Exploration of Voids, Acoustic Properties and Vibration Damping Ratio of Cyperus Pangorei Rottb Fiber and Ramie Fiber Reinforced with Epoxy Resin Hybrid Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
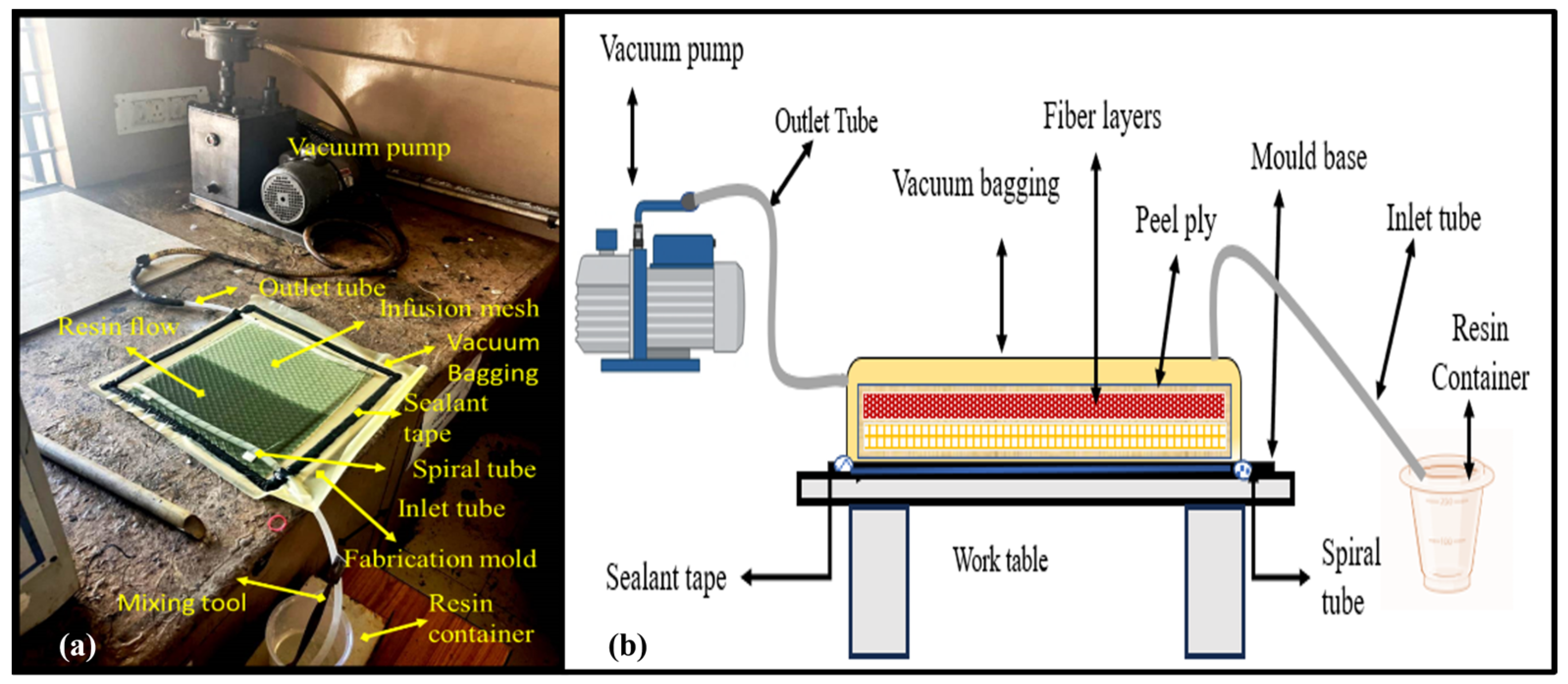
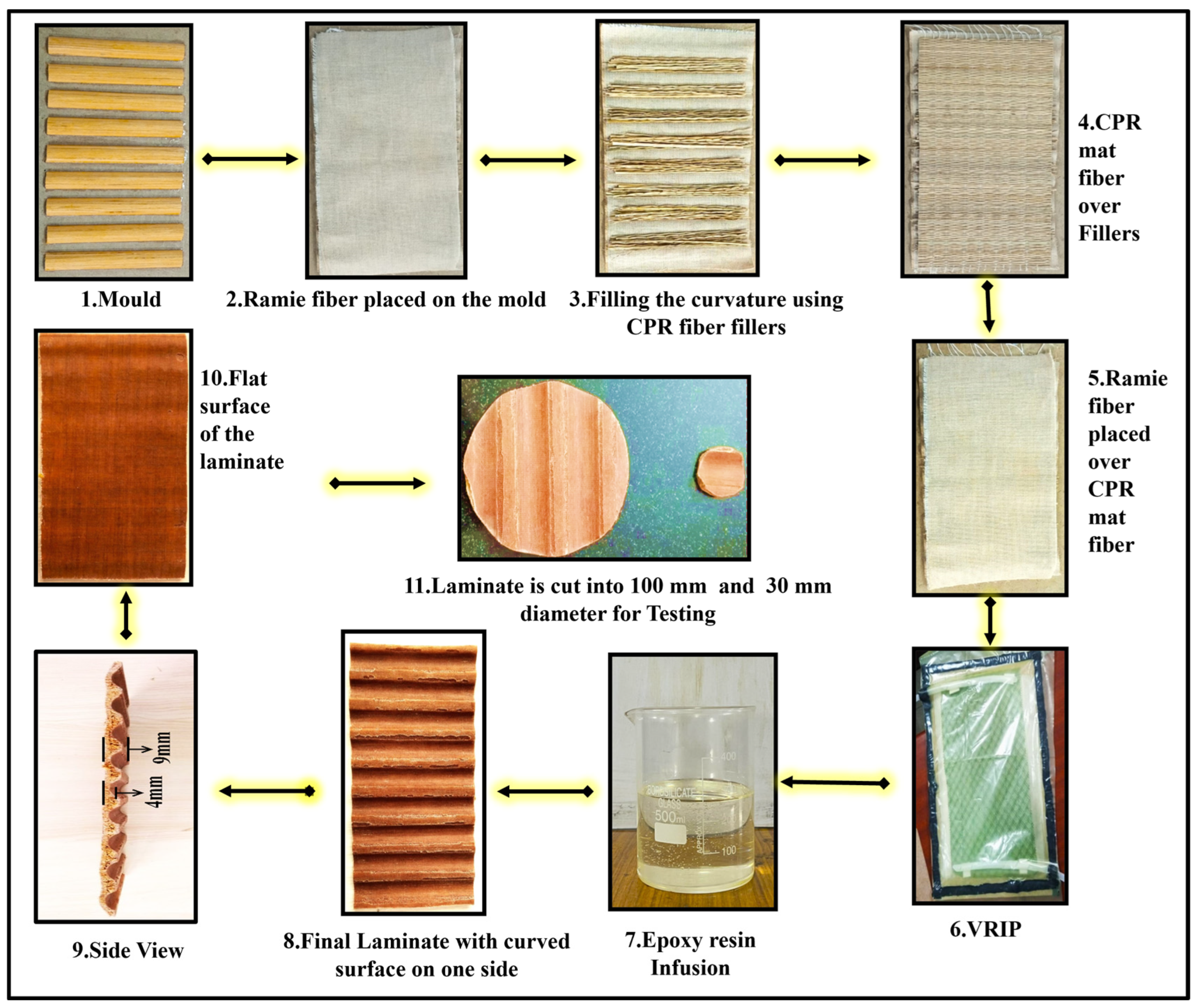
2.2. Fabrication of Panels
2.3. Experimental Studies
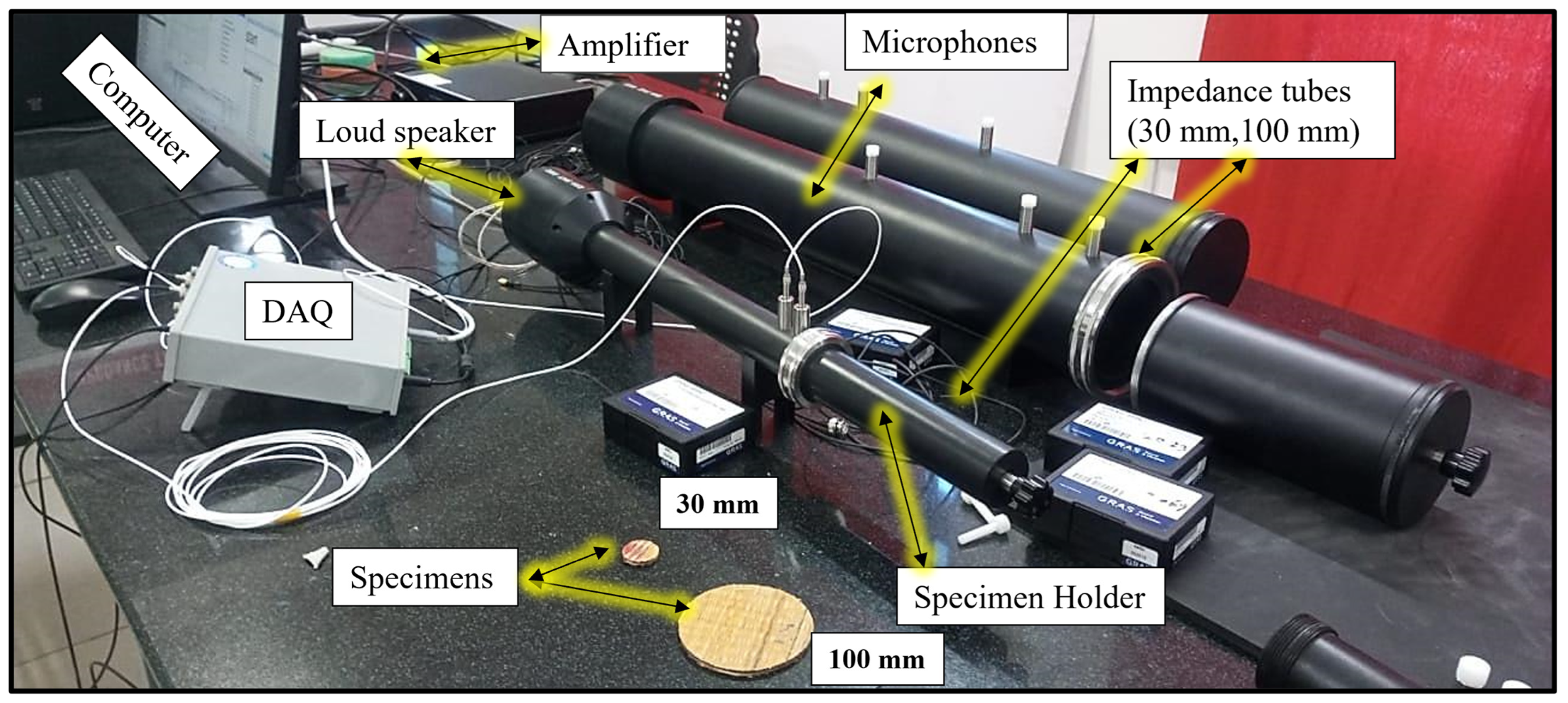
2.3.1. Sound Absorption Coefficient (SAC)
2.3.2. Modal Analysis (Free Vibration Test)
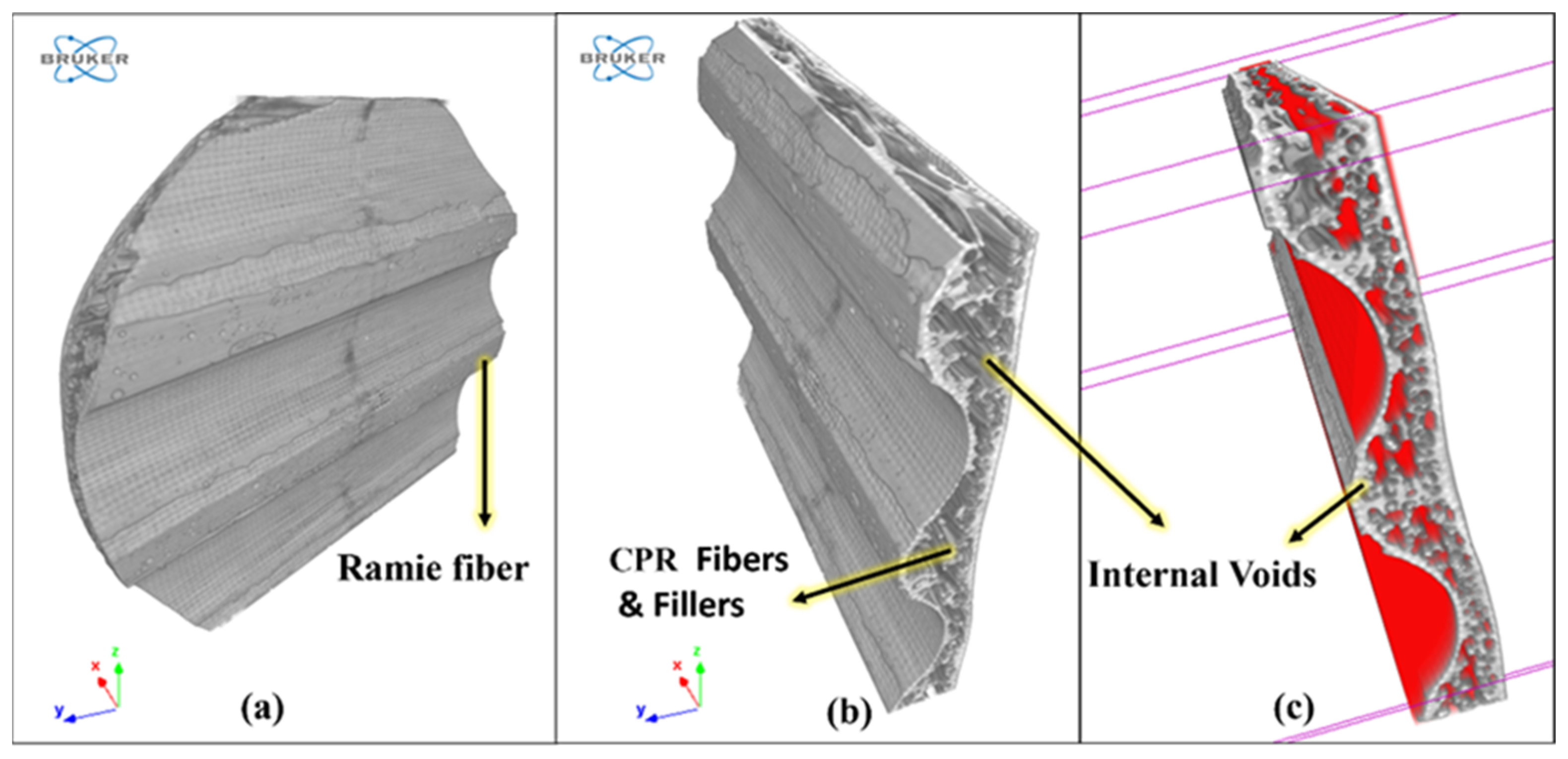
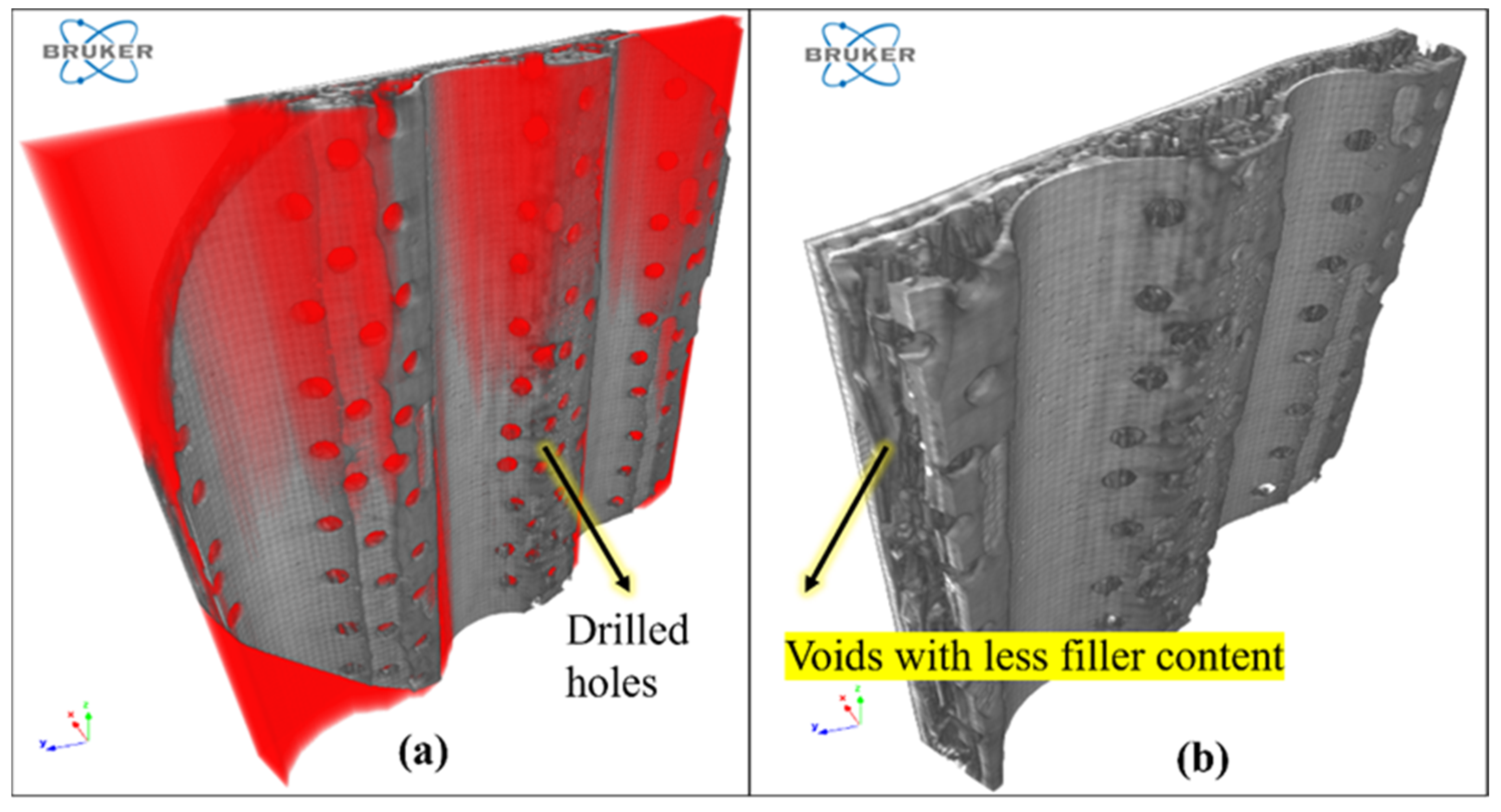
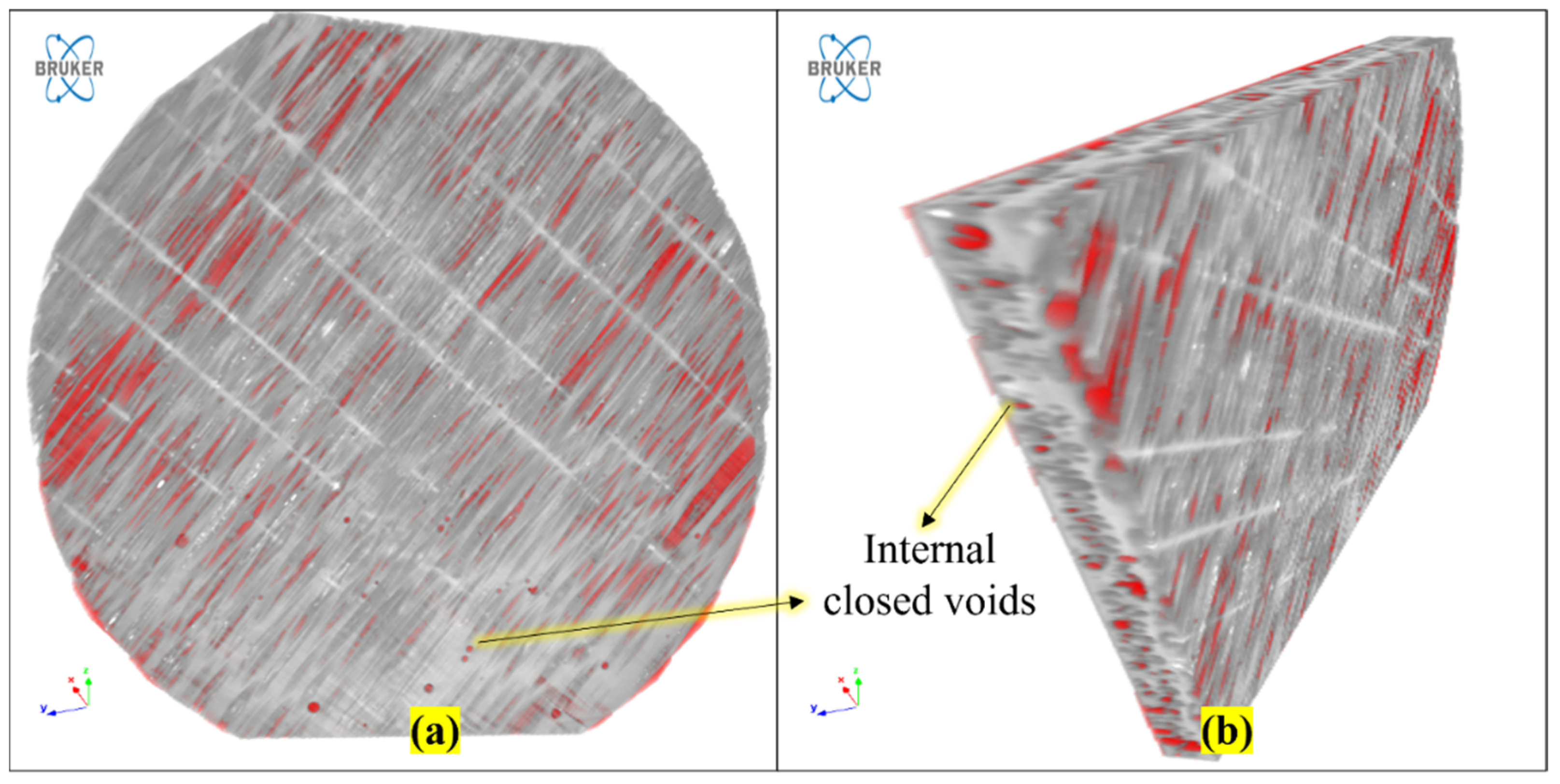
2.3.3. Void Measurements Using CT Scan
3. Results and Discussion
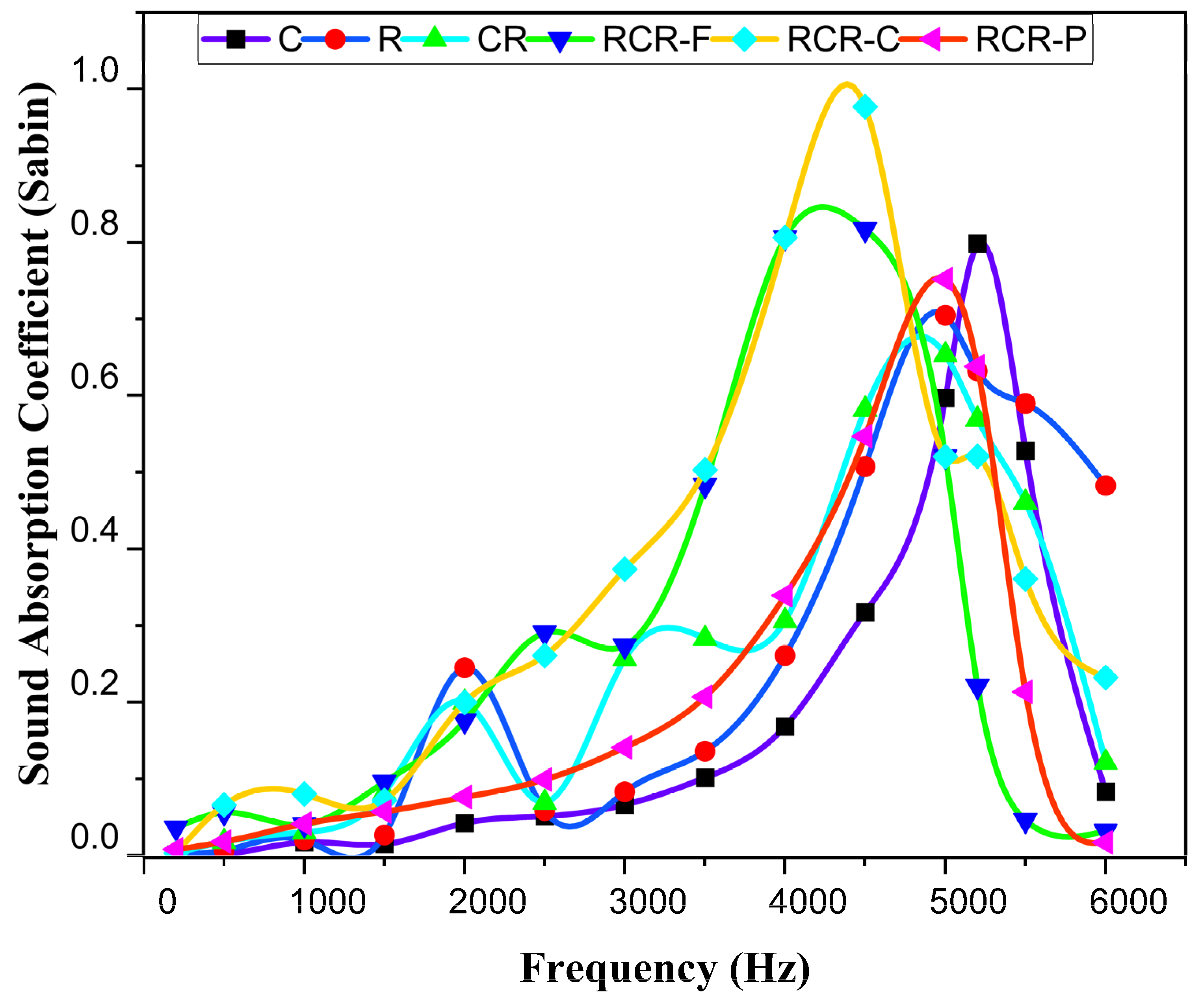
3.1. Sound Absorption Coefficient (SAC)
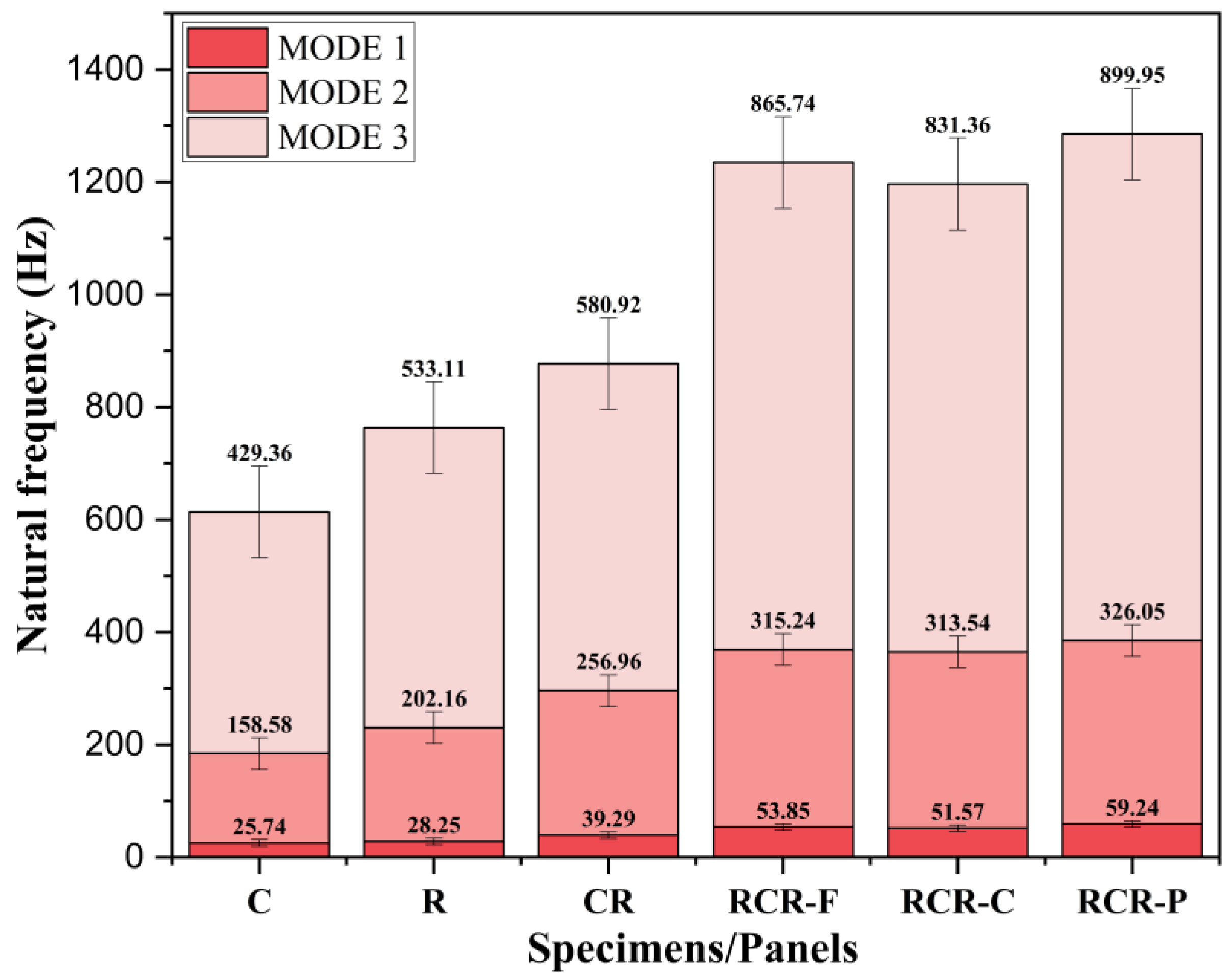
3.2. Analysis of Natural Frequency
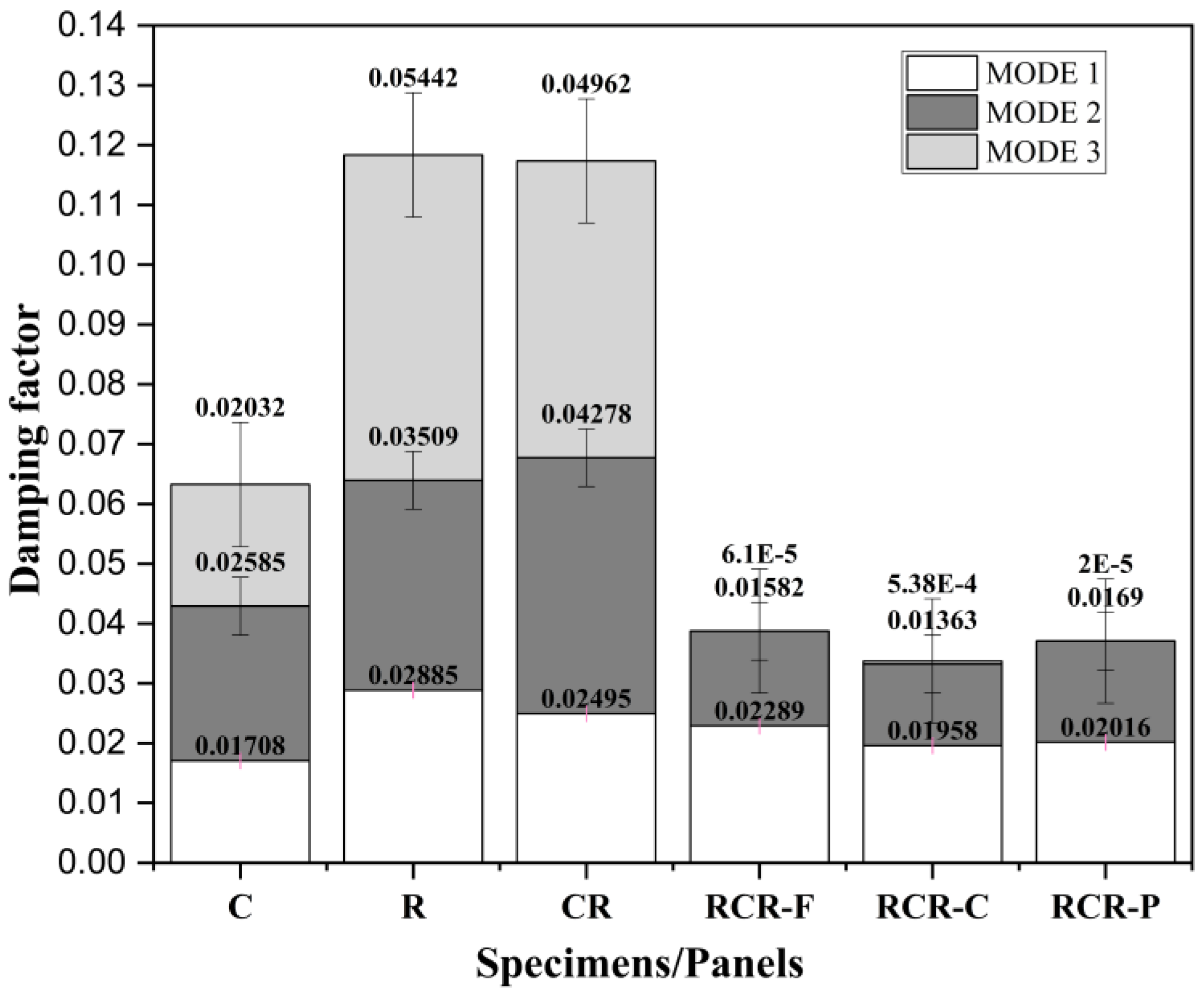
3.3. Analysis of Damping Factor
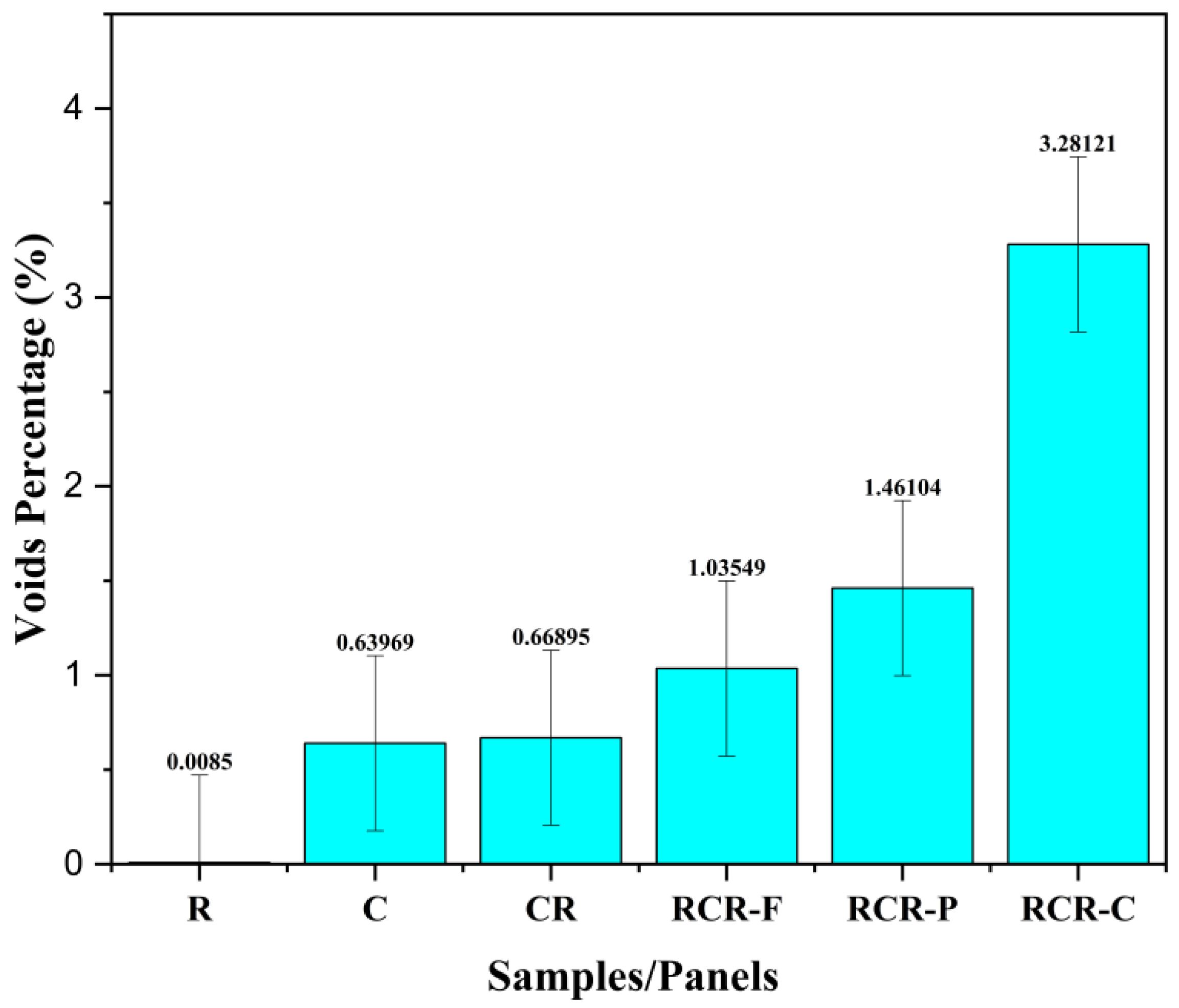
3.4. Voids Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Valipour, F.; Taban, E.; Samaei, S.E.; Pourtaghi, G.; Konjin, Z.N. Improvement of natural fiber’s properties and evaluation of its applicability as eco-friendly materials in noise pollution control. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2022, 20, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhunia, A.K.; Mondal, D.; Parui, S.M.; Mondal, A.K. Characterization of a new natural novel lignocellulose fiber resource from the stem of Cyperus platystylis R.Br. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 9699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayandi, K.; Rajini, N.; Pitchipoo, P.; Jappes, J.T.W.; Rajulu, A.V. Extraction and characterization of new natural lignocellulosic fiber Cyperus pangorei. Int. J. Polym. Anal. Charact. 2016, 21, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benazir, J.F.; Suganthi, R.; Ravichandran, P.; Pooja, M.P. Phytochemical screening and cytotoxicity studies of rhizome extracts of Cyperus pangorei Rottb. Res. Rev. BioSci. 2008, 2, 83–87. [Google Scholar]
- John, M.J.; Anandjiwala, R.D. Recent developments in chemical modification and characterization of natural fiber-reinforced composites. Polym. Compos. 2008, 29, 187–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teja, T.R.; VenkataRao, D.; Naidu, A.L.; Bahubalendruni, M.V.A.R. Mechanical and Chemical Properties of Ramie Reinforced Composites and Manufacturing Techniques: A Review. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/324058516 (accessed on 20 February 2024).
- Pandey, S.N. Ramie fibre: Part I. Chemical composition and chemical properties. A critical review of recent developments. Textile Progress. 2007, 39, 1–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.; Gang, D.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wang, B.; Peng, D.; Liu, L. Ramie, a multipurpose crop: Potential applications, constraints and improvement strategies. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 137, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogard, F.; Bach, T.; Abbes, B.; Bliard, C.; Maalouf, C.; Bogard, V.; Beaumont, F.; Polidori, G. A comparative review of Nettle and Ramie fiber and their use in biocomposites, particularly with a PLA matrix. J. Nat. Fibers 2022, 19, 8205–8229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Li, J.; Ren, J. Study on sound absorption property of ramie fiber reinforced poly(l-lactic acid) composites: Morphology and properties. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2010, 41, 1012–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Li, G.; Zhu, J. Ramie fibers, their composites and applications. In Plant Fibers, Their Composites, and Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 363–378. [Google Scholar]
- Gokulkumar, S.; Thyla, P.R.; Prabhu, L.; Sathish, S.; Karthi, N. A comparative study on epoxy based composites filled with pineapple/areca/ramie hybridized with industrial tea leaf wastes/GFRP. In Materials Today: Proceedings; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 2474–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mawardi, I.; Aprilia, S.; Faisal, M.; Rizal, S. Investigation of thermal conductivity and physical properties of oil palm trunks/ramie fiber reinforced biopolymer hybrid composites as building bio-insulation. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 60, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaiselvi, R.; Infanta Stephy, J.; Pavithra Raj, J.S. Evaluation of Sound Absorption Coefficient—Acoustic Properties of Pattamadai mat. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; Institute of Physics: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benazir, J.A.F.; Manimekalai, V.; Ravichandran, P.; Suganthi, R.; Dinesh, D.C. Properties of fibres/culm strands from mat sedge–cyperus pangorei Rottb. Bioresources 2010, 5, 951–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Xia, F.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, J.; Chen, D.; Zheng, J. Mechanical and dynamic mechanical properties of the amino silicone oil emulsion modified ramie fiber reinforced composites. Polymers 2021, 13, 4083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastner, J.; Plank, B.; Salaberger, D.; Sekelja, J. Defect and porosity determination of fibre reinforced polymers by X-ray computed tomography. In 2nd International Symposium on NDT in Aerospace; NDT: Hamburg, Germany, 2010; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.A.; Umer, R.; Khan, K.A. CT Scan Generated Material Twins for Composites Manufacturing in Industry 4.0; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Mehdikhani, M.; Gorbatikh, L.; Verpoest, I.; Lomov, S.V. Voids in fiber-reinforced polymer composites: A review on their formation, characteristics, and effects on mechanical performance. J. Compos. Mater. 2019, 53, 1579–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcea, S.C.; Wang, Y.; Withers, P.J. X-ray computed tomography of polymer composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 156, 305–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, S.; Toda, K.; Seino, S.; Hoshiyama, K.; Satoh, T. Theoretical and Experimental Analyses on the Sound Absorption Coefficient of Rice and Buckwheat Husks Based on Micro-CT Scan Data. Materials 2023, 16, 5671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Takeda, S.; Wisnom, M.R. Investigation of fracture process zone development in quasi-isotropic carbon/epoxy laminates using in situ and ex situ X-ray Computed Tomography. Compos. Part. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2023, 166, 107395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jebaduraia, D.S.; Babub, A.S. Influence of functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes on mechanical properties of glass fiber reinforced polyester composites. Indian J. Eng. Mater. Sci. 2015, 22, 167–174. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM E1050-08; Standard Test Method for Impedance and Absorption of Acoustical Materials Using A Tube, Two Microphones and A Digital Frequency Analysis System. ASTM: West Conshehoken, PA, USA, 2008.
- ASTM E756; Standard Test Method for Measuring Vibration-Damping Properties of Materials. ASTM: West Conshehoken, PA, USA, 2017.
- Gagauz, I.; Kawashita, L.F.; Hallett, S.R. Understanding the effect of void morphology and characteristics on laminate mechanical properties. ICCM Int. Conf. Compos. Mater. 2017, 2017, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, Y.; Qin, L.; Sun, F.; Zhu, L.; He, X.; Liu, Z. Influence of the Main Components Content of Picea Jezoensis on Acoustic Vibration Properties. Wood Res. 2017, 62, 557–564. [Google Scholar]
- Tiwatane, T.; Barve, S. Thermoacoustic effect: The power of conversion of sound energy & heat energy. Int. J. Res. Technol. Stud. 2014, 1, 20–28. [Google Scholar]
- Sawhney, S.; Sharma, Y.; Parashar, B.; Manimala, S.V. Converting Sound Energy To Electricity. Int. J. Tech. Res. Sci. (Spec. Issue) 2020, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benazir, J.F.; Manimekalai, V.; Ravichandran, P. Waxes from the Mat Sedge-Cyperus pangorei Rottb. Int. J. Bot. 2012, 8, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kumar, J.; Kumar, T.; Chandrasekar, M.; Ganesan, C.; Senthilkumar, K.; Siengchin, S. A review on free vibration characteristics of natural fiber reinforced polymer composites. In AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing: Melville, NY, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Etaati, A.; Mehdizadeh, S.A.; Wang, H.; Pather, S. Vibration damping characteristics of short hemp fibre thermoplastic composites. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2014, 33, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiyagu, C.; Narendrakumar, U. Vibrational analysis of glass/ramie fiber reinforced hybrid polymer composite. Polym. Compos. 2022, 43, 1395–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irawan, A.P. Failure mode analysis of ramie fiber reinforced composite material. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2018; p. 012060. [Google Scholar]
- Raja, T.; Mohanavel, V.; Ravichandran, M.; Kumar, S.S.; Albaqami, M.D.; Alotabi, R.G.; Murugesan, M. Dynamic Mechanical Analysis of Banyan/Ramie Fibers Reinforced with Nanoparticle Hybrid Polymer Composite. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2022, 2022, 1560330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagauz, I.; Kawashita, L.F.; Hallett, S.R. Effect of voids on interlaminar behaviour of carbon/epoxy composites. In Proceedings of the ECCM 2016-Proceeding of the 17th European Conference on Composite Materials, Munich, Germany, 26–30 June 2016; pp. 26–30. [Google Scholar]
- Little, J.E.; Yuan, X.; Jones, M.I. Characterisation of voids in fibre reinforced composite materials. NDT E Int. 2012, 46, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikishkov, Y.; Airoldi, L.; Makeev, A. Measurement of voids in composites by X-ray Computed Tomography. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2013, 89, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Specimen Name | No. of Layers of Reinforcement | Thickness (mm) | Diameter (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| C | 2 | 5 | 30, 100 |
| R | 8 | 5 | 30, 100 |
| RC | C-1, R-4 | 5 | 30, 100 |
| RCR-Flat | C-1, R-4 | 5 | 30, 100 |
| RCR-Curved | C-1, R-4, C-Fillers | 4 & 9 | 30, 100 |
| RCR-Perforated (2.5 mm) | C-1, R-4, C-Fillers | 4 & 9 | 30, 100 |
| Specimen Name | No. of Layers of Reinforcement | Length (mm) | Thickness (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| C | 2 | 200 | 5 |
| R | 8 | 200 | 5 |
| RC | C-1, R-4 | 200 | 5 |
| RCR-Flat | C-1, R-4 | 200 | 5 |
| RCR-Curved | C-1, R-4, C-Fillers | 200 | 4 & 9 |
| RCR-Perforated (2.5 mm) | C-1, R-4, C-Fillers | 200 | 4 & 9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kanniyappan, S.; Selvaraj, S.K. Exploration of Voids, Acoustic Properties and Vibration Damping Ratio of Cyperus Pangorei Rottb Fiber and Ramie Fiber Reinforced with Epoxy Resin Hybrid Composites. Polymers 2024, 16, 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16060832
Kanniyappan S, Selvaraj SK. Exploration of Voids, Acoustic Properties and Vibration Damping Ratio of Cyperus Pangorei Rottb Fiber and Ramie Fiber Reinforced with Epoxy Resin Hybrid Composites. Polymers. 2024; 16(6):832. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16060832
Chicago/Turabian StyleKanniyappan, Sudhakar, and Senthil Kumaran Selvaraj. 2024. "Exploration of Voids, Acoustic Properties and Vibration Damping Ratio of Cyperus Pangorei Rottb Fiber and Ramie Fiber Reinforced with Epoxy Resin Hybrid Composites" Polymers 16, no. 6: 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16060832
APA StyleKanniyappan, S., & Selvaraj, S. K. (2024). Exploration of Voids, Acoustic Properties and Vibration Damping Ratio of Cyperus Pangorei Rottb Fiber and Ramie Fiber Reinforced with Epoxy Resin Hybrid Composites. Polymers, 16(6), 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16060832






