Investigation of the Reinforcement Mechanism and Impact Resistance of Carbon Hollow Microsphere-Reinforced PDMS Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment
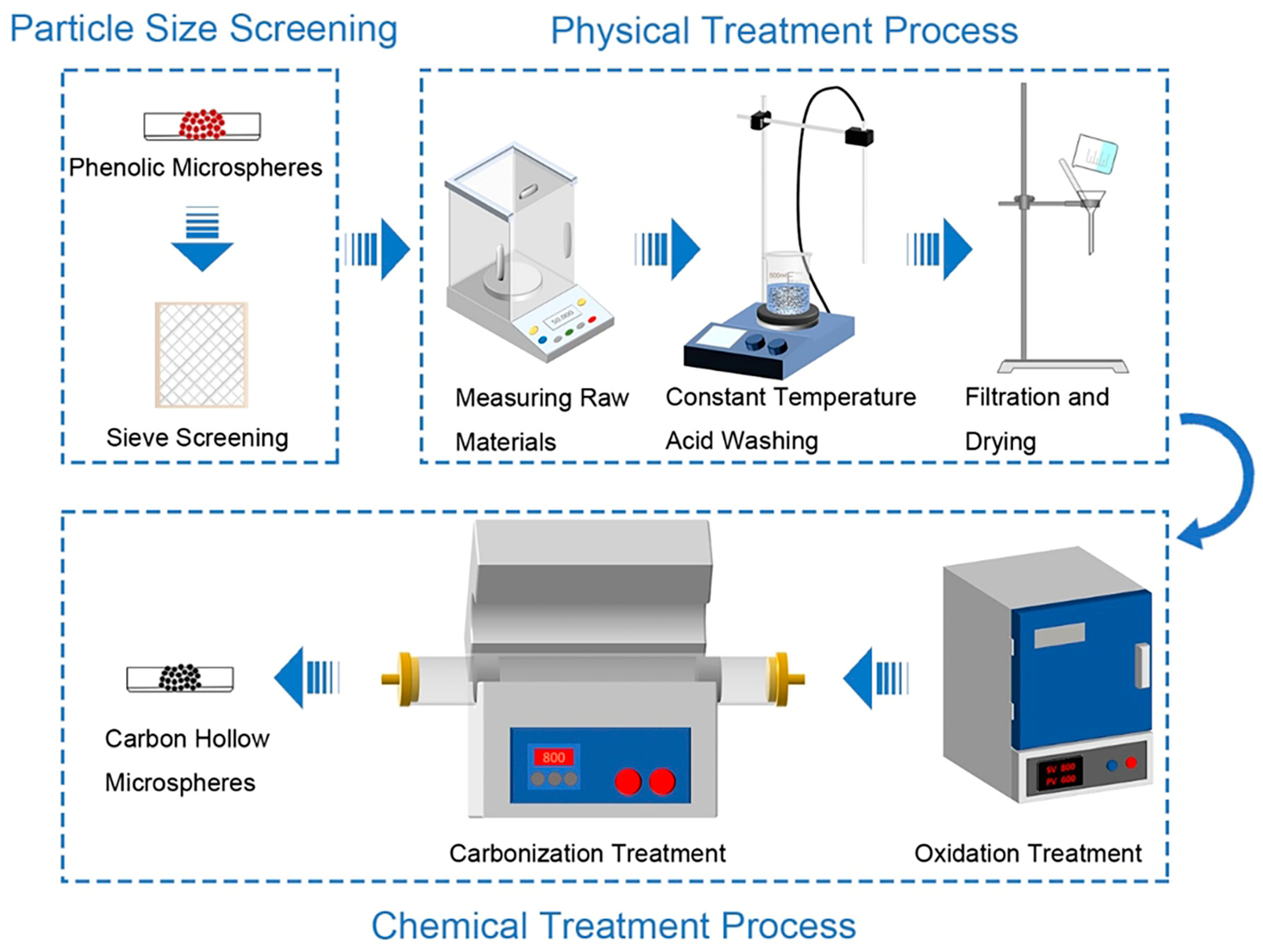
2.1. Preparation of the CHMs
2.2. Preparation of the CHM/PDMS Composites
2.3. Characterization of CHMs and CHM/PDMS Composites
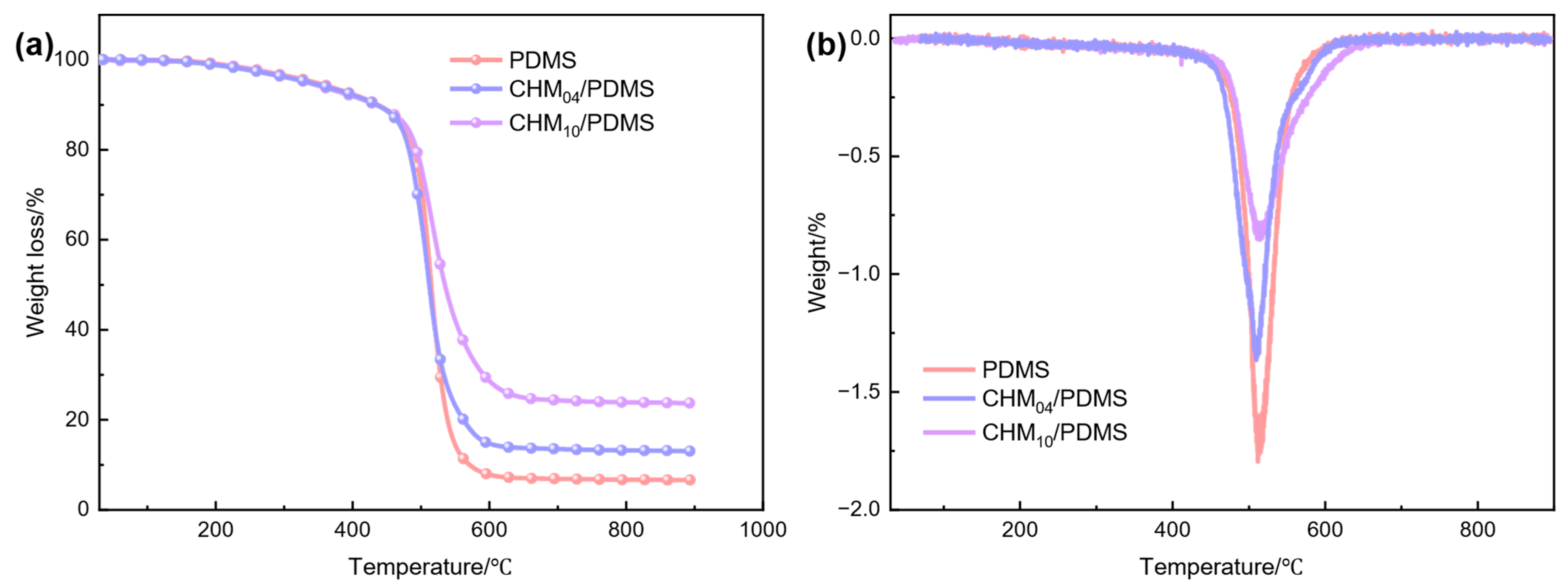
3. Results and Discussion
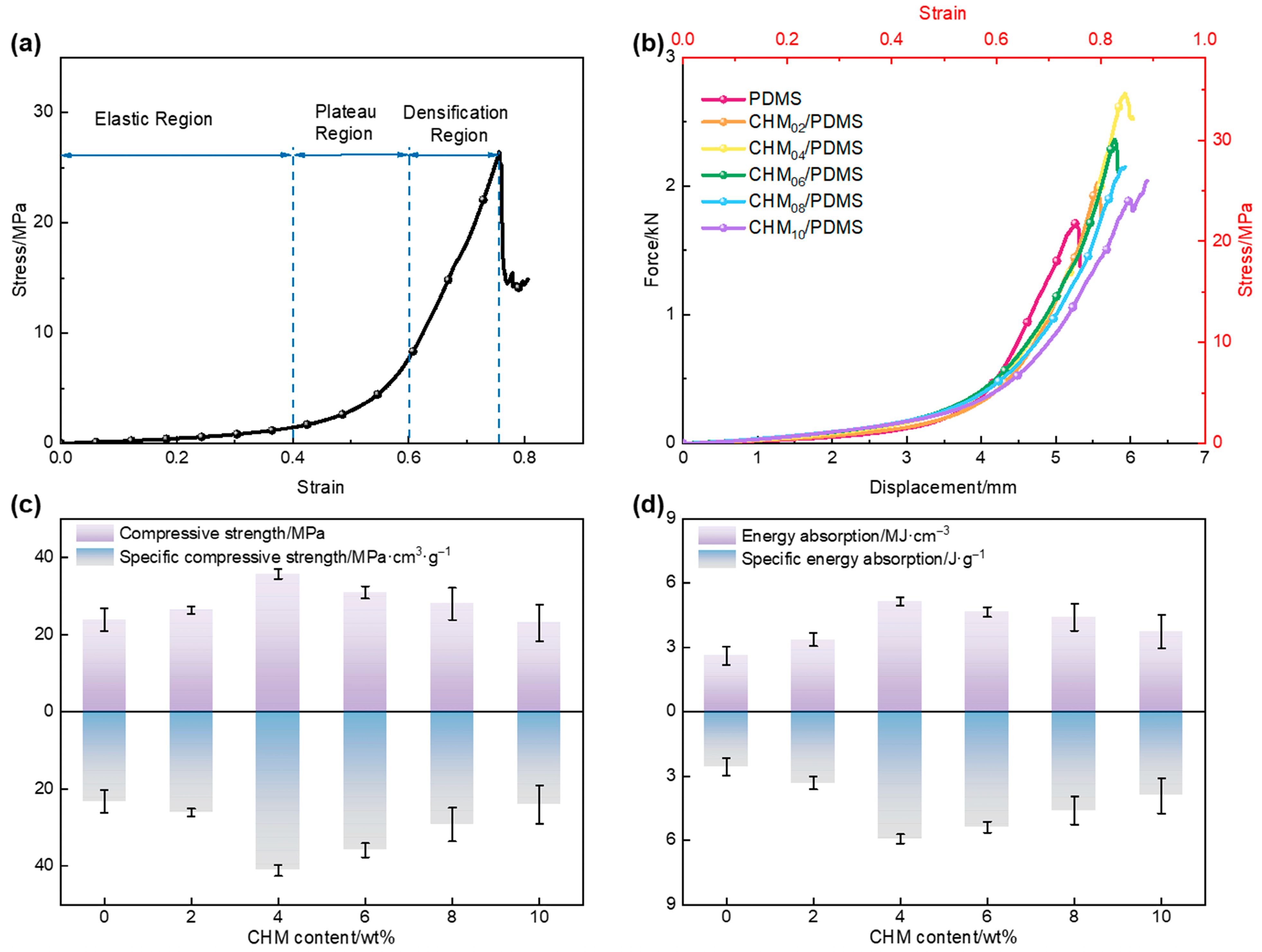
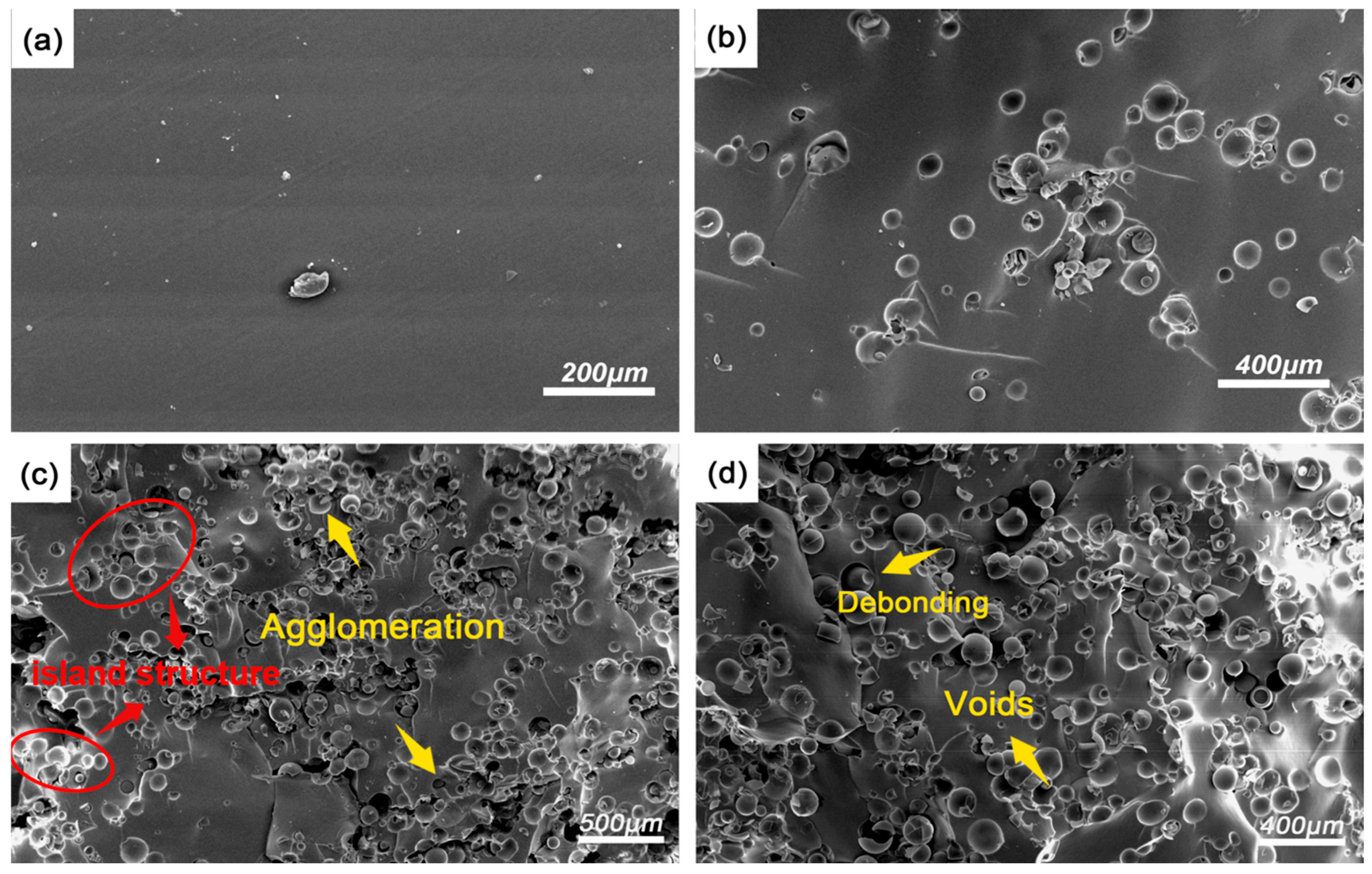
3.1. Quasi-Static Compressive Performance of the CHM/PDMS Composite
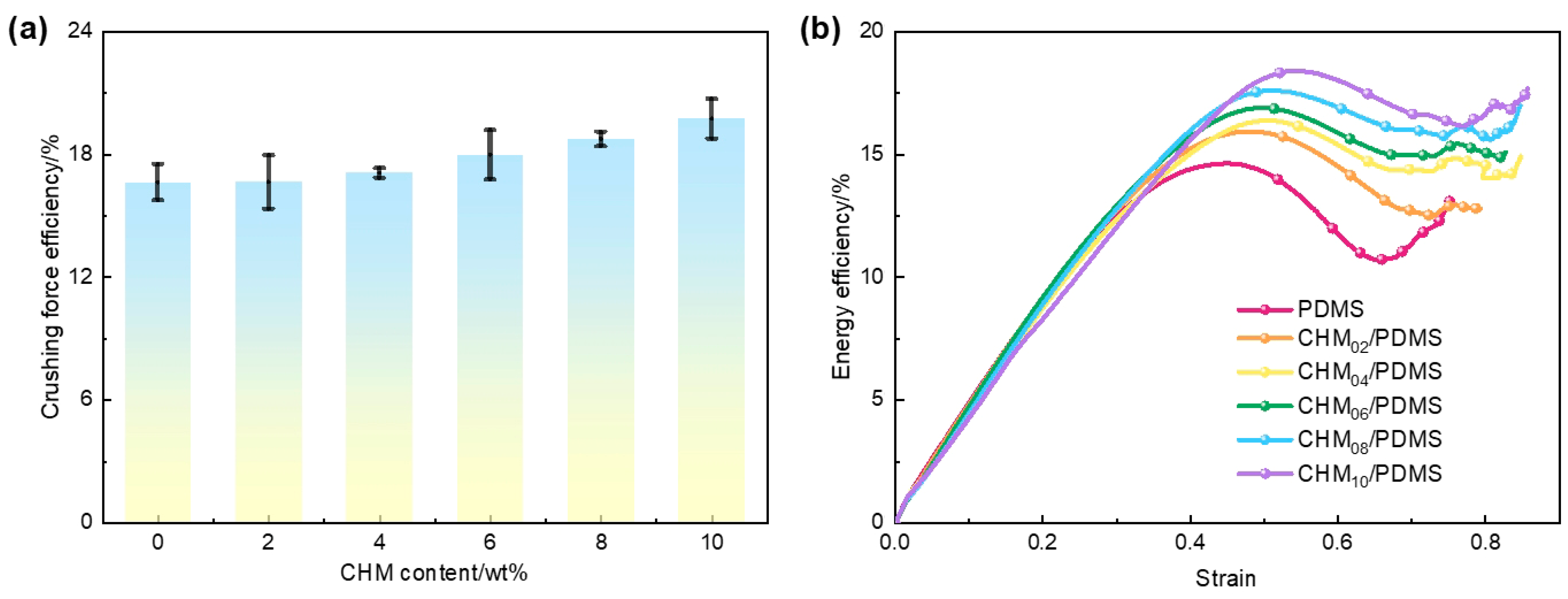
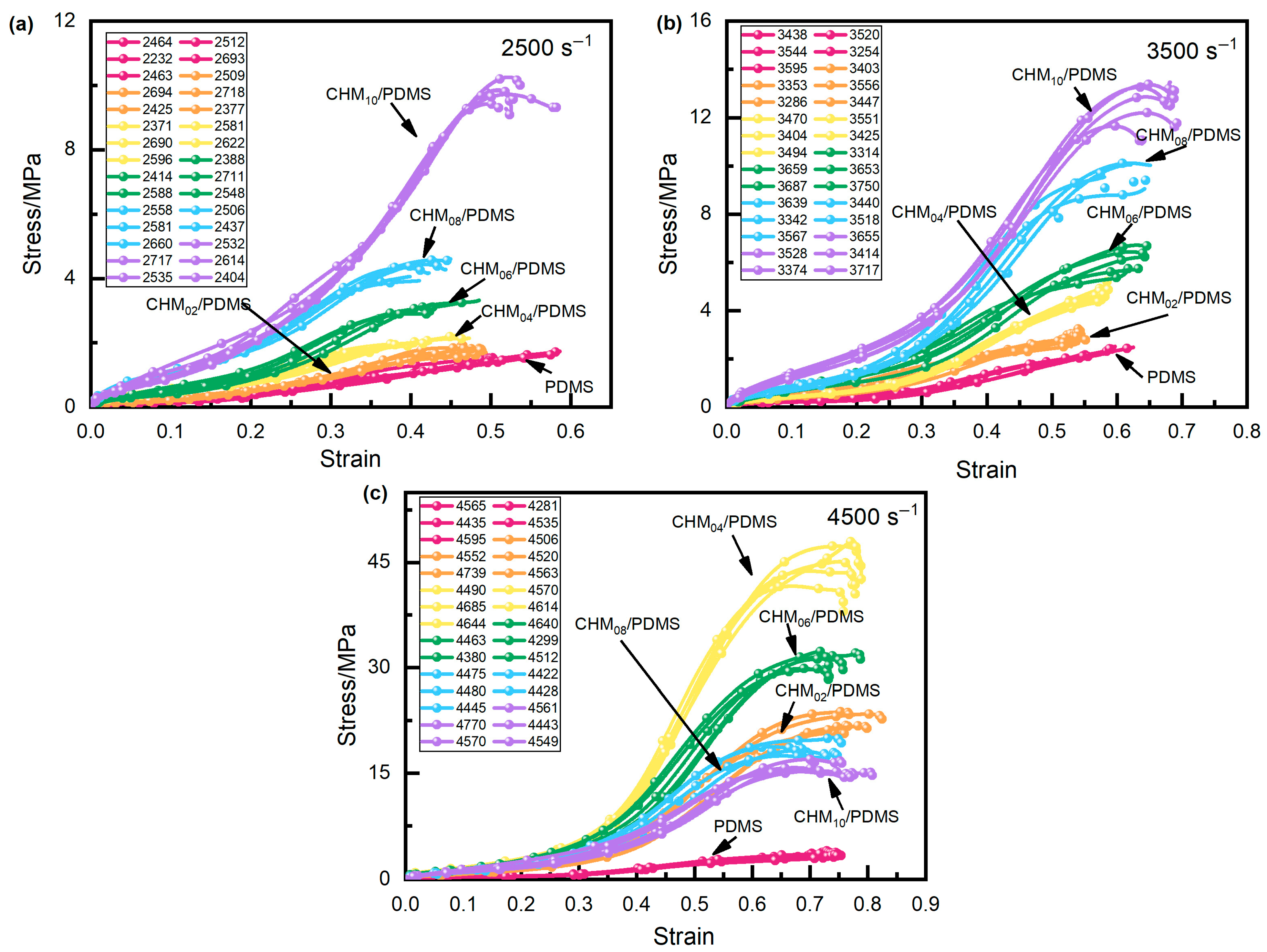
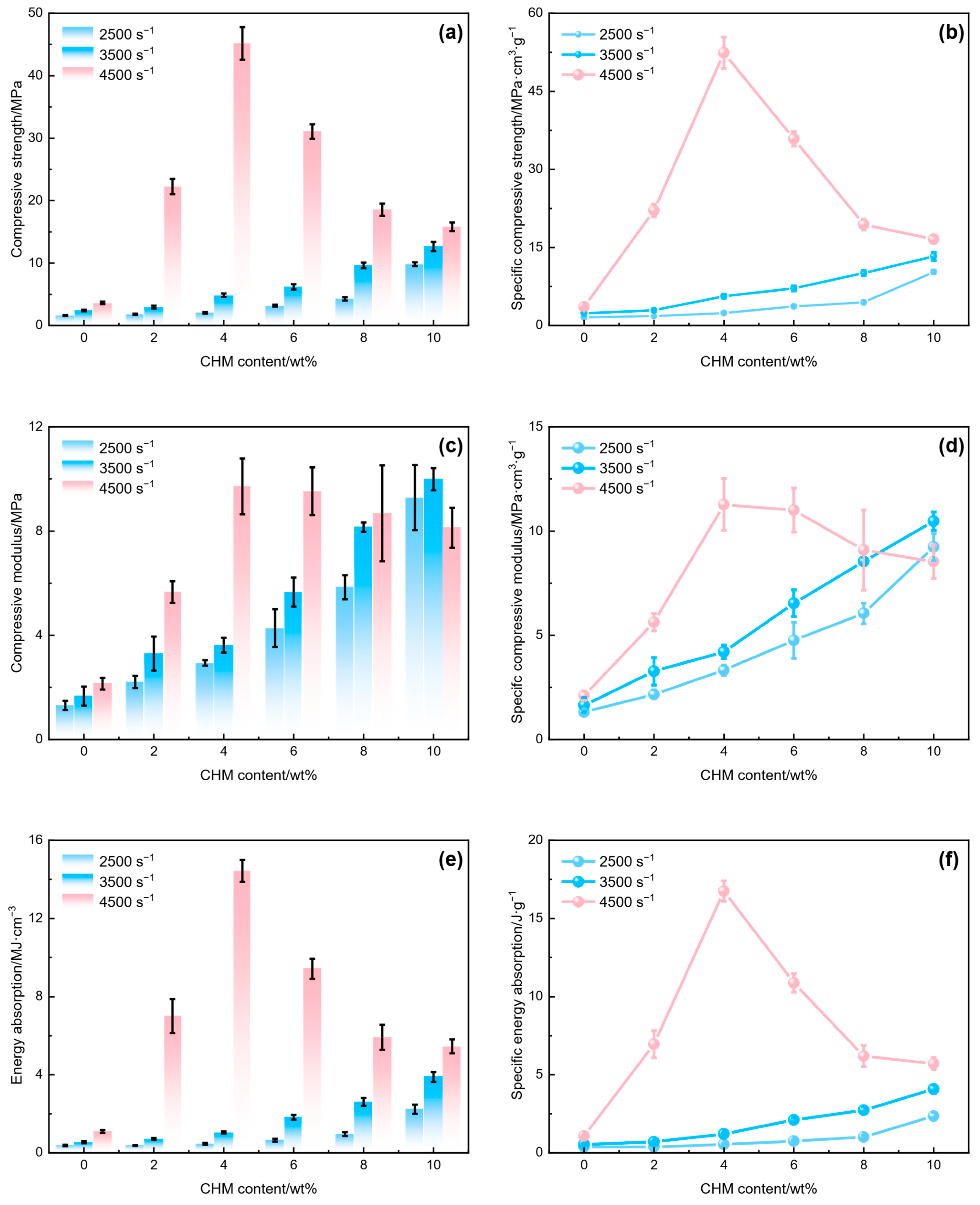
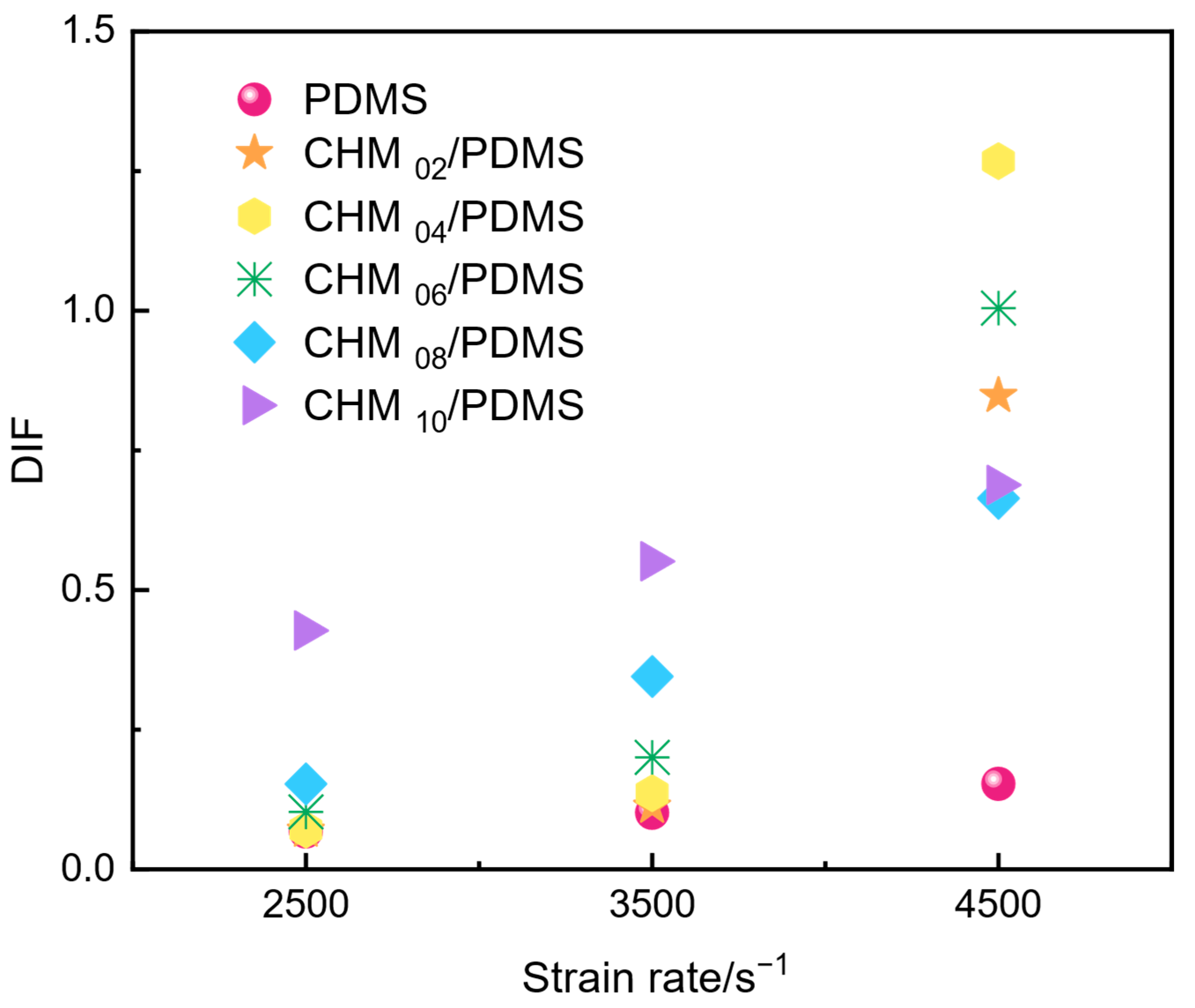
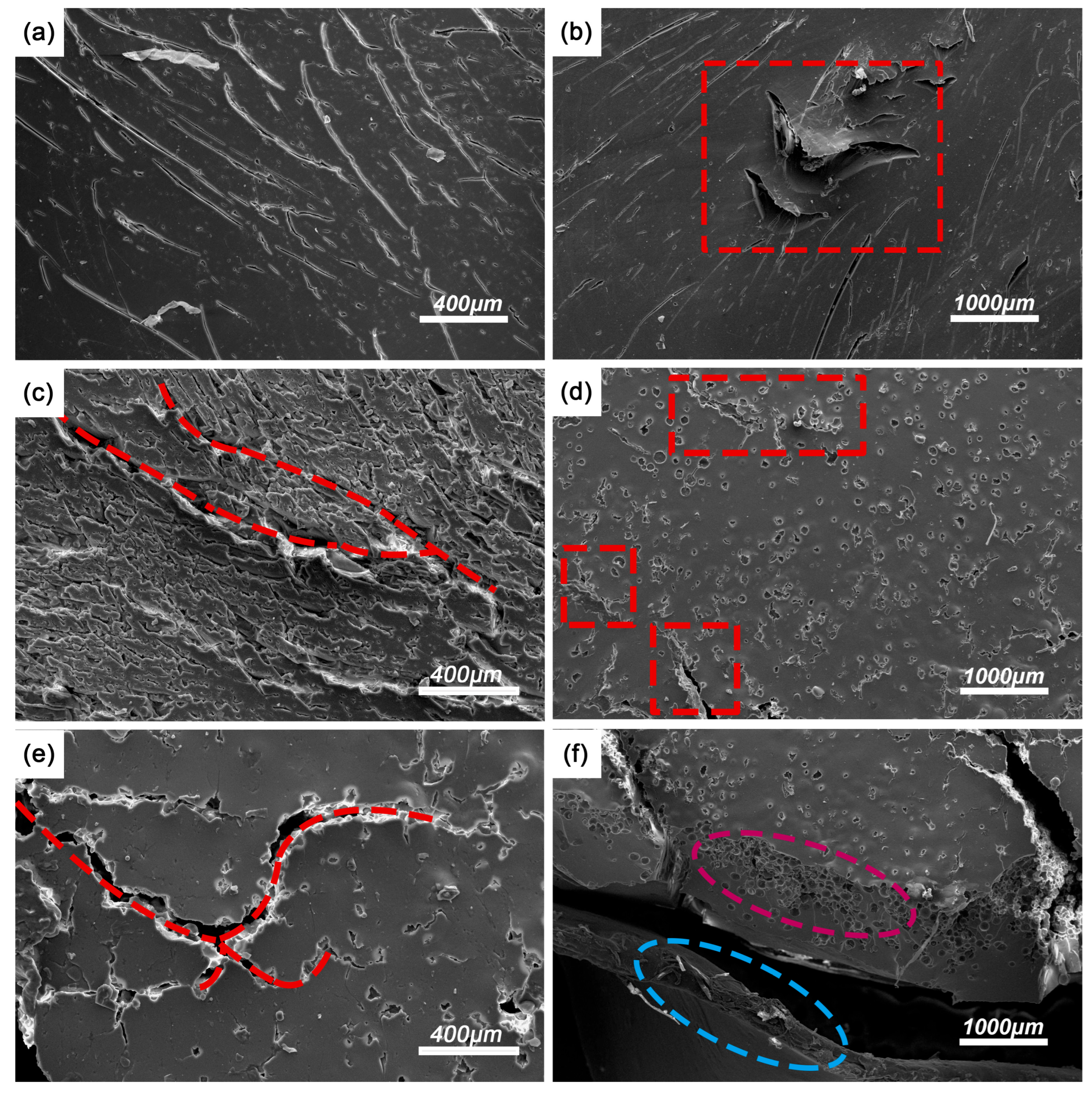
3.2. Dynamic Compressive Performance of the CHM/PDMS Composite
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zalewski, K.; Chyek, Z.; Trzciński, W.A. A Review of Polysiloxanes in Terms of Their Application in Explosives. J. Polym. 2021, 13, 1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wereszczak, A.; Kirkland, T.; Breder, K.; Ferber, M.; Khandelwal, P. High temperature dynamic fatigue performance of a hot isostatically pressed silicon nitride. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1995, 191, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borah, B.; Dash, R.K. Improved dielectric properties of rGO/PDMS composites by incorporation of Ag nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2022, 33, 12334–12350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auliya, D.G.; Setiadji, S.; Fitrilawati, F.; Risdiana, R. Physical Characterization and In Vitro Toxicity Test of PDMS Synthesized from Low-Grade D4 Monomer as a Vitreous Substitute in the Human Eyes. J. Funct. Biomater. 2022, 13, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariati, R.; Sales, F.; Souza, A.; Lima, R.A.; Ribeiro, J. Polydimethylsiloxane Composites Characterization and Its Applications: A Review. J. Polym. 2021, 13, 4258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Li, X. Nanosilica-Reinforced Poly(dimethylsiloxane) Stretchable Transparent Electrodes and Multifunctional Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 59268–59279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, N.; Guo, Q.; Zaïri, F.; Ding, N. Mode I crack propagation in polydimethylsiloxane-short carbon fiber composites. Compos. Struct. 2025, 352, 118682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.W.; Mark, J.E. Reinforcement of poly(dimethylsiloxane) networks by blended and in-situgenerated silica fillers having various sizes, size distributions, and modified surfaces. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 1999, 200, 206–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Deng, Q.; Wang, X.; Chen, L. Deformation and energy absorption properties of hollow glass microsphere/polyurethane lightweight core reinforced carbon fiber tubes under lateral compression. Polym. Compos. 2024, 45, 13791–13802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.K.; Kumar, R.; Rizwee, M.; Kumar, D. Tuning thermal and structural properties of nano-filled PDMS elastomer. Polym. Compos. 2024, 45, 14832–14844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Li, N.; Jian, W.X. Thermal insulation and mechanical properties of carbon fiber-reinforced thermoplastic polyphthalazine ether sulfone ketone composites reinforced by hollow glass beads. Polym. Compos. 2023, 44, 7941–7952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Zeltmann, S.E.; Shunmugasamy, V.C.; Pinisetty, D. Applications of Polymer Matrix Syntactic Foams. JOM 2014, 66, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lyu, Z.; Li, C.; Hu, D.; Li, Q. Lightweight and Dual-Functional Composites with Stiff-Soft Microstructure for Energy Absorption and Thermal Insulation. Compos. Commun. 2021, 26, 100778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Li, Y.; Zhu, J.; Ma, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Yang, S. Highly robust, processable and multi-functional PDMS/graphene composite aerogel constructed by “soft-hard” interface engineering strategy. Compos. Part B Eng. 2025, 288, 11904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakun, A.; Sarlin, E.; Vuorinen, J. Material-Related Losses of Natural Rubber Composites with Surface-Modified Nanodiamonds. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 48629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brachi, M.; Giroud, F.; Cosnier, S.; Le Goff, A. Thiol–yne Click Chemistry on Carbon Nanotubes for Mediated Bioelectrocatalytic Glucose Oxidation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 26681–26686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Gonzales, R.R.; Fu, W.; Xu, G.; Song, Q.; Takagi, R.; Matsuyama, H. Carbon nanotubes regulated polyamide membrane by intercalation to improve the organic solvent nanofiltration performance. J. Carbon 2024, 216, 118582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Zhang, C.; Hu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Lv, Z. Immobilization of Co nanoparticles into N-doped carbon nanotube on g-C3N4 via coordination-polymerization integrated strategy for efficient H2 evolution reaction at all pH values. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2024, 342, 123354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szadkowski, B.; Marzec, A.; Zaborski, M. Effect of different carbon fillers on the properties of nitrile rubber composites. J. Instrum. Sci. Technol. 2019, 26, 729–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wang, Y.-G.; Chen, W.; Xu, R.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, J.; Luo, J.; Shen, R.-A.; Zhu, Y.; Cheong, W.-C.; et al. Hollow N-Doped Carbon Spheres with Isolated Cobalt Single Atomic Sites: Superior Electrocatalysts for Oxygen Reduction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 17269–17272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.L.; Liu, J.; Yan, Z.X.; Jin, M.; Xu, Z.H. Synthesis and use of hollow carbon spheres for electric double-layer capacitors. J. Carbon 2021, 36, 794–809. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, F.; Chen, Y. Preparation and absorbing properties of ultra-light and large size hollow cubic carbon materials. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2024, 35, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, B.; Su, B.; Cao, Y.; Hou, L. Carbon nanotubes and montmorillonite reinforced carbon foam composites containing hollow microspheres. Carbon Lett. 2024, 34, 1755–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Feng, J.; Jiang, Y.; Li, L.; Hu, Y.; Feng, J. High-Yield Preparation and Properties of Phenolic Resin-Based Carbon Microspheres. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 43583–43592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bairi, P.; Sardar, K.; Samanta, M.; Chanda, K.; Chattopadhyay, K.K. Nanoporous nitrogen-doped graphitic carbon hollow spheres with enhanced electrochemical properties. Mater. Chem. Front. 2021, 5, 7645–7653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Tan, Y.; Huang, P.; Sun, H.; Meng, Q.; Rong, Y.; Liu, T.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, H. Nano-architectonics of simple preparation of phenolic resin-based carbon microspheres via aqueous-phase self-catalysis polymerization for enhanced electrochemical performance of supercapacitor electrode materials. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2025, 153, 112057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Luo, R.; Ni, Y. Preparation and characterization of resin-derived carbon foams reinforced by hollow ceramic microspheres. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 3392–3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Priya, S.; Islam, R.; Ricci, W. Characterization of Mechanical and Electrical Properties of Epoxy-Glass Microballoon Syntactic Composites. Ferroelectrics 2006, 345, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniyan, V.; Priyadharshini, G.S.; Thiagarajan, V.; Palanisamy, S.; Suyambulingam, I. Comprehensive glass/banana fiber characterization with zirconium carbide filler-reinforced hybrid composites for lightweight structural applications. Eng. Res. Express 2024, 6, 045524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, O.-K.; Hwang, J.-Y.; Goh, M.; Lee, J.H.; Ku, B.-C.; You, N.-H. Mechanically Strong and Multifunctional Polyimide Nanocomposites Using Amimophenyl Functionalized Graphene Nanosheets. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 3505–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.Y.; Choi, M.; Lee, D.; Ha, C. 2D-Aligned Graphene Sheets in Transparent Polyimide/Graphene Nanocomposite Films Based on Noncovalent Interactions Between Poly(amic acid) and Graphene Carboxylic Acid. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2011, 297, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.-C.; Tian, M.-J.; Huang, C.-Y.; Wang, S.-W.; Li, X.; Hu, Q.-R.; Yuan, M.-Q. Topological study about failure behavior and energy absorption of honeycomb structures under various strain rates. Def. Technol. 2022, 24, 214–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, C.; Meng, F.; Meng, F.; Wang, T.; Luo, Z. Investigation of the Reinforcement Mechanism and Impact Resistance of Carbon Hollow Microsphere-Reinforced PDMS Composites. Polymers 2025, 17, 2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17152087
Yu Y, Zhang Y, Yang C, Meng F, Meng F, Wang T, Luo Z. Investigation of the Reinforcement Mechanism and Impact Resistance of Carbon Hollow Microsphere-Reinforced PDMS Composites. Polymers. 2025; 17(15):2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17152087
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Yingying, Yaxi Zhang, Cheng Yang, Fandong Meng, Fanyi Meng, Tao Wang, and Zhenmin Luo. 2025. "Investigation of the Reinforcement Mechanism and Impact Resistance of Carbon Hollow Microsphere-Reinforced PDMS Composites" Polymers 17, no. 15: 2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17152087
APA StyleYu, Y., Zhang, Y., Yang, C., Meng, F., Meng, F., Wang, T., & Luo, Z. (2025). Investigation of the Reinforcement Mechanism and Impact Resistance of Carbon Hollow Microsphere-Reinforced PDMS Composites. Polymers, 17(15), 2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17152087




