Facile Preparation of iPP Fibrous Membranes from In Situ Microfibrillar Composites for Oil/Water Separation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of iPP Fibrous Membrane
2.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.4. Porosity
2.5. Contact Angle Measurements
2.6. Oil/Water Separation Performance Test
2.7. Oil Adsorption Tests
3. Results and Discussion
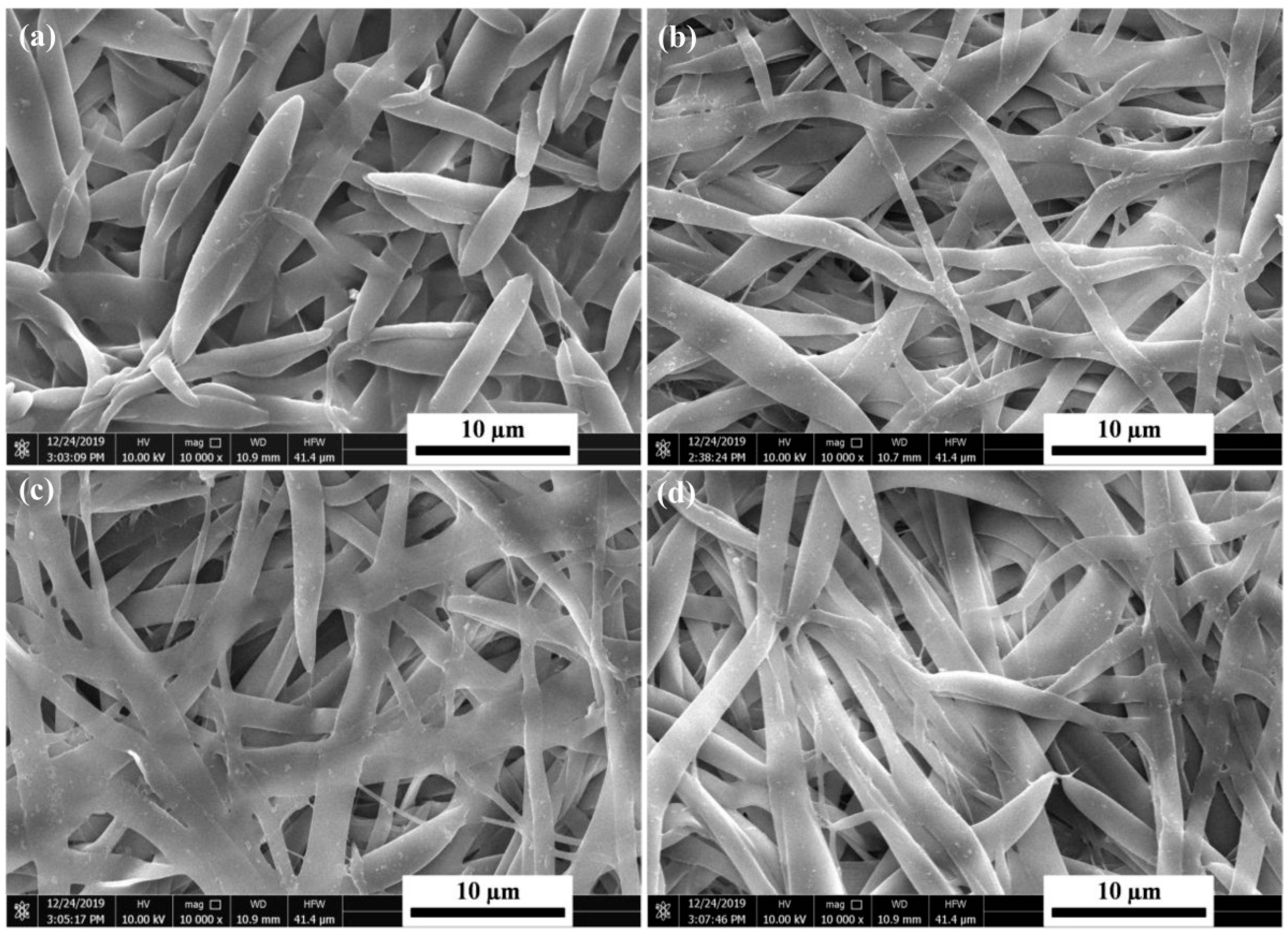
3.1. The Morphology of the iPP Fibrous Membrane
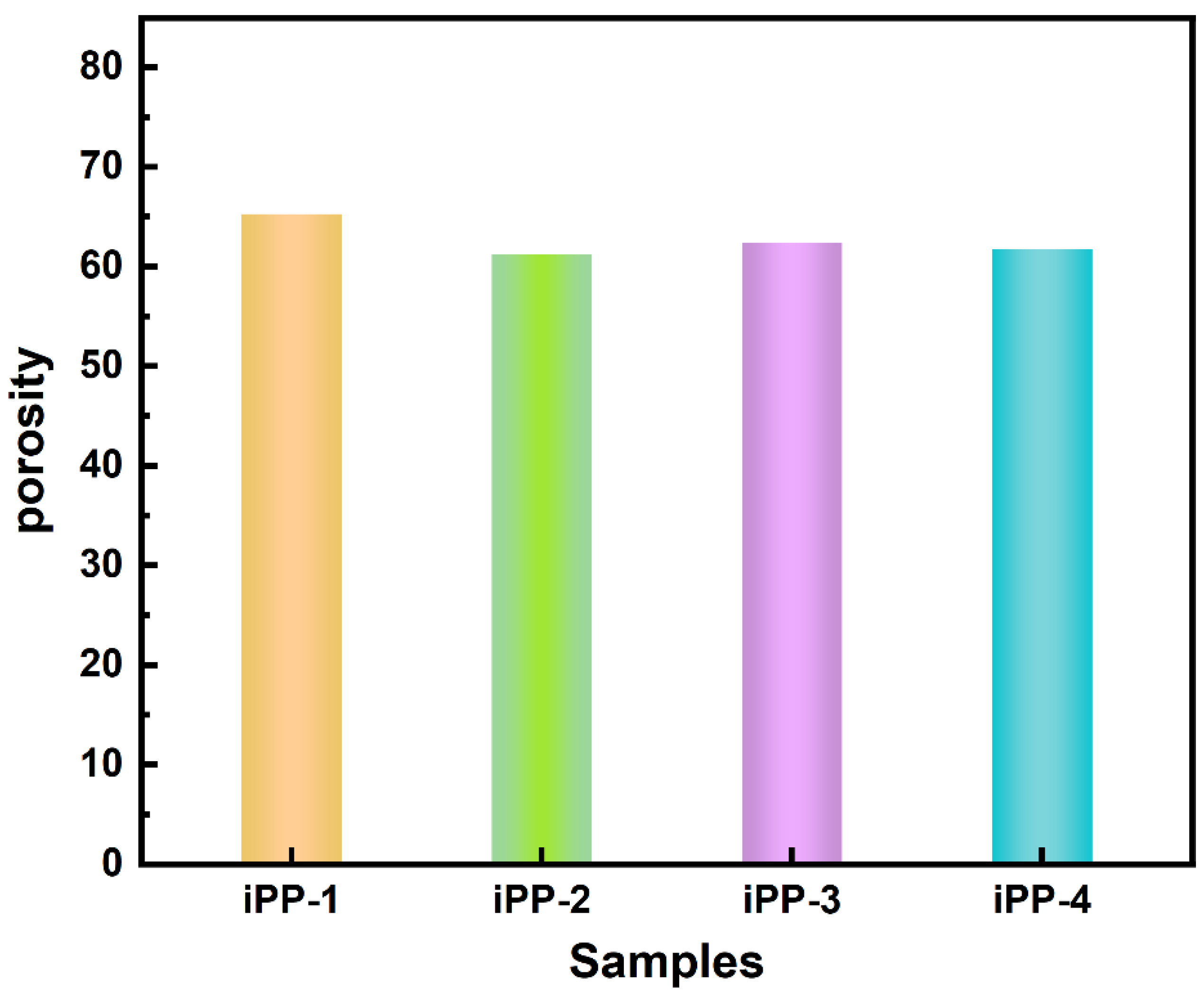
3.2. Surface Wettability and Porosity of iPP Fibrous Membranes
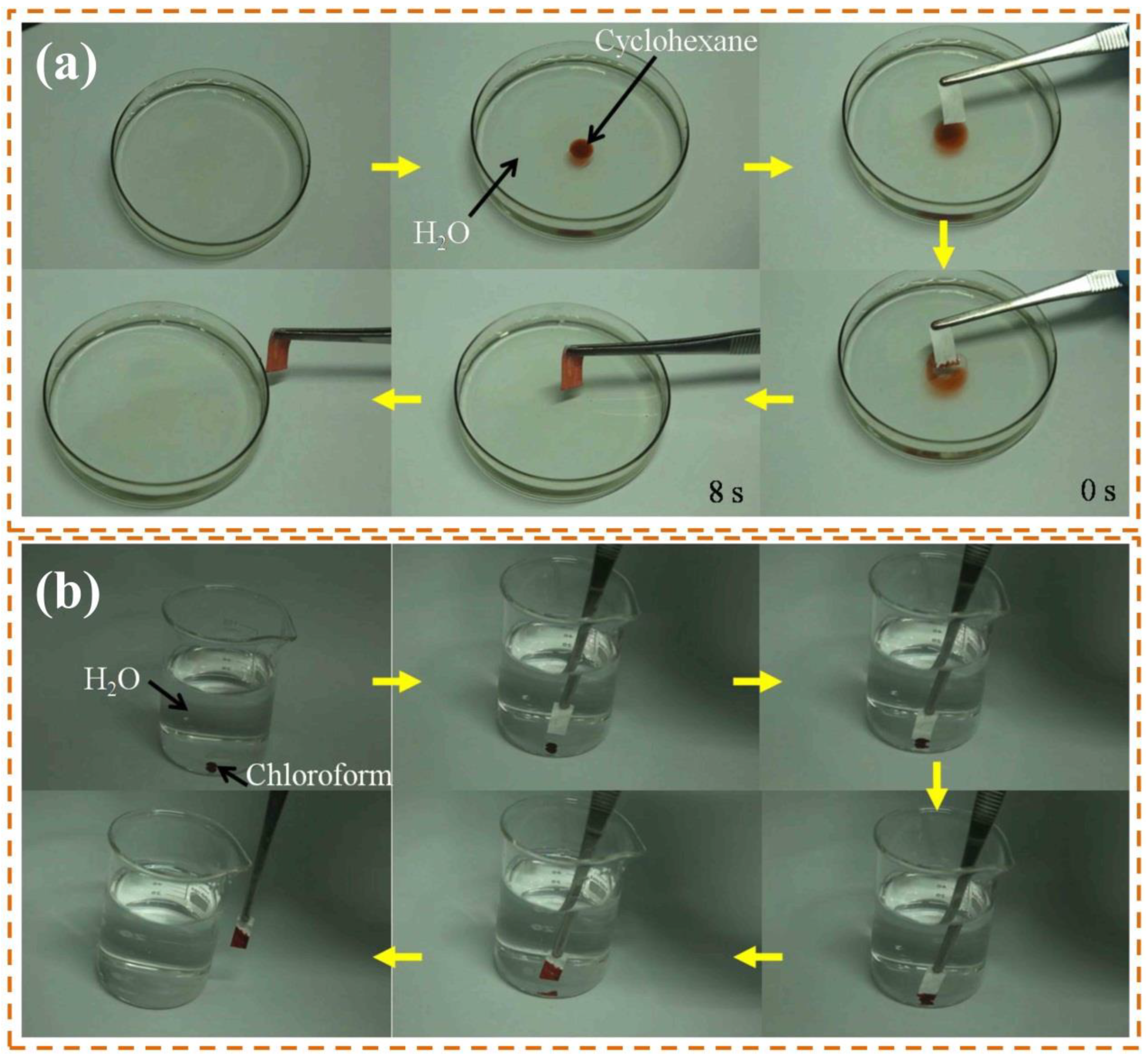
3.3. Oil/Water Separation Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, J.; Cui, Z.; Yu, Y.; Han, H.; Tian, D.; Hu, J.; Qu, J.; Cai, Y.; Luo, J.; Li, J. A 3D smart wood membrane with high flux and efficiency for separation of stabilized oil/water emulsions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 441, 129900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Yu, X.; Wu, J.; Han, J.; Liu, F.; Pan, H. A Comprehensive Review of Ash Issues in Oxyfuel Combustion of Coal and Biomass: Mineral Matter Transformation, Ash Formation, and Deposition. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 17241–17260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radwan, A.M.; Paul, M.C. Plasma assisted NH3 combustion and NOx reduction technologies: Principles, challenges and prospective. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 52, 819–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Folly d’Auris, A.; Rubertelli, F.; Taini, A.; Vocciante, M. A novel polyurethane-based sorbent material for oil spills management. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 111386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.-S.; Mdlovu, N.V.; Wang, H.-P.; Hussain, A. Liquefaction of waste tire rubber chips used for the absorptive recycling of spilled oils. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshmiri-Naqab, R.; Taghavijeloudar, M. Could organoclay be used as a promising natural adsorbent for efficient and cost-effective dye wastewater treatment? J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 342, 118322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Jin, X.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, J. Design and Fabrication of the Evolved Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-Modified Polylactic Acid Nonwoven Fabric for Efficient Oil/Water Separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 14653–14661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Pan, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, H.; Li, N.; Liu, C.; Schubert, D.W.; Shen, C. Facile Fabrication of Superhydrophobic and Eco-Friendly Poly(lactic acid) Foam for Oil–Water Separation via Skin Peeling. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 14362–14367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonhson, W.; Xu, X.; Bian, K.; Xun, Y.; Tan, Y.H.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, D.; Ding, J. 3D-Printed Hierarchical Ceramic Architectures for Ultrafast Emulsion Treatment and Simultaneous Oil–Water Filtration. ACS Mater. Lett. 2022, 4, 740–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.-L. Surface modification to fabricate dual superlyophobic mesh for efficient oil/water separation. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 273, 122872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, K.R.; Dora, D.T.K.; Pant, K.K.; Roy, S. An ultra-light flexible aerogel-based on methane derived CNTs as a reinforcing agent in silica-CMC matrix for efficient oil adsorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 375, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, B.; Wang, B.; Feng, Y.; Han, W.; Liu, C.; Shen, C. Superhydrophobic cellulose acetate/multiwalled carbon nanotube monolith with fiber cluster network for selective oil/water separation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 259, 117750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Xu, G.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Yu, K.; Yan, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, H. Fabrication of bio-based biodegradable poly(lactic acid) (PLA) and poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV) composite foams for highly efficient oil-water separation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 257, 128750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, W.; Ma, W.; Lu, T.; Jiang, Z.; Xiong, R.; Huang, C. Multifunctional nanofibrous membranes with sunlight-driven self-cleaning performance for complex oily wastewater remediation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 608, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baig, U.; Faizan, M.; Sajid, M. Multifunctional membranes with super-wetting characteristics for oil-water separation and removal of hazardous environmental pollutants from water: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 285, 102276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Wang, H.; Lan, W.; Zhang, A.; Liu, C. Fabrication of sugarcane bagasse ester-based porous nanofiber membrane by electrospinning for efficient oil-water separation. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 187, 115480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behroozi, A.H.; Al-Shaeli, M.; Vatanpour, V. Fabrication and modification of nanofiltration membranes by solution electrospinning technique: A review of influential factors and applications in water treatment. Desalination 2023, 558, 116638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Loh, C.-H.; Tian, M.; Wang, R.; Fane, A.G. Progress in electrospun polymeric nanofibrous membranes for water treatment: Fabrication, modification and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2018, 77, 69–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, M. A review on zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 based materials with special wettability for oil/water separation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 111360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Mukai, Y. Electrospun hierarchically structured nanofibrous membrane for highly efficient oil-in-water emulsion coalescence separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 322, 124331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Jia, K.; Lin, G.; Huang, Y.; Liu, C.; Liu, S.; Zhang, S.; Liu, X. Solvent-nonsolvent regulated nano-functionalization of super-wetting membranes for sustainable oil/water separation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 613, 156085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-y.; Li, L.; Feng, M.; Huang, T.; Zhang, N.; Wang, Y. UV-activated superwetting ability of electrospun polysulfone/titanium dioxide membranes toward highly efficient methylene blue removal and oil/water separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2024, 659, 122450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, B.; Ma, H. Constructing CNTs-based composite membranes for oil/water emulsion separation via radiation-induced “grafting to” strategy. Carbon 2021, 178, 678–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.-F.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, N.; Huang, T.; Lei, Y.-Z.; Wang, Y. Electrospun stereocomplex polylactide porous fibers toward highly efficient oil/water separation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 407, 124787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, X.-l.; Sun, D.-x.; Cao, S.; Zhang, N.; Huang, T.; Lei, Y.-z.; Wang, Y. Freely switchable super-hydrophobicity and super-hydrophilicity of sponge-like poly(vinylidene fluoride) porous fibers for highly efficient oil/water separation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Chen, H.; Xiang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Xie, C.; Liu, Y. Superhydrophobic polyurethane sponge based on sepiolite for efficient oil/water separation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 434, 128833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-J.; Zhu, L.-T.; Luo, Z.-H. Electrospun fibrous membrane with enhanced swithchable oil/water wettability for oily water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 287, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Wang, W.; Qi, D.; Luo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Cui, F.; Wang, C.; Chen, X. Calcinable Polymer Membrane with Revivability for Efficient Oily-Water Remediation. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1801870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakroodi, A.R.; Kazemi, Y.; Nofar, M.; Park, C.B. Tailoring poly(lactic acid) for packaging applications via the production of fully bio-based in situ microfibrillar composite films. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 308, 772–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franciszczak, P.; Wojnowski, J.; Kalniņš, K.; Piesowicz, E. The influence of matrix crystallinity on the mechanical performance of short-fibre composites—Based on homo-polypropylene and a random polypropylene copolymer reinforced with man-made cellulose and glass fibres. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 166, 516–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kian, L.K.; Jawaid, M.; Nasef, M.M.; Fouad, H.; Karim, Z. Poly(lactic acid)/poly(butylene succinate) dual-layer membranes with cellulose nanowhisker for heavy metal ion separation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 192, 654–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, K.; Xu, J.; Xie, S.; Zhang, S.; Hou, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J. Microcellular foaming and mechanical properties of iPPF reinforced PPR composites. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2021, 170, 105161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuancharoensri, N.; Ross, G.M.; Kongprayoon, A.; Mahasaranon, S.; Pratumshat, S.; Viyoch, J.; Petrot, N.; Ruanthong, W.; Punyodom, W.; Topham, P.D.; et al. In Situ Compatibilized Blends of PLA/PCL/CAB Melt-Blown Films with High Elongation: Investigation of Miscibility, Morphology, Crystallinity and Modelling. Polymers 2023, 15, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorjan, L.; Galusca, C.; Sami, M.; Sebastian, T.; Clemens, F. Effect of stearic acid on rheological properties and printability of ethylene vinyl acetate based feedstocks for fused filament fabrication of alumina. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 36, 101391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Sun, J.; Huang, A.; Zhang, T.; Wei, L.; Qin, S. In situ fibrillation of isotactic polypropylene in ethylene-vinyl acetate: Toward enhanced rheological and mechanical properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Lv, C.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, G.; Liu, H.; Liu, C.; Guo, Z.; Shen, C. Porous Polyethylene Bundles with Enhanced Hydrophobicity and Pumping Oil-Recovery Ability via Skin-Peeling. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 12580–12585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Liu, S.; Chen, L.; Wu, T.; Tian, X. Nontraditional oil sorbents: Hydrophilic sponges with hydrophobic skin layer for efficient oil spill remediation. Sci. China Mater. 2022, 65, 1929–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-J.; Kwon, T.-H.; Im, H.; Moon, D.-I.; Baek, D.J.; Seol, M.-L.; Duarte, J.P.; Choi, Y.-K. A Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) Sponge for the Selective Absorption of Oil from Water. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 4552–4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.L.; Eberle, S.; Bechtold, T.; Fabbri, F.; Pellis, A.; Guebitz, G.M.; Rohleder, E.; Rabe, M.; Pham, T. Investigation of the influence of the draw ratio on the enzyme catalysed degradation of poly(ethylene terephthalate) fibres using nanoscale surface thermal analysis. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2023, 218, 110593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmanović, M.; Delva, L.; Cardon, L.; Ragaert, K. Relationship between the Processing, Structure, and Properties of Microfibrillar Composites. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2003938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Wang, L.; Sun, J.; Yang, W.; Zhang, H. Morphology and Properties of Polyolefin Elastomer/Polyamide 6/Poly(lactic Acid) In Situ Special-Shaped Microfibrillar Composites: Influence of Viscosity Ratio. Polymers 2022, 14, 4556–4568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Jin, X.-Z.; Huang, T.; Zhang, N.; Qi, X.-d.; Yang, J.-h.; Zhou, Z.-w.; Wang, Y. Electrospun Fibrous Membranes with Dual-Scaled Porous Structure: Super Hydrophobicity, Super Lipophilicity, Excellent Water Adhesion, and Anti-Icing for Highly Efficient Oil Adsorption/Separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 5073–5083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Xue, B.; Tian, Y.; Qin, S.; Xie, L. 3D porous poly(l-lactic acid) materials with controllable multi-scale microstructures and their potential application in oil-water separation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 462, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Liu, N.; Li, J.; Gao, C.; Sun, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Song, L.; Huang, S.; Li, J.; et al. The oil absorption capacity of polypropylene porous absorbents fabricated through iPP/EVA in situ microfibrillar composites: Effect of fibrillar morphology. J. Porous Mater. 2023, 30, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Tang, D.; Kong, M.; Yang, Q.; Huang, Y.; Liao, X.; Niu, Y. Effect of nanoparticles on the morphology and properties of PET/PP in situ microfibrillar reinforced composites. Polym. Compos. 2017, 38, 2718–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, T.; Shen, L.; Wu, H.; Guo, S. Morphologies and properties of polycarbonate/polyethylene in situ microfibrillar composites prepared through multistage stretching extrusion. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 40108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, N.; Wang, L.; Dong, H.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, L. Electrospun Porous Structure Fibrous Film with High Oil Adsorption Capacity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 3207–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, B.; Kim, S.-H.; Kim, E.; Jang, J.-H. Superhydrophobic, Reversibly Elastic, Moldable, and Electrospun (SupREME) Fibers with Multimodal Functions: From Oil Absorbents to Local Drug Delivery Adjuvants. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1702310–1702321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; An, A.K.; Guo, J.; Lee, E.-J.; Farid, M.U.; Jeong, S. CNTs Reinforced Super-Hydrophobic-Oleophilic Electrospun Polystyrene Oil Sorbent for Enhanced Sorption Capacity and Reusability. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 314, 526–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Adsorbents | Type of Oil | Adsorption Capacity (%) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| eleetrospun porous PS membrane | oils | 630—13,160 | [47] |
| electrospun PSF/PGS membrane | oils and organic solvents | 54.7—61.4 | [48] |
| electrospun PS/CNT membrance | oils | 11150—12,280 | [49] |
| electrospun PLA/γ-Fe2O3 membrane | oils and organic solvents | 2300—26,860 | [42] |
| ipp fibrous membrane from MFCs | oils and organic solvents | 118.8—478.6 | this work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, C.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; He, C.; Luo, S.; Tian, Q. Facile Preparation of iPP Fibrous Membranes from In Situ Microfibrillar Composites for Oil/Water Separation. Polymers 2025, 17, 2114. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17152114
Gao C, Zhang L, Liu X, He C, Luo S, Tian Q. Facile Preparation of iPP Fibrous Membranes from In Situ Microfibrillar Composites for Oil/Water Separation. Polymers. 2025; 17(15):2114. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17152114
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Chengtao, Li Zhang, Xianrong Liu, Chen He, Shanshan Luo, and Qin Tian. 2025. "Facile Preparation of iPP Fibrous Membranes from In Situ Microfibrillar Composites for Oil/Water Separation" Polymers 17, no. 15: 2114. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17152114
APA StyleGao, C., Zhang, L., Liu, X., He, C., Luo, S., & Tian, Q. (2025). Facile Preparation of iPP Fibrous Membranes from In Situ Microfibrillar Composites for Oil/Water Separation. Polymers, 17(15), 2114. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17152114






