Surface Modification of Nano-Hydroxyapatite/Polymer Composite for Bone Tissue Repair Applications: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
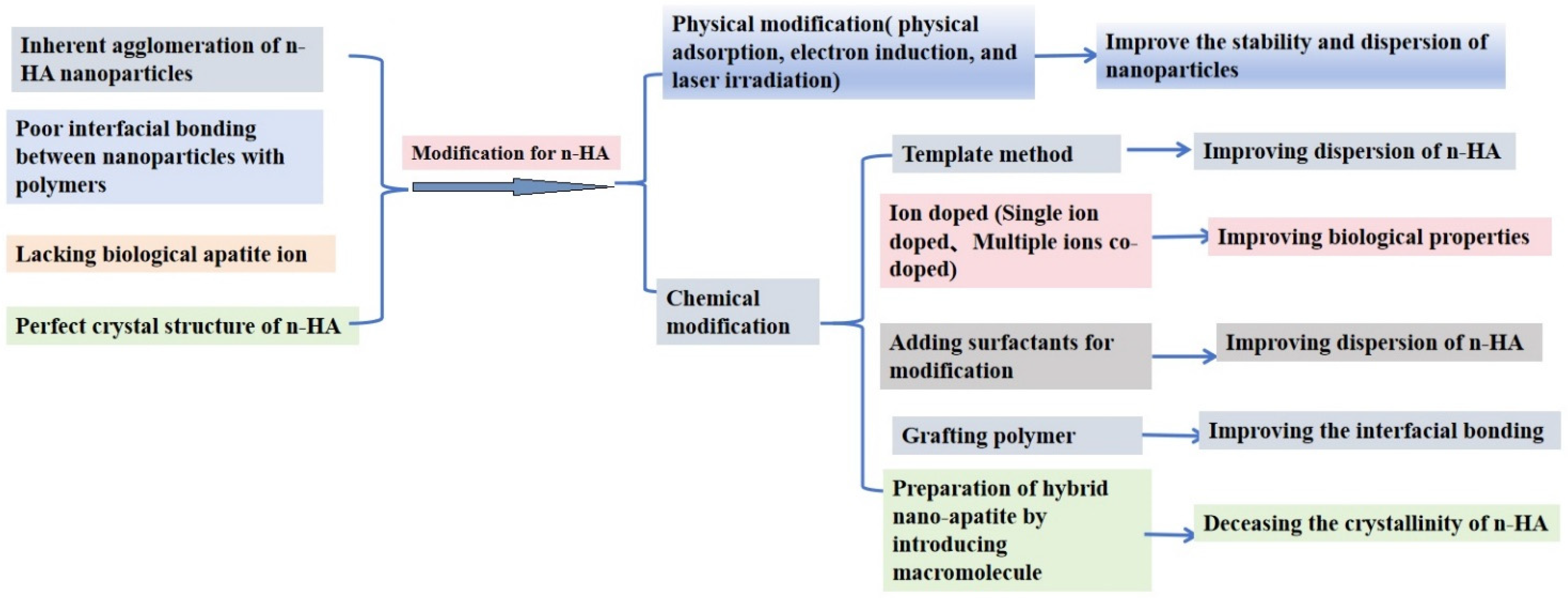
2. Physical Modification
3. Chemical Modification
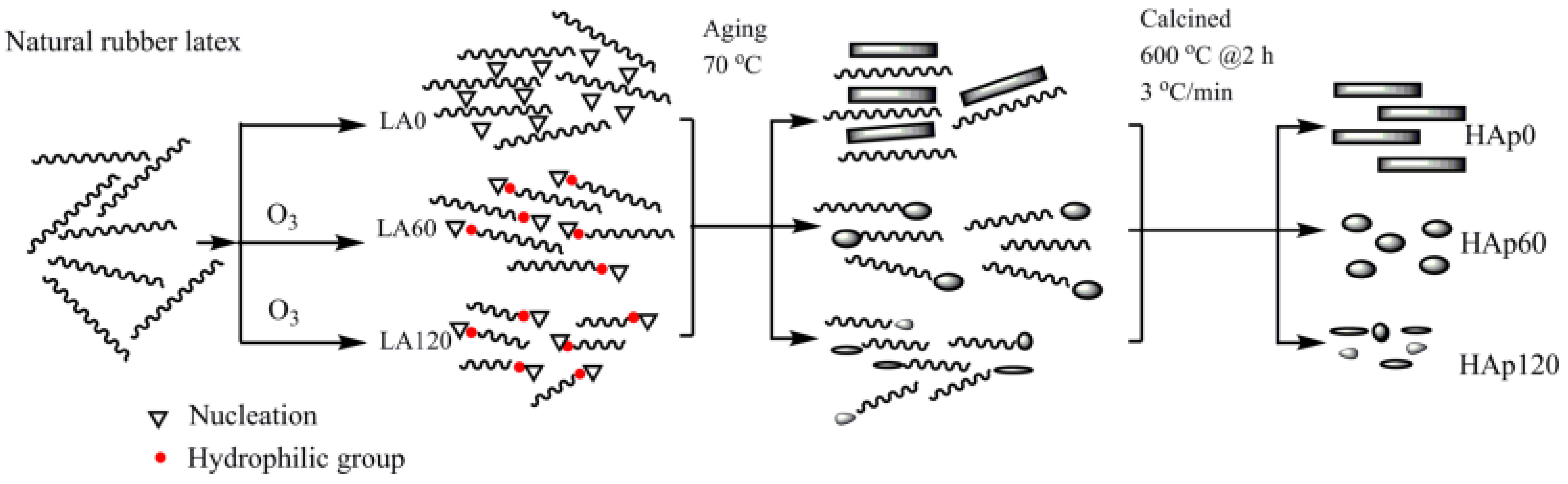
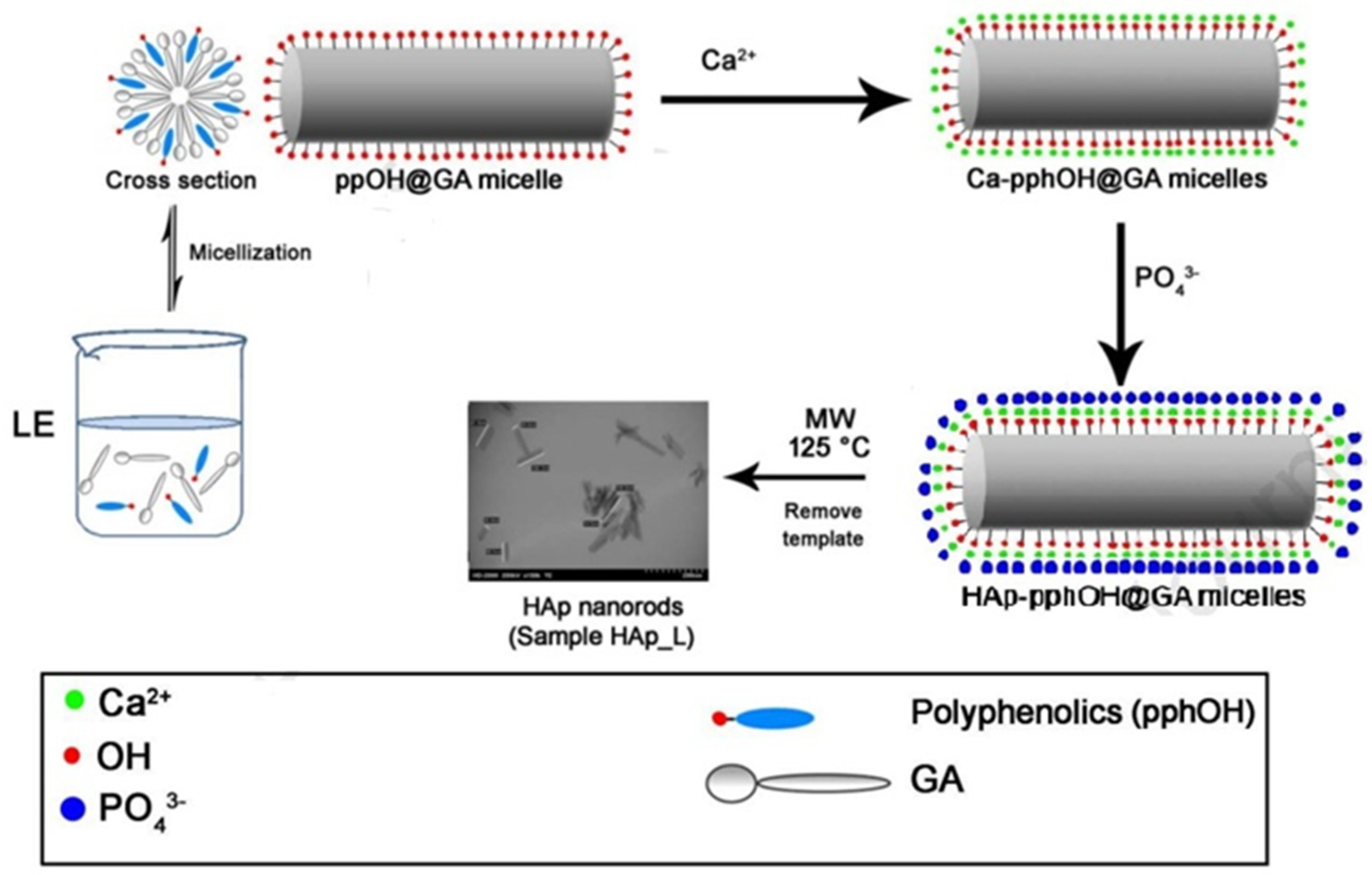
3.1. Template Method
3.2. Ion Doped
3.2.1. Single Ion Doped
3.2.2. Multiple Ions Co-Doped
3.3. Adding Surfactants for Modification
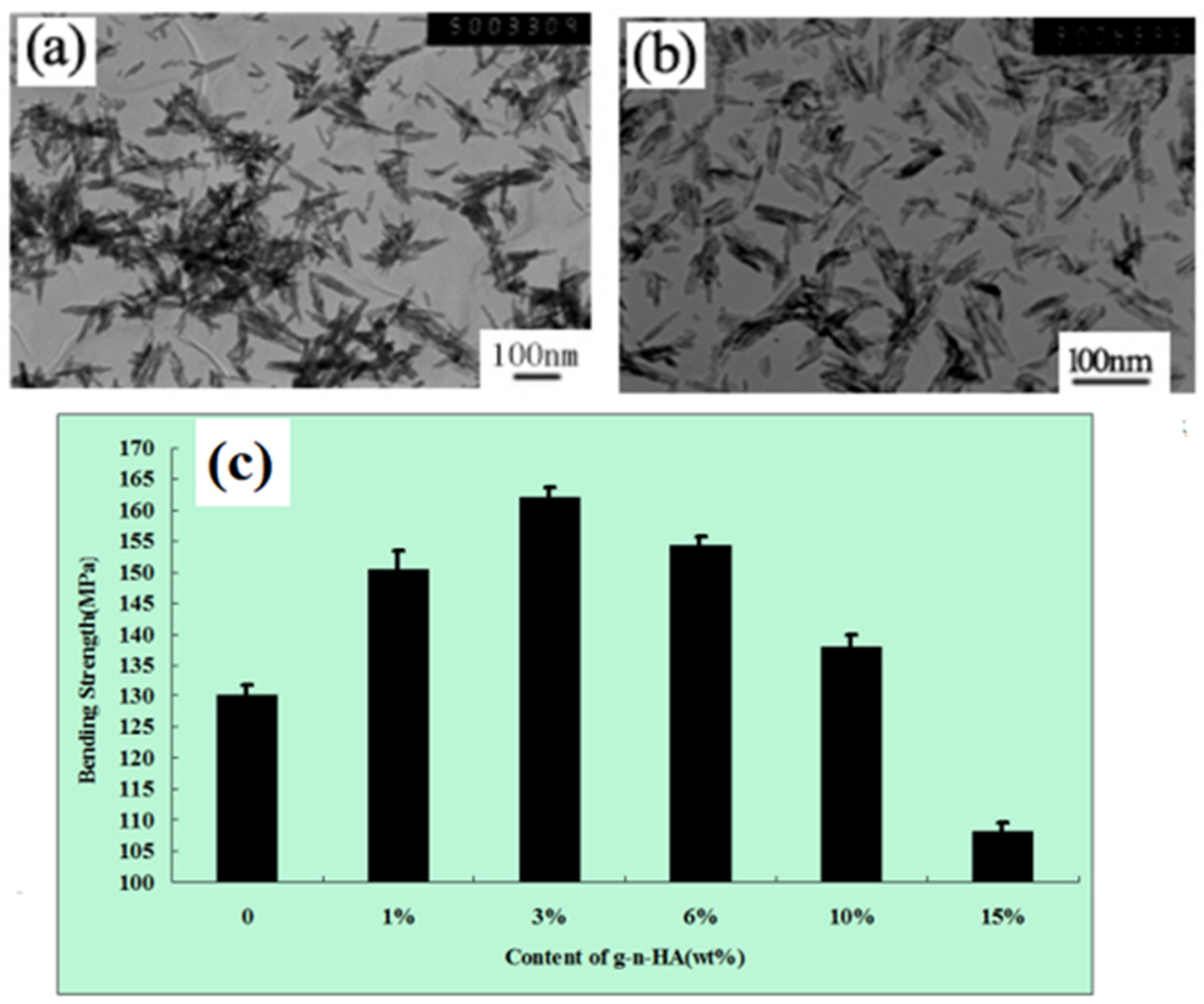
3.4. Surface Modification by Grafting Polymer
3.5. Preparation of Hybrid Nano-Apatite by Introducing Macromolecule
4. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BLA-NCA | Benzyl ester n-carboxylic anhydride |
| BLG-NCA | γ-benzyl-l-glutamate n-carboxyanhydride |
| ChS | Chondroitin sulfate |
| DMF | Dimethylformamide |
| ETD | Etidronic acid |
| PCL-g-HAP | PCL-grafted ethylene glycol-HAP |
| HAPN | Hydroxyapatite nano-crystals |
| HDI | 1,6-hexamethylene diisocyanate |
| HFb | Fibrinogen |
| LE | Licorice root extract |
| m-HA | Modified HA particle |
| oHAP-BC | Original HAP bone cement |
| vHAP-BC | Vinyl trimethoxysilane treated HA bone cement |
| gHAP-BC | HAP-modified PMMA bone cement |
| PANH | Poly (1,6-bis-(p-carboxylphenoxyhexane) co-(sebacic anhydride)) |
| PBLA | Poly (benzyl aspartate) |
| PHBV | poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) |
| PBLG-g-HA | Surface grafting polymerization (γ-benzyl-l-glutamic acid) on n-HA |
| PEEK | Polyether ether ketone |
| PEGMA | Poly ethylene methacrylate |
| PMMA | Polymethyl methacrylate |
| P-MPEG | Polyethylene glycol monomethyl ether phosphate |
| POM | Polyoxymethylene copolymer |
| PVP | Polyvinylpyrrolidone |
| RAFT | Eversible addition fragmentation chain transfer |
| ROP | Ring opening polymerization |
| RPSSD | Riboflavin-5-phosphate sodium |
| DTAB | Dodecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide |
| SDBS | Sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate |
| SDS | Sodium dodecyl sulfate |
| SHA | Surface-modified hydroxyapatite |
| SLS | Selective laser sintering |
| SPCL | Poly(ε-caprolactone) |
| AMP | Adenosine monophosphate |
| Asp | Aspartic acid |
| ATRP | Atom transfer radical polymerization |
| CTAB | Cetyltriethylammonium bromide |
| CTS | Chitosan |
| Gly | Glycine |
| GO | Graphene oxide |
| HA, HAP | Hydroxyapatite |
| HSA | Albumin |
| KH550 | 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane |
| MTT | 3-(4,5)-dimethylthiahiazo (-z-y1)-3,5-di- phenytetrazoliumromide |
| n-HA | Nano-hydroxyapatite |
| PARP | Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase |
| PCL | Polycaprolactone |
| PDA | Polydopamine |
| PEI | Polyethyleneimine |
| PET | Polyethylene terephthalate |
| PLGA | Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) |
| PLLA | Poly-L-lactic acid |
| PU | Polyurethane |
| PVD | Polyvinylpyrrolidone |
| SBF | Simulated body fluid |
| Sr-HA | Strontium substituted hydroxyapatite |
References
- Prakasam, M.; Locs, J.; Salma-Ancane, K.; Loca, D.; Largeteau, A.; Berzina-Cimdina, L. Fabrication, properties and applications of dense hydroxyapatite: A review. J. Funct. Biomater. 2015, 6, 1099–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dileepkumar, V.G.; Sridhar, M.S.; Aramwit, P.; Krut’ko, V.K.; Musskaya, O.N.; Glazov, I.E.; Reddy, N. A review on the synthesis and properties of hydroxyapatite for biomedical applications. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2022, 33, 1980985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, A.; Rashid, A.; Imran, S.; Ibrahim, W.; Rafaqat, H. Extracting hydroxyapatite and its precursors from natural resources. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 1461–1475. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, D.; Figueira, L.; Issa, J.; Cecina, C.; Dias, F.; Cunha, M. Study of the osteoconductive capacity of hydroxyapatite implanted into the femur of ovariectomized rats. Microsc. Res. Technol. 2012, 75, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, S.C.; Walton, R.I.; Mallick, K.K. Comparison of Techniques for the Synthesis of Hydroxyapatite. Bioinspired Biomim. Nanobiomater. 2015, 4, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadat-Shojai, M.; Khorasani, M.T.; Dinpanah-Khoshdargi, E.; Jamshidi, A. Synthesis Methods for Nanosized Hydroxyapatite with Diverse Structures. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 7591–7621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Córdova-Udaeta, M.; Kim, Y.; Yasukawa, K.; Kato, Y.; Fujita, T.; Dodbiba, G. Study on the Synthesis of Hydroxyapatite under Highly Alkaline Conditions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 4385–4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogina, A.; Antunović, M.; Milovac, D. Biomimetic design of bone substitutes based on cuttlefish bone-derived hydroxyapatite and biodegradable polymers. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2019, 107, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronov, D.; Rosen, R.; Ron, E.Z.; Rosenman, G. Electron-induced surface modification of hydroxyapatite-coated implant. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2008, 202, 2093–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, A.C.; Santos, J.D.; Rui, V.; Eugenio, S.; Monteiro, F.J. Laser surface modification of hydroxyapatite and glass-reinforced hydroxyapatite. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 4607–4614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Yang, Y.; Yang, M.; Wang, W.J.; Bi, Y.P. Synthesis of mesoporous hydroxyapatite via a vitamin C templating hydrothermal route. Mater. Lett. 2018, 218, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, A.E.M.; Fagundes, A.P.; Macuvele, D.L.P.; Cesca, K.; Porto, L.; Padoin, N.; Soares, C.; Riella, H.G. Green Synthesis of Nano Hydroxyapatite: Morphology variation and its effect on cytotoxicity against fibroblast. Mater. Lett. 2021, 284, 129023. [Google Scholar]
- Utara, S.; Klinkaewnarong, J. Synthesis and characterization of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles templated by ozonolysed natural rubber latex. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2016, 80, 728–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uskoković, V.U.K. Ion-doped hydroxyapatite: An impasse or the road to follow? Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 11443–11465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Chen, T.; Wu, X.; Hu, Y.; Huang, K.; Wang, Y.; Dai, H. Effects of bioactive strontium-substituted hydroxyapatite on osseointegration of polyethylene terephthalate artificial ligaments. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 6600–6613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.F.; Jiang, Q.H.; Peel, S.; Wang, X.X.; He, F.M. Effects of magnesium-substitute nanohydroxyapatite coating on implant osseointegration. Clin. Oral. Implant. Res. 2013, 24, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbo, C.; Sindilaru, M.; Carlea, A.; Tomoaia, G.; Almasan, V.; Petean, L.; Mocanu, A.; Horovitz, O.; Tomoaia-Cotisel, M. Synthesis and structural characterization of novel porous zinc substituted nanohydroxyapatite powders. Part. Sci. Technol. 2017, 35, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, B.; Alshemary, A.Z.; Evis, Z. Co-doped hydroxyapatites as potential materials for biomedical applications. Microchem. J. 2019, 144, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Predoi, D.; Iconaru, S.L.; Predoi, M.V. Fabrication of Silver- and Zinc-Doped Hydroxyapatite Coatings for Enhancing Antimicrobial Effect. Coatings 2020, 10, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavanya, P.; Vijayakumari, N. Copper and manganese substituted hydroxyapatite/chitosan-polyvinyl pyrrolidone biocomposite for biomedical applications. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2021, 44, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittler, M.L.; Unalan, I.; Grünewald, A.; Beltrán, A.M.; Grillo, C.A.; Destch, R.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Boccaccini, A.R. Bioactive glass (45S5)-based 3D scaffolds coated with magnesium and zinc-loaded hydroxyapatite nanoparticles for tissue engineering applications. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 182, 110346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, G.H.; Cheng, Z.Q.; Li, J.F. Preparation and modification of nano-hydroxyapatite. Chin. J. Tissue Eng. Res. 2013, 17, 2989–2993. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.H.; Wen, B.; Tan, Y.M.; Shao, L.X.; Liu, Y.X. Structure Characterization and Performance Test of PLA Composites Filled with HAp by Wet Modified. Chin. Plast. Ind. 2019, 47, 127–131. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, T.Y.; Xia, Z.G.; Liao, L. Effect of reaction systems and surfactant additives on the morphology evolution of hydroxyapatite nanorods obtained via a hydrothermal route. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 4384–4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.Y. Preparation and Performance of Gelatin/Glycine Modified Nano-Hydroxyapatite for Dental Enamel Repair Membrane. Master’s Thesis, Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Y.J.; Chu, L.G.; Zhu, S.H.; Li, Y.; Yan, C.R.; Shang, J.Y. Adsorption capacity of surfactant-modified nano-hydroxyapatite for Cd2+. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2019, 38, 1901–1908. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.D.; Lin, H.L.; Haung, S.M.; Liu, S.M.; Chen, W.C. Effect of pH on the In Vitro Biocompatibility of Surfactant-Assisted Synthesis and Hydrothermal Precipitation of Rod-Shaped Nano-Hydroxyapatite. Polymers 2021, 13, 2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.G.; Shen, J. The synthesis of hydroxyapatite crystals with various morphologies via the solvothermal method using double surfactants. Mater. Lett. 2020, 259, 126881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, S.H.; Jiang, X.H.; Li, J.; Meng, Z.; Chen, L.L.; Han, C.R. Controlled Synthesis of Hydroxyapatite Using a Novel Natural Rosin-Based Surfactant. Nano 2017, 12, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, F.A.; Ziyad, A.A.; El-Giar, E.M.; Ahmed, M.M.; El-Kady, A.M. Novel green synthesis of hydroxyapatite uniform nanorods via microwave-hydrothermal route using licorice root extract as template. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 3928–3937. [Google Scholar]
- Sezer, D.; Hoşgün, E.Z. Controlled release of acetylsalicylic acid via hydroxyapatite prepared with diferent templates. J. Aust. Ceram. Soc. 2023, 59, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.R.; Fan, T.; Huang, Y.; Ma, L.G.; Liu, F. Synthesis conditions of nano-hydroxyapatite using chondroitin sulfate by co-precipitation method. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 236–238, 2076–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanthi, P.M.S.L.; Ashok, M.; Mangalaraja, R.V.; Balasubramanian, T. Synthesis and characterization of nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite spheroids using anionic template for bioapplications. Key Eng. Mater. 2012, 493–494, 723–727. [Google Scholar]
- Shahid, A.; Mohammad, M. Synthesis of nano-hydroxyapatite by chemical precipitation using different surfactant templates. Biomater. Sci.-Process. Prop. Appl. 2011, 228, 67–74. [Google Scholar]
- Weeraphat, P.O.; Siwaporn, M.; Ming, T.I. Formation of hydroxyapatite crystallites using organic template of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) and sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS). Mater. Chem. Phys. 2008, 112, 453–460. [Google Scholar]
- Langroudi, M.M.; Saravani, M.G.; Nouri, A. Surfactant-Assisted Synthesis of Polyvinylpyrrolidone-hydroxyapatite Composites as a Bone Filler. J. Appl. Biomater. Func. 2017, 15, e334–e340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanthi, P.M.S.L.; Ashok, M.; Uthirakumar, P.; Balasubramanian, T. Influence of Bicationic and Catanionic Surfactants Over the Morphology of Mesoporous Nanohydroxyapatite. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2018, 18, 7064–7071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tari, N.E.; Motlagh, M.M.K.; Sohrabi, B. Synthesis of hydroxyapatite particles in catanionic mixed surfactants template. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2011, 131, 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanthi, P.M.S.L.; Mangalaraja, R.V.; Uthirakumar, A.P.; Velmathi, S.; Balasubramanian, T.; Ashok, M. Synthesis and characterization of porous shell-like nano hydroxyapatite using Cetrimide as template. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 350, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.Y.; Chen, Y.Y.; Qian, J.C.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, S.S. Controllable synthesis of spherical hydroxyapatite nanoparticles using inverse microemulsion method. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2016, 183, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Ning, X.S.; Bai, Y.J.; Jia, W.W. A scalable synthesis of non-agglomerated and low-aspect ratio hydroxyapatite nanocrystals using gelatinized starch matrix. Mater. Lett. 2013, 113, 142–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suslu, A.; Albayrak, A.Z.; Urkmez, A.S.; Bayir, E.; Cocen, U. Effect of surfactant types on the biocompatibility of electrospun HAp/PHBV composite nanofibers. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2014, 25, 2677–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.J.; Song, G.J.; Lou, T. Fabrication and characterization of nano-composite scaffold of PLLA/silane modified hydroxyapatite. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 32, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, H.X.; Si, Y.F.; Zhu, A.P.; Ji, L.Y.; Shi, H.C. Surface modified nano-hydroxyapatite/poly(lactide acid) composite and its osteocyte compatibility. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2012, 32, 1796–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cui, Y.; Jing, X.; Zhang, P.; Chen, X. The nanocomposite scaffold of poly(lactide-co-glycolide) and hydroxyapatite surface-grafted with L-lactic acid oligomer for bone repair. Acta Biomater. 2009, 5, 2680–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.F.; Ling, F.G.; Ma, L.L.; Yang, C.; Chen, X. Electrospun hydroxyapatite grafted poly(L-lactide)/poly(1actic-co-glycolic acid) nanofibers for guided bone regeneration membrane. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2013, 79, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.Q.; Yang, X.P.; Mao, J.F.; Xu, F.J.; Cai, Q. Hydroxyapatite–poly(l-lactide) nanohybrids via surface-initiated ATRP for improving bone-like apatite-formation abilities. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 6823–6830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turki, T.; Othmani, M.; Bac, C.G.; Rachdi, F.; Bouzouita, K. Surface modification of zinc-containing hydroxyapatite by tartaric acid. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 284, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othmani, M.; Aissa, A.; Bac, C.G.; Rachdi, F.; Debbabi, M. Surface modification of calcium hydroxyapatite by grafting of etidronic acid. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 274, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchwald, Z.; Szołyga, M.; Zwolińska, J.; Marciniec, B.; Voelkel, A. Surface modification of hydroxyapatite with polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane. React. Funct. Polym. 2022, 170, 105131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Cui, H.; Zhuang, X.; Zhang, P.; Cui, Y.; Wang, X.; Wei, Y.; Chen, X. Nano-hydroxyapatite surfaces grafted with electroactive aniline tetramers for bone-tissue engineering. Macromol. Biosci. 2013, 13, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.Y.; Xiong, C.D.; Chen, D.L.; Jiang, L.X.; Pang, X.B. Effect of n-HA with different surface-modified on the properties of n-HA/PLGA composite. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 259, 72–78. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.Y.; Xiong, C.D.; Jiang, L.X.; Chen, D.L.; Li, Q. Effect of n-HA content on the isothermal crystallization, morphology and mechanical property of n-HA/PLGA composites. Mater. Res. Bull. 2013, 48, 1233–1238. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.X.; Jiang, L.Y.; Ma, C.; Han, C.T.; Xu, L.J. Preparation and Characterization of Nano-hydroxyapatite/PLGA Composites with Novel Surface-modified Nano-hydroxyapatite. J. Inorg. Mater. 2013, 28, 751–756. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.X.; Jiang, L.Y.; Xu, L.J.; Han, C.T.; Xiong, C.D. Effect of a new surface-grafting method for nano-hydroxyapatite on the dispersion and the mechanical enhancement for poly(lactide-co-glycolide). Express Polym. Lett. 2014, 8, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Liu, S.; Luo, L.; Cao, F.; Wang, C.; Chen, R.; Shen, J. Synthesizing surface modified hydroxyapatite embedded in threedimensional graphene oxide networks for drug loading. Mater. Lett. 2020, 265, 127426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.; Yang, S.; Miron, R.J.; Wei, J.C.; Zhang, Y.F.; Zhang, M. Osteogenic properties of PBLG-g-HA/PLLA nanocomposites. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, P.; Qiu, X.; Yang, L.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, C.; Hu, Y.; Shuai, C. Polydopamine constructed interfacial molecular bridge in nano-hydroxylapatite/polycaprolactone composite scaffold. Colloid Surf. B 2022, 217, 112668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Kim, B.S.; Gupta, K.C.; Lee, D.Y.; Kang, I.K. Hydroxyapatite Nanorod-Modified Sand Blasted Titanium Disk for Endosseous Dental Implant Applications. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2018, 15, 601–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehri, A.; Moussa, S.B.; Laghzizil, A.; Nunzi, J.M.; Badraoui, B. A new in situ enhancement of the hydroxyapatite surface by Tyramine: Preparation and interfacial properties. Colloid Surf. A 2020, 592, 124590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timpu, D.; Sacarescu, L.; Vasiliu, T.; Dinu, M.V.; David, G. Surface cationic functionalized nano-hydroxyapatite-Preparation, characterization, effect of coverage on properties and related applications. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 132, 109759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirhosseini, M.M.; Haddadi-Asl, V.; Zargarian, S.S. Fabrication and characterization of polymer-ceramic nanocomposites containing pluronic F127 immobilized on hydroxyapatite nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 80564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Li, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Fang, L.; Luo, Z.; Xue, B.; Ma, L. Mechanical properties and in vivo study of modified-hydroxyapatite/polyetheretherketone biocomposites. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 73, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kairalla, E.C.; Bressiani, J.C.; de Almeida Bressiani, A.H.; de Carvalho Pinto Ribela, M.T.; Higa, O.Z.; de Queiroz, A.A.A. Queiroz Physicochemical and biological properties of nanohydroxyapatite grafted with star-shaped poly(ε-caprolactone). J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2022, 33, 2353–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.; Ahuja, D. Preparation and characterization of aliphatic polyurethane and modified hydroxyapatite composites for bone tissue engineering. Polym. Bull. 2020, 77, 6049–6062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.F.; Long, L.; Wang, R.X.; Chen, D.F.; Duan, S.; Xu, F.J. Surface-Modified Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticle-Reinforced Polylactides for Three-Dimensional Printed Bone Tissue Engineering Scaffolds. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2018, 14, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, X.J.; Lang, M.D. Preparation of poly(methyl methacrylate) grafted hydroxyapatite nanoparticles via reverse ATRP. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 6233–6238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.F.; Xu, M.; Wei, J.C.; Zhang, H.B.; Chen, Y.W. Surface modification of hydroxyapatite nano-particles by poly(l-phenylalanine) via ROP of l-phenylalanine N-carboxyanhydride (Pha-NCA). Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 2850–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, K.L.; Wu, Y.S.; Wang, C.Y.; Hong, D.W.; Chen, Z.X.; Huang, C.A.; Chu, I.M.; Lai, P.L. Incorporation of surfacemodified hydroxyapatite into poly(methyl methacrylate) to improve biological activity and bone ingrowth. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2019, 6, 182060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, K.L.; Grøndahl, L.; Dao, H.; Du, K.; Puttick, S.; Lai, P.L.; Peng, H.; Chu, I.M.; Whittaker, A.K. In vitro degradation study of polyanhydride copolymers/surface grafted Hydroxyapatite composites for bone tissue application. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2017, 140, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarif, F.; Tabassum, S.; Jamal, A.; Gul, U.; Gilani, M.A.; Sharif, F.; Zahid, S.; Asif, A.; Chaudhry, A.A.; Rehman, I.U. Surface-grafted remedial hydroxyapatite nanoparticles to avoid operational infections. Monatshefte Chem.-Chem. Mon. 2019, 150, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.B.; Fu, Y.; Niu, R.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Nie, J.; Yang, D.Z. Study on the biocomposites with poly(ethylene glycol) dimethacrylate and surfaced-grafted hydroxyapatite nanoparticles. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 127, 1737–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.; Ahuja, D. 3D porous polyurethane (PU)/triethanolamine modified hydroxyapatite (TEA-HA) nano composite for enhanced bioactivity for biomedical applications. J. Polym. Res. 2022, 29, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmanchi, M.; Shokrollahi, P.; Atai, M.; Omidian, H.; Bagheri, R. Supramolecular polycaprolactone nanocomposite based on functionalized hydroxyapatite. J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 2012, 27, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pielichowska, K.; Szuba, P.; Maciocha, J.; Macherzyńska, B.; Nowicka, K.; Szatkowski, P. Preparation, Characterization, and Bioactivity Evaluation of Polyoxymethylene Copolymer/Nanohydroxyapatite-g-Poly(ε-caprolactone) Composites. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, A.J.; Li, J.M.; Song, N. Effect of stearic acid modified HAp nanoparticles in different solvents on the properties of Pickering emulsions and HAp/PLLA composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 79, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.F.; Ling, F.G.; Chen, X.S. Grafting polymerization of L-lactide on hydroxyapatite nanoparticles. Acta Polym. Sin. 2013, 1, 95–101. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.R.; Sun, F.H.; Zhou, X.Y.; Kong, W.B.; Xie, X.Y. Water dispersible hydroxyapatite nanoparticles functionalized by a family of aminoalkyl phosphates. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2015, 26, 1121–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.C.; Liu, A.X.; Chen, L.; Zhang, P.B.; Chen, X.S.; Jing, X.B. The Surface Modification of Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles by the Ring Opening Polymerization of γ-Benzyl-L-glutamate N-carboxyanhydride. Macromol. Biosci. 2009, 9, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makvandi, P.; Esposito Corcione, C.; Paladini, F.; Gallo, A.L.; Montagna, F.; Jamaledin, R.; Pollini, M.; Maffezzoli, A. Antimicrobial modified hydroxyapatite composite dental biteby stereolithography. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2018, 29, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Chen, J.; Xue, Y.; Ding, T.; Zhu, S.; Mao, M.; Zhang, L.; Han, Y. Polymer brush grafted antimicrobial peptide on hydroxyapatite nanorods for highly effective antibacterial performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 423, 130133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tham, D.Q.; Huynh, M.D.; Linh, N.T.D.; Van, D.T.C.; Cong, D.V.; Dung, N.T.K.; Trang, N.T.T.; Lam, P.V.; Hoang, T.; Lam, T.D. PMMA Bone Cements Modified with Silane-Treated and PMMA-Grafted Hydroxyapatite Nanocrystals: Preparation and Characterization. Polymers 2021, 13, 3860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorm, B.C.; Iemma, M.R.C.; Neto, B.D.; Francisco, R.C.L.; Dinić, I.; Ignjatović, N.; Marković, S.; Vuković, M.; Škapin, S.; Trovatti, E.; et al. Synthesis and Biological Properties of Alanine-Grafted Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles. Life 2023, 13, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbasuney, S. Green Synthesis of Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles with Controlled Morphologies and Surface Properties Toward Biomedical Applications. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2020, 30, 899–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Xiong, B.; Shu, Y.; Guo, J.Y.; Shuai, W.Y.; Huang, P. Preparation of nano-HA modified by PBLA. New Chem. Mater. 2020, 48, 282–285. [Google Scholar]
- Heng, C.; Zheng, X.; Liu, M.; Xu, D.; Huang, H.; Deng, F.; Hui, J.; Zhang, X.; Wei, Y. Fabrication of luminescent hydroxyapatite nanorods through surface-initiated RAFT polymerization: Characterization, biological imaging and drug delivery applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 386, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Yang, Z.Y.; Qiu, S.X.; Ding, K.Y.; Luo, J.B.; Xie, X.Y. Synthesis and Characterization of Poly(ethylene glycol)/hydroxyapatite Hybrid Nanomaterials. Chem. J. Chin. Univ. 2012, 33, 22–25. [Google Scholar]
- Carlos, A.M.P.; Jorge, G.M.; Perla, E.G.C.; José, R.F.M.; Humberto, M.R. Preparation of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles facilitated by the presence of β-cyclodextrin. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 536, S432–S436. [Google Scholar]
- Kamel, R.; El-Wakil, N.A.; Abdelkhalek, A.A.; Elkasabgy, N.A. Nanofibrillated cellulose/cyclodextrin based 3D scaffolds loaded with raloxifene hydrochloride for bone regeneration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 156, 704–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.J.; Jiang, L.Y.; Ma, B.L.; Su, S.P. Preparation of a highly dispersed nano-hydroxyapatite by a new surface modification strategy used for a reinforce filler for poly(lactic-co-glycolide). Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 17119–17128. [Google Scholar]
- Haojie, D.; Liuyun, J.; Bingli, M.; Shengpei, S.; Shuo, T.; Chunyan, T.; Jinghui, W.; Zhiwei, L.; Xiang, H. Synthesis of a novel co-hybridization nano-apatite powder with excellent dispersion, well-solubility and good biocompatibility by a new strategy. Adv. Powder Technol. 2019, 30, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.K.; Kai, D.; Tu, G.X.E.; Deen, G.R.; Too, H.P.; Loh, X.J. Enhanced transfection of a macromolecular lignin-based DNA complex with low cellular toxicity. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38, BSR20181021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.; Jiang, L.; Tang, C.; Tang, S.; Ma, B.; Zhang, N.; Wen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sheng, L.; Su, S.; et al. Study on the surface-modification of nano-hydroxyapatite with lignin and the corresponding nanocomposite with poly (lactide-co-glycolide). Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2021, 15, 630–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
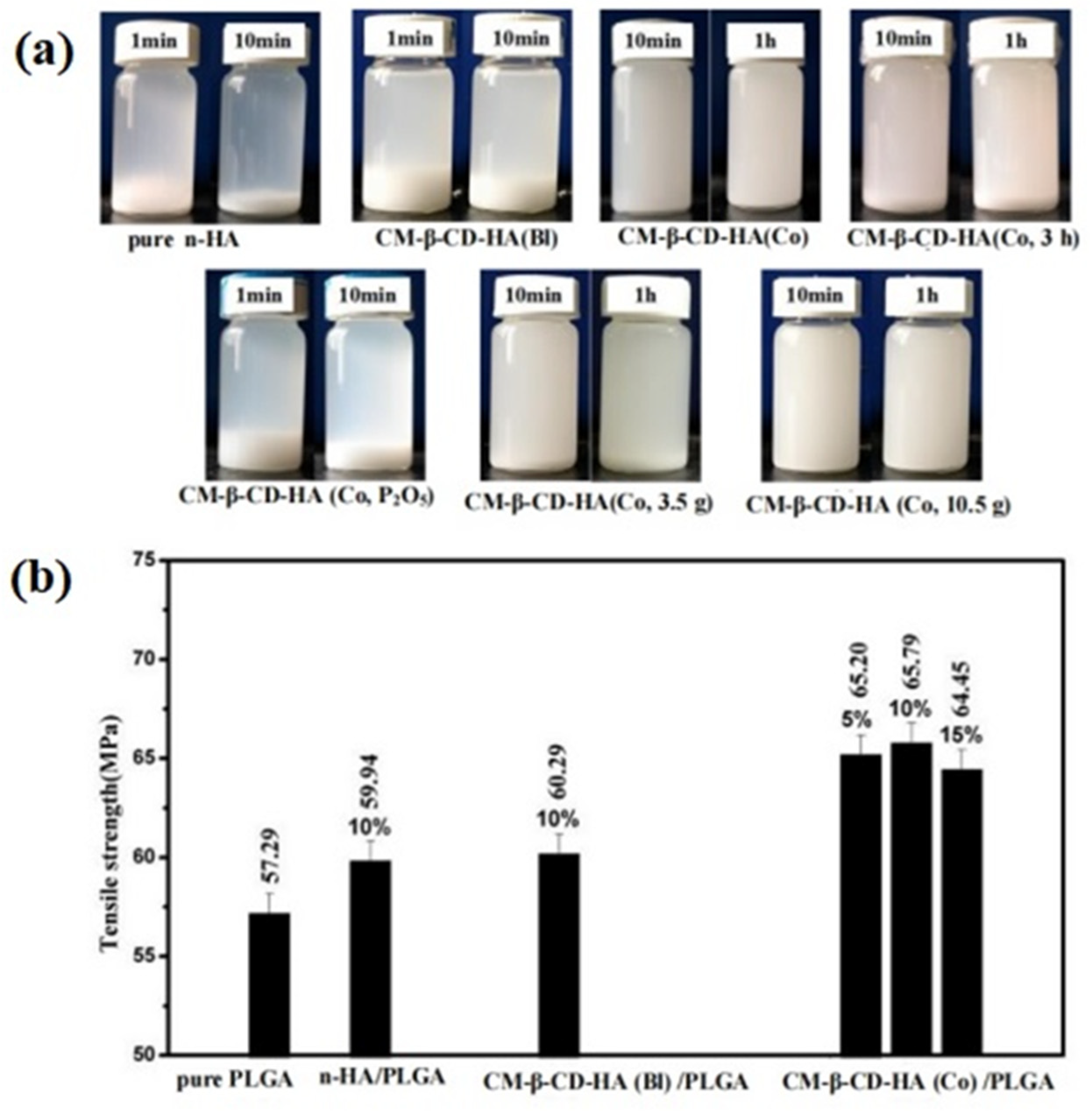
- Chunyan, T.; Haojie, D.; Shuo, T.; Liuyun, J.; Bingli, M.; Yue, W.; Na, Z.; Liping, S.; Shengpei, S. A combined-modification method of carboxymethyl β-cyclodextrin and lignin for nano-hydroxyapatite to reinforce poly(lactide-co-glycolide) for bone materials. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 160, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Modification of n-HA | |
|---|---|
| Physical Modification | Chemical Modification |
| Physical adsorption | Template method |
| Electron induction | Ion doped (Single ion doped, Multiple ions co-doped) |
| Laser irradiation | Adding surfactants for modification |
| Surface modification by grafting polymer | |
| Preparation of hybrid nano-apatite by introducing macromolecule | |
| Methods | Modification Effect | References | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical modification | Physical adsorption, electron induction, and laser irradiation | Improve the stability and dispersion of nano-particles | [9,10] |
| Chemical modification | Template method | The modified n-HA with different morphologies or structures is obtained by removing the template | [11,12,13,14] |
| Ion doped | Adding corresponding ions to the reactants to alter the surface characteristics of n-HA | [15,16,17,18,19,20,21] | |
| Adding surfactants for modification | Adsorption of their groups of surfactants on the n-HA particle surface | [22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42] | |
| Surface modification by grafting polymer | Some polymers were grafted onto n-HA to improve the interface adhesion between n-HA and polymers | [43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79] | |
| Preparation of hybrid nano-apatite by introducing macromolecule | Some amphiphilic macromolecules were introduced to obtain hybrid nano-apatite, which displayed better reinforce effect for polymers | [80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, S.; Shen, Y.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, Y. Surface Modification of Nano-Hydroxyapatite/Polymer Composite for Bone Tissue Repair Applications: A Review. Polymers 2024, 16, 1263. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16091263
Tang S, Shen Y, Jiang L, Zhang Y. Surface Modification of Nano-Hydroxyapatite/Polymer Composite for Bone Tissue Repair Applications: A Review. Polymers. 2024; 16(9):1263. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16091263
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Shuo, Yifei Shen, Liuyun Jiang, and Yan Zhang. 2024. "Surface Modification of Nano-Hydroxyapatite/Polymer Composite for Bone Tissue Repair Applications: A Review" Polymers 16, no. 9: 1263. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16091263
APA StyleTang, S., Shen, Y., Jiang, L., & Zhang, Y. (2024). Surface Modification of Nano-Hydroxyapatite/Polymer Composite for Bone Tissue Repair Applications: A Review. Polymers, 16(9), 1263. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16091263






