Nafion in Biomedicine and Healthcare
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Discussion
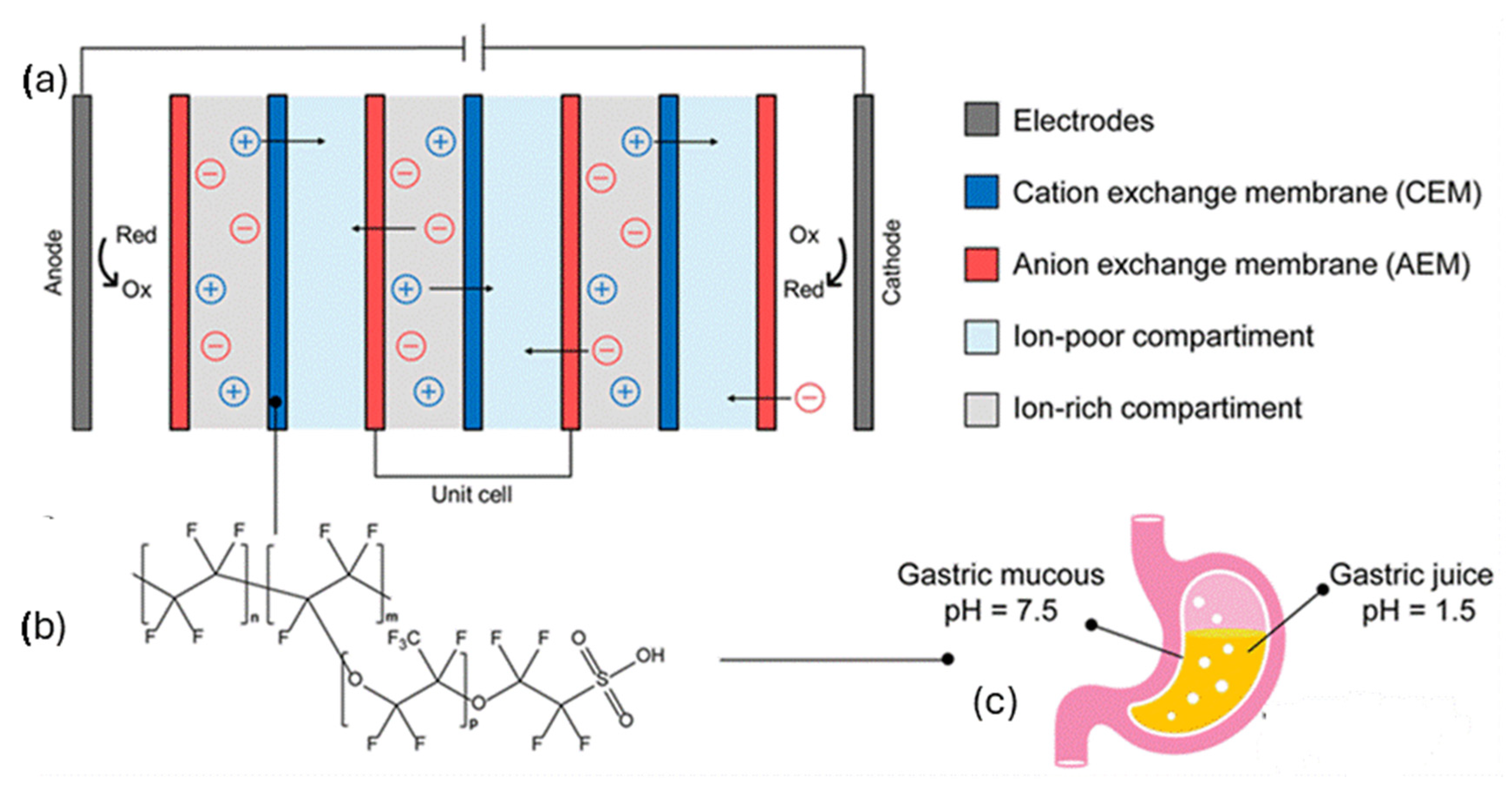
2.1. Bioelectronic Systems for Energy Harvest
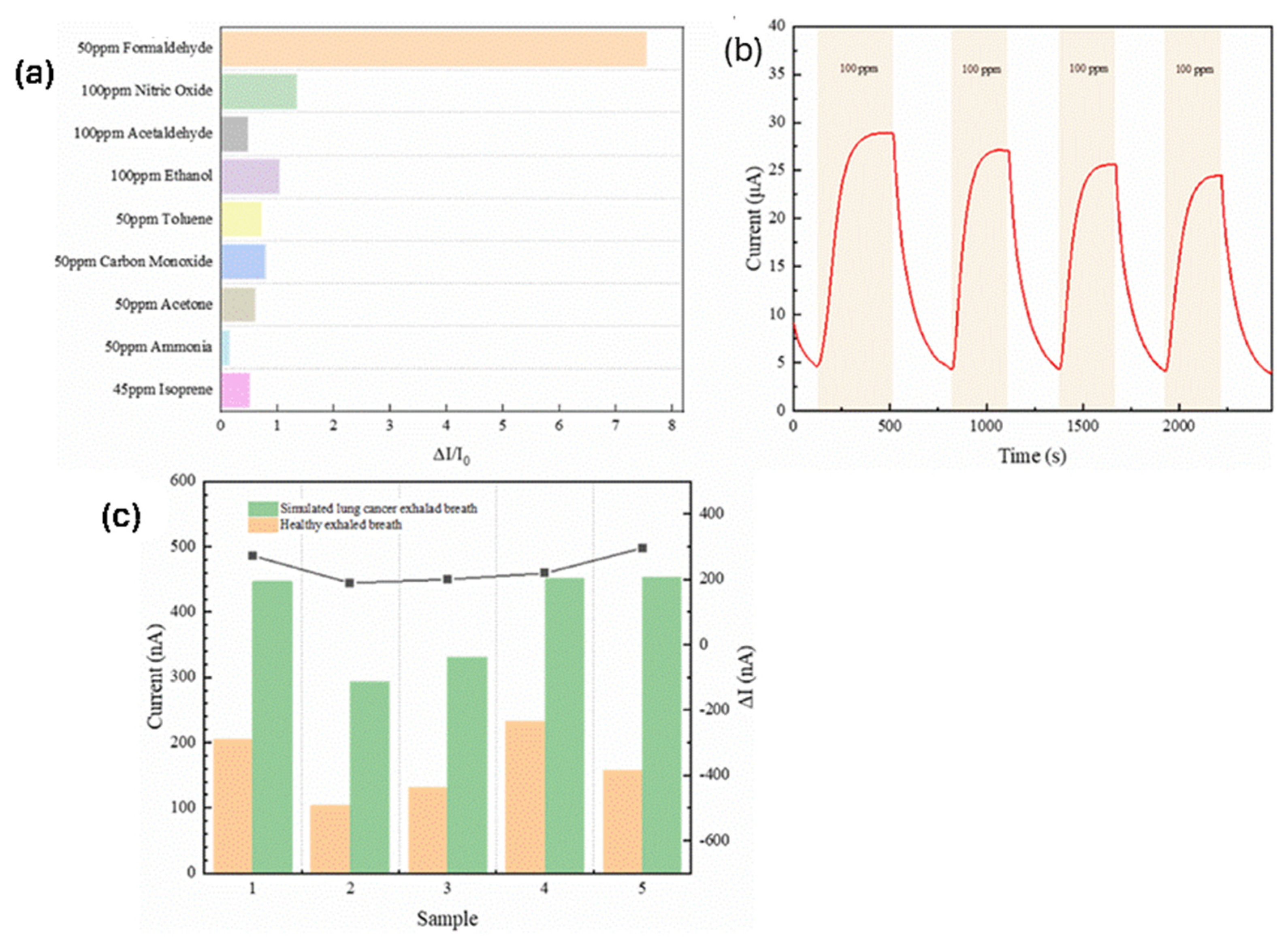
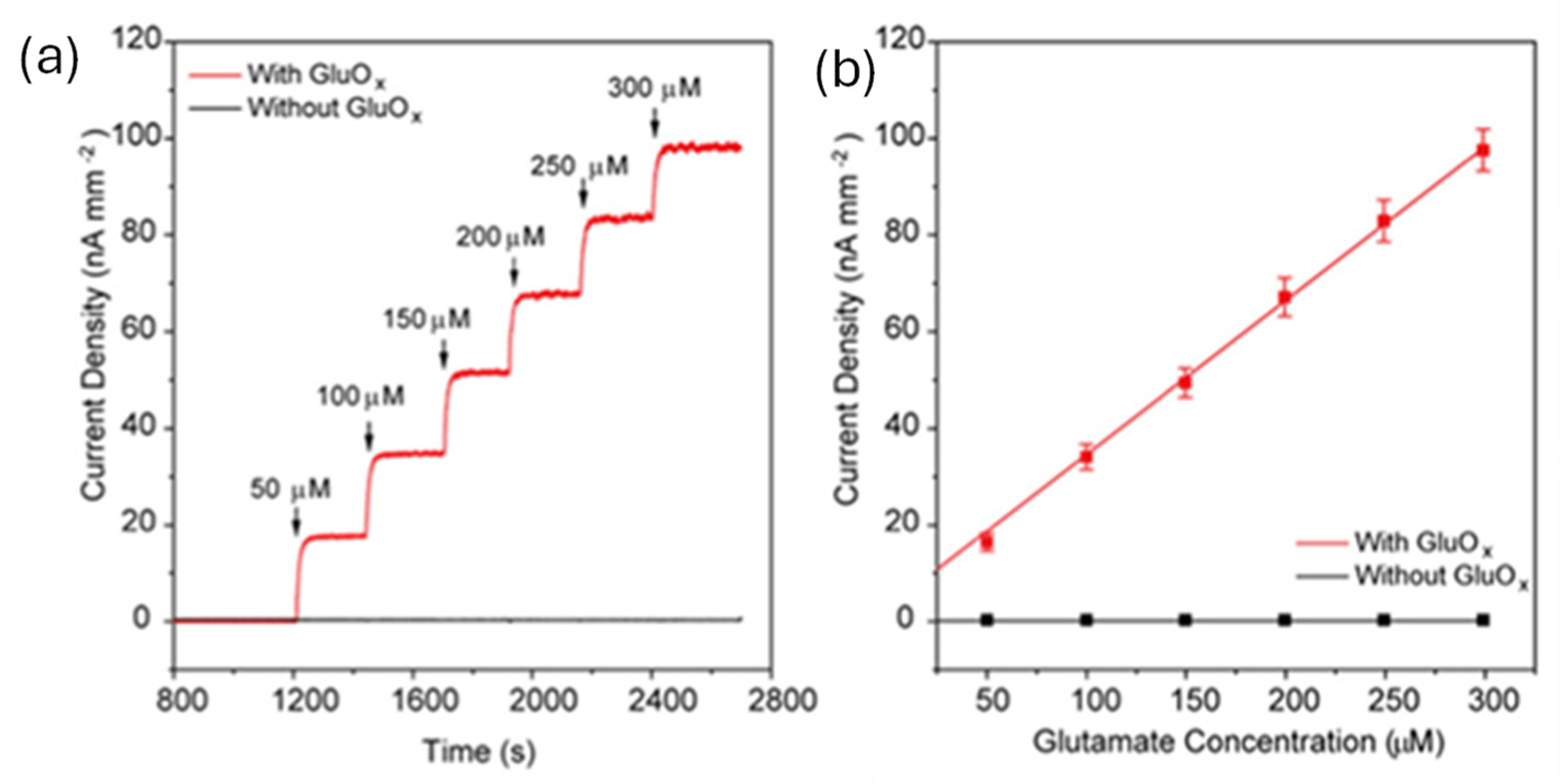
2.2. Biosensing
2.3. Wearable Electronics and Electronic Textiles
2.4. Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine
2.5. Lab-on-a-Chip Microfluid Devices
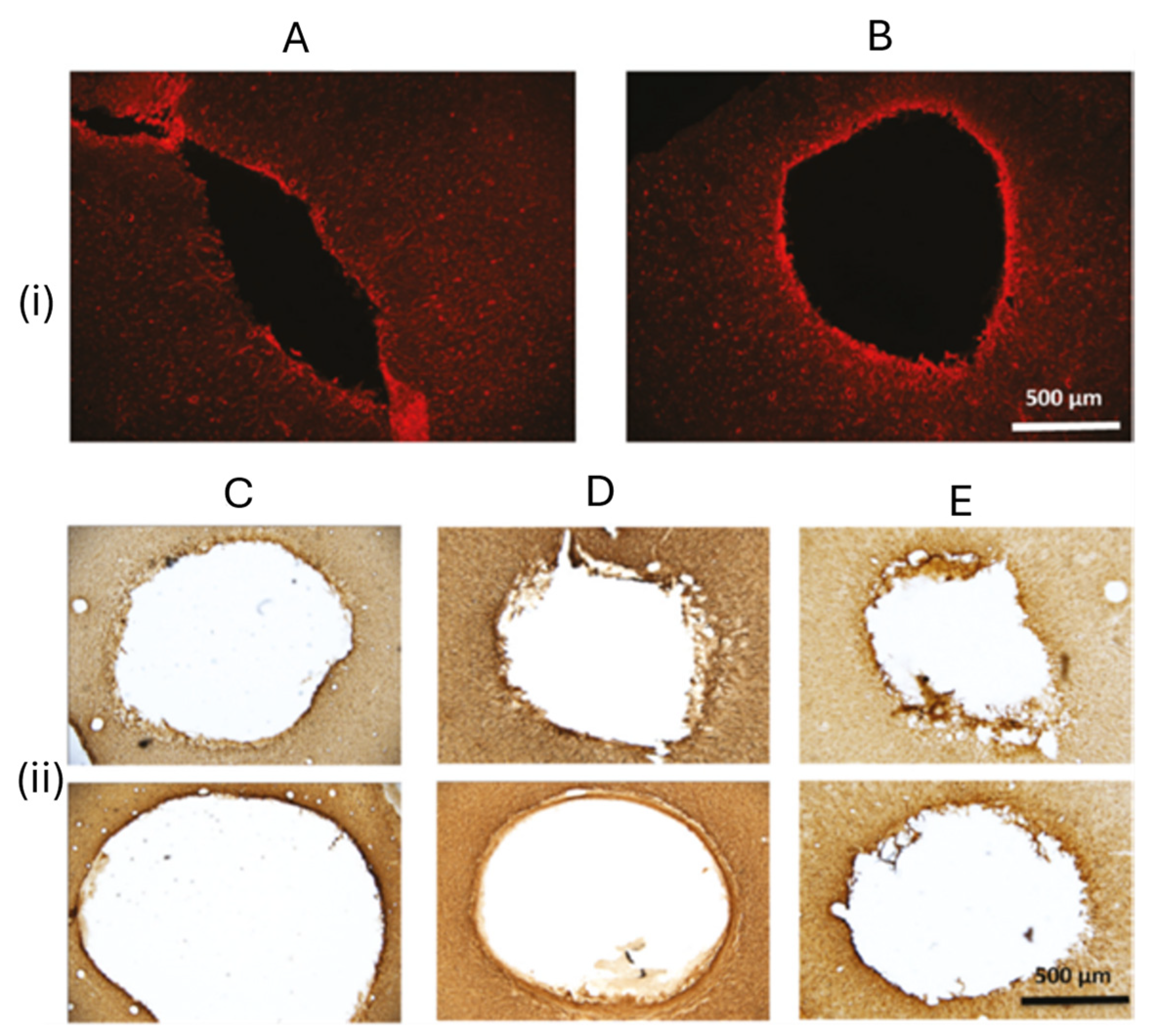
2.6. Implants
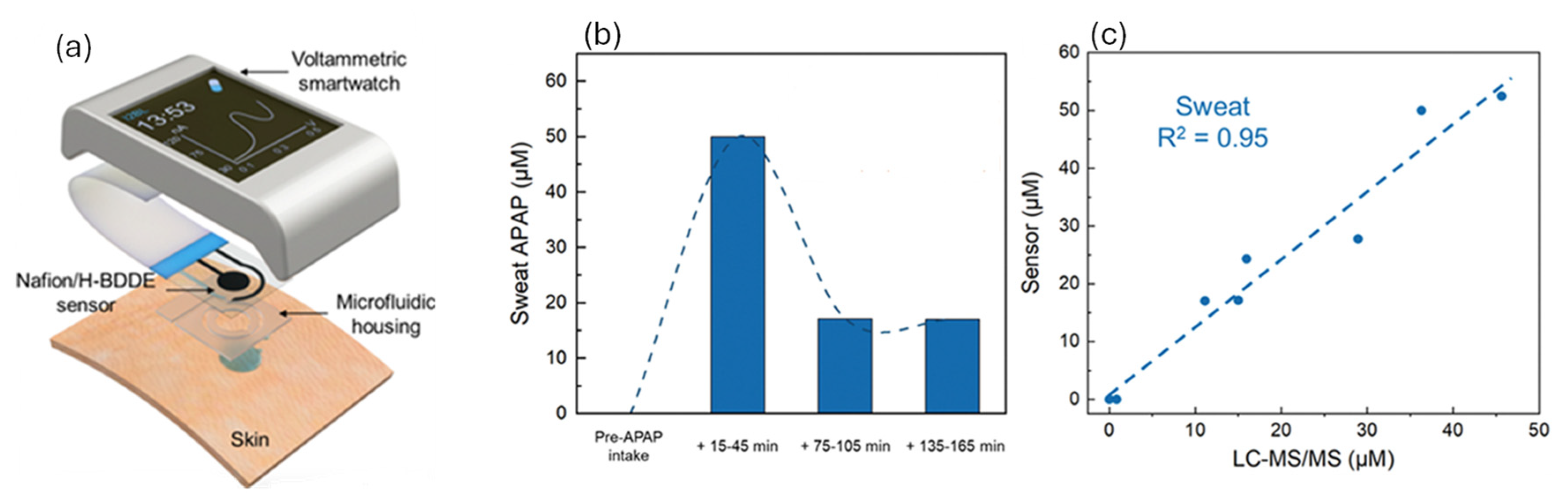
2.7. Biofluid Profiling
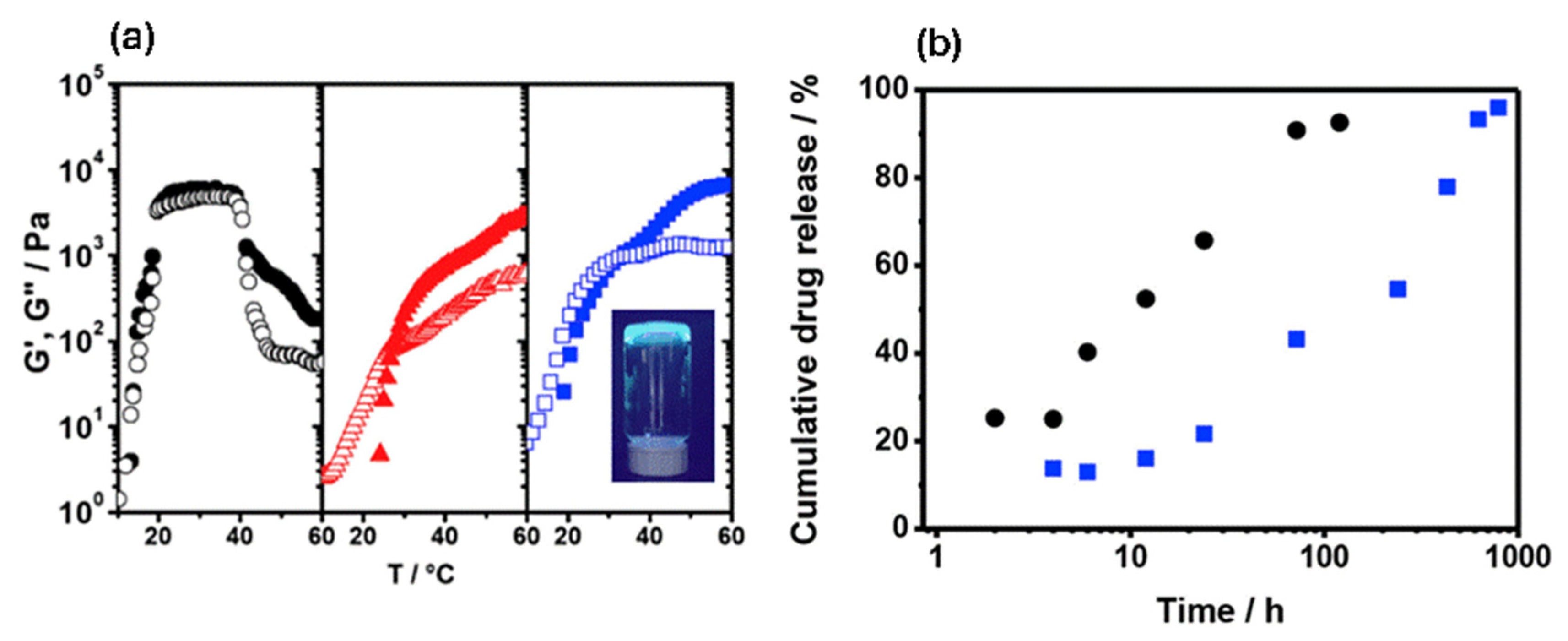
2.8. Drug Delivery and Therapeutics
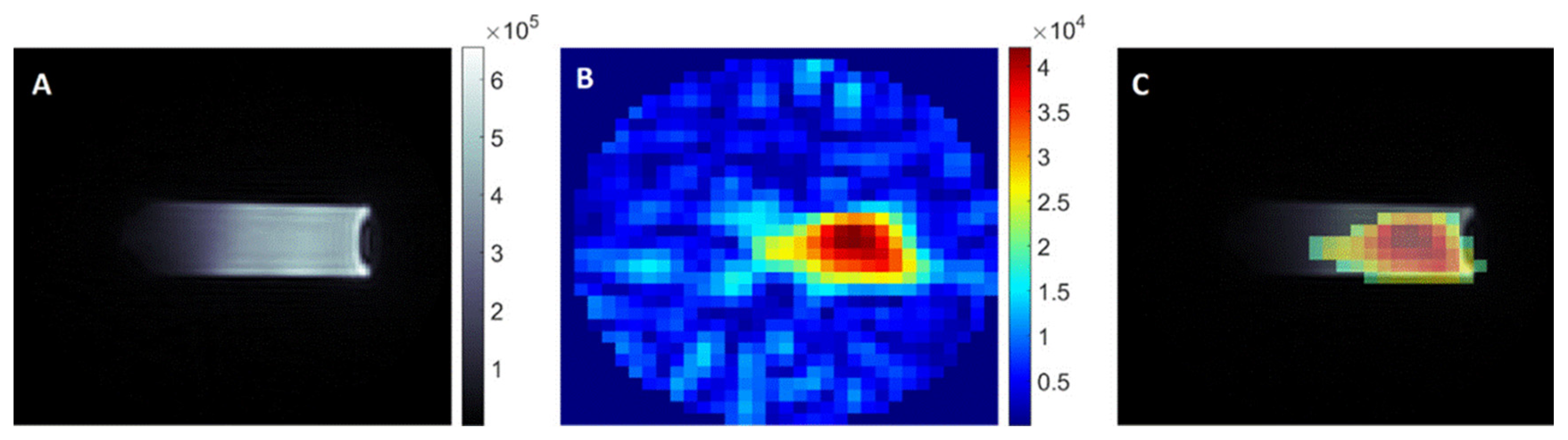
2.9. Diagnostics and Imaging
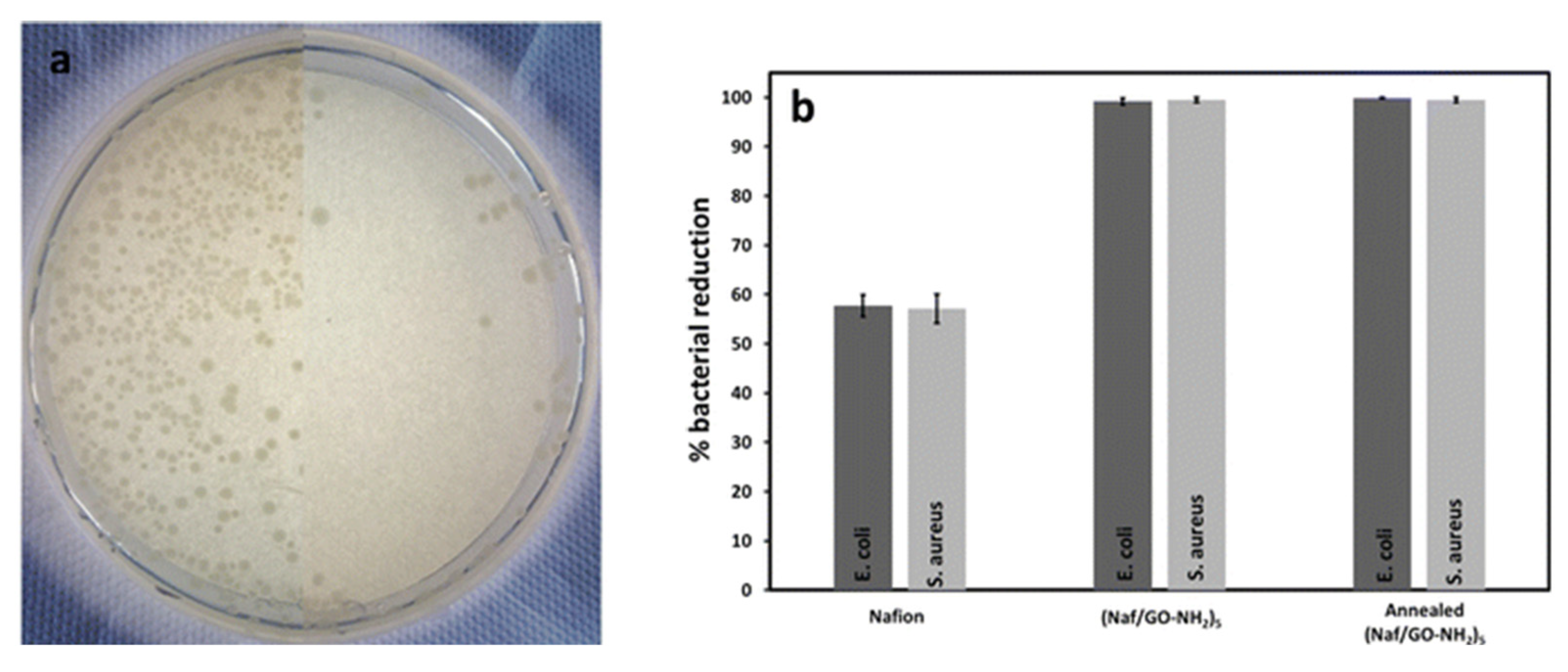
2.10. Antimicrobial Surfaces
3. Outlook
4. Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kusoglu, A.; Weber, A.Z. New Insights into Perfluorinated Sulfonic-Acid Ionomers. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 987–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauritz, K.A.; Moore, R.B. State of Understanding of Nafion. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 4535–4586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Curtin, D.E. Nafion® perfluorinated membranes in fuel cells. J. Fluor. Chem. 2004, 125, 1211–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; He, J.; Wang, L.; Lei, J. Recent developments in high-performance Nafion membranes for hydrogen fuel cells applications. Pet. Sci. 2022, 19, 1371–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.S.; Himabindu, V. Hydrogen production by PEM water electrolysis—A review Hydrogen production by PEM water electrolysis—A review. Mater. Sci. Energy Technol. 2019, 2, 442–454. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.; Negro, E.; Nale, A.; Pagot, G.; Vezzù, K.; Zawodzinski, T.A.; Meda, L.; Gambaro, C.; Di Noto, V. An efficient barrier toward vanadium crossover in redox flow batteries: The bilayer [Nafion/(WO3)x] hybrid inorganic-organic membrane. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 378, 138133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelarakis, A.; Giannelis, E.P. Nafion as Cosurfactant: Solubilization of Nafion in Water in the Presence of Pluronics. Langmuir 2011, 27, 554–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelarakis, A.; Krysmann, M.J. Trivial and Non-Trivial Supramolecular Assemblies Based on Nafion. Colloid Interface Sci. Commun. 2014, 1, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthasarathy, M.; Kakade, B.A.; Pillai, V.K. Tuning the Transport Properties of Poly(oxyethylene)bisamine−Nafion Polyelectrolyte Complexes by Dielectric Manipulation. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 3653–3658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estevez, L.; Kelarakis, A.; Gong, Q.; Da’as, E.H.; Giannelis, E.P. Multifunctional Graphene/Platinum/Nafion Hybrids via Ice Templating. J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 6122–6125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, S.; Kelarakis, A.; Estevez, L.; Giannelis, E.P. Oriented Arrays of Graphene in a Polymer Matrix by in situ Reduction of Graphite Oxide Nanosheets. Small 2010, 6, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Hao, M.; Li, B.; Zhu, Z.; Gou, X.; Li, L. Rapid preparation of a Nafion/Ag NW composite film and its humidity sensing effect. RSC Adv. 2020, 1, 27447–27455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, T.; Saidin, N.U.; Zali, N.M.; Kok, K. Hydrogen and humidity sensing characteristics of Nafion, Nafion/graphene, and Nafion/carbon nanotube resistivity sensors. J. Nanopart. Res. 2022, 24, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Li, W.; Sun, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B.; Lu, Q.; Wang, T.; Liang, X.; Liu, F.; Sun, P.; et al. Expanding the range of trackable environmental pollutants for Nafion based fuel cell type gas sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2024, 399, 134808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palisoc, S.; Sow, V.A.; Natividad, M. Fabrication of a bismuth nanoparticle/Nafion modified screen-printed graphene electrode for in situ environmental monitoring. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 1591–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergamasco, S.; Hein, L.A.; Silvestri, L.; Hartmann, R.; Menegatti, G.; Pozio, A.; Rinaldi, A. Innovative Nafion- and Lignin-Based Cation Exchange Materials Against Standard Resins for the Removal of Heavy Metals During Water Treatment. Separations 2024, 11, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Zhao, C.; Zhao, X.; Mei, D.; Pan, Y.; Li, B.; Li, L.; Wang, Y. Nafion/polyimide based programmable moisture-driven actuators for functional structures and robots. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 393, 134152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, M.; Lin, W.; Tamagawa, H.; Ito, S.; Kikuchi, K. Self-Sensing Control of Nafion-Based Ionic Polymer-Metal Composite (IPMC) Actuator in the Extremely Low Humidity Environment. Actuators 2013, 2, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, R.F.B.; Harrison, D.J.; Rojotte, R.V. Preliminary in vivo biocompatibility studies on perfluorosulphonic acid polymer membranes for biosensor applications. Biomaterials 1991, 12, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.; Kim, H.; Kim, I.J.; Kim, J.R.; Lee, J.I.; Ree, M. Bacterial Adhesion, Cell Adhesion and Biocompatibility of Nafion Films. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2009, 20, 1687–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadzadeh Kakhki, R. Nafion based biosensors: A review of recent advances and applications. Int. J. Polym. Mater. 2024, 73, 1470–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Q.; Feng, S.; Cheng, Y.; Li, T.; Cui, D.; Wang, K. Point-of-care biochemical assays using electrochemical technologies: Approaches, applications, and opportunities. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gluschke, J.G.; Seidl, J.; Lyttleton, R.W.; Nguyen, K.; Lagier, M.; Meyer, F.; Krogstrup, P.; Nygård, J.; Lehmann, S.; Mostert, A.B.; et al. Integrated bioelectronic proton-gated logic elements utilizing nanoscale patterned Nafion. Mater. Horiz. 2021, 8, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, K.; Sato, K.; Ono, T.; Dairaku, T.; Kashiwagi, Y. Preparation of Nafion/Polycation Layer-by-Layer Films for Adsorption and Release of Insulin. Polymers 2018, 10, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierucci, C.; Paleari, L.; Baker, J.; Sproncken, C.C.M.; Folkesson, M.; Wesseler, J.P.; Vracar, A.; Dodero, A.; Nanni, F.; Berrocal, J.A.; et al. Nafion membranes for power generation from physiologic ion gradients. RSC Appl. Polym. 2025, 3, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, D.; Guha Ray, P.; Buchmann, P.; Mansouri, M.; Fussenegger, M. Blood-Glucose-Powered Metabolic Fuel Cell for Self-Sufficient Bioelectronics. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, e2300890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, A.; Supraja, P.; Mishra, S.; Kumar, K.U.; Rakesh Kumar, R.; Haranath, D.; Thirmal, C.; Raju, N.; Rao, T.V.; Balaji, K.; et al. Energy harvesting properties of the Nafion thin films. ERX 2022, 4, 45015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Noy, A. Antifouling strategies for protecting bioelectronic devices. APL Mater. 2021, 9, 020701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Hao, Z.; Wang, X.; Huang, C.; Lin, Q.; Zhao, X.; Pan, Y. Cytokine Storm Biomarkers: A Flexible and Regenerative Aptameric Graphene–Nafion Biosensor for Cytokine Storm Biomarker Monitoring in Undiluted Biofluids toward Wearable Applications (Adv. Funct. Mater. 4/2021). Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2005958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huldin, G.F.; Huang, J.; Reitemeier, J.; Fu, K.X. Nafion coated nanopore electrode for improving electrochemical aptamer-based biosensing. Faraday Discuss. 2025, 257, 316–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Guo, W.; Wei, Q.; Wang, R.; Liu, Y.; Han, F.; Wei, F. High-performance formaldehyde electrochemical sensor utilizing Nafion as solid electrolyte for human exhaled breath detection. Talanta 2025, 293, 128148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, F.O.; Finnerty, N.J.; Lowry, J.P. Nitric oxide monitoring in brain extracellular fluid: Characterisation of Nafion®-modified Pt electrodes in vitro and in vivo. Analyst 2009, 134, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, C.H.; Finnerty, N.J. An electrochemical investigation into the effects of local and systemic administrations of sodium nitroprusside in brain extracellular fluid of mice. Bioelectrochemistry 2020, 132, 107441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zain, Z.M.; O’Neill, R.D.; Lowry, J.P.; Pierce, K.W.; Tricklebank, M.; Dewa, A.; Ghani, S.A. Development of an implantable d-serine biosensor for in vivo monitoring using mammalian d-amino acid oxidase on a poly (o-phenylenediamine) and Nafion-modified platinum–iridium disk electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 25, 1454–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carli, S.; Bianchi, M.; Zucchini, E.; Di Lauro, M.; Prato, M.; Murgia, M.; Fadiga, L.; Biscarini, F. Electrodeposited PEDOT:Nafion Composite for Neural Recording and Stimulation. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, e1900765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzzo, S.; Carli, S.; Pavan, B.; Lunghi, A.; Murgia, M.; Bianchi, M. Evaluation of the In Vitro Biocompatibility of PEDOT:Nafion Coatings. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham Ba, V.A.; Cho, D.; Hong, S. Nafion-Radical Hybrid Films on Carbon Nanotube Transistors for Monitoring Antipsychotic Drug Effects on Stimulated Dopamine Release. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 9716–9723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, P.; Walsh, P.L.; Guillot, T.S.; Gras-Najjar, J.; Takmakov, P.; Crews, F.T.; Wightman, R.M. Chronically Implanted, Nafion-Coated Ag/AgCl Reference Electrodes for Neurochemical Applications. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2011, 2, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta, N.F.; Galal, A.; Azab, S.M. Electrochemical Determination of Neurotransmitters Using Gold Nanoparticles on Nafion/Carbon Paste Modified Electrode. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2012, 159, H765–H771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Nguyen, T.N.H.; Anderson, A.; Cheng, X.; Gage, T.E.; Lim, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, H.; Rodolakis, F.; Zhang, Z.; et al. In Vivo Glutamate Sensing inside the Mouse Brain with Perovskite Nickelate–Nafion Heterostructures. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 24564–24574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, A.I.; Ostergren, I.; Kim, Y.; Fauth, S.; Craighero, M.; Yoon, M.; Lund, A.; Muller, C. All-Polymer Conducting Fibers and 3D Prints via Melt Processing and Templated Polymerization. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 8713–8721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Yu, W.; Wang, B.; Zhao, Y.; En, K.; Zhu, J.; Cheng, X.; Zhou, C.; Lin, H.; Wang, Z.; et al. Noninvasive wearable electroactive pharmaceutical monitoring for personalized therapeutics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 19017–19025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Ma, L.; Su, J.; Jing, W.; Wei, M.; Sha, X. Biocompatibility assessment of porous chitosan-Nafion and chitosan-PTFE composites in vivo. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2014, 102, 2055–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayar, S.; Chakraverty, S. A comparative study to evaluate the osteoblastic cell behavior of two nano coated titanium surfaces with NAFION stabilized the membrane. J. Indian Prosthodont. Soc. 2015, 15, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imani, S.; Zagari, Z.; Rezaei Zarchi, S.; Jorjani, M.; Nasri, S. Functional Recovery of Carbon Nanotube/Nafion Nanocomposite in Rat Model of Spinal Cord Injury. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2016, 44, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Park, H.B.; Sung, S.; Lee, J.K.; Kim, H.J. A polymer-based artificial microenvironment for enhancing cell adhesion. Organoid 2023, 3, e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Yang, H.; Sivagnanam, V.; Gijs, M.A.M. Microfluidic Protein Preconcentrator Using a Microchannel-Integrated Nafion Strip: Experiment and Modeling. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 9989–9997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Yang, R. Enhanced sample preconcentration in microfluidic chip using graphene oxide–Nafion membrane. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2016, 20, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polino, M.; Rho, H.S.; Pina, M.P.; Mallada, R.; Carvalho, A.L.; Romão, M.J.; Coelhoso, I.; Gardeniers, J.G.E.; Crespo, J.G.; Portugal, C.A.M. Protein Crystallization in a Microfluidic Contactor with Nafion®117 Membranes. Membranes 2021, 11, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.; Kim, J. Reversible capture of genomic DNA by a Nafion-coated electrode. Anal. Biochem. 2008, 380, 335–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, M.; Barz, D.P.J. Bonding Nafion® with polydimethysiloxane: A versatile approach towards ion-exchange membrane microfluidic devices. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 537, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdes, T.I.; Ciridon, W.; Ratner, B.D.; Bryers, J.D. Modulation of fibroblast inflammatory response by surface modification of a perfluorinated ionomer. Biointerphases 2011, 6, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitta Raj, R.R.S.; Madhivanan, K.; Ganapathy, D.; Sundramoorthy, A.K. Nafion/ZrO2 Modified NiTi Orthodontic Wire: Preparation, Material Characterization, and Corrosion Studies. Micro Nanosyst. 2024, 16, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, D.; Gartner, P.; Berezkin, I.; Rudat, J.; Bilger, M.; Grünert, T.; Zimmerer, N.; Quarz, P.; Scharfer, P.; Brückel, J.; et al. Selective Peptide Binders to the Perfluorinated Sulfonic Acid Ionomer Nafion (Adv. Funct. Mater. 20/2024). Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2214932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Mofidfar, M.; Zare, R.N. Introducing Nafion for In Situ Desalting and Biofluid Profiling in Spray Mass Spectrometry. Front. Chem. 2022, 9, 807244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Möhwald, H. Highly Stable and Biocompatible Nafion-Based Capsules with Controlled Permeability for Low-Molecular-Weight Species. Chem. A Eur. J. 2002, 8, 4751–4755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, D.; Kluska, W.; Stanislawska, J.; Board, B.; Krysmann, M.J.; Kelarakis, A. Novel hydrogels containing Nafion and poly(ethylene oxide) based block copolymers. Polymer 2017, 114, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sguizzato, M.; Esposito, E.; Drechsler, M.; Gallerani, E.; Gavioli, R.; Mariani, P.; Carducci, F.; Cortesi, R.; Bergamini, P. Nafion®-Containing Solid Lipid Nanoparticles as a Tool for Anticancer Pt Delivery: Preliminary Studies. J. Chem. 2017, 2017, 3206298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.; Maiti, T.K.; Bhattacharyya, T.K. Feasibility Studies on Nafion Membrane Actuated Micropump Integrated With Hollow Microneedles for Insulin Delivery Device. JMEMS 2019, 28, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashazadeh, A.; Landes, R.; Boese, A.; Kreissl, M.C.; Klopfleisch, M.; Friebe, M. Superficial skin cancer therapy with Y-90 microspheres: A feasibility study on patch preparation. Ski. Res. Technol. 2020, 26, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todd, D.J.; Kagan, A.; Chibnik, L.B.; Kay, J. Cutaneous changes of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: Predictor of early mortality and association with gadolinium exposure. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 3433–3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanal, E.; Tweedle, M.F. Residual or Retained Gadolinium: Practical Implications for Radiologists and Our Patients. Radiology 2015, 275, 630–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczęch, M.; Łopuszyńska, N.; Tomal, W.; Jasiński, K.; Węglarz, W.P.; Warszyński, P.; Szczepanowicz, K. Nafion-Based Nanocarriers for Fluorine Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Langmuir 2020, 36, 9534–9539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.J.; Pang, L.Q.; Che, L.M.; Wu, X.E.; Chen, X.D. Nafion coated stainless steel for anti-biofilm application. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 111, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Moraru, C.I. Long-range interactions keep bacterial cells from liquid-solid interfaces: Evidence of a bacteria exclusion zone near Nafion surfaces and possible implications for bacterial attachment. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 162, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbons, E.N.; Winder, C.; Barron, E.; Fernandes, D.; Krysmann, M.J.; Kelarakis, A.; Parry, A.V.S.; Yeates, S.G. Layer by Layer Antimicrobial Coatings Based on Nafion, Lysozyme, and Chitosan. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beg, M.S.; Gibbons, E.N.; Gavalas, S.; Holden, M.A.; Krysmann, M.; Kelarakis, A. Antimicrobial coatings based on amine-terminated graphene oxide and Nafion with remarkable thermal resistance. Nanoscale Adv. 2024, 6, 2594–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beg, M.S.; Gibbons, E.N.; Duncalf, J.; Gavalas, S.; Redman, D.; Holden, M.A.; Kelarakis, A. Heat Sterilizable Coatings Based on Nafion and Graphene Quantum Dots With Advanced Antibacterial Performance. Nano Sel. 2025, e70012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Qu, R.; Habteselassie, M.; Wu, J.; Yang, S.; Sun, P.; Huang, Q.; Wang, Z. Hepatic Transcriptome Responses in Mice (Mus musculus) Exposed to the Nafion Membrane and Its Combustion Products. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conley, J.M.; Lambright, C.S.; Evans, N.; Medlock-Kakaley, E.; Hill, D.; McCord, J.; Strynar, M.J.; Wehmas, L.C.; Hester, S.; MacMillan, D.K.; et al. Developmental toxicity of Nafion byproduct 2 (NBP2) in the Sprague-Dawley rat with comparisons to hexafluoropropylene oxide-dimer acid (HFPO-DA or GenX) and perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS). Environ. Int. 2022, 160, 107056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, J.R.; Strynar, M.J.; Lindstrom, A.B.; Farthing, A.; Huang, H.; Schmid, J.; Hill, D.; Chernoff, N. Toxicity of Balb-C Mice Exposed to Recently Identified 1,1,2,2-Tetrafluoro-2-[1,1,1,2,3,3-hexafluoro-3-(1,1,2,2-tetrafluoroethoxy)propan-2-yl]oxyethane-1-sulfonic acid (PFESA-BP2). Toxicology 2020, 441, 152529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robuck, A.R.; Cantwell, M.G.; McCord, J.P.; Addison, L.M.; Pfohl, M.; Strynar, M.J.; McKinney, R.; Katz, D.R.; Wiley, D.N.; Lohmann, R. Legacy and Novel Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Juvenile Seabirds from the U.S. Atl. Coast. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 12938–12948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotlarz, N.; McCord, J.; Collier, D.; Lea, C.S.; Strynar, M.; Lindstrom, A.B.; Wilkie, A.A.; Islam, J.Y.; Matney, K.; Tarte, P.; et al. Measurement of Novel, Drinking Water-Associated PFAS in Blood from Adults and Children in Wilmington, North Carolina. Environ. Health Perspect. 2020, 128, 77005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corton, J.C.; Gift, J.S.; Auerbach, S.S.; Liu, J.; Das, K.P.; Ren, H.; Lang, J.R.; Chernoff, N.; Lau, C.; Hill, D. Dose–response modeling of effects in mice after exposure to a polyfluoroalkyl substance (Nafion byproduct 2). Toxicol. Sci. 2025, 205, 380–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kelarakis, A. Nafion in Biomedicine and Healthcare. Polymers 2025, 17, 2054. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17152054
Kelarakis A. Nafion in Biomedicine and Healthcare. Polymers. 2025; 17(15):2054. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17152054
Chicago/Turabian StyleKelarakis, Antonios. 2025. "Nafion in Biomedicine and Healthcare" Polymers 17, no. 15: 2054. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17152054
APA StyleKelarakis, A. (2025). Nafion in Biomedicine and Healthcare. Polymers, 17(15), 2054. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17152054





