Selection of Network Parameters in Direct ANN Modeling of Roughness Obtained in FFF Processes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. 3D Printing of the Samples
2.2. Roughness Measurement
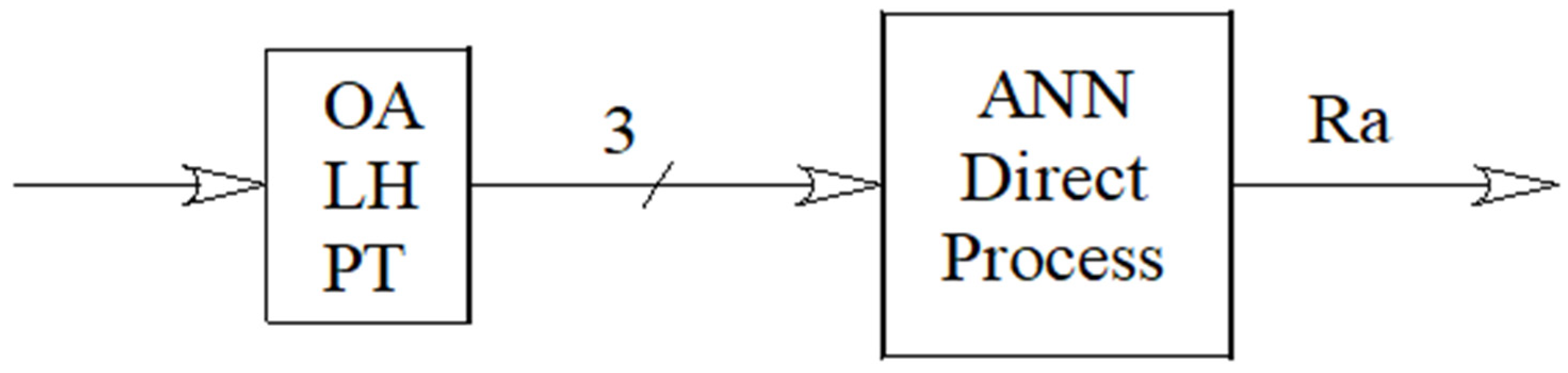
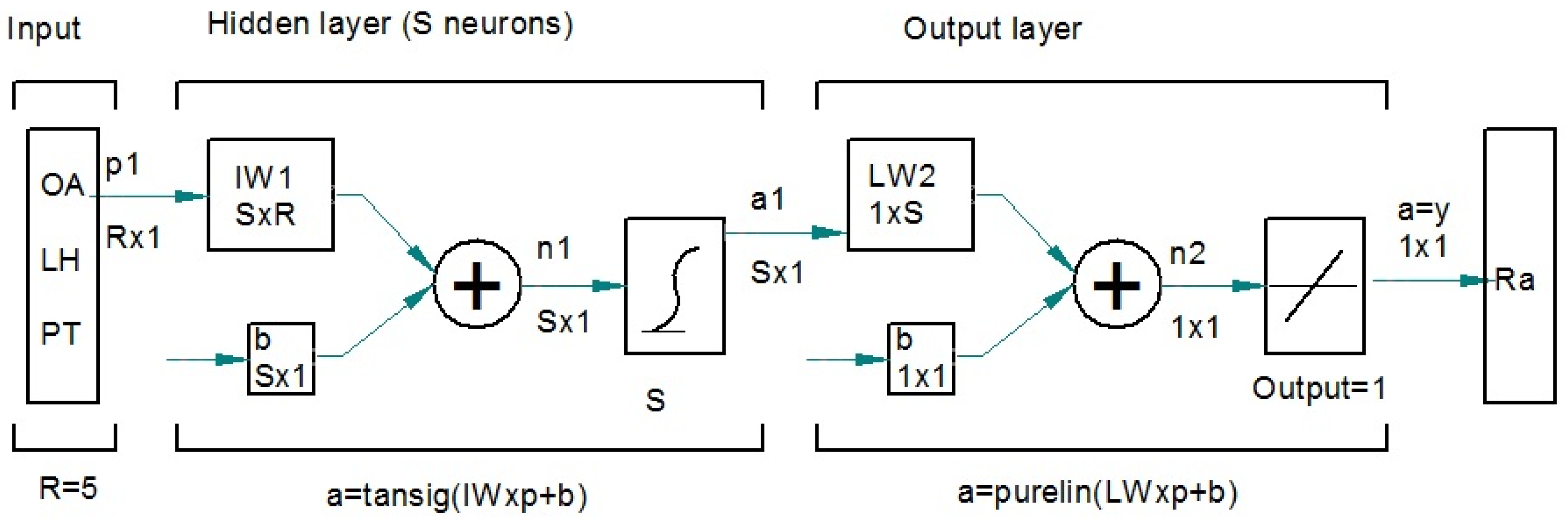
2.3. Neural Networks
- Number of neurons in the hidden layer (4 levels).
- Training algorithm used (3 levels).
- Distribution of the dataset patterns among training, validation and test data (2 levels).
2.3.1. Number of Neurons in the Hidden Layer
2.3.2. Training Algorithm
2.3.3. Distribution of Datasets
3. Results and Discussion
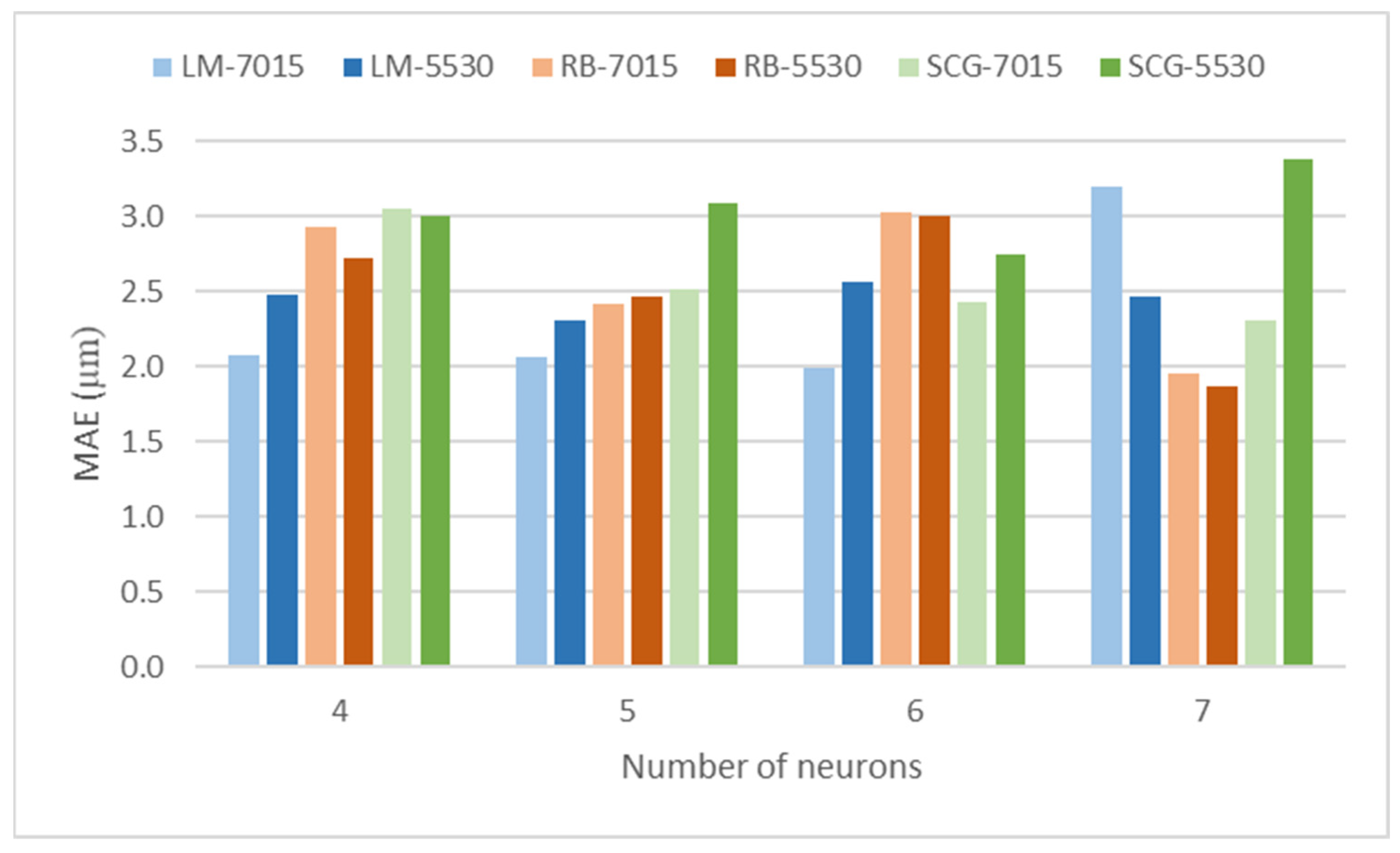
3.1. Study About Different Networks
3.2. Optimization of Simulated Ra Values
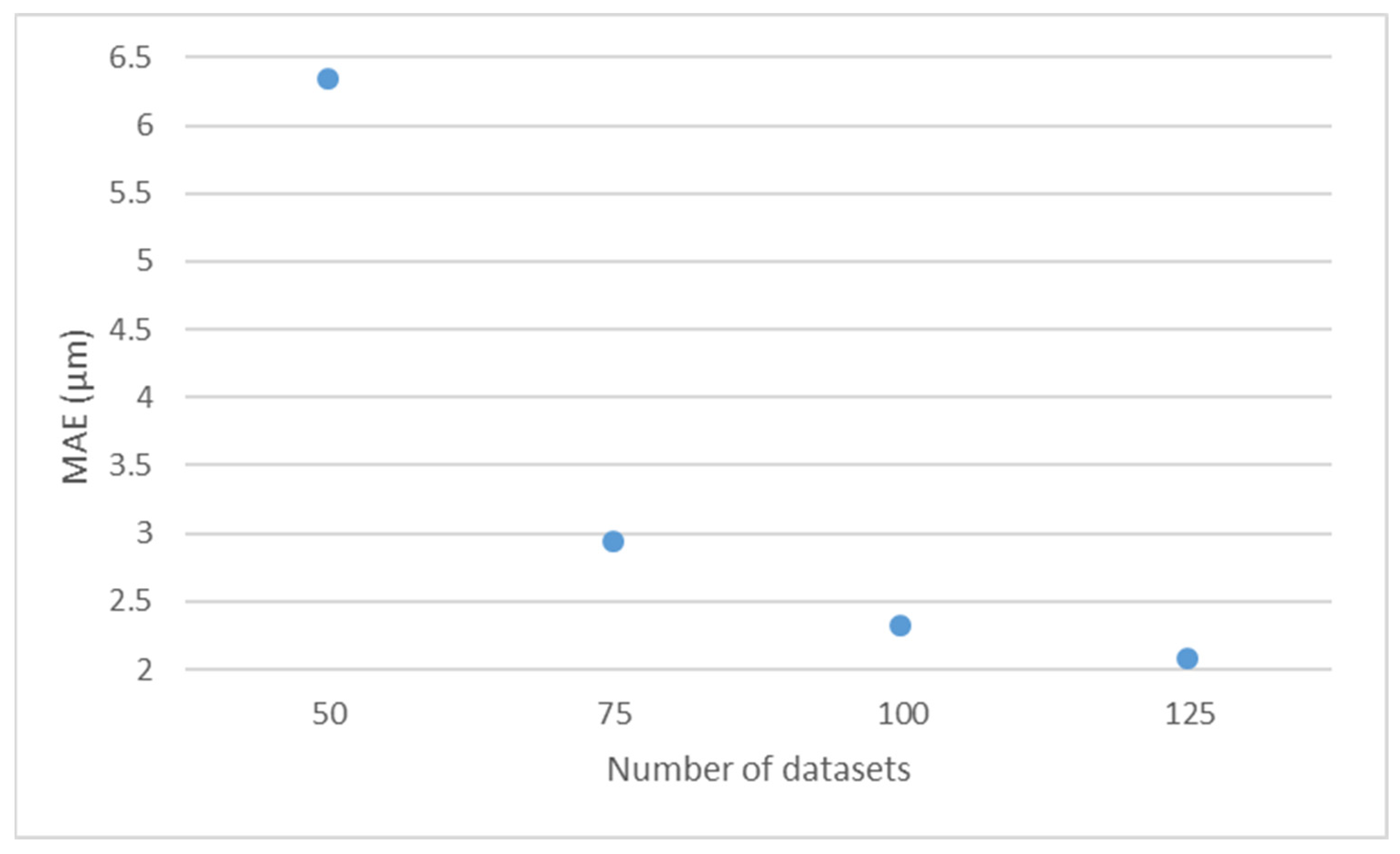
3.3. Study About the Database Size
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Experiment | Layer Height (mm) | Temperature (°C) | Print Orientation Angle (°) | Ra (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.05 | 190 | 0 | 4.770 |
| 2 | 0.15 | 190 | 80 | 18.212 |
| 3 | 0.10 | 200 | 60 | 16.136 |
| 4 | 0.15 | 195 | 40 | 16.468 |
| 5 | 0.05 | 195 | 80 | 12.385 |
| 6 | 0.20 | 205 | 0 | 15.747 |
| 7 | 0.20 | 205 | 40 | 22.477 |
| 8 | 0.05 | 205 | 80 | 10.675 |
| 9 | 0.15 | 190 | 60 | 22.737 |
| 10 | 0.15 | 200 | 80 | 17.327 |
| 11 | 0.05 | 210 | 60 | 9.804 |
| 12 | 0.20 | 200 | 40 | 21.613 |
| 13 | 0.25 | 190 | 80 | 17.120 |
| 14 | 0.20 | 200 | 20 | 15.088 |
| 15 | 0.20 | 190 | 0 | 15.019 |
| 16 | 0.15 | 205 | 60 | 23.517 |
| 17 | 0.25 | 205 | 20 | 19.199 |
| 18 | 0.10 | 190 | 20 | 10.207 |
| 19 | 0.10 | 195 | 80 | 17.068 |
| 20 | 0.10 | 210 | 60 | 18.352 |
| 21 | 0.15 | 205 | 80 | 17.186 |
| 22 | 0.25 | 190 | 40 | 26.255 |
| 23 | 0.05 | 205 | 0 | 5.377 |
| 24 | 0.05 | 195 | 60 | 10.702 |
| 25 | 0.05 | 200 | 80 | 11.011 |
| 26 | 0.15 | 205 | 20 | 13.087 |
| 27 | 0.25 | 200 | 80 | 14.195 |
| 28 | 0.10 | 190 | 60 | 15.856 |
| 29 | 0.05 | 210 | 20 | 5.123 |
| 30 | 0.05 | 190 | 60 | 9.715 |
| 31 | 0.15 | 210 | 20 | 10.966 |
| 32 | 0.25 | 205 | 40 | 28.782 |
| 33 | 0.25 | 195 | 0 | 18.608 |
| 34 | 0.10 | 200 | 40 | 13.320 |
| 35 | 0.20 | 210 | 80 | 13.319 |
| 36 | 0.20 | 190 | 80 | 18.059 |
| 37 | 0.20 | 200 | 60 | 25.140 |
| 38 | 0.25 | 210 | 60 | 32.130 |
| 39 | 0.20 | 200 | 0 | 14.623 |
| 40 | 0.25 | 190 | 0 | 17.659 |
| 41 | 0.05 | 200 | 0 | 3.8395 |
| 42 | 0.10 | 200 | 80 | 15.957 |
| 43 | 0.15 | 210 | 0 | 10.404 |
| 44 | 0.25 | 195 | 40 | 29.163 |
| 45 | 0.25 | 210 | 80 | 17.306 |
| 46 | 0.20 | 195 | 0 | 14.640 |
| 47 | 0.20 | 210 | 20 | 15.477 |
| 48 | 0.25 | 210 | 0 | 17.429 |
| 49 | 0.10 | 205 | 80 | 14.565 |
| 50 | 0.05 | 190 | 80 | 10.966 |
| 51 | 0.05 | 210 | 40 | 9.816 |
| 52 | 0.25 | 195 | 80 | 14.261 |
| 53 | 0.10 | 195 | 0 | 6.968 |
| 54 | 0.15 | 210 | 60 | 24.996 |
| 55 | 0.20 | 190 | 20 | 15.450 |
| 56 | 0.15 | 205 | 0 | 10.067 |
| 57 | 0.15 | 200 | 40 | 18.815 |
| 58 | 0.25 | 210 | 40 | 28.472 |
| 59 | 0.20 | 205 | 80 | 15.486 |
| 60 | 0.15 | 205 | 40 | 18.014 |
| 61 | 0.15 | 210 | 80 | 15.073 |
| 62 | 0.15 | 210 | 40 | 18.563 |
| 63 | 0.15 | 195 | 80 | 15.829 |
| 64 | 0.20 | 195 | 60 | 30.767 |
| 65 | 0.10 | 205 | 20 | 9.166 |
| 66 | 0.05 | 210 | 80 | 11.414 |
| 67 | 0.05 | 205 | 60 | 9.971 |
| 68 | 0.25 | 190 | 20 | 21.956 |
| 69 | 0.20 | 195 | 80 | 21.739 |
| 70 | 0.10 | 205 | 0 | 7.154 |
| 71 | 0.25 | 210 | 20 | 19.904 |
| 72 | 0.25 | 200 | 60 | 30.778 |
| 73 | 0.20 | 195 | 40 | 26.123 |
| 74 | 0.10 | 210 | 40 | 12.475 |
| 75 | 0.05 | 190 | 40 | 8.538 |
| 76 | 0.10 | 200 | 20 | 8.093 |
| 77 | 0.10 | 210 | 20 | 8.470 |
| 78 | 0.10 | 195 | 40 | 12.415 |
| 79 | 0.15 | 190 | 40 | 24.313 |
| 80 | 0.25 | 195 | 20 | 30.005 |
| 81 | 0.15 | 195 | 0 | 10.074 |
| 82 | 0.05 | 205 | 40 | 11.703 |
| 83 | 0.20 | 205 | 60 | 24.597 |
| 84 | 0.10 | 190 | 40 | 16.937 |
| 85 | 0.05 | 200 | 60 | 9.490 |
| 86 | 0.25 | 205 | 80 | 28.090 |
| 87 | 0.05 | 200 | 20 | 7.186 |
| 88 | 0.25 | 195 | 60 | 48.851 |
| 89 | 0.05 | 210 | 0 | 3.880 |
| 90 | 0.20 | 205 | 20 | 21.630 |
| 91 | 0.25 | 200 | 20 | 27.833 |
| 92 | 0.10 | 190 | 0 | 6.609 |
| 93 | 0.10 | 190 | 80 | 21.895 |
| 94 | 0.20 | 210 | 60 | 29.740 |
| 95 | 0.20 | 200 | 80 | 32.232 |
| 96 | 0.05 | 195 | 40 | 9.922 |
| 97 | 0.15 | 190 | 20 | 18.600 |
| 98 | 0.10 | 210 | 0 | 6.792 |
| 99 | 0.15 | 195 | 60 | 33.355 |
| 100 | 0.25 | 205 | 60 | 45.503 |
| 101 | 0.25 | 205 | 0 | 18.356 |
| 102 | 0.05 | 195 | 0 | 4.252 |
| 103 | 0.20 | 210 | 40 | 36.138 |
| 104 | 0.15 | 200 | 20 | 16.747 |
| 105 | 0.15 | 200 | 60 | 25.378 |
| 106 | 0.20 | 190 | 40 | 33.423 |
| 107 | 0.15 | 200 | 0 | 11.104 |
| 108 | 0.05 | 200 | 40 | 7.987 |
| 109 | 0.20 | 210 | 0 | 14.775 |
| 110 | 0.05 | 195 | 20 | 6.834 |
| 111 | 0.20 | 190 | 60 | 40.021 |
| 112 | 0.10 | 205 | 60 | 24.393 |
| 113 | 0.10 | 205 | 40 | 18.439 |
| 114 | 0.05 | 205 | 20 | 7.736 |
| 115 | 0.15 | 195 | 20 | 11.570 |
| 116 | 0.15 | 190 | 0 | 9.994 |
| 117 | 0.25 | 200 | 0 | 17.590 |
| 118 | 0.10 | 195 | 20 | 8.327 |
| 119 | 0.10 | 200 | 0 | 6.645 |
| 120 | 0.10 | 210 | 80 | 13.600 |
| 121 | 0.20 | 195 | 20 | 14.002 |
| 122 | 0.05 | 190 | 20 | 7.576 |
| 123 | 0.25 | 200 | 40 | 30.875 |
| 124 | 0.10 | 195 | 60 | 16.863 |
| 125 | 0.25 | 190 | 60 | 55.106 |
References
- Werz, S.M.; Zeichner, S.J.; Berg, B.I.; Zeilhofer, H.F.; Thieringer, F. 3D Printed Surgical Simulation Models as Educational Tool by Maxillofacial Surgeons. Eur. J. Dent. Educ. 2018, 22, e500–e505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeStefano, V.; Khan, S.; Tabada, A. Applications of PLA in Modern Medicine. Eng. Regen. 2020, 1, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, R.P.; Tekale, S.U.; Shisodia, S.U.; Totre, J.T.; Domb, A.J. Biomedical Applications of Poly (Lactic Acid). Recent Pat. Regen. Med. 2014, 4, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergström, J.S.; Hayman, D. An Overview of Mechanical Properties and Material Modeling of Polylactide (PLA) for Medical Applications. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 44, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, I.; Rosen, D.; Stucker, B. Additive Manufacturing Technologies: 3D Printing, Rapid Prototyping, and Direct Digital Manufacturing, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; ISBN 9781493921133. [Google Scholar]
- Buj-Corral, I.; Zayas-Figueras, E.E. Comparative Study about Dimensional Accuracy and Form Errors of FFF Printed Spur Gears Using PLA and Nylon. Polym. Test. 2022, 117, 107862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidakis, N.; David, C.; Petousis, M.; Sagris, D.; Mountakis, N.; Moutsopoulou, A. The Effect of Six Key Process Control Parameters on the Surface Roughness, Dimensional Accuracy, and Porosity in Material Extrusion 3D Printing of Polylactic Acid: Prediction Models and Optimization Supported by Robust Design Analysis. Adv. Ind. Manuf. Eng. 2022, 5, 100104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kechagias, J.; Chaidas, D.; Vidakis, N.; Salonitis, K.; Vaxevanidis, N.M. Key Parameters Controlling Surface Quality and Dimensional Accuracy: A Critical Review of FFF Process. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2022, 37, 963–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, A.; Kishore, S.R.; Tomy, A.T.; Sugavaneswaran, M.; Scholz, S.G.; Elkaseer, A.; Wilson, V.H.; John Rajan, A. Vapour Polishing of Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM) Parts: A Critical Review of Different Techniques, and Subsequent Surface Finish and Mechanical Properties of the Post-Processed 3D-Printed Parts. Prog. Addit. Manuf. 2023, 8, 1161–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neff, C.; Trapuzzano, M.; Crane, N.B. Impact of Vapor Polishing on Surface Quality and Mechanical Properties of Extruded ABS. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2018, 24, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Y.; Li, R.W.; Perriman, D.M.; Chen, S.; Qin, Q.H.; Smith, P.N. Laser Polishing of Thermoplastics Fabricated Using Fused Deposition Modelling. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 96, 4295–4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buj-Corral, I.; Domínguez-Fernández, A.; Durán-Llucià, R. Influence of Print Orientation on Surface Roughness in Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) Processes. Materials 2019, 12, 3834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooshmand, M.J.; Mansour, S.; Dehghanian, A. Optimization of Build Orientation in FFF Using Response Surface Methodology and Posterior-Based Method. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2021, 27, 967–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abas, M.; Habib, T.; Noor, S.; Khan, K.M. Comparative Study of I-Optimal Design and Definitive Screening Design for Developing Prediction Models and Optimization of Average Surface Roughness of PLA Printed Parts Using Fused Deposition Modeling. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 125, 689–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasudevarao, B.; Natarajan, D.P.; Henderson, M. Sensitivity of Rp Surface Finish to Process. In Proceedings of the International Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium, Austin, TX, USA, 8–10 August 2000; pp. 251–258. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, S.; Zou, B.; Wang, P.; Ding, H. Effects of Nozzle Temperature and Building Orientation on Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of PEEK and PEI Printed by 3D-FDM. Polym. Test. 2019, 78, 105948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslani, K.E.; Chaidas, D.; Kechagias, J.; Kyratsis, P.; Salonitis, K. Quality Performance Evaluation of Thinwalled PLA 3D Printed Parts Using the Taguchi Method and Grey Relational Analysis. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2020, 4, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.; Mhapsekar, K.; Anand, S. Part Build Orientation Optimization and Neural Network-Based Geometry Compensation for Additive Manufacturing Process. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. Trans. ASME 2018, 140, 031009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zain, A.M.; Haron, H.; Sharif, S. Prediction of Surface Roughness in the End Milling Machining Using Artificial Neural Network. Expert Syst. Appl. 2010, 37, 1755–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivatte-Adroer, M.; Llanas-Parra, X.; Buj-Corral, I.; Vivancos-Calvet, J. Indirect Model for Roughness in Rough Honing Processes Based on Artificial Neural Networks. Precis. Eng. 2016, 43, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirmohammadi, M.; Goushchi, S.J.; Keshtiban, P.M. Optimization of 3D Printing Process Parameters to Minimize Surface Roughness with Hybrid Artificial Neural Network Model and Particle Swarm Algorithm. Prog. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 6, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, A.; Singla, R. Surface Roughness Prediction of 3D Printed Surface Using Artificial Neural Networks. In Advances in Interdisciplinary Engineering: Select Proceedings of FLAME 2020; Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, K.C.; Huang, M.S. Quality Prediction for Injection Molding by Using a Multilayer Perceptron Neural Network. Polymers 2020, 12, 1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinchanikar, S.; Shinde, S.; Gaikwad, V.; Shaikh, A.; Rondhe, M.; Naik, M. ANN Modelling of Surface Roughness of FDM Parts Considering the Effect of Hidden Layers, Neurons, and Process Parameters. Adv. Mater. Process. Technol. 2024, 10, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokesh, N.; Praveena, B.A.; Sudheer Reddy, J.; Vasu, V.K.; Vijaykumar, S. Evaluation on Effect of Printing Process Parameter through Taguchi Approach on Mechanical Properties of 3D Printed PLA Specimens Using FDM at Constant Printing Temperature. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 52, 1288–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kugunavar, S.; Viralka, M.; Sangwan, K.S. Development of a Hybrid Model to Estimate Surface Roughness of 3D Printed Parts. Addit. Manuf. 2024, 92, 104368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornik, K.; Stinchcombe, M.; White, H. Multilayer Feedforward Networks Are Universal Approximators. Neural Netw. 1989, 2, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, M.; Petterson, A. Getting Started with Brain Maker: Neural Network Simulation Software User’s Guide and Reference Manual/Introduction to Neural Networks and Disk [Hardcover]; Bks&Disk edition; California Scientific Software: Pleasanton, CA, USA, 1990; ISBN 9991846883. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, C.-X.; Wang, X.; Yu, Z. Neural Networks Modeling of Honing Surface Roughness Parameters Defined by ISO 13565. J. Manuf. Syst. 2002, 21, 395–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowther, P.S.; Cox, R.J. A Method for Optimal Division of Data Sets for Use in Neural Networks. In Knowledge-Based Intelligent Information and Engineering Systems (KES 2005); Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; Volume 3684, pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Guyon, I. A Scaling Law for the Validation-Set Training-Set Size Ratio. ATT Bell Lab. 1997, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Sood, A.K.; Ohdar, R.K.; Mahapatra, S.S. Experimental Investigation and Empirical Modelling of FDM Process for Compressive Strength Improvement. J. Adv. Res. 2012, 3, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, M.S.; Mohd Nor, A.; Abd Rahim, I.; Syahruddin, M.A.; Mat Darus, I.Z. Optimization of FDM Process Parameters to Minimize Surface Roughness with Integrated Artificial Neural Network Model and Symbiotic Organism Search. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 17423–17439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, S.S.; Sood, A.K. Bayesian Regularization-Based Levenberg-Marquardt Neural Model Combined with BFOA for Improving Surface Finish of FDM Processed Part. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2012, 60, 1223–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monticeli, F.M.; Neves, R.M.; Ornaghi, H.L.; Almeida, J.H.S. Prediction of Bending Properties for 3D-Printed Carbon Fibre/Epoxy Composites with Several Processing Parameters Using ANN and Statistical Methods. Polymers 2022, 14, 3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.; Farrokhabadi, A.; Chronopoulos, D. Experimental and Numerical Analysis of Shape Memory Sinusoidal Lattice Structure: Optimization through Fusing an Artificial Neural Network to a Genetic Algorithm. Compos. Struct. 2023, 323, 117454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beresford, R.; Agatonovic-Kustrin, S. Basic Concepts of Artificial Neural Network (ANN) Modeling and Its Application in Pharmaceutical Research. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2000, 22, 717–727. [Google Scholar]


| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Nozzle diameter (mm) | 0.4 |
| Infill ratio (%) | 80 |
| Print speed (mm/s) | 40 |
| Print orientation angle (°) (OA) | 0, 20, 40, 60, and 80 |
| Layer height (mm) (LH) | 0.05, 0.10, 0.15, 0.20, and 0.25 |
| Printing temperature (°C) (PT) | 190, 195, 200, 205, and 210 |
| Number of Neurons in the Hidden Layer | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| Training Algorithm | ||
|---|---|---|
| Levenberg–Marquardt (LM) | Resilient-Backpropagation (RB) | Scaled Conjugate Gradient (SCG) |
| Distribution of Datasets | |
|---|---|
| 70% train + 15% validation (7015) | 55% train + 30% validation (5530) |
| Network Nr. | Network Name | MAE (µm) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | LM-4-7015 | 2.075 |
| 2 | LM-4-5530 | 2.477 |
| 3 | LM-5-7015 | 2.068 |
| 4 | LM-5-5530 | 2.309 |
| 5 | LM-6-7015 | 1.997 |
| 6 | LM-6-5530 | 2.569 |
| 7 | LM-7-7015 | 3.203 |
| 8 | LM-7-5530 | 2.470 |
| 9 | RB-4-7015 | 2.926 |
| 10 | RB-4-5530 | 2.718 |
| 11 | RB-5-7015 | 2.417 |
| 12 | RB-5-5530 | 2.463 |
| 13 | RB-6-7015 | 3.024 |
| 14 | RB-6-5530 | 3.009 |
| 15 | RB-7-7015 | 1.953 |
| 16 | RB-7-5530 | 1.874 |
| 17 | SCG-4-7015 | 3.048 |
| 18 | SCG-4-5530 | 3.006 |
| 19 | SCG-5-7015 | 2.514 |
| 20 | SCG-5-5530 | 3.088 |
| 21 | SCG-6-7015 | 2.425 |
| 22 | SCG-6-5530 | 2.749 |
| 23 | SCG-7-7015 | 2.315 |
| 24 | SCG-7-5530 | 3.381 |
| Experiment | OA (°) | LH (mm) | PT (°C) | Simulated Ra (µm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 89 | 0 | 0.05 | 210 | 2.802 |
| 23 | 0 | 0.05 | 205 | 3.040 |
| 41 | 0 | 0.05 | 200 | 3.678 |
| Configuration | Total Datasets | Test Datasets | Training Datasets |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 125 | 19 | 106 |
| B | 100 | 19 | 81 |
| C | 75 | 19 | 56 |
| D | 50 | 19 | 31 |
| Configuration | MAE (µm) | Average MAE (µm) |
|---|---|---|
| A | 2.068 | 2.068 |
| B_1 | 2.147 | 2.312 |
| B_2 | 2.197 | |
| B_3 | 2.594 | |
| C_1 | 3.594 | 2.940 |
| C_2 | 2.565 | |
| C_3 | 2.661 | |
| D_1 | 7.617 | 6.347 |
| D_2 | 6.447 | |
| D_3 | 4.977 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Buj-Corral, I.; Sivatte-Adroer, M.; Rodero-de-Lamo, L.; Marco-Almagro, L. Selection of Network Parameters in Direct ANN Modeling of Roughness Obtained in FFF Processes. Polymers 2025, 17, 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17010120
Buj-Corral I, Sivatte-Adroer M, Rodero-de-Lamo L, Marco-Almagro L. Selection of Network Parameters in Direct ANN Modeling of Roughness Obtained in FFF Processes. Polymers. 2025; 17(1):120. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17010120
Chicago/Turabian StyleBuj-Corral, Irene, Maurici Sivatte-Adroer, Lourdes Rodero-de-Lamo, and Lluís Marco-Almagro. 2025. "Selection of Network Parameters in Direct ANN Modeling of Roughness Obtained in FFF Processes" Polymers 17, no. 1: 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17010120
APA StyleBuj-Corral, I., Sivatte-Adroer, M., Rodero-de-Lamo, L., & Marco-Almagro, L. (2025). Selection of Network Parameters in Direct ANN Modeling of Roughness Obtained in FFF Processes. Polymers, 17(1), 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17010120








