Review on Oil/Water Emulsion Separation Membrane Material. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, G.; Al Mohawes, K.B.; Khashab, N.M. Smart Membranes for Separation and Sensing. Chem. Sci. 2024, 15, 18772–18788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karunakar, K.K.; Cheriyan, B.V.; Anandakumar, R.; Murugathirumal, A.; Senthilkumar, A.; Nandhini, J.; Kataria, K.; Yabase, L. Stimuli-Responsive Smart Materials: Bridging the Gap between Biotechnology and Regenerative Medicine. Bioprinting 2025, 48, e00415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.; Sohail, M.; Baig, N.; Yuan, K.; Abdala, A.; Wahab, M.A. Next-Generation Stimuli-Responsive Smart Membranes: Developments in Oil/Water Separation. Adv. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2025, 341, 103487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Dong, Y.; Huang, C.; Hussain Abdalkarim, S.Y.; Yu, H.Y.; Tam, K.C. On-Demand plus and Minus Strategy to Design Conductive Nanocellulose: From Low-Dimensional Structural Materials to Multi-Dimensional Smart Sensors. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 510, 161552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korolkov, I.V.; Mashentseva, A.A.; Güven, O.; Gorin, Y.G.; Kozlovskiy, A.L.; Zdorovets, M.V.; Zhidkov, I.S.; Cholach, S.O. Electron/Gamma Radiation-Induced Synthesis and Catalytic Activity of Gold Nanoparticles Supported on Track-Etched Poly(Ethylene Terephthalate) Membranes. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 217, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakarvarti, S.K. Track-Etch Membranes Enabled Nano-/Microtechnology: A Review. Radiat. Meas. 2009, 44, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsbay, M.; Güven, O. Grafting in Confined Spaces: Functionalization of Nanochannels of Track-Etched Membranes. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2014, 105, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, M.K.; Wang, X.; Peng, Y.; Sangaraju, S.; Ran, F. Functional Polymeric Membrane Materials: A Perspective from Versatile Methods and Modification to Potential Applications. Polym. Sci. Technol. 2024, 1, 366–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semsarilar, M.; Abetz, V.; Semsarilar, M.; Abetz, V. Polymerizations by RAFT: Developments of the Technique and Its Application in the Synthesis of Tailored (Co)Polymers. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2021, 222, 2000311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, L.H.; Caldona, E.B.; Advincula, R.C. PET-RAFT Polymerization under Flow Chemistry and Surface-initiated Reactions. Polym. Int. 2022, 72, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamson, A.W.; Klerer, J. Modification of Pet Surfaces with End-Functionalized Polymers Prepared from Raft Agents to Achieve Antibacterial Properties = Modifikasi Permukaan Pet Dengan Polimer-Polimer Fungsional Dari Agen Raft Untuk Mencapai Sifat Antibakteri. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 124, 192C. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Modification-of-Pet-Surfaces-with-Polymers-Prepared-Amora/92e54f4894e2e53aa199c5c167ee5b607c7135ad (accessed on 19 June 2025). [CrossRef]
- Pan, K.; Ren, R.; Li, H.; Cao, B. Preparation of Dual Stimuli-Responsive PET Track-Etched Membrane by Grafting Copolymer Using ATRP. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2013, 24, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeszhanov, A.B.; Korolkov, I.V.; Shakayeva, A.K.; Lissovskaya, L.I.; Zdorovets, M.V. Preparation of Poly(Ethylene Terephthalate) Track-Etched Membranes for the Separation of Water-Oil Emulsions. Eurasian J. Chem. 2023, 2023, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, S.L.; Abidin, M.N.Z.; Ma’amor, A.; Hashim, N.A.; Hashim, M.L.H. Polyethylene Terephthalate Membrane: A Review of Fabrication Techniques, Separation Processes, and Modifications. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 354, 129343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmanbek, N.; Aimanova, N.A.; Mashentseva, A.A.; Barsbay, M.; Abuova, F.U.; Nurpeisova, D.T.; Jakupova, Z.Y.; Zdorovets, M.V. e-Beam and γ-rays Induced Synthesis and Catalytic Properties of Copper Nanoclusters-Deposited Composite Track-Etched Membranes. Membranes 2023, 13, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmanbek, N.; Sütekin, S.D.; Barsbay, M.; Aimanova, N.A.; Mashentseva, A.A.; Alimkhanova, A.N.; Zhumabayev, A.M.; Yanevich, A.; Almanov, A.A.; Zdorovets, M.V. Environmentally Friendly Loading of Palladium Nanoparticles on Nanoporous PET Track-Etched Membranes Grafted by Poly(1-Vinyl-2-Pyrrolidone) via RAFT Polymerization for the Photocatalytic Degradation of Metronidazole. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 18700–18714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friebe, A.; Ulbricht, M. Controlled Pore Functionalization of Poly(Ethylene Terephthalate) Track-Etched Membranes via Surface-Initiated Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization. Langmuir 2007, 23, 10316–10322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolinska, K.; Bryjak, M. Plasma Modified Track-Etched Membranes for Separation of Alkaline Ions. Open Access J. Sci. Technol. AgiAl Publ. House 2014, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakayeva, A.K.; Yeszhanov, A.B.; Zhumazhanova, A.T.; Korolkov, I.V.; Zdorovets, M.V. Fabrication of Hydrophobic PET Track-Etched Membranes Using 2,2,3,3,4,4,4-Heptafluorobutyl Methacrylate for Water Desalination by Membrane Distillation. Eurasian J. Chem. 2024, 29, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakayeva, A.K.; Yeszhanov, A.B.; Borissenko, A.N.; Kassymzhanov, M.T.; Zhumazhanova, A.T.; Khlebnikov, N.A.; Nurkassimov, A.K.; Zdorovets, M.V.; Güven, O.; Korolkov, I.V. Surface Modification of Polyethylene Terephthalate Track-Etched Membranes by 2,2,3,3,4,4,5,5,6,6,7,7-Dodecafluoroheptyl Acrylate for Application in Water Desalination by Direct Contact Membrane Distillation. Membranes 2024, 14, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korolkov, I.V.; Kuandykova, A.; Yeszhanov, A.B.; Güven, O.; Gorin, Y.G.; Zdorovets, M.V. Modification of PET Ion-Track Membranes by Silica Nanoparticles for Direct Contact Membrane Distillation of Salt Solutions. Membranes 2020, 10, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, J.; Gui, X.; Hou, B.; Mo, D.; Lu, L.; Yao, H. Hydrophobic Modified PET Ion Track-Etched Membrane for Oil/Water Separation. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 54, 103997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeszhanov, A.B.; Muslimova, I.B.; Melnikova, G.B.; Petrovskaya, A.S.; Seitbayev, A.S.; Chizhik, S.A.; Zhappar, N.K.; Korolkov, I.V.; Güven, O.; Zdorovets, M.V. Graft Polymerization of Stearyl Methacrylate on PET Track-Etched Membranes for Oil–Water Separation. Polymers 2022, 14, 3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Shaeli, M.; Benkhaya, S.; Al-Juboori, R.A.; Koyuncu, I.; Vatanpour, V. PH-Responsive Membranes: Mechanisms, Fabrications, and Applications. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 946, 173865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maaz, M.; Elzein, T.; Bejjani, A.; Barroca-Aubry, N.; Lepoittevin, B.; Dragoe, D.; Mazerat, S.; Nsouli, B.; Roger, P. Surface Initiated Supplemental Activator and Reducing Agent Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization (SI-SARA-ATRP) of 4-Vinylpyridine on Poly(Ethylene Terephthalate). J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2017, 500, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dansawad, P.; Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Shang, X.; Li, Y.; Guo, Z.; Qing, Y.; Zhao, S.; You, S.; Li, W. Smart Membranes for Oil/Water Emulsions Separation: A Review. Adv. Membr. 2022, 2, 100039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.K.; Dunderdale, G.J.; England, M.W.; Hozumi, A. Oil/Water Separation Techniques: A Review of Recent Progresses and Future Directions. J. Mater. Chem. A Mater. 2017, 5, 16025–16058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasouli, S.; Rezaei, N.; Hamedi, H.; Zendehboudi, S.; Duan, X. Superhydrophobic and Superoleophilic Membranes for Oil-Water Separation Application: A Comprehensive Review. Mater. Des. 2021, 204, 109599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, Y.; Mao, X.; Gao, Z.; Luo, S.; Kipper, M.J.; Huang, L.; Tang, J. Recent Advances in Electrospinning Smart Membranes for Oil/Water Separation. Surf. Interfaces 2024, 55, 105427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muslimova, I.B.; Zhumanazar, N.; Melnikova, G.B.; Yeszhanov, A.B.; Zhatkanbayeva, Z.K.; Chizhik, S.A.; Zdorovets, M.V.; Güven, O.; Korolkov, I.V. Preparation and Application of Stimuli-Responsive PET TeMs: RAFT Graft Block Copolymerisation of Styrene and Acrylic Acid for the Separation of Water-Oil Emulsions. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 14425–14437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.N.; Li, J.J.; Luo, Z.H. Toward Efficient Water/Oil Separation Material: Effect of Copolymer Composition on PH-Responsive Wettability and Separation Performance. AIChE J. 2016, 62, 1758–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Loh, X.J.; Tan, B.H.; Li, Z. PH-Responsive Poly(Dimethylsiloxane) Copolymer Decorated Magnetic Nanoparticles for Remotely Controlled Oil-in-Water Nanoemulsion Separation. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2019, 40, 1800013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muslimova, I.B.; Zhatkanbayeva, Z.K.; Omertasov, D.D.; Melnikova, G.B.; Yeszhanov, A.B.; Güven, O.; Chizhik, S.A.; Zdorovets, M.V.; Korolkov, I.V. Stimuli-Responsive Track-Etched Membranes for Separation of Water-Oil Emulsions. Membranes 2023, 13, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Cameron, A. Dual-Responsive Polymers Synthesized via RAFT Polymerization for Controlled Demulsification and Desorption. J. Polym. Res. 2023, 30, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yu, Q.; Wang, M.; Liu, D.; Dong, L.; Cui, Z.; He, B.; Li, J.; Yan, F. Superhydrophilic/Underwater Superoleophobic PVDF Ultrafiltration Membrane with PH-Responsive Self-Cleaning Performance for Efficient Oil-Water Separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 330, 125420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Deng, X.; An, Z. PH-Induced Inversion of Water-in-Oil Emulsions to Oil-in-Water High Internal Phase Emulsions (HIPEs) Using Core Cross-Linked Star (CCS) Polymer as Interfacial Stabilizer. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2014, 35, 1148–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeszhanov, A.B.; Korolkov, I.V.; Dosmagambetova, S.S.; Zdorovets, M.V.; Güven, O. Recent Progress in the Membrane Distillation and Impact of Track-Etched Membranes. Polymers 2021, 13, 2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korolkov, I.V.; Narmukhamedova, A.R.; Melnikova, G.B.; Muslimova, I.B.; Yeszhanov, A.B.; Zhatkanbayeva, Z.K.; Chizhik, S.A.; Zdorovets, M.V. Preparation of Hydrophobic PET Track-Etched Membranes for Separation of Oil–Water Emulsion. Membranes 2021, 11, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerre, M.; Wahidur Rahaman, S.M.; Améduri, B.; Poli, R.; Ladmiral, V. RAFT Synthesis of Well-Defined PVDF-b-PVAc Block Copolymers. Polym. Chem. 2016, 7, 6918–6933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keddie, D.J. A Guide to the Synthesis of Block Copolymers Using Reversible-Addition Fragmentation Chain Transfer (RAFT) Polymerization. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 496–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, M.J. Modeling the Molecular Weight Distribution of Block Copolymer Formation in a Reversible Addition-Fragmentation Chain Transfer Mediated Living Radical Polymerization. J. Polym. Sci. A Polym. Chem. 2005, 43, 5643–5651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, H.; Wang, C.; Yang, L.; Sun, D.; Song, C.; Zhang, X.; Chen, D.; Ma, Y.; Yang, W. Preparation of Multifunctional PET Membrane and Its Application in High-Efficiency Filtration and Separation in Complex Environment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 474, 134669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Q.; Su, Y.; Ning, X.; Chen, W.; Peng, J.; Jiang, Z. Graft Polymerization of Methacrylic Acid onto Polyethersulfone for Potential PH-Responsive Membrane Materials. J. Memb. Sci. 2010, 347, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Fierro, D.A.; Camacho-Cruz, L.A.; Bustamante-Torres, M.R.; Hidalgo-Bonilla, S.P.; Bucio, E. Modification of Cotton Gauzes with Poly(Acrylic Acid) and Poly(Methacrylic Acid) Using Gamma Radiation for Drug Loading Studies. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2022, 190, 109787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henkel, R.C. Der Einfluss Der UV-Initiierten RAFT-Polymerisation Auf Die Strukturen Und Eigenschaften von Polymernetzwerken. 2014. Available online: https://ediss.uni-goettingen.de/handle/11858/00-1735-0000-0023-98E2-6 (accessed on 19 June 2025).
- Han, S.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lai, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Tan, J. Utilization of Poor RAFT Control in Heterogeneous RAFT Polymerization. Macromolecules 2021, 54, 4669–4681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Hou, Q.; Liu, H.; Ye, X. One-Pot, Surfactant-Free Synthesis of Poly(Styrene-N,N′-Methylenebis(2-Propenamide)-Acrylic Acid) and Poly(Styrene-N,N′-Methylenebis(2-Propenamide)-Methacrylic Acid) Microspheres for Adsorptive Removal of Heavy Metal Ions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 683, 132951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korolkov, I.V.; Yeszhanov, A.B.; Zdorovets, M.V.; Gorin, Y.G.; Güven, O.; Dosmagambetova, S.S.; Khlebnikov, N.A.; Serkov, K.V.; Krasnopyorova, M.V.; Milts, O.S.; et al. Modification of PET Ion Track Membranes for Membrane Distillation of Low-Level Liquid Radioactive Wastes and Salt Solutions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 227, 115694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safarpour, M.; Hosseinpour, S.; Haddad Irani-nezhad, M.; Orooji, Y.; Khataee, A. Fabrication of Ti2SnC-MAX Phase Blended PES Membranes with Improved Hydrophilicity and Antifouling Properties for Oil/Water Separation. Molecules 2022, 27, 8914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Gao, Y.; Yin, W.; Gao, B.; Yue, Q. Multi-Functional Membrane with Double-Barrier and Self-Cleaning Ability for Emulsion Separation: Fouling Model and Long-Term Operation. J. Memb. Sci. 2024, 696, 122466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, T.C.; Ouyang, L.; Yuan, S. Switchable Superlyophobic PAN@Co-MOF Membrane for on-Demand Emulsion Separation and Efficient Soluble Dye Degradation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 331, 125730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Lin, J.; An, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhu, X.; Yang, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, L. Enhancing Hydrophilicity and Comprehensive Antifouling Properties of Microfiltration Membrane by Novel Hyperbranched Poly(N-Acryoyl Morpholine) Coating for Oil-in-Water Emulsion Separation. React. Funct. Polym. 2020, 156, 104735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

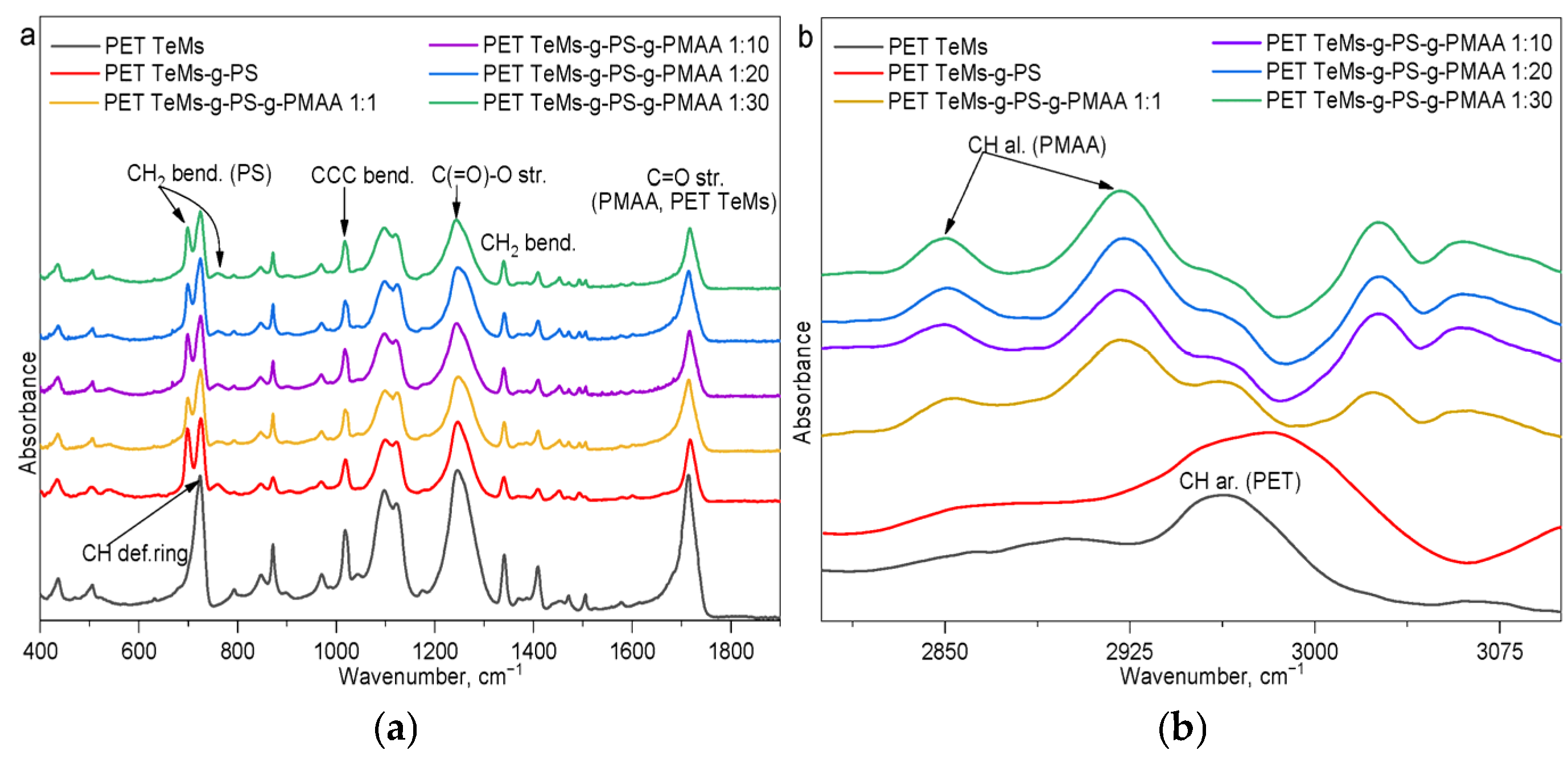


| Sample | I2850/I1409 | I2850/I1245 | I2925/I1409 | I2925/I1245 | I1712/I1409 | I1712/I1245 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PET TeMs | - | - | - | - | 4.91 | 0.93 |
| PET TeMs-g-PS | - | - | - | - | 1.67 | 0.31 |
| PET TeMs-g-PS-g-PMAA RAFT agent–initiator 1:1, DGPMAA = 2.5% | 0.17 | 0.03 | 0.33 | 0.06 | 5.00 | 0.91 |
| PET TeMs-g-PS-g-PMAA RAFT agent–initiator 1:10, DGPMAA = 1.1% | 0.20 | 0.03 | 0.40 | 0.06 | 5.40 | 0.84 |
| PET TeMs-g-PS-g-PMAA RAFT agent–initiator 1:20, DGPMAA = 0.6% | 0.18 | 0.03 | 0.35 | 0.06 | 4.83 | 0.88 |
| PET TeMs-g-PS-g-PMAA RAFT agent–initiator 1:30, DGPMAA = 0.5% | 0.43 | 0.09 | 0.57 | 0.12 | 4.00 | 0.82 |
| Material | Property | Emulsion | Pressure | F, L m−2 h−1 | R, % | FR, % | TR, % | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PET TeMs-g-PS-g-PMAA | Hydrophilicity pH > pKaPMAA | Chloroform in water | 900 mbar | 370 ± 28 | 89 | 88 | 2 | This work |
| 700 mbar | 410 ± 36 | 90 | - | - | ||||
| 500 mbar | 460 ± 39 | 90 | - | - | ||||
| o-Xylene in water | 900 mbar | 195 ± 8.2 | 91 | 69 | 52 | |||
| 700 mbar | 290 ± 9.3 | 92 | - | |||||
| 500 mbar | 420 ± 37 | 91 | - | |||||
| Cetane in water | 900 mbar | 70 ± 2.8 | 98 | 54 | 64 | |||
| 700 mbar | 135 ± 3.6 | 97 | - | |||||
| 500 mbar | 150 ± 11 | 95 | - | |||||
| Hydrophobicity pH < pKaPMAA | Water in chloroform | 900 mbar | 330 ± 10 | 92 | 91 | 25 | ||
| 700 mbar | 420 ± 7.7 | 90 | - | |||||
| 500 mbar | 810 ± 37 | 93 | - | |||||
| Water in o-xylene | 900 mbar | 170 ± 23 | 90 | 81 | 19 | |||
| 700 mbar | 310 ± 9.8 | 91 | ||||||
| 500 mbar | 485 ± 43 | 90 | ||||||
| Water in cetane | 900 mbar | 70 ± 1.4 | 83 | 70 | 10 | |||
| 700 mbar | 80 ± 5.1 | 85 | ||||||
| 500 mbar | 650 ± 58 | 80 | ||||||
| PET TeMs-g-PS-g-PAA | Hydrophilicity pH > pKaPAA | Chloroform in water | 900 mbar | 2500 | 94 ± 5 | 82 | 22 | [31] |
| Hydrophobicity pH < pKaPAA | Water in chloroform | 900 mbar | 1400 | 97 ± 1 | 96 | 46 | ||
| Ti2SnC-MAX-PES | Hydrophilicity | Oil in water | 0.3 kPa | 355 | 80 | 65 | - | [50] |
| MIL88A@TA@APTES-PVDF | Superhydrophilicity | Oil in water | Gravity | 2600 | 99 | 94 | - | [51] |
| PAN@Co-MOF | Superoleophobicity, water wetting | Cyclohexane in water | 2–8 kPa | 1600 | 99 | - | - | [52] |
| Superhydrophobicity, oil wetting | Water incyclohexane | 2–8 kPa | 1040 | 99 | - | - | ||
| M-PD/HPA@PVDF | Hydrophilicity | Hexane in water | 0.3 kPa | 150 | 99 | 83 | 37 | [53] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muslimova, I.B.; Omertassov, D.D.; Zhumanazar, N.; Assan, N.; Zhatkanbayeva, Z.K.; Korolkov, I.V. Preparation of pH-Responsive PET TeMs by Controlled Graft Block Copolymerisation of Styrene and Methacrylic Acid for the Separation of Water–Oil Emulsions. Polymers 2025, 17, 2221. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17162221
Muslimova IB, Omertassov DD, Zhumanazar N, Assan N, Zhatkanbayeva ZK, Korolkov IV. Preparation of pH-Responsive PET TeMs by Controlled Graft Block Copolymerisation of Styrene and Methacrylic Acid for the Separation of Water–Oil Emulsions. Polymers. 2025; 17(16):2221. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17162221
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuslimova, Indira B., Dias D. Omertassov, Nurdaulet Zhumanazar, Nazerke Assan, Zhanna K. Zhatkanbayeva, and Ilya V. Korolkov. 2025. "Preparation of pH-Responsive PET TeMs by Controlled Graft Block Copolymerisation of Styrene and Methacrylic Acid for the Separation of Water–Oil Emulsions" Polymers 17, no. 16: 2221. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17162221
APA StyleMuslimova, I. B., Omertassov, D. D., Zhumanazar, N., Assan, N., Zhatkanbayeva, Z. K., & Korolkov, I. V. (2025). Preparation of pH-Responsive PET TeMs by Controlled Graft Block Copolymerisation of Styrene and Methacrylic Acid for the Separation of Water–Oil Emulsions. Polymers, 17(16), 2221. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17162221







