Risk Assessment of Microplastics in Humans: Distribution, Exposure, and Toxicological Effects
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
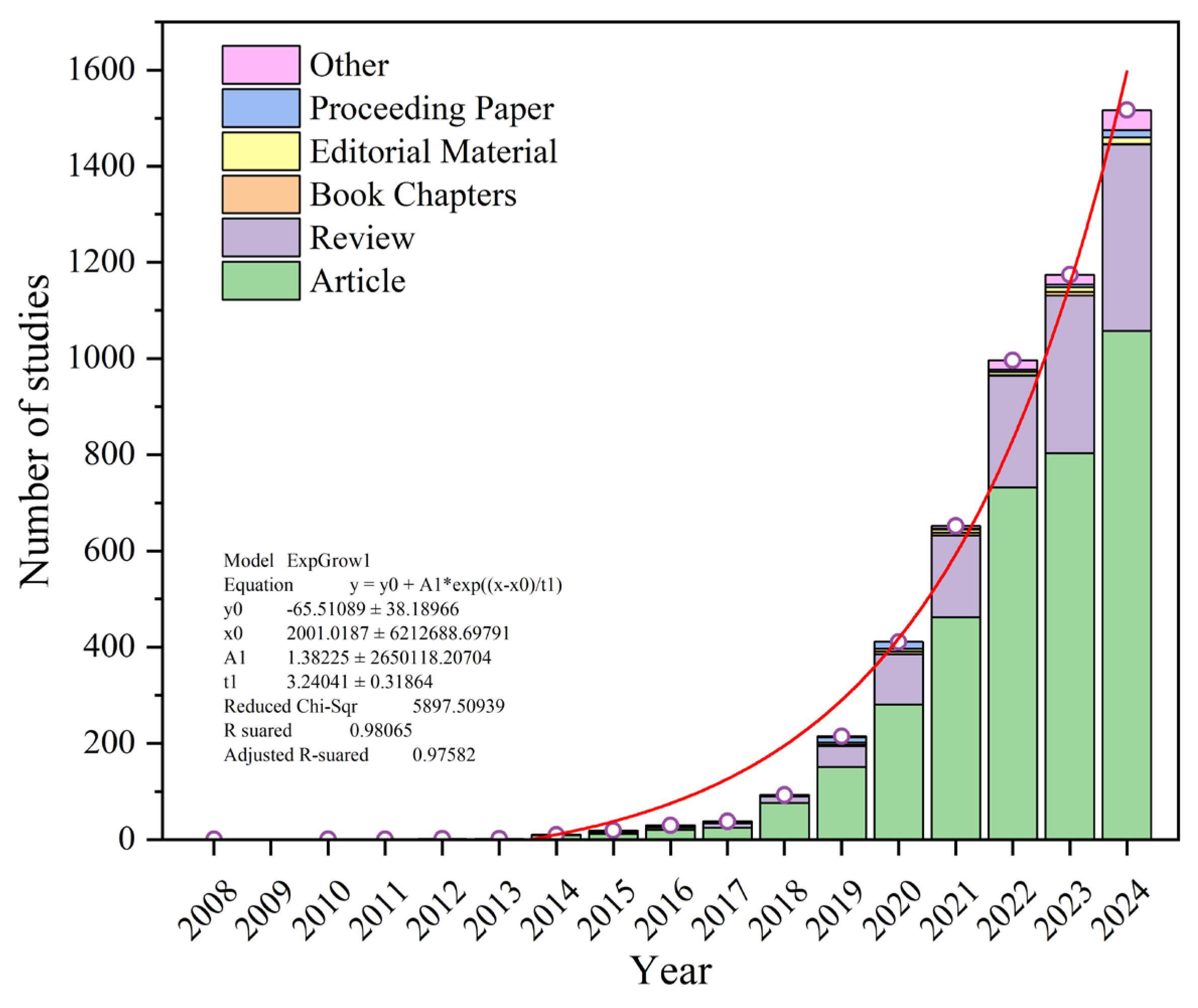
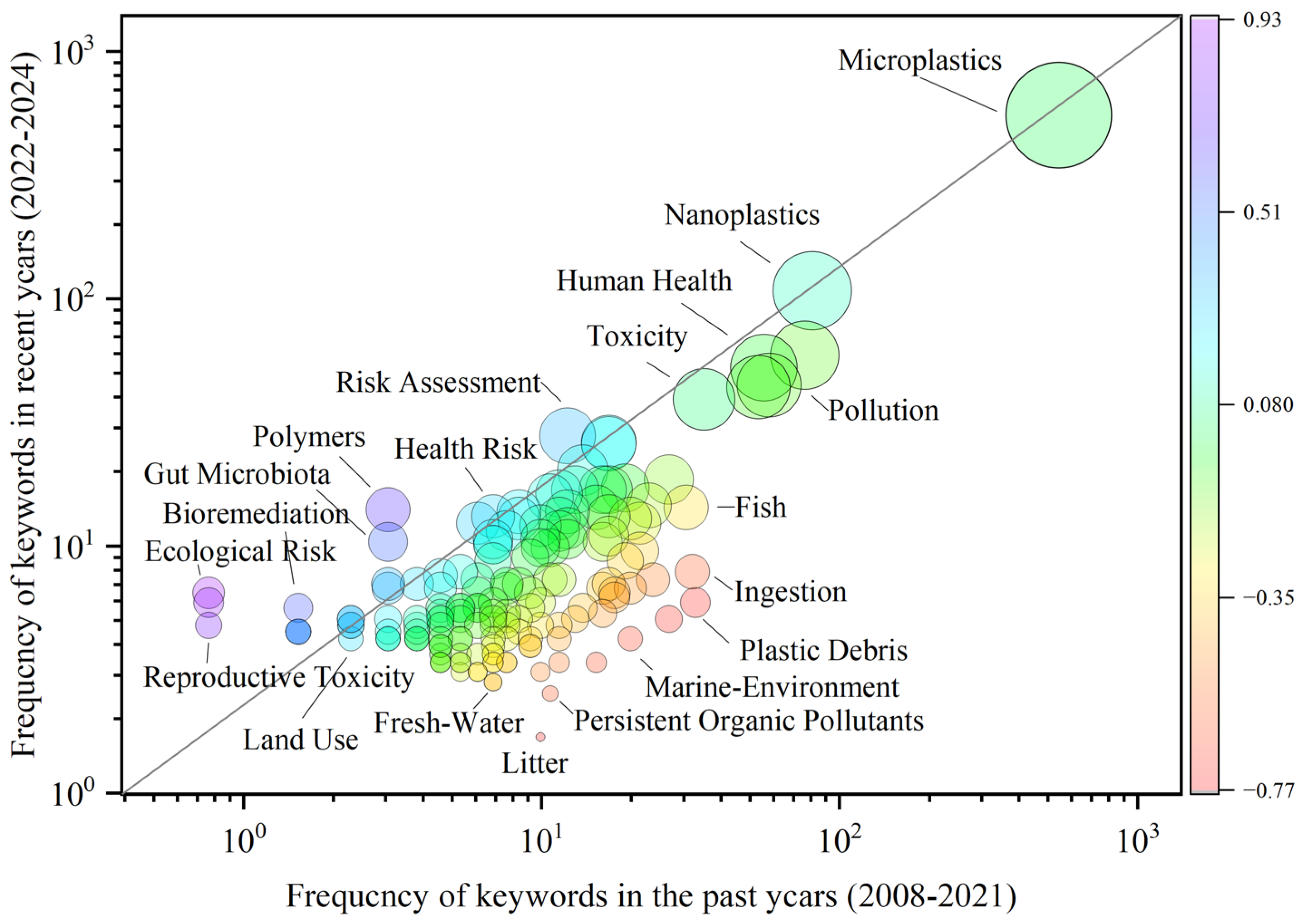
2.1. Bibliometric Analysis and Topic Evolution
2.2. Meta-Analysis
2.3. Machine Learning Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Trends in Microplastic Research Related to Human Health
3.2. Analysis of Research on Microplastic Impacts on Human Health
3.2.1. Pathways of Human Exposure to Microplastics
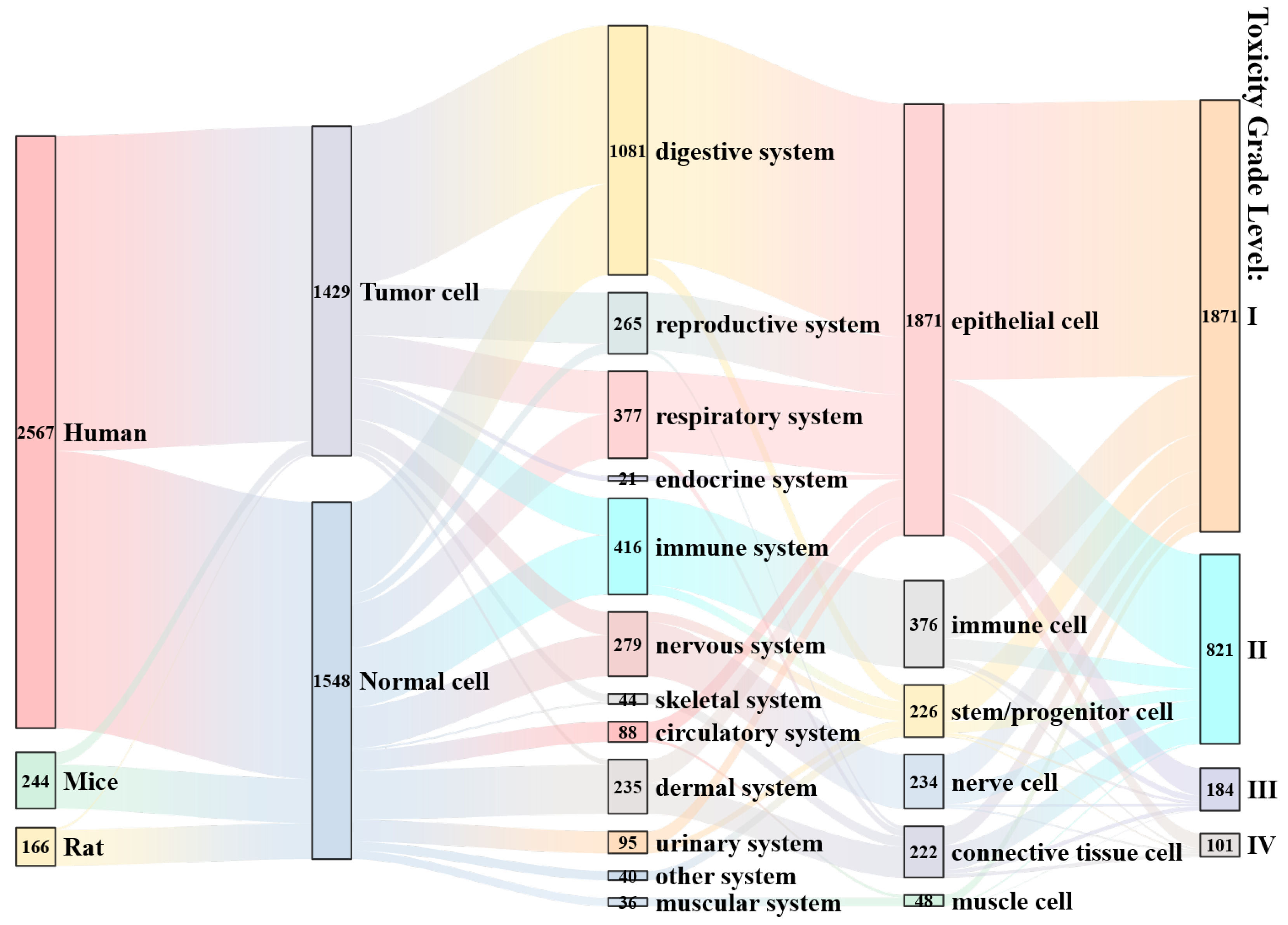
3.2.2. Distribution and Migration of Microplastics in the Human Body
3.2.3. Effects of Microplastic Exposure on Human Health
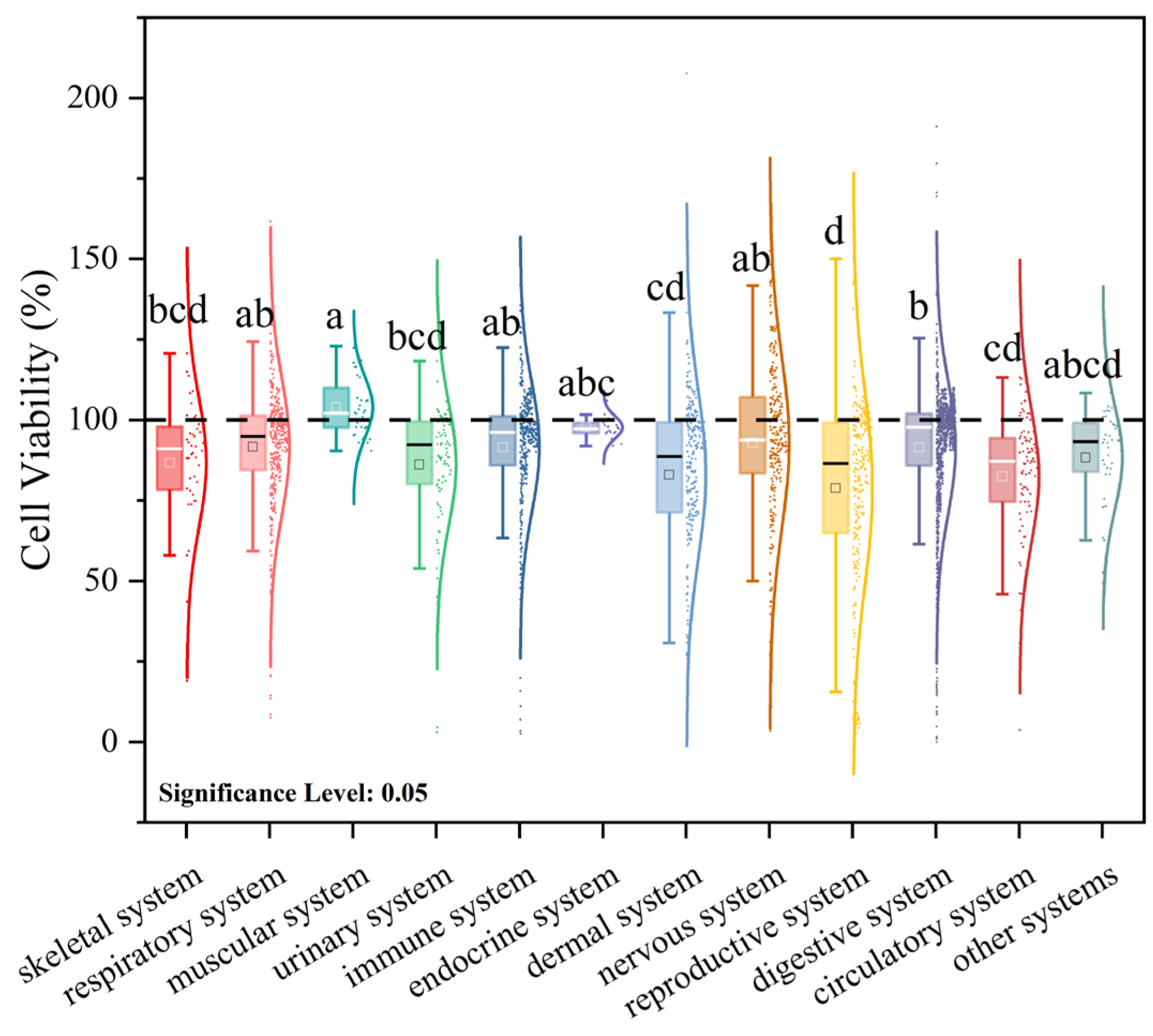
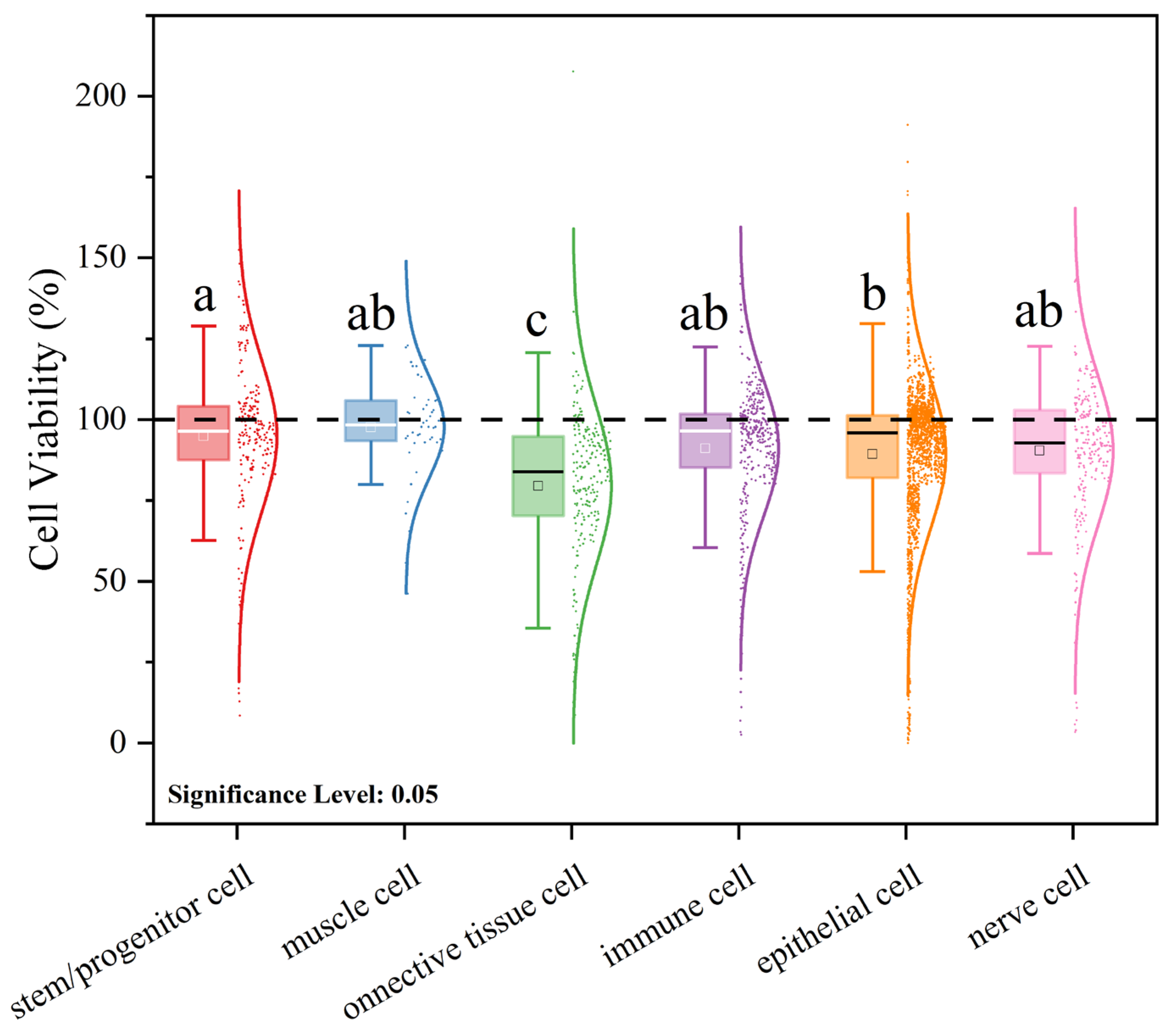
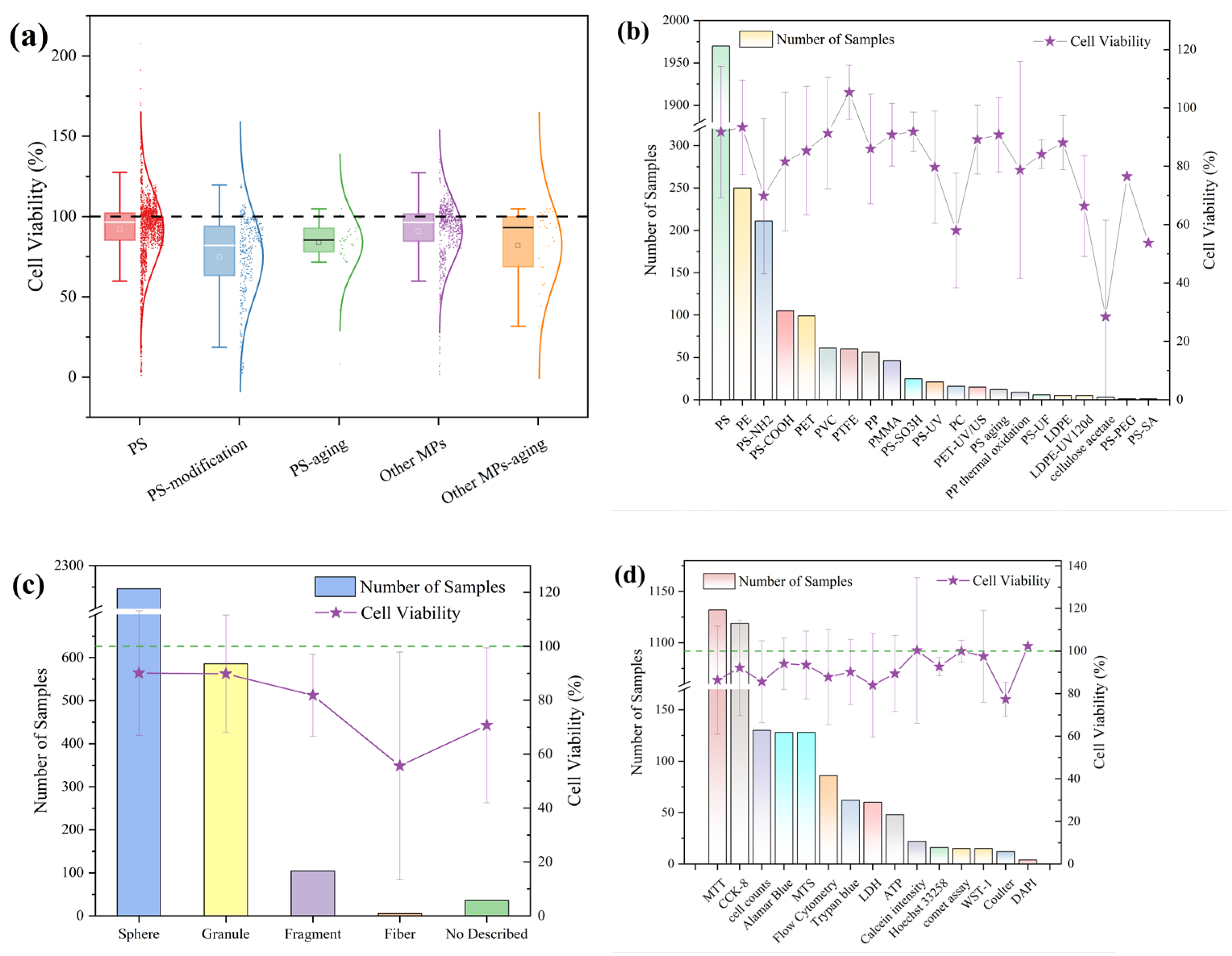
3.3. Meta-Analysis of the Effects of Microplastic Exposure on Cell Viability
3.3.1. Effects of Microplastic Exposure Conditions on Cell Viability
3.3.2. Effects of Cell Status on Viability Under Microplastic Exposure Conditions
3.3.3. Effects of Polymer State on Cell Viability Under Microplastic Exposure Conditions
3.3.4. Comprehensive Impact Analysis
3.4. Machine Learning Analysis of the Effects of Microplastic Exposure on Cell Viability
3.4.1. Regression Analysis of Cell Viability Under Microplastic Exposure
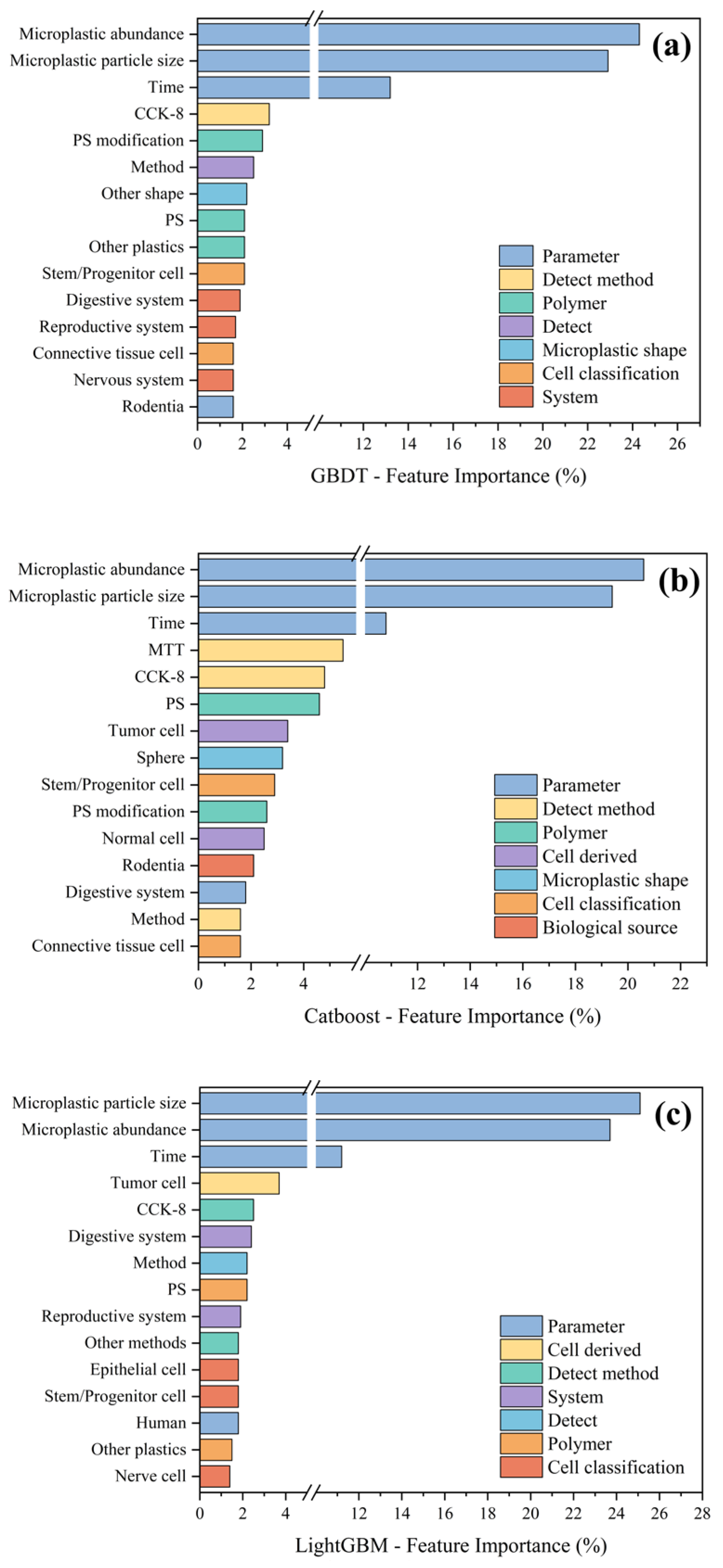
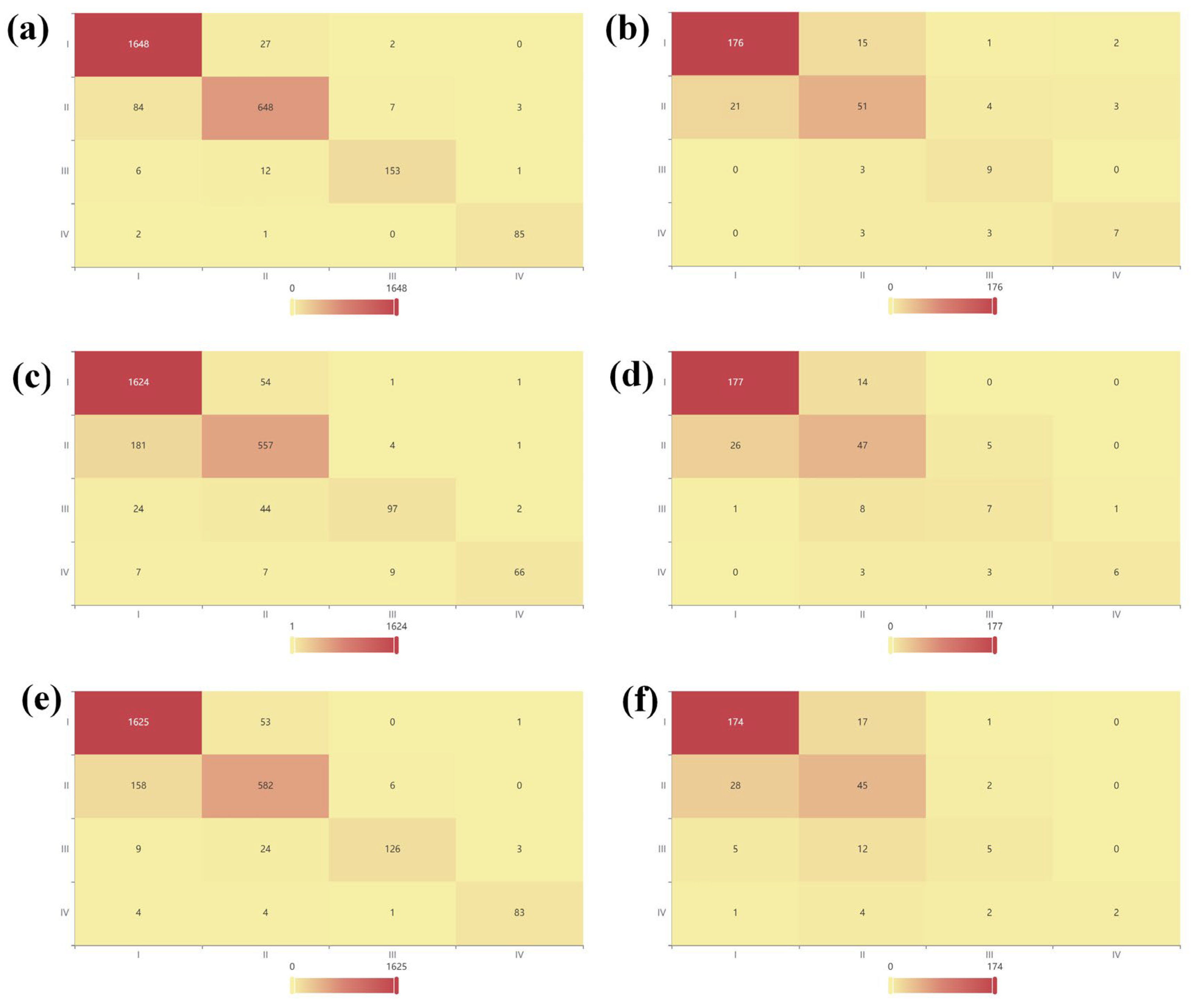
3.4.2. Machine Learning Classification Analysis of Cytotoxic Effects Under Microplastic Exposure Conditions
3.5. Technical Challenges and Future Directions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carpenter, E.J.; Smith, K.L. Plastics on the Sargasso Sea Surface. Science 1972, 175, 1240–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, R.C.; Courtene-Jones, W.; Boucher, J.; Pahl, S.; Raubenheimer, K.; Koelmans, A.A. Twenty years of microplastic pollution research—What have we learned? Science 2024, 386, eadl2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leslie, H.A.; van Velzen, M.J.M.; Brandsma, S.H.; Vethaak, A.D.; Garcia-Vallejo, J.J.; Lamoree, M.H. Discovery and quantification of plastic particle pollution in human blood. Environ. Int. 2022, 163, 107199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Wang, C.; Li, G. Defining Primary and Secondary Microplastics: A Connotation Analysis. ACS ES&T Water 2024, 4, 2330–2332. [Google Scholar]
- Jones-Williams, K.; Primpke, S.; Galloway, T.; Rowlands, E.; Cole, M.; Waluda, C.; Manno, C. Microplastics in Antarctica—A Plastic Legacy in the Antarctic Snow? Res. Sq. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.T.; Diamond, M.L.; Ward, E.; Adams, J.K.; Cherian-Hall, A.; Gamberg, M.; Obediah, T.; Palmer, M.; Platt, A.; Worthy, C.; et al. Snow as an indicator of atmospheric transport of anthropogenic particles (microplastics and microfibers) from urban to Arctic regions. Arct. Sci. 2025, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaduri, R.N.; Sinha, S.; Guererro, A.M.; Jackson, S.L.; Alemán, E.A.; Chatterjee, S. Microplastic contamination and environmental risks in the Beas River, western Himalayas. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 365, 125387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Chen, M.; Chen, S.; Dasgupta, S.; Xu, H.; Ta, K.; Du, M.; Li, J.; Guo, Z.; Bai, S. Microplastics contaminate the deepest part of the world’s ocean. Geochem. Perspect. Lett. 2018, 9, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa, I.D.; Costa, L.L.; da Silva Oliveira, A.; de Carvalho, C.E.V.; Zalmon, I.R. Microplastics in fishes in amazon riverine beaches: Influence of feeding mode and distance to urban settlements. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 863, 160934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamun, A.A.; Prasetya, T.A.E.; Dewi, I.R.; Ahmad, M. Microplastics in human food chains: Food becoming a threat to health safety. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, W.; Shao, X.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Y. Individual Exposure to Microplastics through the Inhalation Route: Comparison of Microplastics in Inhaled Indoor Aerosol and Exhaled Breath Air. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2023, 10, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Ma, M.; Sun, X.; Wu, Z.; Yu, Y.; Kang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xu, Q.; An, L. Microplastics Entry into the Blood by Infusion Therapy: Few but a Direct Pathway. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2024, 11, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragusa, A.; Svelato, A.; Santacroce, C.; Catalano, P.; Notarstefano, V.; Carnevali, O.; Papa, F.; Rongioletti, M.C.A.; Baiocco, F.; Draghi, S.; et al. Plasticenta: First evidence of microplastics in human placenta. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amato-Lourenço, L.F.; Carvalho-Oliveira, R.; Júnior, G.R.; Galvão, L.D.S.; Ando, R.A.; Mauad, T. Presence of airborne microplastics in human lung tissue. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 126124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridgeman, L.; Cimbalo, A.; López-Rodríguez, D.; Pamies, D.; Frangiamone, M. Exploring toxicological pathways of microplastics and nanoplastics: Insights from animal and cellular models. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 490, 137795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Jiang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Geng, J.; Ding, L.; Ren, H. Uptake and Accumulation of Polystyrene Microplastics in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) and Toxic Effects in Liver. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 4054–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagat, J.; Zang, L.; Nishimura, N.; Shimada, Y. Zebrafish: An emerging model to study microplastic and nanoplastic toxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Lu, L.; Zheng, M.; Zhang, X.; Tian, H.; Wang, W.; Ru, S. Polystyrene microplastics cause tissue damages, sex-specific reproductive disruption and transgenerational effects in marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma). Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 113024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, R.; Wang, X.; Yang, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, N.; Xu, F.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L. Polystyrene microplastics cause granulosa cells apoptosis and fibrosis in ovary through oxidative stress in rats. Toxicology 2021, 449, 152665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Ma, T.; Sha, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Meng, X.; Chen, Y.; Han, X.; Ding, J. Polystyrene microplastics induced male reproductive toxicity in mice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Yan, Z.; Shen, R.; Huang, Y.; Ren, H.; Zhang, Y. Enhanced reproductive toxicities induced by phthalates contaminated microplastics in male mice (Mus musculus). J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 406, 124644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Xu, T.; Cui, W.; Qi, X.; Xu, S. Combined negative effects of microplastics and plasticizer DEHP: The increased release of Nets delays wound healing in mice. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 862, 160861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrala, M.; Huovinen, M.; Järvelä, E.; Hellman, J.; Tolonen, P.; Lahtela-Kakkonen, M.; Rysä, J. Micro-sized polyethylene particles affect cell viability and oxidative stress responses in human colorectal adenocarcinoma Caco-2 and HT-29 cells. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 867, 161512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-C.; Chen, K.-F.; Lin, K.-Y.A.; Chen, J.-K.; Jiang, X.-Y.; Lin, C.-H. The nephrotoxic potential of polystyrene microplastics at realistic environmental concentrations. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 427, 127871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Cho, J.; Sohn, J.; Kim, C. Health Effects of Microplastic Exposures: Current Issues and Perspectives in South Korea. Yonsei Med. J. 2023, 64, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirinzi, G.F.; Pérez-Pomeda, I.; Sanchís, J.; Rossini, C.; Farré, M.; Barceló, D. Cytotoxic effects of commonly used nanomaterials and microplastics on cerebral and epithelial human cells. Environ. Res. 2017, 159, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.H.D. A review of the toxic effects of microplastics based on studies on mammals and mammalian cell lines. Environ. Sci. Adv. 2024, 3, 1669–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zong, C.; Chen, S.; Chu, J.; Yang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Yuan, B.; Zhang, H. Machine learning-driven QSAR models for predicting the cytotoxicity of five common microplastics. Toxicology 2024, 508, 153918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, R.O.G.; Nag, R.; Gowen, A.; Xu, J.-L. Deciphering the cytotoxicity of micro- and nanoplastics in Caco-2 cells through meta-analysis and machine learning. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 362, 124971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D. VOSviewer. Tech. Serv. Q. 2018, 35, 219–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arruda, H.; Silva, E.R.; Lessa, M.; Proença, D., Jr.; Bartholo, R. VOSviewer; bibliometrix. J. Med. Libr. Assoc. JMLA 2022, 110, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xueshu, D.; Wenxian, J. COOC is a software for bibliometrics and knowledge mapping [CP/OL]. 2022. Available online: https://gitee.com/academic_2088904822/academic-drip (accessed on 14 May 2025).
- Jin, L.; Lu, J.; Sun, X.; Huang, H.; Ren, H. Data-driven insights into treatment of sulfur-containing organic wastewater. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 433, 139878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Lu, J.; Jin, L.; Ren, H. The Future of Environmental Engineering Technology: A Disruptive Innovation Perspective. Engineering 2024, 41, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dioguardi, M.; Perrone, D.; Troiano, G.; Laino, L.; Ardito, F.; Lauritano, F.; Cicciù, M.; Muzio, L.L. Cytotoxicity evaluation of five different dual-cured resin cements used for fiber posts cementation. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 9327. [Google Scholar]
- Rizo-Gorrita, M.; Herráez-Galindo, C.; Torres-Lagares, D.; Serrera-Figallo, M.-Á.; Gutiérre-Pérez, J.-L. Biocompatibility of Polymer and Ceramic CAD/CAM Materials with Human Gingival Fibroblasts (HGFs). Polymers 2019, 11, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lu, Q.; Xing, Y.; Liu, K.; Ling, W.; Yang, J.; Yang, Q.; Wu, T.; Zhang, J.; Pei, Z.; et al. Review of research on migration, distribution, biological effects, and analytical methods of microfibers in the environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 855, 158922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lu, Q.; Yang, J.; Xing, Y.; Ling, W.; Liu, K.; Yang, Q.; Ma, H.; Pei, Z.; Wu, T.; et al. The fate of microplastic pollution in the Changjiang River estuary: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 425, 138970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ling, W.; Hou, C.; Yang, J.; Xing, Y.; Lu, Q.; Wu, T.; Gao, Z. Global distribution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of microplastics in aquatic organisms based on meta-analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 491, 137977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabi, I.; Bacha, A.-U.-R.; Zhang, L. A review on microplastics separation techniques from environmental media. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 337, 130458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Li, M.; Du, D.; Tang, B.; Yi, W.; He, M.; Liu, R.; Yu, H.; Yu, Y.; Zheng, J. Characteristics and influencing factors of microplastics entering human blood through intravenous injection. Environ. Int. 2025, 198, 109377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Guo, J.; Liu, X.; Yang, R.; Wang, H.; Sun, Y.; Chen, B.; Dong, R. Detection of various microplastics in placentas, meconium, infant feces, breastmilk and infant formula: A pilot prospective study. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 854, 158699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, K.D.; Covernton, G.A.; Davies, H.L.; Dower, J.F.; Juanes, F.; Dudas, S.E. Human Consumption of Microplastics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 7068–7074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, G.; Cai, Z. Getting Health Hazards of Inhaled Nano/Microplastics into Focus: Expectations and Challenges. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 3461–3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuri, G.; Karanasiou, A.; Lacorte, S. Human biomonitoring of microplastics and health implications: A review. Environ. Res. 2023, 237, 116966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ta, A.T.; Babel, S.; Wang, L.P. Prevalence and characteristics of microplastic contamination in soft drinks and potential consumer exposure. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 373, 123810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, T.; Zhou, Y.; He, J.; Dong, R.; Xu, A.; Liu, Y. The released micro/nano-plastics from plastic containers amplified the toxic response of disinfection by-products in human cells. Food Chem. 2025, 470, 142636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, F.; Ren, H.; Zhang, Y. Analysis of Microplastics in Human Feces Reveals a Correlation between Fecal Microplastics and Inflammatory Bowel Disease Status. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafyllaki, M.; Chalvatzaki, E.; Torres-Agullo, A.; Karanasiou, A.; Lacorte, S.; Drossinos, Y.; Lazaridis, M. The fate of airborne microfibers in the human respiratory tract in different microenvironments. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 953, 176000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cary, C.M.; Seymore, T.N.; Singh, D.; Vayas, K.N.; Goedken, M.J.; Adams, S.; Polunas, M.; Sunil, V.R.; Laskin, D.L.; Demokritou, P.; et al. Single inhalation exposure to polyamide micro and nanoplastic particles impairs vascular dilation without generating pulmonary inflammation in virgin female Sprague Dawley rats. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2023, 20, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Kang, H.; Huang, X.; Liu, Y.; He, Y.; Jie, Y. Identification of microplastics in human tear fluid and meibum: Implications for dry eye disease pathogenesis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 489, 137635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ageel, H.K.; Harrad, S.; Abdallah, M.A.-E. Occurrence; human exposure, and risk of microplastics in the indoor environment. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2022, 24, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Li, X.; Lin, W.; Zeng, D.; Yang, P.; Ni, W.; Chen, Z.; Lin, B.; Lai, L.; Ouyang, Z.; et al. Microplastic Particles Detected in Fetal Cord Blood, Placenta, and Meconium: A Pilot Study of Nine Mother–Infant Pairs in South China. Toxics 2024, 12, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, B.; Baek, J.Y.; Koo, J.; Park, S.; Ryu, Y.-K.; Kim, K.-S.; Zhang, S.; Chung, C.; Dogan, R.; Choi, H.-S.; et al. Maternal exposure to polystyrene nanoplastics causes brain abnormalities in progeny. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 426, 127815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Yang, Y.; Du, Z.; Wang, C.; Li, L.; Zhang, M.; Ni, S.; Yue, Z.; Yang, K.; Gao, H.; et al. Percutaneous coronary intervention leads to microplastics entering the blood: Interventional devices are a major source. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 476, 135054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, T.; Liu, K.; Zhu, L.; Wang, X.; Dong, X.; Jabeen, K.; Zong, C.; Wang, X.; Wei, N.; He, Y.; et al. Is intravenous infusion an unrecognized route for internal microplastic human exposure? A general assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 135769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutralam-Muniasamy, G.; Shruti, V.C.; Pérez-Guevara, F.; Roy, P.D. Microplastic diagnostics in humans: “The 3Ps” Progress, problems, and prospects. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 856, 159164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.-W.; Jung, J.; Park, S.-A.; Lee, Y.; Kim, J.; Han, C.; Kim, H.-C.; Lee, J.H.; Hong, Y.-C. Microplastic particles in human blood and their association with coagulation markers. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 30419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; He, Y.; Yin, J.; Zhu, Q.; Liao, C.; Jiang, G. Neurotoxicities induced by micro/nanoplastics: A review focusing on the risks of neurological diseases. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 469, 134054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nihart, A.J.; Garcia, M.A.; El Hayek, E.; Liu, R.; Olewine, M.; Kingston, J.D.; Castillo, E.F.; Gullapalli, R.R.; Howard, T.; Bleske, B.; et al. Bioaccumulation of microplastics in decedent human brains. Nat. Med. 2025, 31, 1114–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.; Kong, Q.; Hua, J.; Chen, Q.; Wang, D. Cardiotoxicity of polystyrene nanoplastics and associated mechanism of myocardial cell injury in mice. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 290, 117712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Ye, T.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, K.; Zhang, H.; Cui, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, L. Hydrogen bonding-mediated interaction underlies the enhanced membrane toxicity of chemically transformed polystyrene microplastics by cadmium. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 478, 135562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.-Y.; Ashim, J.; Park, S.; Kim, W.; Ji, S.; Lee, S.-W.; Jung, Y.-R.; Jeong, S.W.; Lee, S.-G.; Kim, H.-C.; et al. A preliminary study about the potential risks of the UV-weathered microplastic: The proteome-level changes in the brain in response to polystyrene derived weathered microplastics. Environ. Res. 2023, 233, 116411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.; Seo, E.U.; Hwang, K.S.; Kim, H.; Choi, J.; Kim, H.N. Evaluation of size-dependent uptake, transport and cytotoxicity of polystyrene microplastic in a blood-brain barrier (BBB) model. Nano Converg. 2024, 11, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amato-Lourenço, L.F.; Dantas, K.C.; Júnior, G.R.; Paes, V.R.; Ando, R.A.; de Oliveira Freitas, R.; da Costa, O.M.M.M.; Rabelo, R.S.; Bispo, K.C.S.; Carvalho-Oliveira, R.; et al. Microplastics in the Olfactory Bulb of the Human Brain. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e2440018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montano, L.; Giorgini, E.; Notarstefano, V.; Notari, T.; Ricciardi, M.; Piscopo, M.; Motta, O. Raman Microspectroscopy evidence of microplastics in human semen. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 901, 165922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Fang, Z.; Wang, P.; Qian, Z.; Yang, Y.; Ran, L.; Zheng, J.; Tang, Y.; Cui, X.; Li, Y.-Y.; et al. Polylactic Acid Micro/Nanoplastic Exposure Induces Male Reproductive Toxicity by Disrupting Spermatogenesis and Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Mice. ACS Nano 2025, 19, 5589–5603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Li, H.; Cui, C.; Han, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, B.; Li, G. Association between blood microplastic levels and severity of extracranial artery stenosis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 136211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvatits, T.; Tamminga, M.; Liu, B.; Sebode, M.; Carambia, A.; Fischer, L.; Püschel, K.; Huber, S.; Fischer, E.K. Microplastics detected in cirrhotic liver tissue. eBioMedicine 2022, 82, 104147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.E.; Kim, D.Y.; Jeong, T.S.; Park, Y.S. Micro- and Nano-Plastic-Induced Adverse Health Effects on Lungs and Kidneys Linked to Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Life 2025, 15, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuai, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xie, K.; Chen, J.; He, J.; Gao, J.; Yu, C. Long-term exposure to polystyrene microplastics reduces macrophages and affects the microbiota–gut–brain axis in mice. Toxicology 2024, 509, 153951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tian, P.; Yu, L.; Bai, L.; Zhou, F.; Yang, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, F.; et al. Microfluidic-based in vitro thrombosis model for studying microplastics toxicity. Lab A Chip 2022, 22, 1344–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, D.; Bang, J.; Kim, T.; Oh, Y.; Hwang, Y.; Hong, J. In vitro chemical and physical toxicities of polystyrene microfragments in human-derived cells. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 400, 123308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abafe, O.A.; Harrad, S.; Abdallah, M.A.-E. Novel Insights into the Dermal Bioaccessibility and Human Exposure to Brominated Flame Retardant Additives in Microplastics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 10554–10562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, G.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, T.; Wu, X.; Pu, S.; Tang, Z.; Wu, F. The adsorption of PAHs on microplastics and desorption in the simulated human digestive system. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 473, 145157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, L.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Li, L. Effects of microplastics on the accumulation and neurotoxicity of methylmercury in zebrafish larvae. Mar. Environ. Res. 2022, 176, 105615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nor, N.H.M.; Niu, Z.; Hennebelle, M.; Koelmans, A.A. How Digestive Processes Can Affect the Bioavailability of PCBs Associated with Microplastics: A Modeling Study Supported by Empirical Data. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 11452–11464. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, H. Trojan horse in the intestine: A review on the biotoxicity of microplastics combined environmental contaminants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 439, 129652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-W.; Hsu, L.-F.; Wu, I.L.; Wang, Y.-L.; Chen, W.-C.; Liu, Y.-J.; Yang, L.-T.; Tan, C.-L.; Luo, Y.-H.; Wang, C.-C.; et al. Exposure to polystyrene microplastics impairs hippocampus-dependent learning and memory in mice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 430, 128431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Wei, L.; Gao, L.; Liu, M. Oxidized/unmodified-polyethylene microplastics neurotoxicity in mice: Perspective from microbiota-gut-brain axis. Environ. Int. 2024, 185, 108523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.Y.; Park, M.K.; Yang, H.W.; Woo, S.Y.; Jung, H.H.; Son, D.-S.; Choi, B.Y.; Suh, S.W. Effects of Microplastic Accumulation on Neuronal Death After Global Cerebral Ischemia. Cells 2025, 14, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Sharma, A.; John, P.; Bhatnagar, P. Manifestation of polystyrene microplastic accumulation in brain with emphasis on morphometric and histopathological changes in limbic areas of Swiss albino mice. Neurotoxicology 2024, 105, 231–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Hou, J.; Li, M.; Wei, F.; Liao, Y.; Xi, B. Microplastics in the bloodstream can induce cerebral thrombosis by causing cell obstruction and lead to neurobehavioral abnormalities. Sci. Adv. 2025, 11, eadr8243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.; Huang, D.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, G.; Gao, A. Pulmonary Flora-Derived Lipopolysaccharide Mediates Lung-Brain Axis through Activating Microglia Involved in Polystyrene Microplastic-Induced Cognitive Dysfunction. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2404966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofield, C.E.; Anderton, R.S.; Gorecki, A.M. Mind over Microplastics: Exploring Microplastic-Induced Gut Disruption and Gut-Brain-Axis Consequences. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 4186–4202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, Y.H.; Shin, H.S.; Lee, S.H.; Moon, H.J.; Jang, H.J.; Lee, E.-H.; Jung, E.-M. Maternal exposure to polystyrene microplastics impairs social behavior in mouse offspring with a potential neurotoxicity. Neurotoxicology 2023, 99, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaheer, J.; Kim, H.; Ko, I.O.; Jo, E.-K.; Choi, E.-J.; Lee, H.-J.; Shim, I.; Woo, H.-J.; Choi, J.; Kim, G.-H.; et al. Pre/post-natal exposure to microplastic as a potential risk factor for autism spectrum disorder. Environ. Int. 2022, 161, 107121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yöntem, F.D.; Ahbab, M.A.; Ruggles, A.; Benakis, C. Mitochondria as a target of micro- and nanoplastic toxicity. Camb. Prism. Plast. 2024, 2, e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gettings, S.M.; Timbury, W.; Dmochowska, A.; Sharma, R.; McGonigle, R.; MacKenzie, L.E.; Miquelard-Garnier, G.; Bourbia, N. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) micro- and nanoplastic particles affect the mitochondrial efficiency of human brain vascular pericytes without inducing oxidative stress. NanoImpact 2024, 34, 100508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Bian, B.; Ji, R.; Zhu, X.; Wo, X.; Song, Q.; Li, Z.; Wang, F.; Jia, Y. Polyethylene Terephthalate Microplastic Exposure Induced Reproductive Toxicity Through Oxidative Stress and p38 Signaling Pathway Activation in Male Mice. Toxics 2024, 12, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Han, X.; Guo, W.; Wu, Q.; Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; Tang, G.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; et al. Disturbed Gut-Liver axis indicating oral exposure to polystyrene microplastic potentially increases the risk of insulin resistance. Environ. Int. 2022, 164, 107273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Wang, W.-X. Subcellular toxicity assessments of microplastics released from food containers. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 489, 137541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwangbo, S.; Kim, I.Y.; Ko, K.; Park, K.; Hong, J.; Kang, G.; Wi, J.-S.; Kim, J.; Lee, T.G. Preparation of fragmented polyethylene nanoplastics using a focused ultrasonic system and assessment of their cytotoxic effects on human cells. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 362, 125009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortés, C.; Domenech, J.; Salazar, M.; Pastor, S.; Marcos, R.; Hernández, A. Nanoplastics as a potential environmental health factor: Effects of polystyrene nanoparticles on human intestinal epithelial Caco-2 cells. Environ. Sci. Nano 2020, 7, 272–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghinia, H.; Hanachi, P.; Ramezani, R.; Karbalaei, S. Toxic effects of polystyrene nanoplastics on MDA-MB-231 breast cancer and HFF-2 normal fibroblast cells: Viability, cell death, cell cycle and antioxidant enzyme activity. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2025, 37, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Xu, K.; Zhang, B.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, W. Cellular internalization and release of polystyrene microplastics and nanoplastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 779, 146523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.-Y.; Kim, M.S.; Oh, N. Cytotoxicity of amine-modified polystyrene MPs and NPs on neural stem cells cultured from mouse subventricular zone. Heliyon 2024, 10, e30518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, R.; Jo, J.; Acharya, M.; Maharjan, A.; Lee, D.; Pramod Bahadur, K.C.; Kim, C.; Kim, K.; Kim, H.; Heo, Y. Evaluation of potential toxicity of polyethylene microplastics on human derived cell lines. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Choi, D.; Han, S.; Choi, J.; Hong, J. An assessment of the toxicity of polypropylene microplastics in human derived cells. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 684, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danopoulos, E.; Twiddy, M.; West, R.; Rotchell, J.M. A rapid review and meta-regression analyses of the toxicological impacts of microplastic exposure in human cells. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 427, 127861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, M.G.; Casati, L.; Sauro, G.; Taurino, G.; Griffini, E.; Milani, C.; Ventura, M.; Bussolati, O.; Chiu, M. Biological Effects of Micro-/Nano-Plastics in Macrophages. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shengchen, W.; Jing, L.; Yujie, Y.; Yue, W.; Shiwen, X. Polystyrene microplastics-induced ROS overproduction disrupts the skeletal muscle regeneration by converting myoblasts into adipocytes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 417, 125962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, R.; Kong, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, G.; Wu, D.; Lan, H.; Wu, M. Microplastics Exposure Causes the Growth Hormone Resistance on the Stem Cell. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2025, 39, e70176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolff, C.M.; Singer, D.; Schmidt, A.; Bekeschus, S. Immune and inflammatory responses of human macrophages, dendritic cells, and T-cells in presence of micro- and nanoplastic of different types and sizes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 459, 132194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Bang, J.; Choi, D.; Hwang, J.; Kim, T.; Oh, Y.; Hwang, Y.; Choi, J.; Hong, J. Surface Pattern Analysis of Microplastics and Their Impact on Human-Derived Cells. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 2, 4541–4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikuno, Y.; Tsujino, H.; Haga, Y.; Manabe, S.; Idehara, W.; Hokaku, M.; Asahara, H.; Higashisaka, K.; Tsutsumi, Y. Polyethylene, whose surface has been modified by UV irradiation, induces cytotoxicity: A comparison with microplastics found in beaches. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 277, 116346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lithner, D.; Larsson, Å.; Dave, G. Environmental and health hazard ranking and assessment of plastic polymers based on chemical composition. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 3309–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Nag, R.; Cummins, E. Ranking of potential hazards from microplastics polymers in the marine environment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 429, 128399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, K.A.; Romanova, S.; Okur, I.; Zhang, D.; Kuebler, J.; Huang, X.; Wang, B.; Fernandez-Ballester, L.; Lu, Y.; Schubert, M.; et al. Assessing the Release of Microplastics and Nanoplastics from Plastic Containers and Reusable Food Pouches: Implications for Human Health. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 9782–9792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalowska, L. Ban on Plastic Microbeads: Too Narrow, Or Just Narrow Enough? Sustain. Dev. Law Policy 2018, 19, 22. [Google Scholar]
- Hee, Y.Y.; Weston, K.; Suratman, S. The effect of storage conditions and washing on microplastic release from food and drink containers. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2022, 32, 100826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasperi, J.; Wright, S.L.; Dris, R.; Collard, F.; Mandin, C.; Guerrouache, M.; Langlois, V.; Kelly, F.J.; Tassin, B. Microplastics in air: Are we breathing it in? Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2018, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, P.M.; Twayana, K.S.; Ravanan, P.; John, T.; Mukherjee, A.; Jenkins, D.F.; Chandrasekaran, N. Prospects on the nano-plastic particles internalization and induction of cellular response in human keratinocytes. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2021, 18, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Guo, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Liao, K.; Qin, J. Phonocardiogram transfer learning-based CatBoost model for diastolic dysfunction identification using multiple domain-specific deep feature fusion. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 156, 106707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, A.S.; Ashok, A.; Edis, Z.; Bloukh, S.H.; Gaikwad, M.; Patil, R.; Pandey, B.; Bhagat, N. Meta-Analysis of Cytotoxicity Studies Using Machine Learning Models on Physical Properties of Plant Extract-Derived Silver Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancock, J.T.; Khoshgoftaar, T.M. CatBoost for big data: An interdisciplinary review. J. Big Data 2020, 7, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geppner, L.; Ramer, G.; Tomasetig, D.; Grundhöfer, L.; Küss, J.; Kaup, M.; Henjakovic, M. A novel enzymatic method for isolation of plastic particles from human blood. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2023, 104, 104318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, P.A.; Gokul, V.; Swapna, M.N.S.; Sankararaman, S.I. Thermal lens technique’s surrogacy unveiled: A novel tool for microplastic detection and quantification in water. Heliyon 2024, 10, e34532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauert, C.; Charlton, N.; Bagley, A.; Dunlop, S.A.; Symeonides, C.; Thomas, K.V. Assessing the Efficacy of Pyrolysis–Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry for Nanoplastic and Microplastic Analysis in Human Blood. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 1984–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Yi, Z.; Liu, X.; Cai, Y.; Huang, X.; Fang, J.; Shen, R.; Lu, W.; Xiao, Y.; Zhuang, W.; et al. Multimodal detection and analysis of microplastics in human thrombi from multiple anatomically distinct sites. eBioMedicine 2024, 103, 105118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedford, T. Preserving brain health by minimizing microplastic output from resin histology. J. Histotechnol. 2025, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Deng, K.; Zhang, P.; Chen, Q.; Magnuson, J.T.; Qiu, W.; Zhou, Y. Microplastic-mediated new mechanism of liver damage: From the perspective of the gut-liver axis. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 919, 170962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, S.; Khan, R.; Saxena, A.; Sekar, S. Microplastics from face masks: A potential hazard post COVID-19 pandemic. Chemosphere 2022, 302, 134805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, M.; Xu, D.; Zhao, J.; Gao, B. Disposable face masks release micro particles to the aqueous environment after simulating sunlight aging: Microplastics or non-microplastics? J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 443, 130146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, J.; Bjorkland, R.; Boyes, W.K.; Geraci, C.; Hackley, V.A.; Howard, J.; Kennedy, A.; Linkov, I.; Matheson, J.; Mortensen, H.; et al. U.S. federal perspective on critical research issues in nanoEHS. Environ. Sci. Nano 2023, 10, 2623–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




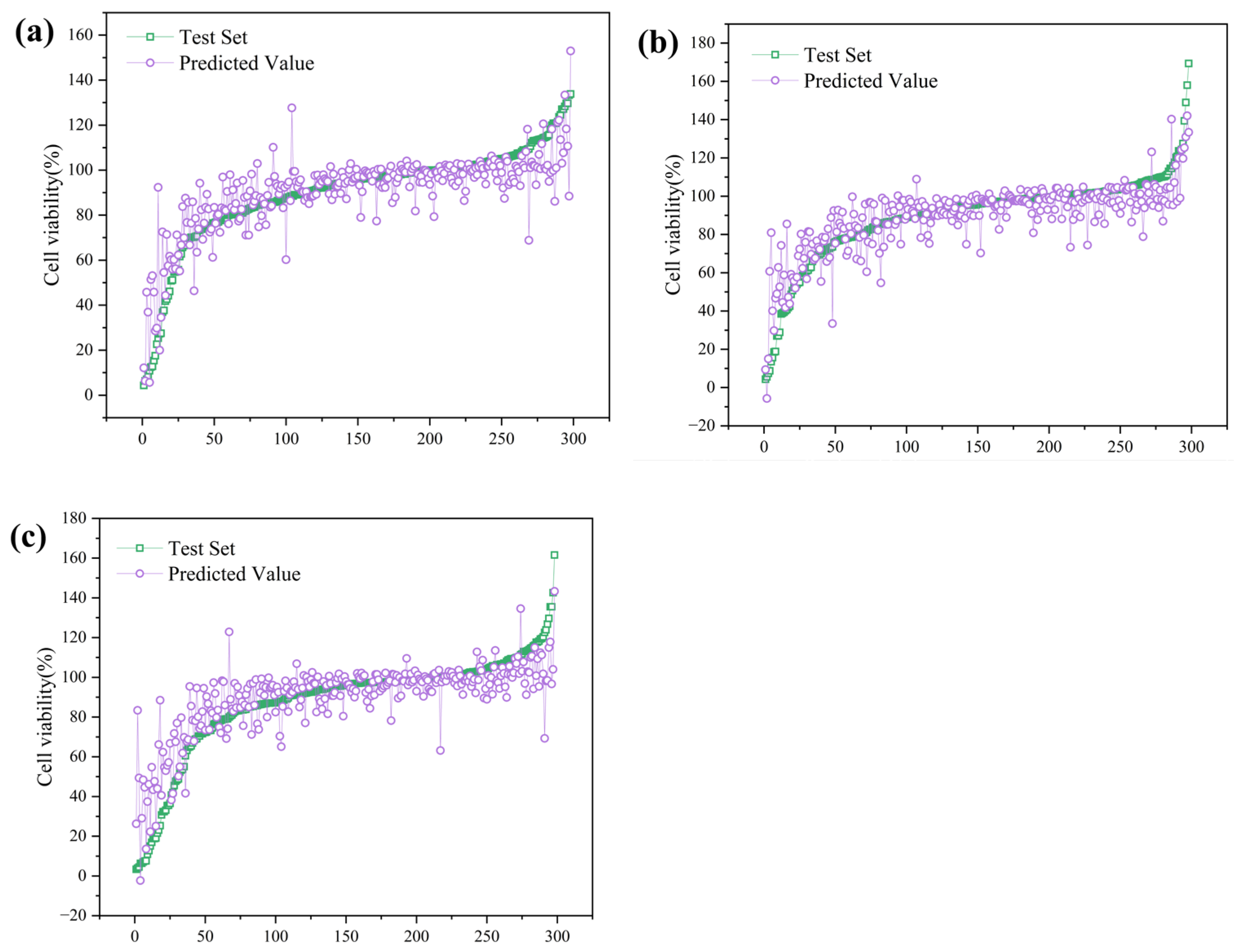

| Model | Dataset | MSE | RMSE | MAE | MAPE | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GBDT | Training | 68.607 | 8.283 | 5.649 | 7.539 | 0.87 |
| Test | 134.118 | 11.581 | 7.6 | 10.026 | 0.737 | |
| CatBoost | Training | 102.161 | 10.107 | 6.996 | 10.446 | 0.806 |
| Test | 141.343 | 11.889 | 7.993 | 11.003 | 0.723 | |
| LightGBM | Training | 122.372 | 11.062 | 7.478 | 10.103 | 0.759 |
| Test | 203.459 | 14.264 | 9.459 | 13.918 | 0.702 |
| Model | Dataset | Accuracy | Recall | Precision | F1 | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GBDT | Training | 0.946 | 0.946 | 0.946 | 0.945 | 0.998 |
| Test | 0.815 | 0.815 | 0.816 | 0.815 | 0.952 | |
| CatBoost | Training | 0.875 | 0.875 | 0.874 | 0.87 | 0.984 |
| Test | 0.795 | 0.795 | 0.788 | 0.789 | 0.945 | |
| LightGBM | Training | 0.902 | 0.902 | 0.902 | 0.9 | 0.99 |
| Test | 0.758 | 0.758 | 0.751 | 0.743 | 0.933 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Ling, W.; Yang, J.; Xing, Y. Risk Assessment of Microplastics in Humans: Distribution, Exposure, and Toxicological Effects. Polymers 2025, 17, 1699. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17121699
Li Y, Ling W, Yang J, Xing Y. Risk Assessment of Microplastics in Humans: Distribution, Exposure, and Toxicological Effects. Polymers. 2025; 17(12):1699. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17121699
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yifei, Wei Ling, Jian Yang, and Yi Xing. 2025. "Risk Assessment of Microplastics in Humans: Distribution, Exposure, and Toxicological Effects" Polymers 17, no. 12: 1699. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17121699
APA StyleLi, Y., Ling, W., Yang, J., & Xing, Y. (2025). Risk Assessment of Microplastics in Humans: Distribution, Exposure, and Toxicological Effects. Polymers, 17(12), 1699. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17121699







