Highly Stable Flexible SERS-Imprinted Membrane Based on Plasmonic MOF Material for the Selective Detection of Chrysoidin in Environmental Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Apparatus and Measurements
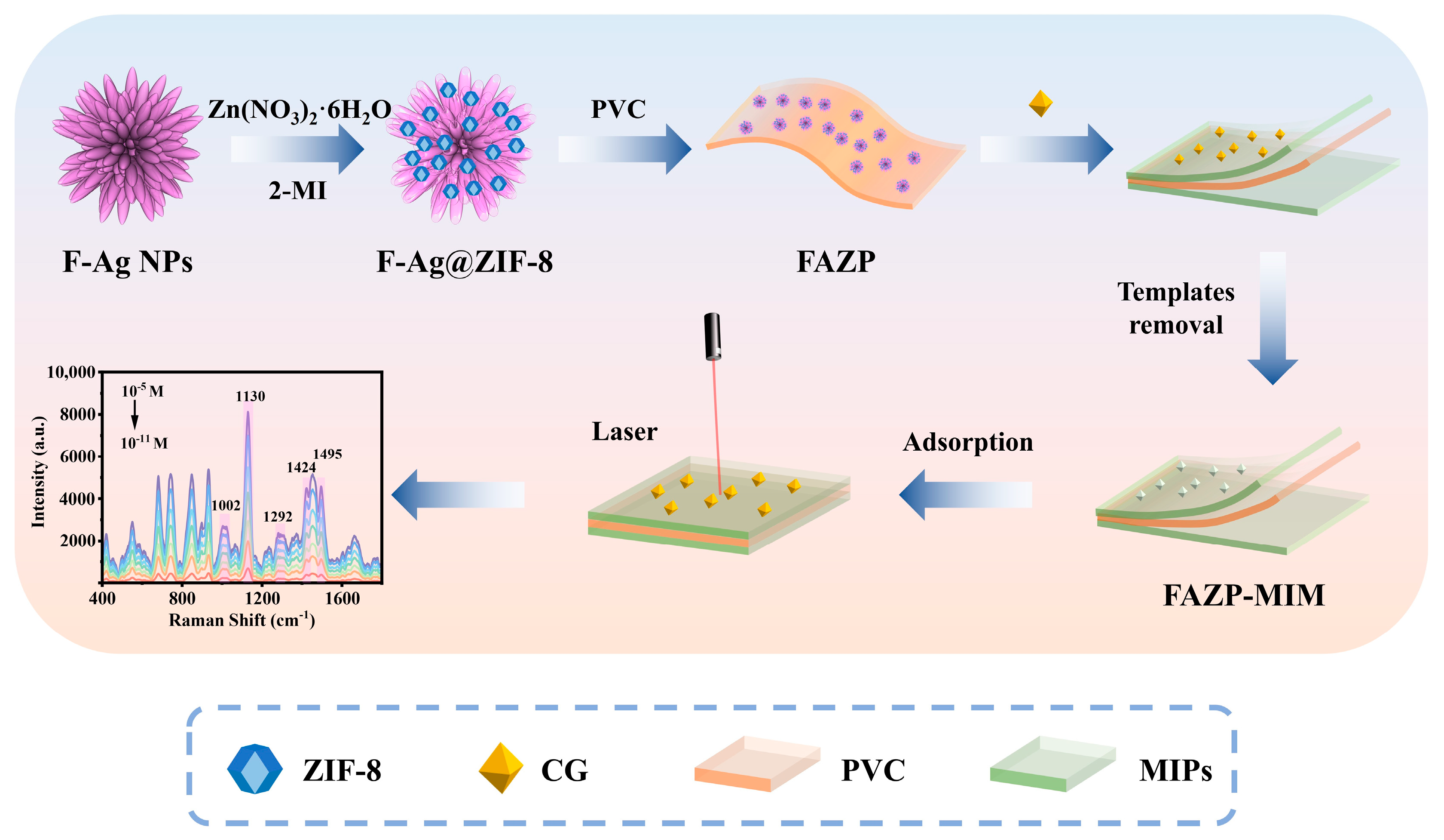
2.3. Preparation of F-Ag NPs
2.4. Preparation of F-Ag@ZIF-8
2.5. Preparation of F-Ag@ZIF-8/PVC
2.6. Preparation of F-Ag@ZIF-8/PVC-MIM
2.7. Raman Detection Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
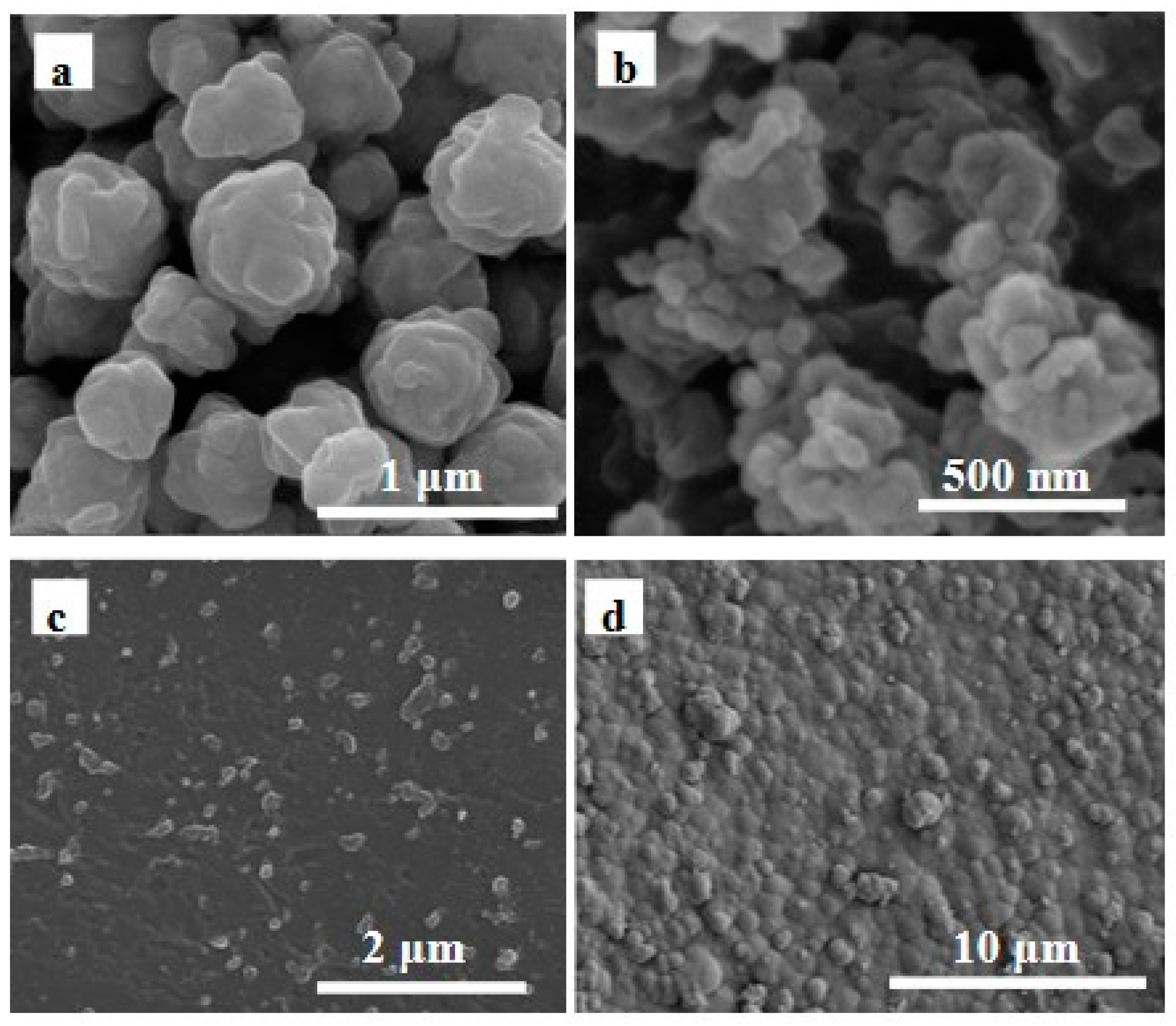
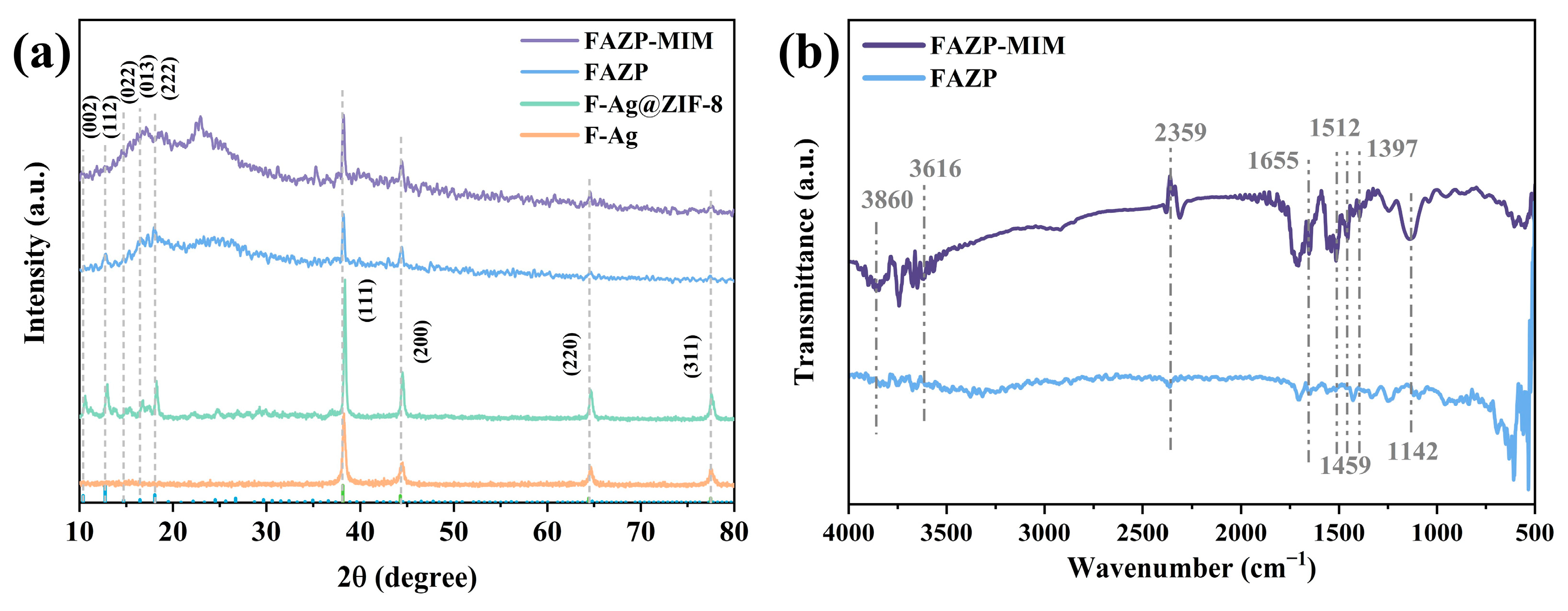
3.1. Synthesis Process and Characterisation of FAZP-MIM
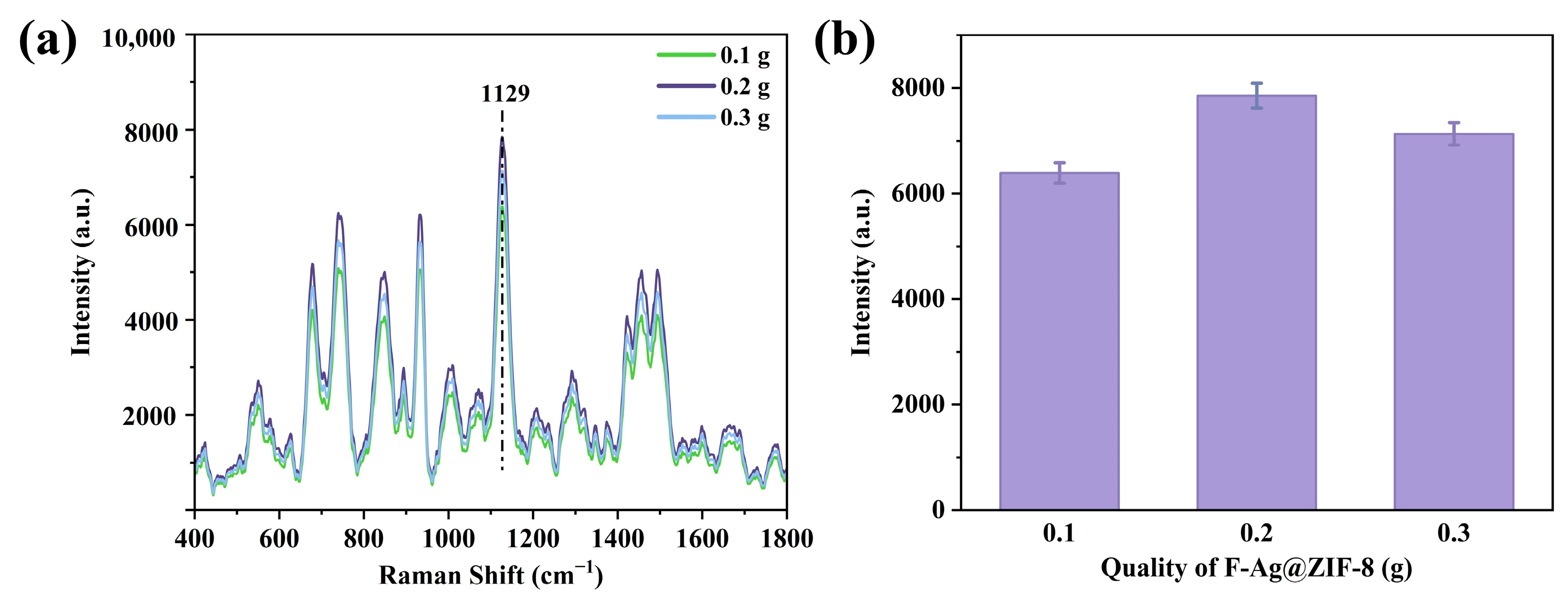
3.2. Optimization of Synthesis Parameters
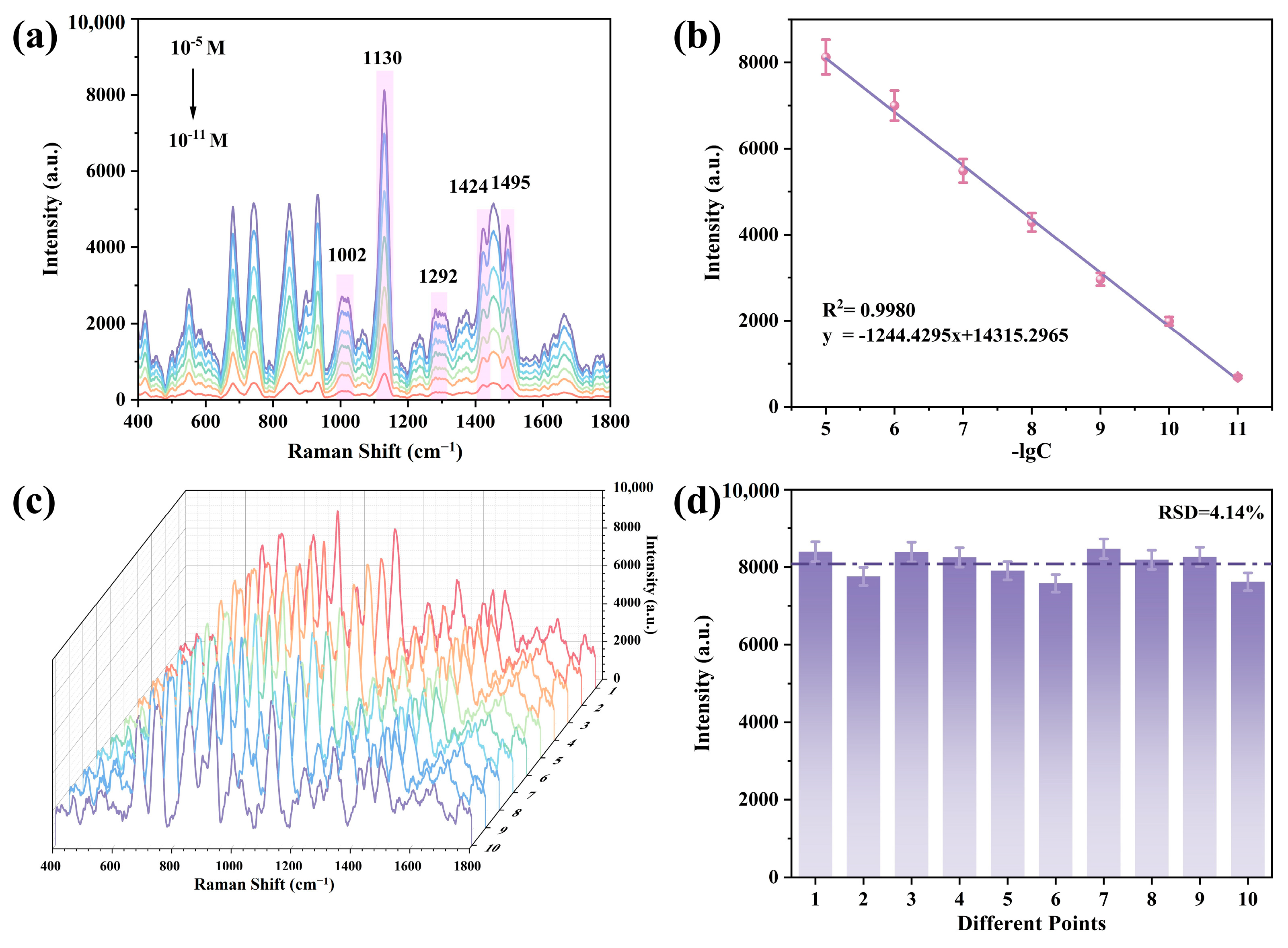
3.3. Sensitivity of FAZP-MIM
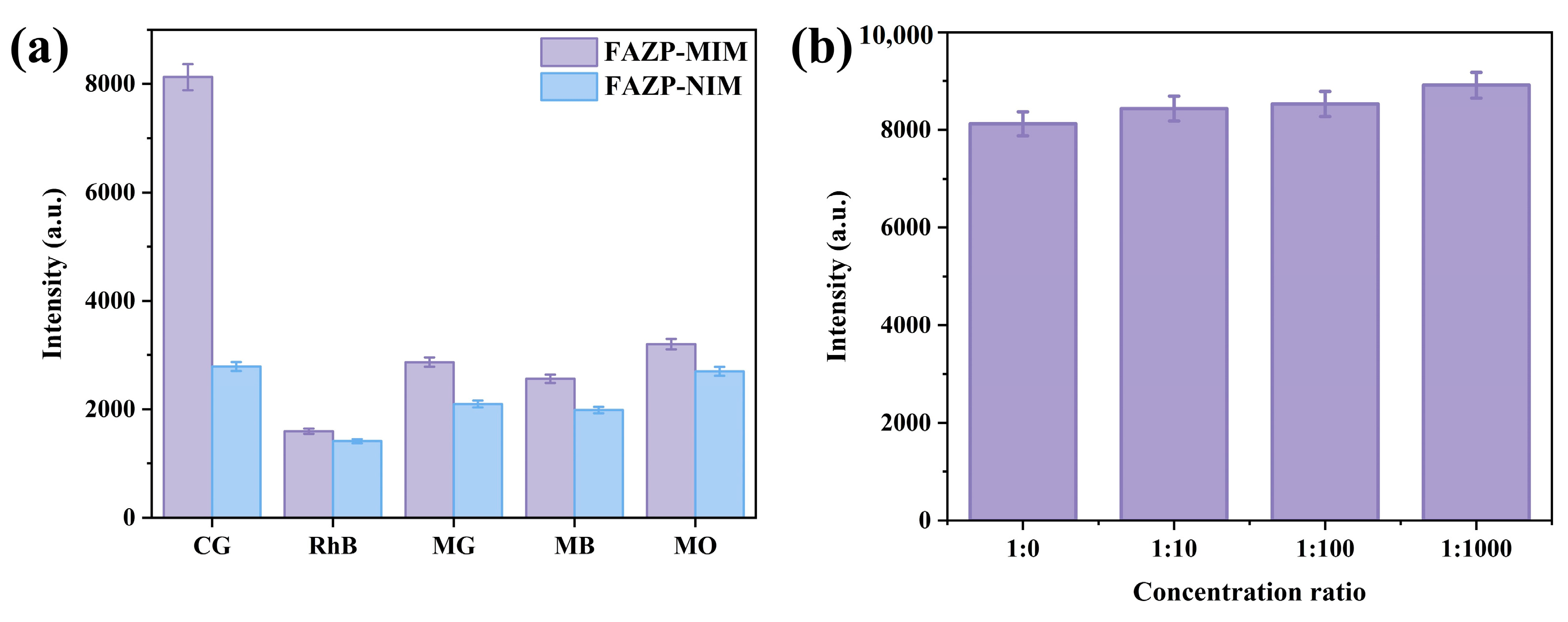
3.4. Selectivity of FAZP-MIM
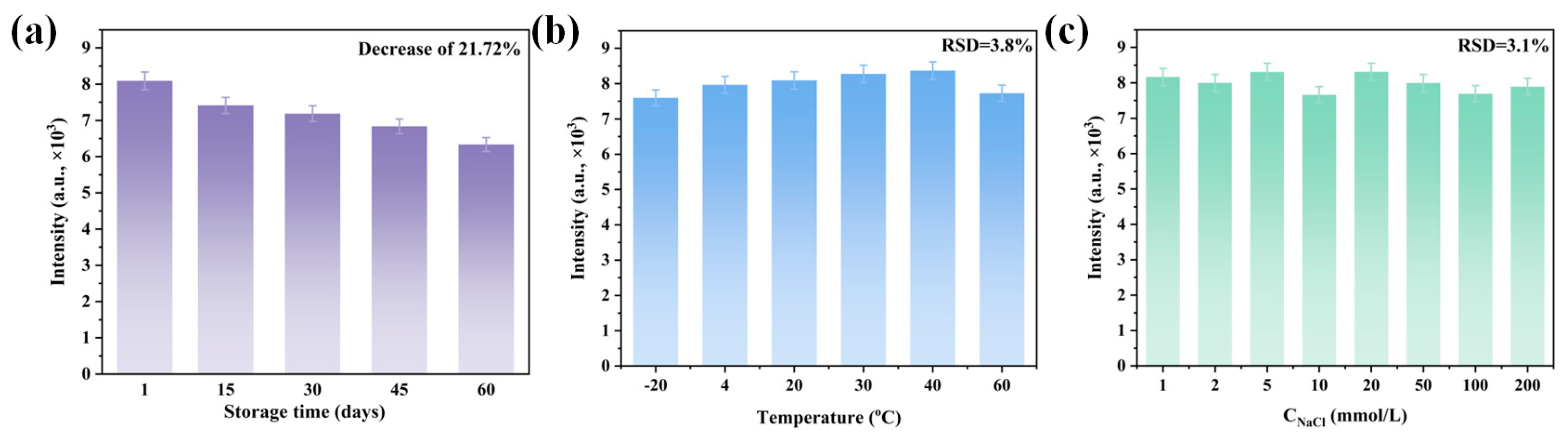
3.5. Stability of FAZP-MIM
3.6. Recycling of FAZP-MIM
3.7. Inspection of Actual Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, L.; Iqbal, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhang, F.; Chen, W.; Wu, T.; Du, Y. Chitosan/Al2O3-HA nanocomposite beads for efficient removal of estradiol and chrysoidin from aqueous solution. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 145, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, Z.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Qiu, H. Selective recognition and discrimination of water-soluble azo dyes by a seven-channel molecularly imprinted polymer sensor array. J. Sep. Sci. 2014, 37, 2764–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Li, M.; Li, J. Synthesis and characterization of molecularly imprinted polymers with modified rosin as a cross-linker and selective SPE-HPLC detection of basic orange II in foods. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 6397–6406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Wu, Y.; Dong, X.; Liu, C.; He, S.; Wang, S. Simultaneous determination of banned acid orange dyes and basic orange dyes in foodstuffs by liquid chromatography-tandem electrospray ionization mass spectrometry via negative/positive ion switching mode. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 3834–3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Chen, W.; Han, Y.; Ling, L. Simultaneous qualitative analysis of basic orange2,metanil yellow, ponceau 2R and other mixed pigments in food by TLC. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2009, 9, 296. [Google Scholar]
- Pramanik, A.; Davis, D.; Patibandla, S.; Begum, S.; Ray, P.; Gates, K.; Gao, Y.P. Chandra Ray; A WS2-gold nanoparticle heterostructure-based novel SERS platform for the rapid identification of antibiotic-resistant pathogens. Nanoscale Adv. 2020, 2, 2025–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Zhu, T.; Liu, Z. Approaching the electromagnetic mechanism of surface-enhanced Raman scattering: From self-assembled arrays to individual gold nanoparticles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 1296–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelouche, S.N.K.; Biglione, C.; Horcajada, P. Advances in plasmonic-based MOF composites, their bio-applications, and perspectives in this field. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2022, 19, 1417–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Shang, W.; Xuan, M.; Ma, G.; Ben, Z. Layered filter paper-silver nanoparticle-ZIF-8 composite for efficient multi-mode enrichment and sensitive SERS detection of thiram. Chemosphere 2022, 288, 132635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Xu, J.; Xu, J.; Ma, J.; Bai, Y.; Cao, S.; Zhang, S.; Pang, H. Metal-organic framework (MOF) composites as promising materials for energy storage applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 307, 102732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Seong, N.H.; Dlott, D.D. Measurement of the distribution of site enhancements in surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Science 2008, 321, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Sun, L.; Bao, S.; Liu, D.; Li, H.; Liu, Y. Self-assembly flexible SERS imprinted membrane based on Ag nanocubes for selective detection of microcystin-LR. Mikrochim. Acta 2023, 191, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.T.; Liu, Y.Y.; Qian, S.Q.; Yang, J.M.; Li, Y.; Gao, J.; Liu, C.G.; Wang, K.; Xia, X.H. Free-Standing Single Ag Nanowires for Multifunctional Optical Probes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 19023–19030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Luo, Z.; Lin, X. An ultrafast electrochemical synthesis of Au@Ag core-shell nanoflowers as a SERS substrate for thiram detection in milk and juice. Food Chem. 2023, 402, 134433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhu, J.; Cheng, Y.; Cai, D. Functionalized UIO-66@Ag nanoparticles substrate for rapid and ultrasensitive SERS detection of di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate in plastics. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 349, 130793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Ouardi, M.; El Aouni, A.; Ahsaine, H.A.; Zbair, M.; BaQais, A.; Saadi, M. ZIF-8 metal organic framework composites as hydrogen evolution reaction photocatalyst: A review of the current state. Chemosphere 2022, 308, 136483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Trinh, B.T.; Kim, K.H.; Moon, J.; Kang, H.; Jo, K.; Akter, R.; Jeong, J.; Lim, E.K.; Jung, J.; et al. Au@ZIF-8 SERS paper for food spoilage detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 179, 113063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Li, A.; Chen, X.; Wang, T. Understanding the Role of Metal-Organic Frameworks in Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Application. Small 2020, 16, e2004802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cai, X.; Yin, N.; Che, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Yu, J.; Liu, C. Hierarchical PVDF/ZnO/Ag/ZIF-8 nanofiber membrane used in trace-level Raman detection of H2S. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 471, 134441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, C.; Zhao, C.; Wang, H.; Ma, N.; Li, J.; Qiao, Y.; Chang, L.; Zhao, B. Highly sensitive SERS behavior and wavelength-dependence charge transfer effect on the PS/Ag/ZIF-8 substrate. Spectrochim. Acta. Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 247, 119126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.Q.; Hou, R.N.; Zhu, Y.Z.; Wang, X.T.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.J.; Zhang, L.; Tian, Z.Q.; Li, J.F. Au@ZIF-8 Core-Shell Nanoparticles as a SERS Substrate for Volatile Organic Compound Gas Detection. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 7188–7195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Miao, P.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhang, B.; Du, Y.; Han, X.; Sun, J.; Xu, P. Recent Advances in Plasmonic Nanostructures for Enhanced Photocatalysis and Electrocatalysis. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2000086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gellé, A.; Jin, T.; de la Garza, L.; Price, G.D.; Besteiro, L.V.; Moores, A. Applications of Plasmon-Enhanced Nanocatalysis to Organic Transformations. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 986–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; Zhou, R.; Takei, K.; Hong, M. Toward Flexible Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) Sensors for Point-of-Care Diagnostics. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1900925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Hashemi, S.A.; Rahmanian, V.; Kalashgrani, M.Y.; Gholami, A.; Omidifar, N.; Chiang, W.H. Highly Sensitive Flexible SERS-Based Sensing Platform for Detection of COVID-19. Biosensors 2022, 12, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Zhong, L.B.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, X.; Zheng, Y.M. Polymer induced one-step interfacial self-assembly method for the fabrication of flexible, robust and free-standing SERS substrates for rapid on-site detection of pesticide residues. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 12829–12836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, G.; Yang, J.; Li, J.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, J. Ag triangle nanoplates assembled on PVC/SEBS membrane as flexible SERS substrates for skin cortisol sensing. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2023, 303, 123154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Qiao, X.; Liu, K.; Bai, W.; Wang, T. Hollow Metal Organic Framework Improves the Sensitivity and Anti-Interference of the Detection of Exhaled Volatile Organic Compounds. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2202805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Xu, Z.; Liu, Z. Molecularly Imprinting-Aptamer Techniques and Their Applications in Molecular Recognition. Biosensors 2022, 12, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, W. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for the Identification and Separation of Chiral Drugs and Biomolecules. Polymers 2016, 8, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Guo, J.; Wang, Y.; Dong, W.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, L. Bio-Inspired Imprinting Materials for Biomedical Applications. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, e2202038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, S.; Karimi, M. Recent configurations and progressive uses of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for drug analysis. Talanta 2017, 167, 470–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Wang, D.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, J.; Yang, W.; Su, Z.; Sun, W.; Li, C. Light-Initiated Imprinted Membrane-Based Biomimetic SERS Sensor toward Selective Detection of Trace MC-LR. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 5887–5896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.P.; Jia, C.; He, X.W.; Li, W.Y.; Zhang, Y.K. Thermosensitive Metal Chelation Dual-Template Epitope Imprinting Polymer Using Distillation-Precipitation Polymerization for Simultaneous Recognition of Human Serum Albumin and Transferrin. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 9060–9068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez-Climente, R.; Clavié, M.; Dumy, P.; Mehdi, A.; Subra, G. Sol-gel process: The inorganic approach in protein imprinting. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 2155–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yuan, N.; Chen, T.; Li, B.; Wang, Q. Fabrication of hydrangea-shaped Bi2WO6/ZIF-8 visible-light responsive photocatalysts for degradation of methylene blue. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Pan, M.; Yang, X.; Liu, K.; Song, Y.; Wang, S. Effective adsorption and in-situ SERS detection of multi-target pesticides on fruits and vegetables using bead-string like Ag NWs@ZIF-8 core-shell nanochains. Food Chem. 2022, 395, 133623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, D.; Wang, J.; Yu, H.; Huang, C.; Jiang, W.; Liu, C.; Che, G.; Wang, D. A novel imprinted sensor based on Ag-modified composite MOFs for selective detection of Rhodamine B in river. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Lin, X.; Huang, H.; Li, P.; Wu, J.; Huang, X.; Cai, H.; Han, H.; Zheng, J.; Zhou, H. Au@Ag@ZIF-8 multifunction probe with internally o-phenylenediamine encoding for the colorimetric, fluorescence, and SERS multi-mode optical detection of reactive sulfur species. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 361, 131762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.; Lei, Q.; Xia, C.; Guan, Y.; Yang, Y.; He, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, M. Synthesis of Ag and AgCl co-doped ZIF-8 hybrid photocatalysts with enhanced photocatalytic activity through a synergistic effect. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 698–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Li, W.; Zhao, L.; Li, F.; Xie, Y.; Yao, W.; Liu, W.; Lin, Z. Simultaneous SERS detection of illegal food additives rhodamine B and basic orange II based on Au nanorod-incorporated melamine foam. Food Chem. 2021, 357, 129741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Xu, Q.; Liu, Q.; Wang, T.; Liu, Z. Post-synthetic modification of a magnetic covalent organic framework with alkyne linkages for efficient magnetic solid-phase extraction and determination of trace basic orange II in food samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2023, 1690, 463777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Hao, R.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Y. Green synthesis of multi-dimensional plasmonic coupling structures: Graphene oxide gapped gold nanostars for highly intensified surface enhanced Raman scattering. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 349, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Sun, L.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, Y.; Hu, H.; Iqbal, J.; Du, Y. Rapid determination of illegal additives chrysoidin and malachite green by surface-enhanced Raman scattering with silanized support based substrate. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2018, 29, 981–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample | Added (mol·L−1) | Found (mol·L−1) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CG | 1 × 10−5 | 1.095 × 10−5 | 109.50 | 4.082 |
| CG | 2 × 10−5 | 1.973 × 10−5 | 98.65 | 3.571 |
| CG | 3 × 10−5 | 2.879 × 10−5 | 95.96 | 2.964 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Li, H.; Wang, D.; Lu, J.; Wu, Y.; Sun, W. Highly Stable Flexible SERS-Imprinted Membrane Based on Plasmonic MOF Material for the Selective Detection of Chrysoidin in Environmental Water. Polymers 2025, 17, 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17010081
Liu X, Li H, Wang D, Lu J, Wu Y, Sun W. Highly Stable Flexible SERS-Imprinted Membrane Based on Plasmonic MOF Material for the Selective Detection of Chrysoidin in Environmental Water. Polymers. 2025; 17(1):81. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17010081
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xinyi, Hongji Li, Dandan Wang, Jian Lu, Yilin Wu, and Wei Sun. 2025. "Highly Stable Flexible SERS-Imprinted Membrane Based on Plasmonic MOF Material for the Selective Detection of Chrysoidin in Environmental Water" Polymers 17, no. 1: 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17010081
APA StyleLiu, X., Li, H., Wang, D., Lu, J., Wu, Y., & Sun, W. (2025). Highly Stable Flexible SERS-Imprinted Membrane Based on Plasmonic MOF Material for the Selective Detection of Chrysoidin in Environmental Water. Polymers, 17(1), 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17010081









