Influence of Strong Shear Field on Structure and Performance of HDPE/PA6 In Situ Microfibril Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
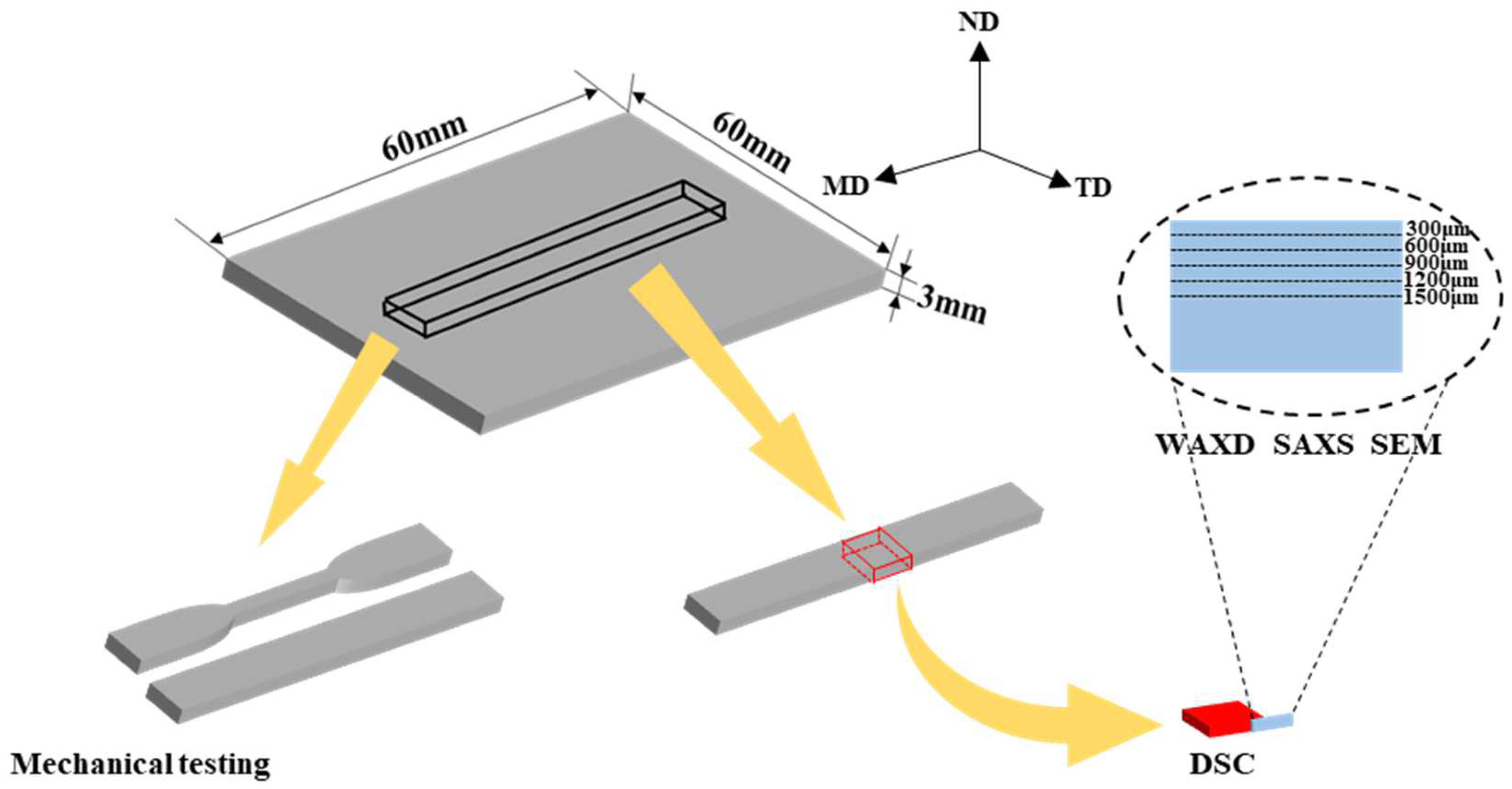
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
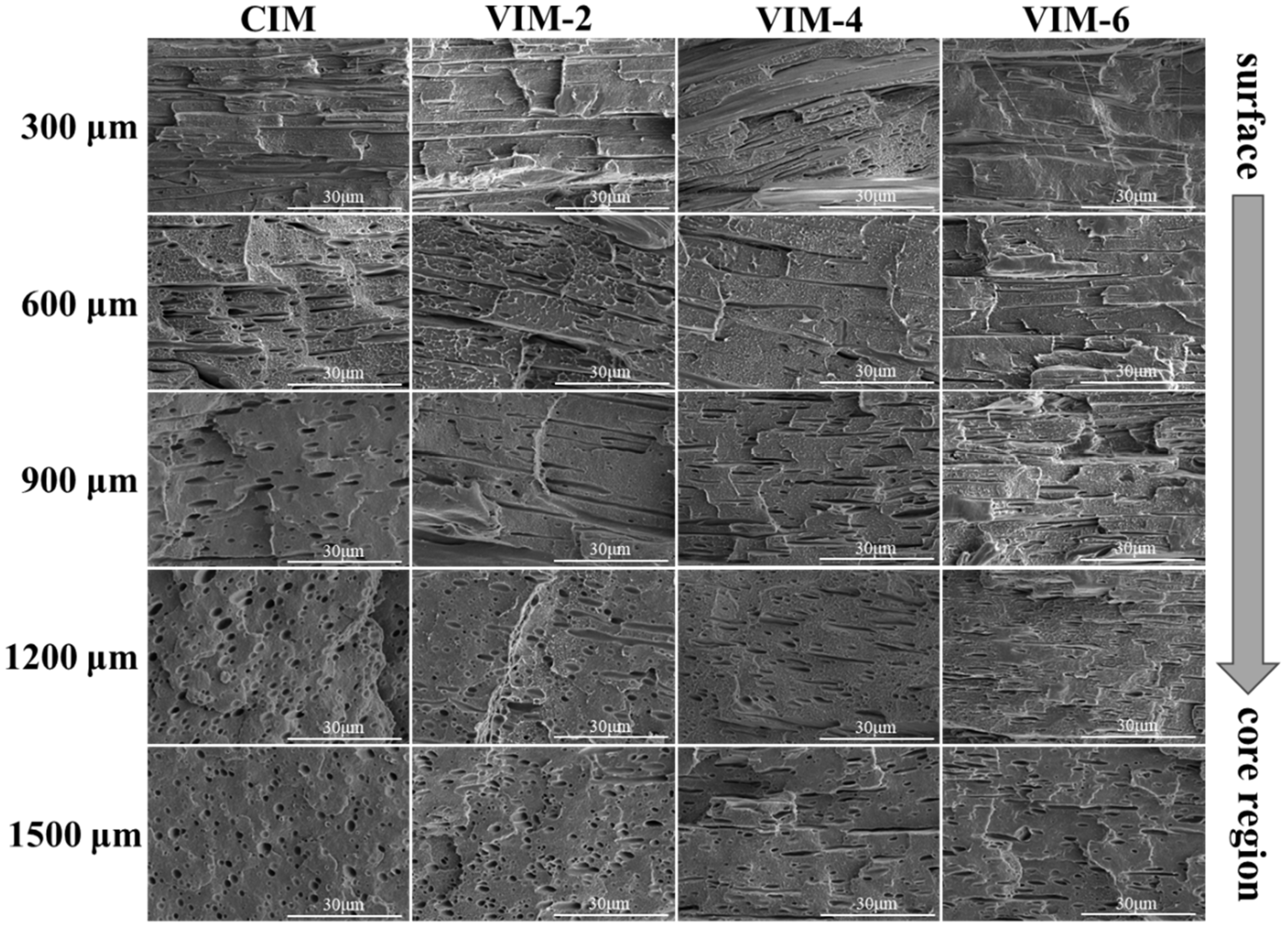
2.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
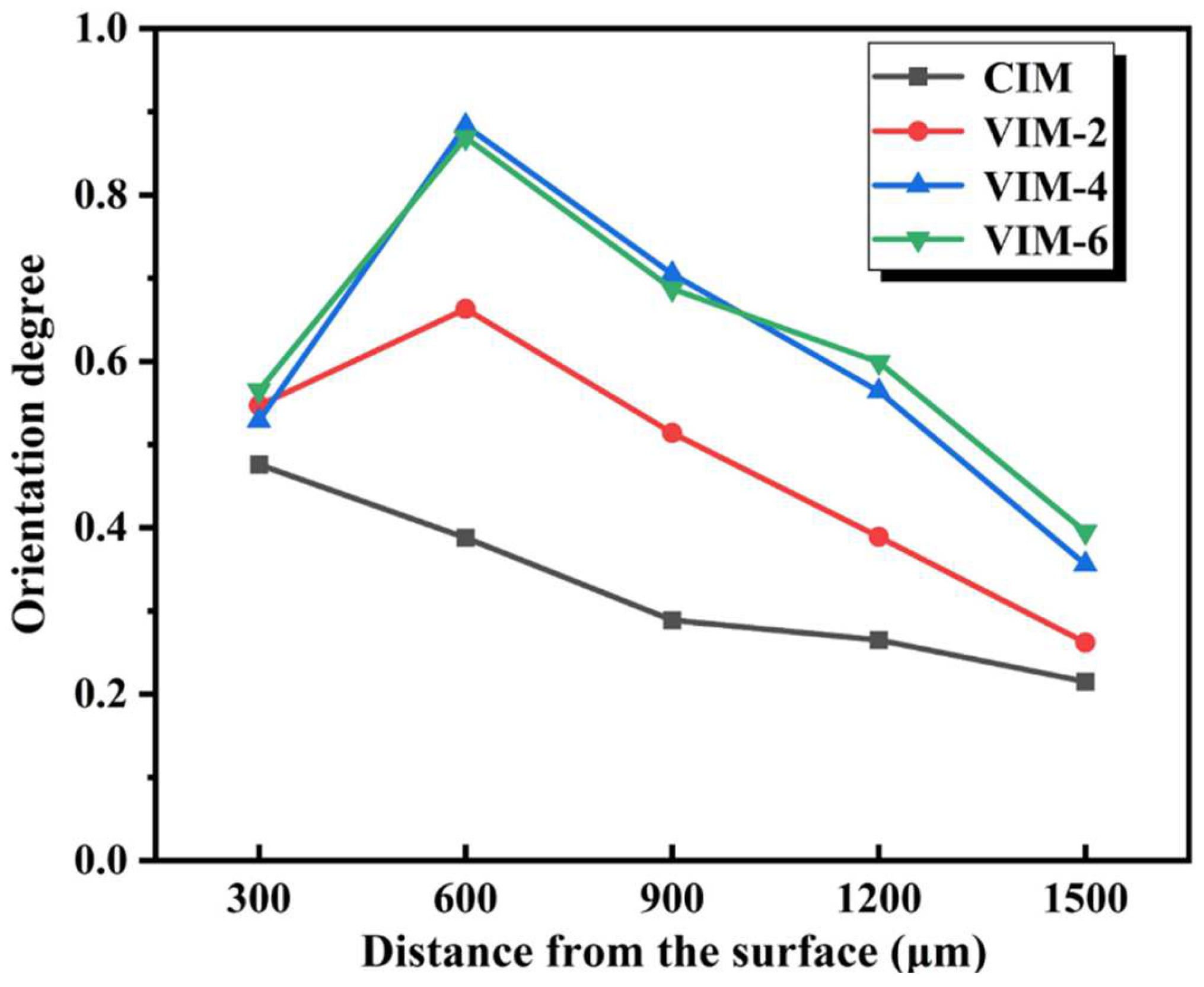
2.5. 2D-WAXD and 2D-SAXS Measurements
2.6. Mechanical Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Phase Morphology
3.2. Thermal Behavior
3.3. Crystalline Structure
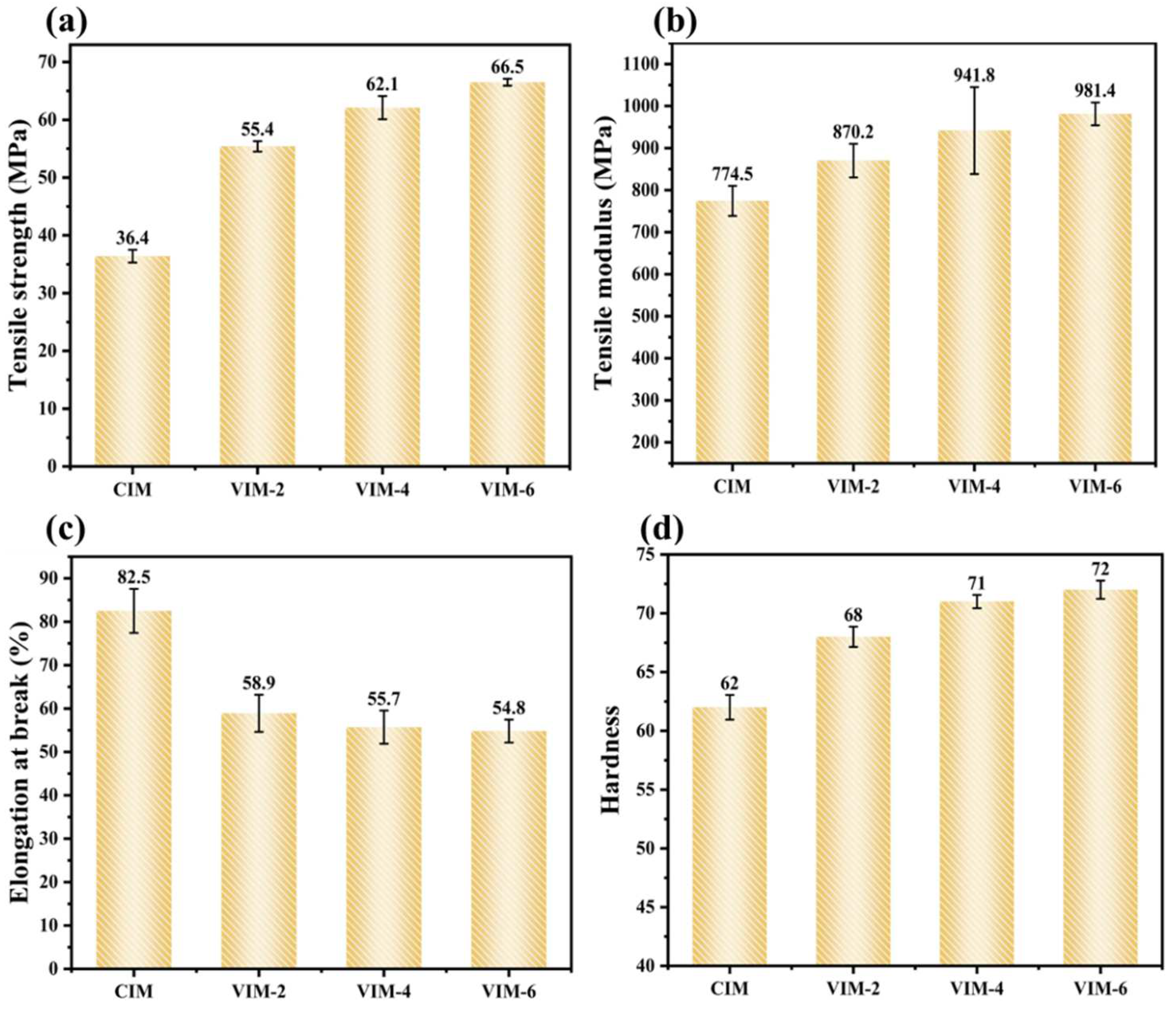
3.4. Mechanical Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amjadi, M.; Fatemi, A. Tensile behavior of high-density polyethylene including the effects of processing technique, thickness, temperature, and strain rate. Polymers 2020, 12, 1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanal, S.; Zhang, W.P.; Ahmed, S.; Ali, M.; Xu, S. Effects of intumescent flame retardant system consisting of tris (2-hydroxyethyl) isocyanurate and ammonium polyphosphate on the flame retardant properties of high-density polyethylene composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2018, 112, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wang, Z.W.; Yan, S.M.; Gao, X.Q.; Deng, C.; Zhang, J.; Shen, K.Z. The morphology and tensile strength of high density polyethylene/nano-calcium carbonate composites prepared by dynamic packing injection molding. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2012, 51, 1127–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Zhang, R.Y.; Wu, J.J.; Yang, W.; Yang, M.-B. Largely enhanced molecular orientation and mechanical property of injection-molded high-density polyethylene parts via the synergistic effect of polyamide 6 in situ microfibrillar and intense shear flow. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2014, 292, 3033–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xie, Z.X.; Zhong, G.J.; Lei, J.; Gao, X.; Jiang, L. Effect of cellulose nanocrystals and hot stretching on shish-kebab structures of high-density polyethylene. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2023, 62, 15018–15028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salakhov, I.; Shaidullin, N.M.; Chalykh, A.E.; Matsko, M.A.; Shapagin, A.V.; Batyrshin, A.Z.; Shandryuk, G.A.; Nifant’ev, I.E. Low-temperature mechanical properties of high-density and low-density polyethylene and their blends. Polymers 2021, 13, 1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, I.L.M.; Zanini, N.C.; Mulinari, D.R. Thermal and mechanical properties of hdpe reinforced with al2o3 nanoparticles processed by thermokinectic mixer. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2021, 31, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.X.; Mi, D.S.; Wang, Y.X.; Wang, T.; Shen, K.; Zhang, J. Composite contains large content of in situ microfibril, prepared directly by injection molding: Morphology and property. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2018, 303, 1800270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Ou, Y.C.; Feng, Y.P. Studies on the mechanical-properties and crystallization behavior of polyethylene composites. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 1995, 13, 218–227. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.L.; Liu, F.; Liu, D.Y.; Liu, Y. Review of strain rate effects of fiber-reinforced polymer composites. Polymers 2021, 13, 2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.T.A.; Singh, K.K.; Azam, M.S. Fatigue damage analysis of fiber-reinforced polymer composites-a review. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2018, 37, 636–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cech, V.; Palesch, E.; Lukes, J. The glass fiber-polymer matrix interface/interphase characterized by nanoscale imaging techniques. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2013, 83, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thieme, M.; Boehm, R.; Gude, M.; Hufenbach, W. Probabilistic failure simulation of glass fibre reinforced weft-knitted thermoplastics. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2014, 90, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Liao, X.W.; Qin, Q.H.; Wang, G. The fabrication and characterization of high density polyethylene composites reinforced by carbon nanotube coated carbon fibers. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2019, 121, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Doshi, H.; Srinivasarao, M.; Park, J.O.; Schiraldi, D.A. Fibers from polypropylene/nano carbon fiber composites. Polymer 2002, 43, 1701–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, H.-C.; Chang, R.-Y.; Hsu, C.H. Numerical predictions of fiber orientation and mechanical properties for injection-molded long-glass-fiber thermoplastic composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 150, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.M.; Yang, M.B.; Huang, R.; Yang, W.; Feng, J.M. Poly(ethylene terephthalate)/polyethylene composite based on in-situ microfiber formation. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2002, 41, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.X.; Mi, D.S.; Wang, Y.X.; Wang, T.; Shen, K.; Zhang, J. Insight into understanding the influence of blending ratio on the structure and properties of high-density polyethylene/polystyrene microfibril composites prepared by vibration injection molding. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 1190–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayanarayanan, K.; Thomas, S.; Joseph, K. Morphology, static and dynamic mechanical properties of in situ microfibrillar composites based on polypropylene/poly (ethylene terephthalate) blends. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2008, 39, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, A.; Tabatabaei, A.; Barzegari, M.R.; Mahmood, S.H.; Park, C.B. In situ fibrillation of co2-philic polymers: Sustainable route to polymer foams in a continuous process. Polymer 2013, 54, 4645–4652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmanovic, M.; Delva, L.; Cardon, L.; Ragaert, K. The effect of injection molding temperature on the morphology and mechanical properties of pp/pet blends and microfibrillar composites. Polymers 2016, 8, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, S.; Lu, X.; Lv, S.-Y.; Xu, W.-H.; Zhang, H.-H.; Tan, L.-C.; Qu, J.-P. Simultaneously toughening and reinforcing high-density polyethylene via an industrial volume-pulsatile injection molding machine and poly (ethylene terephthalate). Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 198, 108243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.Q.; Yang, W.; Huang, L.; Li, Z.-M.; Yang, M.-B.; Yin, B.; Li, Q.; Liu, C.-T.; Shen, C.-Y. The role of gas penetration on morphological formation of polycarbonate/polyethylene blend molded by gas-assisted injection molding. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 7275–7285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Wang, M.; Li, J.; Guo, S. In situ fibrillation of polyamide 6 in isotactic polypropylene occurring in the laminating-multiplying die. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2011, 22, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Yang, Q.; Kong, M.; Tang, D.; Chen, Q.; Liu, Y.; Lou, F.; Huang, Y.; Liao, X. Unusual hierarchical structures of micro-injection molded isotactic polypropylene in presence of an in situ microfibrillar network and a β-nucleating agent. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 43571–43580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Nie, M.; Wang, Q. Biaxial reinforcements for polybutene-1 medical-tubes achieved via flow-design controlled morphological development of incorporated polystyrene: In-situ microfibrillation, alignment manipulation and performance optimization. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2015, 119, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Wu, J.; Leng, J.; Cardon, L.; Zhang, J. Reinforced and toughened pp/ps composites prepared by Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF) with in-situ microfibril and shish-kebab structure. Polymer 2020, 186, 121971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Yang, S.-G.; Lei, J.; Hsiao, B.S.; Li, Z.-M. Role of stably entangled chain network density in shish-kebab formation in polyethylene under an intense flow field. Macromolecules 2015, 48, 6652–6661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Jiang, H.-W.; Zhang, H.-H.; Huang, Z.-X.; Qu, J.-P. Simultaneously achieving super toughness and reinforcement of immiscible high-density polyethylene/poly (ethylene terephthalate) composite via oriented spherical crystal structure. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2022, 163, 107186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.-C.; Xie, Z.-X.; Gao, N.; Zhong, G.-J.; Deng, C.; Gao, X.-Q. Regulating crystalline morphology jointly by dynamic shearing and solid phase stretching endows polyethylene high modulus, strength and heat-resistance. Polymer 2023, 283, 126219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Wang, K.; Tang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Du, R.; Fu, Q. Unexpected molecular weight dependence of shish-kebab structure in the oriented linear low density polyethylene/high density polyethylene blends. J. Chem. Phys. 2008, 128, 174902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Na, B.; Fu, Q. Super polyolefin blends achieved via dynamic packing injection molding: Morphology and properties. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2003, 21, 505–514. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Li, W.; Geng, L.; Chen, B.; Mi, H.; Hong, K.; Peng, X.; Kuang, T. Formation of stretched fibrils and nanohybrid shish-kebabs in isotactic polypropylene-based nanocomposites by application of a dynamic oscillatory shear. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 348, 546–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, L.; Li, L.; Mi, H.; Chen, B.; Sharma, P.; Ma, H.; Hsiao, B.S.; Peng, X.; Kuang, T. Superior impact toughness and excellent storage modulus of poly (lactic acid) foams reinforced by shish-kebab nanoporous structure. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 21071–21076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Huang, A.; Geng, L.H.; Lian, X.-H.; Chen, B.-Y.; Hsiao, B.S.; Kuang, T.-R.; Peng, X.-F. Ultra-strong, tough and high wear resistance high-density polyethylene for structural engineering application: A facile strategy towards using the combination of extensional dynamic oscillatory shear flow and ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 167, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, D.; Hou, F.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, J. Improving the mechanical and thermal properties of shish-kebab via partial melting and re-crystallization. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 101, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.L.; Deng, C.J.; Gu, X.B.; Fu, Q.; Zhang, J. Manipulating the strength-toughness balance of poly(l-lactide) (plla) via introducing ductile poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) and strong shear flow. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 1000–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Li, W.; Li, L.; Peng, X.; Kuang, T. Effect of dynamic oscillation shear flow intensity on the mechanical and morphological properties of high-density polyethylene: An integrated experimental and molecular dynamics simulation study. Polym. Test. 2019, 80, 106122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, D.; Xia, C.; Jin, M.; Wang, F.; Shen, K.; Zhang, J. Quantification of the effect of shish-kebab structure on the mechanical properties of polypropylene samples by controlling shear layer thickness. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 4571–4578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dencheva, N.V.; Oliveira, M.J.; Pouzada, A.S.; Kearns, M.P.; Denchev, Z.Z. Mechanical properties of polyamide 6 reinforced microfibrilar composites. Polym. Compos. 2011, 32, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, L.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.Y.; Hou, W. Effects of hydrothermal aging on moisture absorption and property prediction of short carbon fiber reinforced polyamide 6 composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 153, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J.; Hu, M.; Yan, Z.; Wang, T.; Fu, Q.; Gao, X.; Zhang, J. Preparation of ppr/ps blends by multiflow vibration injection molding: Influence of shish–kebab structures and in situ fibers. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2024, 63, 2769–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stack, G.M.; Mandelkern, L.; Kröhnke, C.; Wegner, G. Melting and crystallization kinetics of a high molecular-weight n-alkane—c192h386. Macromolecules 1989, 22, 4351–4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappello, M.; Strangis, G.; Cinelli, P.; Camodeca, C.; Filippi, S.; Polacco, G.; Seggiani, M. From waste vegetable oil to a green compatibilizer for hdpe/pa6 blends. Polymers 2023, 15, 4178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, A.; Kumar, S. Effects of graphene nanoparticles with organic wood particles: A synergistic effect on the structural, physical, thermal, and mechanical behavior of hybrid composites. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2022, 33, 3201–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
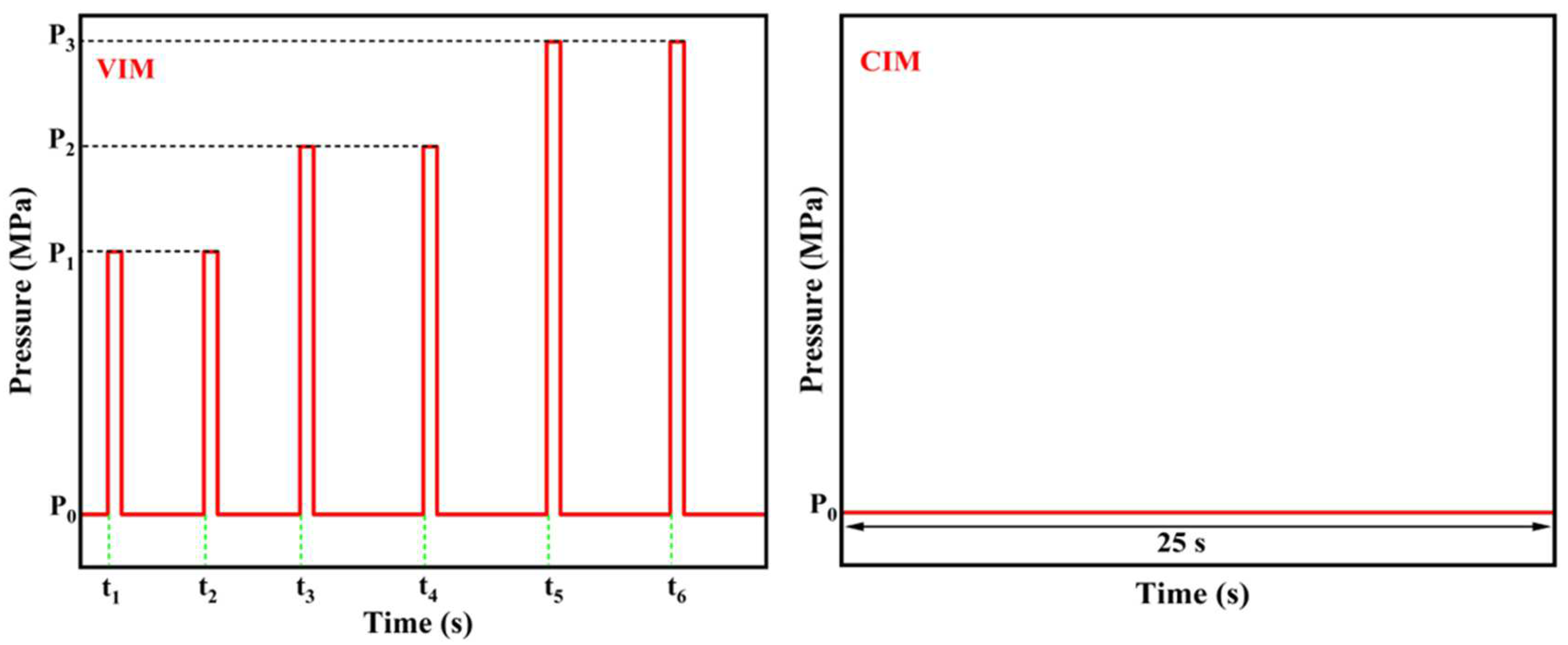





| Packing Pressure (P0) | 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th | 6th | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | t1 | P1 | t2 | P2 | t3 | P2 | t4 | P3 | t5 | P3 | t6 | ||
| VIM-2 | 30 | 80 | 1 | 80 | 4.5 | ||||||||
| VIM-4 | 80 | 1 | 80 | 4.5 | 100 | 9 | 100 | 13.5 | |||||
| VIM-6 | 80 | 1 | 80 | 4.5 | 100 | 9 | 100 | 13.5 | 120 | 18 | 120 | 22.5 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Luo, M.; Zhang, J. Influence of Strong Shear Field on Structure and Performance of HDPE/PA6 In Situ Microfibril Composites. Polymers 2024, 16, 1032. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16081032
Zhang J, Zhang Y, Li Y, Luo M, Zhang J. Influence of Strong Shear Field on Structure and Performance of HDPE/PA6 In Situ Microfibril Composites. Polymers. 2024; 16(8):1032. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16081032
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Junwen, Yiwei Zhang, Yanjiang Li, Mengna Luo, and Jie Zhang. 2024. "Influence of Strong Shear Field on Structure and Performance of HDPE/PA6 In Situ Microfibril Composites" Polymers 16, no. 8: 1032. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16081032
APA StyleZhang, J., Zhang, Y., Li, Y., Luo, M., & Zhang, J. (2024). Influence of Strong Shear Field on Structure and Performance of HDPE/PA6 In Situ Microfibril Composites. Polymers, 16(8), 1032. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16081032







