Comparative Study on Pervaporation Performance of Polyphosphazene Membranes with Different Fluorine Side Groups for Thiophene/n-Heptane Separation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fabrication of Membranes
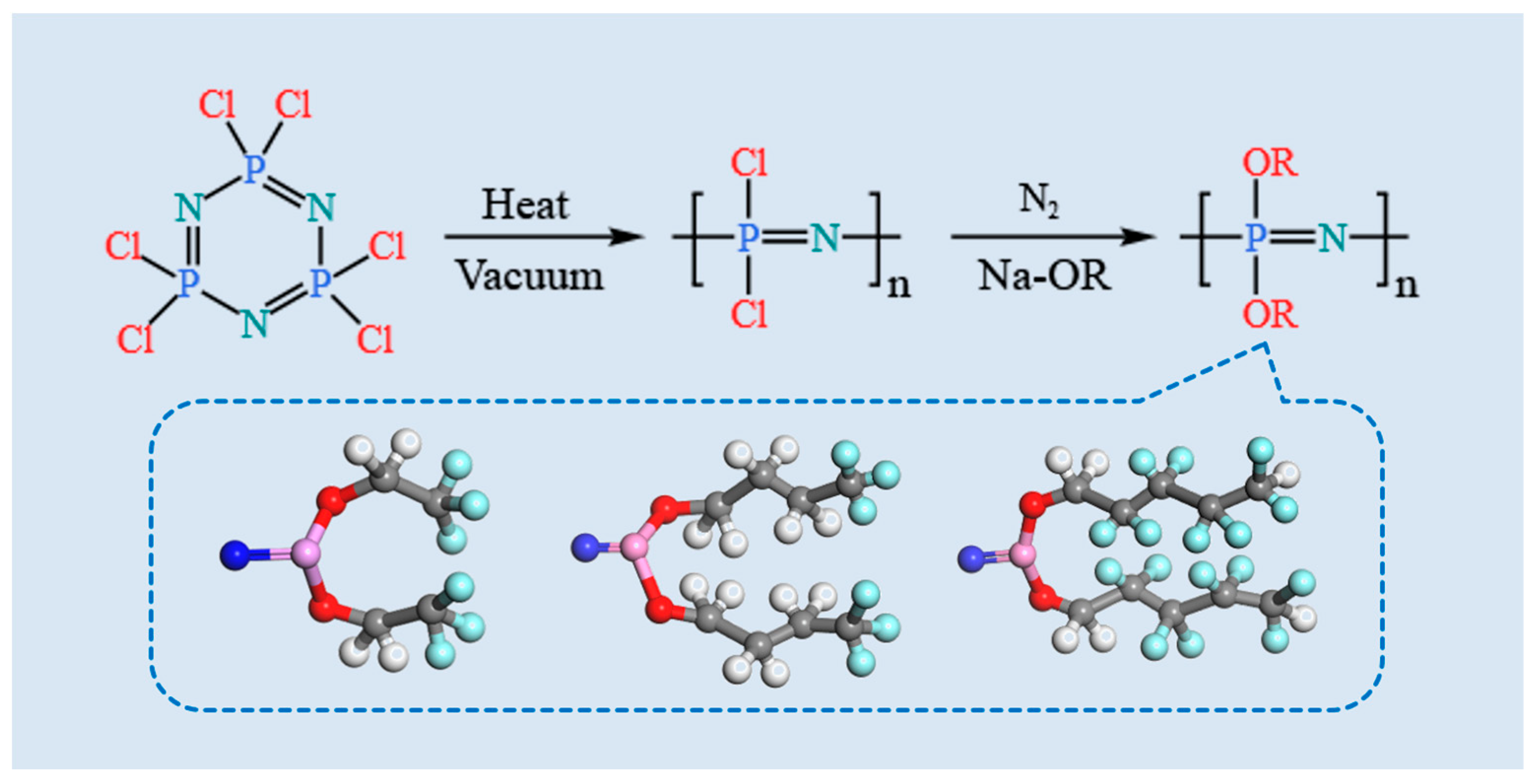
2.1.1. Synthesis of POP Materials
2.1.2. Preparation of Homogeneous Membranes
2.1.3. Preparation of Composite Membranes
2.2. Characterization and Pervaporation Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization
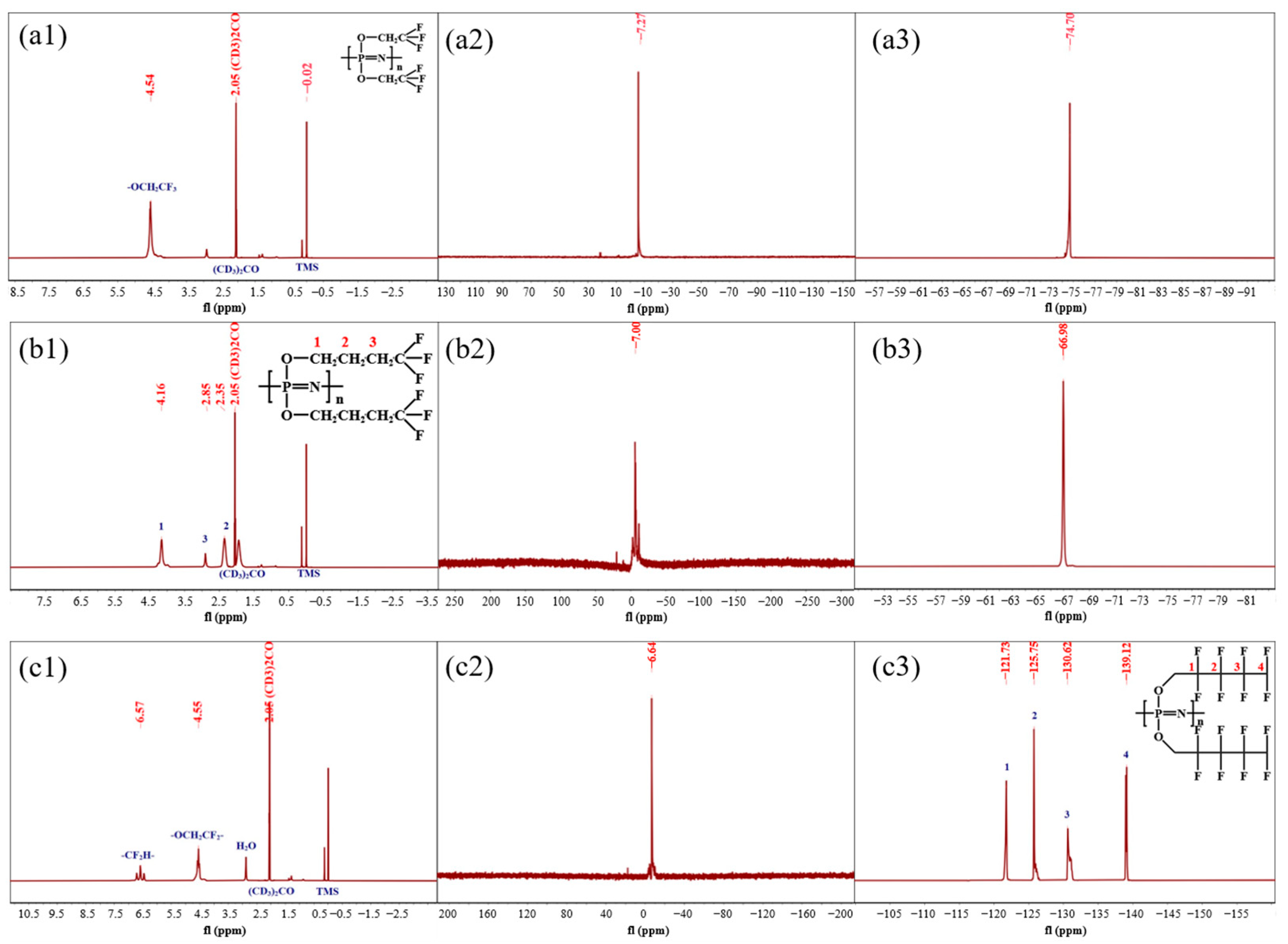
3.1.1. NMR
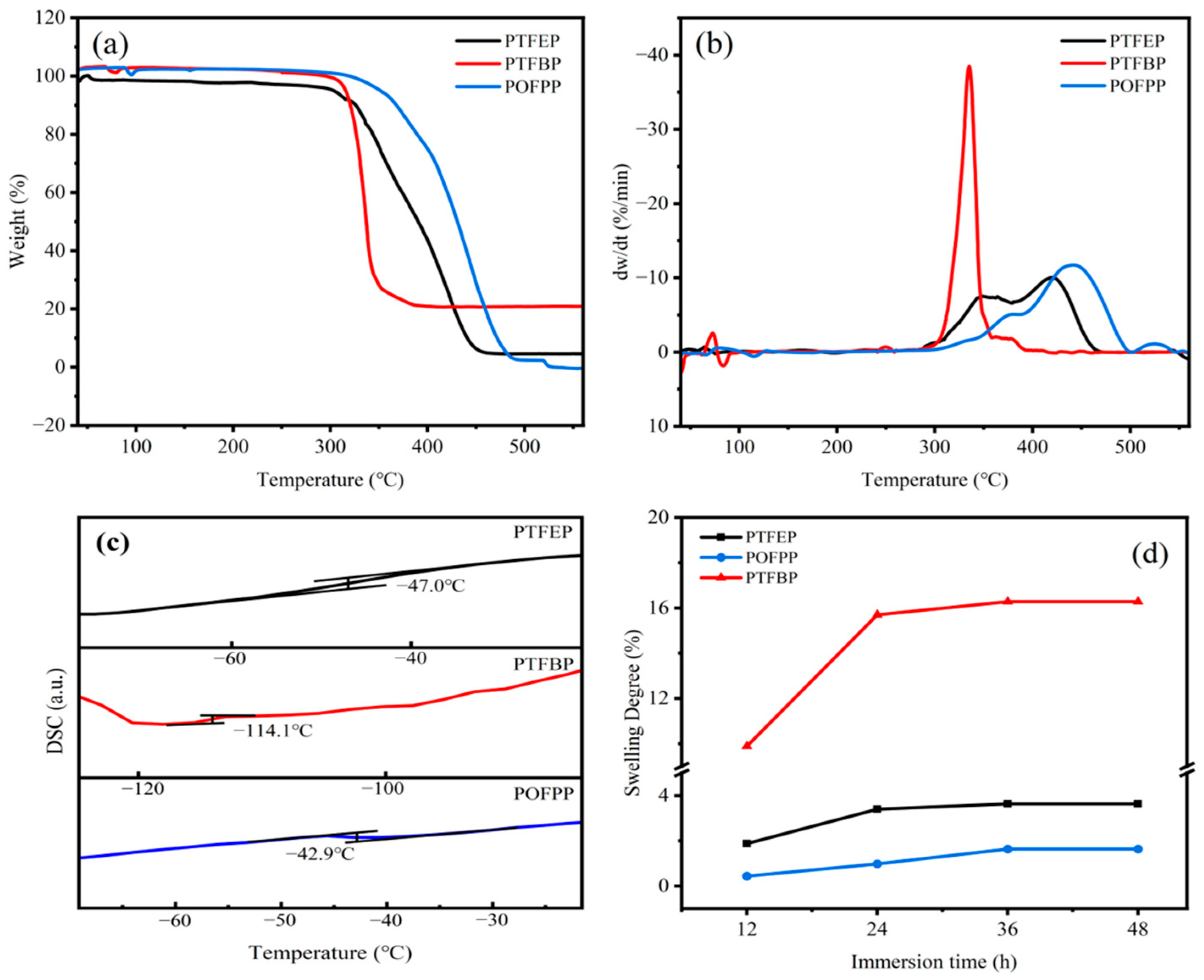
3.1.2. TGA
3.1.3. DSC
3.1.4. SD
3.1.5. Homogeneous Membrane Morphology
3.1.6. FT-IR
3.1.7. XPS
3.1.8. SEM
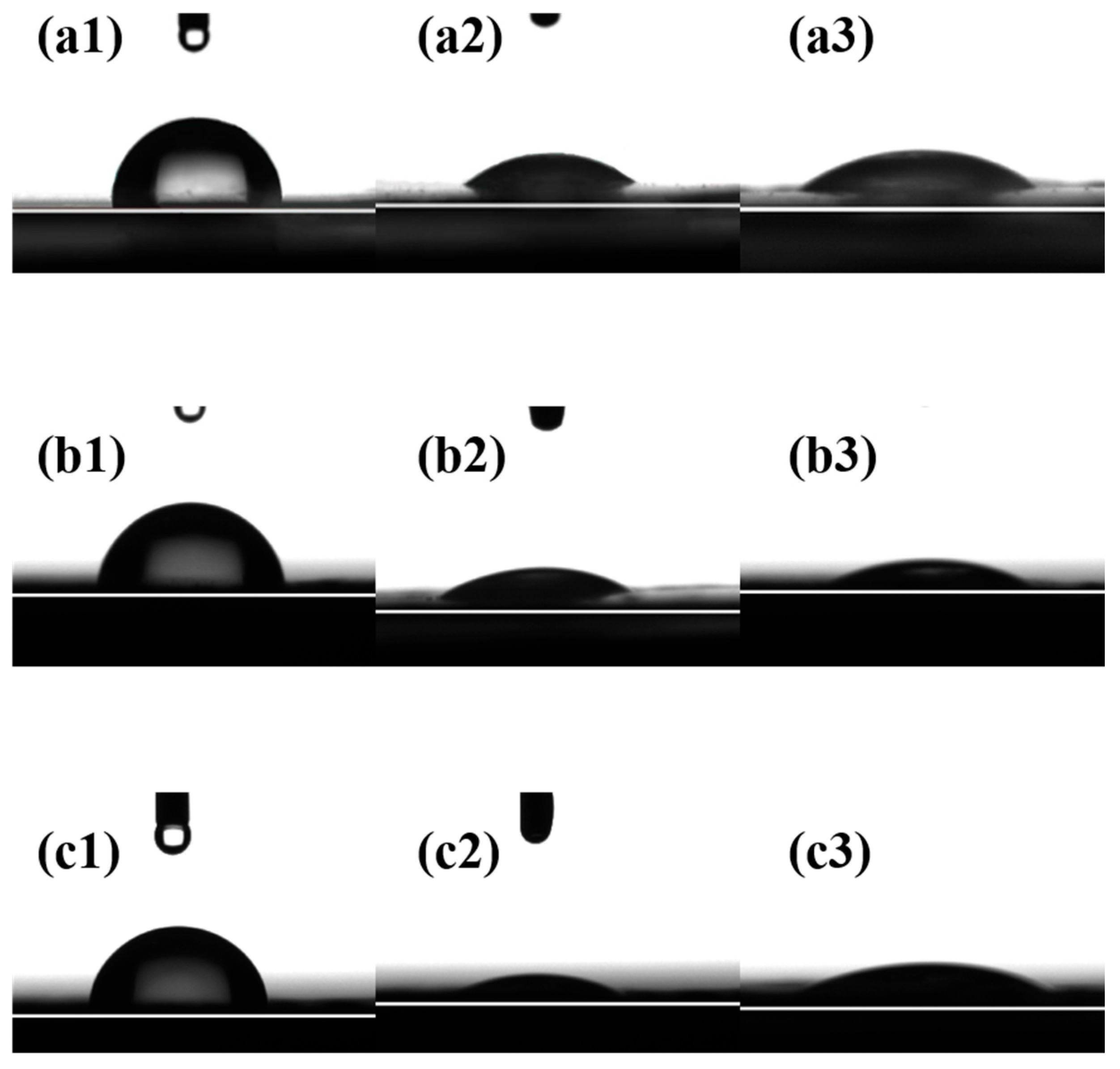
3.1.9. Contact Angles
3.2. Pervaporation Performance
3.2.1. Influence of Feed Temperature
3.2.2. Influence of Feed Concentration
3.2.3. Influence of Side Group
3.2.4. Comparison of Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| POP | polyphosphazene |
| PTFEP | Poly[bis(trifluoroethoxy)phosphazene] |
| PTFBP | Poly[bis(trifluorobutoxy)phosphazene] |
| POFPP | Poly[bis(octafluoropentyloxy)phosphazene] |
| FCC | fluid catalytic cracking |
| PV | pervaporation |
| PI | polyimide |
| PEG | polyethylene glycol |
| PEBAX | poly(ether-block-amide) |
| PDMS | polydimethylsiloxane |
| EC | ethylcellulose |
| PDCP | Poly(dichlorophosphazene) |
| HCCP | Hexachlorocyclotriphosphazene |
| THF | tetrahydrofuran |
| SD | swelling degree |
References
- Parizad, B.; Shahhosseini, S.; Farrokhzad, H.; Kazemi, A.; Manteghi, F. Enhanced desulfurization properties of MOF-808-embedded polysulfone membranes via pervaporation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 116134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 17930-2016; Gasoline for Motor Vehicles. S. AQSIQ: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Liu, J.; Tian, Y.; Song, Y. Overview and comparative analysis of catalytic cracking gasoline desulfurization technology. J. Liaoning Chem. Ind. 2023, 52, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Wei, M.; Liu, D.; Wang, H. Development of deep desulfurization process for FCC gasoline. J. Liaoning Shihua Univ. 2016, 36, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Zhang, J. Catalytic Gas Desulfurization and Its Development Trend. J. Guangzhou Chem. Ind. 2011, 39, 42–45. Available online: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:101304521 (accessed on 15 July 2024).
- Gao, X.; Xu, Y.; Yin, Y.; Gu, N.; Zeng, Y. Nickel ion-exchanged anionic Cu-MOF with hierarchically porous structure for adsorption desulfurization. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 111070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Pan, Y.; Wang, W.; Yuan, H.; Gu, H. A comprehensive back-extraction methodology for the regeneration of ionic liquids in oil extraction desulfurization. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 364, 132441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Zamzami, M.A.; Ahmad, V.; Al-Thawadi, S.; Akhtar, M.S.; Khan, M.J. Bacterial Biological Factories Intended for the Desulfurization of Petroleum Products in Refineries. Fermentation 2023, 9, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Qiu, X.; Zhu, L.; Wang, C.; Li, H.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, M.; Li, H.; Zhu, W. Engineering high specific surface area over poly (ionic liquids)-derived molybdenum-silica hybrid materials for enhanced oxidative desulfurization. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 111487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Yang, B.; Ma, H.; Wu, Z. Graphene modified porous organic polymer supported phosphotungstic acid catalyst for alkylation desulfurization. J. Fuel 2021, 293, 120438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Wu, S.; Hu, C.; Zhang, H.; Cui, Q.; Bao, X.; Yuan, P. In-situ synthesis of Ni2P/Al2O3 catalyst with liquid-phase phosphidation for enhancing hydrogenation and desulfurization performance in C9 petroleum resin. J. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2024, 286, 119648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L. Comparison of FCC Naphtha Desulfurization Process Schemes and Application Analysis. J. Pet. Refin. Eng. 2008, 38, 11–15. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=2Z_8GvOTliWhRyzecbfrRC0_6Ao9teWkzmyQNU_TaSwl-OkxZ-bZL_aPZnYfs9x9Mx0T3b2wvoJAmS7HxlfDQnF5bCJGHLB2hU9X3v7A9Tjc7ycgQzwgvVB2KAPY9xHxc1hSKEno5Jl99QoIa_d7SnkRwQnbqZc8qPONX9xUmSSKhIp4lzalmDJV7fw8lrBthJSMoGCIkdc=&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 17 July 2024).
- Zhan, X.; Gao, K.; Jia, Y.; Den, W.; Liu, N.; Guo, X.; Li, H.; Li, J. Enhanced Desulfurization Performance of ZIF−8/PEG MMMs: Effect of ZIF−8 Particle Size. Membranes 2023, 13, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Ye, H.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Zhao, B.; Lin, Y. An asymmetric membrane of polyimide 6FDA-BDAF and its pervaporation desulfurization for n-heptane/thiophene mixtures. J. Integr. Agric. 2015, 14, 2529–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Han, X.; Bai, F.; Hua, C.; Cao, X. Enhanced desulfurization performance of polyethylene glycol membrane by incorporating metal organic framework MOF-505. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 272, 118924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Fang, C.; Li, Z.; Young, M. Separation of thiophene/n-heptane mixtures using PEBAX/PVDF-composited membranes via pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 451, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.A.; Sengupta, S. Octyl silane modified nano alumina-polydimethylsiloxane composite membrane for pervaporative desulfurization of model gasoline. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Liu, M.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Kong, Y.; Yao, G. Preparation process optimization of crosslinked EC pervaporationmembrane for gasoline desulfurization. J. Mod. Chem. Ind. 2016, 36, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, X.; Sun, X.; Xu, H.; Li, J.D. Membrane materials for desulfurization of gasoline via pervaporation. J. Prog. Chem. 2019, 31, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Wei, W.; Jin, W.; Xu, N. Polymer/ceramic composite membranes and their application in pervaporation process. J. Chin. Chem. Eng. 2012, 20, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potin, P.; Jaeger, R. Polyphosphazenes: Synthesis, structures, properties, applications. J. Euro. Polym. 1991, 27, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Fu, J.; Pan, Y.; Huang, X.; Tang, X. Pervaporation of ethanol aqueous solution by polyphosphazene membranes: Effect of pendant groups. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 66, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizone, T.; Goseki, R. Synthesis of polymers carrying adamantyl substituents in side chain. J. Polym. 2018, 50, 805–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orme, C.; Harrup, M.; Mccoy, J.; Weinkauf, D.; Stewart, F. Pervaporation of water–dye, alcohol–dye, and water–alcohol mixtures using a polyphosphazene membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 197, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Zheng, C.; Zhao, Q. Mechanisms of drug resistance reversal in dox-resistant MCF-7 cells by pH-responsive amphiphilic polyphosphazene containing diisopropylamino side groups. J. Mol. Pharm. 2012, 9, 1109–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, M.; Orme, C.; Peteson, E.; Bauer, W.; Stewart, F.; Harrup, M.; Luther, T.; Klaehn, J.; Way, J. Water transport polymers—Structure/property relationships of a series of phosphazene polymers. J. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2010, 45, 1880–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Zhang, X.; Wu, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Jiang, Z. Enhanced pervaporative desulfurization by polydimethylsiloxane membranes embedded with silver/silica core-shell microspheres. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 187, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalili, P.; Abdolmaleki, A.; Riazi, M.; Davarpanah, A. Enhanced desulfurization Pervaporate via tailored Polypyrrolidone membranes with functionalized graphene oxide nanoparticles and silver ions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 364, 132562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Chen, J. Polyphosphazene membrane for desulfurization: Selecting poly[bis(trifluoroethoxy) phosphazene] for pervaporative removal of thiophene. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 93, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Fan, X.; Han, X.; Li, J.; Vardhan, H. Improved Desulfurization Performance of Polyethyleneglycol Membrane by Incorporating Metal Organic Framework CuBTC. Polymers 2020, 12, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q. Synthesis and Properties Study of Octafluoropentoxy Polyacrylate Water and Oil Repellent Finishing Agent. Master’s Thesis, Sichuan University of Science & Engineering, Zigong, China, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Jiang, C. Synthesis of Ethyl 4,4,4-Trifluoroc rotonate. J. Agrochem. 2015, 54, 254–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allcock, H.R.; Kugel, R.L.; Valan, K.J. Phosphonitrilic compounds. VI. high molecular weight poly(alkoxy- and aryloxyphosphazenes). J. Inorg. Chem. 1966, 5, 1709–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Magnuson, Z.; He, W. PEG@ZIF-8/PVDF Nanocomposite Membrane for Efficient Pervaporation Desulfurization via a Layer-by-Layer Technology. J. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 20664–20671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedors, R.F. A method for estimating both the solubility parameters and molar volumes of liquids. J. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1974, 14, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehnen, S.; Schafer, L.L.; Lectka, T.; Togni, A. Fluorine: A very special element and its very special impacts on chemistry. J. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 23, 9013–9019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhou, T.; Liu, W. Enhanced desulfurization performance of PDMS membranes by incorporating silver decorated dopamine nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 12907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Lin, L.; Zhang, Y. Studies on polyethylene glycol/polyethersulfone composite membranes for FCC gasoline desulphurization by pervaporation. J. Euro. Polym. 2008, 44, 3335–3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Pan, F.; Yang, S. Enhanced pervaporation performance of MIL-101 (Cr) filled polysiloxane hybrid membranes in desulfurization of model gasoline. J. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 135, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Jiang, Z.; Li, W. Elevated performance of hybrid membranes by incorporating metal organic framework CuBTC for pervaporative desulfurization of gasoline. J. Chem. Eng. Process.-Process Intensif. 2017, 123, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Jiang, Z.; Ding, H. Elevated pervaporation performance of polysiloxane membrane using channels and active sites of metal organic framework CuBTC. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 481, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodadadi, D.A.; Mortaheb, H.R.; Mokhtarani, B. Pervaporative performance of polydimethylsiloxane–graphene/polyethersolfune hybrid membrane: Effects of graphene structure and surface properties. J. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2017, 124, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; Wang, M.; Ding, H. Embedding Ag+ @COFs within Pebax membrane to confer mass transport channels and facilitated transport sites for elevated desulfurization performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 552, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Z.Y.; Song, J. Elevated pervaporative desulfurization performance of Pebax-Ag+@MOFs hybrid membranes by integrating multiple transport mechanisms. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 16911–16921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




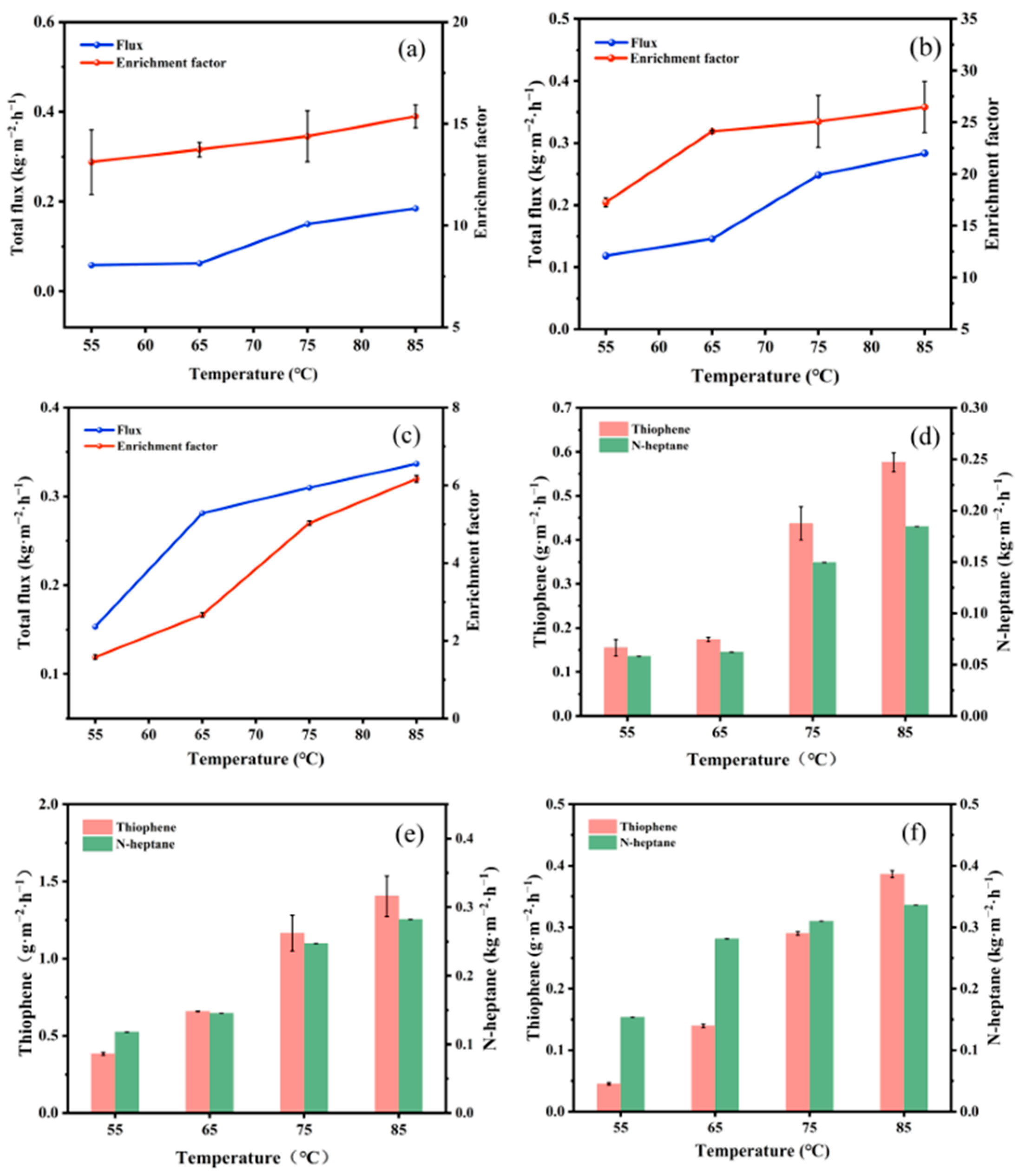
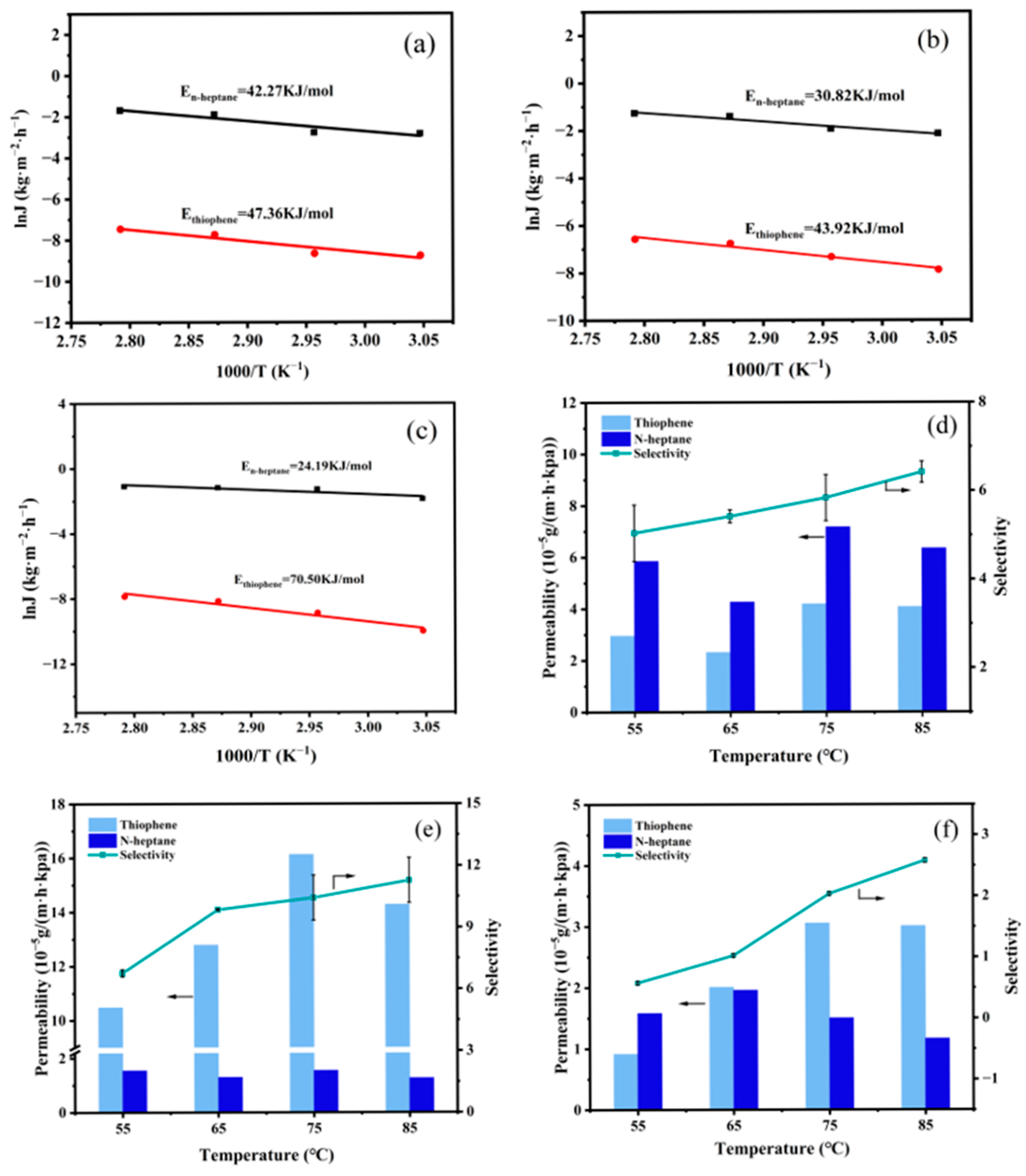
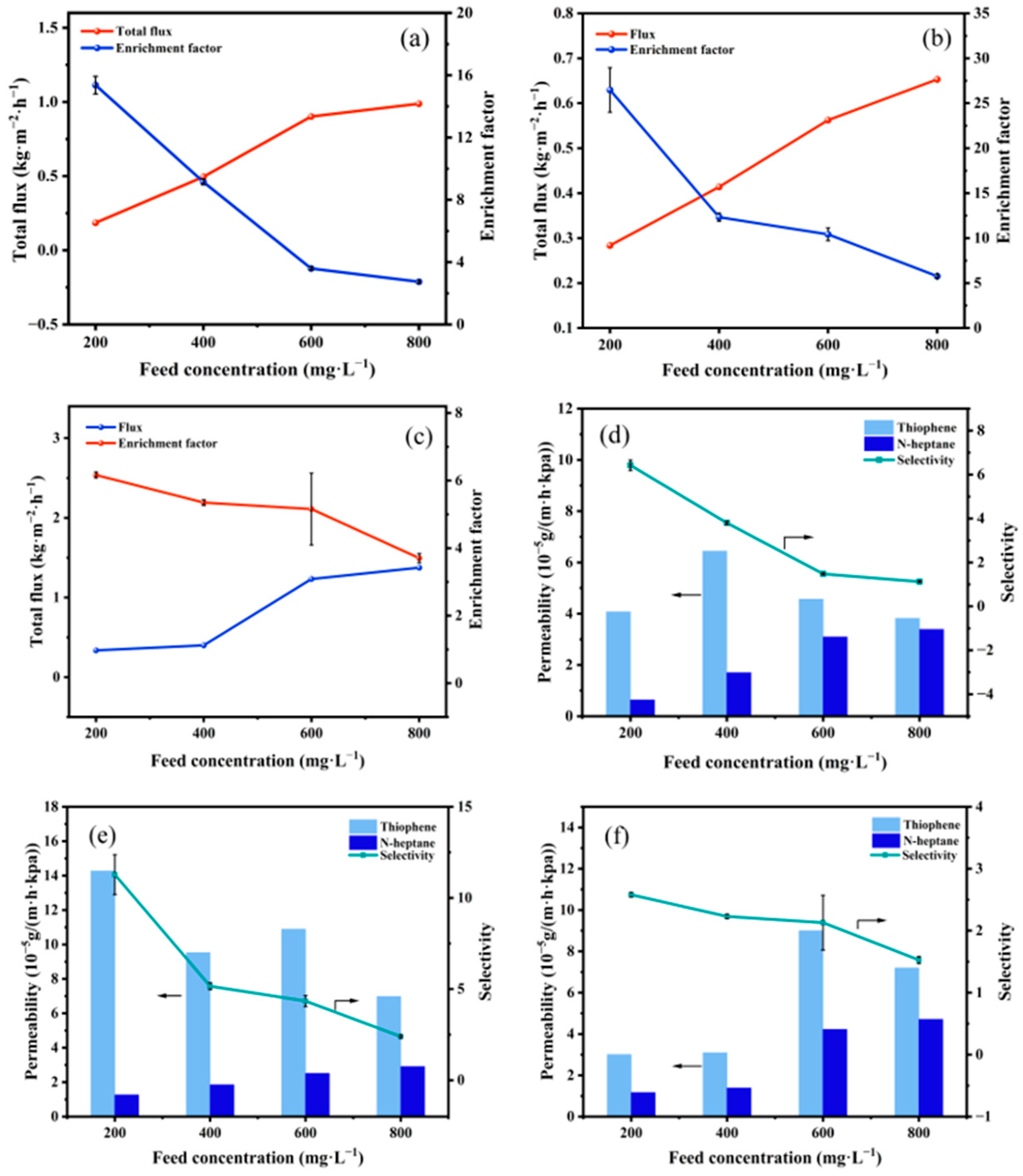
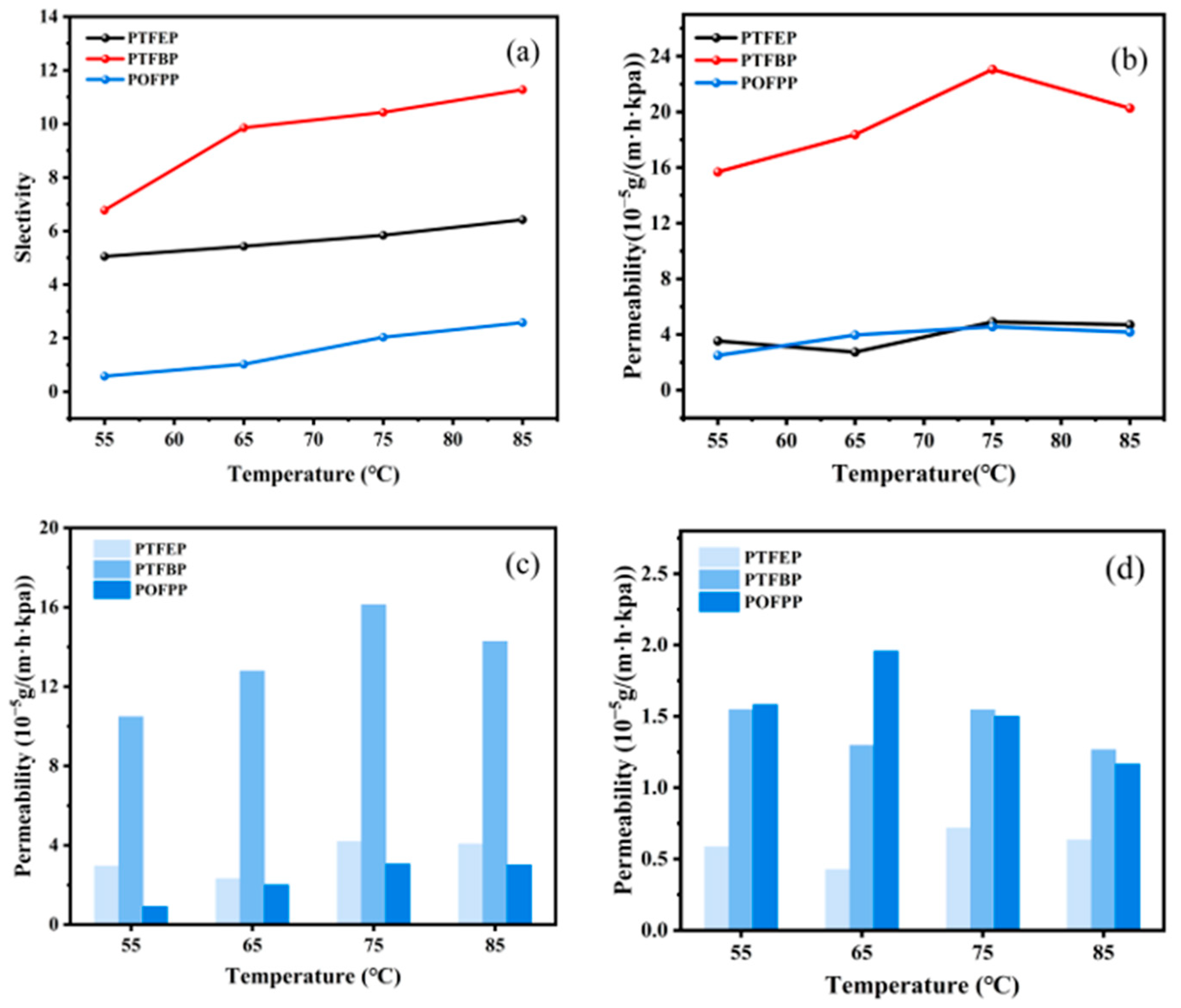
| F/% | C/% | O/% | N/% | P/% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PTFEP | 29.23 | 20.98 | 10.77 | 5.07 | 5.01 |
| PTFBP | 27.02 | 36.11 | 13.38 | 5.04 | 5.30 |
| POFPP | 32.58 | 19.53 | 4.62 | 2.11 | 1.89 |
| Composite Membrane | Total Flux/(kg·m−2·h−1) | Enrichment Factor | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| PDMS/PSF | 8.22 | 5.03 | Liu [37] |
| PEG/PES | 3.37 | 3.63 | Kong [38] |
| MIL-101(Cr)PDMS | 5.20 | 5.60 | Yu [39] |
| CuBTC/PEBAX | 16.45 | 4.04 | Yu [40] |
| PEG@ZIF-8/PVDF | 3.08 | 7.60 | Sun [34] |
| PEBAX/PVDF | 3.80 | 4.00 | Liu [16] |
| CuBTC/PDMS | 5.25 | 5.20 | Yu [41] |
| PDMS-GNS/PVDF | 6.22 | 3.58 | Khodadadi [42] |
| Ag+@COFs/PEBAX | 16.35 | 6.80 | Pan [43] |
| PEBAX-Ag+@MOFs | 22.11 | 5.92 | Zhang [44] |
| PTFEP/PVDF | 0.1 | 15.69 | Yang [29] |
| PTFBP/PVDF | 0.284 | 26.48 | This work |
| PTFEP/PVDF | 0.18 | 15.37 | This work |
| POFPP/PVDF | 0.34 | 6.17 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, B.; Zhang, X.; He, W.; Han, X. Comparative Study on Pervaporation Performance of Polyphosphazene Membranes with Different Fluorine Side Groups for Thiophene/n-Heptane Separation. Polymers 2025, 17, 1573. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17111573
Xu B, Zhang X, He W, Han X. Comparative Study on Pervaporation Performance of Polyphosphazene Membranes with Different Fluorine Side Groups for Thiophene/n-Heptane Separation. Polymers. 2025; 17(11):1573. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17111573
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Bingcong, Xingmei Zhang, Wenwen He, and Xiaolong Han. 2025. "Comparative Study on Pervaporation Performance of Polyphosphazene Membranes with Different Fluorine Side Groups for Thiophene/n-Heptane Separation" Polymers 17, no. 11: 1573. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17111573
APA StyleXu, B., Zhang, X., He, W., & Han, X. (2025). Comparative Study on Pervaporation Performance of Polyphosphazene Membranes with Different Fluorine Side Groups for Thiophene/n-Heptane Separation. Polymers, 17(11), 1573. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17111573







