Development and Characteristics of Protein Edible Film Derived from Pork Gelatin and Beef Broth
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Material
2.2. Preparation of Edible Protein Films
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.3.1. Film Thickness
2.3.2. Swelling in Water
2.3.3. Opacity
2.3.4. Water Content
2.3.5. Solubility in Water
2.3.6. Structure
2.3.7. Mechanical Properties
2.3.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Influence of Gelatin and Beef Broth Concentration on the Thickness of Edible Protein Films
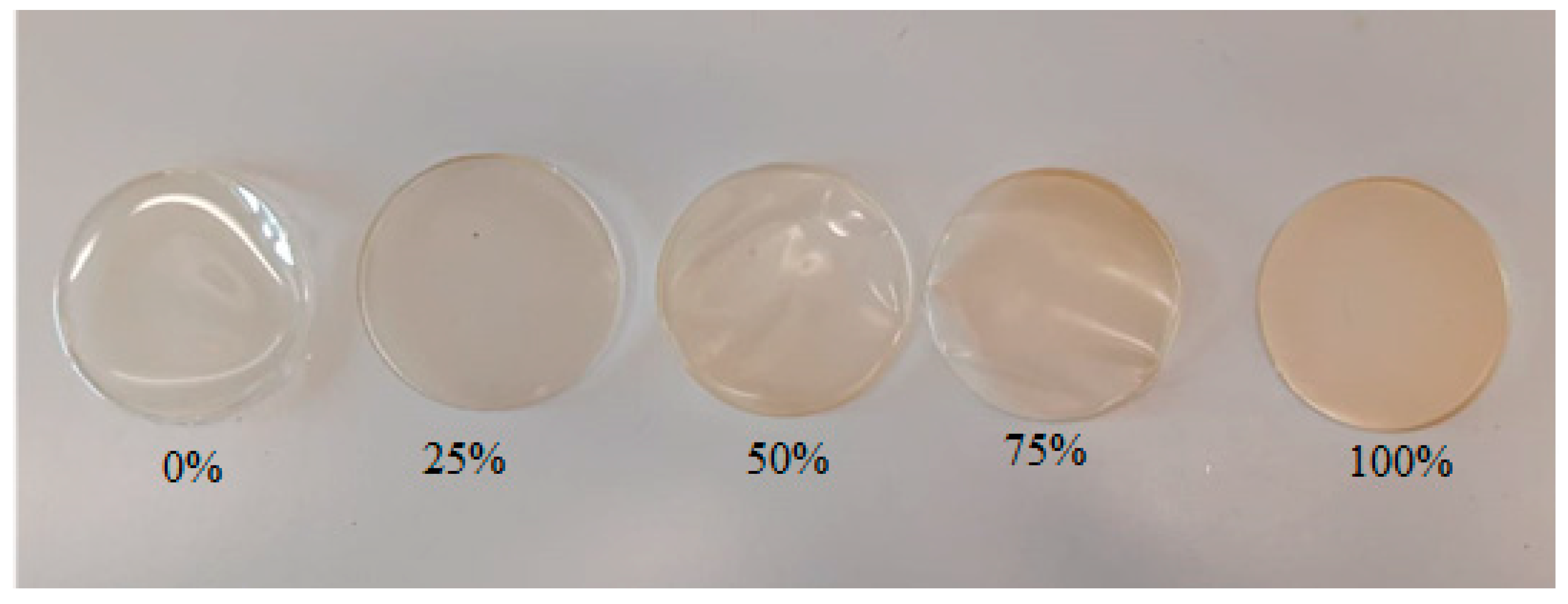
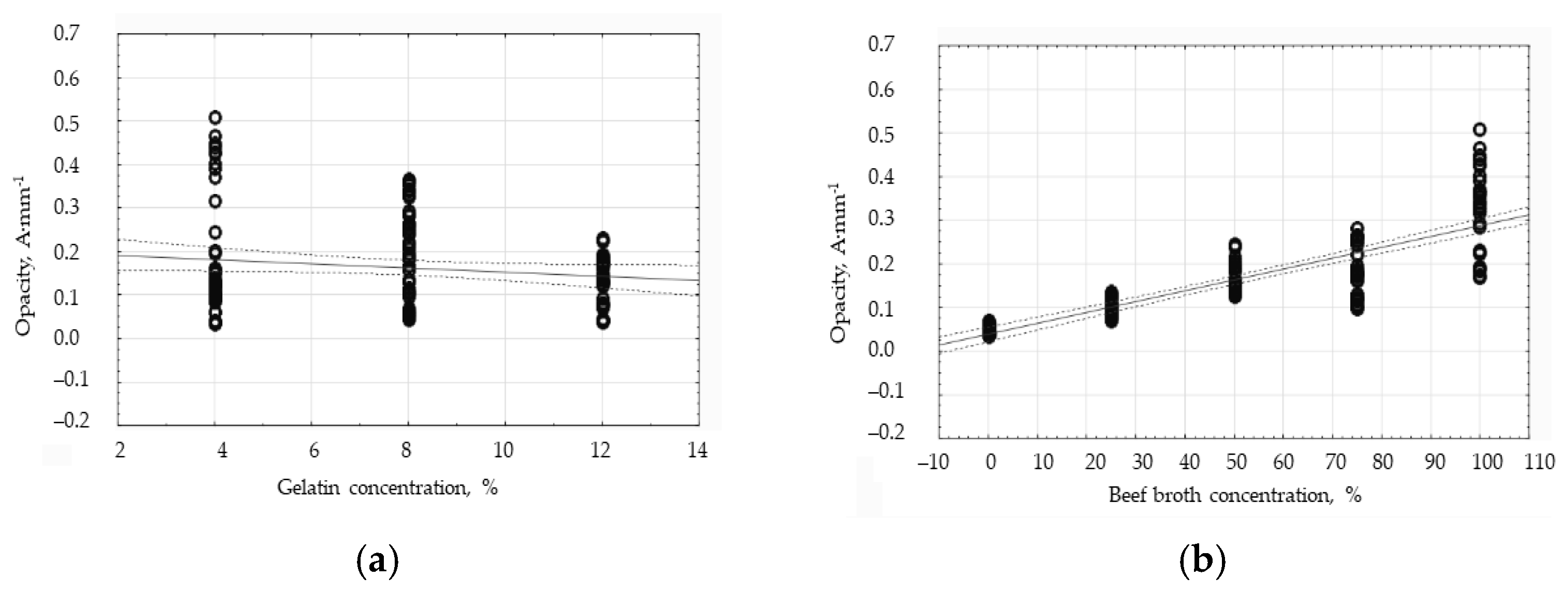
3.2. The Influence of Gelatin and Beef Broth Concentration on the Opacity of Edible Protein Films
3.3. The Influence of Gelatin and Beef Broth Concentration on the Swelling of Protein Edible Films in Water
3.4. The Influence of Gelatin and Beef Broth Concentration on the Water Content of Protein Edible Films
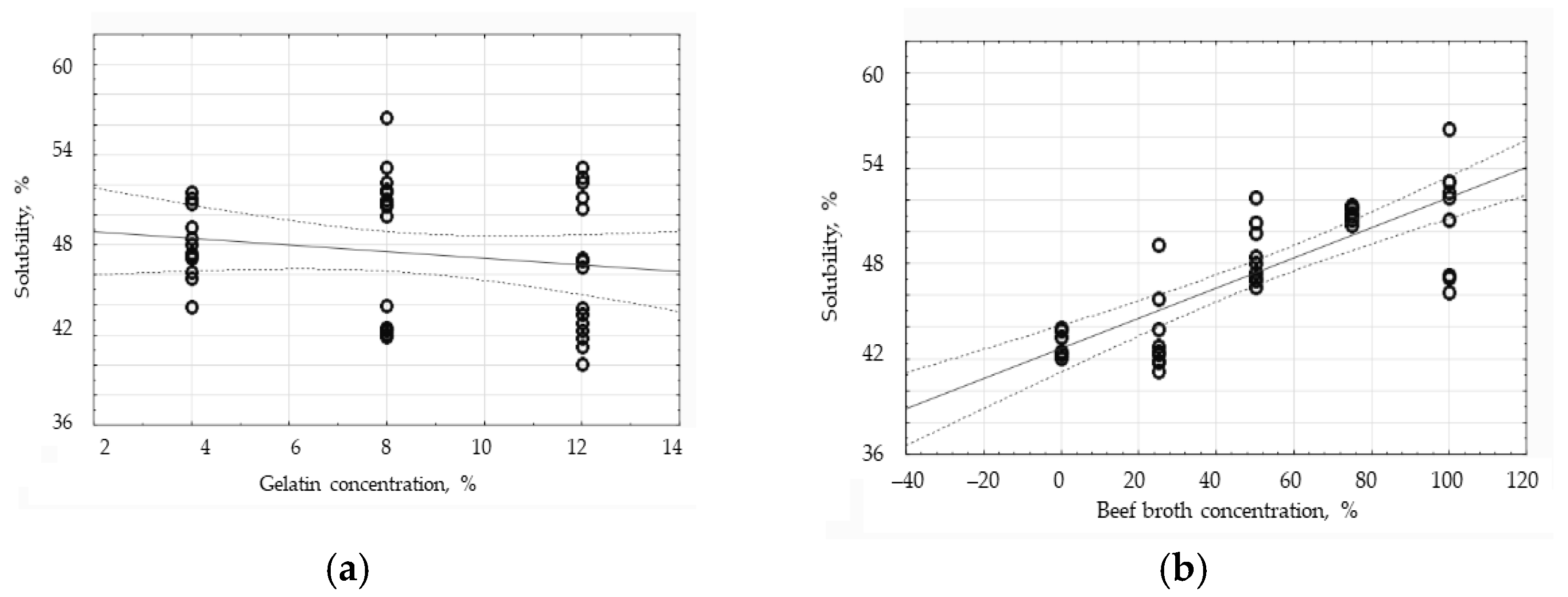
3.5. The Influence of Gelatin and Beef Broth Concentration on the Water Solubility of Protein Edible Films
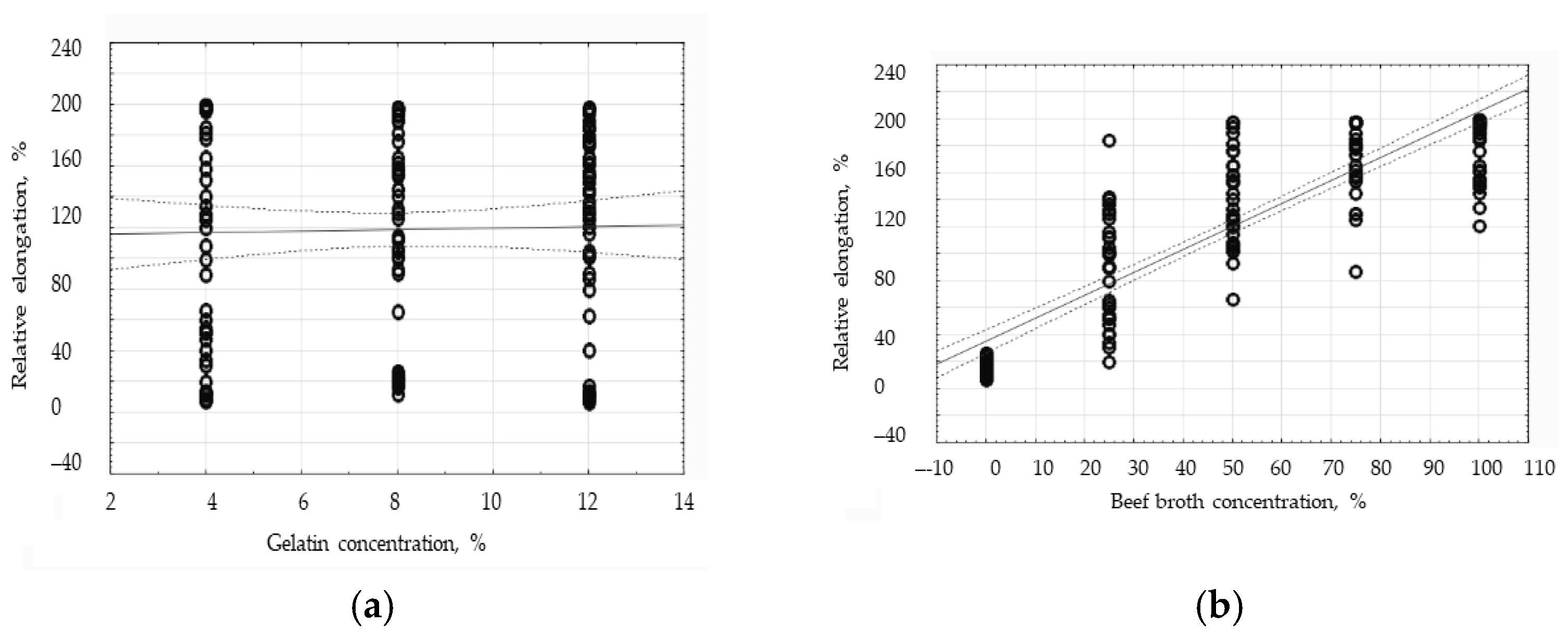
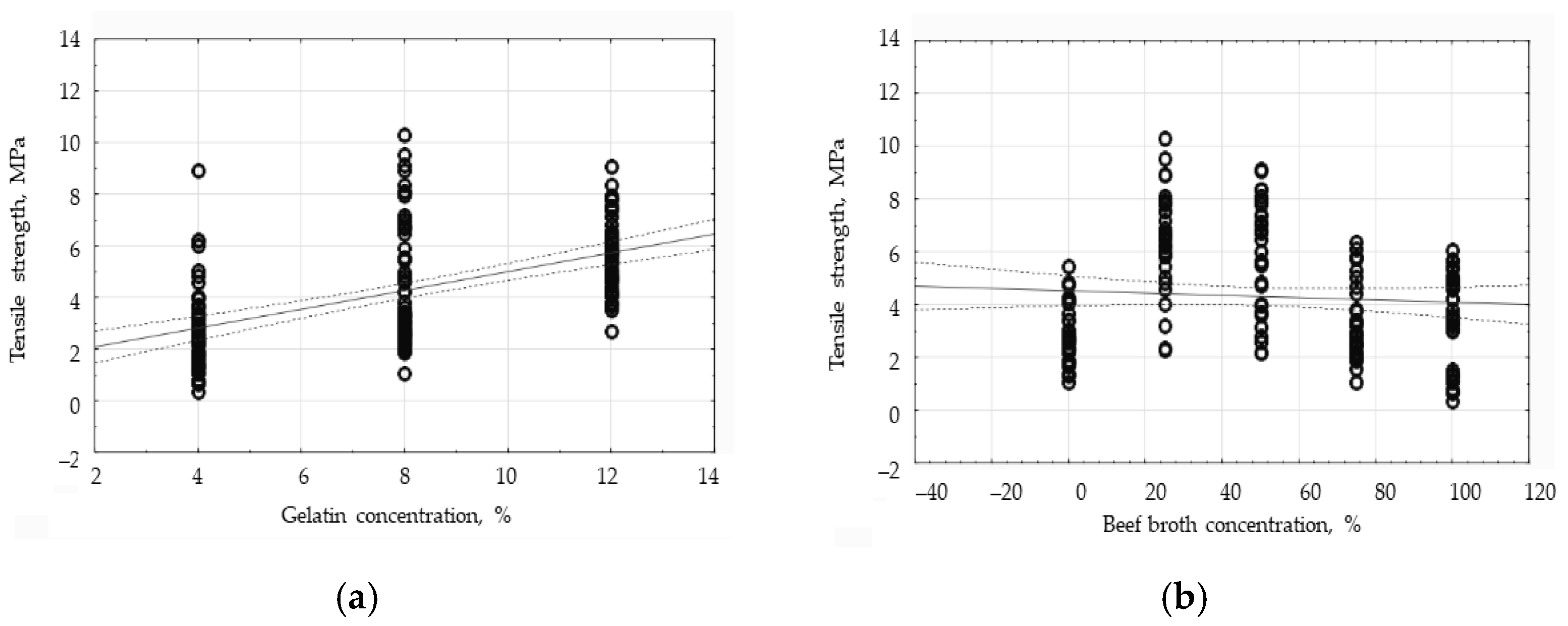
3.6. The Influence of Gelatin and Beef Broth Concentration on the Mechanical Properties of Edible Protein Films
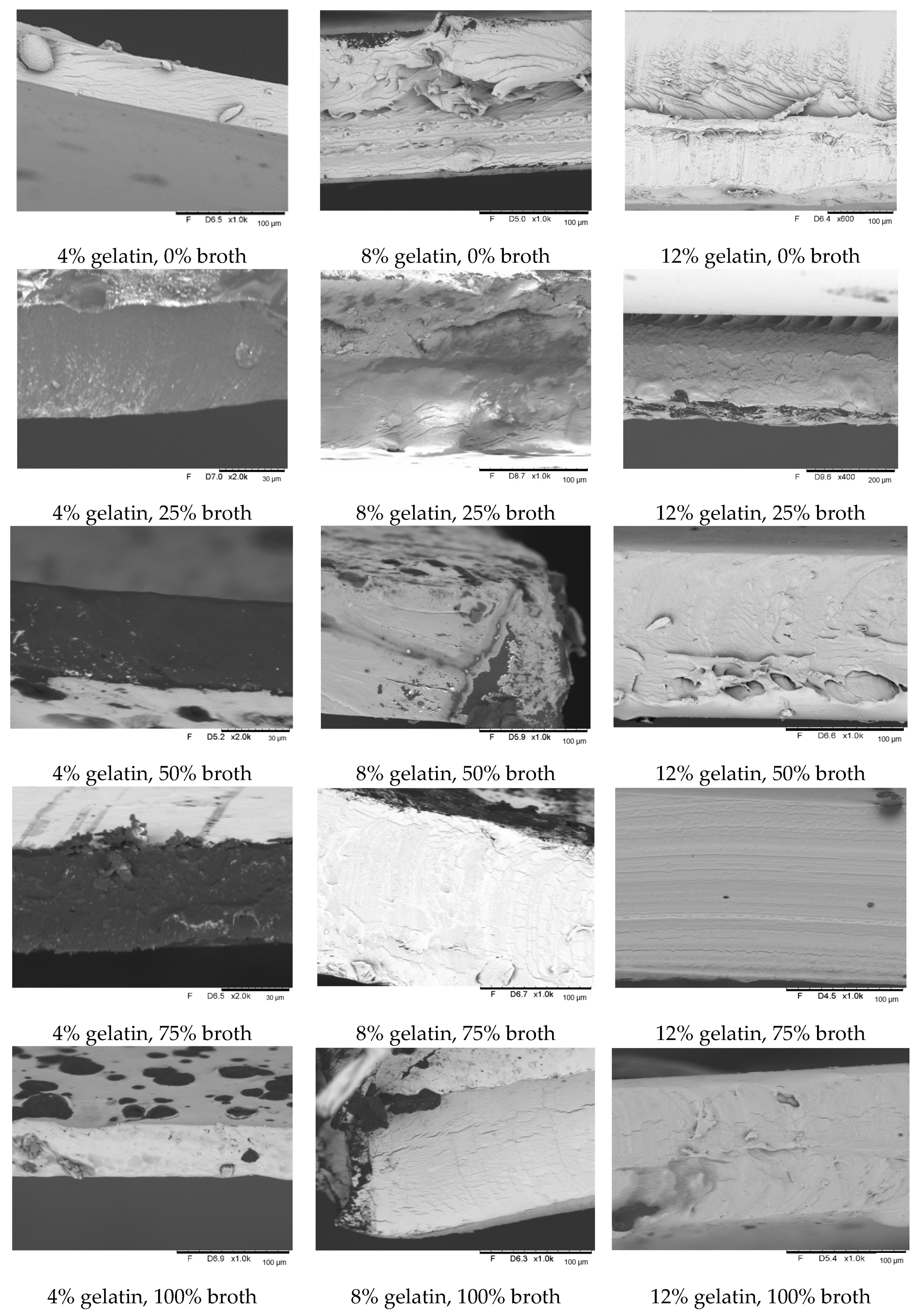
3.7. The Influence of Gelatin and Beef Broth Concentration on the Structure of Edible Protein Films
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ganiari, S.; Choulitoudi, E.; Oreopoulou, V. Edible and Active Films and Coatings as Carriers of Natural Antioxidants for Lipid Food. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 68, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avramescu, S.M.; Butean, C.; Popa, C.V.; Ortan, A.; Moraru, I.; Temocico, G. Edible and Functionalized Films/Coatings—Performances and Perspectives. Coatings 2020, 10, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, J.; Omre, P.K.; Ahmad Azad, Z.R.A. Edible Coating for Preservation of Perishable Foods: A Review. J. Ready Eat. Food 2015, 2, 81–88. [Google Scholar]
- Sucheta; Chaturvedi, K.; Sharma, N.; Yadav, S.K. Composite Edible Coatings from Commercial Pectin, Corn Flour and Beetroot Powder Minimize Post-Harvest Decay, Reduces Ripening and Improves Sensory Liking of Tomatoes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 133, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Shi, J.; Zou, X.; Huang, X.; Zhang, D.; Sun, Y.; Yang, Z.; Holmes, M.; et al. Natural Biomaterial-Based Edible and PH-Sensitive Films Combined with Electrochemical Writing for Intelligent Food Packaging. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 12836–12846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nussinovitch, A. Biopolymer Films and Composite Coatings. In Modern Biopolymer Science; Ebnesajjad, S., Ed.; Wiliam Andrew Publishing: Norwich, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 295–326. [Google Scholar]
- Basiak, E.; Galus, S.; Lenart, A. Characterisation of Composite Edible Films Based on Wheat Starch and Whey-protein Isolate. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Adhikari, R.; Guo, Q.; Adhikari, B. Preparation and characterization of glicerol plasticized (high-amylose) starch-chitosan films. J. Food Eng. 2013, 116, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Feng, Y.; Feng, T.; Wang, X.; Xia, S.; Zhang, X. Modulation effect of glicerol on plasticization and water distribution of vacuum-dried calcium alginate gel beads encapsulating peppermint oil/β-cyclodextrin complex. Food Biosci. 2021, 41, 100968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sothornvit, R.; Krochta, J.M. Plasticizers in Edible Films and Coatings. In Innovations in Food Packaging; Han, H.J., Ed.; Elsevier: Winnipeg, MB, Canada, 2005; pp. 403–433. [Google Scholar]
- Valcarcel, J.; Fraguas, J.; Hermida-Merino, C.; Hermida-Merino, D.; Piñeiro, M.M.; Vázquez, J.A. Production and Physicochemical Characterization of Gelatin and Collagen Hydrolysates from Turbot Skin Waste Generated by Aquaculture Activities. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowski, A.; Gwiazda, S.; Dąbrowski, K. Kompendium Dodatków Do Żywności; Hortimex: Konin, Poland, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Uddin, S.M.K.; Hossain, M.A.M.; Sagadevan, S.; Al Amin, M.; Johan, M.R. Halal and Kosher Gelatin: Applications as well as Detection Approaches with Challenges and Prospects. Food Biosci. 2021, 44, 101422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, O.T. Machine for Testing Jelly Strength of Glues, Gelatins, and the Like. U.S. Patent 1,540,979, 9 June 1925. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Luo, Q.; Chu, Y.; Tao, N.; Deng, S.; Wang, L.; Li, L. Application of Gelatin in Food Packaging: A Review. Polymers 2022, 14, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Channa, I.A.; Ashfaq, J.; Siddiqui, M.A.; Chandio, A.D.; Shar, M.A.; Alhazaa, A. Multi-Shaded Edible Films Based on Gelatin and Starch for the Packaging Applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 5020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.T.V.; Nguyen, N.-N.; Nguyen, Q.-D.; Nguyen, T.-P.; Lien, T.-N. Gelatin/carboxymethyl cellulose edible films: Modification of physical properties by different hydrocolloids and application in beef preservation in combination with shallot waste powder. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 10005–10014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Paulson, A.T. Effects of Lipids on Mechanical and Moisture Barrier Properties of Edible Gellan Film. Food Res. Int. 2000, 33, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galus, S.; Lenart, A. Wpływ Emulsji Tłuszczowej Na Właściwości Mechaniczne i Strukturę Powłok Serwatkowych. Acta Agrophys. 2010, 16, 275–284. [Google Scholar]
- Galus, S.; Kadzińska, J. Moisture Sensitivity, Optical, Mechanical and Structural Properties of Whey Protein-Based Edible Films Incorporated with Rapeseed Oil. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2016, 54, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.H.; Floros, J.D. Casting Antimicrobial Packaging Films and Measuring Their Physical Properties and Antimicrobial Activity. J. Plast. Film Sheet. 1997, 13, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhim, J.-W.; Gennadios, A.; Weller, C.L.; Cezeirat, C.; Hanna, M.A. Soy Protein Isolate–Dialdehyde Starch Films. Ind. Crops Prod. 1998, 8, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Xu, R.; Hu, W.; Li, C.; Abdel-Samie, M.A.; Lin, L. Effect of Soy Protein Isolate Nanoparticles Loaded with Litsea Cubeba Essential Oil on Performance of Lentinan Edible Films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242, 124686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susilawati, S.; Rostini, I.; Pratama, R.I.; Rochima, E. Characterization of Bioplastic Packaging from Tapioca Flour Modified with the Addition of Chitosan and Fish Bone Gelatin. World Sci. News 2019, 135, 85–98. [Google Scholar]
- Benbettaïeb, N.; Kurek, M.; Bornaz, S.; Debeaufort, F. Barrier, Structural and Mechanical Properties of Bovine Gelatin Chitosan Blend Films Related to Biopolymer Interactions. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 94, 2409–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, Y.A.; Bhatia, S.; Al-Harrasi, A.; Afzaal, M.; Saeed, F.; Anwer, M.K.; Khan, M.R.; Jawad, M.; Akram, N.; Faisal, Z. Mechanical Properties of Protein-Based Food Packaging Materials. Polymers 2023, 15, 1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gumus, T.; Kaynarca, G.B.; Kamer, D.D.A. Optimization of an edible film formulation by incorporating carrageenan and red wine lees into fish gelatin film matrix. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 258, 128854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Tung, M.A.; Britt, I.J.; Yada, S.; Dalgleish, D.G. Tensile and Barrier Properties of Edible Films Made from Whey Proteins. J. Food Sci. 2002, 67, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, M.; Albors, A.; Chiralt, A.; González-Martínez, C. Characterization of Chitosan–Oleic Acid Composite Films. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 536–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, W.; Zheng, H. Effect of Transglutaminase on Properties of Tilapia Scale Gelatin Films Incorporated with Soy Protein Isolate. Food Chem. 2015, 169, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, R.; Mohammadifar, M.A.; Rouhi, M.; Kariminejad, M.; Mortazavian, A.M.; Sadeghi, E.; Hasanvand, S. Physico-Mechanical and Structural Properties of Eggshell Membrane Gelatin- Chitosan Blend Edible Films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
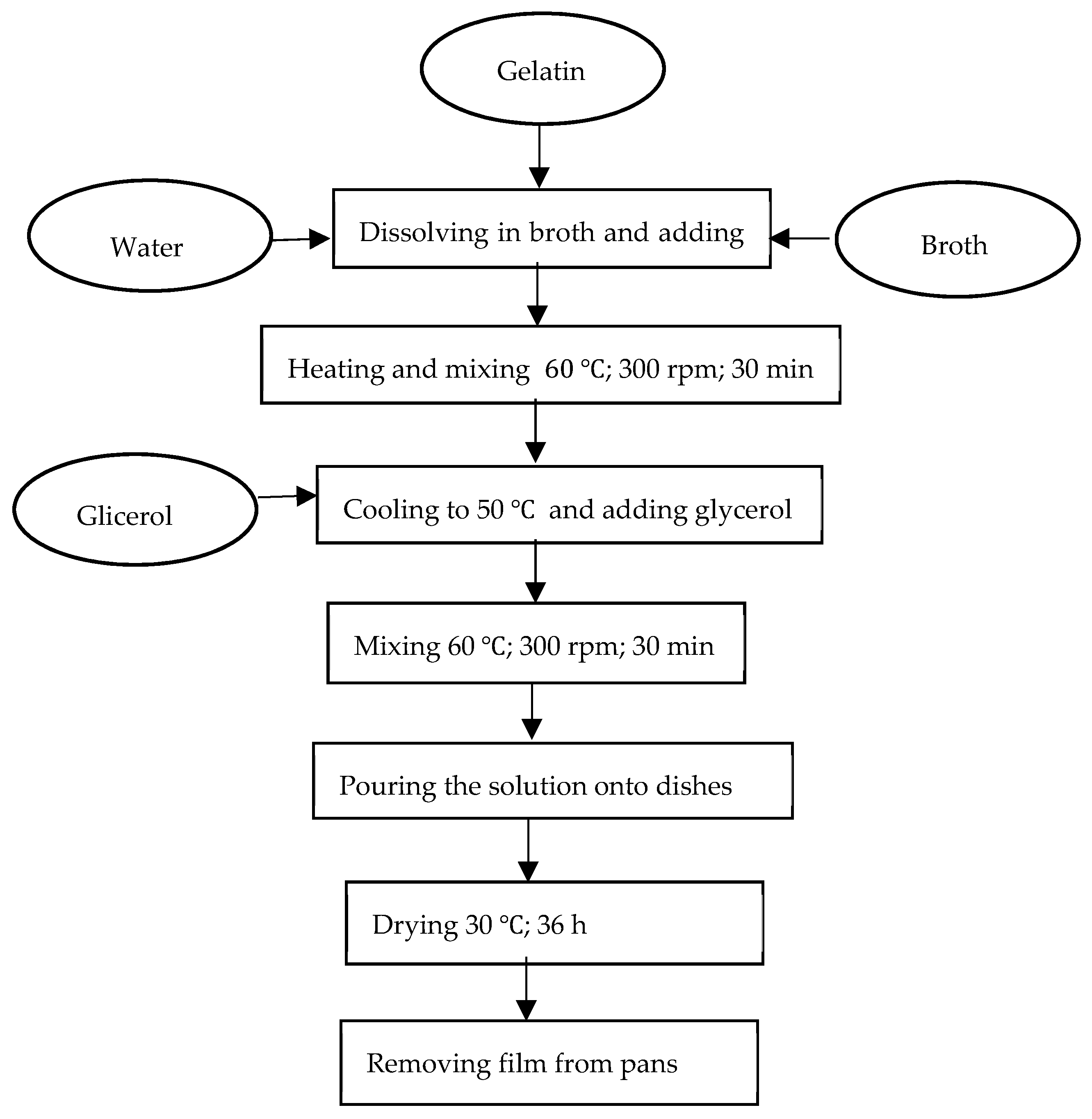



| Solution Number | Amount of Broth [% vol. Solution] | Gelatin Concentration [%] | Glycerol Concentration [%] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 4 | 2 |
| 2 | 8 | 4 | |
| 3 | 12 | 6 | |
| 4 | 25 | 4 | 2 |
| 5 | 8 | 4 | |
| 6 | 12 | 6 | |
| 7 | 50 | 4 | 2 |
| 8 | 8 | 4 | |
| 9 | 12 | 6 | |
| 10 | 75 | 4 | 2 |
| 11 | 8 | 4 | |
| 12 | 12 | 6 | |
| 13 | 100 | 4 | 2 |
| 14 | 8 | 4 | |
| 15 | 12 | 6 |
| Amount of Broth (% vol. Solution) | Gelatin Concentration [%] | Film Thickness [μm] | Weight d.s./cm2 [g d.s./cm2] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 4 | c 107.23 ± 27.0 | 0.0100 |
| 8 | ef 162.41 ± 13.8 | 0.0210 | |
| 12 | i 235.17 ± 22 | 0.0250 | |
| 25 | 4 | a 50.2 ± 9.5 | 0.0113 |
| 8 | d 141.9 ± 5.5 | 0.0212 | |
| 12 | f 167.2 ± 14.2 | 0.0258 | |
| 50 | 4 | b 78.2 ± 18.8 | 0.0121 |
| 8 | de 151.2 ± 18.4 | 0.0226 | |
| 12 | h 191.6 ± 13.9 | 0.0265 | |
| 75 | 4 | a 54.0 ± 3.1 | 0.0129 |
| 8 | fg 174 ± 17.9 | 0.0234 | |
| 12 | f 168 ± 20.3 | 0.0271 | |
| 100 | 4 | bc 92.5 ± 15.7 | 0.0137 |
| 8 | de 152.1 ± 4.5 | 0.0242 | |
| 12 | gh 188.6 ± 12.7 | 0.0277 |
| Opacity ± Standard Deviation [A/mm] | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Broth Concentration [%] | Gelatin Concentration [4%] | Gelatin Concentration [8%] | Gelatin Concentration [12%] |
| 0 | a 0.40 ± 0.01 | a 0.353 ± 0.01 | a 0.18 ± 0.00 |
| 25 | b 1.87 ± 0.01 | bc 0.79 ± 0.01 | b 0.56 ± 0.02 |
| 50 | e 2.13 ± 0.04 | g 1.31 ± 0.03 | d 0.71 ± 0.01 |
| 75 | c 2.14 ± 0.01 | h 1.45 ± 0.02 | ef 1.05 ± 0.01 |
| 100 | j 4.54 ± 0.05 | i 2.21 ± 0.03 | fg 1.04 ± 0.02 |
| Swelling in Water ± Standard Deviation [%] | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Broth Concentration [%] | Gelatin Concentration [4%] | Gelatin Concentration [8%] | Gelatin Concentration [12%] |
| 0 | a 124.9 ± 80.34 | abc 223.01 ± 113.26 | d 482.29 ± 287.51 |
| 25 | cd 372.47 ± 30.24 | abc 276.93 ± 20.09 | abc 239.53 ± 113.24 |
| 50 | bcd 326.69 ± 57.94 | abc 244.02 ± 66.32 | ab 162.00 ± 15.34 |
| 75 | cd 362.02 ± 94.02 | ab 188.58 ± 35.31 | ab 195.88 ± 5.47 |
| 100 | bc 309.55 ± 94.60 | abc 209.66 ± 56,62 | ab 174 ± 13.13 |
| Degrees of Freedom | SS | MS | F | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Broth concentration [%] | 4 | 27.699 | 6925 | 1.3578 | 0.272763 |
| Gelatin concentration [%] | 2 | 55.749 | 27.875 | 5.4657 | 0.009676 |
| Broth concentration [%] and gelatin concentration [%] | 8 | 139.997 | 17.500 | 3.4313 | 0.006755 |
| Degrees of Freedom | SS | MS | F | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Broth concentration [%] | 3 | 21.896 | 7299 | 1.9648 | 0.146201 |
| Gelatin concentration [%] | 2 | 146.230 | 73.115 | 19.6826 | 0.000009 |
| Broth concentration [%] and gelatin concentration [%] | 6 | 10.016 | 1669 | 0.4494 | 0.838217 |
| Water Content ± Standard Deviation [%] | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Broth Concentration [%] | Gelatin Concentration [4%] | Gelatin Concentration [8%] | Gelatin Concentration [12%] |
| 0 | f 36.69 ± 1.53 | bcd 15.25 ± 0.83 | a 10.06 ± 0.10 |
| 25 | e 20.72 ± 1.15 | e 21.78 ± 0.99 | d 16.46 ± 0.25 |
| 50 | d 17.52 ± 1.69 | e 21.3 ± 2.66 | bcd 15.56 ± 2.71 |
| 75 | cd 15.79 ± 2.69 | e 21.54 ± 3.04 | d 16.84 ± 1.93 |
| 100 | ab 12.68 ± 0.77 | bcd 15.27 ± 2.01 | bc 13.26 ± 0.41 |
| Solubility in Water ± Standard Deviation [%] | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Broth Concentration [%] | Gelatin Concentration [4%] | Gelatin Concentration [8%] | Gelatin Concentration [12%] |
| 0 | 100 | a 42.84 ± 0.99 | ab 43.14 ± 0.76 |
| 25 | bc 46.32 ± 2.69 | a 42.26 ± 0.30 | a 41.94 ± 0.82 |
| 50 | cd 47.96 ± 0.51 | de 50.92 ± 1.19 | c 46.88 ± 0.31 |
| 75 | de 51.15 ± 0.34 | e 51.42 ± 0.36 | c 47.25 ± 6.22 |
| 100 | c 46.88 ± 0.60 | e 53.47 ± 2.89 | e 52.64 ± 0.52 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ciurzyńska, A.; Janowicz, M.; Karwacka, M.; Nowacka, M.; Galus, S. Development and Characteristics of Protein Edible Film Derived from Pork Gelatin and Beef Broth. Polymers 2024, 16, 1009. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16071009
Ciurzyńska A, Janowicz M, Karwacka M, Nowacka M, Galus S. Development and Characteristics of Protein Edible Film Derived from Pork Gelatin and Beef Broth. Polymers. 2024; 16(7):1009. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16071009
Chicago/Turabian StyleCiurzyńska, Agnieszka, Monika Janowicz, Magdalena Karwacka, Małgorzata Nowacka, and Sabina Galus. 2024. "Development and Characteristics of Protein Edible Film Derived from Pork Gelatin and Beef Broth" Polymers 16, no. 7: 1009. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16071009
APA StyleCiurzyńska, A., Janowicz, M., Karwacka, M., Nowacka, M., & Galus, S. (2024). Development and Characteristics of Protein Edible Film Derived from Pork Gelatin and Beef Broth. Polymers, 16(7), 1009. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16071009










