The Influence of the Manufacturing Technology on the Mechanical Properties of Woven Jute Fiber-Reinforced Epoxy Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
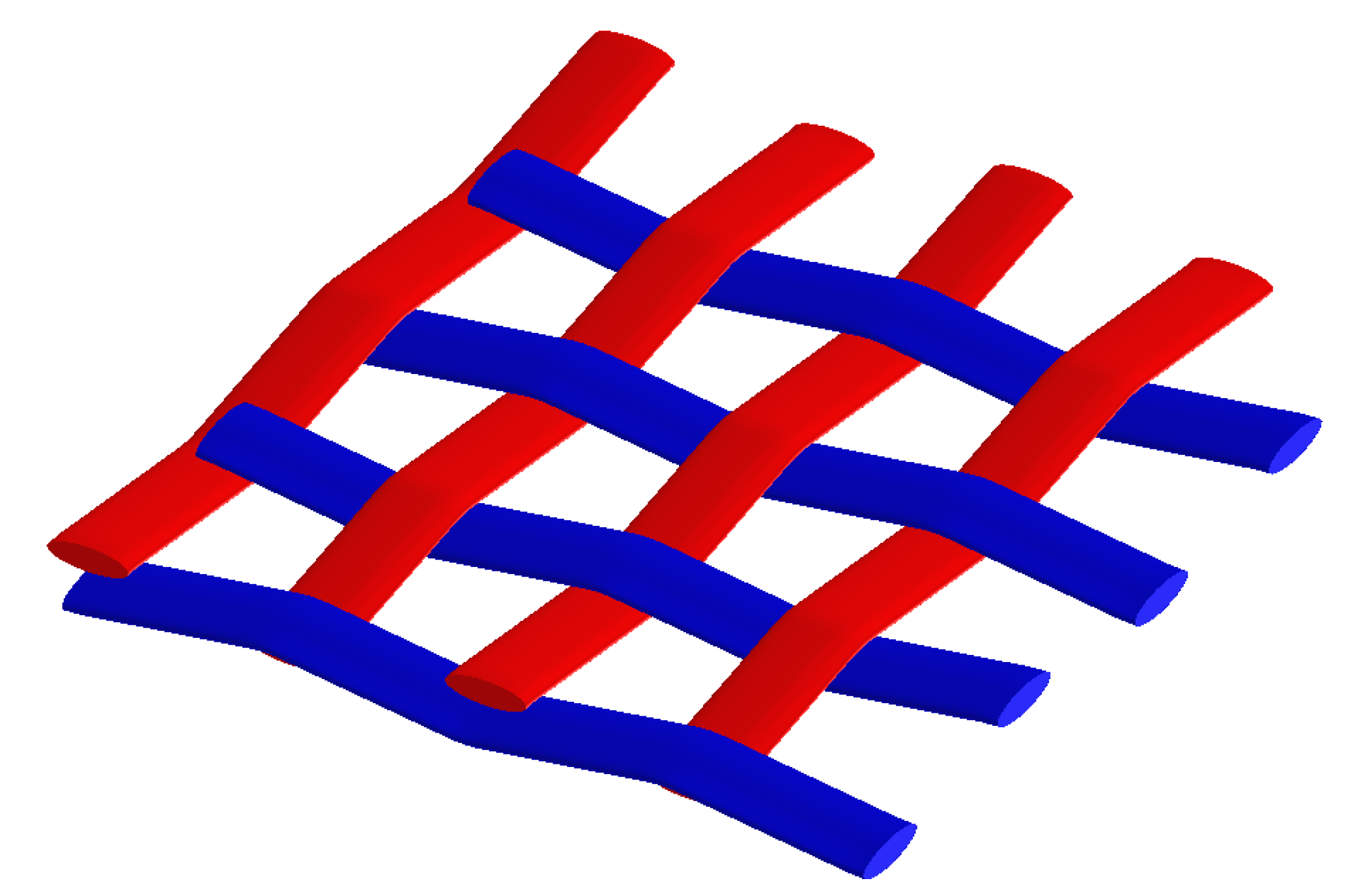
2. Materials and Methods
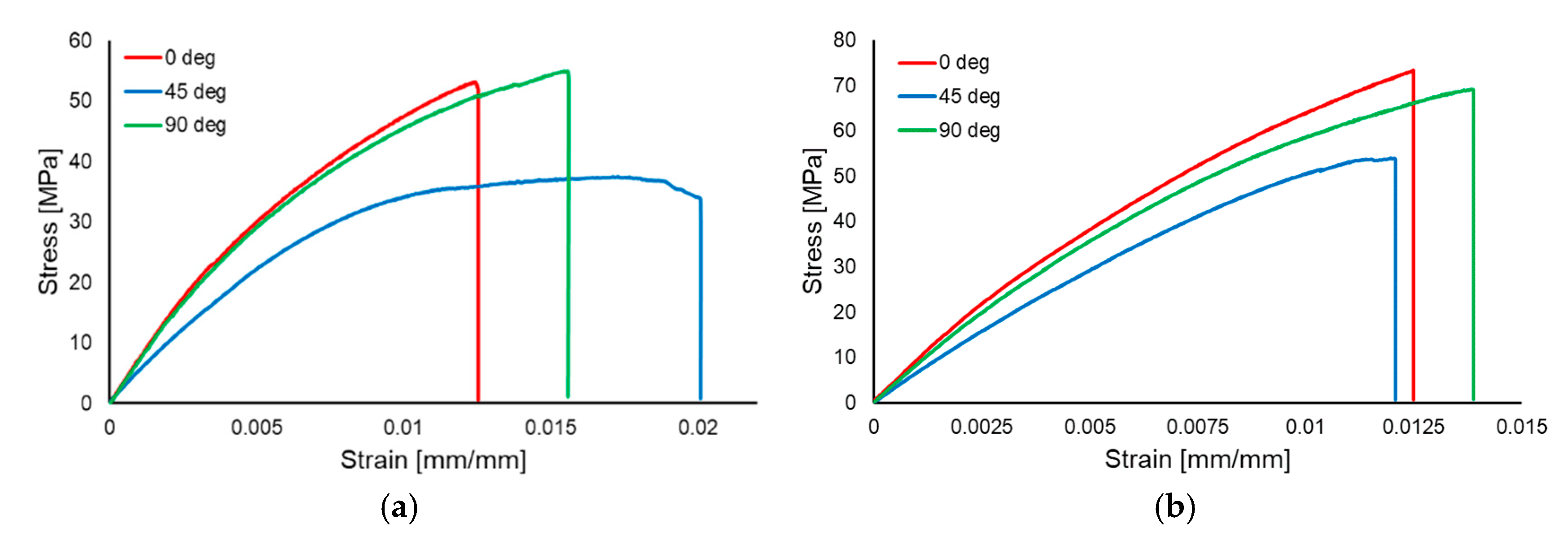
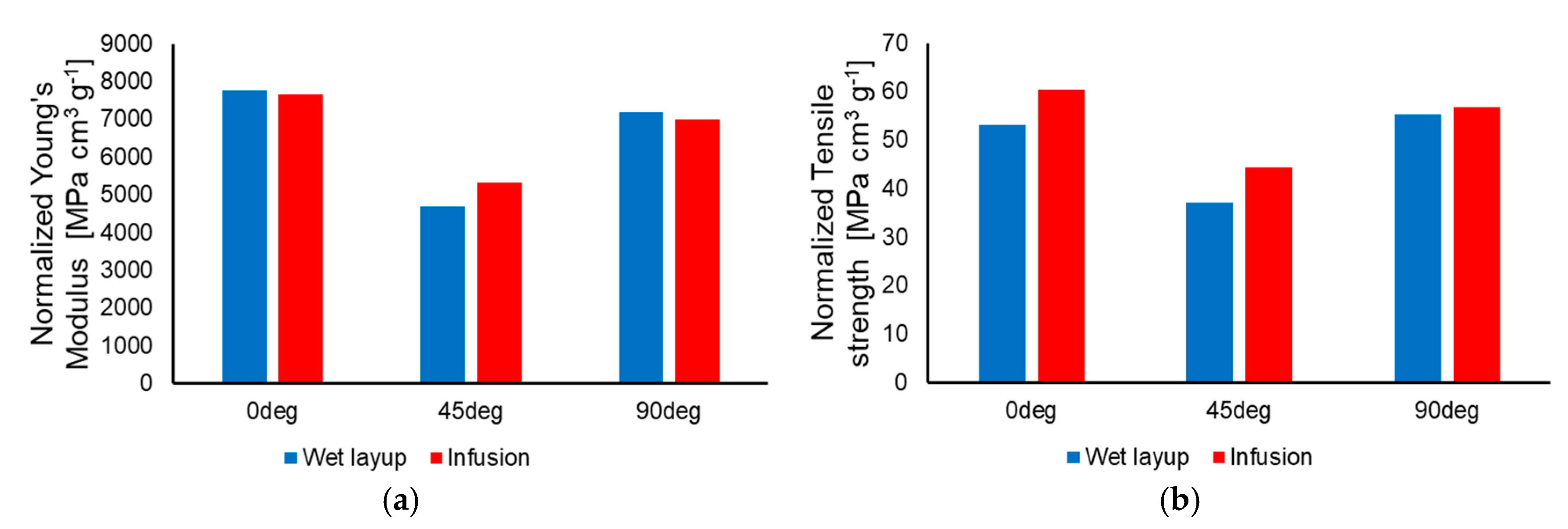
3. Results and Discussions
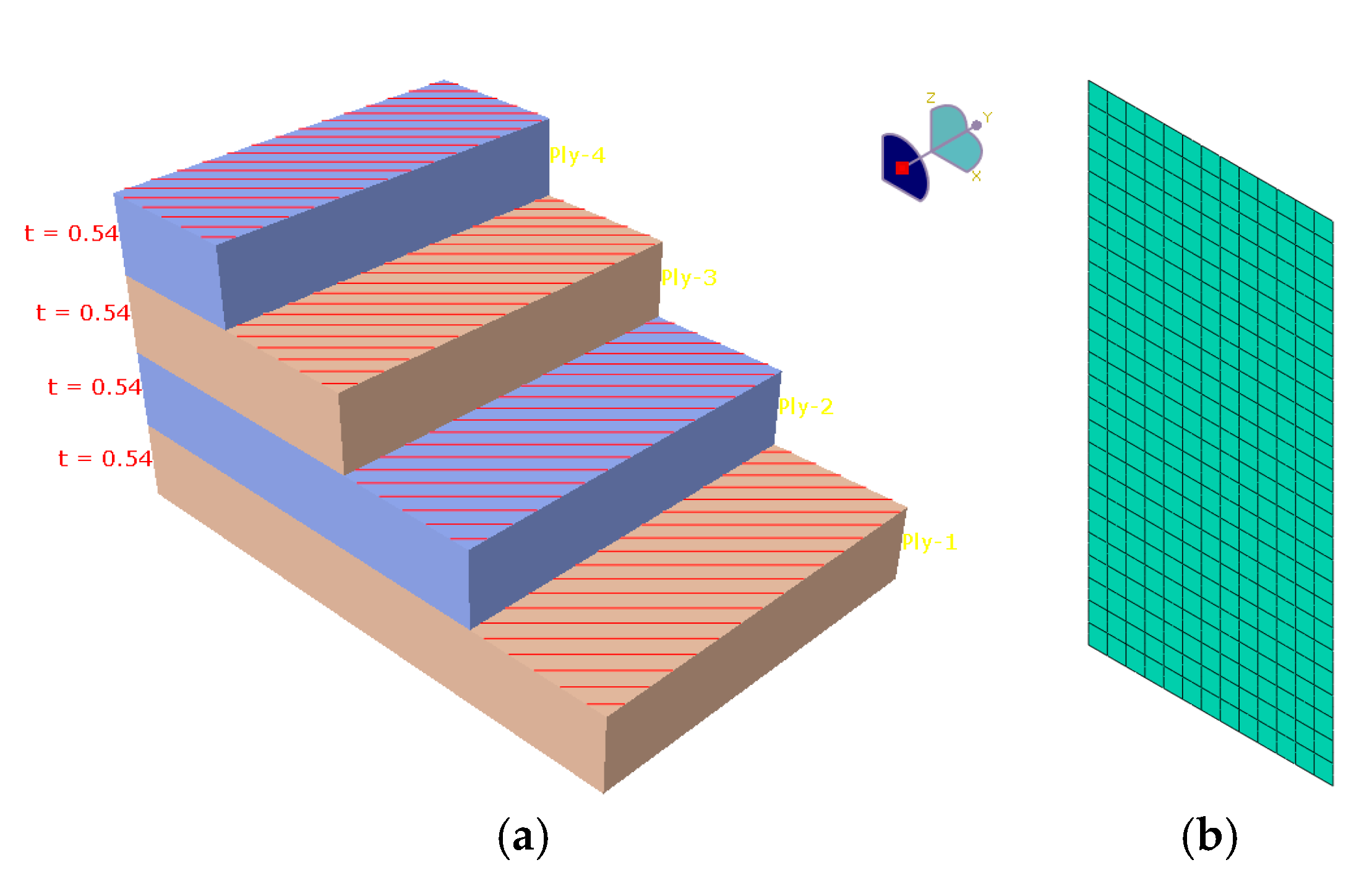
4. Multi-Scale Modeling
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Das, T.; Ghosh, P.; Das, N. Preparation, development, outcomes, and application versatility of carbon fiber-based polymer composites: A review. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2019, 2, 214–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajak, D.; Pagar, D.; Menezes, P.; Linul, E. Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Composites: Manufacturing, Properties, and Applications. Polymers 2019, 11, 1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, J. A Review of Fibre Reinforced Polymer Structures. Fibers 2022, 10, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, I.; Summerscales, J. Woven Fabrics for Composite Reinforcement: A Review. J. Compos. Sci. 2024, 8, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sîrbu, R.; Coșa, A.; Negru, R.; Rusu, L.; Șerban, D. Experimental investigations regarding the anisotropic properties of pre-impregnated woven carbon fibre-reinforced epoxy resin. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering: Proceedings of the Advanced Materials and Structures Conference (AMS 2024), Timișoara, Romania, 30 May–1 June 2024; IOP Publishing Ltd.: Bristol, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, A.; Negru, R.; Coșa, A.; Marșavina, L.; Șerban, D. Multi-scale modelling of woven carbon fibre reinforced epoxy. In Proceedings of the Materials Today-Proceedings: 8th International Conference on Advanced Materials and Structures (AMS), Timișoara, Romania, 7–9 October 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miracle, D.; Donaldson, S. ASM International Handbook Volume 21: Composites; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; You, M.; Guo, Q.; Li, C.; Zhang, D.; Shi, D.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, P.; Wang, T.; et al. A review of the formability of woven fabrics for composite materials. Polym. Compos. 2024, 45, 14498–14520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hexcel. Woven reinforcements. Hexcel. Available online: https://www.hexcel.com/Resources/DataSheets/Reinforcements/Woven-Reinforcements (accessed on 2 June 2025).
- ACP Composites. Fabrics. ACP Composites. Available online: https://acpcomposites.com/category/fabrics (accessed on 2 June 2025).
- Toray Industries. Data Sheets—Carbon Fiber Composite Materials. Toray Industries. Available online: https://www.cf-composites.toray/resources/data_sheets/#anc2 (accessed on 2 June 2025).
- Wu, C.; Xu, F.; Wang, H.; Liu, H.; Yan, F.; Ma, C. Manufacturing Technologies of Polymer Composites—A Review. Polymers 2022, 15, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Xu, H.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Kormakov, S.; Wu, D.; Sun, J. Overview of Injection Molding Technology for Processing Polymers and Their Composites. ES Mater. Manuf. 2020, 8, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M. A mini review on manufacturing defects and performance assessments of complex shape prepreg-based composites. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 115, 3393–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somarathna, Y.; Herath, M.; Epaarachchi, J.; Islam, M. Formulation of Epoxy Prepregs, Synthesization Parameters, and Resin Impregnation Approaches—A Comprehensive Review. Polymers 2024, 16, 3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Department of Transportation Federal Aviation Administration. State of the Industry—Resin Infusion: A Literature Review; US Department of Transportation Federal Aviation Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2024.
- Williams, C.; Summerscales, J.; Grove, S. Resin Infusion under Flexible Tooling (RIFT): A review. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 1996, 27, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajjar, T.; Shah, D.; Joshi, S.; Patel, K. Analysis of Process Parameters for Composites Manufacturing using Vacuum Infusion Process. In Proceedings of the ICRACM-2019, Varanasi, India, 25–28 February 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abanilla, V.M.; Karbhari, M.A. Design factors, reliability, and durability prediction of wet layup carbon/epoxy used in external strengthening. Compos. Part B Eng. 2007, 38, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phiri, R.; Rangappa, S.M.; Siengchin, S.; Oladijo, O.; Ozbakkaloglu, T. Advances in lightweight composite structures and manufacturing technologies: A comprehensive review. Heliyon 2024, 10, e39661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourad, A.; Zaaroura, N.; Cherupurakal, N. Wet lay-up technique for manufacturing of advanced laminated composites. Karbala Int. J. Mod. Sci. 2019, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahiparsa, H.; Shahmirzaloo, A.; Teuffel, P.; Blok, R. A review of recent developments in structural applications of natural fiber-Reinforced composites (NFRCs). Compos. Adv. Mater. 2023, 32, 263498332211475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, N.; Varley, R.; Hummel, M.; Trogen, M.; Byrne, N. A review of future directions in the development of sustainable carbon fiber from bio-based precursors. Mater. Today Sustain. 2022, 20, 100251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liddell, H.; Ogale, A.; Miao, Z.; Ijeoma, M.; Carbajales-Dale, M. A critical review and meta-analysis of energy demand, carbon footprint, and other environmental impacts from carbon fiber manufacturing. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2025, 219, 108302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawajiri, K.; Sakamoto, K. Environmental impact of carbon fibers fabricated by an innovative manufacturing process on life cycle greenhouse gas emissions. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2022, 31, e00365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinçaud, M.; Aymonier, C.; Loppinet-Serani, A.; Perry, N.; Sonnemann, G. Environmental Feasibility of the Recycling of Carbon Fibers from CFRPs by Solvolysis Using Supercritical Water. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1498–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, S.; Islam, M.R.; Uddin, M.A.; Afroj, S.; Eichhorn, S.J.; Karim, N. Sustainable Fiber-Reinforced Composites: A Review. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2022, 6, 2200258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Săftoiu, G.; Constantin, C.; Nicoară, A.; Pelin, G.; Ficai, D.; Ficai, A. Glass Fibre-Reinforced Composite Materials Used in the Aeronautical Transport Sector: A Critical Circular Economy Point of View. Sustainability 2024, 16, 4632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aisyah, H.A.; Paridah, M.T.; Sapuan, S.; Ilyas, R.; Khalina, A.; Nurazzi, N.; Lee, S.; Lee, C. A Comprehensive Review on Advanced Sustainable Woven Natural Fibre Polymer Composites. Polymers 2021, 13, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, M.; Srovastava, R.; Bisaria, H. Potential of Jute Fibre Reinforced Polymer Composites: A review. Int. J. Fiber Text. Res. 2015, 5, 30–38. [Google Scholar]
- Pandita, S.; Yuan, X.; Manan, M.; Lau, C.; Subramanian, A.; Wei, J. Evaluation of Jute/glass Hybrid Composite Sandwich: Water Resistance, Impact Properties and Life Cycle Assessment. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2014, 33, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saw, S.; Yadav, N.; Singh, A.; Akhtar, K. Hybrid Composites Made from Jute/Coir Fibers: Water Absorption, Thickness Swelling, Density, Morphology, and Mechanical Properties. J. Nat. Fibers 2014, 11, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.; Zwawi, M.; Nehran, M.; Kanthasamy, R.; Bahadar, A. Jute Based Bio and Hybrid Composites and Their Applications. Fibers 2019, 7, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, M. The Effects of Alkali Treatment on the Mechanical Properties of Jute Fabric Reinforced Epoxy Composites. Int. J. Fiber Text. Res. 2014, 4, 32–40. [Google Scholar]
- Sathishkumar, T.; Rajeshkumar, L.; Rajeshkumar, G.; Sanjay, M.; Siengchin, S.; Thakrishnan, N. Improving the mechanical properties of jute fiber woven mat reinforced epoxy composites with addition of zinc oxide filler. E3S Web Conf. 2022, 355, 02006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. The Clean Industrial Deal: A Joint Roadmap for Competitiveness and Decarbonization; European Commission: Bruxelles, Belgium, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- tesaturi-textile. Panza de iuta. Available online: https://tesaturi-textile.ro/produs/panza-de-iuta/ (accessed on 4 February 2025).
- Vosschemie. Epoxy BK A+B—Technical Data Sheet; Vosschemie GMBH: Uetersen, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Easy Composites. IN2 Epoxy Infusion Resin—Technical Data Sheet; Easy Composites: Stoke on Trent, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 527; Plastics—Determination of Tensile Properties. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Swizerland, 1996.
- Hill, R. A Theory of the Yielding and Plastic Flow of Anisotropic Metals. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A 1948, 193, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Șerban, D.; Marșavina, L.; Rusu, L.; Negru, R. Numerical study of the behavior of magnesium alloy AM50 in tensile and torsional loadings. Arch. Appl. Mech. 2019, 89, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsson, L.; Adams, D.; Pipes, R. Basic experimental characterization of polymer matrix composite materials. Polym. Rev. 2013, 53, 277–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
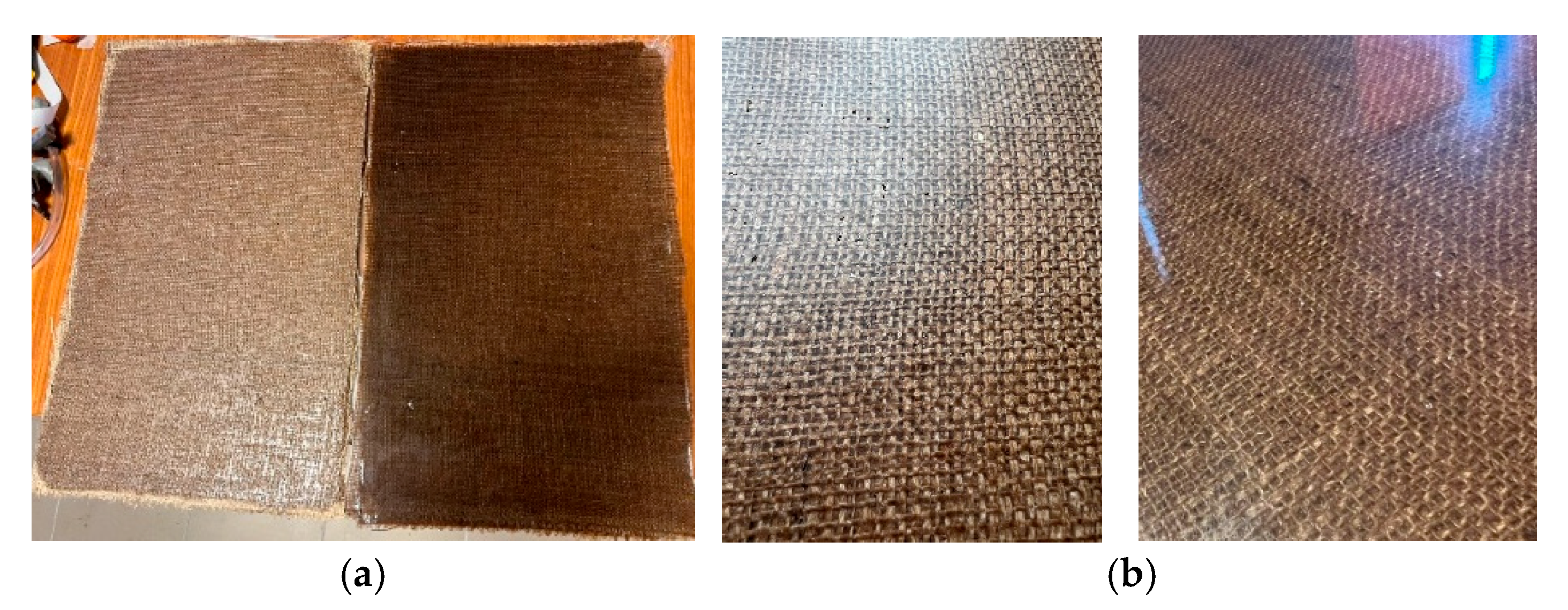
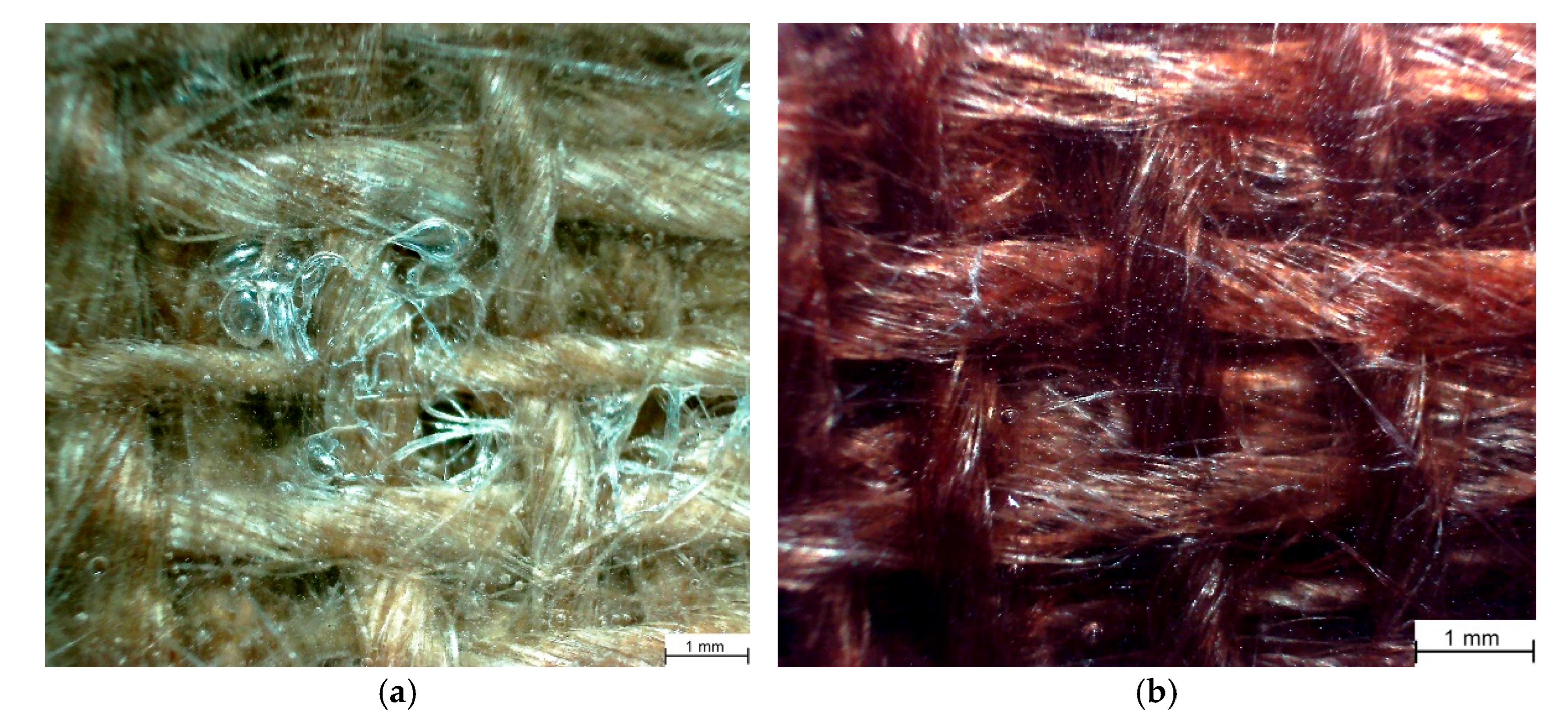













| Fiber | Young’s Modulus [GPa] | Tensile Strength [MPa] | Density [g·cm−3] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon | 200–500 | 3000–7000 | 1.8 |
| Aramid | 60–80 | 2500–3200 | 1.5 |
| E-Glass | 70–90 | 1800–4500 | 2.5 |
| Flax | 27–85 | 345–2000 | 1.54 |
| Hemp | 17–70 | 368–800 | 1.47 |
| Jute | 10–55 | 393–773 | 1.44 |
| Manufacturing Process | Average Thickness [mm] | Standard Deviation [mm] | Average Surface Area [mm2] | Standard Deviation [mm2] | Average Mass [g] | Standard Deviation [g] | Average Density [g·cm−3] | Standard Deviation [g·cm−3] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wet layup | 2.296 | 0.0921 | 5088.67 | 287.151 | 11.787 | 0.979 | 1.008 | 0.0286 |
| Infusion | 2.147 | 0.0615 | 5057.69 | 296.178 | 13.131 | 1.121 | 1.208 | 0.0358 |
| Young’s Modulus [MPa] | St. Deviation [MPa] | Tensile Strength [MPa] | St. Deviation [MPa] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WL 0° | 7850.76 | 637.53 | 53.64 | 2.74 |
| WL 45° | 4789.26 | 474.14 | 37.86 | 2.21 |
| WL 90° | 7268.75 | 418.144 | 53.07 | 3.35 |
| Inf 0° | 9159.99 | 1256.38 | 72.04 | 4.31 |
| Inf 45° | 6429.58 | 390.62 | 53.63 | 2.24 |
| Inf 90° | 8497.91 | 337.49 | 68.97 | 2.81 |
| E·ρ−1 [MPa·cm3·g−1] | σmax·ρ−1 [MPa·cm3·g−1] | |
|---|---|---|
| WL 0° | 7763.05 | 53.06 |
| WL 45° | 4693.37 | 37.09 |
| WL 90° | 7383.47 | 53.94 |
| Inf 0° | 7669.55 | 60.49 |
| Inf 45° | 5324.88 | 44.41 |
| Inf 90° | 6995.58 | 56.76 |
| Young’s Modulus [MPa] | St. Deviation [MPa] | Tensile Strength [MPa] | St. Deviation [MPa] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epoxy BK | 3230.96 | 265.81 | 23.24 | 8.31 |
| IN2 | 3013.98 | 342.76 | 48.69 | 2.93 |
| Material | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wet layup | 2.37–2.45 | 1.86–1.88 | 1.82–1.84 | 0.245–0.249 | 0.311–0.312 | 0.321–0.322 |
| Resin infusion | 2.64–2.69 | 2.13–2.17 | 2.11–2.13 | 0.25–0.253 | 0.311–0.313 | 0.319–0.321 |
| Material | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wet layup | 7850 | 6800 | 0.247 | 2410 | 1870 | 1830 |
| Resin infusion | 9130 | 8550 | 0.251 | 2670 | 2180 | 2120 |
| Material | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wet layup | 1 | 0.98 | 1 | 0.69 | 0.69 | 0.69 |
| Resin infusion | 1 | 0.93 | 1 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.77 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Negru, R.; Coșa, A.-V.; Ianto, A.; Tătar, B.; Sîrbu, R.-C.; Șerban, D.-A. The Influence of the Manufacturing Technology on the Mechanical Properties of Woven Jute Fiber-Reinforced Epoxy Composites. Polymers 2025, 17, 1649. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17121649
Negru R, Coșa A-V, Ianto A, Tătar B, Sîrbu R-C, Șerban D-A. The Influence of the Manufacturing Technology on the Mechanical Properties of Woven Jute Fiber-Reinforced Epoxy Composites. Polymers. 2025; 17(12):1649. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17121649
Chicago/Turabian StyleNegru, Radu, Alexandru-Viorel Coșa, Adrian Ianto, Bogdan Tătar, Robert-Cătălin Sîrbu, and Dan-Andrei Șerban. 2025. "The Influence of the Manufacturing Technology on the Mechanical Properties of Woven Jute Fiber-Reinforced Epoxy Composites" Polymers 17, no. 12: 1649. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17121649
APA StyleNegru, R., Coșa, A.-V., Ianto, A., Tătar, B., Sîrbu, R.-C., & Șerban, D.-A. (2025). The Influence of the Manufacturing Technology on the Mechanical Properties of Woven Jute Fiber-Reinforced Epoxy Composites. Polymers, 17(12), 1649. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17121649







