Self-Powered Triboelectricity-Driven Multiple-Input–Single-Output Occupancy Detection System Using a Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Energy Management
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
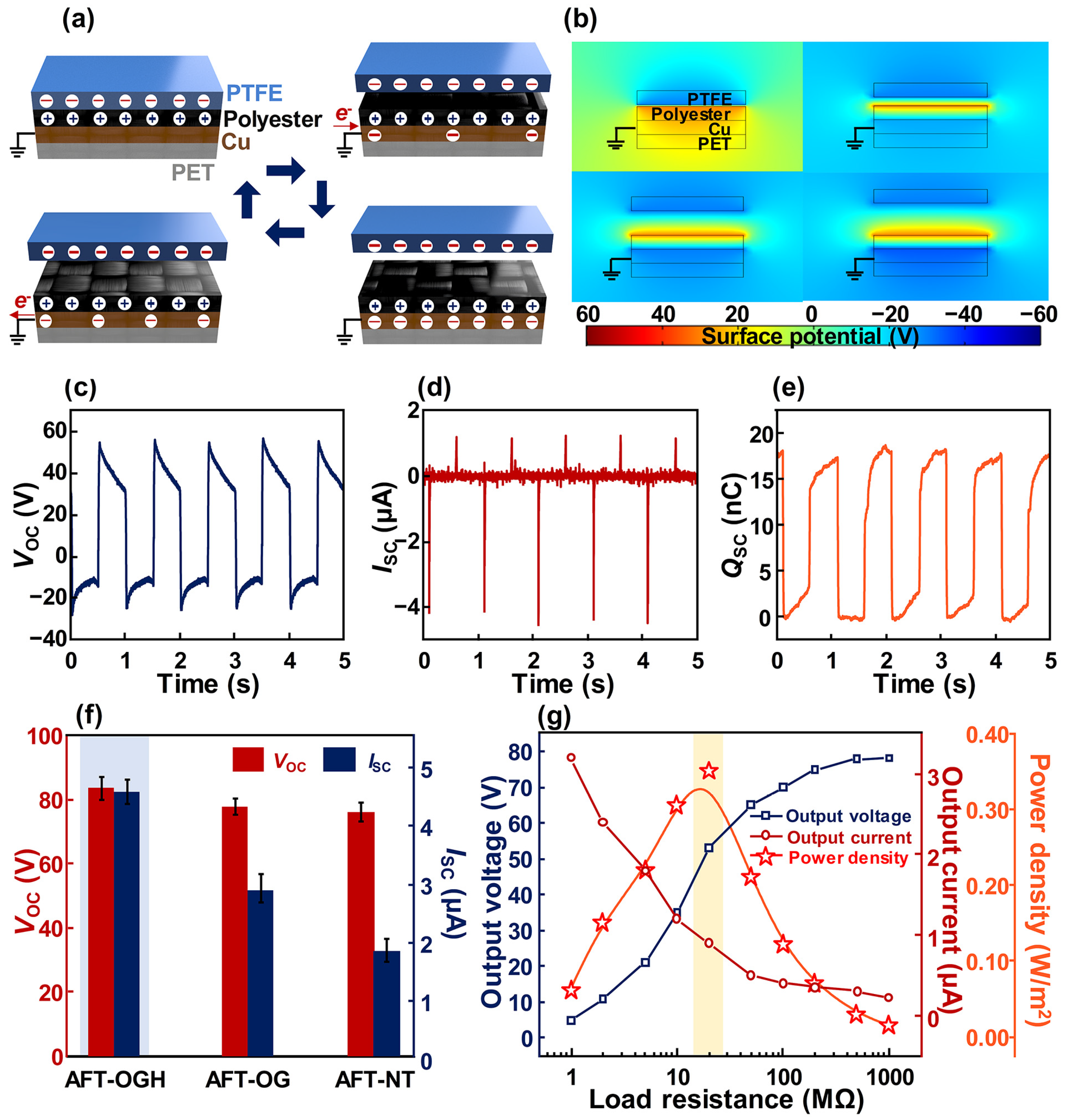
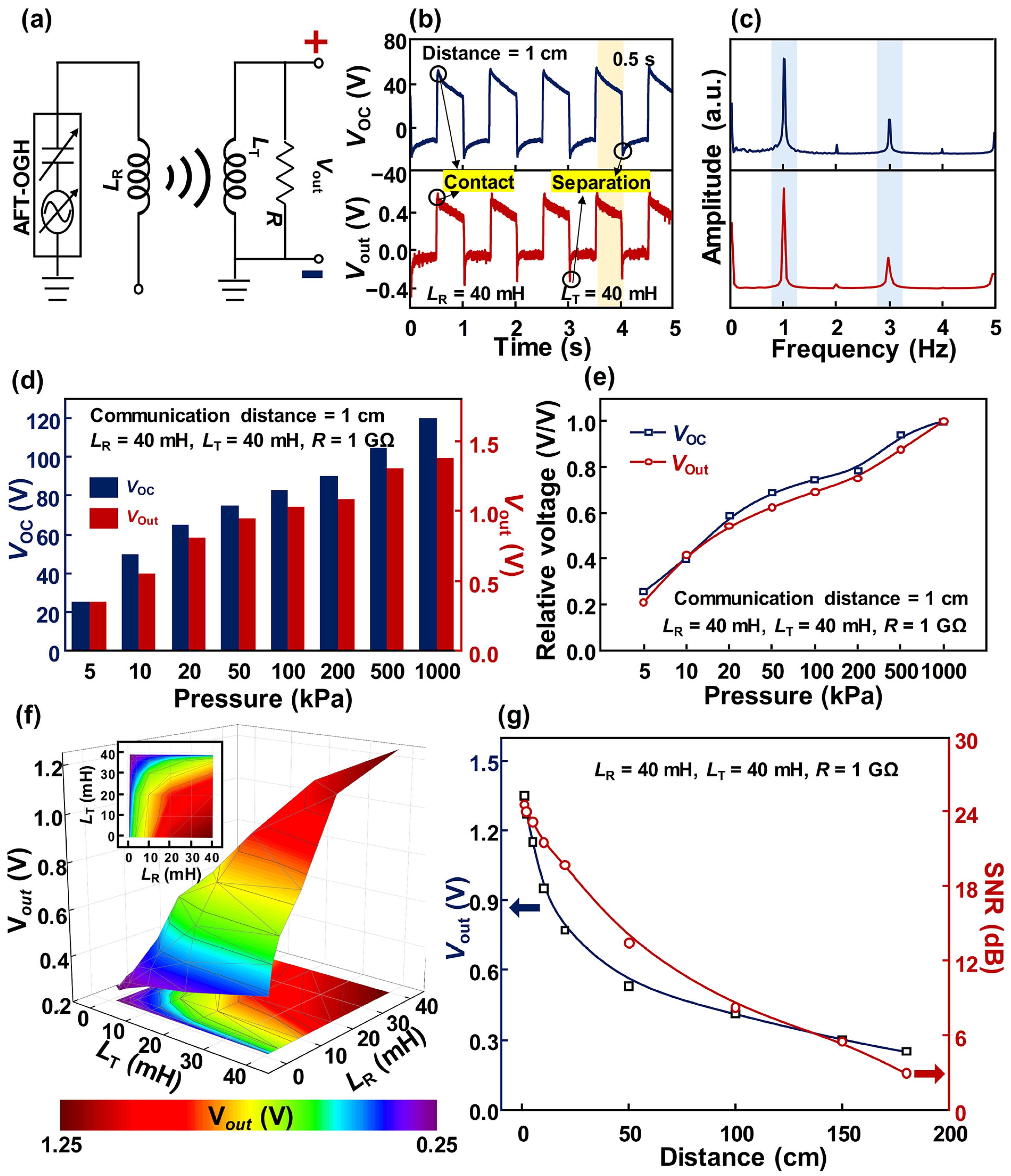
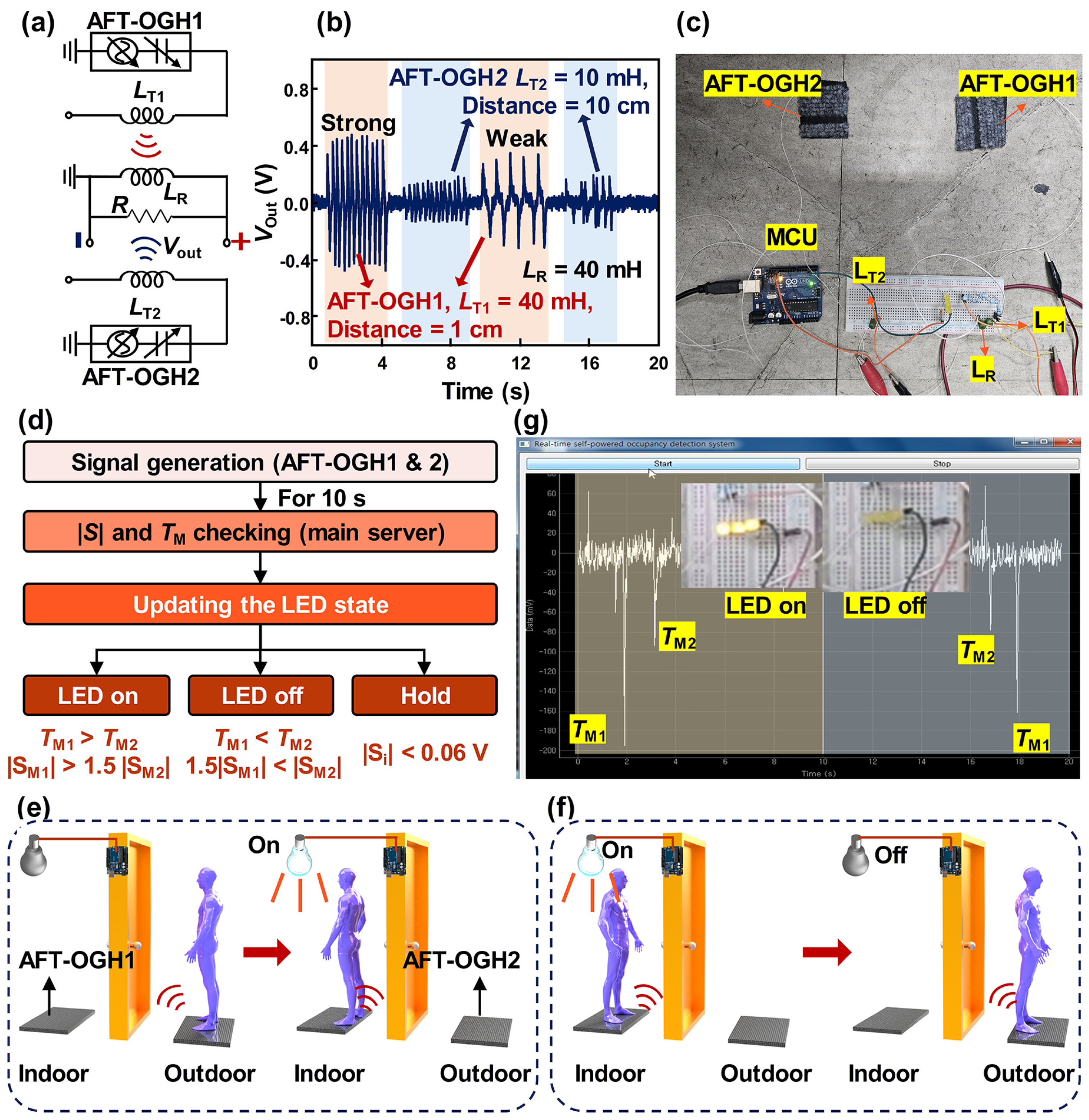
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, C.; Cong, S.; Tian, Z.; Song, Y.; Yu, L.; Lu, C.; Shao, Y.; Li, J.; Zou, G.; Rümmeli, M.H.; et al. Flexible Perovskite Solar Cell-Driven Photo-Rechargeable Lithium-Ion Capacitor for Self-Powered Wearable Strain Sensors. Nano Energy 2019, 60, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halme, J.; Saarinen, J.; Lund, P. Spray Deposition and Compression of TiO2 Nanoparticle Films for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells on Plastic Substrates. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2006, 90, 887–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Wang, J.; Bi, P.; Ren, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Hou, J. Tandem Organic Solar Cell with 20.2% Efficiency. Joule 2022, 6, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Xu, J.; Wei, M.; Wang, Y.; Qin, Z.; Liu, Z.; Wu, J.; Xiao, K.; Chen, B.; Park, S.M.; et al. All-Perovskite Tandem Solar Cells with Improved Grain Surface Passivation. Nature 2022, 603, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Lee, J.W.; Jung, H.S.; Shin, H.; Park, N.G. High-Efficiency Perovskite Solar Cells. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 7867–7918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shittu, S.; Li, G.; Zhao, X.; Ma, X.; Akhlaghi, Y.G.; Ayodele, E. High Performance and Thermal Stress Analysis of a Segmented Annular Thermoelectric Generator. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 184, 180–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xie, T.; Xie, H. Experimental Study of the Effects of the Thermal Contact Resistance on the Performance of Thermoelectric Generator. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 130, 847–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraemer, D.; Poudel, B.; Feng, H.P.; Caylor, J.C.; Yu, B.; Yan, X.; Ma, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, D.; Muto, A.; et al. High-Performance Flat-Panel Solar Thermoelectric Generators with High Thermal Concentration. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.; Kim, I.; Kim, D. Hybrid Tribo-Thermoelectric Generator for Effectively Harvesting Thermal Energy Activated by the Shape Memory Alloy. Nano Energy 2021, 82, 105696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saqib, Q.M.; Chougale, M.Y.; Khan, M.U.; Shaukat, R.A.; Kim, J.; Bae, J.; Lee, H.W.; Park, J.I.; Kim, M.S.; Lee, B.G. Natural Seagrass Tribopositive Material Based Spray Coatable Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2021, 89, 106458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Yang, Y.; Shi, Q.; Xu, S.; Sun, Z.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Kwong, D.L.; Zhou, G.; Ang, K.W.; et al. Wearable Triboelectric-Human-Machine Interface (THMI) Using Robust Nanophotonic Readout. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 8915–8930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Hu, Y.; Yang, Q.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Yang, H.; Ji, P.; Xi, Y.; Wang, Z.L. A Robust Constant–Voltage DC Triboelectric Nanogenerator Using the Ternary Dielectric Triboelectrification Effect. Adv. Energy Mater. 2023, 13, 2202921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.H.; Zhou, Z.; Li, J.; Shen, B.; Zhu, T.; Gao, X.; Tao, R.; Guo, X.; Hu, X.; Shi, Y.; et al. Coupling Enhanced Performance of Triboelectric-Piezoelectric Hybrid Nanogenerator Based on Nanoporous Film of Poly(Vinylidene Fluoride)/BaTiO3 Composite Electrospun Fibers. ACS Mater. Lett. 2022, 4, 847–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.; Jayababu, N.; Kim, D. Self-Powered Transparent and Flexible Touchpad Based on Triboelectricity towards Artificial Intelligence. Nano Energy 2020, 78, 105325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K., II; Xu, S.; Liu, Y.; Hwang, G.T.; Kang, S.J.L.; Wang, Z.L.; Lee, K.J. Piezoelectric BaTiO3 Thin Film Nanogenerator on Plastic Substrates. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 4939–4943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Guo, H.; Ribera, J.; Wu, C.; Tu, K.; Binelli, M.; Panzarasa, G.; Schwarze, F.W.M.R.; Wang, Z.L.; Burgert, I. Sustainable and Biodegradable Wood Sponge Piezoelectric Nanogenerator for Sensing and Energy Harvesting Applications. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 14665–14674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Shi, Q.; Hasan, D.; Yazici, M.S.; Zhu, M.; Ma, Y.; Dong, B.; Liu, Y.; Lee, C. Self-Powered Multifunctional Monitoring System Using Hybrid Integrated Triboelectric Nanogenerators and Piezoelectric Microsensors. Nano Energy 2019, 58, 612–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Liu, J.; Cui, N.; Xu, Q.; Du, T.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Long, C.; Qin, Y. Enhancing the Current Density of a Piezoelectric Nanogenerator Using a Three-Dimensional Intercalation Electrode. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Wang, P.; Rui, P.; Wei, X.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Tu, X.; Chen, C.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Z.; et al. Broadband and Output-Controllable Triboelectric Nanogenerator Enabled by Coupling Swing-Rotation Switching Mechanism with Potential Energy Storage/Release Strategy for Low-Frequency Mechanical Energy Harvesting. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 2270194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajra, S.; Padhan, A.M.; Sahu, M.; Alagarsamy, P.; Lee, K.; Kim, H.J. Lead-Free Flexible Bismuth Titanate-PDMS Composites: A Multifunctional Colossal Dielectric Material for Hybrid Piezo-Triboelectric Nanogenerator to Sustainably Power Portable Electronics. Nano Energy 2021, 89, 106316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Wu, F.; Lee, C.; Yuce, M.R. Self-Powered Control Interface Based on Gray Code with Hybrid Triboelectric and Photovoltaics Energy Harvesting for IoT Smart Home and Access Control Applications. Nano Energy 2020, 70, 104456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, S.; Wang, J.; Yang, L.; Wang, H.; Luo, H.; Liao, R.; Wang, Z.L. Auto-Switching Self-Powered System for Efficient Broad-Band Wind Energy Harvesting Based on Dual-Rotation Shaft Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2101194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Wang, X.; Dai, X.; Lu, W.; Tang, Y.; Kong, J. Ultraflexible, Highly Efficient Electromagnetic Interference Shielding, and Self-Healable Triboelectric Nanogenerator Based on Ti3C2Tx MXene for Self-Powered Wearable Electronics. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 100, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, D.; Song, M.; Chung, S.H.; Cha, K.; Kim, Y.; Chung, J.; Hwang, P.T.J.; Lee, J.; Jung, H.; Jin, Y.; et al. Inhalation-Driven Vertical Flutter Triboelectric Nanogenerator with Amplified Output as a Gas-Mask-Integrated Self-Powered Multifunctional System. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 2201001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera Anaya, D.; He, T.; Lee, C.; Yuce, M.R. Self-Powered Eye Motion Sensor Based on Triboelectric Interaction and near-Field Electrostatic Induction for Wearable Assistive Technologies. Nano Energy 2020, 72, 104675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Wang, Z.L. Theoretical Systems of Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2014, 14, 161–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Zhang, Z. Fundamental Theories and Basic Principles of Triboelectric Effect: A Review. Friction 2019, 7, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Lin, L.; Zhou, Y.S.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Theoretical Investigation and Structural Optimization of Single-Electrode Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 3332–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Wang, S.; Lin, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.S.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Theoretical Study of Contact-Mode Triboelectric Nanogenerators as an Effective Power Source. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 3576–3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Yang, J.; Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Wei, W.; Liu, J.; Chen, J.; Yang, J. Large-Scale and Washable Smart Textiles Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerator Arrays for Self-Powered Sleeping Monitoring. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1704112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, S.; Zhou, J.; Li, F.; Li, J.; Cao, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, B.; Wang, Y.; et al. Advanced Triboelectric Nanogenerator with Multi-Mode Energy Harvesting and Anti-Impact Properties for Smart Glove and Wearable e-Textile. Nano Energy 2020, 78, 105291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhang, X.S.; Wang, Y.; Gong, W.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.; Brugger, J. All-Fiber Hybrid Piezoelectric-Enhanced Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Wearable Gesture Monitoring. Nano Energy 2018, 48, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Lu, S.; Xie, W.; Chen, X.; Wu, L.; Wang, T.; Wang, A.; Yue, C.; Tong, D.; Lei, W.; et al. A Self-Powered and Self-Functional Tracking System Based on Triboelectric-Electromagnetic Hybridized Blue Energy Harvesting Module. Nano Energy 2020, 72, 104684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, J.; Xuan, W.; Huang, S.; Shi, L.; Cao, Z.; Ye, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Dong, S.; et al. Triboelectric Nanogenerator-Enabled Fully Self-Powered Instantaneous Wireless Sensor Systems. Nano Energy 2022, 92, 106770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, X.; Guo, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, X.; Xi, Y.; Hu, C.; Wang, Z.L. Eye Motion Triggered Self-Powered Mechnosensational Communication System Using Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1700694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.; Gu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Yang, F.; Zhao, L.; Zheng, M.; Cheng, G.; Du, Z. The Self-Powered CO2 Gas Sensor Based on Gas Discharge Induced by Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2018, 53, 898–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Zheng, Q.; Hou, W.; Zheng, L.; Li, H. A Self-Powered Vibration Sensor Based on the Coupling of Triboelectric Nanogenerator and Electromagnetic Generator. Nano Energy 2022, 97, 107164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, S.M.S.; Salauddin, M.; Sharifuzzaman, M.; Lee, S.H.; Do Shin, Y.; Song, H.; Jeong, S.H.; Bhatta, T.; Shrestha, K.; Park, J.Y. Ultrahigh-Output Triboelectric and Electromagnetic Hybrid Generator for Self-Powered Smart Electronics and Biomedical Applications. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 2202238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, B.; Yang, O.; Yuan, W.; Zhou, L.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.L. A Dual-Mode Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Wind Energy Harvesting and Self-Powered Wind Speed Monitoring. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 6244–6254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.B.; Kim, W.G.; Park, S.J.; Tcho, I.W.; Jin, I.K.; Han, J.K.; Kim, D.; Choi, Y.K. Self-Powered Wearable Touchpad Composed of All Commercial Fabrics Utilizing a Crossline Array of Triboelectric Generators. Nano Energy 2019, 65, 103994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Yang, P.; Liu, Z.; Huang, G.; Tao, X.; Qin, S.; Dong, X.; Zheng, L.; Li, H.; Chen, X.; et al. Boosting the Output of Liquid–Solid Triboelectric Nanogenerator by an External Charge-Pumping Strategy. Adv. Energy Mater. 2024, 14, 2303912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, D.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, W.; Sun, Y.; Guo, Y.; Ji, Y. Eco-Friendly Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Self-Powering Stacked In2O3 Nanosheets/PPy Nanoparticles-Based NO2 Gas Sensor. Nano Energy 2024, 128, 109987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.C.; Dai, Z.; Ma, H.; Zheng, J.; Leng, J.; Xie, C.; Yuan, Y.; Yang, W.; Yalikun, Y.; Song, X.; et al. Self-Powered and Speed-Adjustable Sensor for Abyssal Ocean Current Measurements Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, J.; Xuan, W.; Huang, S.; You, B.; Li, W.; Sun, L.; Jin, H.; Wang, X.; Dong, S.; et al. Conjunction of Triboelectric Nanogenerator with Induction Coils as Wireless Power Sources and Self-Powered Wireless Sensors. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Xuan, W.; Chen, J.; Zhang, C.; Tang, Y.; Huang, X.; Li, W.; Jin, H.; Dong, S.; Yin, W.; et al. Fully Self-Powered Instantaneous Wireless Humidity Sensing System Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2021, 83, 105814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallineni, S.S.K.; Dong, Y.; Behlow, H.; Rao, A.M.; Podila, R. A Wireless Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1702736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Fu, X.; Li, C.; Liu, G.; Gao, Y.; Qi, Y.; Bu, T.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.L.; Zhang, C. Raindrop Energy-Powered Autonomous Wireless Hyetometer Based on Liquid–Solid. Contact Electrif. 2022, 8, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, T.; Gao, Y.; So, M.Y.; Tan, D.; Lu, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Q.; Liu, X.; Xu, B. Diamond-Structured Fabric-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Energy Harvesting and Healthcare Application. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2408680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.T.; Lei, Y.; Zhao, X.H.; Li, R.; Lai, Q.T.; Liu, S.Z.; Chen, H.; Fan, J.C.; Xu, Y.; Tang, X.G.; et al. Printed-Scalable Microstructure BaTiO3/Ecoflex Nanocomposite for High-Performance Triboelectric Nanogenerators and Self-Powered Human-Machine Interaction. Nano Energy 2024, 131, 110324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.; Kim, I.; Kim, D. Triboelectric Energy Harvesting Using Inductor towards Self-Powered Real-Time Wireless Communication System. Nano Energy 2023, 115, 108760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Abbreviation | Definition | Abbreviation | Definition |
|---|---|---|---|
| CPF | Conductive PET fabric | CPF-NT | CPF without any treatment |
| OG | Surface treatment process composed of O2 plasma treatment and GO/TA coating | CPF-G | CPF with only GO/TA coating |
| OGH | OG with hexane and 1-octadecanethiol coating | AFT | All-fiber-based TENG |
| AFT-OGH | AFT using CPF-OGH | ||
| CPF-OGH | CPF conducting OGH | AFT-OG | AFT using CPF-OG |
| CPF-OG | CPF conducting OG | AFT-NT | AFT using CPF-NT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yun, J.; Kim, D. Self-Powered Triboelectricity-Driven Multiple-Input–Single-Output Occupancy Detection System Using a Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Energy Management. Polymers 2025, 17, 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17010034
Yun J, Kim D. Self-Powered Triboelectricity-Driven Multiple-Input–Single-Output Occupancy Detection System Using a Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Energy Management. Polymers. 2025; 17(1):34. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17010034
Chicago/Turabian StyleYun, Jonghyeon, and Daewon Kim. 2025. "Self-Powered Triboelectricity-Driven Multiple-Input–Single-Output Occupancy Detection System Using a Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Energy Management" Polymers 17, no. 1: 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17010034
APA StyleYun, J., & Kim, D. (2025). Self-Powered Triboelectricity-Driven Multiple-Input–Single-Output Occupancy Detection System Using a Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Energy Management. Polymers, 17(1), 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17010034










