The Effects of Shellac and Glycerol on the Physicochemical Properties of Chitosan Films
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Film Preparation
2.2. ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy
2.3. SEM Analysis
2.4. AFM Analysis
2.5. Contact Angle Measurements and Surface Free Energy Determination
2.6. TGA
2.7. Mechanical Testing
2.8. Swelling Analysis
3. Results
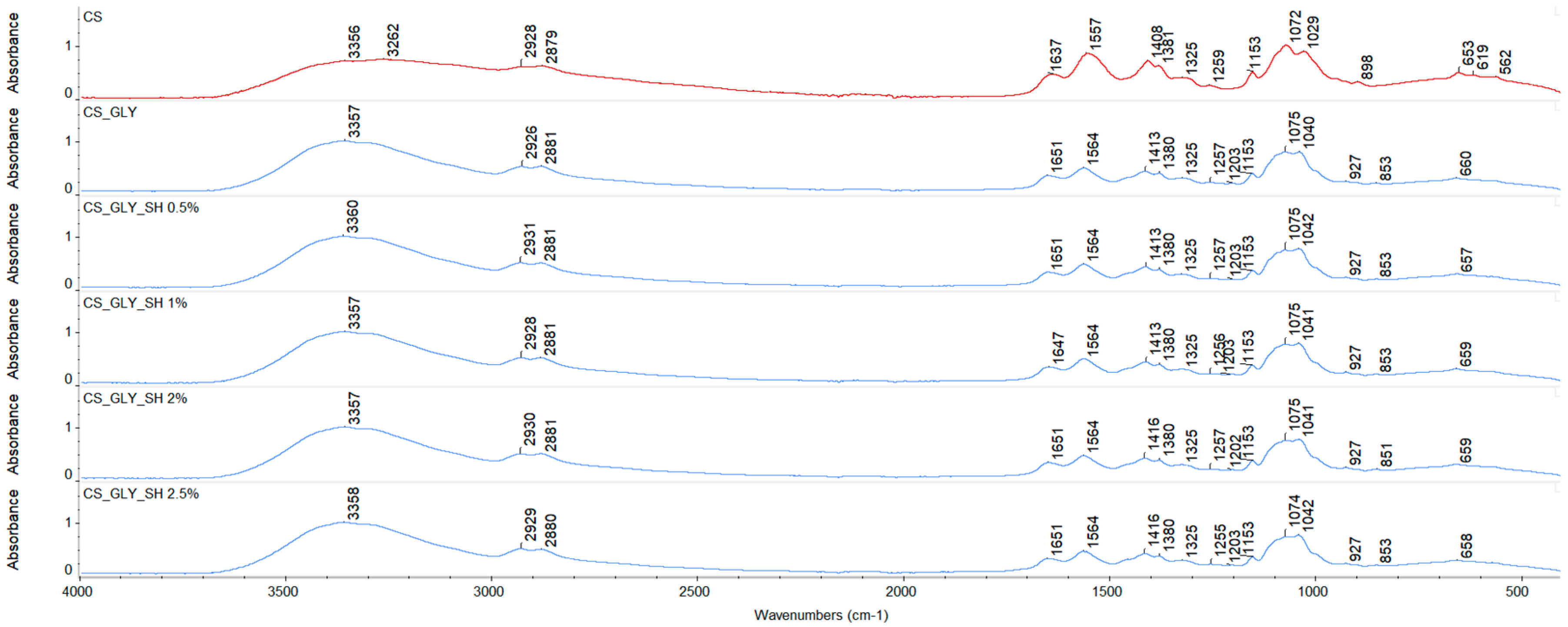
3.1. ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy
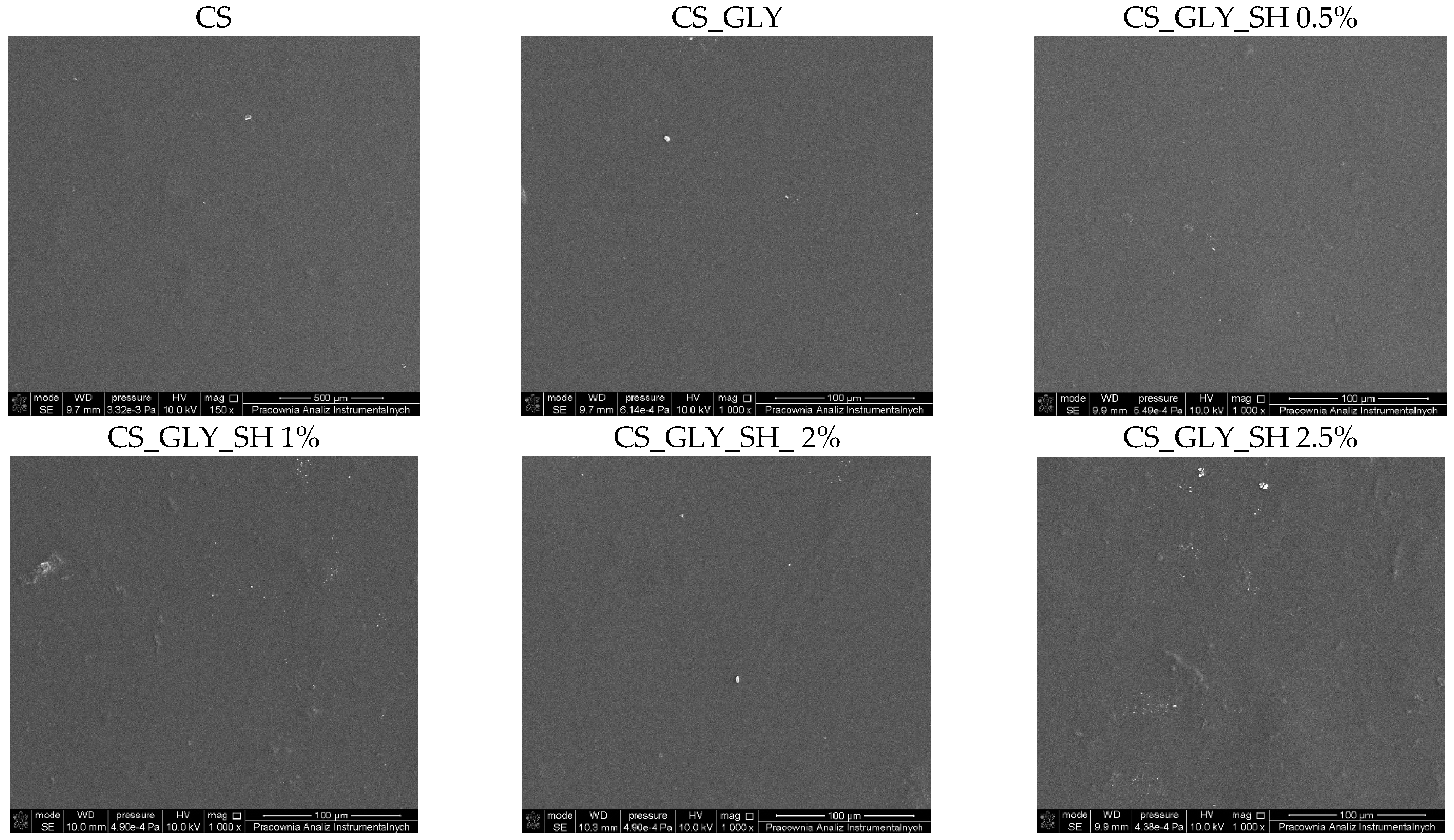
3.2. SEM Analysis
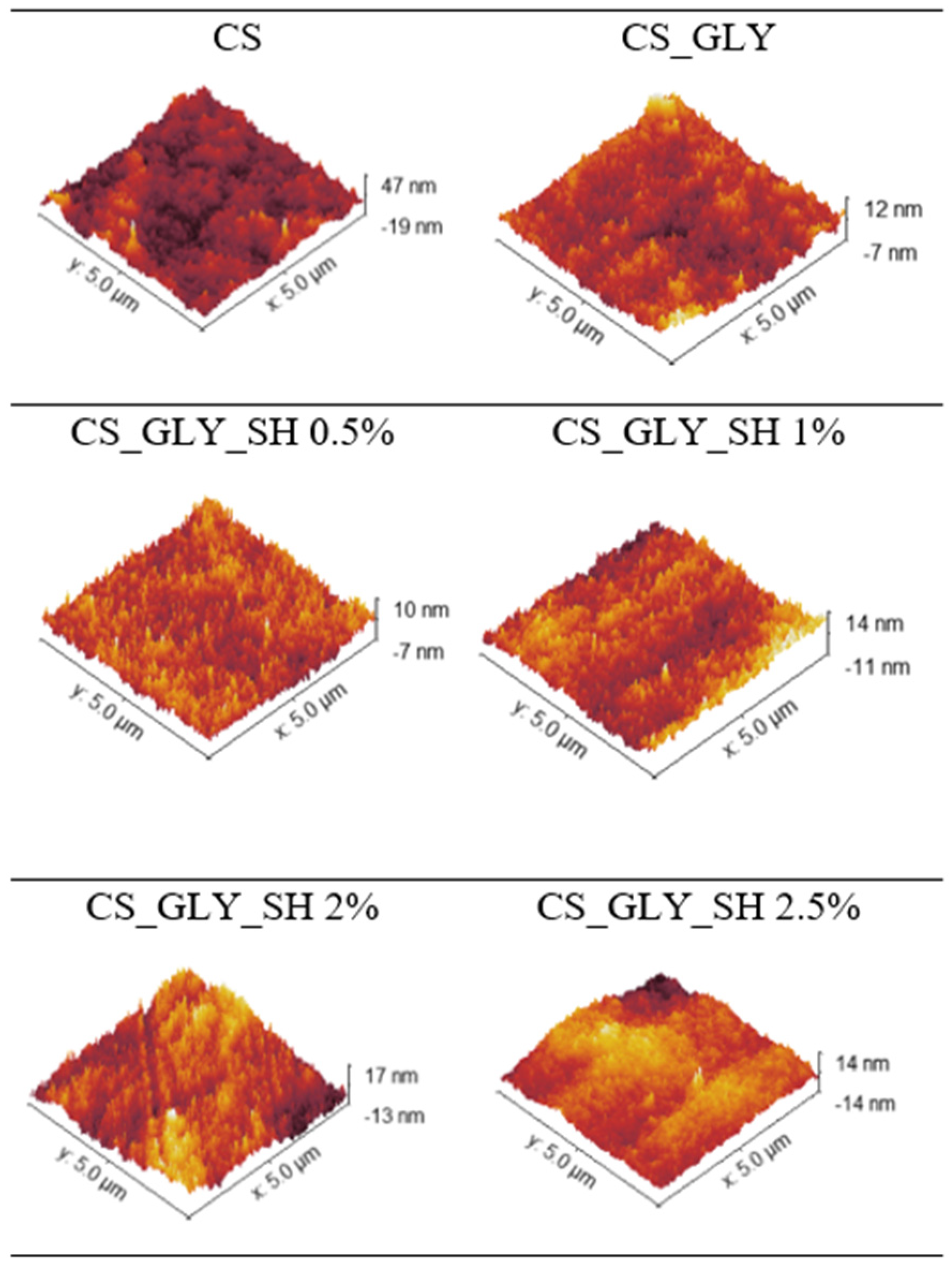
3.3. AFM Analysis
3.4. Contact Angle Measurements and Surface Free Energy Determination
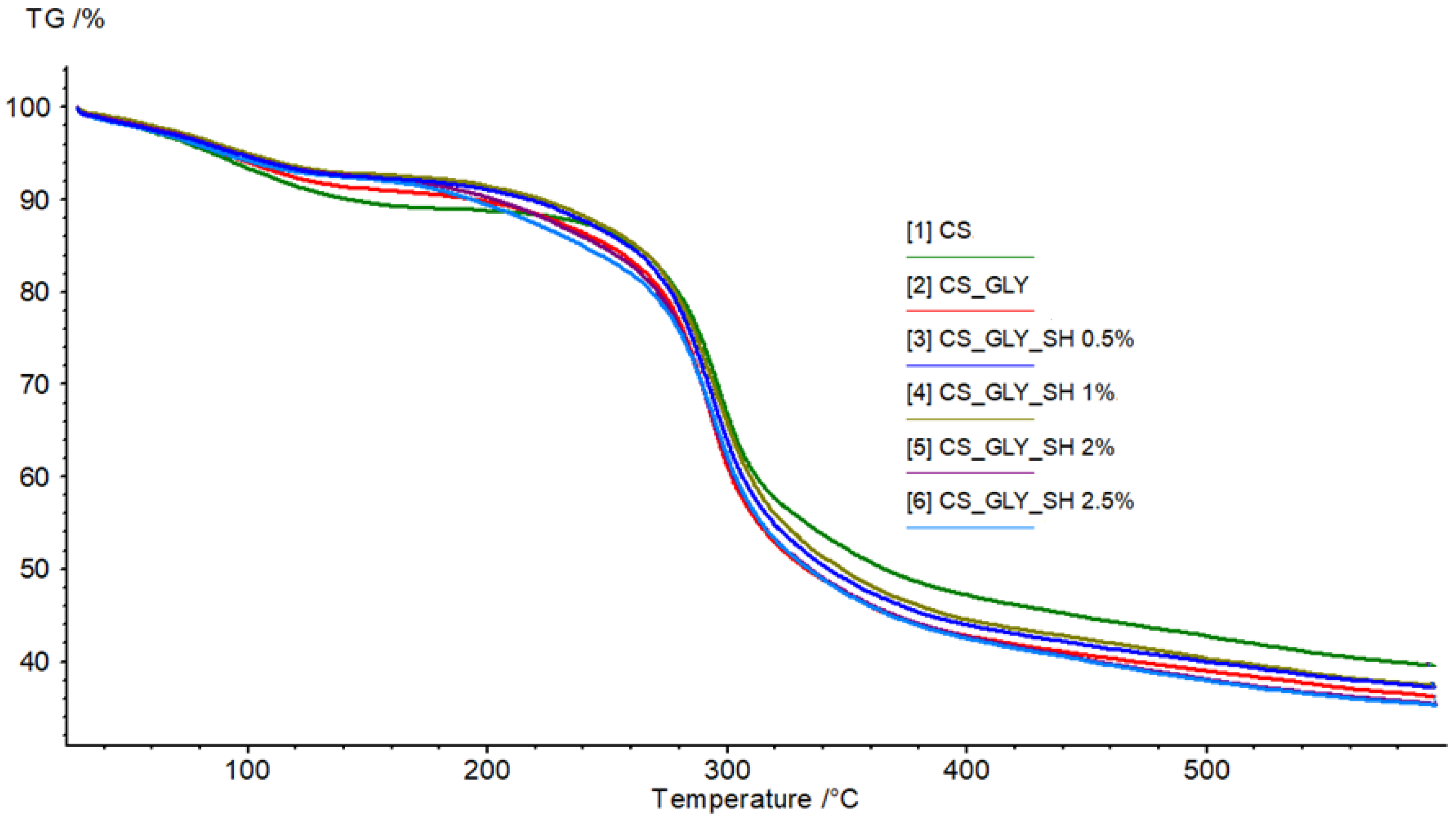
3.5. TGA
3.6. Mechanical Testing
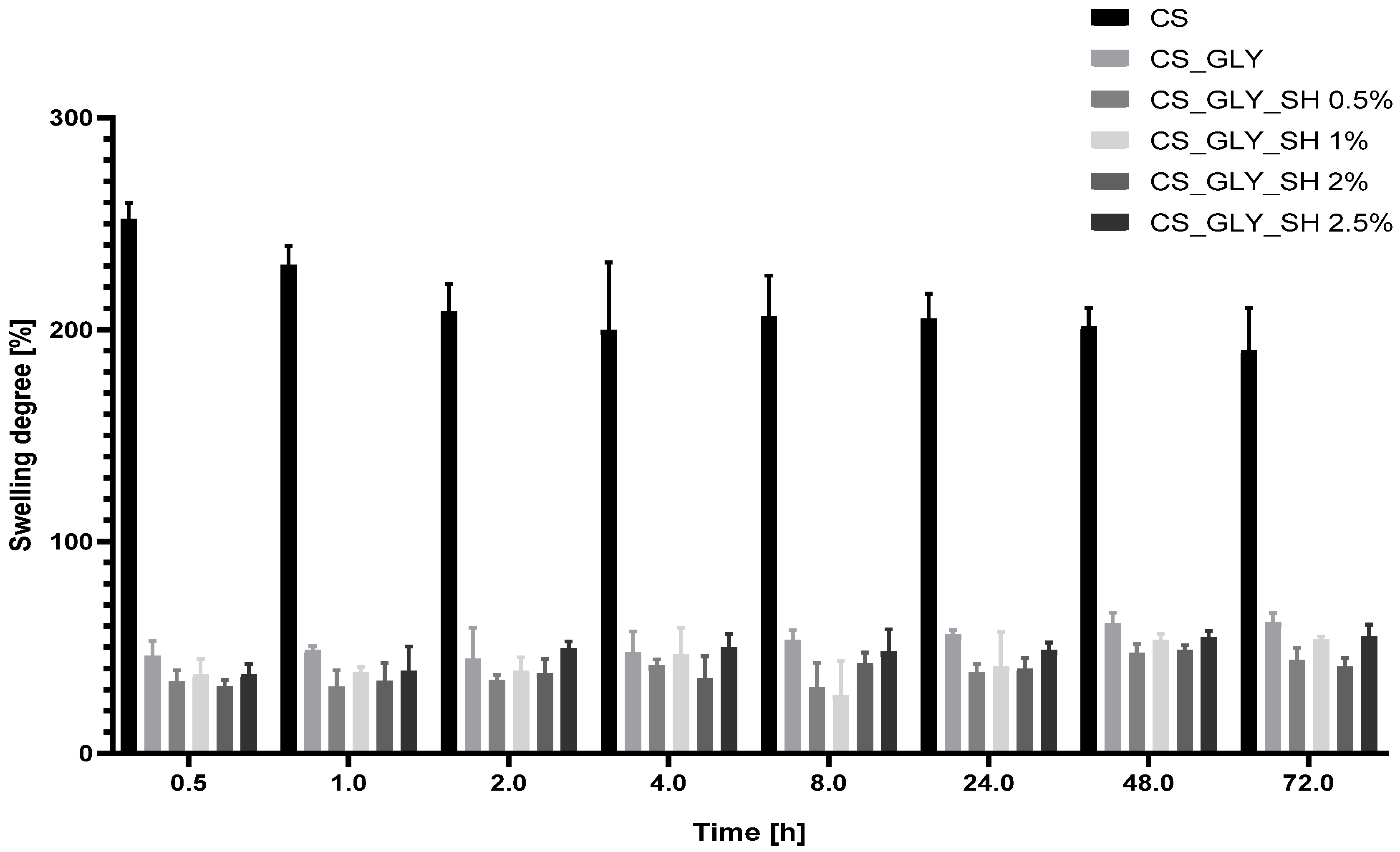
3.7. Swelling Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guerra-Rodríguez, M.F.E.; Cazón, P.; Vázquez, M. Chitosan for Food Packaging: Recent Advances in Active and Intelligent Films. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 124, 107328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, A.; Patel, R.; Padhan, B.; Palimkar, S.; Galgali, P.; Adhikari, A.; Varga, I.; Patel, M. Chitosan Based Biodegradable Composite for Antibacterial Food Packaging Application. Polymers 2023, 15, 2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrońska, N.; Katir, N.; Nowak-Lange, M.; El Kadib, A.; Lisowska, K. Biodegradable Chitosan-Based Films as an Alternative to Plastic Packaging. Foods 2023, 12, 3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, A.; Khan, S.; Iqbal, D.N.; Shrahili, M.; Haider, S.; Mohammad, K.; Mohammad, A.; Rizwan, M.; Kanwal, Q.; Mustafa, G. Advances in Chitosan-Based Drug Delivery Systems: A Comprehensive Review for Therapeutic Applications. Eur. Polym. J. 2024, 210, 112983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mawazi, S.M.; Kumar, M.; Ahmad, N.; Ge, Y.; Mahmood, S. Recent Applications of Chitosan and Its Derivatives in Antibacterial, Anticancer, Wound Healing, and Tissue Engineering Fields. Polymers 2024, 16, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulka, K.; Sionkowska, A. Chitosan Based Materials in Cosmetic Applications: A Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shang, J.; Chen, Y.; Feng, X. Potential Applications of Chitosan in Seborrheic Dermatitis and Other Skin Diseases: A Comprehensive Review. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2025, 18, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Dong, Q.; Xu, C.; Deng, S.; Kang, Y.; Fan, M.; Li, L. Application of Functionalized Chitosan in Food: A Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 235, 123716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ta, Q.; Ting, J.; Harwood, S.; Browning, N.; Simm, A.; Ross, K.; Olier, I.; Al-Kassas, R. Chitosan Nanoparticles for Enhancing Drugs and Cosmetic Components Penetration through the Skin. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 160, 105765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi-Maleh, H.; Ayati, A.; Davoodi, R.; Tanhaei, B.; Karimi, F.; Malekmohammadi, S.; Orooji, Y.; Fu, L.; Sillanpää, M. Recent Advances in Using of Chitosan-Based Adsorbents for Removal of Pharmaceutical Contaminants: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 291, 125880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, S.; Pathak, R.; Punetha, V.D.; Punetha, M. Chitosan Nanocomposites as a Nano-Bio Tool in Phytopathogen Control. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 331, 121858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasaj, M.; Chehelgerdi, M.; Asghari, B.; Ahmadieh-Yazdi, A.; Asgari, M.; Kabiri-Samani, S.; Sharifi, E.; Arabestani, M. Factors Influencing the Antimicrobial Mechanism of Chitosan Action and its Derivatives: A Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 277, 134321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, M.; Kaushik, B.; Rao, G.K.; Srivastava, C.M.; Vaya, D. Advances and Challenges in the Use of Chitosan and its Derivatives in Biomedical Fields: A Review. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2023, 5, 100323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, C.-L.; Deng, F.-S.; Chuang, C.-Y.; Lin, C.-H. Antimicrobial Actions and Applications of Chitosan. Polymers 2021, 13, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Araby, A.; Janati, W.; Ullah, R.; Ercisli, S.; Errachidi, F. Chitosan, Chitosan derivatives, and Chitosan-Based Nanocomposites: Eco-friendly Materials for Advanced Applications (A Review). Front. Chem. 2024, 11, 1327426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, F.; Qiu, P.; Wang, Y.; Ren, P.; Liu, J.; Zhao, J.; Gou, D. Chitosan-Based Hydrogels: From Preparation to Applications, a Review. Food Chem. 2024, 21, 101095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edo, G.E.; Yousif, E.; Al-Mashhadani, M.H. Modified Chitosan: Insight on Biomedical and Industrial Applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 275, 133526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, M.; Sionkowska, A. Effect of Polydopamine and Curcumin on Physicochemical and Mechanical Properties of Polymeric Blends. Materials 2023, 16, 5758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, N.H.N.; Truong, Q.T.; Le, P.K.; Ha, A.C. Recent Developments in Chitosan Hydrogels Carrying Natural Bioactive Compounds. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 294, 119726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Tebar, N.; Pérez-Álvarez, J.A.; Fernández-López, J.; Viuda-Martos, M. Chitosan Edible Films and Coatings with Added Bioactive Compounds: Antibacterial and Antioxidant Properties and Their Application to Food Products: A Review. Polymers 2023, 15, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thombare, N.; Kumar, S.; Kumari, U.; Sakare, P.; Kumar Yogi, R.; Prasad, N.; Krishan Sharma, K. Shellac as a Multifunctional Biopolymer: A Review on Properties, Application and Future Potential. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 215, 203–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; He, N.; Xue, Q.; Guo, Q.; Dong, L.; Haruna, M.H.; Zhang, X.; Li, B.; Li, L. Shellac: A Promising Natural Polymer in the Food Industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 109, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrabič-Brodnjak, U. Bio-Based Adhesives Formulated from Tannic Acid, Chitosan, and Shellac for Packaging Materials. Polymers 2023, 15, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Pan, X.; Rong, L.; Dong, A.; He, Y.; Song, X.; Li, J. Polymer Carriers for Controlled Fragrance Release. Mater Res. Express 2020, 7, 082001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Pan, Z.; Xue, Q.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, B.; Li, L. Improving the Properties of Chitosan Films by Incorporating Shellac Nanoparticles. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 110, 106164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Sun, R.; Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Xia, N.; Guo, P.; Jiang, L.W.; Zhang, X.N.; Rayan, A.M. Effects of Pine Needle Essential Oil Combined with Chitosan Shellac on Physical and Antibacterial Properties of Emulsions for Egg Preservation. Food Biophys. 2022, 17, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasamy, S.; Nallasamy, S.; Sellamuthu, A.; Srinivasan, D.P.; Kumaravel, A.; Kumaresan, S.; Chidhambaram, S.; Berlin, A.; Peter, A.; Govindaraj, K.; et al. Characteristics of Chitosan-Shellac Based Biocomposite Fabric for Packaging. Asian J. Biol. Life Sci. 2024, 13, 696–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, S.A.A.; Mekkey, S.D.; Othman, A.M.; El-Sakhawy, M. Novel Antimicrobial Biodegradable Composite Films as Packaging Materials Based on Shellac/Chitosan, and ZnAl2O4 or CuAl2O4 Spinel Nanoparticles. Sci Rep 2024, 14, 27824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Liu, Y.; Xu, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, H. An Insect Lac Blanket-Mimetic and Degradable Shellac Hydrogel/Chitosan Packaging Film with Controllable Gas Permeation for Fresh-Cut Vegetables Preservation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 275, 133131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Gang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Ren, Y.; Wang, J.; Niu, B.; Li, W. Preparation of Composite Films Composed of Polyvinyl Alcohol, Shellac and Carboxymethyl Chitosan-CuO Nanoparticles and their Application in Food Preservation. J. Polym. Res. 2023, 30, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Li, S.; Guo, X.; Fang, M.; Liu, X.; Gong, Z. Preparation of Shellac Nanoparticles-Chitosan Complexes Stabilized Pickering Emulsion Gels and its Application in β-Carotene Delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 281, 136583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, M.; Wang, X.; Li, L.; Wang, L. Fabrication and Characterization of Quercetagetin-Loaded Nanoparticles Based on Shellac and Quaternized Chitosan: Improvement of Encapsulation Efficiency and Acid and Storage Stabilities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 15670–15680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Yu, H.; Kong, J.; Ge, X.; Sun, Y.; Mao, M.; Wang, D.Y.; Wang, Y. Preparation, Characterization, Stability, and Controlled Release of Chitosan-Coated Zein/Shellac Nanoparticles for the Delivery of Quercetin. Food Chem. 2024, 444, 138634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraisit, P.; Limmatvapirat, S.; Nunthanid, J.; Sriamornsak, P.; Luangtana-anan, M. Nanoparticle Formation by Using Shellac and Chitosan for a Protein Delivery System. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2012, 18, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Guo, J.; Luo, X.; Liu, S.; Miao, S. Encapsulation of SOD in Chitosan-Coated Gel Particles of Alginate or Mixture of Alginate and Shellac for Targeted Intestinal Delivery. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 142, 108778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein Ali, S.; Al-Obaidy, S.S.M.; Hamood Mohammed, F. Enhancing the Antibacterial and Anticancer Activity of Ciprofloxacin by Encapsulating into Shellac-Chitosan Nano Particles (CNPs). J. Nanostruct. 2022, 12, 546–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, B.K.; Fahmy, S.A. Development of Coated Beads for Oral Controlled Delivery of Cefaclor: In Vitro Evaluation. Acta Pharm. 2013, 63, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghrabia, A.E.; Boughdady, M.F.; Meshali, M.M. New Perspective Enteric-Coated Tablet Dosage Form for Oral Administration of Ceftriaxone: In Vitro and In Vivo Assessments. AAPS Pharm. Sci. Tech. 2019, 20, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwesh, A.Y.; El-Dahhan, M.S.; Meshali, M.M. A New Dual Function Orodissolvable/Dispersible Meclizine HCL Tablet to Challenge Patient Inconvenience: In Vitro Evaluation and In Vivo Assessment in Human Volunteers. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2021, 11, 2209–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; He, N.; Dong, L.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, X.; Li, B.; Li, L. Multiscale Shellac-Based Delivery Systems: From Macro- to Nanoscale. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 18794–18821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendelovici, E.; Frost, R.L.; Kloprogge, T. Cryogenic Raman Spectroscopy of Glycerol. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2000, 31, 1121–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q.; Wu, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Qin, Y. Enhancing Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Zein Films via Shellac Incorporation Using Coaxial Electrospinning. LWT 2025, 219, 117556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Wang, L.; Mu, R.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, D.; Wu, C.; Pang, J. Fabrication of Novel Konjac Glucomannan/Shellac Film with Advanced Functions for Food Packaging. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 131, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, E.P.; de S. Tavares, W.; Matos, R.S.; Ferreira, A.M.; Menezes, R.P.; da Costa, M.E.H.M.; de Souza, T.M.; Ferreira, I.M.; de Sousa, F.F.O.; Zamora, R.R.M. Influence of Low and High Glycerol Concentrations on Wettability and Flexibility of Chitosan Biofilms. Quím. Nova. 2018, 41, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, M.H.; Razavi, S.H.; Mousavi, M.A. Antimicrobial, Physical and Mechanical Properties of Chitosan-Based Films Incorporated with Thyme, Clove and Cinnamon Essential Oils. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2009, 33, 727–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Li, Y. Combined Effects of Two Kinds of Essential Oils on Physical, Mechanical and Structural Properties of Chitosan Films. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 36, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, X.; Dong, G.; Zhang, H.; Tao, Y.-F.; He, R.; Xu, J.; Ma, J.; Tang, B.; Zhou, B. Bioinspired Natural Shellac Dressing for Rapid Wound Sealing and Healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 1944–8244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaf, D.A.; Gomes, T.C.; Majidzadeh, R.; Hussein, R.N.; Carmichael, T.; Rondeau-Gagné, S. Shellac as Dielectric Materials in Organic Field-Effect Transistors: From Silicon to Paper Substrates. Flex. Print. Electron. 2023, 8, 024002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Samrat; Goyal, P.; Dhingra, K.; Singh, A.; Sarkar, A.; Poddar, D. Shellac: Bridging the Gap Between Chemistry and Sustainability—A Comprehensive Review of its Multifunctional Coating Applications for Food, Drug, and Paper Packaging. J. Macromol. Sci. A 2024, 61, 691–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irimia-Vladu, M.; Głowacki, E.; Schwabegger, G.; Leonat, L.; Akpinar, H.Z.; Sitter, H.; Bauer, S.; Sariciftci, N.S. Natural Resin Shellac as a Substrate and a Dielectric Layer for Organic Field-Effect Transistors. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 1473–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardenas, G.; Anaya, P.; del Rio, R.; Schrebler, R.; Von Plessing, C.; Schneider, M. Scanning Electron Microscopy and Atomic Force Microscopy of Chitosan Composite Films. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2010, 55, 352–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Huang, Q.; Liu, L.; Yam, K.L. Microstructure and Molecular Interaction in Glycerol Plasticized Chitosan/Poly(vinyl alcohol) Blending Films. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2009, 210, 832–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soradech, S.; Nunthanid, J.; Limmatvapirat, S.; Luangtana-anan, M. An Approach for the Enhancement of the Mechanical Properties and Film Coating Efficiency of Shellac by the Formation of Composite Films Based on Shellac and Gelatin. J. Food Eng. 2012, 108, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Specimen | 2% Chitosan Solution in 0.1 mol/L Acetic Acid Solution [g] | 5% Shellac Solution in Ethyl Alcohol [g] | Glycerol [g] |
|---|---|---|---|
| CS | 25 | - | - |
| CS_GLY | 25 | - | 0.25 |
| CS_GLY_SH 0.5% | 25 | 0.05 | 0.25 |
| CS_GLY_SH 1% | 25 | 0.1 | 0.25 |
| CS_GLY_SH 2% | 25 | 0.2 | 0.25 |
| CS_GLY_SH 2.5% | 25 | 0.25 | 0.25 |
| Specimen | Characteristic Bands [cm−1] | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -OH and -NH Stretch | C-H Stretch | Amide I | Amide II | CH2 Bend | Amide III | C-O Stretch/C-O-C Asymmetric Stretch | C-O Stretch/C-O-C Symmetric Stretch | |
| CS | 3356 | 2928/2879 | 1637 | 1557 | 1408 | 1259 | 1072 | 1029 |
| CS_GLY | 3357 | 2926/2881 | 1651 | 1564 | 1413 | 1257 | 1075 | 1040 |
| CS_GLY_SH 0.5% | 3360 | 2931/2881 | 1651 | 1564 | 1413 | 1257 | 1075 | 1042 |
| CS_GLY_SH 1% | 3357 | 2928/2881 | 1647 | 1564 | 1413 | 1256 | 1075 | 1041 |
| CS_GLY_SH 2% | 3357 | 2930/2881 | 1651 | 1564 | 1416 | 1257 | 1075 | 1041 |
| CS_GLY_SH 2.5% | 3358 | 2929/2880 | 1651 | 1564 | 1416 | 1255 | 1074 | 1042 |
| Specimen | Rq [nm] | Ra [nm] |
|---|---|---|
| CS | 7.37 ± 0.82 | 5.88 ± 0.71 |
| CS_GLY | 2.69 ± 0.57 | 2.07 ± 0.44 |
| CS_GLY_SH 0.5% | 1.78 ± 0.03 | 1.41 ± 0.02 |
| CS_GLY_SH 1% | 3.17 ± 0.03 | 2.52 ± 0.05 |
| CS_GLY_SH 2% | 4.22 ± 0.16 | 3.35 ± 0.13 |
| CS_GLY_SH 2.5% | 3.74 ± 0.60 | 2.81 ± 0.40 |
| Specimen | ΘG | ΘD | γs [mJ/m2] | γsd [mJ/m2] | γsp [mJ/m2] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS | 92.9 ± 4.3 | 54.0 ± 2.7 | 31.99 | 31.63 | 0.37 |
| CS_GLY | 89.6 ± 5.6 | 50.8 ± 5.5 | 33.58 | 32.94 | 0.64 |
| CS_GLY_SH 0.5% | 90.9 ± 2.4 | 38.9 ± 4.0 | 41.11 | 41.06 | 0.04 |
| CS_GLY_SH 1% | 93.7 ± 5.6 | 48.2 ± 3.9 | 35.93 | 38.85 | 0.07 |
| CS_GLY_SH 2% | 85.3 ± 5.4 | 44.4 ± 4.1 | 36.91 | 35.95 | 0.96 |
| CS_GLY_SH 2.5% | 80.7 ± 3.3 | 44.6 ± 3.3 | 36.64 | 34.53 | 2.11 |
| Parameter | CS | CS_GLY | CS_GLY_SH 0.5% | CS_GLY_SH 1% | CS_GLY_SH 2% | CS_GLY_SH 2.5% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step I | Tmax1 [°C] | 94.1 | 89.9 | 88.4 | 89.2 | 88.7 | 82.9 |
| Mass loss [%/min] | −2.54 | −2.33 | −1.86 | −1.91 | −1.89 | −1.94 | |
| Mass loss in Tmax1 [%] | 5.94 | 4.96 | 4.42 | 4.11 | 4.36 | 4.41 | |
| Step II | Tmax2 [°C] | 295.9 | 291.9 | 292.9 | 294.4 | 292.1 | 293.8 |
| Mass loss [%/min] | −16.15 | −17.88 | −16.61 | −15.92 | −16.42 | −15.75 | |
| Mass loss in Tmax2 [%] | 29.98 | 32.14 | 30.61 | 30.13 | 32.14 | 33.20 | |
| Residual mass [%] | 39.46 | 36.22 | 37.17 | 37.4 | 35.42 | 35.32 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brudzyńska, P.; Sionkowska, A. The Effects of Shellac and Glycerol on the Physicochemical Properties of Chitosan Films. Polymers 2025, 17, 1298. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101298
Brudzyńska P, Sionkowska A. The Effects of Shellac and Glycerol on the Physicochemical Properties of Chitosan Films. Polymers. 2025; 17(10):1298. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101298
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrudzyńska, Patrycja, and Alina Sionkowska. 2025. "The Effects of Shellac and Glycerol on the Physicochemical Properties of Chitosan Films" Polymers 17, no. 10: 1298. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101298
APA StyleBrudzyńska, P., & Sionkowska, A. (2025). The Effects of Shellac and Glycerol on the Physicochemical Properties of Chitosan Films. Polymers, 17(10), 1298. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101298








