Development and Characterization of Adeno-Associated Virus-Loaded Coaxial Electrospun Scaffolds for Potential Viral Vector Delivery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
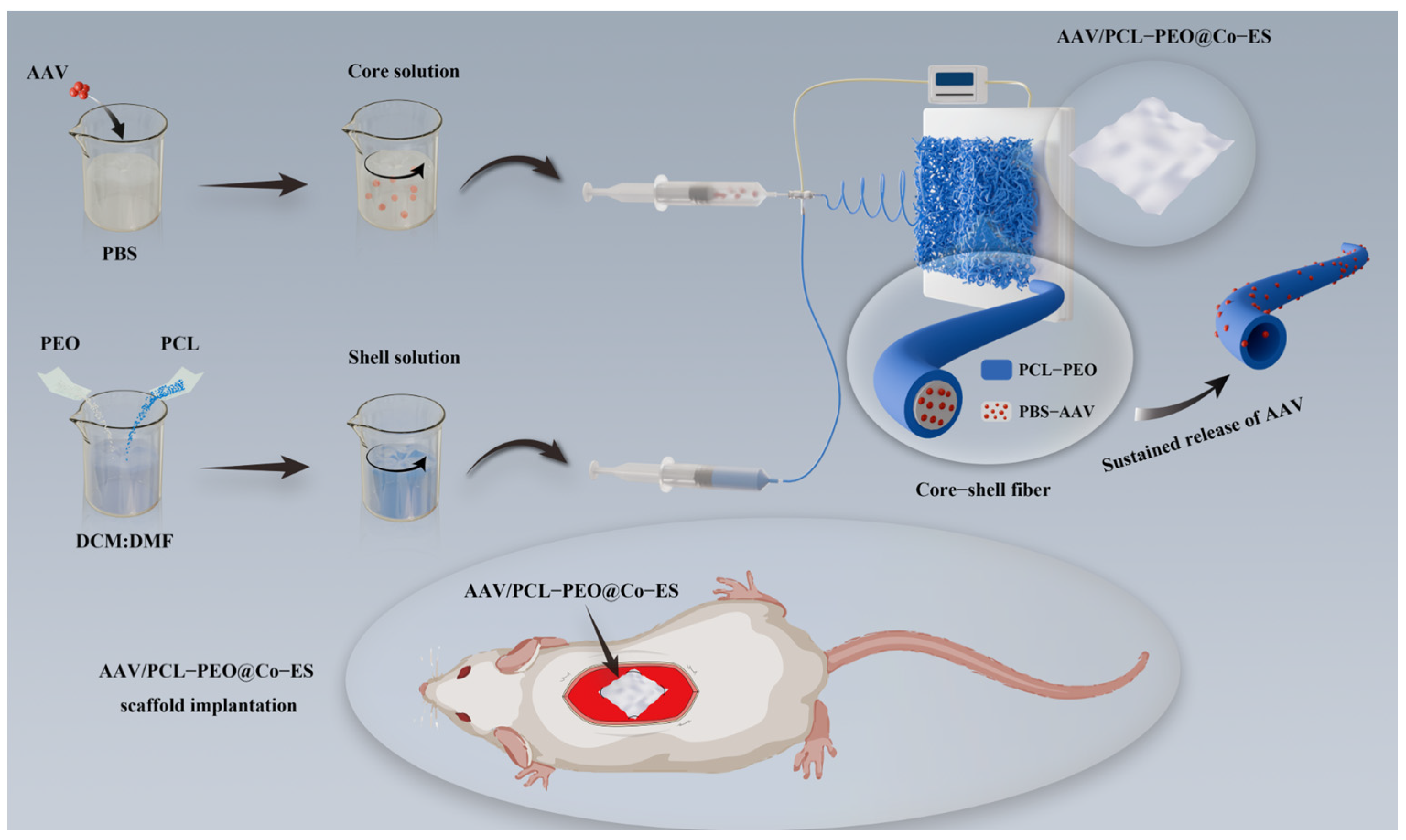
2.2. Fabrication of AAV-Loaded Scaffolds
2.3. Characterization of the Physicochemical Properties of the Scaffold
2.3.1. Micromorphology Characterization
2.3.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Analysis
2.3.3. Mechanical Properties Tests
2.3.4. Surface Wettability Analysis
2.3.5. Degradation Performance Tests
2.4. Cell Characterization of the Scaffold
2.4.1. Cell Culture
2.4.2. Cell Adhesion Assay
2.4.3. Cell Proliferation Assay
2.5. In Vitro AAV Release and Cell Transduction Assay
2.5.1. AAV Release in the Scaffold Leaching Solution
2.5.2. Cell Transduction
2.6. In Vivo Animal Experiment
2.6.1. AAV-Loaded Scaffold Implantation
2.6.2. Histological Examinations
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of the Physicochemical Properties of the Scaffold
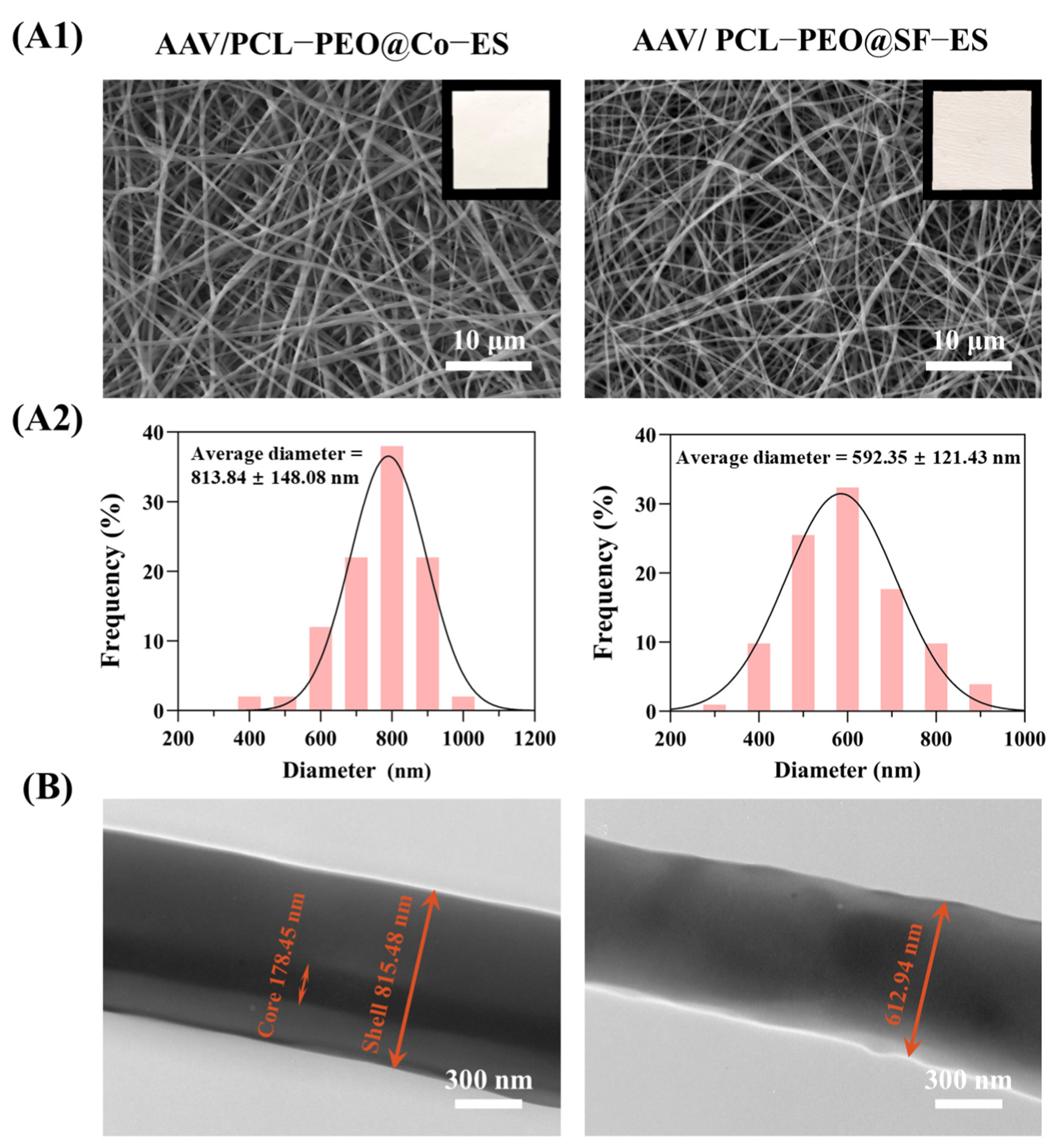
3.1.1. Micromorphology Characterization
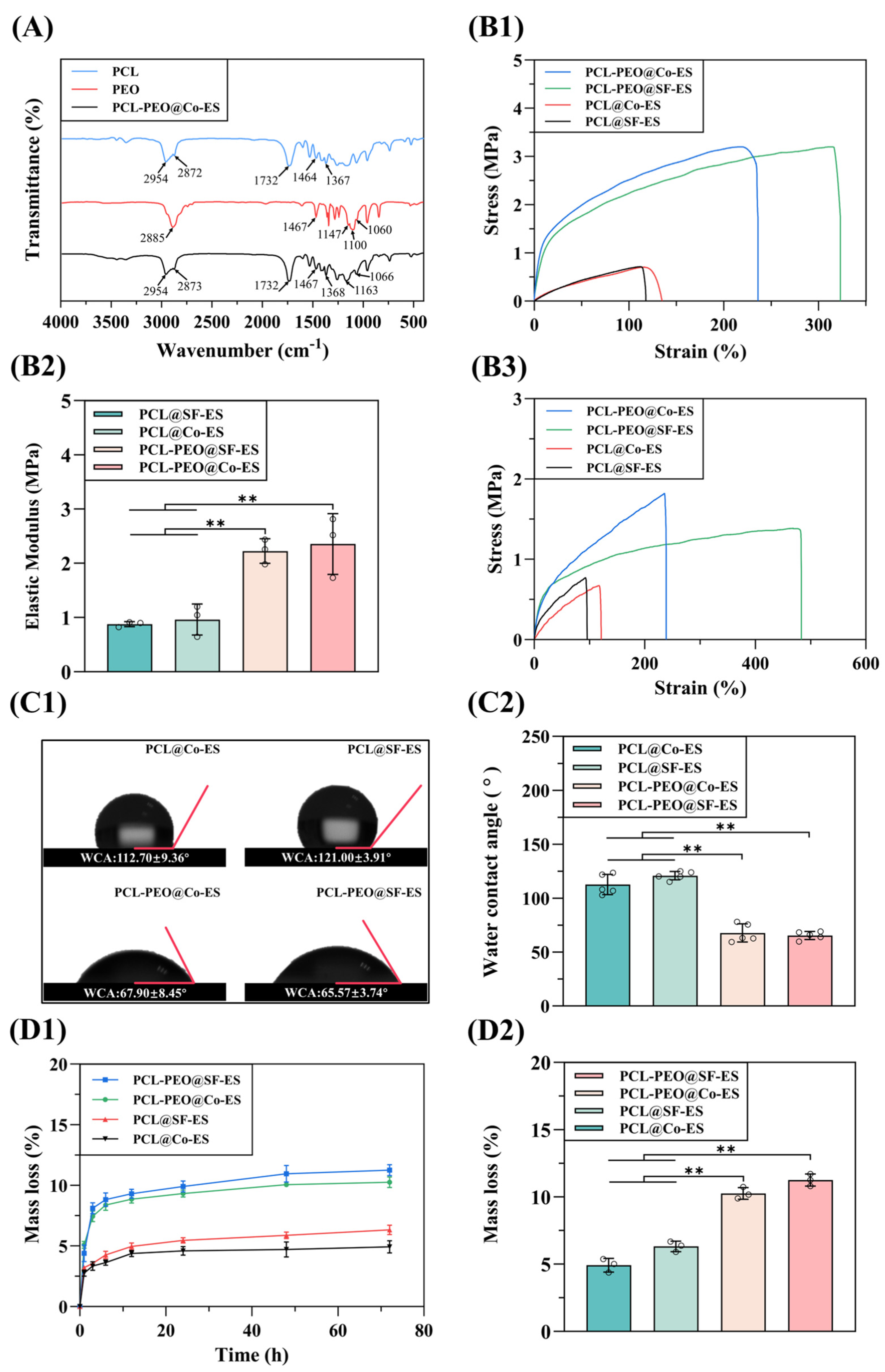
3.1.2. FTIR Analysis
3.1.3. Mechanical Properties Evaluation
3.1.4. Surface Wettability Analysis
3.1.5. Degradation Performance Tests
3.2. Cell Characterization of Scaffold
3.2.1. Cell Adhesion Analysis
3.2.2. Cell Proliferation Assay
3.3. In Vitro AAV Release and Cell Transduction Assay
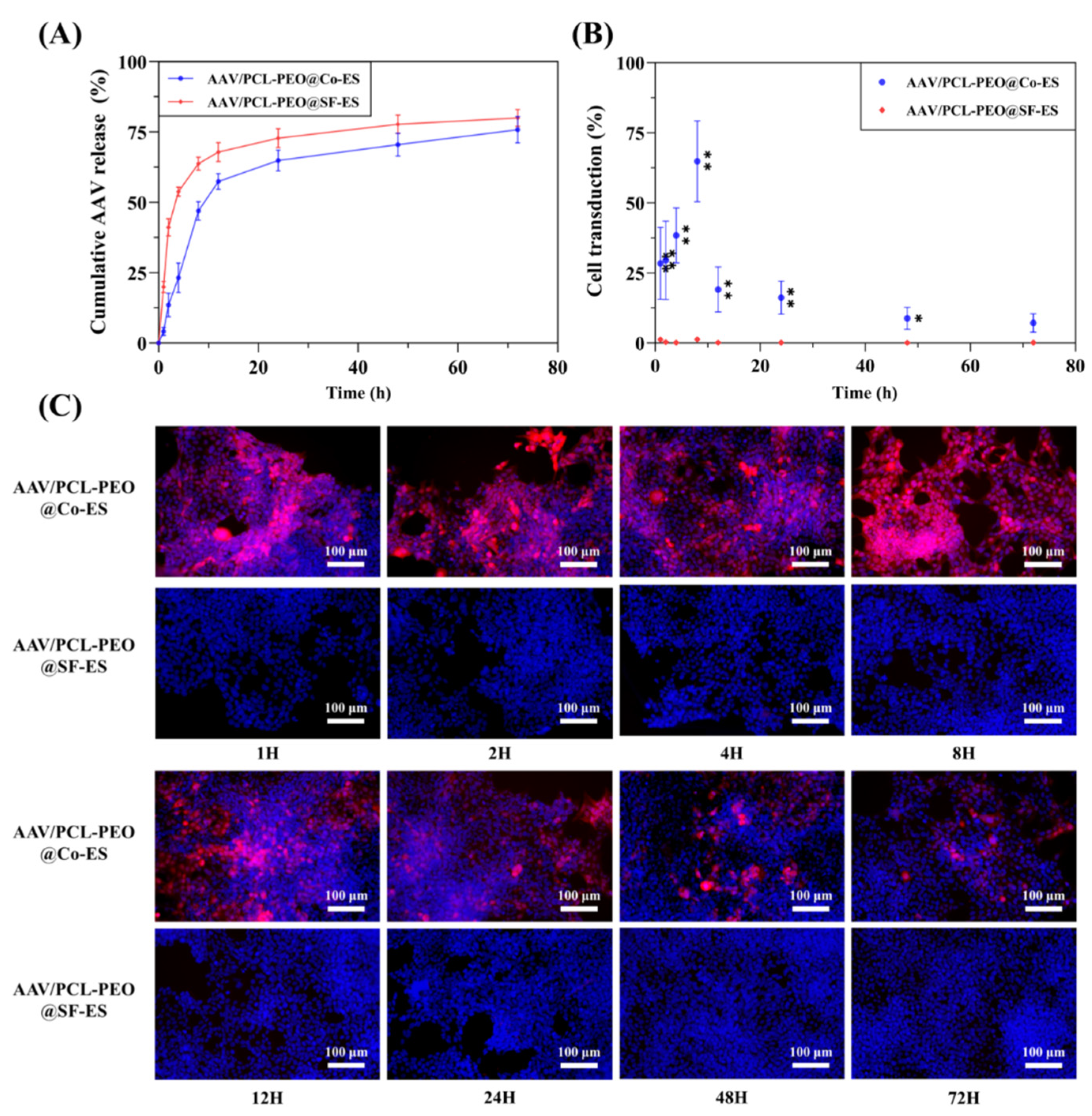
3.3.1. Quantitative Analysis of AAV Release
3.3.2. Cell Transduction
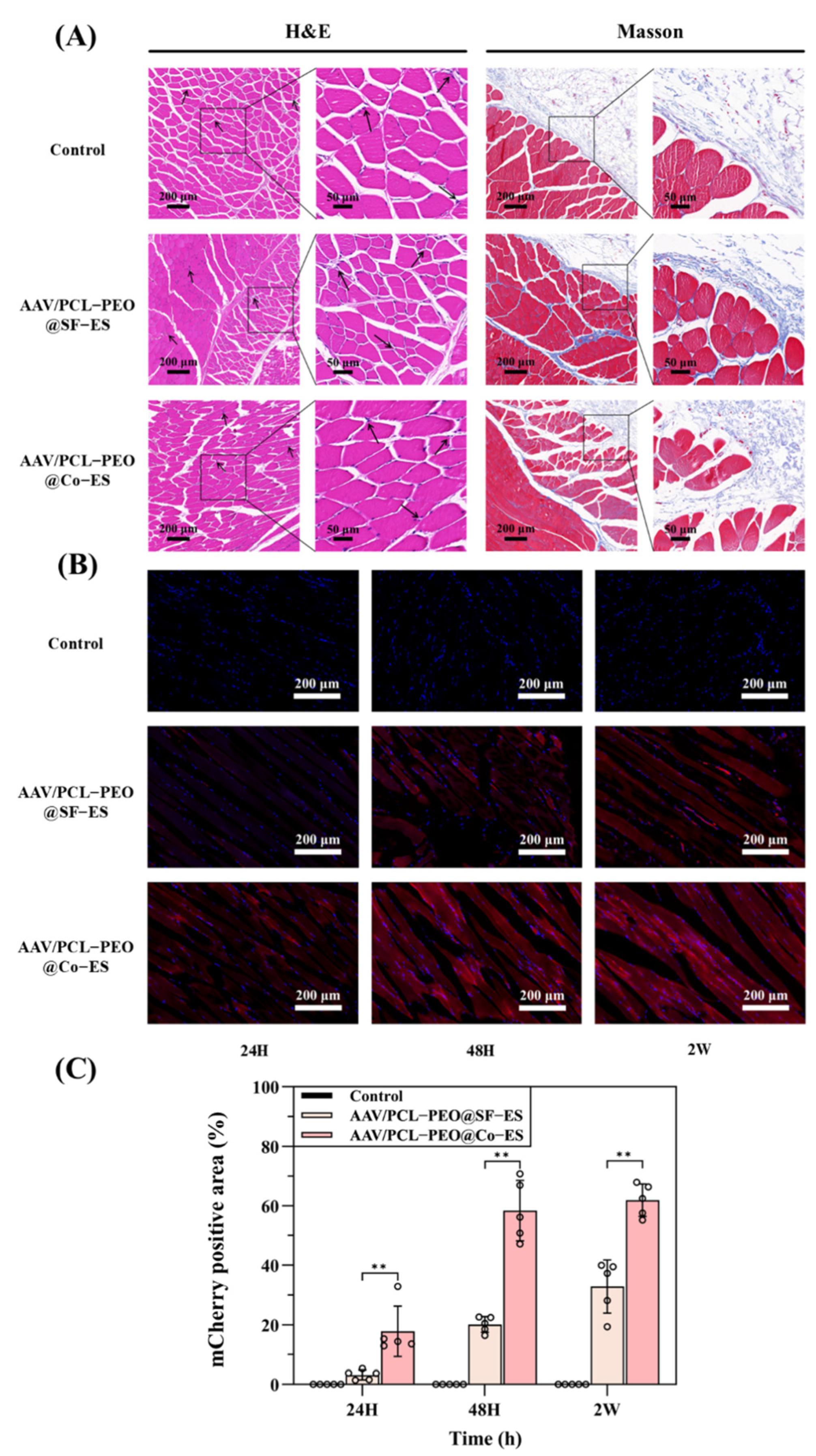
3.4. Histological Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AAV | adeno-associated virus |
| PCL | polycaprolactone |
| PEO | polyethylene oxide |
| WCA | water contact angle |
| ECM | extracellular matrix |
| SF-ES | single-fluid electrospinning |
| ELP | elastin-like polypeptide |
| Co-ES | coaxial electrospinning |
| PEUU | polyester urethane urea |
| PEEUU | polyester ether urethane urea |
| FBGC | foreign body giant cells |
| SD | Sprague Dawley |
| DCM | dichloromethane |
| DMF | N, N dimethylformamide |
| PBS | phosphate-buffered saline |
| SEM | scanning electron microscopy |
| TEM | transmission electron microscopy |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared spectrometer |
| HUVECs | human umbilical vein endothelial cells |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium |
| FBS | fetal bovine serum |
| CCK-8 | cell counting kit-8 |
| H&E | hematoxylin and eosin |
| Masson | Masson’s trichrome |
| SD | standard deviation |
| ANOVA | analysis of variance |
References
- High, K.A.; Roncarolo, M.G. Gene Therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Veroniaina, H.; Su, N.; Sha, K.; Jiang, F.; Wu, Z.; Qi, X. Applications and developments of gene therapy drug delivery systems for genetic diseases. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 16, 687–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quadir, S.S.; Choudhary, D.; Singh, S.; Choudhary, D.; Chen, M.-H.; Joshi, G. Genetic frontiers: Exploring the latest strategies in gene delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 101, 106316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shao, W. Innate Immune Response to Viral Vectors in Gene Therapy. Viruses 2023, 15, 1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atasoy-Zeybek, A.; Kose, G.T. Gene Therapy Strategies in Bone Tissue Engineering and Current Clinical Applications. In Cell Biology and Translational Medicine, Vol 4: Stem Cells and Cell Based Strategies in Regeneration; Turksen, K., Ed.; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 1119, pp. 85–101. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.-H.; Gessler, D.J.; Zhan, W.; Gallagher, T.L.; Gao, G. Adeno-associated virus as a delivery vector for gene therapy of human diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Anselmo, A.C.; Mitragotri, S. Viral vector-based gene therapies in the clinic. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2022, 7, e10258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Le, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Nian, X.; Liu, B.; Yang, X. Viral Vector-Based Gene Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirley, J.L.; de Jong, Y.P.; Terhorst, C.; Herzog, R.W. Immune Responses to Viral Gene Therapy Vectors. Mol. Ther. 2020, 28, 709–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, M.H.; Zaman, M.; Ahmad, A.; Khan, R.; Mallhi, T.H.; Hasan, M.M.; Khan, Y.H.; Hafeez, S.; Massoud, E.E.S.; Rahman, M.H.; et al. Appraisal for the Potential of Viral and Nonviral Vectors in Gene Therapy: A Review. Genes 2022, 13, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rincon, M.Y.; VandenDriessche, T.; Chuah, M.K. Gene therapy for cardiovascular disease: Advances in vector development, targeting, and delivery for clinical translation. Cardiovasc. Res. 2015, 108, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Meel, R.; Vehmeijer, L.J.C.; Kok, R.J.; Storm, G.; van Gaal, E.V.B. Ligand-targeted particulate nanomedicines undergoing clinical evaluation: Current status. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 1284–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selkirk, S.M. Gene therapy in clinical medicine. Postgrad. Med. J. 2004, 80, 560–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, J.K.; Krol, A.; Li, Y.P.; Li, C.Y.; Yuan, F. Systemic dissemination of viral vectors during intratumoral injection. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2003, 2, 1233–1242. [Google Scholar]
- Hadjizadeh, A.; Ghasemkhah, F.; Ghasemzaie, N. Polymeric Scaffold Based Gene Delivery Strategies to Improve Angiogenesis in Tissue Engineering: A Review. Polym. Rev. 2017, 57, 505–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Bruggeman, K.F.; Franks, S.; Gautam, V.; Hodgetts, S.I.; Harvey, A.R.; Williams, R.J.; Nisbet, D.R. Is Viral Vector Gene Delivery More Effective Using Biomaterials? Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2001238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer, S.J.; Hilfinger, J.M.; Davidson, B.L. Extended release of adenovirus from polymer microspheres: Potential use in gene therapy for brain tumors. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1997, 27, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, M.E.; Shin, S.; Shea, L.D. Fibrin hydrogels for lentiviral gene delivery in vitro and in vivo. J. Control. Release 2012, 157, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puhl, D.L.; Mohanraj, D.; Nelson, D.W.; Gilbert, R.J. Designing electrospun fiber platforms for efficient delivery of genetic material and genome editing tools. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2022, 183, 114161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Sun, Y.; Yang, F.; van den Beucken, J.J.J.P.; Fan, M.; Chen, Z.; Jansen, J.A. Bioactive Electrospun Scaffolds Delivering Growth Factors and Genes for Tissue Engineering Applications. Pharm. Res. 2011, 28, 1259–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Jin, G.; Jang, J.-H. Electrospun nanofibers as versatile interfaces for efficient gene delivery. J. Biol. Eng. 2014, 8, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Milbreta, U.; Chin, J.S.; Pinese, C.; Lin, J.; Shirahama, H.; Jiang, W.; Liu, H.; Mi, R.; Hoke, A.; et al. Biomimicking Fiber Scaffold as an Effective In Vitro and In Vivo MicroRNA Screening Platform for Directing Tissue Regeneration (vol 6, 1800808, 2019). Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2201954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zulkifli, M.Z.A.; Nordin, D.; Shaari, N.; Kamarudin, S.K. Overview of Electrospinning for Tissue Engineering Applications. Polymers 2023, 15, 2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuno, K.; Suzuki, K.; Sakai, S. Transduction and Genome Editing of the Heart with Adeno-Associated Viral Vectors Loaded onto Electrospun Polydioxanone Nonwoven Fabrics. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Son, Y.-W.; Hwang, K.; Park, H.-W.; Kim, Y.; Kim, M.; Shin, J.E.; Park, K.I.; Lee, S.; Jang, J.-H. Synergistic Enhancement of Adeno-Associated Virus-Mediated In Vivo Direct Neuronal Reprogramming by Spatially Aligned Fibrous Matrices in Spinal Cord Injury Models. Adv. Ther. 2023, 6, 2300040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, J.-S.; Chu, H.S.; Kim, G.-W.; Won, J.-I.; Jang, J.-H. Electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds for controlled release of adeno-associated viral vectors. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 3868–3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Matsumura, Y.; Tang, Y.; Roy, S.; Hoff, R.; Wang, B.; Wagner, W.R. Sustained viral gene delivery from a micro-fibrous, elastomeric cardiac patch to the ischemic rat heart. Biomaterials 2017, 133, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharon, D.; Kamen, A. Advancements in the design and scalable production of viral gene transfer vectors. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2018, 115, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayerossadat, N.; Maedeh, T.; Ali, P.A. Viral and nonviral delivery systems for gene delivery. Adv. Biomed. Res. 2012, 1, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pupo, A.; Fernandez, A.; Low, S.H.; Francois, A.; Suarez-Amaran, L.; Samulski, R.J. AAV vectors: The Rubik’s cube of human gene therapy. Mol. Ther. 2022, 30, 3515–3541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hezi-Yamit, A.; Sullivan, C.; Wong, J.; David, L.; Chen, M.; Cheng, P.; Shumaker, D.; Wilcox, J.N.; Udipi, K. Impact of polymer hydrophilicity on biocompatibility: Implication for DES polymer design. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2009, 90A, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.A.; Chang, D.T.; Meyerson, H.; Colton, E.; Kwon, I.K.; Matsuda, T.; Anderson, J.M. Proteomic analysis and quantification of cytokines and chemokines from biomaterial surface-adherent macrophages and foreign body giant cells. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2007, 83A, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitxelena-Iribarren, O.; Riera-Pons, M.; Pereira, S.; Jose Calero-Castro, F.; Castillo Tunon, J.M.; Padillo-Ruiz, J.; Mujika, M.; Arana, S. Drug-loaded PCL electrospun nanofibers as anti-pancreatic cancer drug delivery systems. Polym. Bull. 2023, 80, 7763–7778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Hu, Q.; Liu, S.; Yao, G.; Zhang, H. Electrospinning drug-loaded polycaprolactone/polycaprolactone-gelatin multi-functional bilayer nanofibers composite scaffold for postoperative wound healing of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Biomed. Technol. 2024, 8, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, S.M.; Paiva, I.M.; Vakili, M.R.; Soudy, R.; Agopsowicz, K.; Soleimani, A.H.; Hitt, M.; Kaur, K.; Lavasanifar, A. Traceable PEO-poly(ester) micelles for breast cancer targeting: The effect of core structure and targeting peptide on micellar tumor accumulation. Biomaterials 2017, 144, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asghari, F.; Faradonbeh, D.R.; Malekshahi, Z.V.; Nekounam, H.; Ghaemi, B.; Yousefpoor, Y.; Ghanbari, H.; Faridi-Majidi, R. Hybrid PCL/chitosan-PEO nanofibrous scaffolds incorporated with A. euchroma extract for skin tissue engineering application. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 278, 118926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Tang, W.; Song, Y.; Zhang, H. Preparation and characterization of drug-loaded coaxial electrospun nanofibers membranes with pH-responsive and antibacterial properties. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2025, 104, 106533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Song, Y.; Shi, H.; Yang, D.; Zhang, H.; Gu, Y. 3D printing/electrospinning of a bilayered composite patch with antibacterial and antiadhesive properties for repairing abdominal wall defects. J. Mater. Chem. B 2024, 12, 10054–10067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Hu, Q.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Jia, L.; Hu, X.; Huang, C.; Zhang, H. 3D printed biomimetic composite scaffolds with sequential releasing of copper ions and dexamethasone for cascade regulation of angiogenesis and osteogenesis. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 496, 153662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Hu, Q.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Yao, G. Electrospinning/3D printing drug-loaded antibacterial polycaprolactone nanofiber/sodium alginate-gelatin hydrogel bilayer scaffold for skin wound repair. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 275, 129705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahani, E.; Mianehro, A. Electrospun scaffold based on poly(ethylene oxide)/poly(ε-caprolactone) for prolonged intravaginal antiviral drug release. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 88, 104856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupka, V.; Dvorakova, E.; Manakhov, A.; Michlicek, M.; Petrus, J.; Vojtova, L.; Zajickova, L. Well-Blended PCL/PEO Electrospun Nanofibers with Functional Properties Enhanced by Plasma Processing. Polymers 2020, 12, 1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, T.; Ramakrishna, S.; Liu, Y. Progress of Improving Mechanical Strength of Electrospun Nanofibrous Membranes. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2020, 305, 2000230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Hu, H. Spacer fabric-based exuding wound dressing—Part II: Comparison with commercial wound dressings. Text. Res. J. 2017, 87, 1481–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Wu, J.; Zhang, H.; Dong, W.; Gu, Y.; Liu, S. Designing Double-Layer Multimaterial Composite Patch Scaffold with Adhesion Resistance for Hernia Repair. Macromol. Biosci. 2022, 22, 2100510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abadi, B.; Goshtasbi, N.; Bolourian, S.; Tahsili, J.; Adeli-Sardou, M.; Forootanfar, H. Electrospun hybrid nanofibers: Fabrication, characterization, and biomedical applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 986975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondesert, H.; Bossard, F.; Favier, D. Anisotropic electrospun honeycomb polycaprolactone scaffolds: Elaboration, morphological and mechanical properties. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2021, 113, 104124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.T.; Hu, Q.X.; Liu, Q.; Liu, S.H.; Wang, Y.H.; Zhang, H.G. Design and fabrication of drug-loaded alginate/hydroxyapatite/collagen composite scaffolds for repairing infected bone defects. J. Mater. Sci. 2023, 58, 911–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steyaert, I.; Van der Schueren, L.; Rahier, H.; de Clerck, K. An Alternative Solvent System for Blend Electrospinning of Polycaprolactone/Chitosan Nanofibres. Macromol. Symp. 2012, 321, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoolaert, E.; Steyaert, I.; Vancoillie, G.; Geltmeyer, J.; Lava, K.; Hoogenboom, R.; De Clerck, K. Blend electrospinning of dye-functionalized chitosan and poly(ε-caprolactone): Towards biocompatible pH-sensors. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 4507–4516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Lin, H.; Tang, Y.; Xiang, S.; Xue, J.; Yin, W.; Tan, J.; Peng, H.; Alexander, P.G.; Tuan, R.S.; et al. Injectable BMP-2 gene-activated scaffold for the repair of cranial bone defect in mice. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2020, 9, 1631–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, H.; Wang, C.-H. Fabrication and characterization of PLGA/HAp scaffolds for delivery of BMP-2 plasmid composite DNA. J. Control. Release 2007, 120, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Hu, Q.; Liu, S.; Zhang, H. Synergy of engineered gelatin methacrylate-based porous microspheres and multicellular assembly to promote osteogenesis and angiogenesis in bone tissue reconstruction. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 283, 137228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Go, N.; Ahn, C.; Lee, J.Y. Enhancing transduction efficiency of adeno-associated virus 9 by cell line engineering: Implication for gene therapy potency assay. Biotechnol. Bioprocess. Eng. 2024, 29, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Zhou, B.; Dong, W.; Song, Y.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Yu, M.; Zhu, G.; Sun, Y.; Feng, J. Development and Characterization of Adeno-Associated Virus-Loaded Coaxial Electrospun Scaffolds for Potential Viral Vector Delivery. Polymers 2025, 17, 1381. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101381
Zhang H, Zhou B, Dong W, Song Y, Hu Q, Zhang H, Yu M, Zhu G, Sun Y, Feng J. Development and Characterization of Adeno-Associated Virus-Loaded Coaxial Electrospun Scaffolds for Potential Viral Vector Delivery. Polymers. 2025; 17(10):1381. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101381
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Haiguang, Bing Zhou, Wei Dong, Yongteng Song, Qingxi Hu, Heng Zhang, Min Yu, Guanglang Zhu, Yudong Sun, and Jiaxuan Feng. 2025. "Development and Characterization of Adeno-Associated Virus-Loaded Coaxial Electrospun Scaffolds for Potential Viral Vector Delivery" Polymers 17, no. 10: 1381. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101381
APA StyleZhang, H., Zhou, B., Dong, W., Song, Y., Hu, Q., Zhang, H., Yu, M., Zhu, G., Sun, Y., & Feng, J. (2025). Development and Characterization of Adeno-Associated Virus-Loaded Coaxial Electrospun Scaffolds for Potential Viral Vector Delivery. Polymers, 17(10), 1381. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101381






