A Novel Approach for Microencapsulating Salt Hydrate-Based Phase Change Materials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
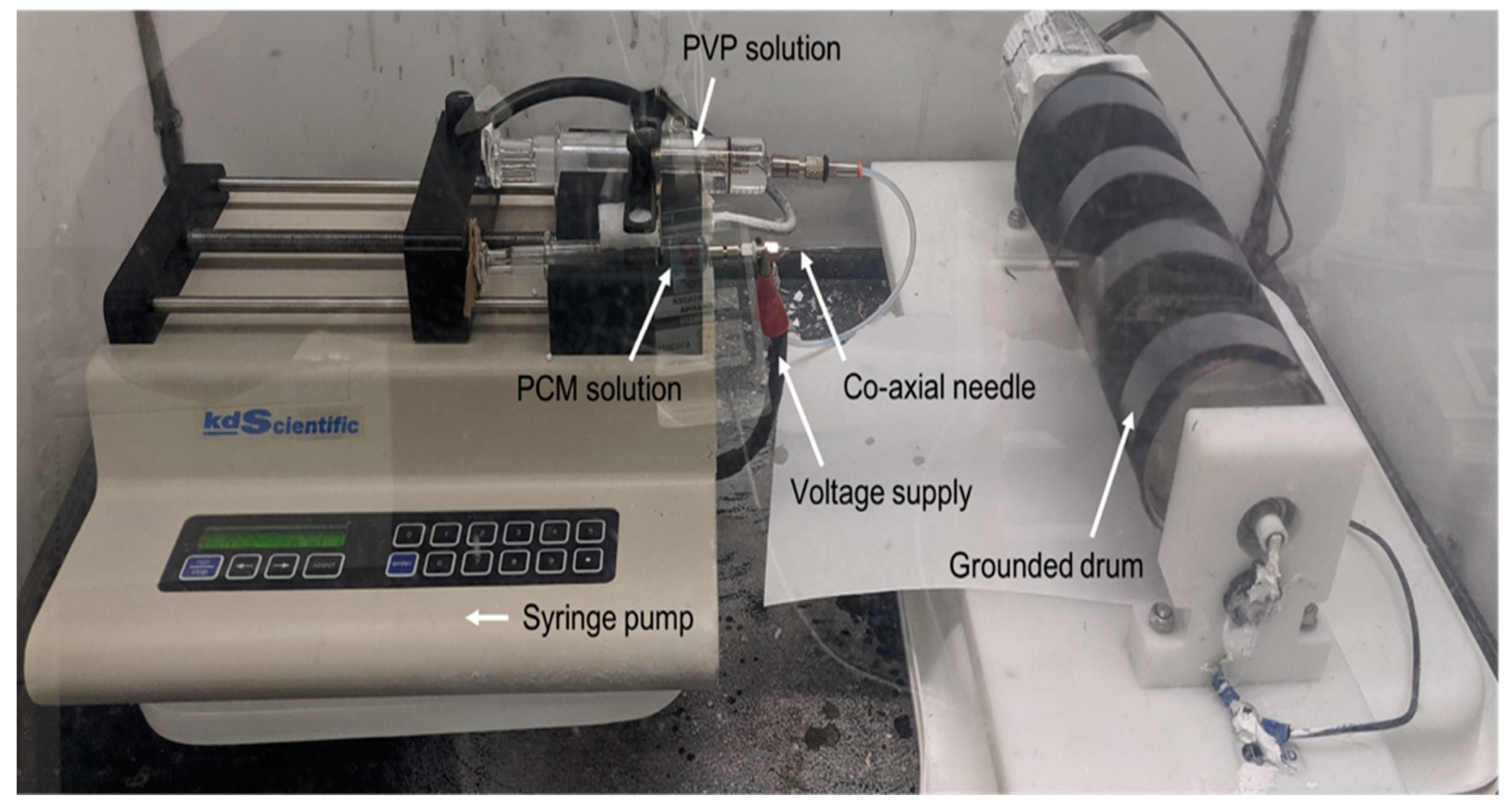
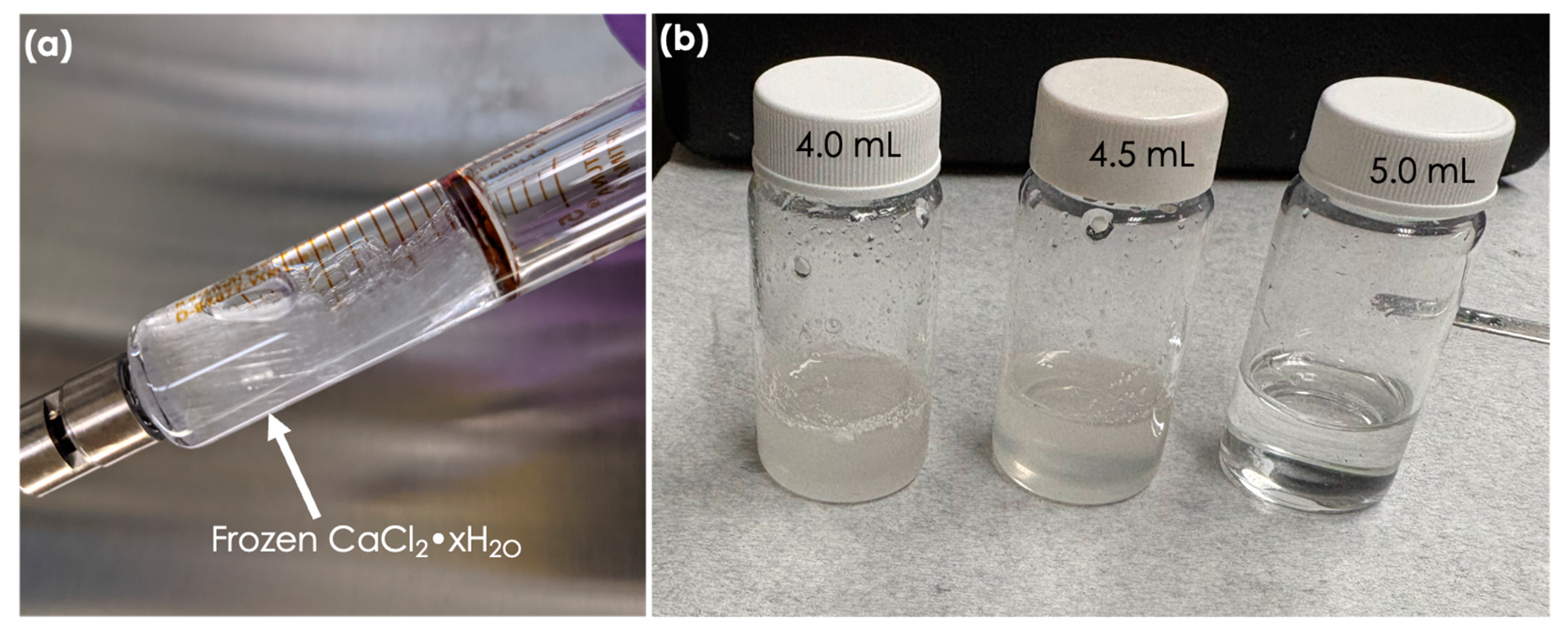
2.2. Electrospinning
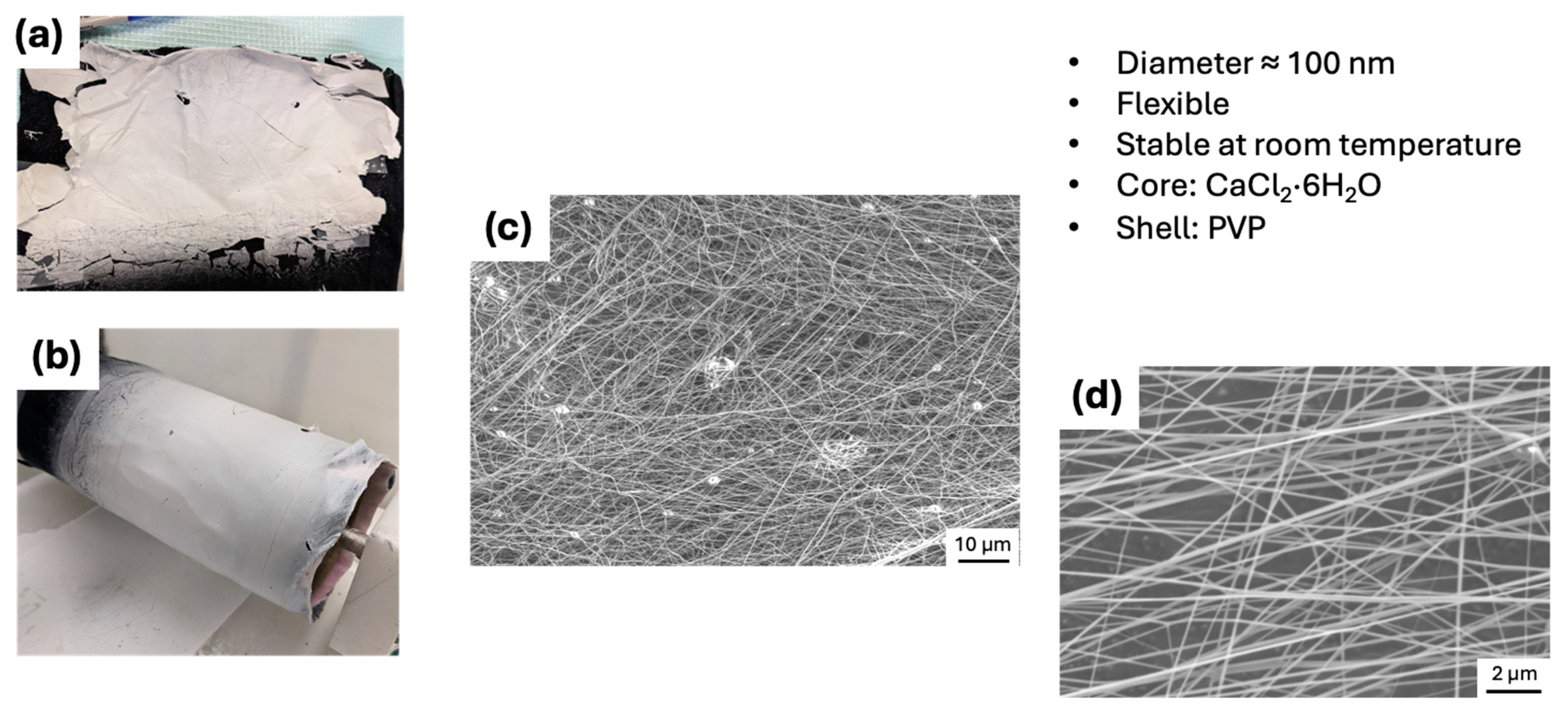
2.3. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Analysis
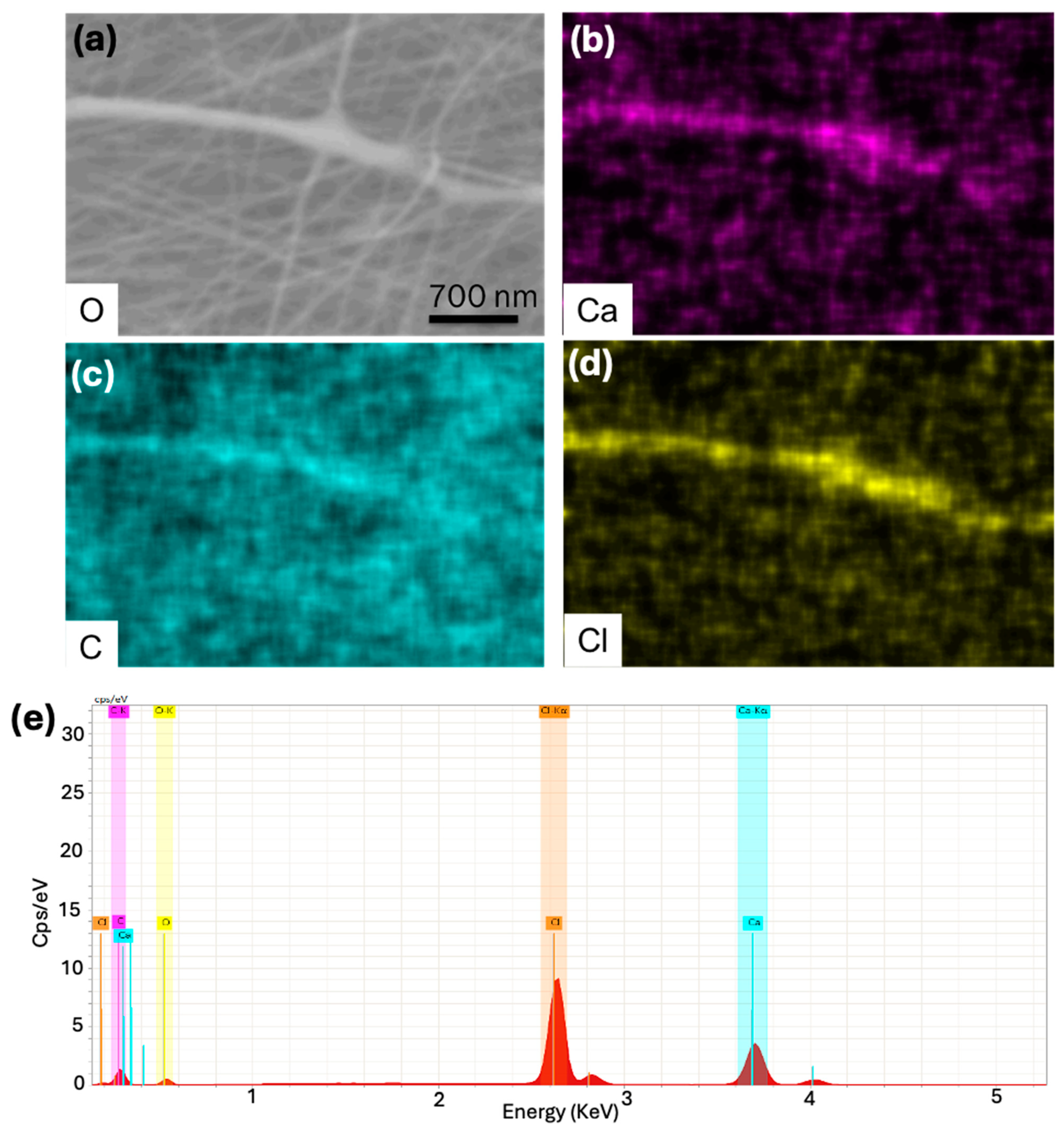
2.4. X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Analysis
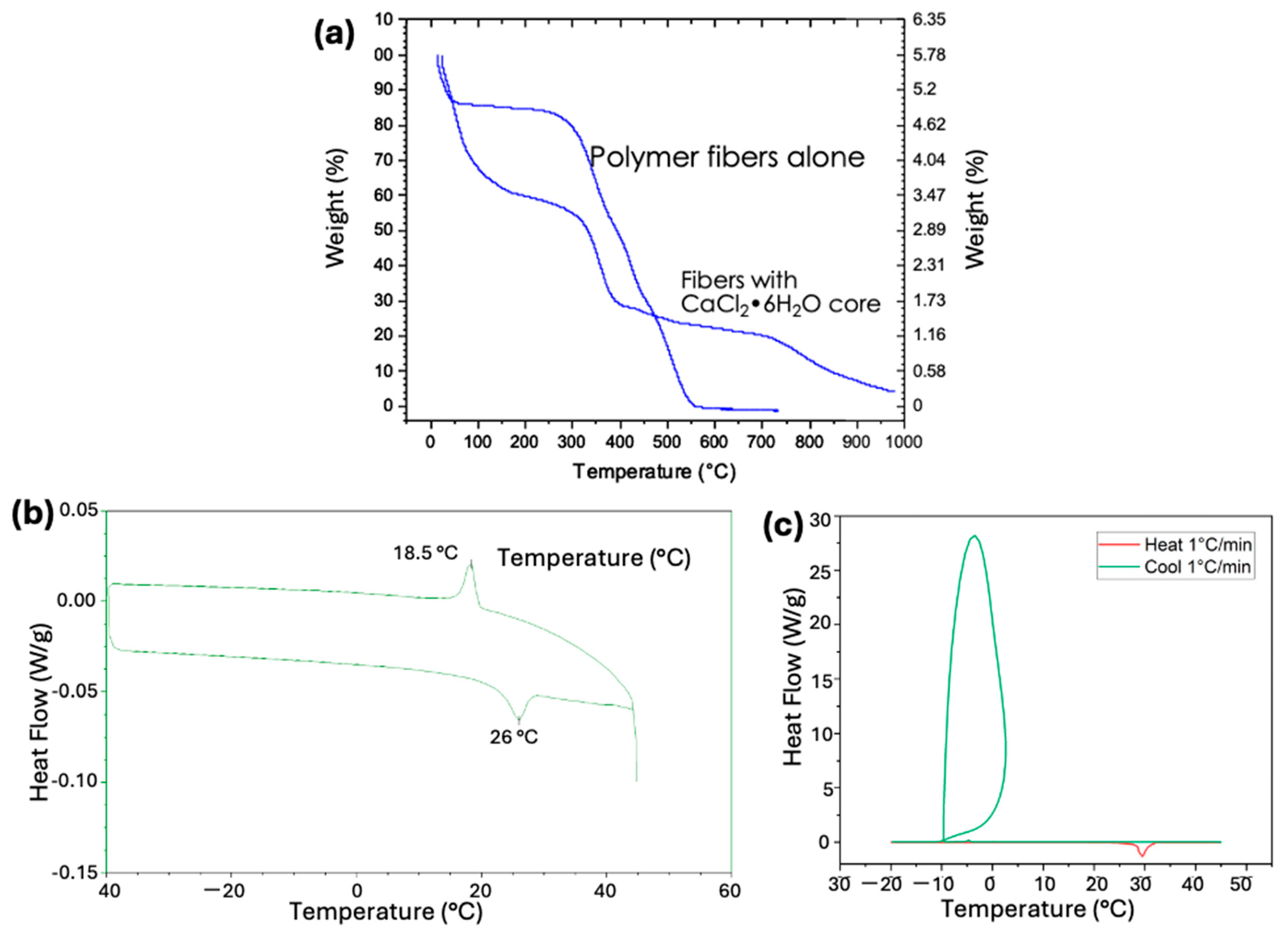
2.5. Thermogravimetric Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hook, M.; Tang, X. Depletion of fossil fuels and anthropogenic climate change—A review. Energy Policy 2013, 52, 797–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahabuddin, M.; Alim, M.A.; Alam, T.; Mofijur, M.; Ahmed, S.F.; Perkins, G. A critical review on the development and challenges of concentrated solar power technologies. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2021, 47, 101434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtola, T.; Zahedi, A. Technical challenges in the application of renewable energy: A review. Int. J. Smart Grid Clean Energy 2020, 9, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahshan, R.; Iqbal, M.; Mann, G.K.; Quaicoe, J.E. Microgrid reliability evaluation considering the intermittency effect of renewable energy sources. Int. J. Smart Grid Clean Energy 2017, 6, 252–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muruganantham, B.; Gnanadass, R.; Padhy, N.P. Challenges with renewable energy sources and storage in practical distribution systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 73, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullich-Massague, E.; Cifuentes-Garcia, F.-J.; Glenny-Crende, I.; Cheah-Mane, M.; Aragues-Penalba, M.; Díaz-Gonzalez, F.; Gomis-Bellmunt, O. A review of energy storage technologies for large scale photovoltaic power plants. Appl. Energy 2020, 274, 115213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- N’Tsoukpoe, K.E.; Liu, H.; Pierres, N.L.; Luo, L. A review on long-term sorption solar energy storage. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2009, 13, 2385–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo, A.J.; Gonzalez-Aguilar, J.; Romero, M.; Coronado, J.M. Solar energy on demand: A review on high temperature thermochemical heat storage systems and materials. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 4777–4816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mofijur, M.; Mahlia, T.M.I.; Silitonga, A.S.; Ong, H.C.; Silakhori, M.; Hasan, M.H.; Putra, N.; Rahman, S.M.A. Phase Change Materials (PCM) for Solar Energy Usages and Storage: An Overview. Energies 2019, 12, 3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenisarin, M.; Mahkamov, K. Solar energy storage using phase change materials. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2007, 11, 1913–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocak, B.; Fernandez, A.I.; Paksoy, H. Review on sensible thermal energy storage for industrial solar applications and sustainability aspects. Sol. Energy 2020, 209, 135–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, D.M.R.; Senthilkumar, R.; Lakshmanarao, G.; Krishnan, S.; Prasad, B.S.N. A critical review on thermal energy storage materials and systems for solar applications. AIMS Energy 2019, 7, 507–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, K.; Halcovitch, N.R.; Griffin, J.M. Long-term solar energy storage under ambient conditions in a mof-based solid–solid phase-change material. Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 9925–9936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alazwari, M.A.; Abu-Hamdeh, N.H.; Khoshaim, A.; Ashour, A.I.; Nusier, O.K.; Karimipour, A. Effects of examine the phase change material through applying the solar collectors: Exergy analysis of an air handling unit equipped with the heat recovery unit. J. Energy Storage 2021, 41, 103002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmit, H.; Rathgeber, C.; Hoock, P.; Hiebler, S. Critical review on measured phase transition enthalpies of salt hydrates in the context of solid-liquid phase change materials. Thermochim. Acta 2020, 683, 178477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xie, M.; Gao, X.; Yang, Y.; Sang, Y. Experimental exploration of incorporating form-stable hydrate salt phase change materials into cement mortar for thermal energy storage. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 140, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.S.; Mudgal, V.; Mallick, T.K. Review of latent heat thermal energy storage for improved material stability and effective load management. J. Energy Storage 2018, 15, 205–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarbu, I.; Sebarchievici, C. A Comprehensive Review of Thermal Energy Storage. Sustainability 2018, 10, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, N.; Huang, Z.; Luo, Z.; Gao, X.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, Z. Inorganic salt hydrate for thermal energy storage. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Z.; Xu, T.; Liu, C.; Zheng, Z.; Liang, L.; Hong, K. Experimental study on thermal properties and thermal performance of eutectic hydrated salts/expanded perlite form-stable phase change materials for passive solar energy utilization. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2018, 188, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Gracia, A.; Cabeza, L.F. Phase change materials and thermal energy storage for buildings. Energy Build. 2015, 103, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Wu, X.; Dong, X.; Ye, G.; Zhang, G.; Yang, X. Ultrareliable Composite Phase Change Material for Battery Thermal Management Derived from a Rationally Designed Phase Changeable and Hydrophobic Polymer Skeleton. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2021, 4, 3832–3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, C.; Loharkar, P.K. A Review of Phase Change Materials as an Alternative for Solar Thermal Energy Storage. Mater. Today Proc. 2017, 4, 10264–10267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pielichowska, K.; Pielichowski, K. Phase change materials for thermal energy storage. Prog. Material. Sci. 2014, 65, 67–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraj, K.; Khaled, M.; Faraj, J.; Hachem, F.; Castelain, C. A review on phase change materials for thermal energy storage in buildings: Heating and hybrid applications. J. Energy Storage 2021, 33, 101913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milian, Y.E.; Gutierrez, A.; Grageda, M.; Ushak, S. A review on encapsulation techniques for inorganic phase change materials and the influence on their thermophysical properties. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 73, 983–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xu, X.; Yang, L.; Wu, J.; Zhao, F.; Li, C. Molten salts/ceramic-foam matrix composites by melt infiltration method as energy storage material. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mater. Sci. Ed. 2009, 24, 651–653. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, W.; Cheng, X.; Li, Y. Thermal compatibility of sodium nitrate/ expanded perlite composite phase change materials. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 103, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, S.A.; Al-Sulaiman, F.A.; Ibrahim, N.I.; Zahir, M.d.H.; Al-Ahmed, A.; Saidur, R.; Yılbas, B.S.; Sahin, A.Z. A review on current status and challenges of inorganic phase change materials for thermal energy storage systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 70, 1072–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Hirschey, J.; LaClair, T.J.; Gluesenkamp, K.R.; Graham, S. Review of stability and thermal conductivity enhancements for salt hydrates. J. Energy Storage 2019, 24, 100794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, T.E.; Dhau, J.S.; Goswami, D.Y.; Stefanakos, E. Macroencapsulation and characterization of phase change materials for latent heat thermal energy storage systems. Appl. Energy 2015, 154, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sozen, Z.Z.; Grace, J.R.; Pinder, K.L. Thermal energy storage by agitated capsules of phase change material. 1. Pilot scale experiments. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1988, 27, 679–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Song, G.; He, X.; Sui, C.; Li, M. Structural and phase change characteristics of inorganic microencapsulated core/shell Al–Si/Al2O3 micro-particles during thermal cycling. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 10689–10696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Chao, S.; He, X.; Li, M. Inorganic microencapsulated core/shell structure of Al–Si alloy micro-particles with silane coupling agent. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 6865–6874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Gao, X.; Luo, Y. Core–shell particles of poly (methyl methacrylate)-block-poly (n-butyl acrylate) synthesized via reversible addition–fragmentation chain-transfer emulsion polymerization and the polymer’s application in toughening polycarbonate. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 42833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, M.; Shchukina, E.; De Castro, P.F.; Shchukin, D. Nanocapsules containing salt hydrate phase change materials for thermal energy storage. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 16906–16912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platte, D.; Helbig, U.; Houbertz, R.; Sextl, G. Microencapsulation of alkaline salt hydrate melts for phase change applications by surface thiol-Michael addition polymerization. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2013, 298, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, T.; Ko, Y.G.; Chun, Y.; Choi, U.S. Encapsulation of Phase Change Material with Water-Absorbable Shell for Thermal Energy Storage. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 2874–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Xiao, X.; Zhan, Y.; Huan, C.; Qi, S.; Cheng, H.; Xu, G. Core-Sheath Paraffin-Wax-Loaded Nanofibers by Electrospinning for Heat Storage. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 12759–12767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babapoor, A.; Karimi, G.; Golestaneh, S.I.; Mezjin, M.A. Coaxial electro-spun PEG/PA6 composite fibers: Fabrication and characterization. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 118, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Deng, P.; Feng, R.; Song, J. Novel gelatinous shape- stabilized phase change materials with high heat storage density. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2011, 95, 1213–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, J.; Polizos, G.; Jafta, C.J.; Wood, D.; Li, J. Electrospun Inorganic Solid-State Electrolyte Fibers for Battery Applications. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2022, 169, 050527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Composition | Electrospinning |
|---|---|
| CaCl2·6H2O alone | No |
| PVP alone | Yes |
| 90% CaCl2·6H2O in water (core) + 10% PVP in DMF (shell) | Yes |
| Entity Name | Weights |
|---|---|
| CaCl2·6H2O | 1.0 g |
| PVP | 0.1 g |
| Piece of cloth without fibers | 9.13 g |
| Piece of cloth with fibers | 9.96 g |
| Amount of fibers | 0.75 g |
| Electrospinning yield | ≈75% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sharma, J.; Polizos, G.; Jafta, C.J.; Datta, S.; Gluesenkamp, K.R.; Nawaz, K. A Novel Approach for Microencapsulating Salt Hydrate-Based Phase Change Materials. Polymers 2025, 17, 1322. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101322
Sharma J, Polizos G, Jafta CJ, Datta S, Gluesenkamp KR, Nawaz K. A Novel Approach for Microencapsulating Salt Hydrate-Based Phase Change Materials. Polymers. 2025; 17(10):1322. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101322
Chicago/Turabian StyleSharma, Jaswinder, Georgios Polizos, Charl J. Jafta, Siddhant Datta, Kyle R. Gluesenkamp, and Kashif Nawaz. 2025. "A Novel Approach for Microencapsulating Salt Hydrate-Based Phase Change Materials" Polymers 17, no. 10: 1322. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101322
APA StyleSharma, J., Polizos, G., Jafta, C. J., Datta, S., Gluesenkamp, K. R., & Nawaz, K. (2025). A Novel Approach for Microencapsulating Salt Hydrate-Based Phase Change Materials. Polymers, 17(10), 1322. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101322





