The Microscopic Mechanism of High Temperature Resistant Core-Shell Nano-Blocking Agent: Molecular Dynamics Simulations
Abstract
1. Introduction
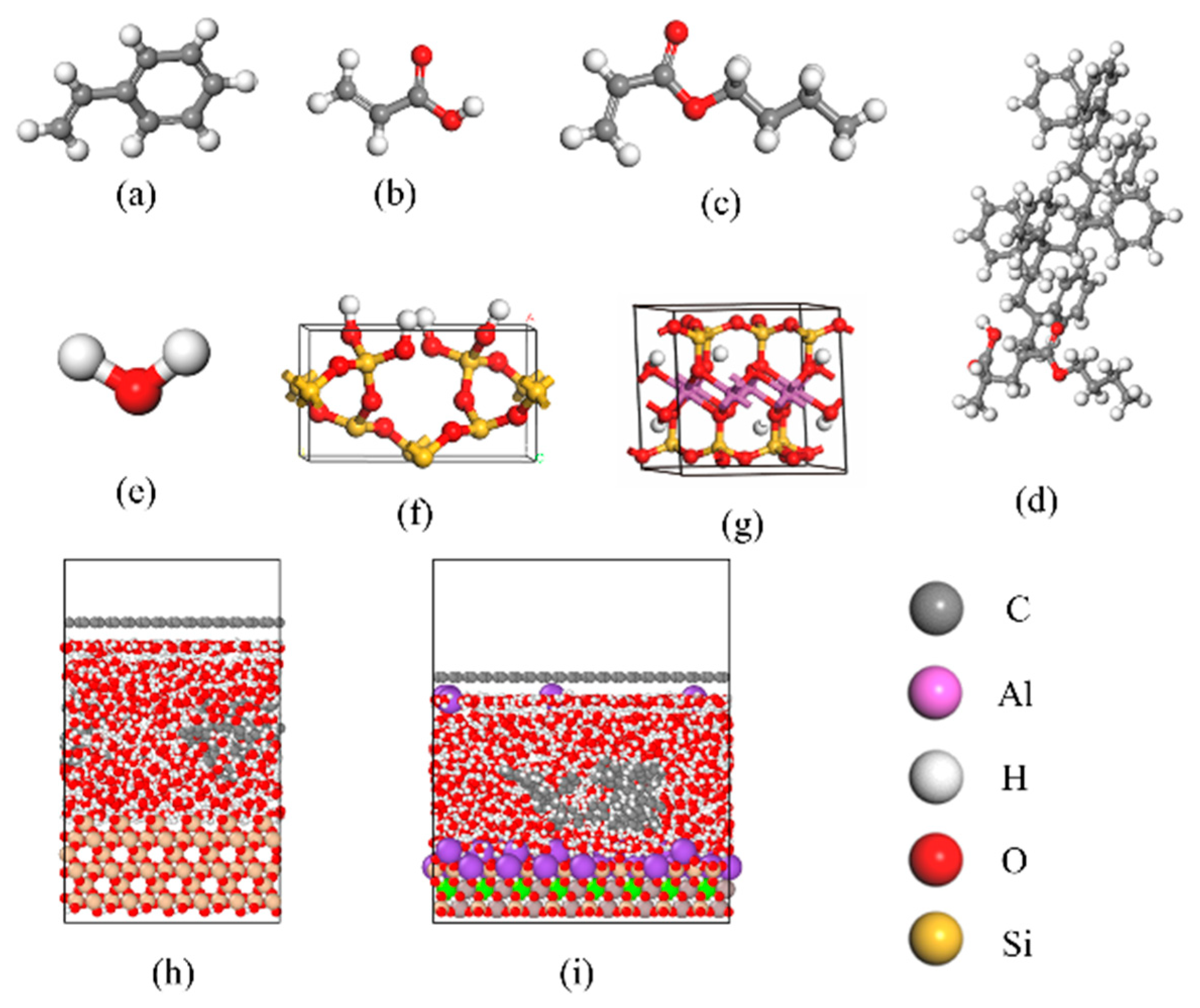
2. Methods
3. Result and Discussion
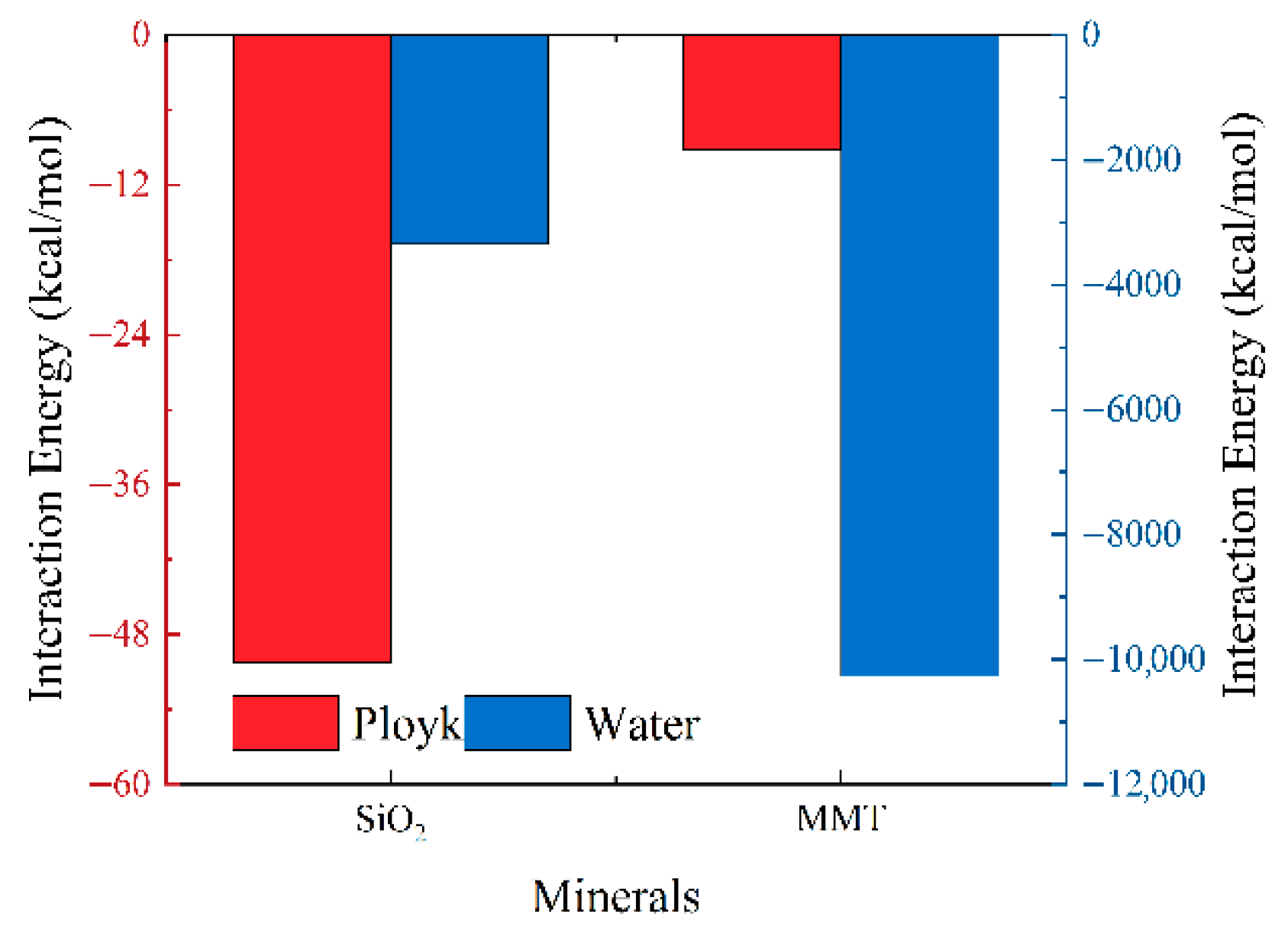
3.1. Interaction Studies Between Ployk Molecules and Different Minerals
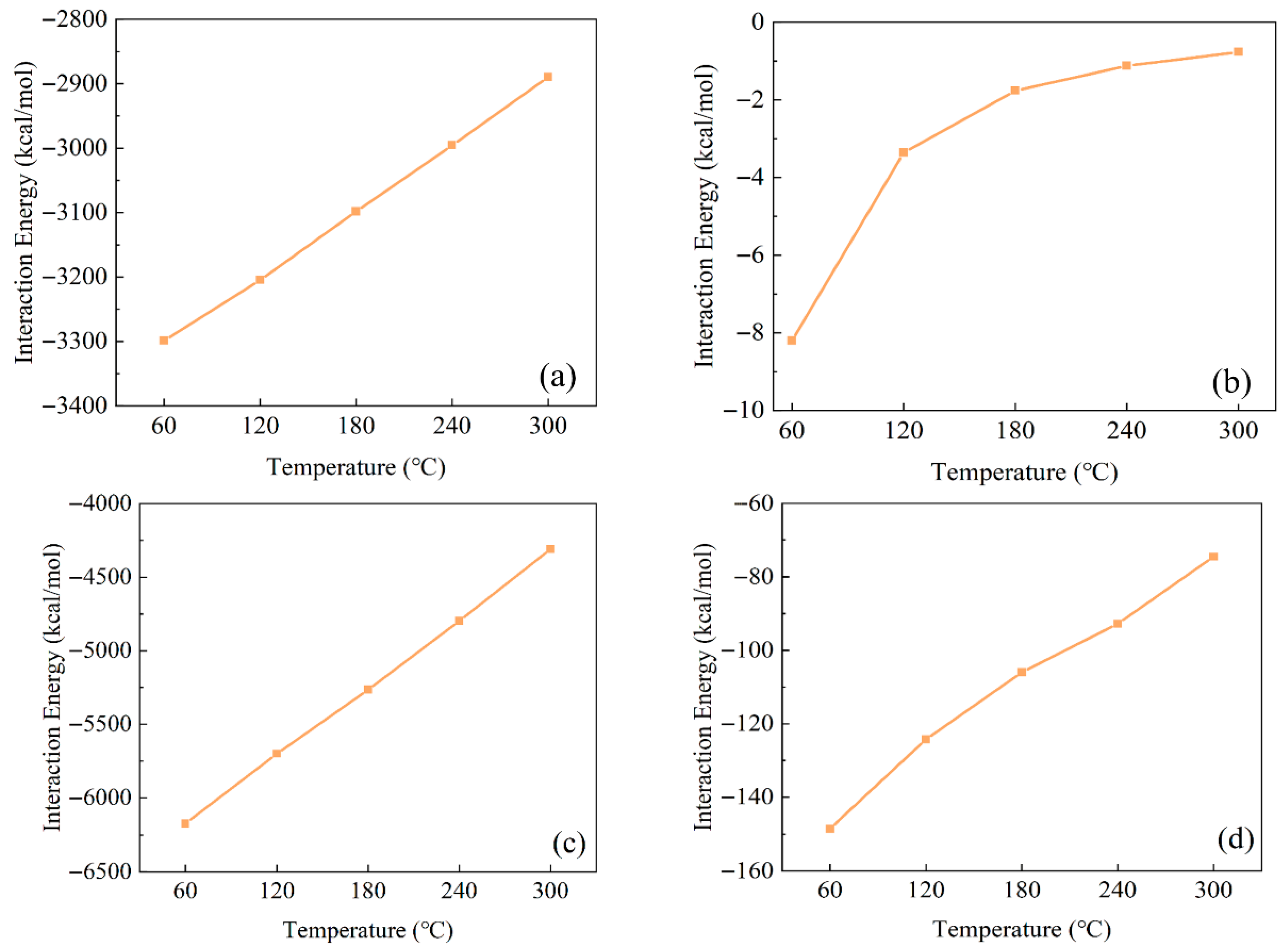
3.2. Effect of Temperature on the Interaction Between Ployk and SiO2
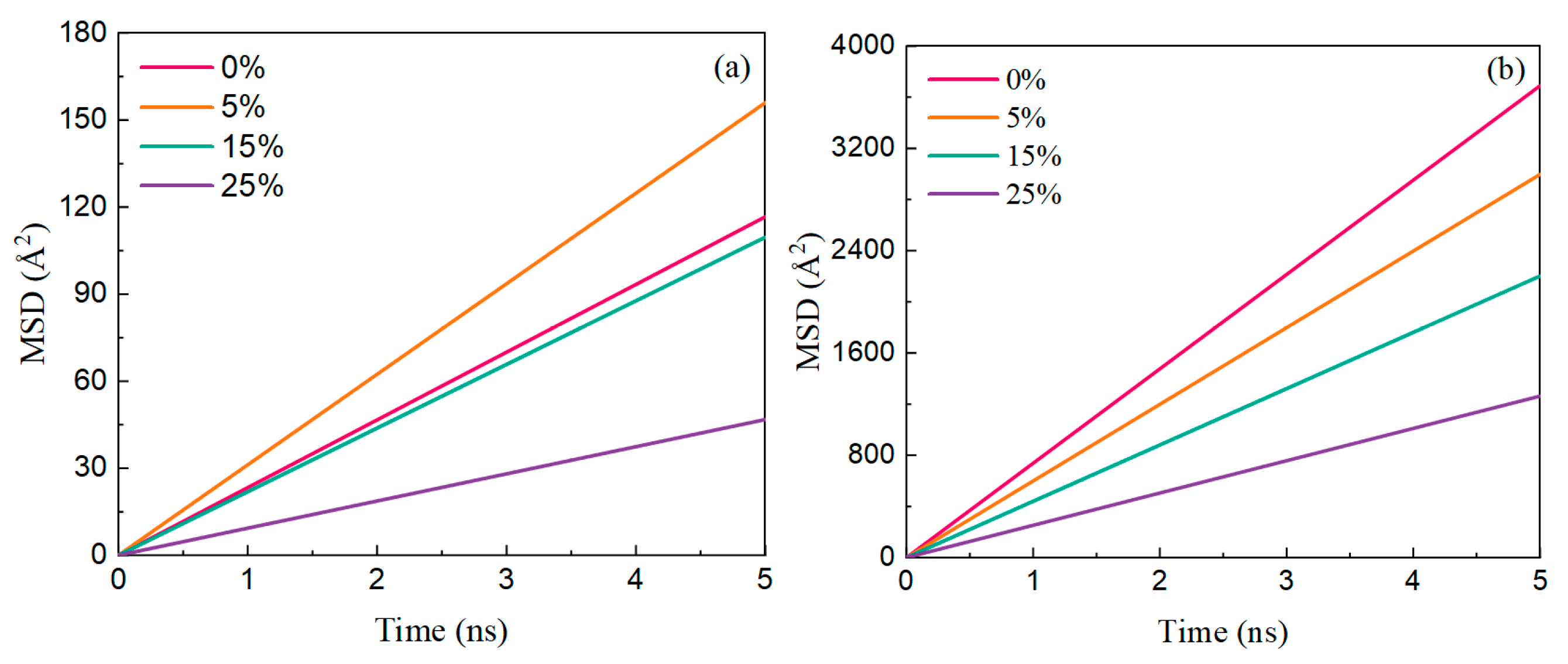
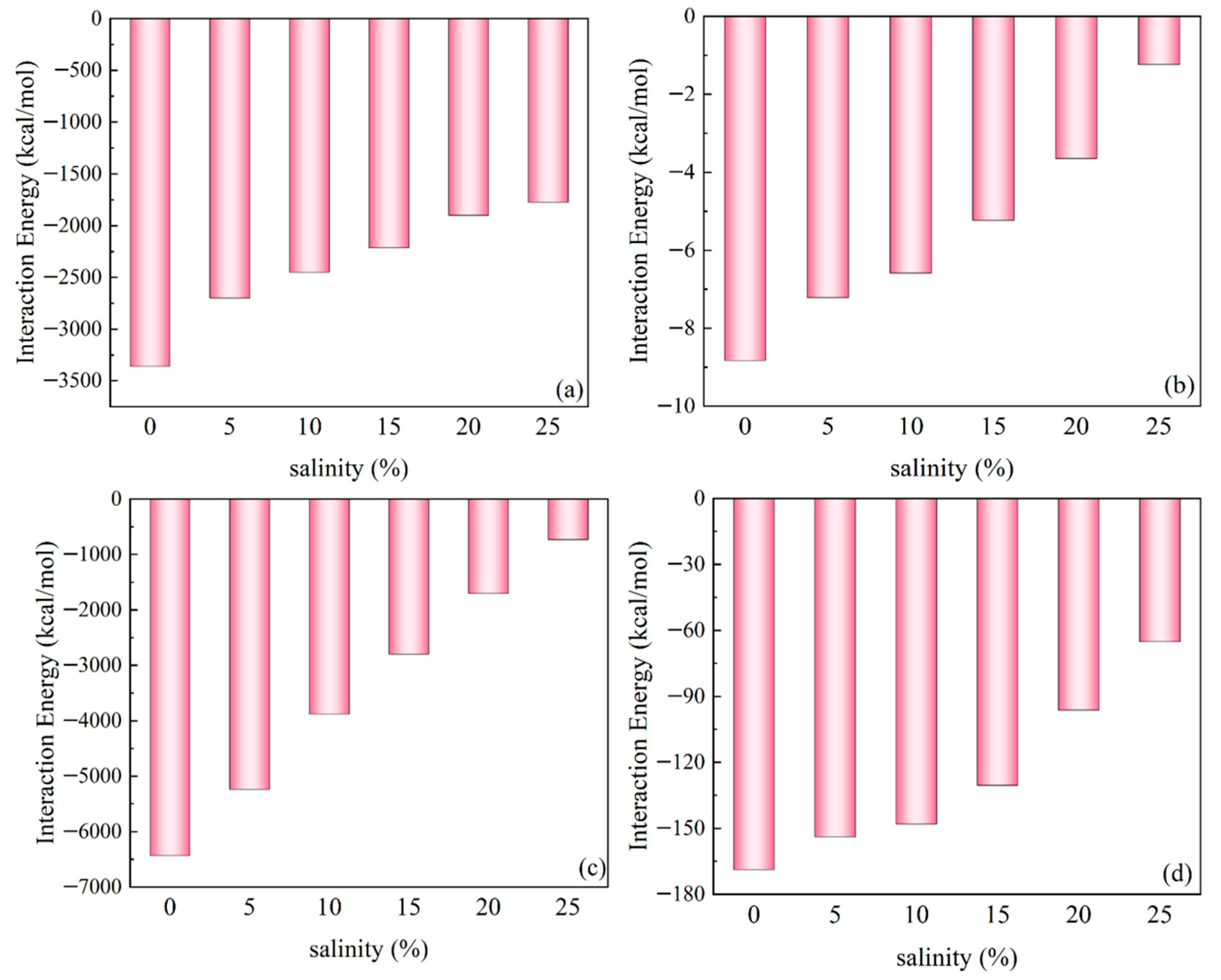
3.3. Effect of Salinity on the Interaction Between Ployk and SiO2
4. Conclusions
- Ployk exhibits distinct adsorption characteristics on different mineral components. Analysis of interaction energy profiles and density distribution results demonstrates that Ployk shows strong adsorption affinity for reservoir mineral (SiO2), while exhibiting weaker adsorption for swelling clay mineral montmorillonite. These results indicate robust interactions between the nanosealant and wellbore walls, which is favorable for sealing micro-fractures and pores.
- Temperature demonstrates a significant influence on Ployk’s behavior. Elevated temperatures reduce the interaction strength between Ployk and SiO2, simultaneously accelerating Ployk’s mobility. This temperature-dependent behavior suggests potential impacts on sealant performance under varying downhole conditions.
- Salinity shows comparatively minor effects on Ployk’s interactions. While increased salinity slightly weakens the Ployk–SiO2 interaction, the variation remains negligible within the 5–15% salinity range. This indicates that the nanosealant possesses considerable salt tolerance, maintaining its fracture-sealing capabilities under moderate salinity conditions.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hou, J.; Ma, Y.; Li, S.; Teng, J. Development and utilization of oil shale worldwide. Chem. Ind. Eng. Prog. 2015, 34, 1183–1190. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, X.; Li, M.; Li, B.; Wang, T.; Hui, S.; Liu, Y.; Liu, G.; Hu, T.; Xu, T.; Jiang, F.; et al. Main controlling factors and movability evaluation of continental shale oil. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2023, 243, 104472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.L.; Wang, J.Q.; Li, S.Y. World’s Oil Shale Available Retorting Technologies and The Forecast of Shale Oil Production. In Proceedings of the 18th International Offshore and Polar Engineering Conference (ISOPE 2008), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 6 July 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Guo, Q.; Chen, X.; Liu, Z.; Bai, X.; Fan, L.; He, W. Geological characteristics and resource potential of shale oil in major basins of China. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2024, 42, 1533–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Li, Z. Advances in Shale Oil /Gas Research in North America and Considerations on Exploration for Continental Shale Oil /Gas in China. Adv. Earth Sci. 2014, 29, 700–711. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, J.; Yang, J. Classification, exploration and development status and development trend of continental shale oil in China. China Pet. Explor. 2023, 28, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, H.M.; Kamal, M.S.; Mahmoud, M.; Hussain, S.S.; Abouelresh, M.; Al-Harthi, M.A. Organophilic Clay-Based Drilling Fluids for Mitigation of Unconventional Shale Reservoirs Instability and Formation Damage. J. Energy Resour. Technol. 2019, 141, 093102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Jarni, H.H.; Aftab, A.; Ismail, A.R.; Saady, N.M.C.; Sahito, M.F.; Keshavarz, A.; Iglauer, S.; Sarmadivaleh, M. Nanomaterial-Based Drilling Fluids for Exploitation of Unconventional Reservoirs: A Review. Energies 2020, 13, 3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, X.; Huang, L. Experimental investigation on the sudden cooling effect of oil-based drilling fluid on the dynamic compressive behavior of deep shale reservoirs. Energy 2023, 282, 128680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; You, L.; Xu, X.; Liao, Z. Prevention of Formation Damage Induced by Mud Lost in Deep Fractured Tight Gas Reservoir in Western Sichuan Basin. J. Can. Pet. Technol. 2012, 51, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Qiang, L.; Li, J.; Song, F.; Liu, H. Research development on formation damage induced by shale drilling. Chem. Eng. Oil Gas 2013, 42, 49–52. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Xu, C.; Kang, Y.; Jing, H.; Zhang, J.; Yang, B.; You, L.; Zhang, H.; Long, Y. Formation damage mechanism and control strategy of the compound function of drilling fluid and fracturing fluid in shale reservoirs. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2024, 51, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Yang, B.; You, L.; Chen, Q.; Yu, Y. Damage evaluation of oil-based drill-in fluids to shale reservoirs. Nat. Gas Ind. 2013, 33, 99–104. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Yang, Z.; Xu, W.; Yang, Q.; Yang, Z. Optimized and Fast Drilling Technology for Deep Shale Gas Horizontal Wells in Luzhou Block. Pet. Drill. Technol. 2023, 51, 16–21. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Yu, X.; Lai, Y.; Liu, H.; Wen, W.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, S. Lost Circulation Mechanism and Main Controlling Factors in Deep Brittle Shale Wells. Spec. Oil Gas Reserv. 2022, 29, 162–169. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, X.; Kang, Y.; You, L.; Xu, C.; Lin, C.; Zhang, J. Drill-in fluid loss mechanisms in brittle gas shale: A case study in the Longmaxi Formation, Sichuan Basin, China. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 174, 394–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; You, L.; Kang, Y.; Deng, S.; Xu, C. Formation Damage Induced by Oil-Based Drilling Fluid in a Longmaxi Shale Gas Reservoir: A Comprehensive View of the Drilling, Stimulation, and Production Processes. Energy Fuels 2022, 37, 945–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Li, J.; Sun, Y.; Guan, J.; Kuang, X.; Zheng, L. Development and application of an oil-based circulating micro-foam drilling fluid. Nat. Gas Ind. 2014, 34, 78–84. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, M.; Yuan, Z.; Li, X.; Huang, J.; Tian, Y. Performance Evaluation and Field Application of Nano Plugging Agent for Shale Water-Based Drilling Fluid. Energies 2022, 15, 7529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Ma, C.; Li, L.; Liu, G.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wu, H. Study on the multicomponent collaborative sealing mechanism of shale formations. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Energy Engineering and Environmental Protection (EEEP), Sanya, China, 19–21 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, J.; Wang, X.; Lu, Z.; Bu, W.; Sun, L.; Jing, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wen, L. Technology of Strong Plugging Constant Rheology Oil-Based Drilling Fluid for Shale Oil Reservoir in Damintun Sag of Liaohe Basin. Spec. Oil Gas Reserv. 2023, 30, 163–168. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Sun, J.; Lv, K.; Liu, J.; Shen, H.; Zhang, F. Application of core-shell structural acrylic resin/nano-SiO2 composite in water based drilling fluid to plug shale pores. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2018, 55, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhong, Y.; She, J.; Kuang, J. Experimental study of nano-drilling fluid based on nano temporary plugging technology and its application mechanism in shale drilling. Appl. Nanosci. 2019, 9, 1637–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Jiang, G.; Ni, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Luo, X. Styrene butadiene resin/nano-SiO2 composite as a water-and-oil-dispersible plugging agent for oil-based drilling fluid. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 606, 125245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Quan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, S.; Feng, Q.; Zhang, X. Preparation and Performance Evaluation of High-Temperature Polymer Nano-Plugging Agents for Water-Based Drilling Fluids Systems Applicable to Unconventional Reservoirs. Polymers 2025, 17, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, D.d.C.J.d.; Nojabaei, B. Phase Behavior and Composition Distribution of Multiphase Hydrocarbon Binary Mixtures in Heterogeneous Nanopores: A Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, D. A review of phase behavior simulation of hydrocarbons in confined space: Implications for shale oil and shale gas. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2019, 68, 102901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Liu, Z.; Cao, D. A permeation model of shale gas in cylindrical-like kerogen pores at geological conditions. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2019, 207, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Chang, S. Molecular dynamics investigation of shale oil occurrence and adsorption in nanopores: Unveiling wettability and influencing factors. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 481, 148380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.Q.; Tao, T.; Su, J.; Wang, Q.; Yang, P.; Bai, Y. Review of Application of Molecular Simulation in Inhibiting Surface Hydration Expansion of Clay Minerals. Chem. Technol. Fuels Oils 2022, 58, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fang, T.; Ding, B.; Wang, W.; Yan, Y.; Li, Z.; Guo, W.; Zhang, J. Migration of oil/methane mixture in shale inorganic nano-pore throat: A molecular dynamics simulation study. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2020, 187, 106784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Li, Z.; Xu, D.; Yan, L.; Wang, L.; Ye, Y. Study on the Dispersion Stability and Sealing Performance of Nanoscale Plugging Materials for Shale Formations. SPE J. 2024, 29, 2908–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Fu, J.; Chen, P.; Du, Z.; Qin, L. Experimental study and molecular simulation of gas dissolution and diffusion behavior in drilling fluid. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2016, 36, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Luo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, Y. Interfacial Friction Evolution in an Oil-Based Drilling Fluid Environment: An Atomic Understanding from ReaxFF Simulations. Tribol. Lett. 2023, 71, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Shen, J.; Sui, S. Preparation and Performance Evaluation of Core-shell Nano Plugging Agent with High Temperature Resistance Using in Oil-based Drilling Fluid. Oilfield Chem. 2022, 39, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, A.P.; Aktulga, H.M.; Berger, R.; Bolintineanu, D.S.; Brown, W.M.; Crozier, P.S.; in ‘t Veld, P.J.; Kohlmeyer, A.; Moore, S.G.; Nguyen, T.G.; et al. LAMMPS-a flexible simulation tool for particle-based materials modeling at the atomic, meso, and continuum scales. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2022, 271, 108171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cygan, R.T.; Liang, J.-J.; Kalinichev, A.G. Molecular Models of Hydroxide, Oxyhydroxide, and Clay Phases and the Development of a General Force Field. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 1255–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Chandrasekhar, J.; Madura, J.D.; Impey, R.W.; Klein, M.L. Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 79, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Maxwell, D.S.; Tirado-Rives, J. Development and Testing of the OPLS All-Atom Force Field on Conformational Energetics and Properties of Organic Liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 11225–11236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, B.; Wang, J.; Li, M.-C.; Lv, K.; Wang, Q.; Li, J.; Huang, X.; Wang, R.; Lv, X.; Chen, Z.; et al. Microscopic molecular and experimental insights into multi-stage inhibition mechanisms of alkylated hydrate inhibitor. Energy 2023, 279, 128045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, B.; Sun, J.; Wang, J.; Lv, X.; Wang, J.; Guo, J.; Lv, K.; Wang, R.; Zheng, J.; Chen, Z. Development of novel natural gas hydrate inhibitor and the synergistic inhibition mechanism with NaCl: Experiments and molecular dynamics simulation. Fuel 2023, 353, 129162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Ployk (Å2/ps) | Water (Å2/ps) | |
|---|---|---|
| 60 °C | 27.59 | 1020.58 |
| 120 °C | 53.92 | 1299.84 |
| 180 °C | 123.32 | 2188.59 |
| 300 °C | 414.55 | 4989.54 |
| Ployk (Å2/ps) | Water (Å2/ps) | |
|---|---|---|
| 0% | 29.16 | 922.517 |
| 5% | 38.99 | 749.19 |
| 15% | 27.40 | 693.96 |
| 25% | 11.69 | 550.43 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, Z.; Xv, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, K.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, Q.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Liao, B. The Microscopic Mechanism of High Temperature Resistant Core-Shell Nano-Blocking Agent: Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Polymers 2025, 17, 1969. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17141969
Du Z, Xv J, Wang J, Zhang J, Zhao K, Wang Q, Zheng Q, Wang J, Li J, Liao B. The Microscopic Mechanism of High Temperature Resistant Core-Shell Nano-Blocking Agent: Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Polymers. 2025; 17(14):1969. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17141969
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Zhenghong, Jiaqi Xv, Jintang Wang, Juyuan Zhang, Ke Zhao, Qi Wang, Qian Zheng, Jianlong Wang, Jian Li, and Bo Liao. 2025. "The Microscopic Mechanism of High Temperature Resistant Core-Shell Nano-Blocking Agent: Molecular Dynamics Simulations" Polymers 17, no. 14: 1969. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17141969
APA StyleDu, Z., Xv, J., Wang, J., Zhang, J., Zhao, K., Wang, Q., Zheng, Q., Wang, J., Li, J., & Liao, B. (2025). The Microscopic Mechanism of High Temperature Resistant Core-Shell Nano-Blocking Agent: Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Polymers, 17(14), 1969. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17141969






