Investigation of Physical Properties of Polymer Composites Filled with Sheep Wool
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
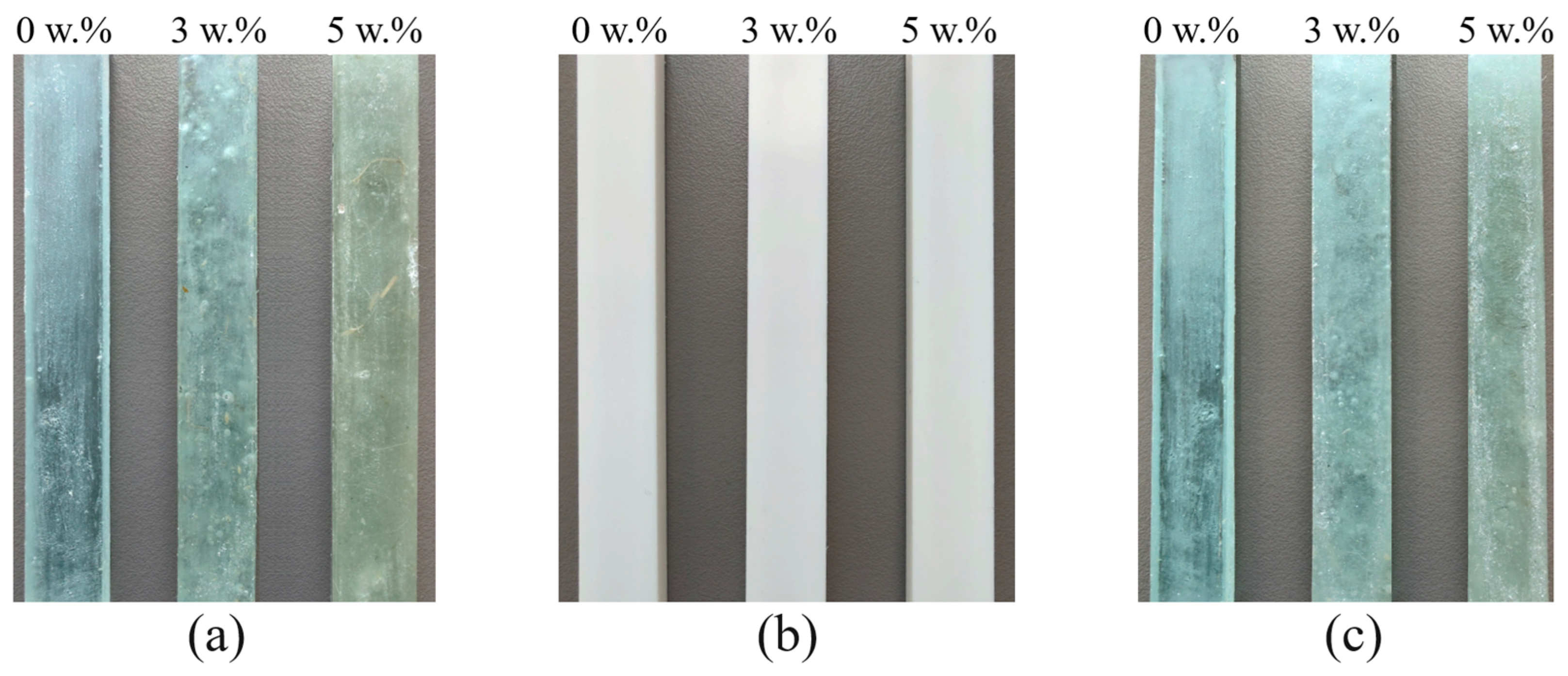
2.1. Production of Polymer Composite Samples
2.2. Measurement Methodology
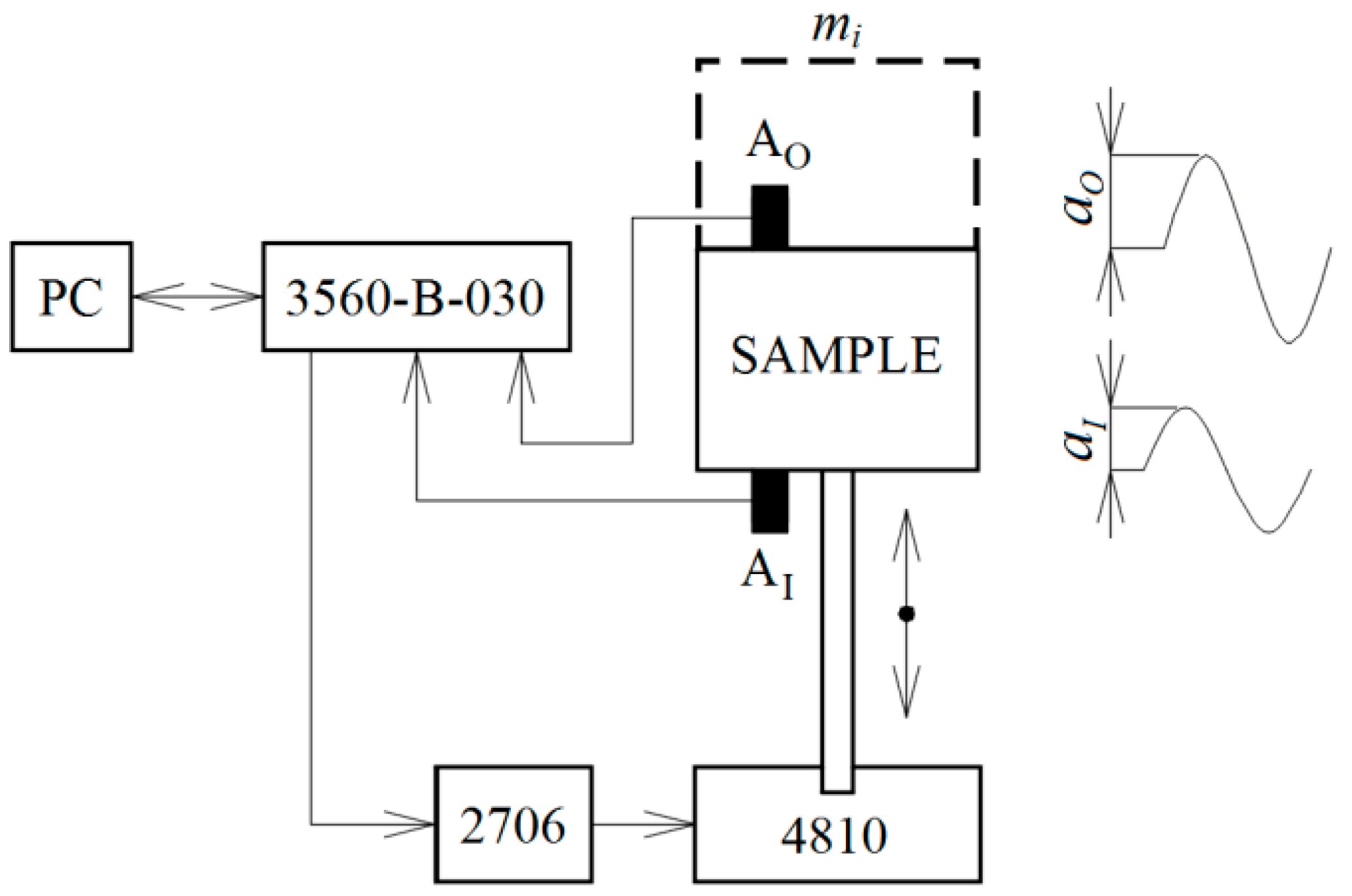
2.2.1. Vibration Damping Testing
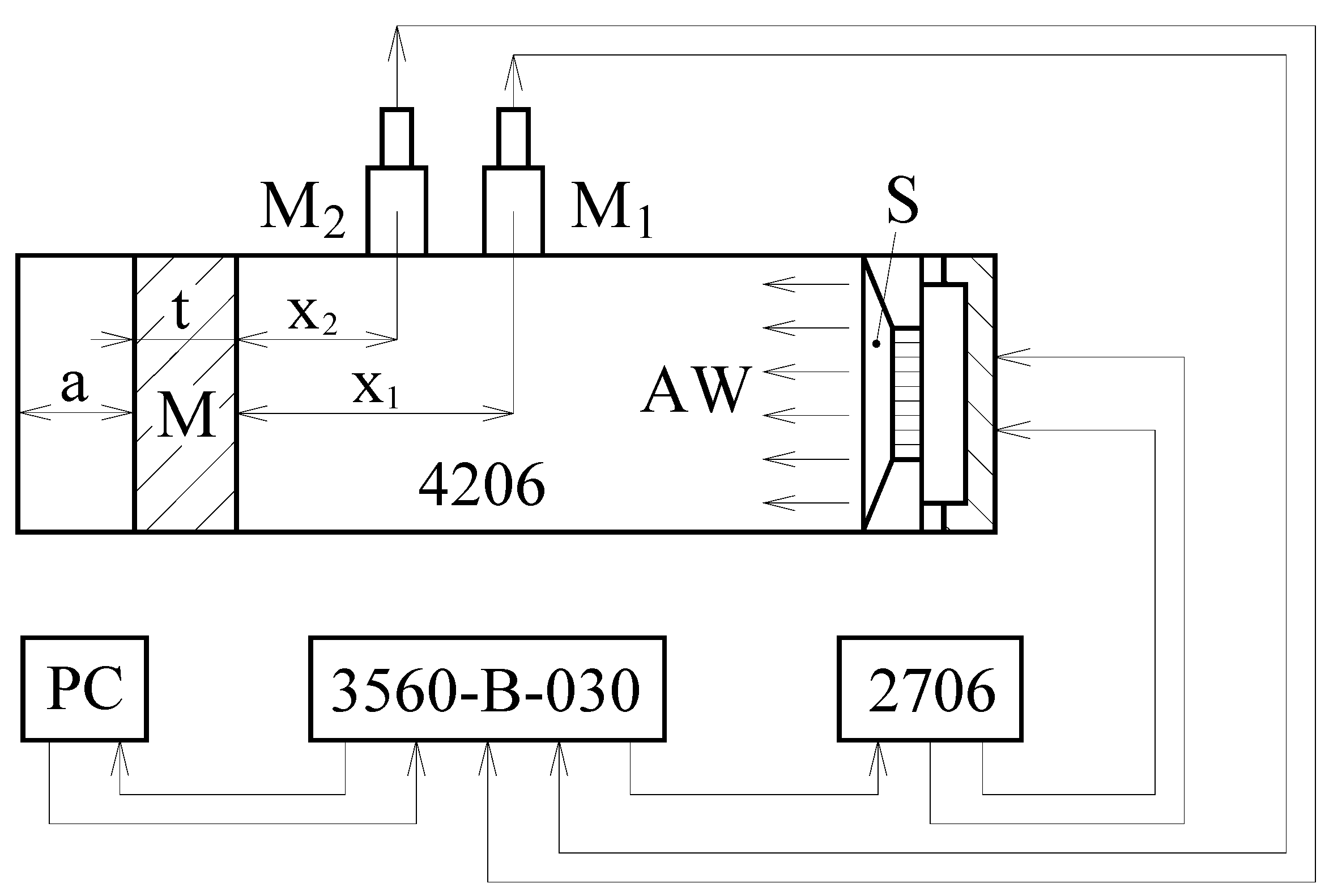
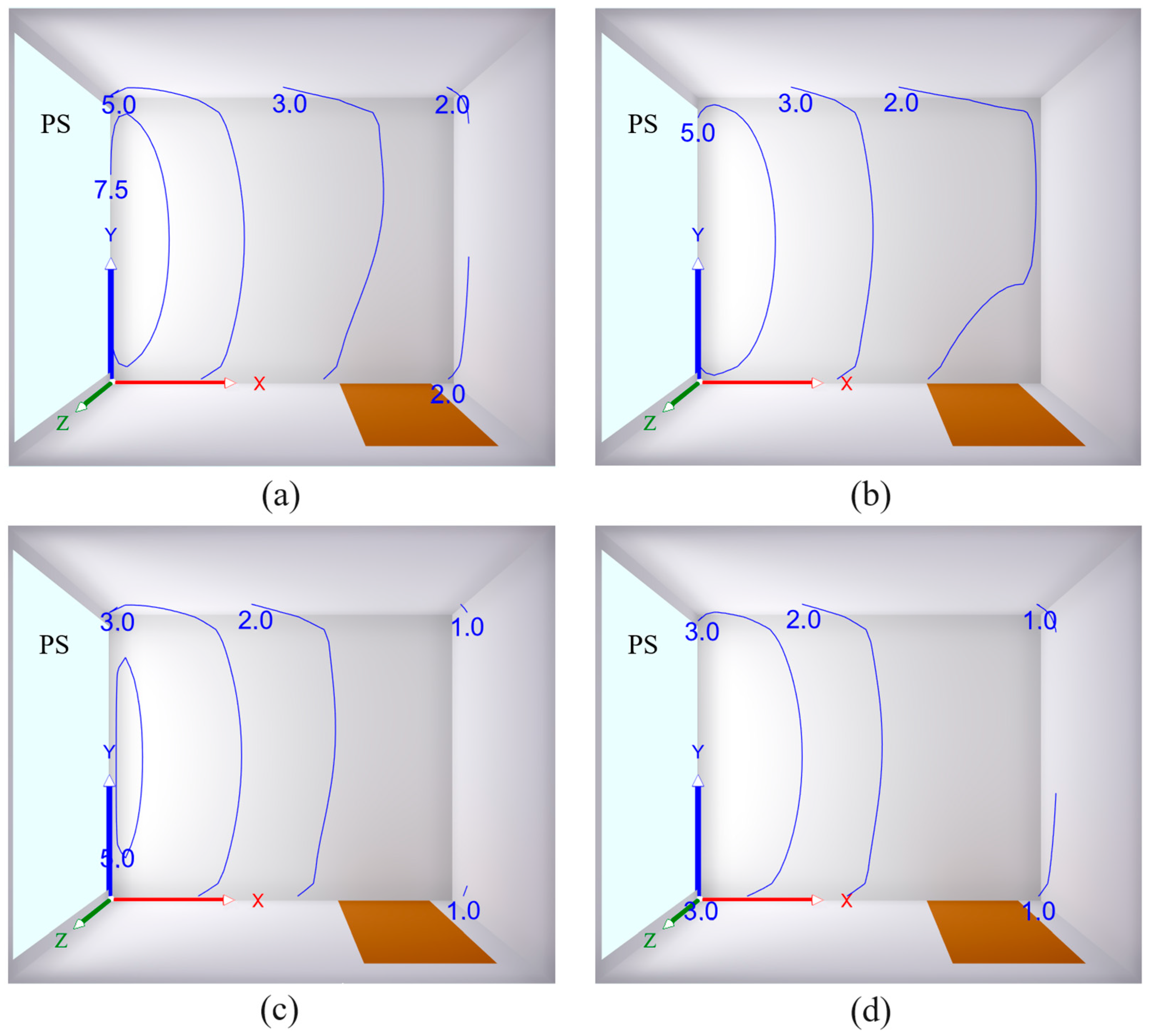
2.2.2. Sound Absorption Properties
2.2.3. DC Electrical Conductivity Testing
2.2.4. Light Transmission Properties
3. Results and Discussion
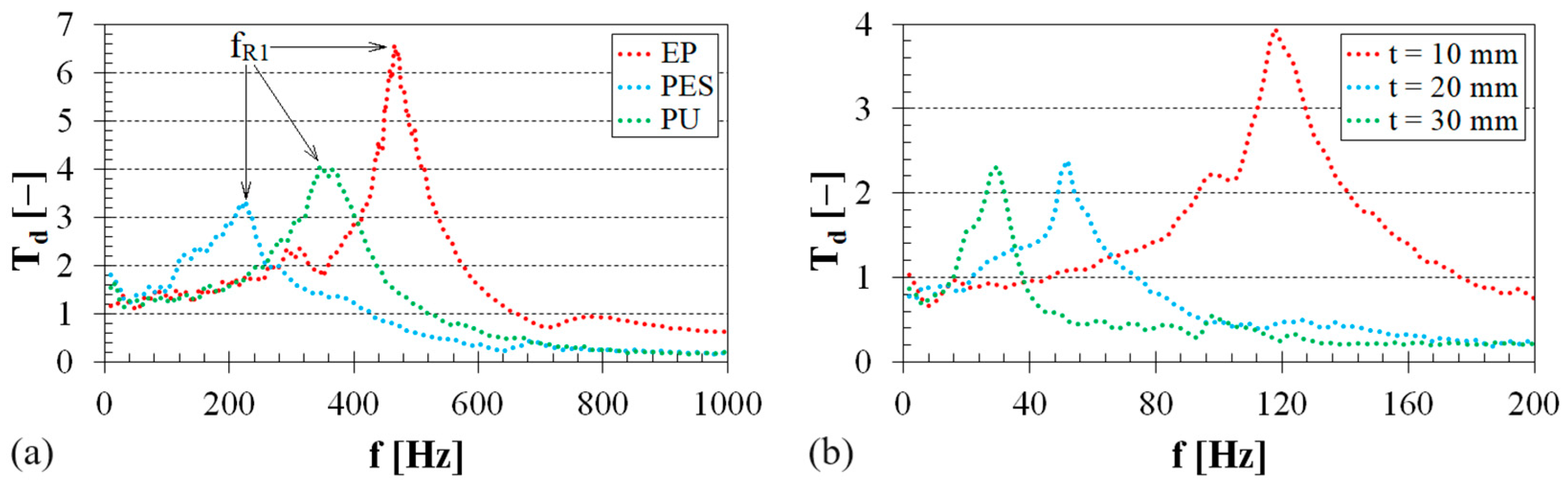
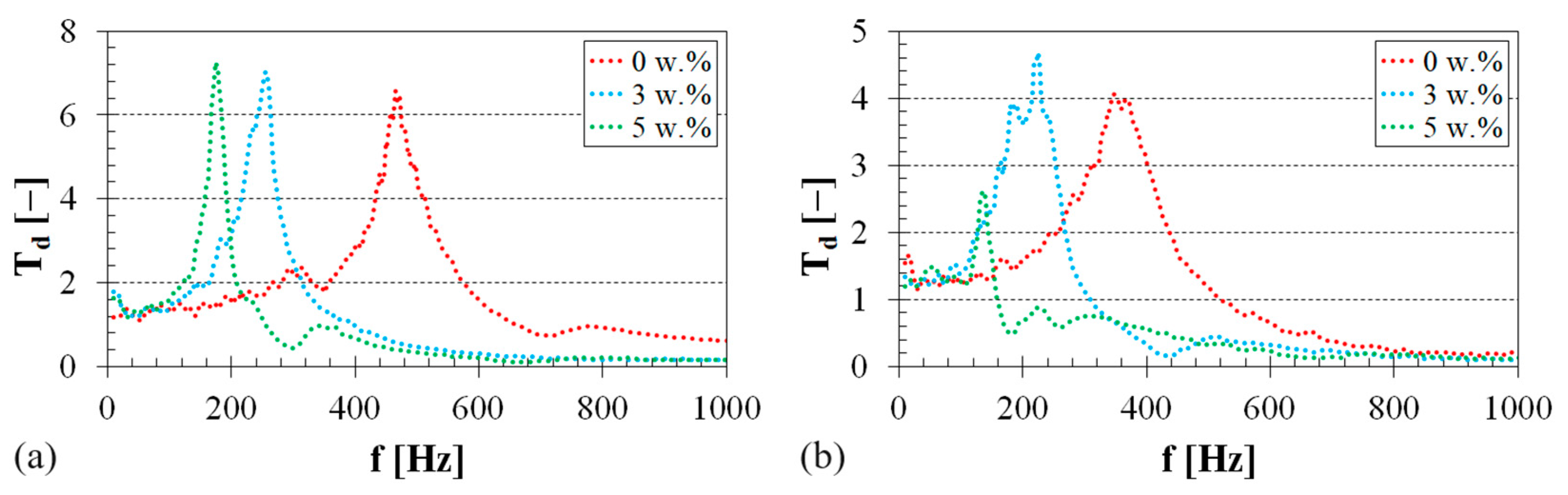
3.1. Vibration Damping Properties
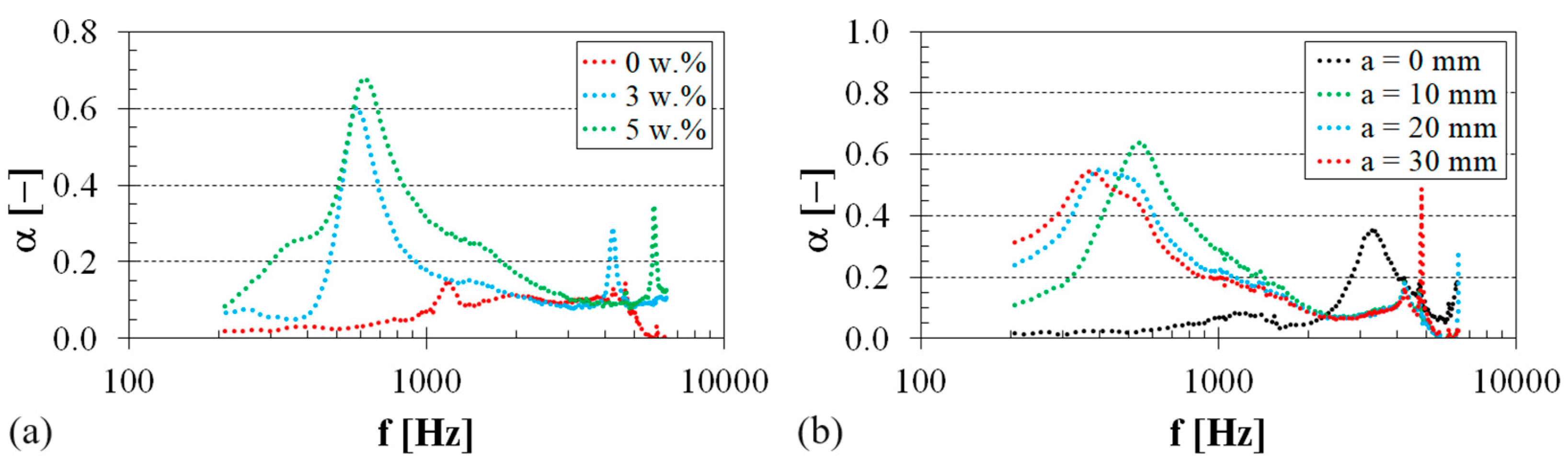
3.2. Sound Absorption Properties
3.3. Electrical Conductivity
3.4. Light Transmission
3.5. Comparison and Application of Natural Fibers Composites
- AFs: Animal fibers, derived from animal hair or secretions;
- VFs: Vegetal (plant) fibers, derived from various plant parts;
- MFs: Mineral fibers, derived from inorganic natural resources.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parlato, M.C.M.; Valenti, F.; Midolo, G.; Porto, S.M.C. Livestock Wastes Sustainable Use and Management: Assessment of Raw Sheep Wool Reuse and Valorization. Energies 2022, 15, 3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlato, M.C.M.; Cuomo, M.; Porto, S.M.C. Natural Fibers Reinforcement for Earthen Building Components: Mechanical Performances of a Low Quality Sheep Wool (“Valle Del Belice” Sheep). Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 326, 126855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.; Jose, S. Wool Fiber Reinforced Polymer Composites; The Textile Institute Book Series, 1st ed.; Elsevier Science Publishing Co., Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 49–71. [Google Scholar]
- Kulkarni, M.B.; Gavande, V.; Mahanwar, P.A.; Shah, A.R.; Shuib, R.K.; Khare, A.M.; Radhakrishnan, S. Review on Biomass Sheep Wool–Based Polymer Composites. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2023; 1–22, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Altin, M.; Yildirim, G. Investigation of Usability of Boron Doped Sheep Wool as Insulation Material and Comparison with Existing Insulation Materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 331, 127303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korjenic, A.; Klarić, S.; Hadžić, A.; Korjenic, S. Sheep Wool as a Construction Material for Energy Efficiency Improvement. Energies 2015, 8, 5765–5781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegyi, A.; Bulacu, C.; Szilagyi, H.; Lăzărescu, A.-V.; Meită, V.; Vizureanu, P.; Mihaela Sandu, M. Improving Indoor Air Quality by Using Sheep Wool Thermal Insulation. Materials 2021, 14, 2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, I.A.; Kumar, R.U.R. Experimental Investigation on Using Sheep Wool as Fiber Reinforcement in Concrete Giving Increment in Overall Strength. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 45, 4405–4409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braniša, J.; Jomová, K.; Lapčík, Ľ.; Porubská, M. Testing of Electron Beam Irradiated Sheep Wool for Adsorption of Cr(III) and Co(II) of Higher Concentrations. Polym. Test. 2021, 99, 107191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetimy, S.; Megahed, N.; Eleinen, O.A.; Elgheznawy, D. Exploring the Potential of Sheep Wool as an Eco-Friendly Insulation Material: A Comprehensive Review and Analytical Ranking. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2024, 39, e00812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiuc, A.E.; Nemeş, O.; Vermeşan, H.; Vasile, O. Innovative Use of Sheep Wool for Obtaining Materials with Improved Sound-Absorbing Properties. Materials 2020, 13, 694. [Google Scholar]
- Tabbaa, M.J.; Al-Azzawi, W.A.; Campbell, D. Variation in Fleece Characteristics of Awassi Sheep at Different Ages. Small Rumin. Res. 2001, 41, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kicinska- Jakubowska, A.; Morales Villavicencio, A.; Zimniewska, M.; Przybylska, P.; Kwiatkowska, E. Evaluation of Wool Quality Parameters of Polish Sheep Breeds. J. Nat. Fibers 2021, 18, 5880–5887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilkumar, N.; Chowdhury, S.; Sanpui, P. Extraction of Keratin from Keratinous Wastes: Current Status and Future Directions. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2023, 25, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chereji, B.D.; Munteanu, F.D. The Impact of Sheep Wool Waste on the Environment. Sci. Pap. Ser. E—Land Reclam. Earth Obs. Surv. Environ. Eng. 2022, 11, 458–463. [Google Scholar]
- Petek, B.; Logar, R.M. Management of Waste Sheep Wool as Valuable Organic Substrate in European Union Countries. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 1234, 23, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabinejad, H.; Bucişcanu, I.-I.; Maier, S.S. Current Approaches for Raw Wool Waste Management and Unconventional Valorization: A review. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2019, 18, 1439–1456. [Google Scholar]
- Fiore, V.; Di Bella, G.; Valenza, A. Effect of Sheep Wool Fibers on Thermal Insulation and Mechanical Properties of Cement-Based Composites. J. Nat. Fibers 2019, 17, 1532–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyousef, R.; Alabduljabbar, H.; Mohammadhosseini, H.; Mohamed, A.M.; Siddika, A.; Alrshoudi, F.; Alaskar, A. Utilization of Sheep Wool as Potential Fibrous Materials in the Production of Concrete Composites. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 30, 101216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mounir, S.; Khabbazi, A.; Khaldoun, A.; Maaloufa, Y.; El Hamdouni, Y. Thermal Inertia and Thermal Properties of the CompoSite Material Clay-Wool. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2015, 19, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantilli, A.P.; Jóźwiak-Niedźwiedzka, D.; Denis, P. Bio-Fibres as a Reinforcement of Gypsum Composites. Materials 2021, 14, 4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atbir, A.; Khabbazi, A.; Cherkaoui, M.; Ibaaz, K.; El Wardi, F.Z.; Chebli, S. Improvement of Thermomechanical Properties of Porous Plaster Reinforced with a Network of Morocco Sheep Wool Skeletons for Energy Efficiency. Build. Environ. 2023, 234, 110171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia Pederneiras, C.; Veiga, R.; de Brito, J. Rendering Mortars Reinforced with Natural Sheep’s Wool Fibers. Materials 2019, 12, 3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dénes, T.-O.; Tămaş-Gavrea, D.-R. Mechanical Properties of Lime Based Composites. Procedia Manuf. 2020, 46, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, Y.K.; Meena, A.; Sahu, M.; Dalai, A. Experimental Investigation on Mechanical and Thermal Characteristics of Waste Sheep Wool Fiber-Filled Epoxy Composites. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, in press.
- Semitekolos, D.; Pardou, K.; Georgiou, P.; Koutsouli, P.; Bizelis, I.; Zoumpoulakis, L. Investigation of Mechanical and Thermal Insulating Properties of Wool Fibres in Epoxy Composites. Polym. Polym. Compos. 2021, 29, 1412–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharath, K.N.; Pasha, M.; Nizamuddin, B.A. Characterization of Natural Fiber (Sheep Wool)-Reinforced Polymer-Matrix Composites at Different Operating Conditions. J. Ind. Text. 2016, 45, 730–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, S.; Thomas, S.; Jibin, K.P.; Sisanth, K.S.; Kadam, V.; Shakyawar, D.B. Surface Modification of Wool Fabric Using Sodium Lignosulfonate and Subsequent Improvement in the Interfacial Adhesion of Natural Rubber Latex in the Wool/Rubber Composites. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 177, 114489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlak, F.; Aldas, M.; Parres, F.; López-Martínez, J.; Arrieta, M.P. Silane-Functionalized Sheep Wool Fibers from Dairy Industry Waste for the Development of Plasticized PLA Composites with Maleinized Linseed Oil for Injection-Molded Parts. Polymers 2020, 12, 2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangat, A.S.; Singh, S.; Gupta, M.; Sharma, R. Experimental investigations on natural fiber embedded additive manufacturing-based biodegradable structures for biomedical applications. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2018, 24, 1221–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manivannan, J.; Rajesh, S.; Mayandi, K.; Rajini, N.; Ismail, S.O.; Mohammad, F.; Kuzman, M.K.; Al-Lohedan, H.A. Animal fiber characterization and fiber loading effect on mechanical behaviors of sheep wool fiber reinforced polyester composites. J. Nat. Fibers 2020, 19, 4007–4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tusnim, J.; Jenifar, N.S.; Hasan, M. Properties of jute and sheep wool fiber reinforced hybrid polypropylene composites. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 438, 012029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tămaş-Gavrea, D.R.; Dénes, T.O.; Iştoan, R.; Tiuc, A.E.; Manea, D.L.; Vasile, O. A Novel Acoustic Sandwich Panel Based on Sheep Wool. Coatings 2020, 10, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dénes, T.O.; Iştoan, R.; Tǎmaş-Gavrea, D.R.; Manea, D.L.; Hegyi, A.; Popa, F.; Vasile, O. Analysis of sheep wool-based composites for building insulation. Polymers 2022, 14, 2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urdanpilleta, M.; Leceta, I.; Guerrero, P.; de la Caba, K. Sustainable sheep wool/soy protein biocomposites for sound absorption. Polymers 2022, 14, 5231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharath, K.N.; Binoj, J.S.; Mansingh, B.B.; Manjunath, G.B.; Raghu, G.V.; Siengchin, S.; Sanjay, M.R. Effect of stacking sequence and interfacial analysis of biomass sheep wool/glass fiber reinforced epoxy biocomposites. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2023, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pina, A.C.; Tancredi, N.; Baldan, M.; Marcuzzo, J.S.; Amaya, A. CO2 Capture and Biomethane Obtention Using Activated Carbon Filter of Animal Origin. MRS Adv. 2018, 3, 3589–3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafikov, A.; Mirzayev, N.; Alimkhanova, S. Multilayer Nonwoven Lining Materials Made of Wool and Cotton for Clothing and Footwear. J. Ind. Text. 2022, 51, 6173S–6194S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.S. Mechanical Vibrations, 5th ed.; Pearson Education, Inc.: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 281–287. [Google Scholar]
- Latif, N.A.; Rus, A.Z.M. Vibration Transmissibility Study of High Density Solid Waste Biopolymer Foam. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Mechanical Engineering Research, High Tatras, Slovakia, 28–31 May 2012; pp. 426–429. [Google Scholar]
- Stephen, N. On Energy Harvesting from Ambient Vibration. J. Sound Vib. 2006, 293, 409–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Q.; Yao, Z. Analysis of the Effects of Nonlinear Viscous Damping on Vibration Isolator. Nonlinear Dyn. 2015, 79, 2325–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.; Lang, Z.; Billings, S.A. The Benefits of Nonlinear Cubic Viscous Damping of the Force Transmissibility of a Duffing-Type Vibration Isolator. In Proceedings of the UKACC International Conference on Control, Cardiff, UK, 3–5 September 2012; pp. 479–484. [Google Scholar]
- Sgard, F.; Castel, F.; Atalla, N. Use of a Hybrid Adaptive Finite Element/Modal Approach to Assess the Sound Absorption of Porous Materials with Meso-Heterogeneities. Appl. Acoust. 2011, 72, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 10534-2; International Organization for Standardization. Acoustics-Determination of Sound Absorption Coefficient and Impedance in Impedance Tubes-Part 2: Transfer-Function Method; ISO/TC 43/SC2 Building Acoustics. CEN, European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 1998; pp. 10534–10542.
- Han, F.S.; Seiffert, G.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Gibbs, B. Acoustic Absorption Behaviour of an Open-Celled Alluminium Foam. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 2003, 36, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.J.; Cha, D.J. Determination of an Acoustic Reflection Coefficient at the Inlet of a Model Gas Turbine Combustor for Power Generation. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 164, 012010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Wang, W.; Zhang, F.; Dai, K.; Li, C.B.; Fan, Y.; Chen, G.M.; Zheng, Q.B. Soft Organic Thermoelectric Materials: Principles, Current State of the Art and Applications. Small 2022, 18, 2104922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taherian, R. Development of an Equation to Model Electrical Conductivity of Polymer-Based Carbon Nanocomposites. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2014, 3, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiersma, D.S.; Bartolini, P.; Lagendijk, A.; Righini, R. Localization of Light in a Disordered Medium. Nature 1997, 390, 671–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ČSN 36 0011-2; Lighting Measurement in Interiére-Part 2: Daylighting Measurement. Prague, Czech Office for Standards, Metrology and Testing: Prague, Czech Republic, 2006.
- Dolnikova, E.; Katunsky, D.; Vertal, M.; Zozulak, M. Influence of Roof Windows Area Changes on the Classroom Indoor Climate in the Attic Space: A Case Study. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalauni, K.; Pawar, S.J. A Review on the Taxonomy, Factors Associated with Sound Absorption and Theoretical Modeling of Porous Sound Absorbing Materials. J. Porous Mater. 2019, 26, 1795–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Fu, Q.; Si, Y.; Ding, B.; Yu, J. Porous Materials for Sound Absorption. Compos. Commun. 2018, 10, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everest, F.A. Absorption of sound. In Master Handbook of Acoustics, 4th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 179–233. [Google Scholar]
- Monkova, K.; Vasina, M.; Monka, P.P.; Kozak, D.; Vanca, J. Effect of the Pore Shape and Size of 3D-Printed Open-Porous ABS Materials on Sound Absorption Performance. Materials 2020, 13, 4474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peña-García, A.; Gil-Martín, L.M.; Hernández-Montes, E. Use of Sunlight in Road Tunnels: An Approach to the Improvement of Light-Pipes’ Efficacy through Heliostats. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2016, 60, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murillo, M.; Sánchez, A.; Gil, A.; Araya-Letelier, G.; Burbano, C.; Silva, Y.F. Use of animal fiber-reinforcement in construction materials: A review. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 20, e02812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starkova, O.; Sabalina, A.; Voikiva, V.; Osite, A. Environmental Effects on Strength and Failure Strain Distributions of Sheep Wool Fibers. Polymers 2022, 14, 2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, H.; Ho, M.; Lau, K.; Cardona, F.; Hui, D. Natural fibre-reinforced composites for bioengineering and environmental engineering applications. Compos. Part B Eng. 2009, 40, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlato, M.C.M.; Porto, S.M.C. Organized framework of main possible applications of sheep wool fibres in building components. Sustainability 2020, 12, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singha, K. A short review on basalt fiber. Int. J. Text. Sci. 2012, 1, 19–28. [Google Scholar]
- Thapliyal, D.; Verma, S.; Sen, P.; Kumar, R.; Thakur, A.; Tiwari, A.K.; Singh, D.; Verros, G.D.; Arya, R.K. Natural Fibers Composites: Origin, Importance, Consumption Pattern, and Challenges. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.; Patil, R.S.; John, J.; Patil, M. A Comprehensive Outlook of Scope within Exterior Automotive Plastic Substrates and Its Coatings. Coatings 2023, 13, 1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthalagu, R.; Murugesan, J.; Sathees Kumar, S.; Sridhar Babu, B. Tensile attributes and material analysis of kevlar and date palm fibers reinforced epoxy composites for automotive bumper applications. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 46, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
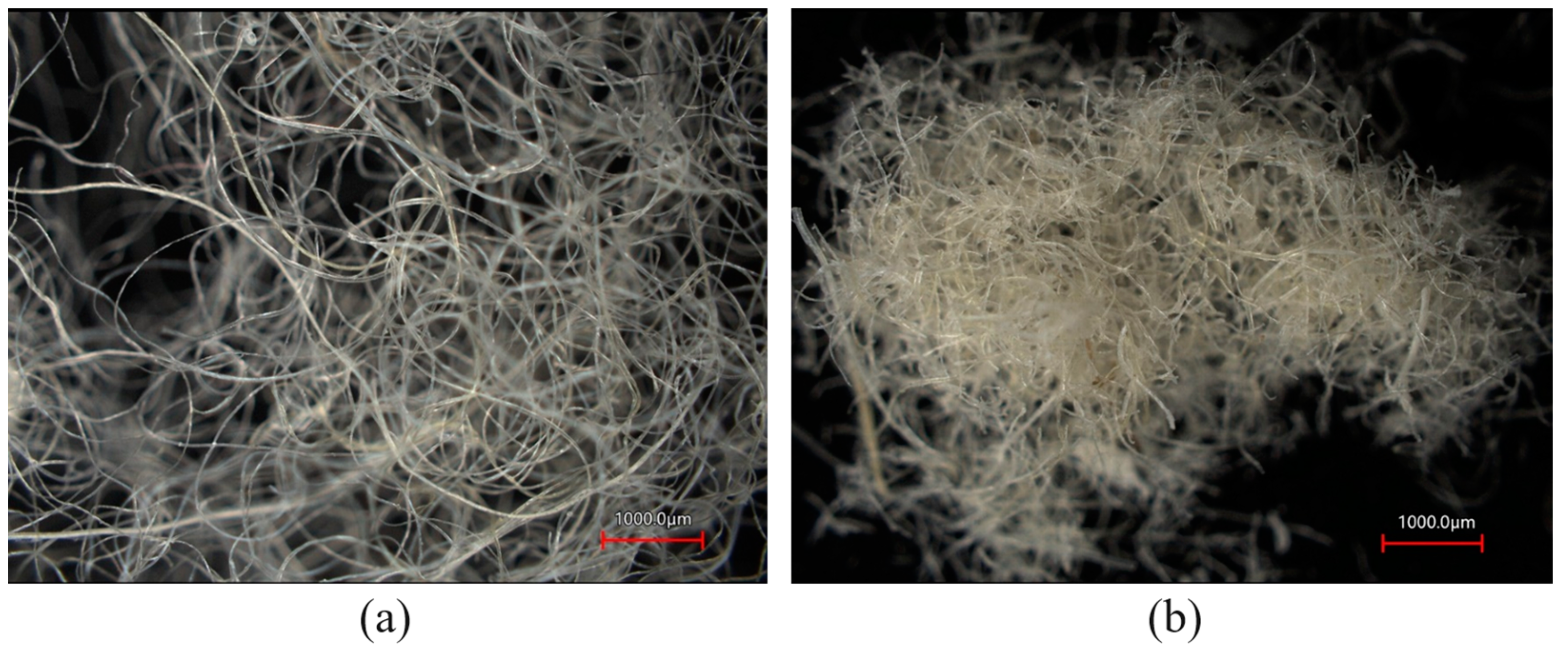



| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Thickness (mm) | 50 * |
| Mass per unit area (g/m2) | 500 * |
| Thermal conductivity coefficient (W·m−1·K−1) | 0.042 * |
| Heat transfer coefficient (W·m−2·K−1) | 1.07 * |
| Sorption mass moisture (%) | 20 * |
| Maximum temperature (°C) | 170 * |
| Parameter | Matrix | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| EP | PES | PU | |
| Resin type | EPOX G20 | GPE 100 | GAFORM R30 |
| Resin/hardener mixing ratio (–) | 100/23 * | 100/1.25 * | 100/100 * |
| Resin viscosity (mPa·s) | 450 * (at 23 °C) | 200 * (at 23 °C) | 285 * (at 20 °C) |
| Hardener viscosity (mPa·s) | 30 * (at 23 °C) | 10 ÷ 20 * (at 23 °C) | 150 * (at 20 °C) |
| Density (g·cm−3) | 1.00 ÷ 1.05 * | 1.12 * | 1.09 * |
| Material Type | Wr (w.%) | fR1 (Hz) |
|---|---|---|
| EP | 0 | 466 ± 21 |
| 3 | 253 ± 11 | |
| 5 | 174 ± 9 | |
| PU | 0 | 339 ± 12 |
| 3 | 217 ± 9 | |
| 5 | 130 ± 6 | |
| PES | 0 | 219 ± 10 |
| 3 | 154 ± 8 | |
| 5 | 112 ± 5 |
| Material Type | t (mm) | fR1 (Hz) |
|---|---|---|
| Sheep wool | 10 | 115 ± 5 |
| 20 | 51 ± 3 | |
| 30 | 28 ± 2 |
| Material Type | Wr (w.%) | τ (–) |
|---|---|---|
| EP | 0 | 0.69 ± 0.03 |
| 3 | 0.43 ± 0.02 | |
| 5 | 0.37 ± 0.02 | |
| PES | 0 | 0.72 ± 0.04 |
| 3 | 0.58 ± 0.03 | |
| 5 | 0.53 ± 0.03 |
| Surface | ρ (–) |
|---|---|
| Walls | 0.94 |
| Ceiling | 0.94 |
| Floor | 0.65 |
| Brown door | 0.16 |
| Material Type | Wr (w.%) | DFmin (%) | DFm (%) | DFmax (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP | 0 | 8.8 | 4.4 | 1.5 |
| 3 | 5.3 | 2.7 | 0.9 | |
| 5 | 4.5 | 2.3 | 0.8 | |
| PES | 0 | 8.5 | 4.3 | 1.4 |
| 3 | 7.1 | 3.6 | 1.2 | |
| 5 | 6.5 | 3.3 | 1.1 |
| Group of NFs | Type of NFs | Density (g·cm−3) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Young’s Modulus (GPa) | Elongation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Afs | Sheep wool | 1.5–2.0 | 120–174 | 1.0–4.8 | 25–45 |
| Spider silk | 1.34–1.38 | 25–50 | 2.0–6.0 | 10–40 | |
| Chicken feather | 0.80–0.89 | 187 | 4.6 | 8 | |
| VFs | Cotton | 1.21 | 287–597 | 6–10 | 2–10 |
| Flax | 1.38 | 343–1035 | 50–70 | 7 | |
| Jute | 1.23 | 187–773 | 20–55 | 1.5–3.1 | |
| Hemp | 1.47 | 580–1110 | 30–60 | 1.6–4.5 | |
| Pineapple | 1.50 | 170–1627 | 60–82 | 1.0–3.0 | |
| Sisal | 1.20 | 507–855 | 9–22 | 1.9–3.0 | |
| Kenaf | 1.20 | 295–930 | 22–60 | 2.7–6.9 | |
| Bamboo | 0.6–1.1 | 270–862 | 18–89 | 1.6–8.0 | |
| MFs | Basalt | 2.7 | 2130 | 93 | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vasina, M.; Straznicky, P.; Hrbacek, P.; Rusnakova, S.; Bosak, O.; Kubliha, M. Investigation of Physical Properties of Polymer Composites Filled with Sheep Wool. Polymers 2024, 16, 690. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16050690
Vasina M, Straznicky P, Hrbacek P, Rusnakova S, Bosak O, Kubliha M. Investigation of Physical Properties of Polymer Composites Filled with Sheep Wool. Polymers. 2024; 16(5):690. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16050690
Chicago/Turabian StyleVasina, Martin, Premysl Straznicky, Pavel Hrbacek, Sona Rusnakova, Ondrej Bosak, and Marian Kubliha. 2024. "Investigation of Physical Properties of Polymer Composites Filled with Sheep Wool" Polymers 16, no. 5: 690. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16050690
APA StyleVasina, M., Straznicky, P., Hrbacek, P., Rusnakova, S., Bosak, O., & Kubliha, M. (2024). Investigation of Physical Properties of Polymer Composites Filled with Sheep Wool. Polymers, 16(5), 690. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16050690








