A Novel Approach to Automatically Balance Flow in Profile Extrusion Dies Through Computational Modeling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Modeling Solver
- 1.
- The calculation of the temperature shift factor (aT), which is given as follows:
- 2.
- Then, fluid viscosity, is calculated as follows:
2.2. heatConvection Boudary Condition
2.3. Performance Quantification
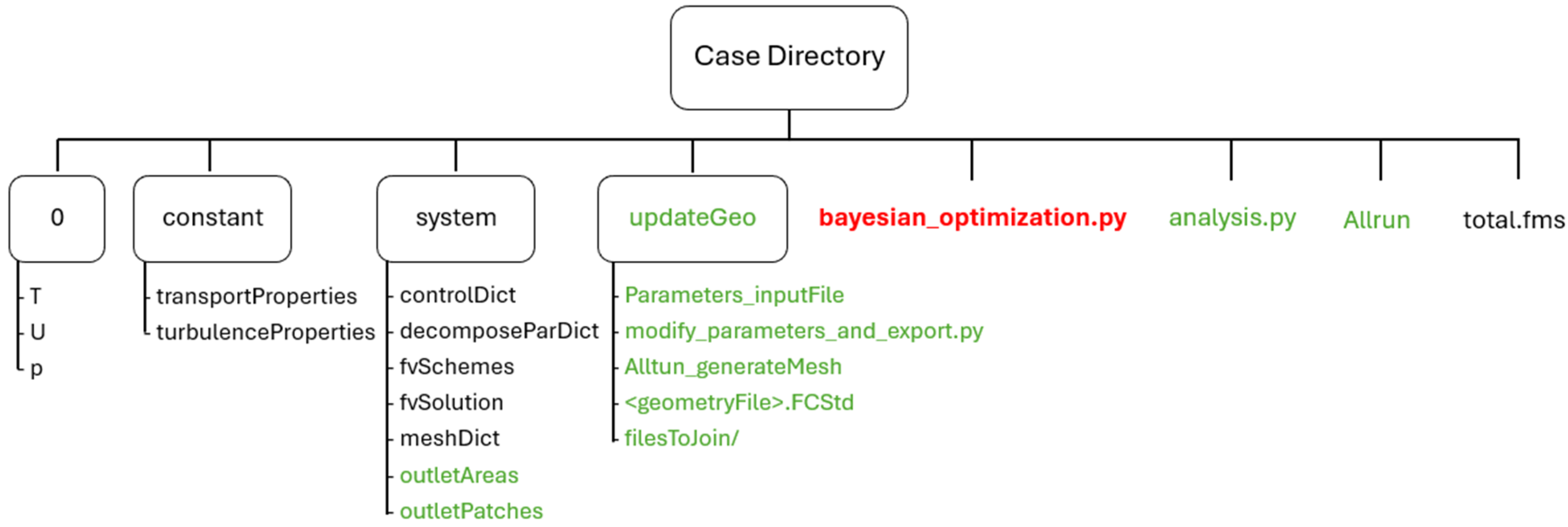
2.4. Optimization Framework
2.4.1. Geometry
2.4.2. Mesh
2.4.3. Run Simulation
2.4.4. Analyze Results
- 1—Pressure Drop ():
- 2—Velocity Uniformity ():
2.4.5. Propose New Parameter Combination
3. Case Study
- Maximizing velocity uniformity across the elemental sections (ES) to ensure a homogeneous extrudate profile;
- Minimizing the overall pressure drop along the channel, reducing energy consumption;
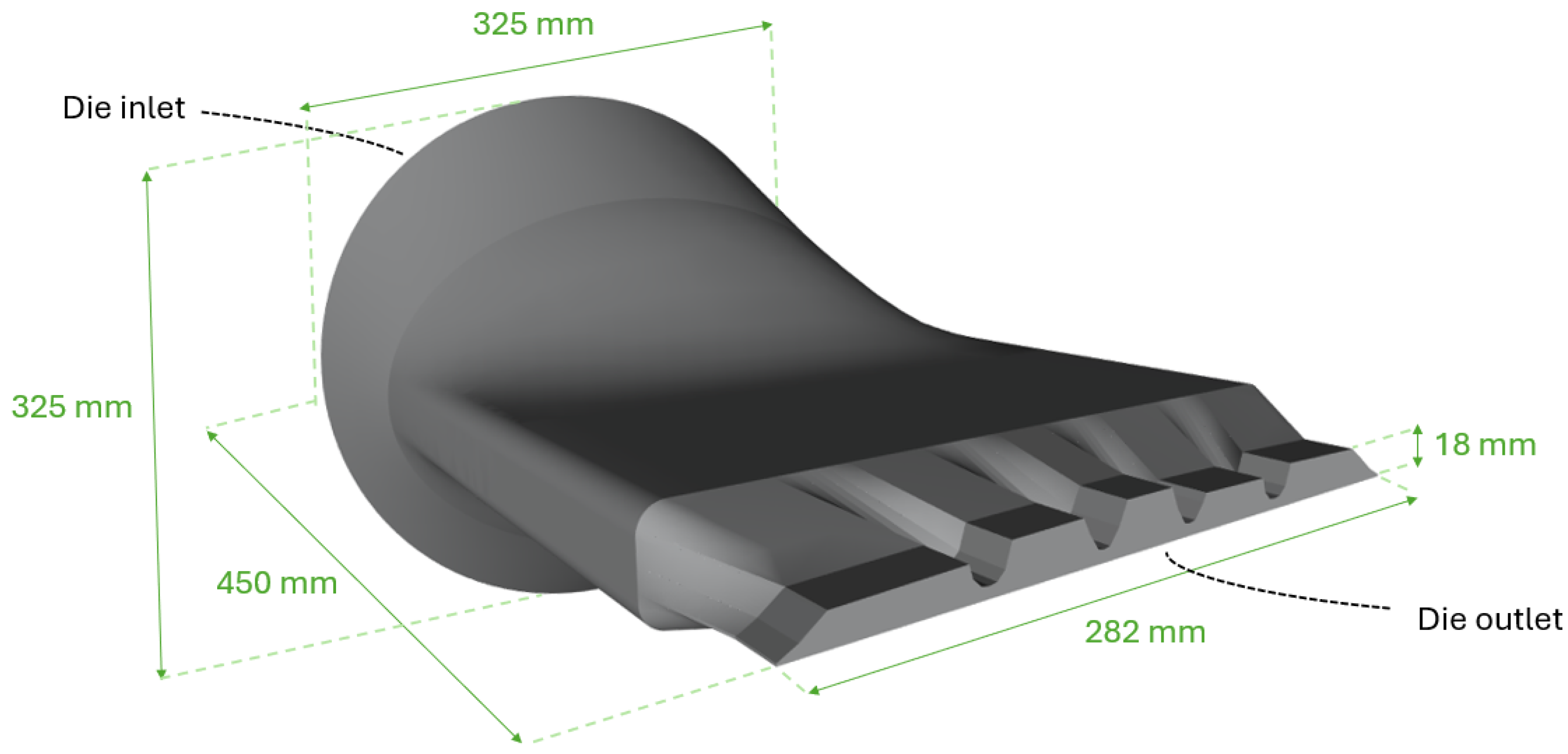
3.1. Extrusion Die Geometry
3.2. Material Properties
3.3. Boundary Conditions
3.4. Case Setup
4. Results and Discussion
- A = 40.00 mm, B = 2.00 mm, C = 2.00 mm, D = 40.00 mm, E = 16.16 mm;
- Objective function value: 0.2001;
- Velocity uniformity: 0.8137;
- Pressure drop: 9.3612 MPa.
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carneiro, O.S.; Nóbrega, J.M. Design of Extrusion Forming Tools; Smithers Rapra: Shropshire, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.; Bai, J.; Zhao, H.; Wang, R.; Li, H. Study on the extrusion molding process of polylactic acid micro tubes for biodegradable vascular stents. Polymers 2022, 14, 4790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauwendaal, C. Polymer Extrusion, 5th ed.; Hanser Publishers: Munich, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Carneiro, O.S.; Nobrega, J.M. Recent developments in automatic die design for profile extrusion. Plast. Rubber Compos. 2004, 33, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, O.S.; Nóbrega, J.M.; Oliveira, P.J.; Pinho, F.T. Flow balancing in extrusion dies for thermoplastic profiles: Part II: Influence of the design strategy. Int. Polym. Process. 2003, 18, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Ma, B. Ultraviolet-Follow Curing-Mediated Extrusion Stabilization for Low-Yield-Stress Silicone Rubbers: From Die Swell Suppression to Dimensional Accuracy Enhancement. Polymers 2025, 17, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanjaards, M.; Peters, G.; Hulsen, M.; Anderson, P. Numerical study of the effect of thixotropy on extrudate swell. Polymers 2021, 13, 4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkumar, A.; Ferrás, L.L.; Fernandes, C.; Carneiro, O.S.; Becker, M.; Nóbrega, J.M. Design guidelines to balance the flow distribution in complex profile extrusion dies. Int. Polym. Process. 2017, 32, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopmann, C.; Michaeli, W. Extrusion Dies for Plastics And Rubber: Design and Engineering Computations; Hanser Publishers: Munich, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Nóbrega, J.M.; Carneiro, O.S.; Oliveira, P.J.; Pinho, F.T. Flow balancing in extrusion dies for thermoplastic profiles: Part I: Automatic design. Int. Polym. Process. 2003, 18, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nóbrega, J.M.; Carneiro, O.S.; Pinho, F.T.; Oliveira, P.J. Flow balancing in extrusion dies for thermoplastic profiles: Part III: Experimental assessment. Int. Polym. Process. 2004, 19, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyvärinen, M.; Jabeen, R.; Kärki, T. The modelling of extrusion processes for polymers—A review. Polymers 2020, 12, 1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Huang, X.; Li, S.; Xia, C.; Deng, T. Improved inverse design method for thin-wall hollow profiled polymer extrusion die based on FEM-CFD simulations. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 106, 2909–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Marchesini, F.H.; Cardon, L.; D’hooge, D.R. State of the-art for extrudate swell of molten polymers: From fundamental understanding at molecular scale toward optimal die design at final product scale. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2020, 305, 2000340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, N.D.; Carneiro, O.S.; Nóbrega, J.M. Design of complex profile extrusion dies through numerical modeling. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 2013, 200, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkumar, A.; Ferrás, L.L.; Fernandes, C.; Carneiro, O.S.; Sacramento, A.; Nóbrega, J.M. An open-source framework for the computer aided design of complex profile extrusion dies. Int. Polym. Process. 2018, 33, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, N.D.; Teixeira, P.; Ferrás, L.L.; Afonso, A.M.; Nóbrega, J.M.; Carneiro, O.S. Design and optimization of an extrusion die for the production of wood–plastic composite profiles. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2015, 55, 1849–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Zhang, G.; Deng, T. Improved Optimization of a Coextrusion Die with a Complex Geometry Using the Coupling Inverse Design Method. Polymers 2023, 15, 3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legat, V.; Marchal, J.M. Die design: An implicit formulation for the inverse problem. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 1993, 16, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddah, A.; Jafari, A. Optimizing die profiles using a hybrid optimization algorithm for the precise control of extrudate swell in polymer solutions. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 2024, 330, 105277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgeti, S.; Probst, M.; Windeck, C.; Behr, M.; Michaeli, W.; Hopmann, C. Numerical shape optimization as an approach to extrusion die design. Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 2012, 61, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, G.B.; Wang, M.J.; Zhao, D.Y.; Tian, H.Q.; Jin, Y.F. Design and experiments of extrusion die for polypropylene five-lumen micro tube. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2014, 214, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, O.; Gunes, H.; Kirkkopru, K. Optimization of a profile extrusion die for flow balance. Fibers Polym. 2014, 15, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegbert, R.; Yesildag, N.; Frings, M.; Schmidt, F.; Elgeti, S.; Sauerland, H.; Behr, M.; Windeck, C.; Hopmann, C.; Queudeville, Y.; et al. Individualized production in die-based manufacturing processes using numerical optimization. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 80, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.C.; Jeong, J.; Jo, S.; Choi, D.Y.; Kim, G.M.; Kim, W. Development of a subpath extrusion tip and die for peripheral inserted central catheter shaft with multi lumen. Polymers 2021, 13, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal, J.P.O.; Oliveira, M.; Srivastava, A.; Sacramento, A.; Aali, M.; Guerrero, J.; Nóbrega, J.M. Enhancing extrusion die design efficiency through high-performance computing based optimization. Meccanica 2024, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razeghiyadaki, A.; Wei, D.; Perveen, A.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Y. Effects of melt temperature and non-isothermal flow in design of coat hanger dies based on flow network of non-newtonian fluids. Polymers 2022, 14, 3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.W.; Sung, M.F.; Kuan, Y.D. Numerical simulation and experimental investigation of 3D non-isothermal tread co-extrusion. In ASTFE Digital Library; Begel House Inc.: Danbury, CT, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelshahid, B.; Nassar, K.; Youssef, P.; Sayed-Ahmed, E.; Darwish, M. Evolutionary Algorithm-Based Design and Performance Evaluation of Wood–Plastic Composite Roof Panels for Low-Cost Housing. Polymers 2025, 17, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazier, P.I. A tutorial on Bayesian optimization. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.02811. [Google Scholar]
- Daniels, S.J.; Rahat, A.A.; Tabor, G.R.; Fieldsend, J.E.; Everson, R.M. Automated shape optimisation of a plane asymmetric diffuser using combined Computational Fluid Dynamic simulations and multi-objective Bayesian methodology. Int. J. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 2019, 33, 256–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OpenFOAM. Available online: https://www.openfoam.com/ (accessed on 31 March 2025).
- FreeCAD: Your Own 3D Parametric Modeler. Available online: https://www.freecad.org/ (accessed on 31 March 2025).
- Scikit-Optimize: Sequential Model-Based Optimization in Python—Scikit-Optimize 0.8.1 Documentation. Available online: https://scikit-optimize.github.io/stable/ (accessed on 31 March 2025).
- OpenFOAM Documentation—Simplefoam. Available online: https://doc.openfoam.com/2306/tools/processing/solvers/rtm/incompressible/simpleFoam/ (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- OpenFOAM: API Guide: BirdCarreau Class Reference. Available online: https://www.openfoam.com/documentation/guides/latest/api/classFoam_1_1laminarModels_1_1generalizedNewtonianViscosityModels_1_1BirdCarreau.html#details (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Welcome to Python.org. Available online: https://www.python.org/ (accessed on 31 March 2025).
- Bash—GNU Project—Free Software Foundation. Available online: https://www.gnu.org/software/bash/ (accessed on 31 March 2025).
- cfMesh Introduction. Available online: https://cfmesh.com/welcome/ (accessed on 31 March 2025).
- Bayesian Optimization with Skopt—Scikit-Optimize 0.8.1 Documentation. Available online: https://scikit-optimize.github.io/stable/auto_examples/bayesian-optimization.html (accessed on 31 March 2025).
- Skopt.gp_Minimize—Scikit-Optimize 0.8.1 Documentation. Available online: https://scikit-optimize.github.io/stable/modules/generated/skopt.gp_minimize.html#skopt.gp_minimize (accessed on 31 March 2025).
- OpenFOAM: Manual Pages: Surfacefeatureedges(1). Available online: https://www.openfoam.com/documentation/guides/v2206/man/surfaceFeatureEdges.html (accessed on 31 March 2025).
- Juretić, F. cfMesh User Guide. 2015. Available online: https://cfmesh.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/09/User_Guide-cfMesh_v1.1.pdf (accessed on 31 March 2025).
- OpenFOAM-2.1.x/applications/utilities/postProcessing/patch/patchIntegrate/patchIntegrate.C. Available online: https://github.com/OpenFOAM/OpenFOAM-2.1.x/blob/master/applications/utilities/postProcessing/patch/patchIntegrate/patchIntegrate.C (accessed on 31 March 2025).
- 1.7. Gaussian Processes—Scikit-Learn 1.6.1 Documentation. Available online: https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/gaussian_process.html (accessed on 31 March 2025).
- OpenFOAM: API Guide: Table< Type > Class Template Reference. Available online: https://www.openfoam.com/documentation/guides/v2206/api/classFoam_1_1Function1Types_1_1Table.html#details (accessed on 1 April 2025).













| Property | Description | Value | Units |
|---|---|---|---|
| Viscosity at zero shear rate | 107 | Pa.s | |
| Viscosity at infinite shear rate | 100 | Pa.s | |
| Characteristic time | 100 | s | |
| Power-law index | 0.2 | ||
| Ratio between activation energy and the universal gas constant | 1000 | K | |
| Reference temperature | 330 | K | |
| Thermal diffusivity | 1.28 × 10−7 | m2/s | |
| Specific heat capacity | 1700 | J/(kg.K) | |
| Density | 1150 | kg/m3 |
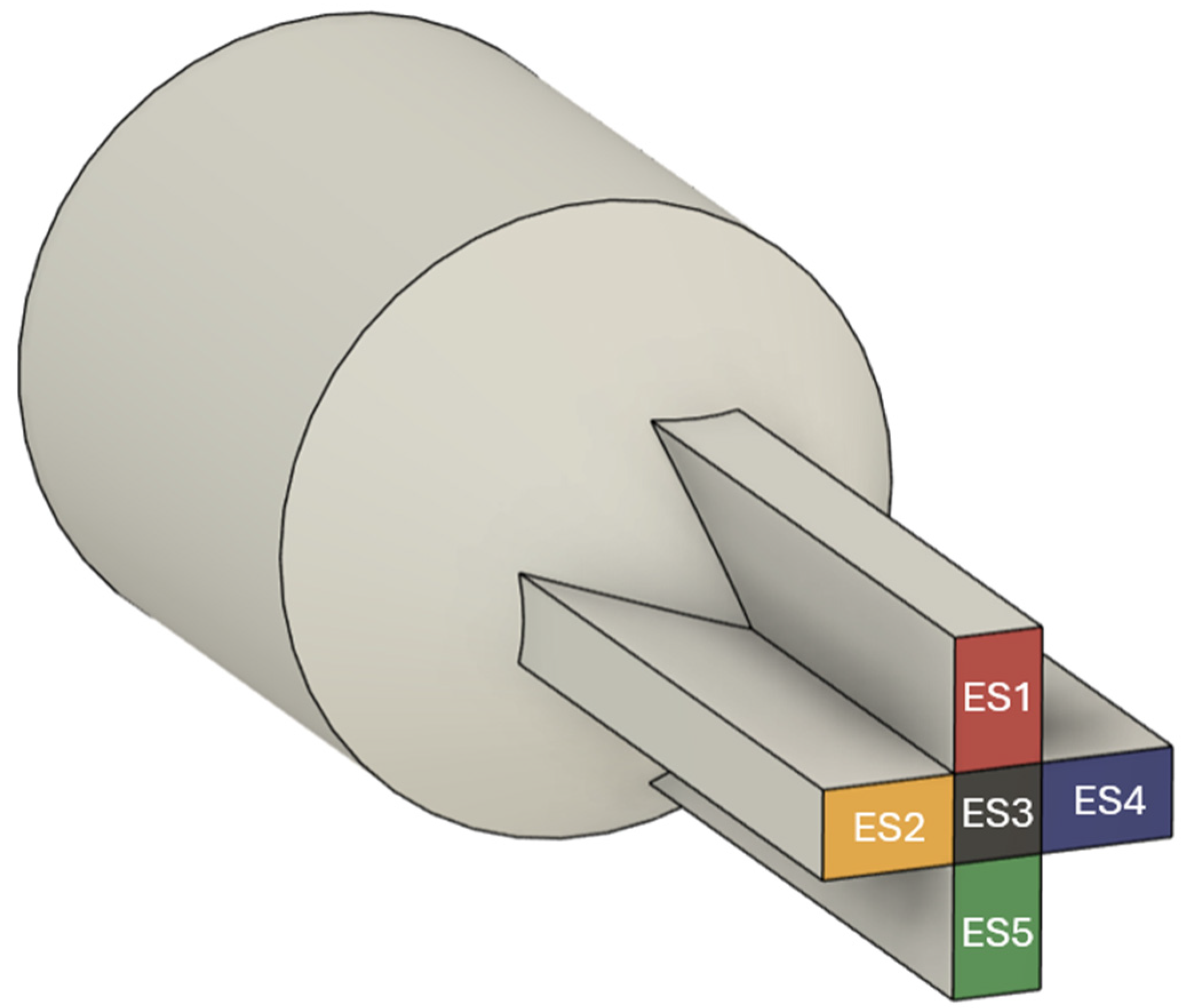
| Field | Inlet | Outlets (ES1 to ES12) | Walls |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pressure | Null normal gradient | 0 [Pa] | Null normal gradient |
| Velocity | Flow rate from 0.01 [cm3/s] to 2.898 [cm3/s] | Null normal gradient | noSlip |
| Temperature | 363.15 [K] | Null normal gradient | heatConvectionBC with = 0.25 [W/m2.K] = 363.15 [K] = 0.25 [W/m.K] |
| A [mm] | B [mm] | C [mm] | B [mm] | C [mm] | [MPa] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40.00 | 40.00 | 40.00 | 40.00 | 40.00 | 8.4307 | 0.6568 |
| Trial | A [mm] | B [mm] | C [mm] | D [mm] | E [mm] | [MPa] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 13.36 | 28.56 | 17.92 | 5.24 | 22.46 | 9.9151 | 0.6292 | 0.3782 |
| 2 | 32.90 | 5.72 | 8.08 | 26.26 | 19.22 | 9.5613 | 0.7591 | 0.2548 |
| 3 | 37.86 | 25.58 | 13.64 | 27.64 | 6.96 | 9.5098 | 0.6597 | 0.3315 |
| 4 | 30.92 | 19.84 | 17.48 | 14.54 | 25.08 | 9.5206 | 0.7106 | 0.2914 |
| 5 | 11.78 | 19.00 | 20.36 | 21.82 | 8.10 | 10.1620 | 0.5354 | 0.4668 |
| 6 | 3.06 | 13.44 | 20.98 | 2.10 | 2.56 | 12.0722 | 0.3334 | 0.7333 |
| 7 | 23.18 | 35.16 | 38.50 | 32.60 | 7.02 | 9.0088 | 0.4944 | 0.4362 |
| 8 | 13.90 | 17.66 | 7.02 | 17.64 | 35.54 | 9.7914 | 0.4928 | 0.4805 |
| 9 | 36.94 | 36.16 | 6.24 | 25.34 | 18.20 | 9.2974 | 0.6872 | 0.2978 |
| 10 | 6.82 | 31.08 | 10.88 | 20.28 | 39.58 | 9.2398 | 0.5455 | 0.4080 |
| 11 | 40.00 | 2.00 | 40.00 | 40.00 | 12.18 | 9.0725 | 0.6284 | 0.3325 |
| 12 | 40.00 | 33.52 | 40.00 | 40.00 | 40.00 | 8.4828 | 0.6601 | 0.2748 |
| 13 | 40.00 | 12.62 | 2.00 | 40.00 | 25.10 | 9.1944 | 0.7976 | 0.2039 |
| 14 | 40.00 | 8.80 | 15.42 | 29.30 | 23.82 | 9.3614 | 0.7887 | 0.2202 |
| 15 | 40.00 | 2.00 | 40.00 | 25.32 | 35.16 | 9.0329 | 0.7294 | 0.2496 |
| 16 | 23.50 | 40.00 | 40.00 | 17.50 | 40.00 | 8.7703 | 0.6060 | 0.3339 |
| 17 | 40.00 | 17.22 | 40.00 | 32.44 | 30.90 | 8.6860 | 0.6480 | 0.2956 |
| 18 | 40.00 | 40.00 | 2.00 | 40.00 | 40.00 | 8.8295 | 0.7207 | 0.2453 |
| 19 | 38.50 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 40.00 | 2.00 | 9.6116 | 0.7753 | 0.2446 |
| 20 | 32.42 | 14.22 | 2.00 | 40.00 | 17.74 | 9.4469 | 0.7471 | 0.2581 |
| 21 | 40.00 | 2.00 | 9.50 | 26.54 | 24.34 | 9.4036 | 0.8066 | 0.2082 |
| 22 | 37.10 | 2.66 | 40.00 | 2.00 | 28.56 | 9.5401 | 0.7559 | 0.2562 |
| 23 | 40.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 40.00 | 30.72 | 9.3470 | 0.7505 | 0.2499 |
| 24 | 40.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 24.66 | 18.58 | 9.7672 | 0.8200 | 0.2174 |
| 25 | 40.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 40.00 | 16.16 | 9.3612 | 0.8137 | 0.2001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wagner, G.; Vidal, J.; Barbat, P.; Gonnet, J.-M.; Nóbrega, J.M. A Novel Approach to Automatically Balance Flow in Profile Extrusion Dies Through Computational Modeling. Polymers 2025, 17, 1498. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17111498
Wagner G, Vidal J, Barbat P, Gonnet J-M, Nóbrega JM. A Novel Approach to Automatically Balance Flow in Profile Extrusion Dies Through Computational Modeling. Polymers. 2025; 17(11):1498. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17111498
Chicago/Turabian StyleWagner, Gabriel, João Vidal, Pierre Barbat, Jean-Marc Gonnet, and João M. Nóbrega. 2025. "A Novel Approach to Automatically Balance Flow in Profile Extrusion Dies Through Computational Modeling" Polymers 17, no. 11: 1498. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17111498
APA StyleWagner, G., Vidal, J., Barbat, P., Gonnet, J.-M., & Nóbrega, J. M. (2025). A Novel Approach to Automatically Balance Flow in Profile Extrusion Dies Through Computational Modeling. Polymers, 17(11), 1498. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17111498






