Effect of Starch Variety and Environmental Conditions on the Aerobic Biodegradation of Citric Acid-Compatibilized Thermoplastic Starch/Polylactic Acid Blends
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Preparation and Conditioning of TPS/CA/PLA Blends
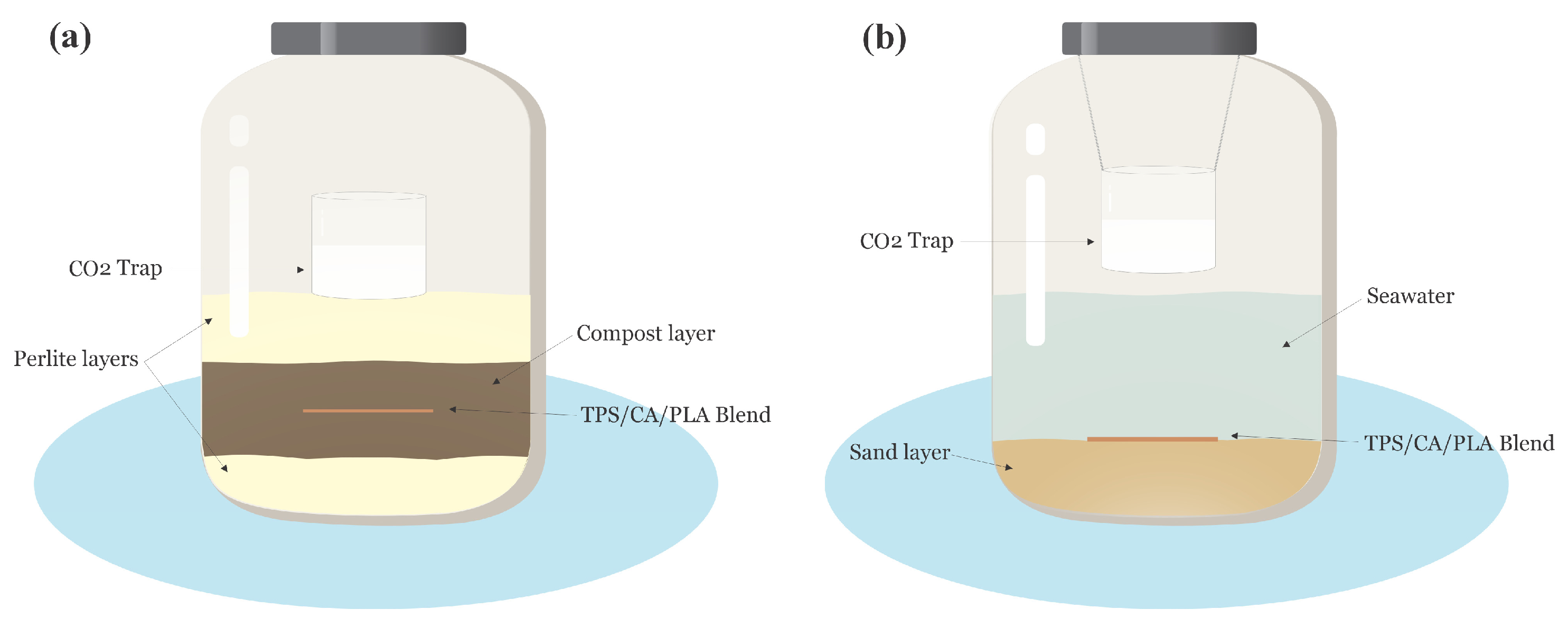
2.3. Degradation of TPS/CA/PLA Blends in Compost
2.4. Degradation of TPS/CA/PLA Blends in Seawater Environment
2.5. Biodegradability Assessment
2.6. Morphological Characterization
2.7. Thermal Characterization
2.8. Preparation of Blends and Environment Characterization
2.9. Data Analysis and Processing
2.9.1. Design of Experiments
2.9.2. Analysis of Variance
2.9.3. Tukey’s Multiple Comparisons Test
3. Results
3.1. Weight Loss Assessment in Compost and Seawater
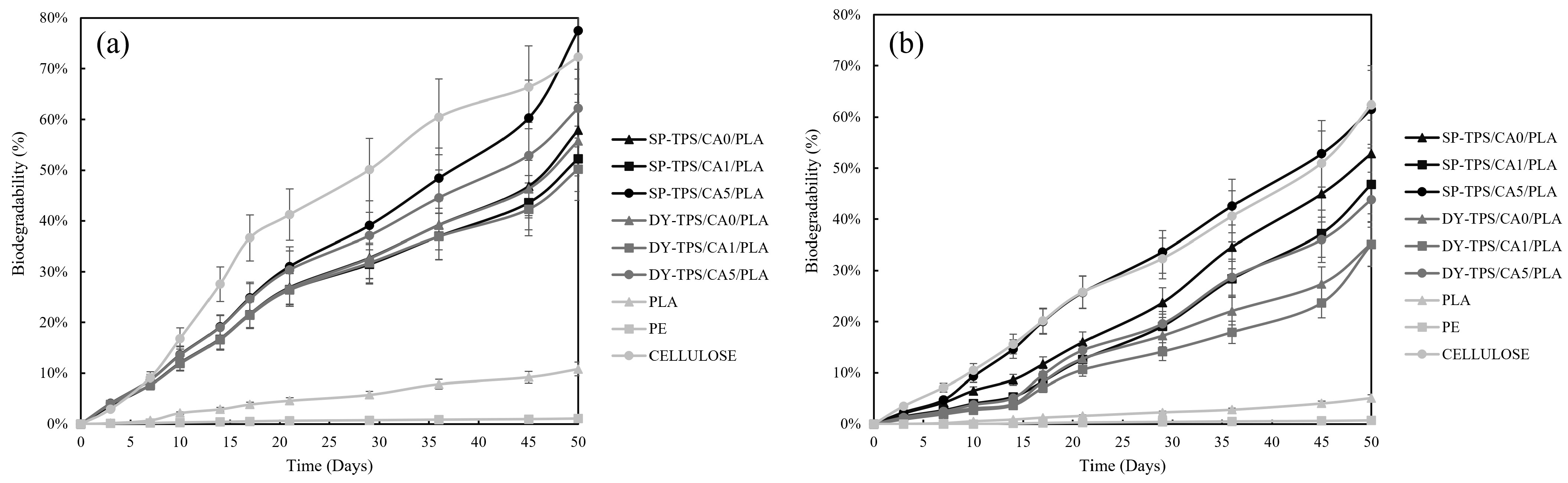
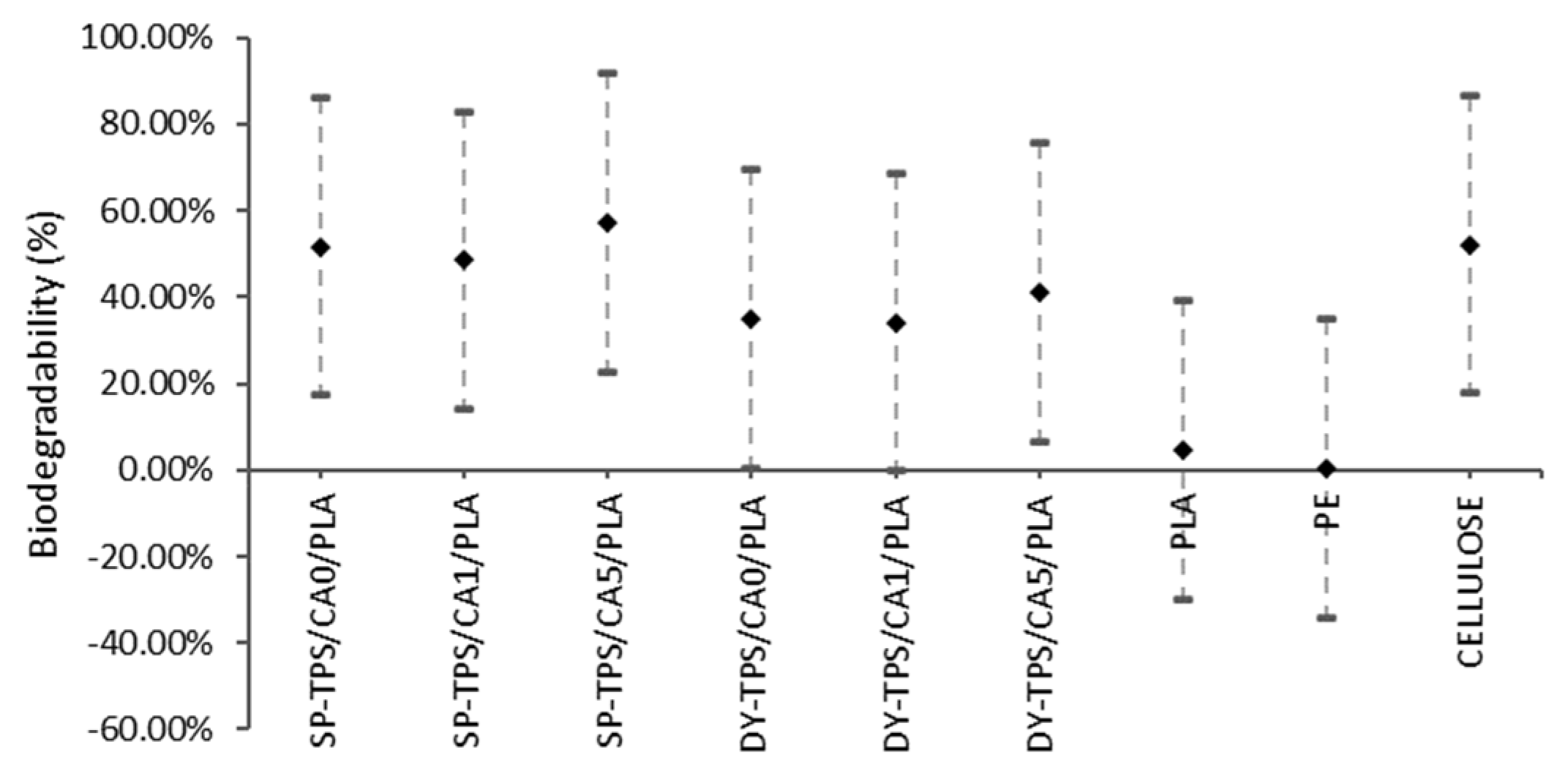
3.2. Biodegradability Assessment Based on CO2 Evolution
3.3. Morphological Characterization
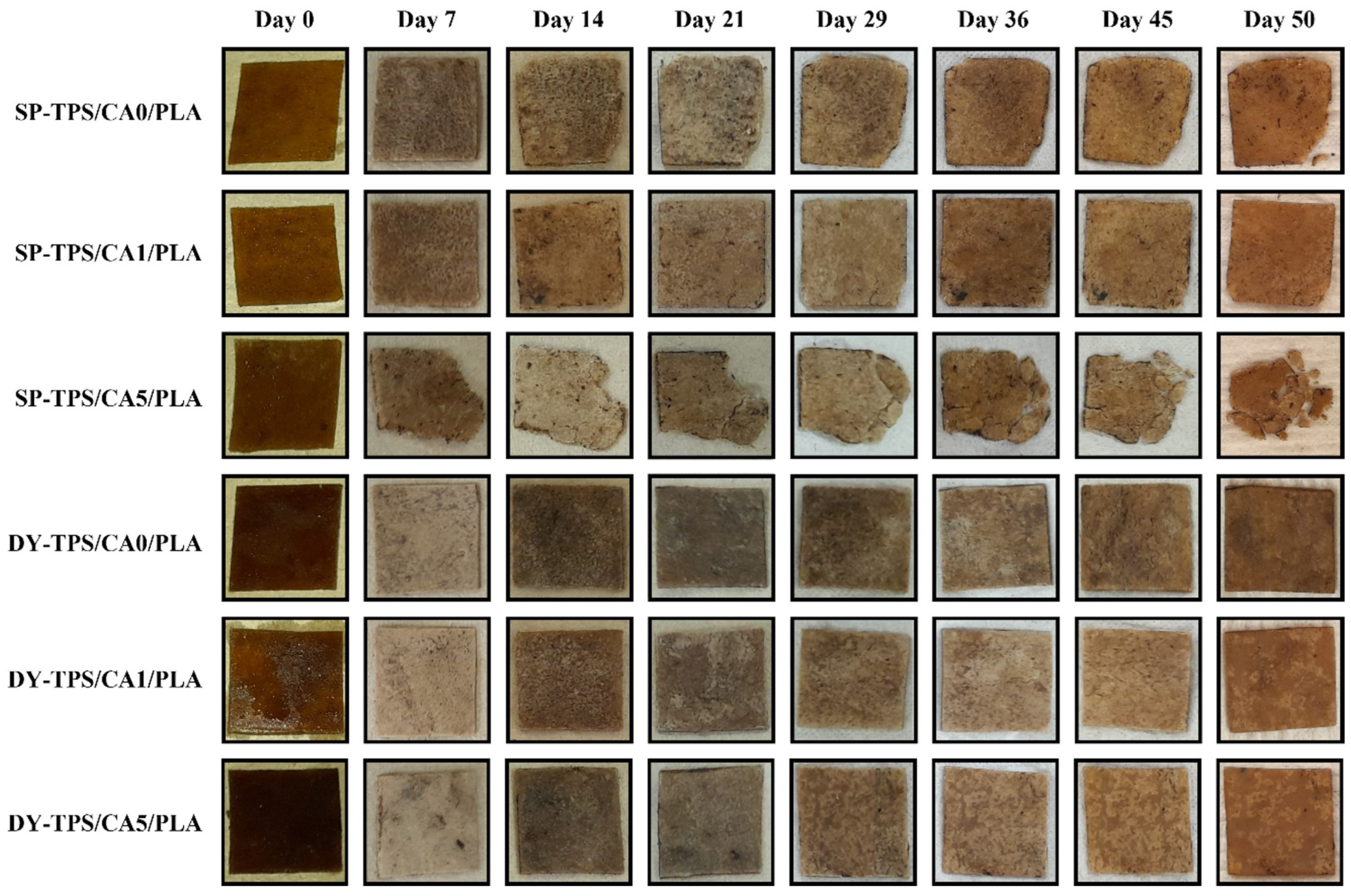
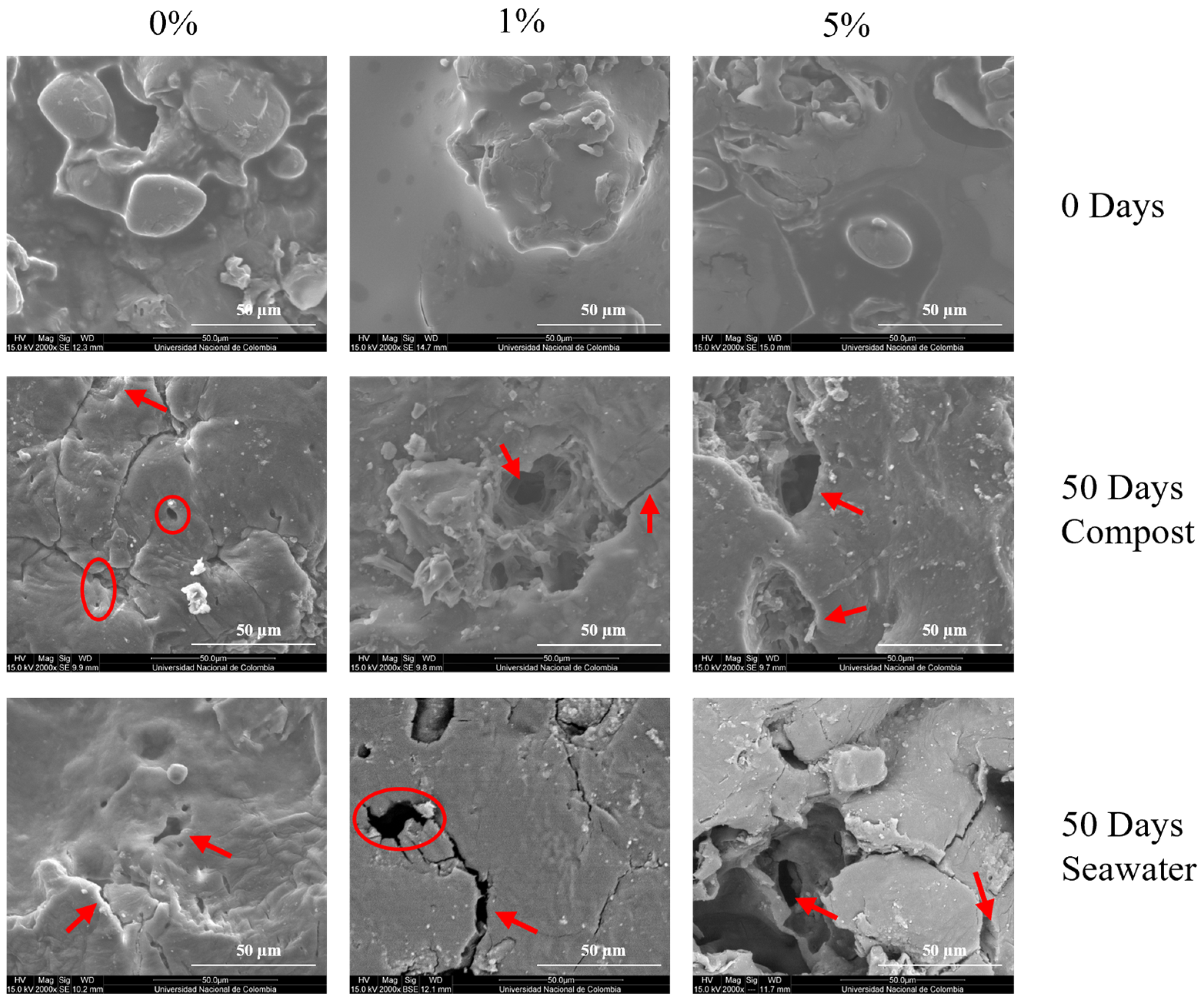
3.3.1. Morphological Changes After Degradation in Compost
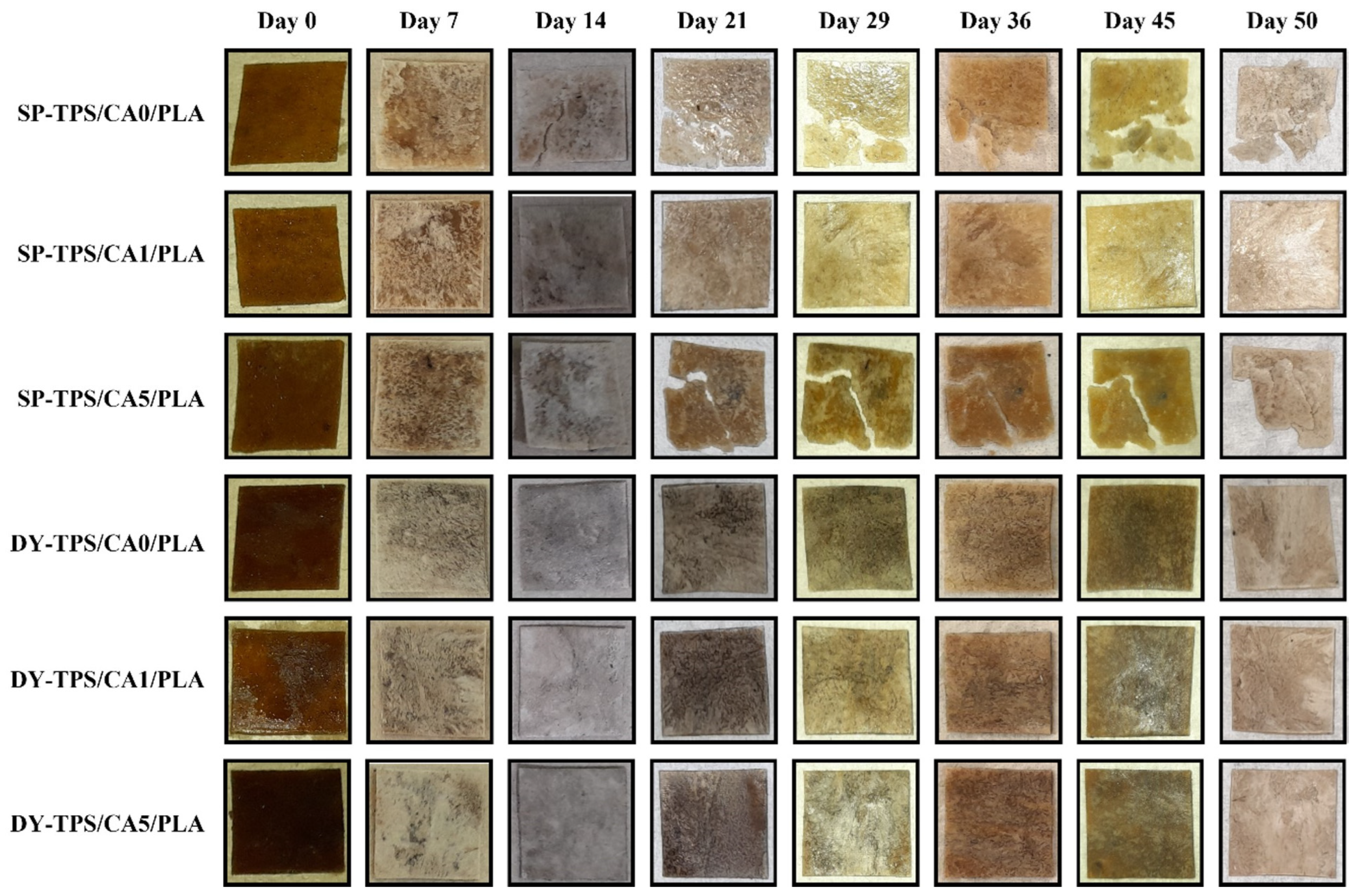
3.3.2. Morphological Changes After Degradation in Seawater
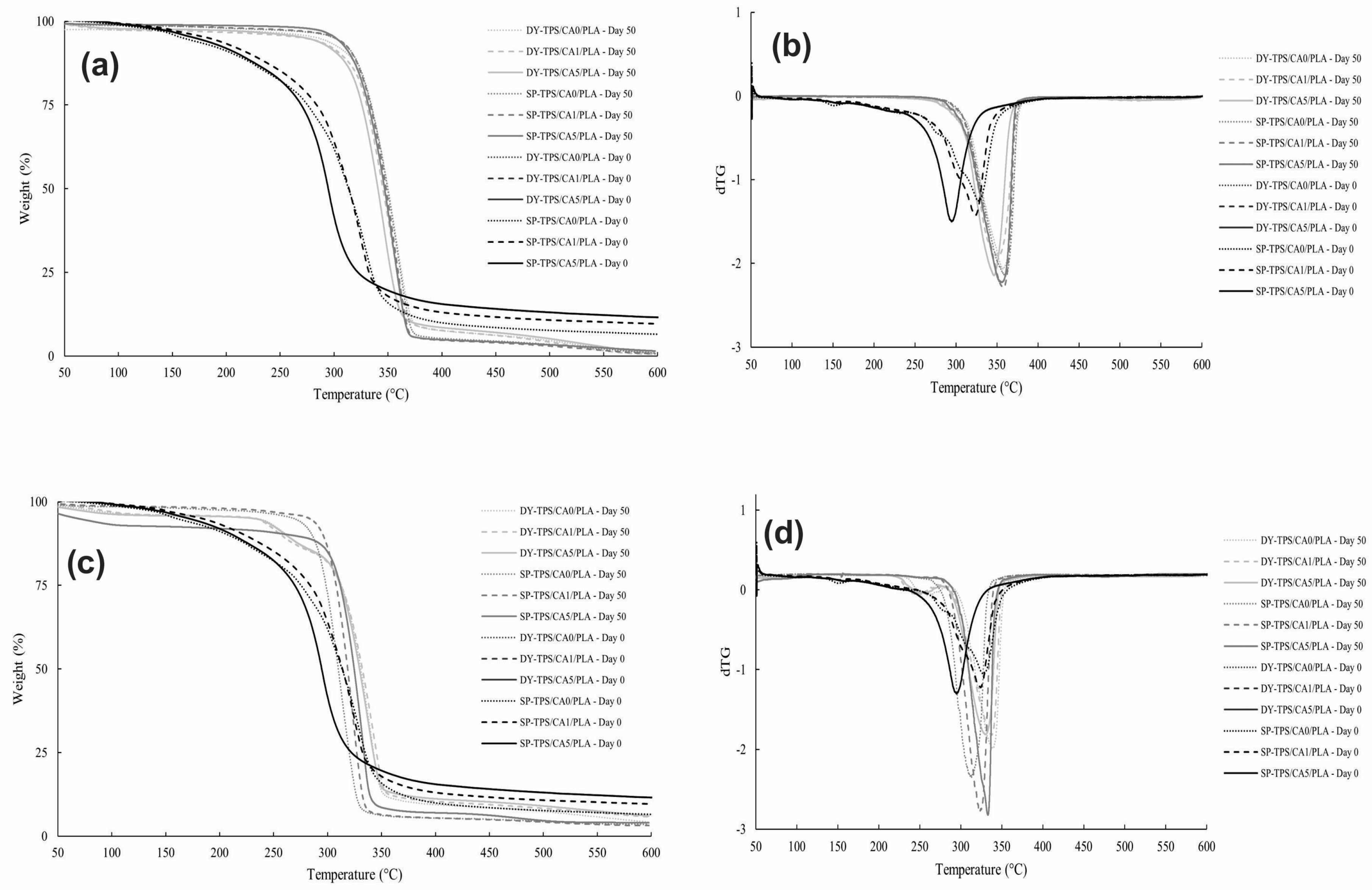
3.4. Thermal Stability and Degradation Behavior of TPS/CA/PLA Blends
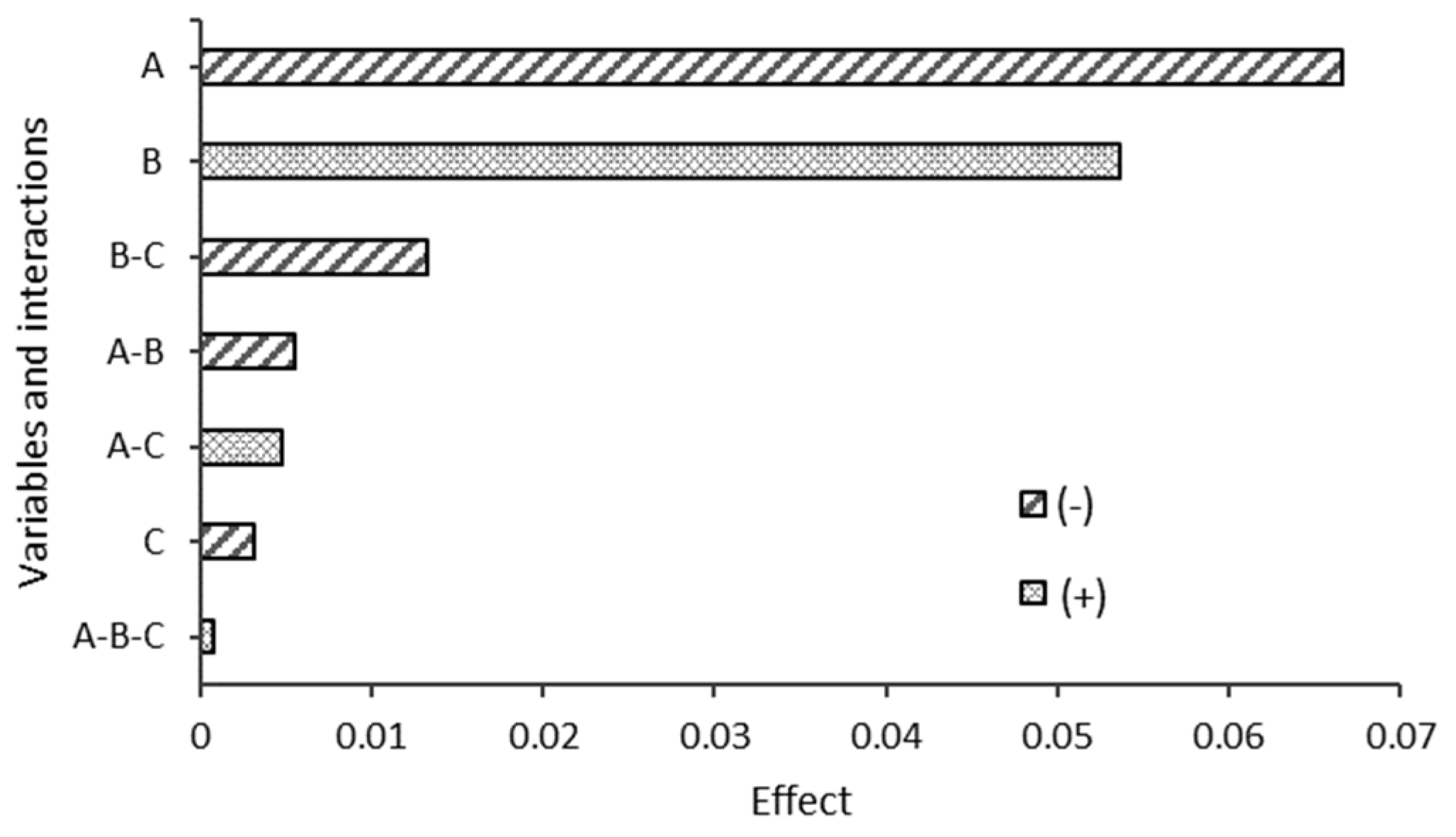
3.5. Statistical Analysis Results
3.5.1. Analysis of Variance at 21 Days
3.5.2. Analysis of Variance at 50 Days
3.5.3. Comparison of Results Between 21 and 50 Days
3.5.4. Tukey’s Multiple Comparisons Test in Seawater
3.5.5. Tukey’s Multiple Comparisons Test in Compost
- The SP-TPS/CA0/PLA and SP-TPS/CA1/PLA blends showed similar biodegradability, suggesting that the CA ratio did not have a significant impact on the degradability of blends with 0% and 1% CA in the compost.
- SP-TPS/CA5/PLA: This blend had the highest biodegradability, which is similar to that of cellulose. This suggests that a higher CA ratio (5%) significantly increased the degradability of the blends in the compost.
- The DY-TPS/CA0/PLA, DY-TPS/CA1/PLA, and DY-TPS/CA5/PLA blends with DY starch showed similar biodegradability regardless of the CA ratio. This indicates that in the case of DY starch, the variation in the CA ratio did not have a significant impact on the degradability of the compost.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chamas, A.; Moon, H.; Zheng, J.; Qiu, Y.; Tabassum, T.; Jang, J.H.; Abu-Omar, M.; Scott, S.L.; Suh, S. Degradation Rates of Plastics in the Environment. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, A.A. Plastic Pollution: When Do We Know Enough? J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 422, 126885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Davey, C.J.E.; van der Maas, K.; van Putten, R.J.; Tietema, A.; Parsons, J.R.; Gruter, G.J.M. Biodegradability of Novel High Tg Poly(Isosorbide-Co-1,6-Hexanediol) Oxalate Polyester in Soil and Marine Environments. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 815, 152781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, C.J. Plastic Pollution and Potential Solutions. Sci. Prog. 2018, 101, 207–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, M.; Shim, W.J.; Han, G.M.; Cho, Y.; Hong, S.H. Plastic Debris as a Mobile Source of Additive Chemicals in Marine Environments: In-Situ Evidence. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 856, 158893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, N.; Aqeel, M.; Noman, A.; Hashem, M.; Mostafa, Y.S.; Alhaithloul, H.A.S.; Alghanem, S.M. Linking Effects of Microplastics to Ecological Impacts in Marine Environments. Chemosphere 2021, 264, 128541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Xiong, Z.Y.; Fei, P.; Cai, J.; Walayat, N.; Xiong, H. An Approach for Compatibilization of the Starch with Poly(Lactic Acid) and Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate-Glycidyl-Methacrylate. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 161, 44–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmona, V.B.; Corrêa, A.C.; Marconcini, J.M.; Mattoso, L.H.C. Properties of a Biodegradable Ternary Blend of Thermoplastic Starch (TPS), Poly(ε-Caprolactone) (PCL) and Poly(Lactic Acid) (PLA). J. Polym. Environ. 2015, 23, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaseem, M.; Hamad, K.; Deri, F. Preparation and Studying Properties of Thermoplastic Starch/Acrylonitrile–Butadiene–Styrene Blend. Int. J. Plast. Technol. 2012, 16, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Ogunseitan, O.A.; Wong, M.H.; Tang, Y. Sustainable Materials Alternative to Petrochemical Plastics Pollution: A Review Analysis. Sustain. Horiz. 2022, 2, 100016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garlotta, D. A Literature Review of Poly(Lactic Acid). J. Polym. Environ. 2001, 9, 63–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Zhang, J. Biodegradable and Biobased Polymers. In Applied Plastics Engineering Handbook: Processing, Materials, and Applications, 2nd ed.; Plastics Design Library: Fargo, ND, USA, 2017; pp. 127–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Liang, X.; Zhou, W.; Peng, S. Strategies and Techniques for Improving Heat Resistance and Mechanical Performances of Poly(Lactic Acid) (PLA) Biodegradable Materials. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 218, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez Villadiego, K.; Arias Tapia, M.J.; Useche, J.; Escobar Macías, D. Thermoplastic Starch (TPS)/Polylactic Acid (PLA) Blending Methodologies: A Review. J. Polym. Environ. 2021, 30, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammache, Y.; Serier, A.; Chaoui, S. The Effect of Thermoplastic Starch on the Properties of Polypropylene/High Density Polyethylene Blend Reinforced by Nano-Clay. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 025308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somwanshi, S.B.; Dolas, R.T.; Wagh, V.D.; Kotade, K.B. Pharmaceutically used plasticizers: A review. Eur. J. Biomed. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 3, 277–285. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Rempel, C.; McLaren, D. Thermoplastic Starch. In Innovations in Food Packaging, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 391–412. ISBN 9780123946010. [Google Scholar]
- Bercini Martins, A.; Campomares Santana, R.M. Effect of Carboxylic Acids as Compatibilizer Agent on Mechanical Properties of Thermoplastic Starch and Polypropylene Blends. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 135, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bercini Martins, A.; Cattelan, A.K.; Campomares Santana, R.M.C. How the Compatibility between Polyethylene and Thermoplastic Starch Can Be Improved by Adding Organic Acids? Polym. Bull. 2017, 75, 2197–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bercini Martins, A.; Capomares Santana, R.M. Structure-Properties Correlation in PP/Thermoplastic Starch Blends Containing Sustainable Compatibilizer Agent. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 095336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiugao, Y.; Ning, W.; Xiaofei, M. The Effects of Citric Acid on the Properties of Thermoplastic Starch Plasticized by Glycerol. Starch-Stärke 2005, 57, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, N.; Wahab, M.K.A. Acidolysis Effect on Starch in Polylactic Acid (PLA)/Thermoplastic Starch (TPS) Blend. Solid. State Phenom. 2017, 264, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waha, M.K.A.; Ismail, H.; Othman, N. Characterization of Citric Acid-Modified Tapioca Starch and Its Influence on Thermal Behavior and Water Absorption of High Density Polyethylene/Natural Rubber/Thermoplastic Tapioca Starch Blends. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2011, 50, 748–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniyasamy, S.; Ofosu, O.; John, M.J.; Anandjiwala, R.D. Mineralization of Poly(Lactic Acid) (PLA), Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate-Co-Valerate) (PHBV) and PLA/PHBV Blend in Compost and Soil Environments. J. Renew. Mater. 2016, 4, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, A. Super Producción de Ñame, Yuca y Maíz: Montes de María Clama Ayuda. Available online: https://www.elheraldo.co/bolivar/2020/09/29/super-produccion-de-name-yuca-y-maiz-montes-de-maria-clama-ayuda/ (accessed on 18 April 2020).
- Martinez Villadiego, K.; Arias Tapia, M.J.; Useche, J.; Ledesma, Y.; Leyton, A. Thermal and Morphological Characterization of Native and Plasticized Starches of Sweet Potato (Ipomoea Batatas) and Diamante Yam (Dioscorea Rotundata). J. Polym. Environ. 2020, 29, 871–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Villadiego, K.; Arias-Tapia, M.J.; Jaramillo, A.F. Improving Thermal Stability of Starches Native Cross-Linked with Citric Acid as a Compatibilizer for Thermoplastic Starch/Polylactic Acid Blends. Polym. Bull. 2024, 81, 13253–13274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Książek, E. Citric Acid: Properties, Microbial Production, and Applications in Industries. Molecules 2023, 29, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taiatele Junior, I.; Dal Bosco, T.C.; Bertozzi, J.; Michels, R.N.; Mali, S. Biodegradability Assessment of Starch/Glycerol Foam and Poly(Butylene Adipate-Co-Terephthalate)/Starch Film by Respirometric Tests. Braz. J. Food Technol. 2020, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomadolo, N.; Dada, O.E.; Swanepoel, A.; Mokhena, T.; Muniyasamy, S. A Comparative Study on the Aerobic Biodegradation of the Biopolymer Blends of Poly(Butylene Succinate), Poly(Butylene Adipate Terephthalate) and Poly(Lactic Acid). Polymers 2022, 14, 1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corti, A.; Sudhakar, M.; Chiellini, E. Assessment of the Whole Environmental Degradation of Oxo-Biodegradable Linear Low Density Polyethylene (LLDPE) Films Designed for Mulching Applications. J. Polym. Environ. 2012, 20, 1007–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 19679:2020; Plastics—Determination of Aerobic Biodegradation of Non-Floating Plastic Materials in a Seawater/Sediment Interface—Method by Analysis of Evolved Carbon Dioxide. International Organization for Standarization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
- ASTM D5338; American Society for Testing and Materials Standard Test Method for Determining Aerobic Biodegradation of Plastic Materials Under Controlled Composting Conditions, Incorporating Thermophilic Temperatures. American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM): West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021.
- Mantia, F.P.L.; Ascione, L.; Mistretta, M.C.; Rapisarda, M.; Rizzarelli, P. Comparative Investigation on the Soil Burial Degradation Behaviour of Polymer Films for Agriculture before and after Photo-Oxidation. Polymers 2020, 12, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, N.; Wahab, M.K.A.; Uylan, D.N.; Ismail, H. Physical and Degradation Properties of Polylactic Acid and Thermoplastic Starch Blends-Effect of Citric Acid Treatment on Starch Structures. Bioresources 2017, 12, 3076–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, S.; Ray, D.; Mitra, D. Role of Crosslinker on the Biodegradation Behavior of Starch/Polyvinylalcohol Blend Films. J. Polym. Environ. 2012, 20, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briassoulis, D.; Pikasi, A.; Papardaki, N.G.; Mistriotis, A. Aerobic Biodegradation of Bio-Based Plastics in the Seawater/Sediment Interface (Sublittoral) Marine Environment of the Coastal Zone–Test Method under Controlled Laboratory Conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 722, 137748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarbuk, A.; Čorak, I.; Đorđević, D.; Draczyński, Z. Accelerated hydrolysis of PLA fibers at low temperature. In Proceedings of the 21st World Textile Conference, Lodz, Poland, 7 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Cuevas-Carballo, Z.B.; Duarte-Aranda, S.; Canché-Escamilla, G. Properties and Biodegradability of Thermoplastic Starch Obtained from Granular Starches Grafted with Polycaprolactone. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2017, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momeni, S.; Rezvani Ghomi, E.; Shakiba, M.; Shafiei-Navid, S.; Abdouss, M.; Bigham, A.; Khosravi, F.; Ahmadi, Z.; Faraji, M.; Abdouss, H.; et al. The Effect of Poly (Ethylene Glycol) Emulation on the Degradation of PLA/Starch Composites. Polymers 2021, 13, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méité, N.; Konan, L.K.; Tognonvi, M.T.; Doubi, B.I.H.G.; Gomina, M.; Oyetola, S. Properties of Hydric and Biodegradability of Cassava Starch-Based Bioplastics Reinforced with Thermally Modified Kaolin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 254, 117322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Lin, Q.; Zeng, J.; Gao, H.; Muratkhan, M.; Li, W. Understanding the Improvement of Sorghum Starch Acid Hydrolysis Modification by E-Beam Irradiation: A Supramolecular Structure Perspective. Food Chem. 2024, 437, 137820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bher, A. Preparación y Caracterización de Almidón de Mandioca Termoplástico Combinado Con Poli (Ácido Láctico); Estudio Del Comportamiento Producido Por El Agregado de Grafeno Como Material de Carga; Universidad Nacional de General San Martín: San Martín, Argentina, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Sarazin, P.; Orts, W.J.; Imam, S.H.; Favis, B.D. Biodegradation of Thermoplastic Starch and Its Blends with Poly(Lactic Acid) and Polyethylene: Influence of Morphology. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2011, 212, 1147–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho-Muñoz, R.; Villada-Castillo, H.S.; Solanilla-Duque, J.F. Anaerobic Biodegradation under Slurry Thermophilic Conditions of Poly(Lactic Acid)/Starch Blend Compatibilized by Maleic Anhydride. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 1859–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar-Sánchez, M.R.; Delgado-Calvache, L.I.; Casas-Zapata, J.C.; Villada-Castillo, H.S.; Solanilla-Duque, J.F. Soil Biodegradation of a Blend of Cassava Starch and Polylactic Acid. Ing. E Investig. 2022, 42, e93710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punia Bangar, S.; Ashogbon, A.O.; Singh, A.; Chaudhary, V.; Whiteside, W.S. Enzymatic Modification of Starch: A Green Approach for Starch Applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 287, 119265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Li, D.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y. Biodegradation Behavior and Digestive Properties of Starch-Based Film for Food Packaging—A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 63, 6923–6945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masoudi, M. Biochar Based Composite Material: Study of Mechanical and Physicochemical Properties; University of Saskatchewan: Saskatoon, SK, Canada, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, F.; Meng, W.; Li, C.; Cui, R.; Xia, Z.; Liu, C. Polyurethane Prepolymer-Modified High-Content Starch-PBAT Films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 253, 117168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, S.X.; Andriyana, A.; Ong, H.C.; Lim, S.; Pang, Y.L.; Ngoh, G.C. A Comprehensive Review on the Emerging Roles of Nanofillers and Plasticizers towards Sustainable Starch-Based Bioplastic Fabrication. Polymers 2022, 14, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruginescu, R.; Purcarea, C. Plastic-Degrading Enzymes from Marine Microorganisms and Their Potential Value in Recycling Technologies. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turco, R.; Ortega-Toro, R.; Tesser, R.; Mallardo, S.; Collazo-Bigliardi, S.; Boix, A.C.; Malinconico, M.; Rippa, M.; di Serio, M.; Santagata, G. Poly (Lactic Acid)/Thermoplastic Starch Films: Effect of Cardoon Seed Epoxidized Oil on Their Chemicophysical, Mechanical, and Barrier Properties. Coatings 2019, 9, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas-Carballo, Z.B.; Duarte-Aranda, S.; Canché-Escamilla, G. Properties and Biodegradation of Thermoplastic Starch Obtained from Grafted Starches with Poly(Lactic Acid). J. Polym. Environ. 2019, 27, 2607–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Shi, Q.; Guo, S. Study of the Preparation and Properties of TPS/PBSA/PLA Biodegradable Composites. J. Compos. Sci. 2021, 5, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romera-Castillo, C.; Mallenco-Fornies, R.; Saá-Yánez, M.; Álvarez-Salgado, X.A. Leaching and Bioavailability of Dissolved Organic Matter from Petrol-Based and Biodegradable Plastics. Mar. Environ. Res. 2022, 176, 105607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Blend | TPS (%) | PLA (%) | CA (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| DY-TPS/CA0/PLA | 60.0 | 40.0 | 0.0 |
| DY-TPS/CA1/PLA | 59.4 | 39.6 | 1.0 |
| DY-TPS/CA5/PLA | 57.0 | 38.0 | 5.0 |
| SP-TPS/CA0/PLA | 60.0 | 40.0 | 0.0 |
| SP-TPS/CA1/PLA | 59.4 | 39.6 | 1.0 |
| SP-TPS/CA5/PLA | 57.0 | 38.0 | 5.0 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Humidity (%) * | 6.00 |
| Ash (%) * | 48.90 |
| Total Organic Carbon [TOC] (%) * | 18.60 |
| Total Nitrogen | 1.56 |
| Assimilable Phosphorus [P2O5] (%) * | 3.20 |
| Water-soluble Potassium [K2O] (%) * | 1.00 |
| pH | 6.50 |
| Density (g/cm3) | 0.46 |
| Cation Exchange Capacity (meq/100 g) * | 71.30 |
| Humidity Retention Capacity (%) * | 149.0 |
| Dry Solids (%) | 55.00 |
| Volatile Solids (%) | 53.00 |
| C/N Ratio | 11.92 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Salinity (ppt) | 30.75 |
| Acidity | - |
| Alkalinity [CaCO3] (mg/L) | 105.0 |
| Carbon Dioxide [CO2] (mg/L) | 25.00 |
| Nitrite [NO2-N] (mg/L) | <0.66 |
| Nitrate [NO3-N] (mg/L) | <10.0 |
| Phosphate [PO4] (mg/L) | 5.00 |
| Dissolved Oxygen [O2] (mg/L) | 6.00 |
| Density (g/cm3) | 1.014 |
| pH | 7.06 |
| Total Organic Carbon [TOC] (mg/L) | 112.95 |
| Conductivity (mS/cm) | 45.80 |
| Temperature (°C) | 27.00 |
| Variable | Levels | Coded Variables |
|---|---|---|
| Type of starch (A) | SP | −1 |
| DY | 1 | |
| CA concentration (B) | 0% | −1 |
| 1% | 0 | |
| 5% | 1 | |
| Degradation medium (C) | Compost | −1 |
| Seawater | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moreno-Bohorquez, E.; Arias-Tapia, M.J.; Martínez-Villadiego, K.; Rhenals-Julio, J.D.; Jaramillo, A.F. Effect of Starch Variety and Environmental Conditions on the Aerobic Biodegradation of Citric Acid-Compatibilized Thermoplastic Starch/Polylactic Acid Blends. Polymers 2025, 17, 1295. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101295
Moreno-Bohorquez E, Arias-Tapia MJ, Martínez-Villadiego K, Rhenals-Julio JD, Jaramillo AF. Effect of Starch Variety and Environmental Conditions on the Aerobic Biodegradation of Citric Acid-Compatibilized Thermoplastic Starch/Polylactic Acid Blends. Polymers. 2025; 17(10):1295. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101295
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoreno-Bohorquez, Elizabeth, Mary Judith Arias-Tapia, Keydis Martínez-Villadiego, Jesús D. Rhenals-Julio, and Andrés F. Jaramillo. 2025. "Effect of Starch Variety and Environmental Conditions on the Aerobic Biodegradation of Citric Acid-Compatibilized Thermoplastic Starch/Polylactic Acid Blends" Polymers 17, no. 10: 1295. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101295
APA StyleMoreno-Bohorquez, E., Arias-Tapia, M. J., Martínez-Villadiego, K., Rhenals-Julio, J. D., & Jaramillo, A. F. (2025). Effect of Starch Variety and Environmental Conditions on the Aerobic Biodegradation of Citric Acid-Compatibilized Thermoplastic Starch/Polylactic Acid Blends. Polymers, 17(10), 1295. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101295






