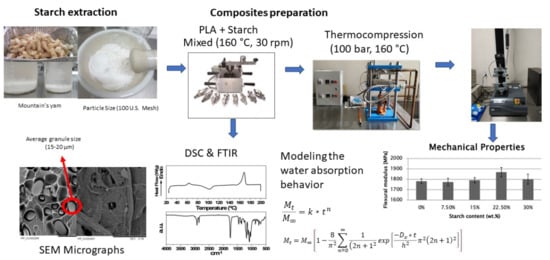
Characterization of Polylactic Acid Biocomposites Filled with Native Starch Granules from Dioscorea remotiflora Tubers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
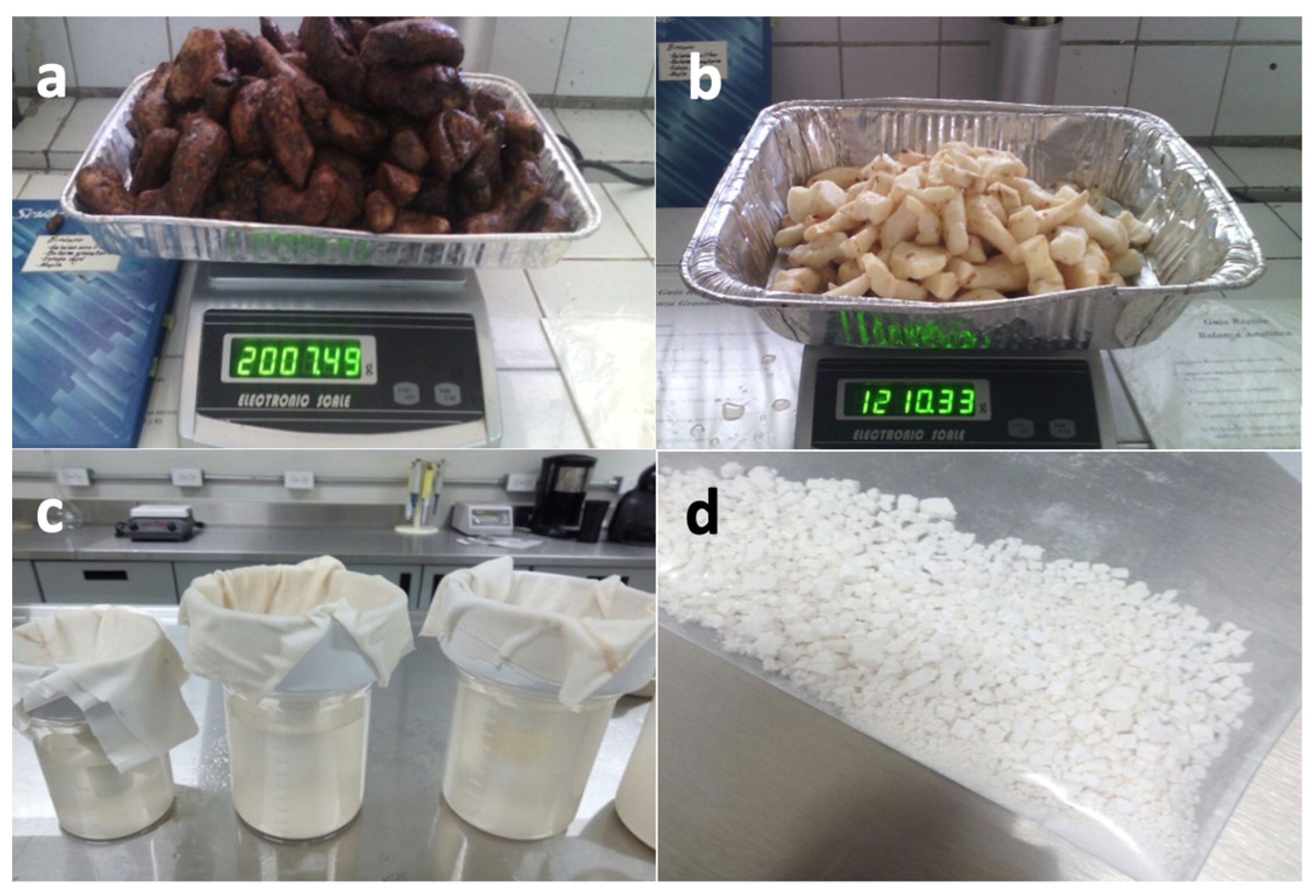
2.2.1. Starch Extraction
2.2.2. Amylose Content and Yield
2.2.3. Biocomposite Preparation
2.2.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.2.5. FTIR-Attenuated Total Reflectance
2.2.6. Thermal Analysis
2.2.7. X-ray Diffraction
2.2.8. Water Absorption Kinetics
2.2.9. Mechanical Properties
2.2.10. Dynamic Mechanical Analysis
2.2.11. Color
2.2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Starch Yield
3.2. Amylose Content
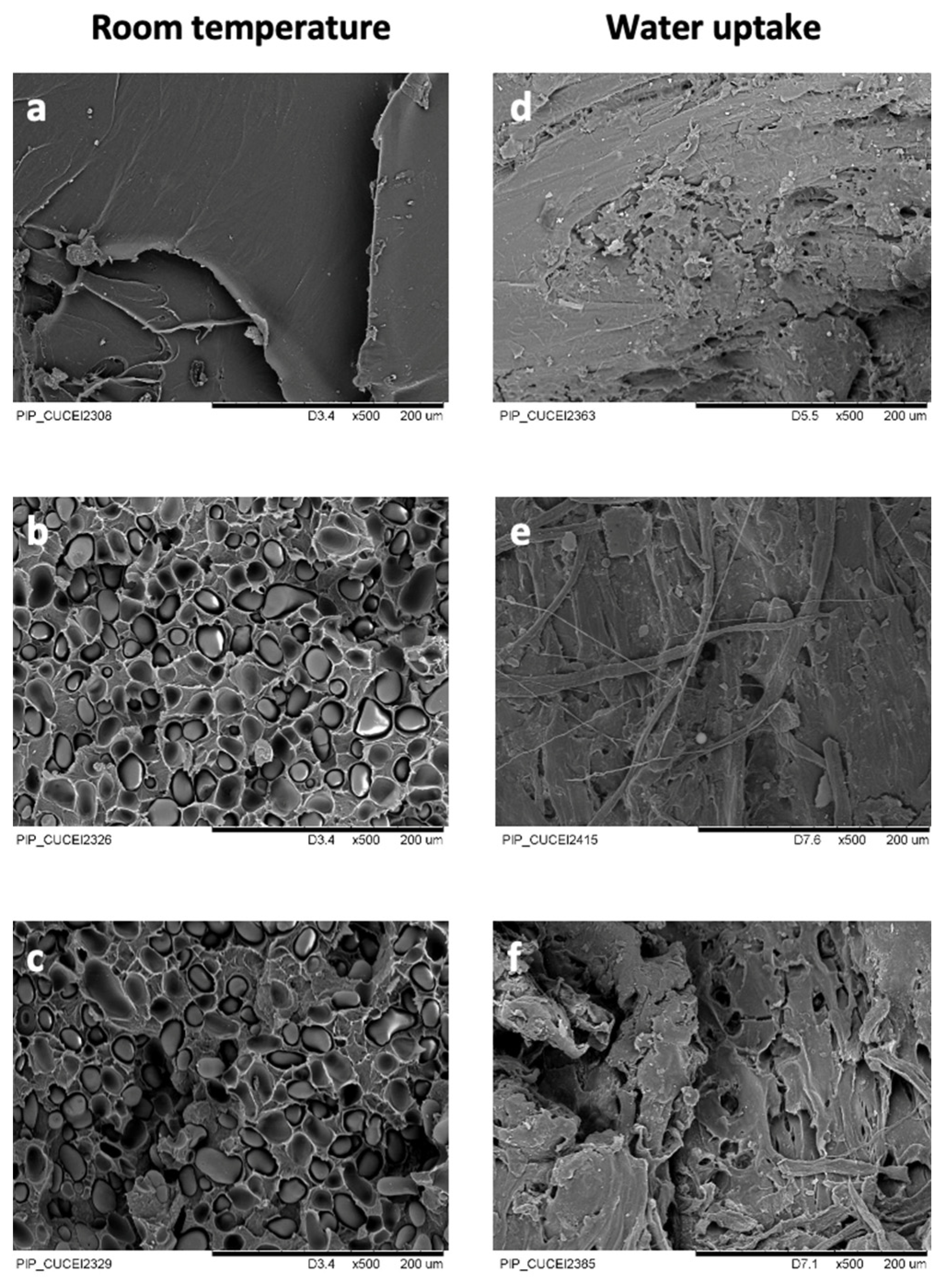
3.3. Morphology
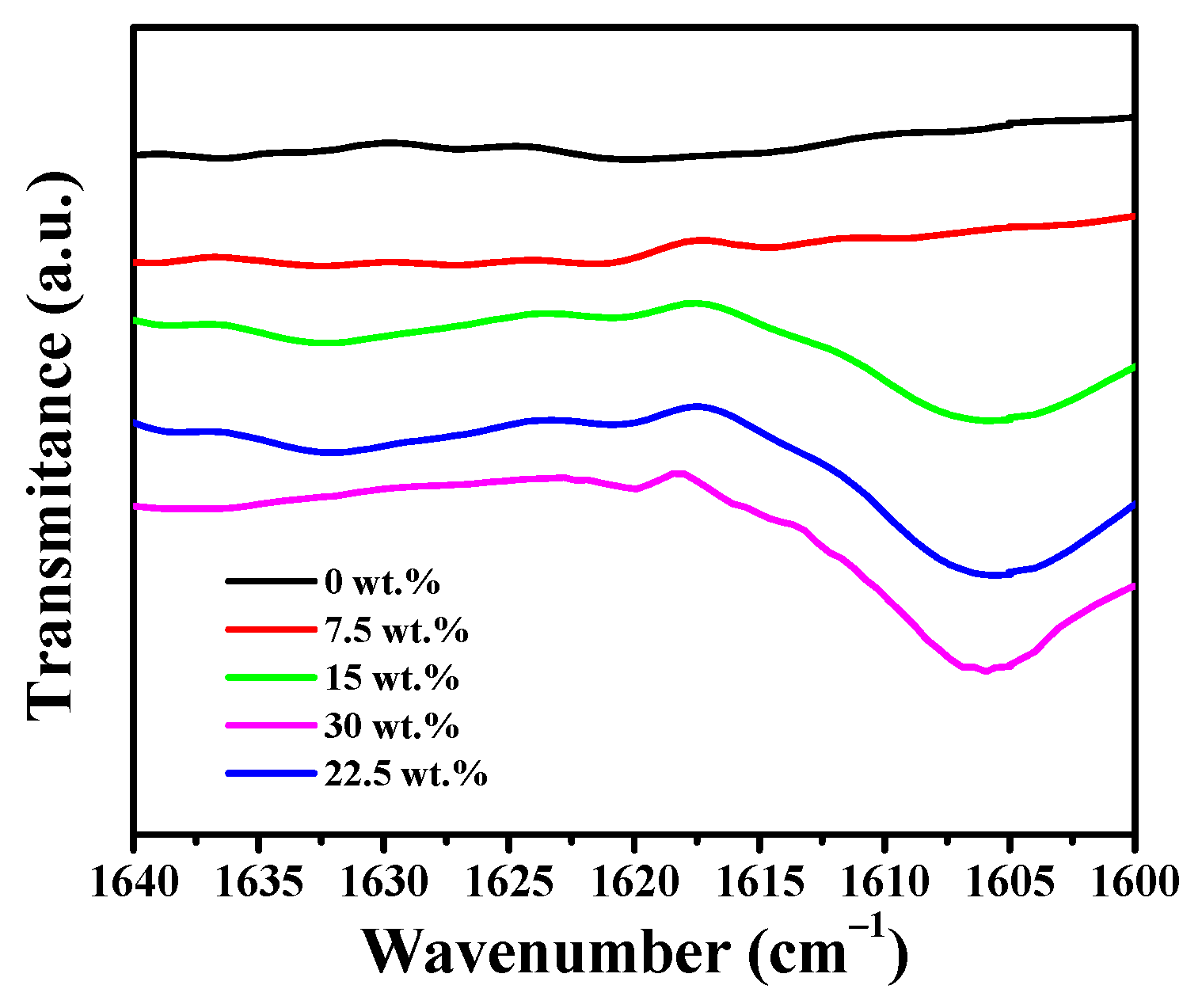
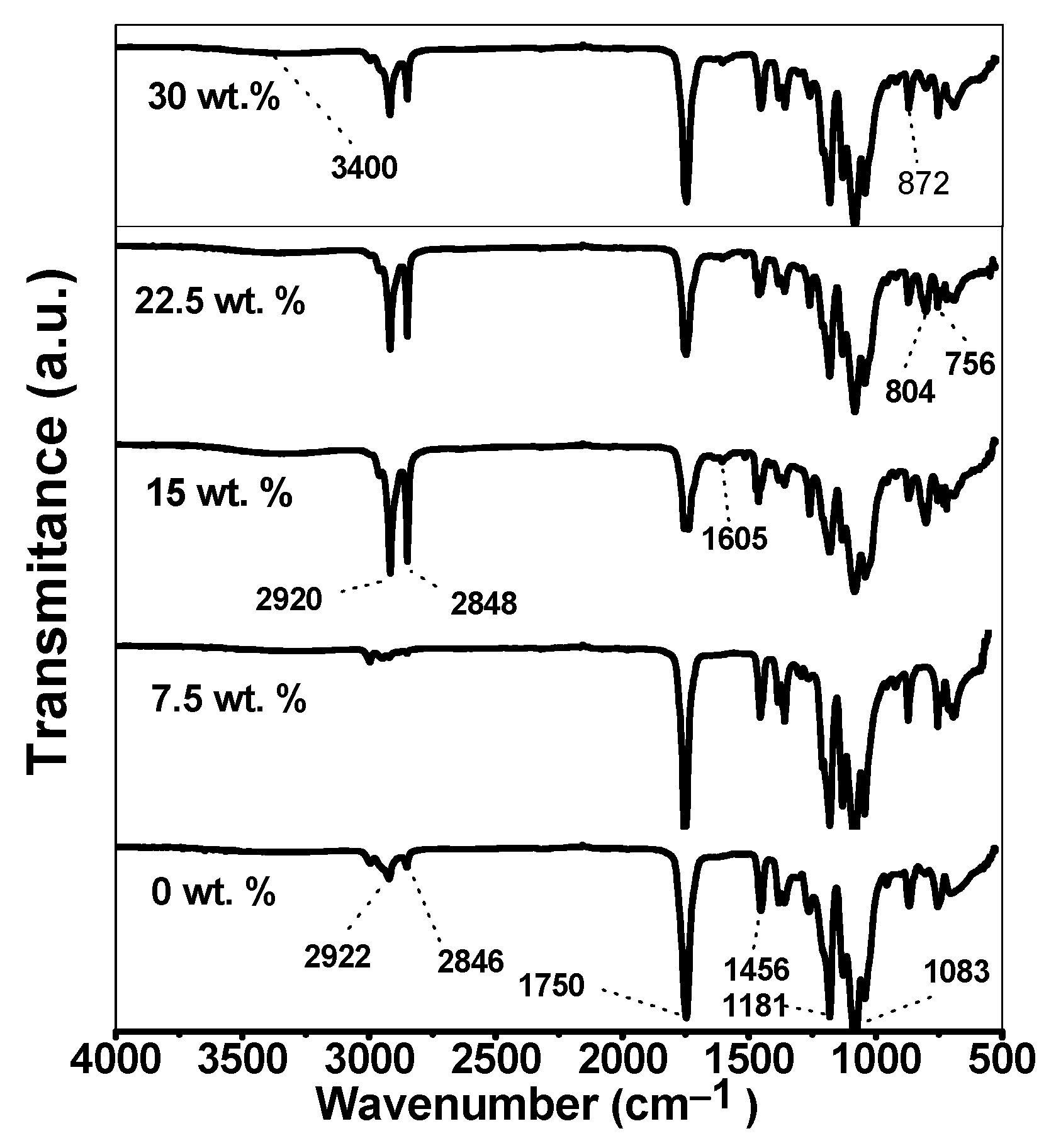
3.4. Infrared Spectra
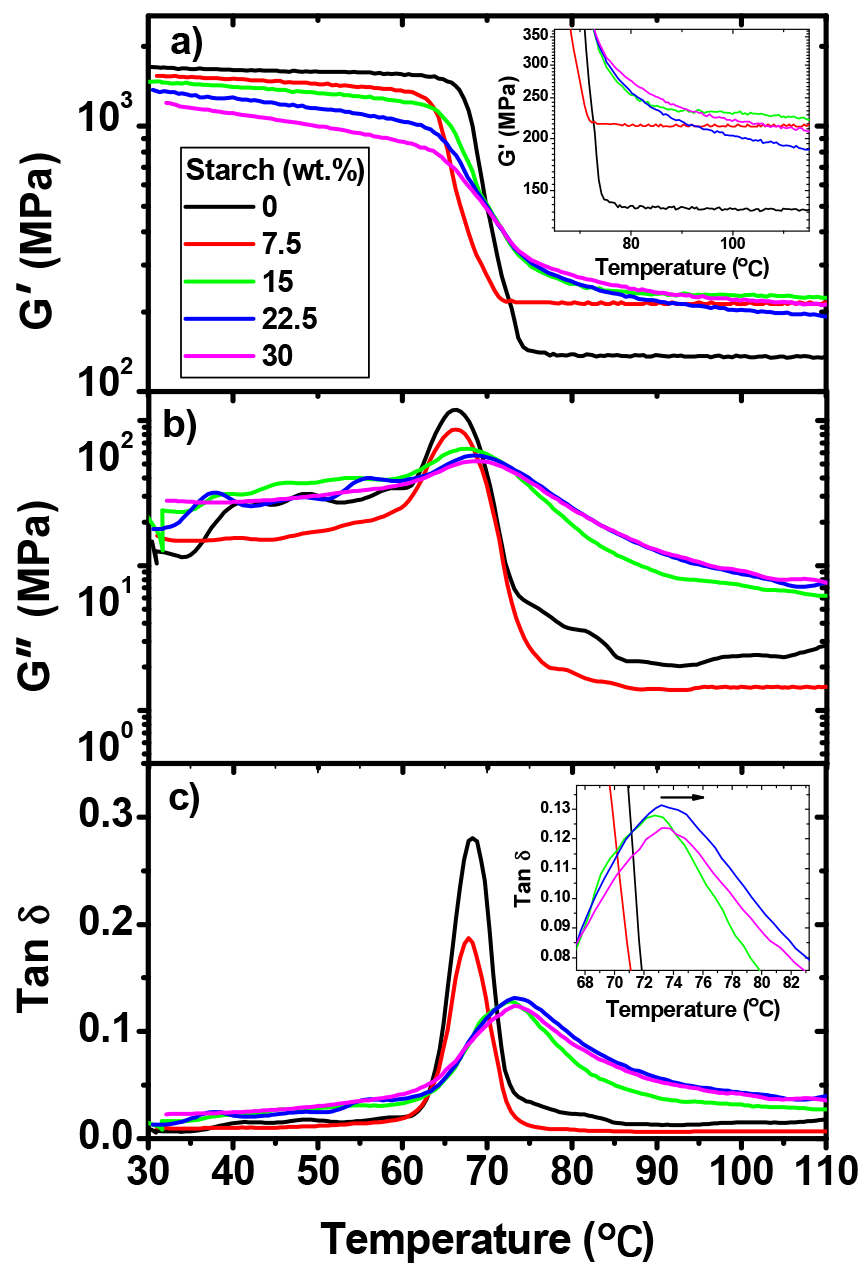
3.5. Thermal Properties
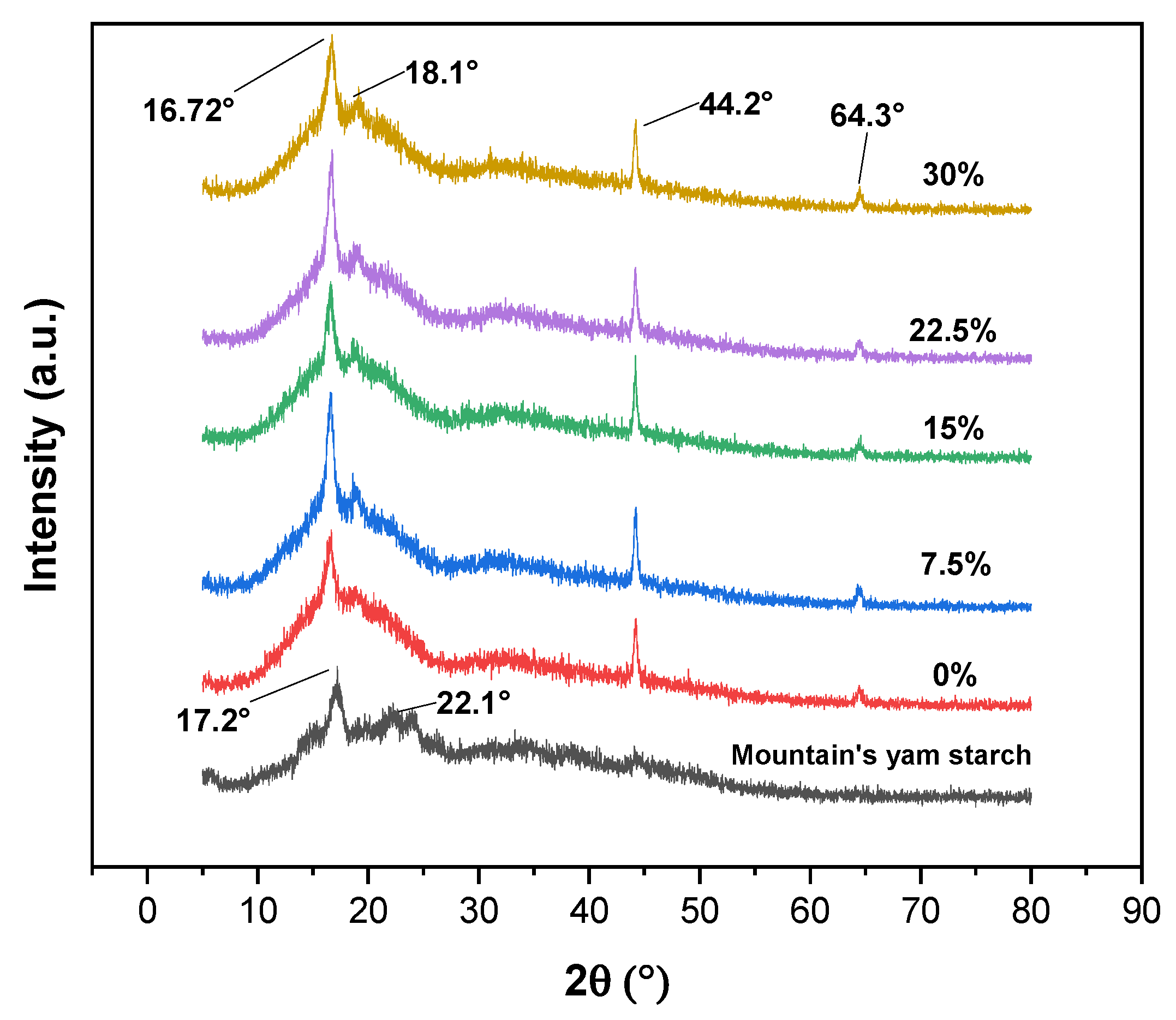
3.6. X-ray Diffraction
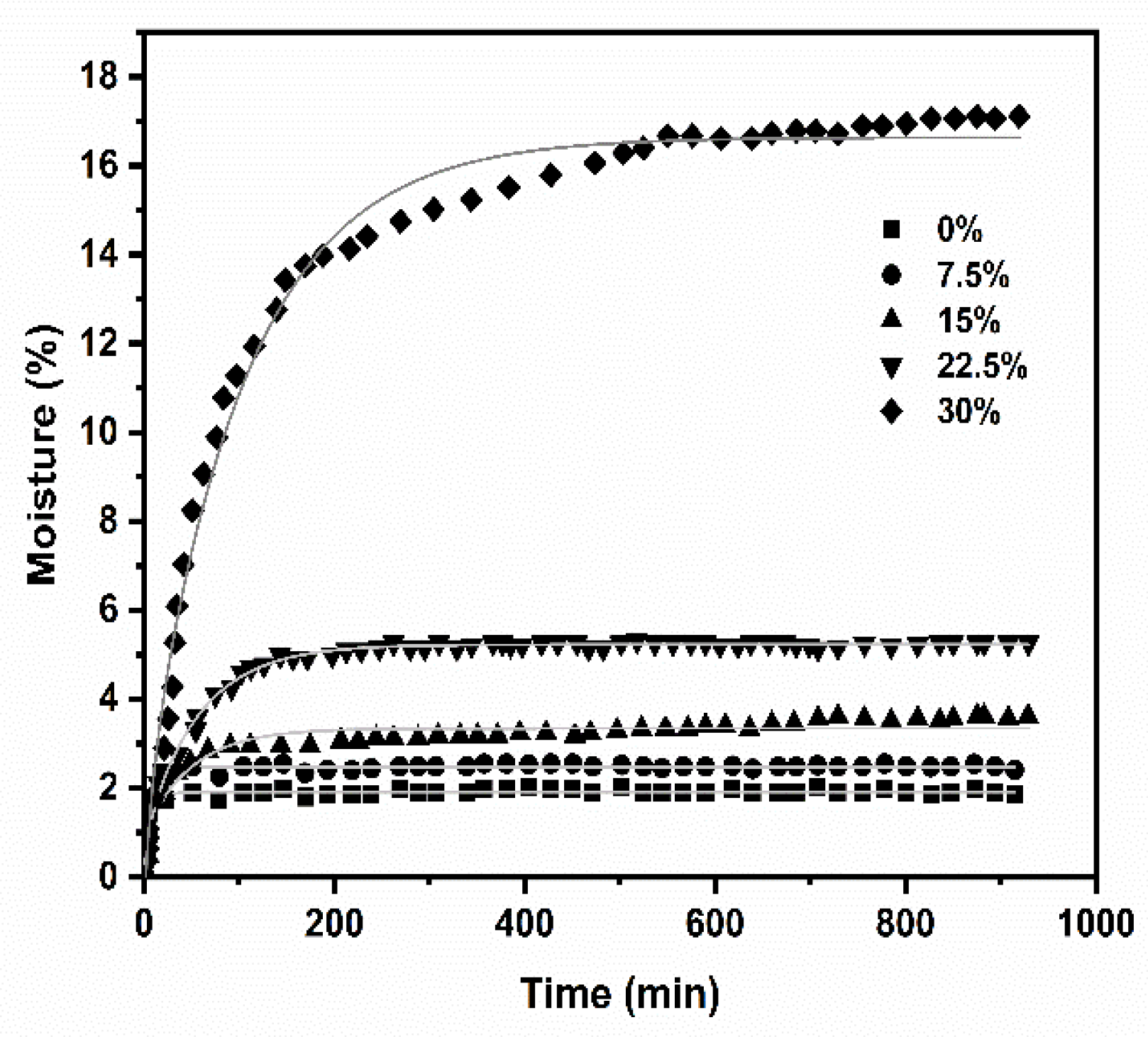
3.7. Water Absorption and Kinetics
3.8. Mechanical Properties
3.9. Dynamic Mechanical Properties
3.10. Color Parameters
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Hottle, T.A.; Bilec, M.M.; Landis, A.E. Sustainability assessments of bio-based polymers. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 1898–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luyt, A.S.; Malik, S.S. Can biodegradable plastics solve plastic solid waste accumulation? In Plastics to Energy; William Andrew: Norwich, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 403–423. [Google Scholar]
- Moshood, T.D.; Nawanir, G.; Mahmud, F.; Mohamad, F.; Ahmad, M.H.; AbdulGhani, A. Sustainability of biodegradable plastics: New problem or solution to solve the global plastic pollution? Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2022, 5, 100273–100291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farah, S.; Anderson, D.G.; Langer, R. Physical and mechanical properties of PLA, and their functions in widespread applications—A comprehensive review. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107, 367–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, J.; González-Martínez, C.; Chiralt, A. Combination of poly (lactic) acid and starch for biodegradable food packaging. Materials 2017, 10, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taib, N.-A.A.B.; Rahman, R.; Huda, D.; Kuok, K.K.; Hamdan, S.; Bin Bakri, M.K.; Bin Julaihi, M.R.M.; Khan, A. A review on poly lactic acid (PLA) as a biodegradable polymer. Polym. Bull. 2022, 80, 1179–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diyana, Z.N.; Jumaidin, R.; Selamat, M.Z.; Ghazali, I.; Julmohammad, N.; Huda, N.; Ilyas, R.A. Physical properties of thermoplastic starch derived from natural resources and its blends: A review. Polymers 2021, 13, 1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, L.; Ansari, M.N.; Pua, G.; Jawaid, M.; Islam, M.S. A review on natural fiber reinforced polymer composite and its applications. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2015, 2015, 243947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siakeng, R.; Jawaid, M.; Ariffin, H.; Sapuan, S.M.; Asim, M.; Saba, N. Natural fiber reinforced polylactic acid composites: A review. Polym. Compos. 2019, 40, 446–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moscoso-Sánchez, F.J.; Alvarado, A.; Martínez-Chávez, L.; Hernández-Montelongo, R.; Escamilla, V.V.F.; Escamilla, G.C. The effects of henequen cellulose treated with polyethylene glycol on properties of polylactic acid composites. BioResources 2019, 14, 2707–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Misra, M.; Mohanty, A.K. Challenges and new opportunities on barrier performance of biodegradable polymers for sustainable packaging. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2021, 117, 101395–101435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustățea, G.; Ungureanu, E.L.; Belc, N. Polylactic acid (PLA) for food packaging applications-a short overview. Ann. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 20, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Polman, E.M.; Gruter, G.J.M.; Parsons, J.R.; Tietema, A. Comparison of the aerobic biodegradation of biopolymers and the corresponding bioplastics: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 753, 141953–141966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadhave, R.V.; Das, A.; Mahanwar, P.A.; Gadekar, P.T. Starch Based Bio-Plastics: The Future of Sustainable Packaging. Open J. Polym. Chem. 2018, 8, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashogbon, A.O. Dual modification of various starches: Synthesis, properties and applications. Food Chem. 2021, 342, 128325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaseem, M.; Hamad, K.; Deri, F. Thermoplastic starch blends: A review of recent works. Polym. Sci. A 2012, 54, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Godwin, P.; Jin, Y.; Xiao, H. Biodegradable polymers and green-based antimicrobial packaging materials: A mini-review. Adv. Ind. Eng. Polym. 2020, 3, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surendren, A.; Mohanty, A.K.; Liu, Q.; Misra, M. A review of biodegradable thermoplastic starches, their blends and composites: Recent developments and opportunities for single-use plastic packaging alternatives. Green Chem. 2022, 22, 8606–8636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrus, M.; Wojtowicz, A.; Moscicki, L. Biodegradable polymers and their practical utility. In Thermoplastic Starch: A Green Material for Various Industries; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Montañez-Soto, J.L.; Venegas-González, J.; Bernardino-Nicanor, A.; González Cruz, L.; Yáñez Fernández, J. Chemical characterization and nutritional evaluation of mountain’s yam (Dioscorea remotiflora Kunth) Tubers. Adv. Bioresearch 2014, 5, 153–160. [Google Scholar]
- Guízar Miranda, A.; Montañez Soto, J.L.; García Ruiz, I. Partial characterization of new starch from camote (Dioscorea spp.) tuber. Rev. Iber. Tecnol. Postcosecha 2008, 9, 81–88. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, A.J.F. Starch: Major Sources, Properties and Applications as Thermoplastic Materials. In Monomers, Polymers and Composites from Renewable Resources; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 321–342. [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz-Gimena, P.F.; Oliver-Cuenca, V.; Peponi, L.; López, D. A review on reinforcements and additives in starch-based composites for food packaging. Polymers 2023, 15, 2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dularia, C.; Sinhmar, A.; Thory, R.; Pathera, A.K.; Nain, V. Development of starch nanoparticles based composite films from non-conventional source-Water chestnut (Trapa bispinosa). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 136, 1161–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Gidley, M.J.; Dhital, S. High-amylose starches to bridge the “fiber gap”: Development, structure, and nutritional functionality. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 362–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jobling, S. Improving starch for food and industrial applications. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2004, 7, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wokadala, O.C.; Emmambux, N.M.; Ray, S.S. Inducing PLA/starch compatibility through butyl-etherification of waxy and high amylose starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 112, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, P.; Zou, W.; Yu, L.; Xie, F.; Pu, H.; Liu, H.; Chen, L. Extrusion Processing and Characterization of Edible Starch Films with Different Amylose Contents. J. Food Eng. 2011, 106, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slade, L.; Levine, H. Non-equilibrium melting of native granular starch: Part I. Temperature location of the glass transition associated with gelatinization of A-type cereal starches. Carbohydr. Polym. 1988, 8, 183–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez Villadiego, K.; Arias Tapia, M.J.; Useche, J.; Escobar Macías, D. Thermoplastic starch (TPS)/polylactic acid (PLA) blending methodologies: A review. J. Polym. Environ. 2022, 30, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Hu, S.; Su, F.; Zhang, J.; Tang, G. Mechanical, thermal, and biodegradability properties of PLA/modified starch blends. Polym. Compos. 2011, 32, 2093–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Yu, J.; Chang, P.R.; Ma, X. Influence of formamide and water on the properties of thermoplastic starch/poly(lactic acid) blends. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 71, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Luo, C.; Zhou, J.; Dong, L.; Chen, Y.; Liu, G.; Qiao, S. The role of the Interface of PLA with thermoplastic starch in the nonisothermal crystallization behavior of PLA in PLA/thermoplastic starch/SiO2 Composites. Polymers 2023, 15, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huneault, M.A.; Li, H. Morphology and properties of compatibilized polylactide/thermoplastic starch blends. Polymer 2007, 48, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.F.; Sun, X. Mechanical properties of poly(lactic acid)/Starch composites compatibilized by maleic anhydride. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 1446–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Chen, C.; Gao, L.; Jiao, L.; Xu, H.; Guo, W. Physical and degradation properties of binary or ternary blends composed of poly (lactic acid), thermoplastic starch and GMA grafted POE. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2011, 96, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yussuf, A.A.; Massoumi, I.; Hassan, A. Comparison of polylactic acid/kenaf and polylactic acid/rise husk composites: The influence of the natural fibers on the mechanical, thermal and biodegradability properties. J. Polym. Environ. 2011, 18, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Hu, B.; Chang, F.; Chen, L.; Cao, X.; He, G. Improved compatibility of PLA/Starch blends with Binary functional monomers through UV-induced reactive extrusion. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 197, 116635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Finne-Wistrand, A.; Hakkarainen, M. Improved dispersion of grafted starch granules leads to lower water resistance for starch-g-PLA/PLA composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2013, 86, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Sun, X.; Seib, P. Strengthening blends of poly(lactic acid) and starch with methylenediphenyl diisocyanate. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2001, 82, 1761–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Dean, K.; Li, L. Polymer blends and composites from renewable Resources. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2006, 31, 576–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Singh, P.; Tanwar, S.; Varshney, G.; Yadav, S. Assessment of bio-based polyurethanes: Perspective on applications and bio-degradation. Macromol 2022, 2, 284–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelkmann, M.; Leichner, C.; Menzel, C.; Kreb, V.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A. Cationic starch derivatives as mucoadhesive and soluble excipients in drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 570, 118664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, A.M.; Wang, L.J.; Li, D.; Adhikari, B. Characterization of starch films containing starch nanoparticles: Part 1: Physical and mechanical properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 96, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remya, R.; Jyothi, A.N.; Sreekumar, J. Effect of chemical modification with citric acid on the physicochemical properties and resistant starch formation in different starches. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 202, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colussi, R.; El Halal, S.L.M.; Pinto, V.Z.; Bartz, J.; Gutkoski, L.C.; da Rosa Zavareze, E.; Dias, A.R.G. Acetylation of rise in an aqueous medium for use in food. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 62, 1076–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, S.; Yu, L.; Meng, L.; Liu, H.; Ali, A.; Chen, L. Poly(lactic acid)/starch composites: Effect of microstructure and morphology of starch granules on performance. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 45504–45516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battegazzore, D.; Alongi, J.; Frache, A. Poly(lactic acid)-based composites containing natural fillers: Thermal, mechanical and barrier properties. J. Polym. Environ. 2014, 22, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righetti, M.C.; Cinelli, P.; Mallegni, N.; Massa, C.A.; Aliotta, L.; Lazzeri, A. Thermal, mechanical, viscoelastic and morphological properties of poly(lactic acid) based biocomposites with potato pulp powder treated with waxes. Materials 2019, 12, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukhija, S.; Singh, S.; Riar, C.S. Effect of oxidation, cross-linking and dual modification on physicochemical, crystallinity, morphological, pasting and thermal characteristics of elephant foot yam (Amorphophallus paeoniifolius) starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 55, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoover, R.; Ratnayake, W.S. Determination of total amylose content of starch. In Current Protocols in Food Analytical Chemistry (CPFA); Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001; pp. E2.3.1–E2.3.5. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Sun, H.; Sui, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, H.; Wu, X.; Zhao, Q. Composite mesoporous silica nanoparticle/chitosan nanofibers for bone tissue engineering. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 17541–17549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molenda, M.; Stasiak, M.; Horabik, J.; Fornal, J.; Blaszczak, W.; Ornowski, A. Microstructure and mechanical parameters of five types of starch. Pol. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2006, 15, 161. [Google Scholar]
- Aguilar, J.; Moscoso, F.; Rios, O.; Ceja, I.; Sánchez, J.C.; Bautista, F.J.; Puig, E.; Fernández, V.V.A. Swelling Behavior of Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Nanogels with Narrow Size Distribution Made by Semi-Continuous Inverse Heterophase Polymerization. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A Pure Appl. Chem. 2014, 51, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Misra, M.; Mohanty, A.K. Injection-moulded biocomposites from polylactic acid (PLA) and recycled carbon fibre: Evaluation of mechanical and thermal properties. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2014, 27, 1286–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segal, L.; Creely, J.J.; Martin, A.E.; Conrad, C.M. An empirical method for estimating the degree of crystallinity of native cellulose using the X-ray diffractometer. Text. Res. J. 1959, 29, 786–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaludin, N.H.I.; Ismail, H.; Rusli, A.; Ting, S.S. Thermal behavior and water absorption kinetics of polylactic acid/chitosan biocomposites. Iran. Polym. J. 2021, 30, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueribiz, D.; Jacquemin, F.; Fréour, S. A moisture diffusion coupled model for composite materials. Eur. J. Mech. A/Solids 2013, 42, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure, F.; Perrot, A.; Pimbert, S.; Lecompte, T. Water absorption measurements on WPCs: Assessment of size and direction dependencies in order to design fast and accurate quality control tests. Polym. Test. 2019, 77, 105899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D638-01; Standart Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2001.
- ASTM D790-03; Flexural Properties of Unreinforced Plastics and Electrical Insulating Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2001.
- Pathare, P.B.; Opara, U.L.; Al-Said, F.A.J. Colour Measurement and Analysis in Fresh and Processed Foods: A Review. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2013, 6, 36–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharlina, M.E.; Yaacob, W.A.; Lazim, A.M.; Fazry, S.; Lim, S.J.; Abdullah, S.; Noordin, A.; Kumaran, M. Physicochemical properties of starch from Dioscorea pyrifolia tubers. Food Chem. 2017, 220, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercado, A.N.A.; Assia, I.S.S.; Mendoza, J.G.S. Development and productivity in yam (Dioscorea trifida and Dioscorea esculenta) under different water conditions. Acta Agronómica 2015, 64, 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Cornejo-Ramírez, Y.I.; Martínez-Cruz, O.; Del Toro-Sánchez, C.L.; Wong-Corral, F.J.; Borboa-Flores, J.; Cinco-Moroyoqui, F.J. The structural characteristics of starches and their functional properties. CYTA—J. Food 2018, 16, 1003–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Uribe, J.P.; Meza-Nieto, M.; Palma-Rodríguez, H.M.; Navarro-Cortez, R.O.; Guzmán-Ortiz, F.A.; Bello-Pérez, L.A.; Vargas-Torres, A. Physicochemical, Morphological, and Molecular Properties of starch Isolated from Dioscorea and Oxalis Tubers from Hidalgo State, Mexico. Starch-Stärke 2020, 72, 2000074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, R.; Singh, N.; Kaur, A.; Inouchi, N. Structural, morphological, functional and digestibility properties of starches from cereals, tubers and legumes: A comparative study. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 3799–3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Gao, W. Physicochemical properties of starches from two different yam (Dioscorea opposita Thunb.) residues. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2011, 54, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazrati, K.Z.; Sapuan, S.M.; Zuhri, M.Y.M.; Jumaidin, R. Extraction and characterization of potential biodegradable materials based on Dioscorea hispida tubers. Polymers 2021, 13, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouadio, O.K.; N’dri, D.Y.; Nindjin, C.; Marti, A.; Casiraghi, M.C.; Faoro, F.; Erba, D.; Bonfoh, B.; Amani, N.G. Effect of resistant starch on the cooking quality of yam (Dioscorea spp.) and cassava (Manihot esculenta) based paste products. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 64, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shujun, W.; Hongyan, L.; Wenyuan, G.; Haixia, C.; Jiugao, Y.; Peigen, X. Characterization of new starches separated from different Chinese yam (Dioscorea opposita Thunb.) cultivars. Food Chem. 2006, 99, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Hernández, C.G.; Colín-Cruz, A.; Velasco-Santos, C.; Castaño, V.M.; Rivera-Armenta, J.L.; Almendarez-Camarillo, A.; García-Casillas, P.E.; Martínez-Hernández, A.L. All green composites from fully renewable biopolymers: Chitosan-Starch reinforced with Keratin from feathers. Polymers 2014, 6, 686–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavuz, H.; Babaç, C. Preparation and Biodegradation of Starch/Polycaprolactone Films. J. Polym. Environ. 2003, 11, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, A.H.D.; Chalimah, S.; Primadona, I.; Hanantyo, M.H.G. Physical and chemical properties of corn, cassava, and potato starchs. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 160, 012003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falade, K.O.; Christopher, A.S. Physical, functional, pasting and thermal properties of flours and starches of six Nigerian rice cultivars. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 44, 478–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, I.; Al-Omari, M.H.; Leharne, S.A.; Chowdhry, B.Z.; Badwan, A. Starch gelatinization using sodium silicate: FTIR, DSC, XRPD, and NMR studies. Starch 2012, 64, 713–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanks, R.; Gunaratne, L. Gelatinization and retrogradation of thermoplastic starch characterized using modulated temperature differential scanning calorimetry. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2011, 106, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, T.; Sun, X. Effects of moisture content and heat treatment on the physical properties of starch and poly (lactic acid) blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2001, 81, 3069–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Soest, J.J.G.; Vliegenthart, J.F.G. Crystallinity in starch plastics: Consequences for material properties. Trends Biotechnol. 1997, 15, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahesh, B.; Kathyayani, D.; Channe Gowda, D.; Mrutunjaya, K. Blends of synthetic plastic-derived polypeptide with Hydroxypropylmethylcellulose and polyvinyl alcohol: Unraveling the specific interaction parameters, morphology and thermal stability of the polymers couple. J. Polym. Res. 2020, 27, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dome, K.; Podgorbunskikh, E.; Bychkov, A.; Lomovsky, O. Changes in the Crystallinity Degree of Starch Having Different Types of Crystal Structure after Mechanical Pretreatment. Polymers 2020, 12, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Zahmi, S.; Alhammadi, S.; El Hassan, A.; Ahmed, W. Carbon Fiber/PLA Recycled Composite. Polymers 2022, 14, 2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Bian, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, R.; Yang, B. Study of Crystallinity and Conformation of Poly (lactic acid) by Terahertz Spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 11104–11111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chotiprayon, P.; Chaisawad, B.; Yoksan, R. Thermoplastic cassava starch/poly (lactic acid) blend reinforced with coir fibres. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 156, 960–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menard, K.P.; Menard, N.R. Dynamic mechanical analysis in the analysis of polymers and rubbers. In Encyclopedia of Polymer Science and Technology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs, J.G.; Tabi, T. Examination of starch preprocess drying and water absorption of injection-molded starch-filled poly(lactic acid) products. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2011, 51, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safri, S.N.A.; Sultan, M.T.H.; Saba, N.; Jawaid, M. Effect of benzoyl treatment on flexural and compressive properties of sugar palm/glass fibres/epoxy hybrid composites. Polym. Test. 2018, 71, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Södergård, A.; Stolt, M. Properties of lactic acid based polymers and their correlation with composition. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2002, 27, 1123–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybytek, A.; Sienkiewicz, M.; Kucin-Lipka, J.; Janik, H. Preparation and characterization of biodegradable and compostable PLA/TPS/ESO compositions. Ind. Crops Prods. 2018, 122, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wypych, G. Handbook of polymers. In Handbook of Fillers, 4th ed.; Wypych, G., Ed.; Chem Tec Publishing: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2016; p. 303. [Google Scholar]
- Signori, F.; Pelagaggi, M.; Bronco, S.; Righetti, M.C. Amorphous/Crystal and Polymer/Filler Interphases in Biocomposites from Poly(butylene succinate). Thermochim. Acta 2012, 543, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.Y.; Feng, X.Q.; Lauke, B.; Mai, Y.W. Effects of particle size, particle/matrix interface adhesion and particle loading on mechanical properties of particulate–polymer composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2008, 39, 933–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pothana, L.A.; Oommenb, Z.; Thomas, S. Dynamic mechanical analysis of banana fiber reinforced polyester composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, L.E.; Landel, R.F. Mechanical Properties of Polymers; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Adekunte, A.; Tiwari, B.; Cullen, P.; Scannel, A.; O’Donnell, C. Effect of sonication on colour, ascorbic acid and yeast inactivation in tomato juice. Food Chem. 2010, 122, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Starch (wt.%) | a IC (%) | b Tg (°C) | * Tc (°C) | * ΔHc (J/g) | * Tm (°C) | * ΔHm (J/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw Starch Flour | 8.82 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 0.0 | 65.57 | 68.25 | 102.03 ± 1.42 | 30.19 ± 1.82 | 168.37 ± 1.27 | 46.00 ± 1.89 |
| 7.5 | 70.02 | 67.85 | 104.06 ± 1.51 | 23.67 ± 2.1 | 165.00 ± 1.43 | 40.94 ± 1.65 |
| 15.0 | 71.78 | 72.74 | 106.00 ± 1.89 | 16.17 ± 2.63 | 147.22 ± 1.61 | 37.00 ± 1.3 |
| 22.5 | 73.46 | 73.19 | 110.31 ± 2.1 | 12.21 ± 2.94 | 147.89 ± 1.18 | 36.94 ± 1.48 |
| 30.0 | 75.53 | 73.23 | 109.98 ± 1.96 | 11.63 ± 2.25 | 147.23 ± 1.42 | 26.70 ± 1.5 |
| Samples, (wt.%) | * K, (s−1) | * n | M∞, (%) | α D × 10−9, (cm2/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | −2.054 | 0.363 | 1.915 | 2.018 |
| 7.5 | −2.494 | 0.392 | 2.411 | 2.001 |
| 15 | −2.180 | 0.420 | 3.615 | 2.010 |
| 22.5 | −2.156 | 0.569 | 5.212 | 1.932 |
| 30 | −2.138 | 0.849 | 17.107 | 1.167 |
| Starch (wt.%) | Mechanical Properties | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flexural Strength (σflex, MPa) | Flexural Modulus (Eflex, MPa) | Tensile Strength (σ, MPa) | Tensile Modulus (E, MPa) | |
| 0.0 | 72.89 ± 1.19 e | 1719.32 ± 15.20 a | 79.11 ± 0.40 e | 968.35 ± 6.37 c,d,e |
| 7.5 | 68.50 ± 0.52 d | 1774.01 ± 36.35 b | 76.54 ± 2.21 d | 939.01 ± 30.20 c,d |
| 15.0 | 57.98 ± 1.32 b,c | 1792.08 ± 10.82 b,c | 68.04 ± 2.24 c | 914.73 ± 38.84 b,c |
| 22.5 | 55.32 ± 2.21 b | 1868.73 ± 44.97 d | 61.88 ± 1.78 a | 845.23 ± 14.89 a |
| 30.0 | 45.02 ± 2.47 a | 1800.96 ± 47.80 c,d | 62.73 ± 1.11 a,b | 849.45 ± 37.20 a,b |
| Treatment | Starch (wt.%) | L* | a* | b* | bΔE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.0 | 82.97 ± 0.70 a | 0.63 ± 0.03 a | 3.58 ± 0.13 a | - |
| 2 | 7.5 | 74.18 ± 0.15 b | 0.68 ± 0.10 b | 9.66 ± 0.12 b | 10.69 |
| 3 | 15.0 | 72.41 ± 0.37 b,c | 1.08 ± 0.09 c | 10.97 ± 0.07 b,c | 12.91 |
| 4 | 22.5 | 71.98 ± 0.52 c,d | 1.27 ± 0.03 d | 12.16 ± 0.32 d | 13.86 |
| 5 | 30.0 | 70.22 ± 0.24 e | 1.53 ± 0.04 e | 13.50 ± 0.42 e | 15.39 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Estrada-Girón, Y.; Fernández-Escamilla, V.V.A.; Martín-del-Campo, A.; González-Nuñez, R.; Canché-Escamilla, G.; Uribe-Calderón, J.; Tepale, N.; Aguilar, J.; Moscoso-Sánchez, F.J. Characterization of Polylactic Acid Biocomposites Filled with Native Starch Granules from Dioscorea remotiflora Tubers. Polymers 2024, 16, 899. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16070899
Estrada-Girón Y, Fernández-Escamilla VVA, Martín-del-Campo A, González-Nuñez R, Canché-Escamilla G, Uribe-Calderón J, Tepale N, Aguilar J, Moscoso-Sánchez FJ. Characterization of Polylactic Acid Biocomposites Filled with Native Starch Granules from Dioscorea remotiflora Tubers. Polymers. 2024; 16(7):899. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16070899
Chicago/Turabian StyleEstrada-Girón, Yokiushirdhilgilmara, Víctor Vladimir Amílcar Fernández-Escamilla, Angelina Martín-del-Campo, Rubén González-Nuñez, Gonzalo Canché-Escamilla, Jorge Uribe-Calderón, Nancy Tepale, Jacobo Aguilar, and Francisco Javier Moscoso-Sánchez. 2024. "Characterization of Polylactic Acid Biocomposites Filled with Native Starch Granules from Dioscorea remotiflora Tubers" Polymers 16, no. 7: 899. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16070899
APA StyleEstrada-Girón, Y., Fernández-Escamilla, V. V. A., Martín-del-Campo, A., González-Nuñez, R., Canché-Escamilla, G., Uribe-Calderón, J., Tepale, N., Aguilar, J., & Moscoso-Sánchez, F. J. (2024). Characterization of Polylactic Acid Biocomposites Filled with Native Starch Granules from Dioscorea remotiflora Tubers. Polymers, 16(7), 899. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16070899