New Challenges in Assessment of the Acoustic Properties of Coating Polymers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples Preparation
2.2. Experimental Set-Up
2.2.1. The Modal Analysis of Varnished Plates
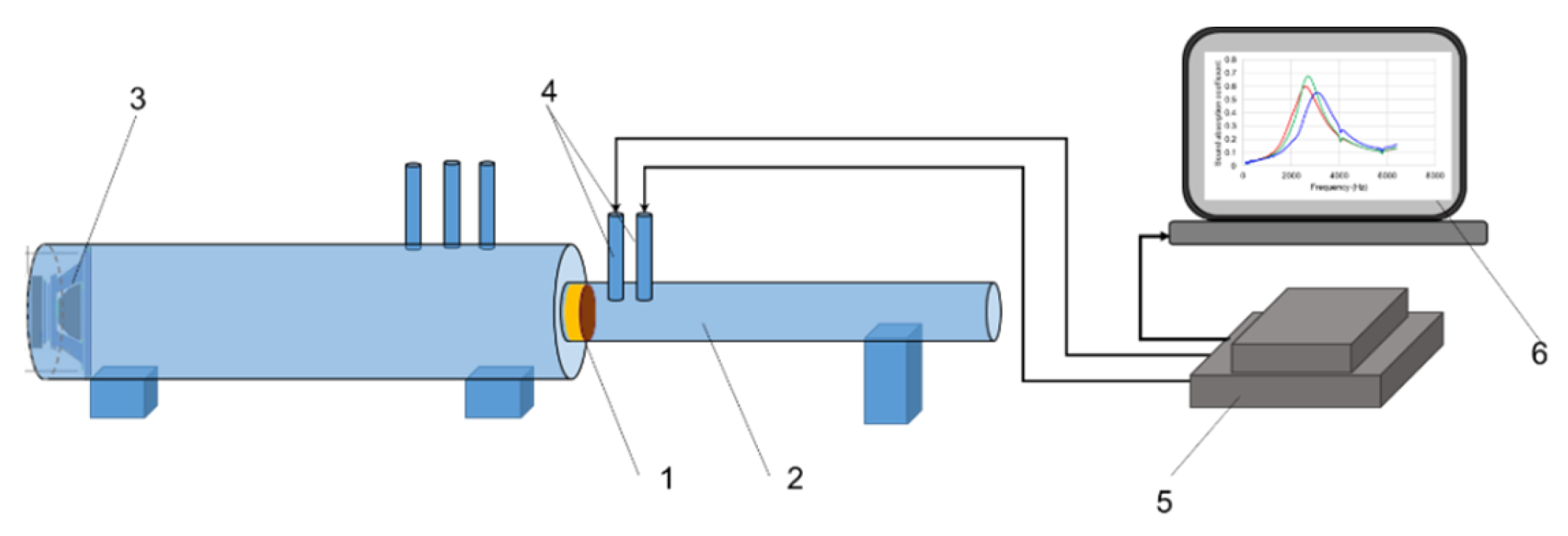
2.2.2. The Impedance Tube Method
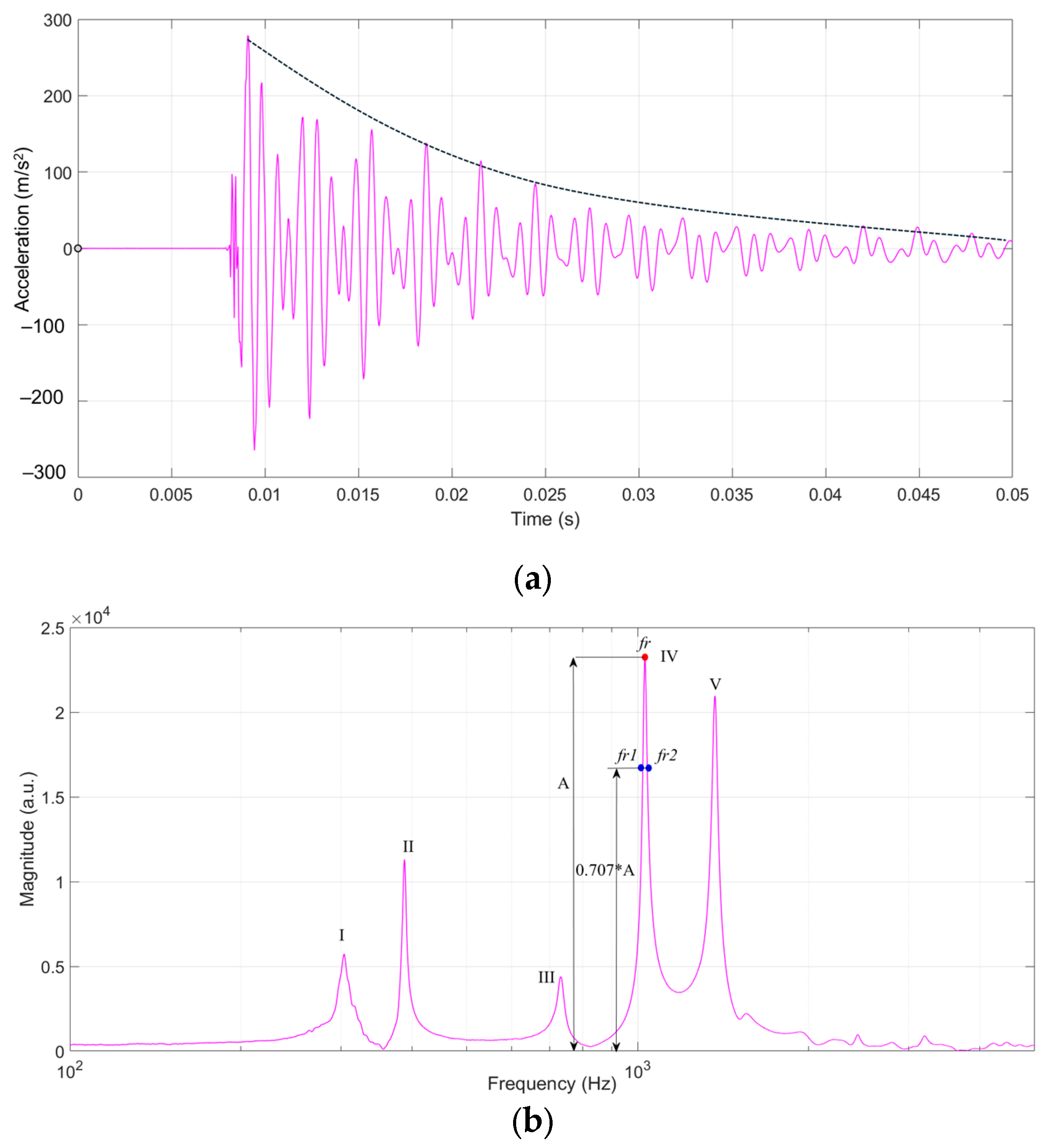
2.2.3. The Processing Data
3. Results and Discussion
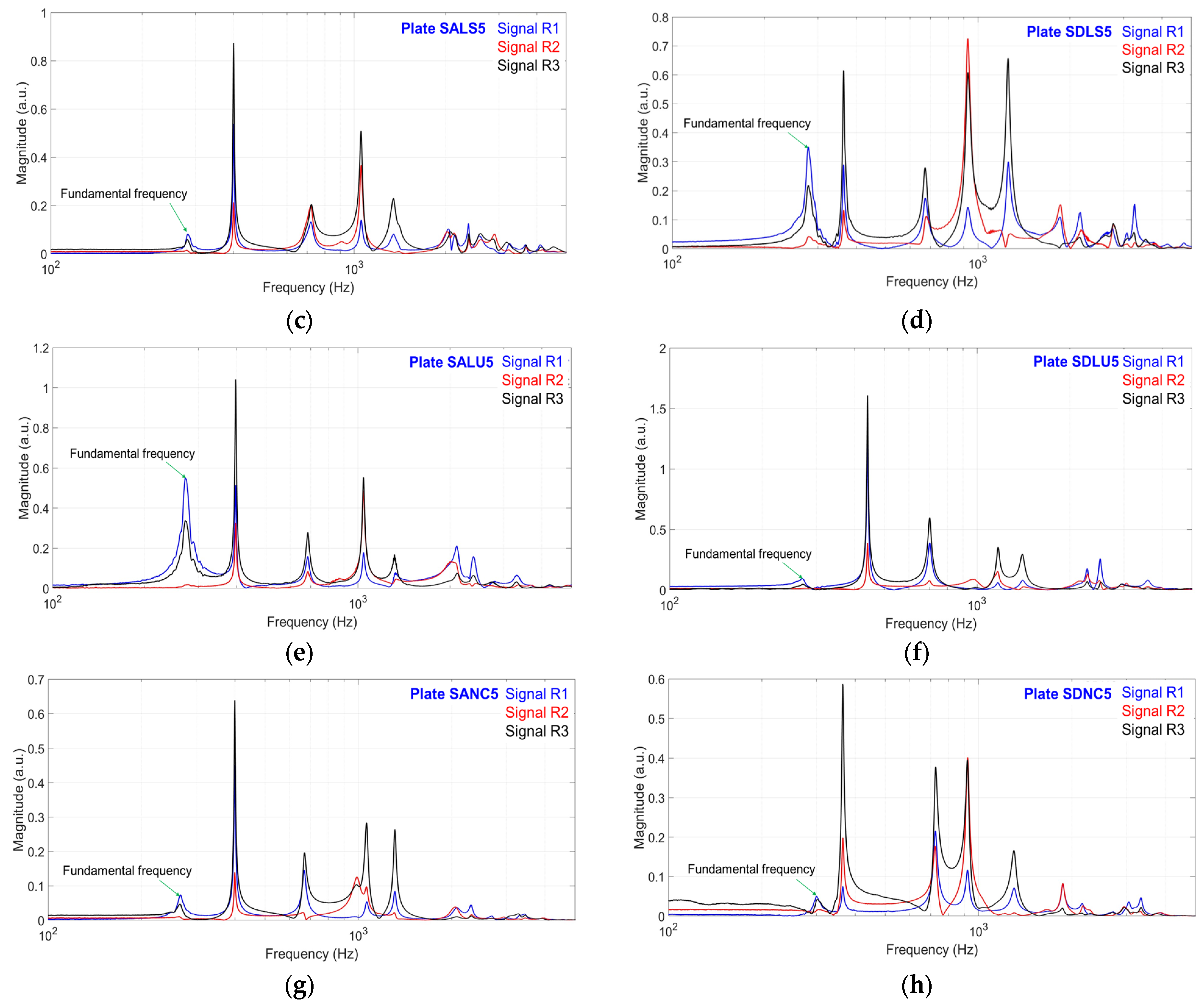
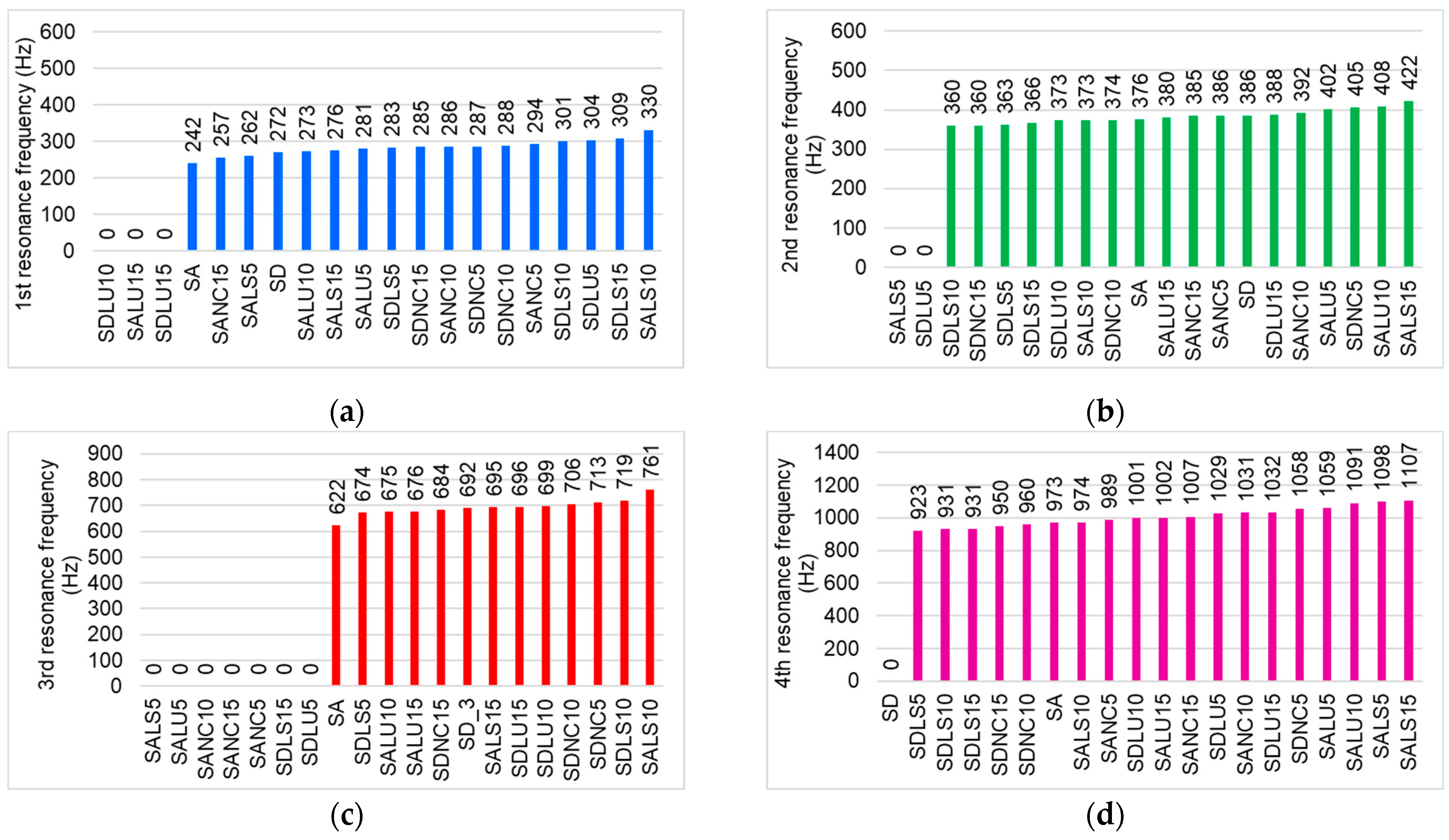
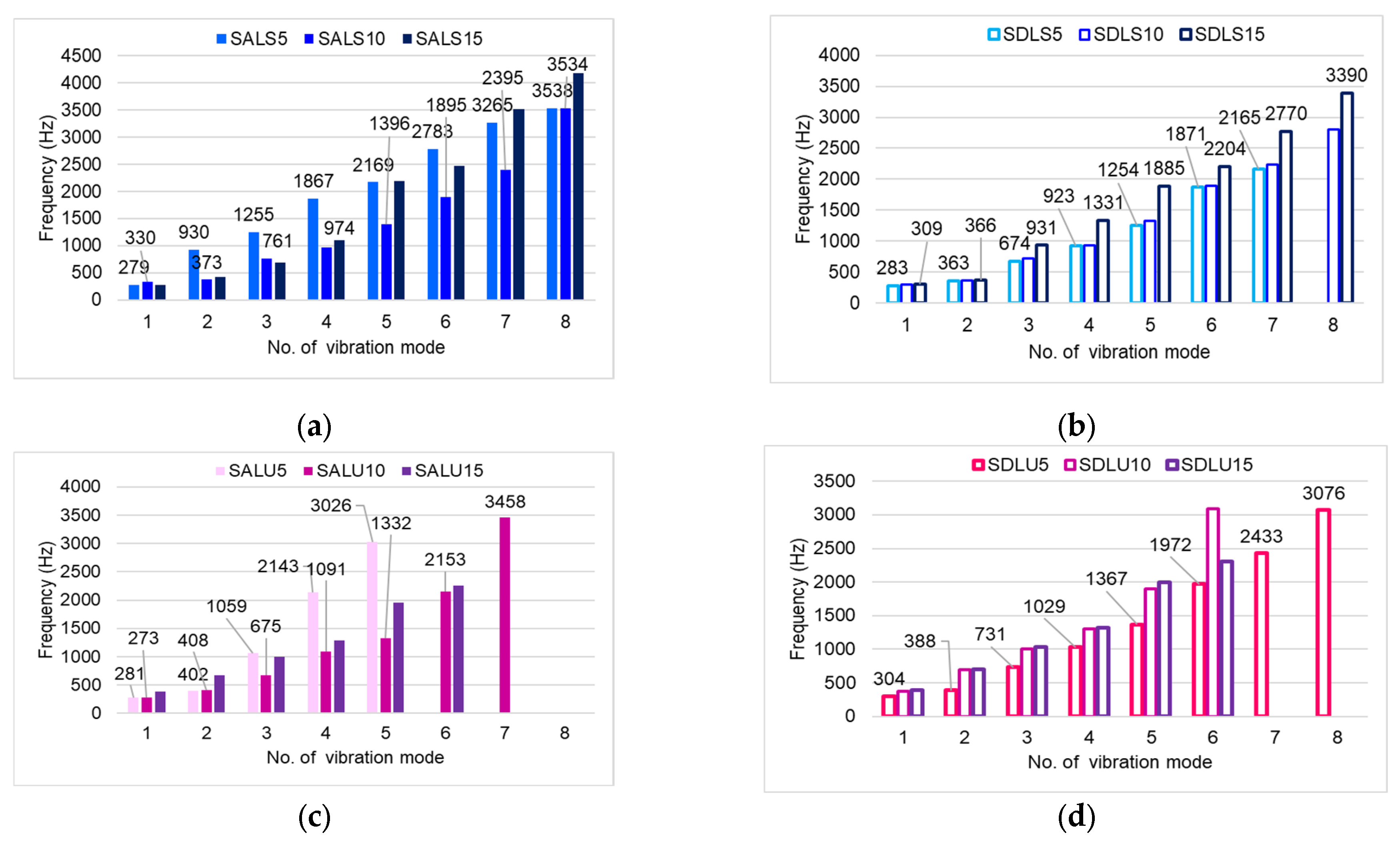
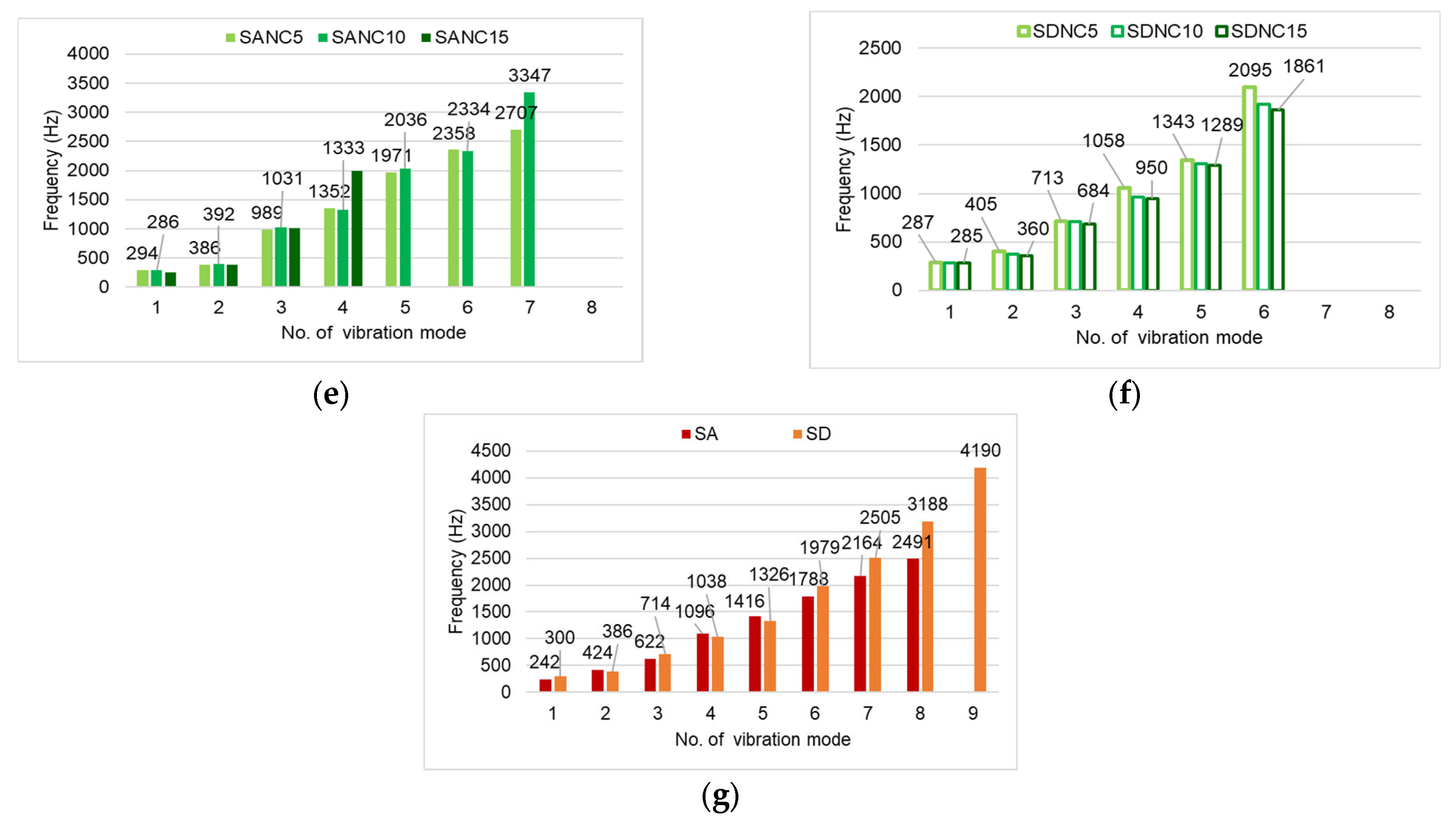
3.1. Resonance Frequencies Spectrum
3.2. Damping of Varnished Plates
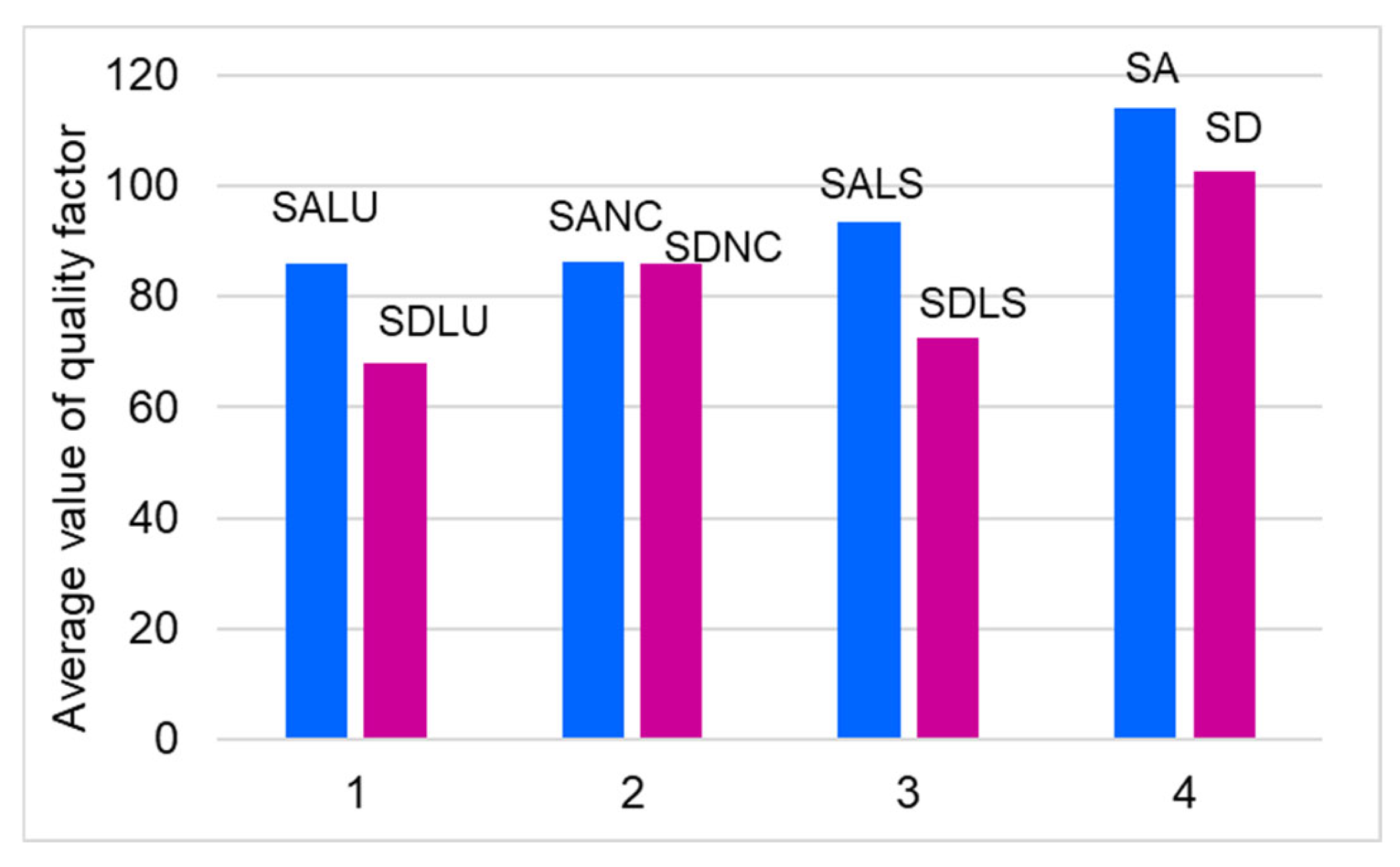
3.3. Quality Factor
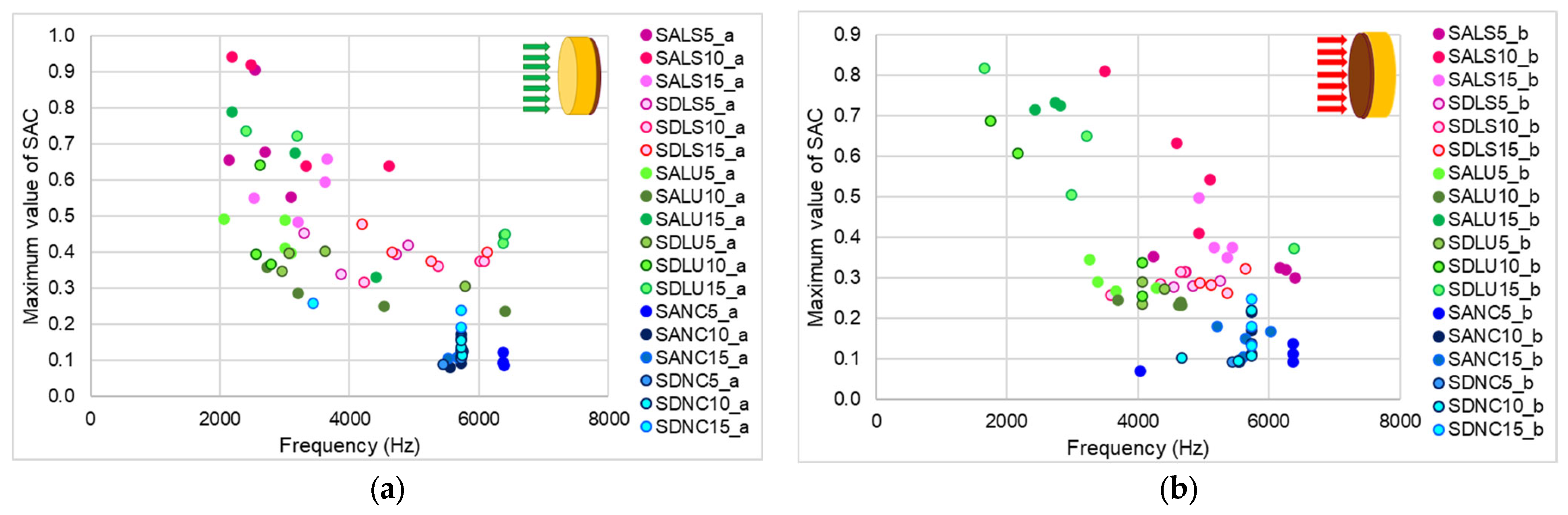
3.4. Sound Absorption Coefficient
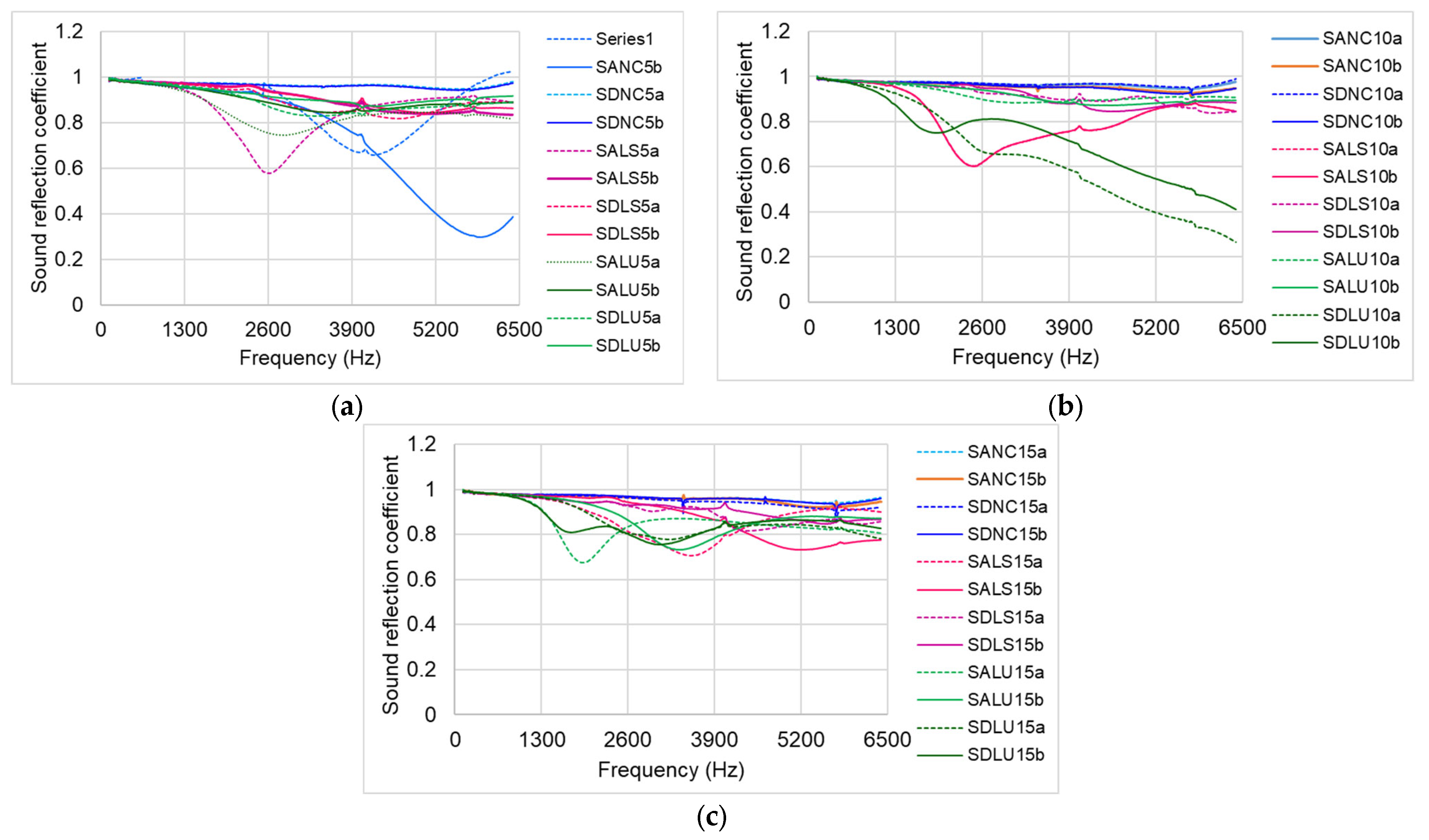
3.5. Sound Reflection Coefficient
4. Conclusions
- The varnish film alters the frequency spectrum, both in terms of the number and values of resonant frequencies, due to increased stiffness of the plates. The fundamental frequency is higher than that of unvarnished wood.
- Unvarnished spruce wood exhibits the highest quality factor (Q). The quality factor is influenced by the anatomical quality of the spruce wood in correlation with the type of varnish applied.
- The highest damping coefficient values were observed in class D spruce boards varnished with oil-based and nitrocellulose varnishes. The highest acoustic absorption coefficients were found in samples varnished with 15 layers of oil-based varnish at 2672 Hz, and in those coated with 10 layers of spirit varnish at 4650 Hz.
- The richest frequency spectrum was recorded in boards coated with spirit varnish, though all samples exhibited frequencies within the 270–3500 Hz range.
- The sound absorption of unvarnished surfaces is significantly affected by the presence of varnish on the opposite surface.
- The highest reflection coefficient values were recorded in samples varnished with nitrocellulose varnish.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bucur, V.; Archer, R.R. Elastic constants for wood by an ultrasonic method. Wood Sci. Technol. 1984, 18, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucur, V. Acoustics of Wood, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 173–196. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, L.; Fu, Q.; Si, Y.; Ding, B.; Yu, J. Porous materials for sound absorption. Compos. Commun. 2018, 10, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodhouse, J. On the Playability of violins. Part I: Reflection Functions. Acta Acust. United Acust. 1993, 78, 125–136. [Google Scholar]
- Eun-Suk, J.; Chun-Won, K. Sound absorption characteristics of three species (binuang, balsa and paulownia) of low density hardwood. Holzforschung 2021, 75, 1115–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedighi Gilani, M.; Pflaum, J.; Hartmann, S.; Kaufmann, R.; Baumgartner, M.; Schwarze, F.W.M.R. Relationship of vibro-mechanical properties and microstructure of wood and varnish interface in string instruments. Appl. Phys. A 2016, 122, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viala, R.; Placet, V.; Cogan, S. Simultaneous non-destructive identification of multiple elastic and damping properties of spruce tonewood to improve grading. J. Cult. Herit. 2020, 42, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spycher, M.; Schwarze, F.W.M.R.; Steiger, R. Assessment of resonance wood quality by comparing its physical and histological properties. Wood Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 325–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schelleng, J.C. Acoustical Effects of Violin Varnish. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1968, 44, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleske, M. Contemporary violin making. Analysis of design, materials, varnish and normal modes. Catgut Acoust. Soc. J. 2002, 4, 50–65. [Google Scholar]
- Obataya, E.; Ohno, Y.; Norimoto, M.; Tomita, B. Effects of oriental lacquer (urushi) coating on the vibrational properties of wood used for the soundboards of musical instruments. Acoust. Sci. Technol. 2001, 22, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lämmlein, S.L.; Mannes, D.; Schwarze, F.W.M.; Burgert, I.; Sedighi Gilani, M. Combined Experimental and Numerical Investigation of Vibro-Mechanical Properties of Varnished Wood for Stringed Instruments. In Model Validation and Uncertainty Quantification; Conference Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Mechanics Series; Barthorpe, R., Platz, R., Lopez, I., Moaveni, B., Papadimitriou, C., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lämmlein, S.L.; Van Damme, B.; Mannes, D.; Schwarze, F.W.M.; Burgert, I. Violin varnish induced changes in the vibro-mechanical properties of spruce and maple wood. Holzforschung 2020, 74, 765–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lämmlein, S.; Künniger, T.; Rüggeberg, M.; Schwarze, F.W.M.R.; Mannes, D.; Burgert, I. Frequency dependent mechanical properties of violin varnishes and their im-pact on vibro-mechanical tonewood properties. Results Mater. 2020, 9, 100137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echard, J.P.; Lavédrine, B. Review on the characterization of ancient stringed musical instruments varnishes and implementation of an analytical strategy. J. Cult. Herit. 2008, 9, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, W.Y. SHP Studies on the vibrational modal analysis of solid woods for making the violin—Part 2. The effects of coating materials on the resonant frequency of European spruce and maple. Korea Furnit. Soc. 2000, 11, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Woodhouse, J. The acoustics of “A0-B0 mode matching” in the violin. Acust. Acta Acust. 1998, 84, 947–956. [Google Scholar]
- Gough, C. The violin. Chladni patterns, plates, shells and sounds. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2007, 14, 77–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissinger, G. Structural acoustics of good and bad violins. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2008, 124, 1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali Ahmed, S.; Adamopoulos, S. Acoustic properties of modified wood under different humid conditions and their relevance for musical instruments. Appl. Acoust. 2018, 140, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, T. Effects of varnishing on acoustic characteristics of wood used for musical instrument soundboards. J. Acoust. Soc. Jpn. 1993, 14, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrodzka, E.B.; Linde, B.B.J.; Krupa, A. Modal parameters of two violins with different varnish layers and subjective evaluation of their sound quality. Arch. Acoust. 2013, 38, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucur, V. Chapter 3—Mechanical Characterization of Materials for String Instruments. In Handbook of Materials for String Musical Instruments; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 93–132. [Google Scholar]
- Bucur, V. Chapter 8—Ageing of musical instruments—About the old and new instruments. In Handbook of Materials for String Musical Instruments; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 325–372. [Google Scholar]
- Stanciu, M.D.; Nastac, S.M.; Savin, A. Comparison Between Acoustic Spectral Evolutions of Violins Before and After Varnishing. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference Interdisciplinarity in Engineering, Târgu Mureș, Romania, 6–7 October 2022; Inter-Eng 2022, Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems. Moldovan, L., Gligor, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; Volume 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, C.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Miao, H.; Zhou, L.; Liu, F. Experimental and Theoretical Modal Analysis of Full-Sized Wood Composite Panels Supported on Four Nodes. Materials 2017, 10, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guiman, M.V.; Stanciu, M.D.; Nastac, S.M.; Gliga, V.G.; Savin, A. Free Vibration Analysis of Orthotropic Thin Rectangular Plates. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference Interdisciplinarity in Engineering, Târgu Mureș, Romania, 5–6 October 2023; Inter-ENG 2023, Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems. Moldovan, L., Gligor, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; Volume 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, N.; Sheldon, R.; Johnston, J.A. Recreation of the Particulate Ground Varnish Layer Used on Many Violins Made before 1750. J. Violin. Soc. Am. VSA Pap. 2007, XXI, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Y.; Guan, W. Sound Absorption Characteristics of Unsaturated Porous Material Calculated by Modified Transfer Matrix Method. Buildings 2024, 14, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Fang, X.; Han, J.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, J. Effect of Coating Thickness on Sound Absorption Property of Four Wood Species Commonly Used for Piano Soundboards. Wood Fiber Sci. 2020, 52, 28–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinulică, F.; Stanciu, M.D.; Savin, A. Correlation between Anatomical Grading and Acoustic–Elastic Properties of Resonant Spruce Wood Used for Musical Instruments. Forests 2021, 12, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanciu, M.D.; Cosnita, M.; Gliga, G.V.; Gurau, L.; Timar, C.M.; Guiman, M.V.; Năstac, S.M.; Roșca, I.C.; Bucur, V.; Dinulică, F. Tunable Acoustic Properties Using Different Coating Systems on Resonance Spruce Wood. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 1, 2300781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanciu, M.D.; Dinulica, F.; Bucur, V.; Gliga, G.V.; Nastac, S.M.; Campean, M. Changing the vibrational behavior of the wooden thin arched plates—The maestro violins experimental study case. Thin-Walled Struct. 2022, 174, 109042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, X.; He, L.; Wan, K.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, J.; Miao, Y.; Liu, Z. The Changes of Acoustic Vibration Properties of Spruce Wood During the Multi-Layered Alcohol Varnish Coating Process. Forests 2024, 15, 2212. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 11654:1997; Acoustics: Sound Absorbers for Use in Buildings. Rating of Sound Absorption. International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 1997.
- ISO 10534:1998; Acoustics—Determination of Sound Absorption Coefficient and Impedance in Impedance Tubes: Part 1: Method Using Standing Wave Ratio, Part 2: Transfer-Function Method. International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 1998.
- ASTM E1050:1998; Standard Test Method for Impedance and Absorption of Acoustical Materials Using a Tube, Two Microphones and a Digital Frequency Analysis System. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1998.
- Akar, Ö.; Willner, K. Investigating the modal behavior of a violin top and a back plate. In Proceedings of the 40th IMAC, A Conference and Exposition on Structural Dynamics, Orlando, FL, USA, 7–10 February 2022; Topics in Modal Analysis & Parameter Identification. Volume 8, pp. 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Yazdkhasti, A.; Mao, Y.; Siciliano, A.P.; Dai, J.; Jing, S.; Xie, H.; Li, Z. A scalable High-Porosity Wood for Sound Absorption and Thermal Insulation. Nat. Sustain. 2023, 6, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Physical Features | Grade/Average Value/STDV | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | STDV | D | STDV | |
| Annual rings width (mm) | 0.71 | 0.005 | 2.28 | 0.005 |
| Early wood width (mm) | 0.54 | 0.011 | 1.74 | 0.029 |
| Late wood width (mm) | 0.18 | 0.013 | 0.54 | 0.026 |
| Early wood proportion (%) | 74.97 | 1.519 | 76.36 | 1.138 |
| Late wood proportion (%) | 25.03 | 1.519 | 23.64 | 1.136 |
| Density ρ (kg/m3) | 409.5 | 28.50 | 420.00 | 26.00 |
| Type of Varnished Samples | No. of Samples | Thickness of Varnish Layer (μm) | Mass (g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SALU5 | 4 | 40 ± 10 | 1.146 |
| SALS5 | 1.167 | ||
| SANC5 | 1.348 | ||
| SALU10 | 4 | 80 ± 10 | 1.322 |
| SALS10 | 1.188 | ||
| SANC10 | 1.449 | ||
| SALU15 | 4 | 130 ± 10 | 1.376 |
| SALS15 | 1.327 | ||
| SANC15 | 1.517 | ||
| SDLU5 | 4 | 35 ± 10 | 1.186 |
| SDLS5 | 1.125 | ||
| SDNC5 | 1.144 | ||
| SDLU10 | 4 | 70 ± 10 | 1.258 |
| SDLS10 | 1.168 | ||
| SDNC10 | 1.215 | ||
| SDLU15 | 4 | 120 ± 10 | 1.337 |
| SDLS15 | 1.189 | ||
| SDNC15 | 1.443 |
| Samples | Average Value of Damping & STDV | Minimum Value of Damping tan δ | Frequency (Hz) for Minim tan δ | Maximum Value of Damping tan δ | Frequency (Hz) for Maxim tan δ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SA | 0.023 (0.0099) | 0.007 | 425 | 0.041 | 319 |
| SALS5 | 0.035 (0.0090) | 0.020 | 3265 | 0.050 | 279 |
| SALS10 | 0.024 (0.0083) | 0.008 | 373 | 0.033 | 330 |
| SALS15 | 0.027 (0.0120) | 0.009 | 422 | 0.040 | 276 |
| SALU5 | 0.031 (0.0180) | 0.010 | 402 | 0.060 | 2143 |
| SALU10 | 0.032 (0.0160) | 0.012 | 408 | 0.059 | 273 |
| SALU15 | 0.032 (0.0110) | 0.013 | 380 | 0.045 | 1290 |
| SANC5 | 0.026 (0.0080) | 0.010 | 386 | 0.035 | 989 |
| SANC10 | 0.034 (0.0180) | 0.010 | 392 | 0.057 | 2036 |
| SANC15 | 0.028 (0.0130) | 0.016 | 385 | 0.043 | 257 |
| SD | 0.028 (0.0100) | 0.009 | 446 | 0.040 | 300 |
| SDLS5 | 0.028 (0.0100) | 0.011 | 363 | 0.042 | 283 |
| SDLS10 | 0.031 (0.0150) | 0.011 | 360 | 0.057 | 1324 |
| SDLS15 | 0.033 (0.0033) | 0.027 | 931 | 0.036 | 1331 |
| SDLU5 | 0.032 (0.0190) | 0.015 | 388 | 0.072 | 1972 |
| SDLU10 | 0.034 (0.0180) | 0.013 | 373 | 0.063 | 1896 |
| SDLU15 | 0.034 (0.0097) | 0.015 | 388 | 0.042 | 1995 |
| SDNC5 | 0.030 (0.0140) | 0.010 | 405 | 0.045 | 287 |
| SDNC10 | 0.032 (0.0170) | 0.011 | 374 | 0.063 | 288 |
| SDNC15 | 0.036 (0.0190) | 0.016 | 950 | 0.063 | 285 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stanciu, M.D.; Guiman, M.V.; Năstac, S.M. New Challenges in Assessment of the Acoustic Properties of Coating Polymers. Polymers 2025, 17, 1418. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101418
Stanciu MD, Guiman MV, Năstac SM. New Challenges in Assessment of the Acoustic Properties of Coating Polymers. Polymers. 2025; 17(10):1418. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101418
Chicago/Turabian StyleStanciu, Mariana Domnica, Maria Violeta Guiman, and Silviu Marian Năstac. 2025. "New Challenges in Assessment of the Acoustic Properties of Coating Polymers" Polymers 17, no. 10: 1418. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101418
APA StyleStanciu, M. D., Guiman, M. V., & Năstac, S. M. (2025). New Challenges in Assessment of the Acoustic Properties of Coating Polymers. Polymers, 17(10), 1418. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101418








