Hygrothermal Effect on GF/VE and GF/UP Composites: Durability Performance and Laboratory Assessment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods of Hygrothermal Aging and Immersion
2.3. Mechanical Properties Testing
2.4. Testing and Characterization
3. Results
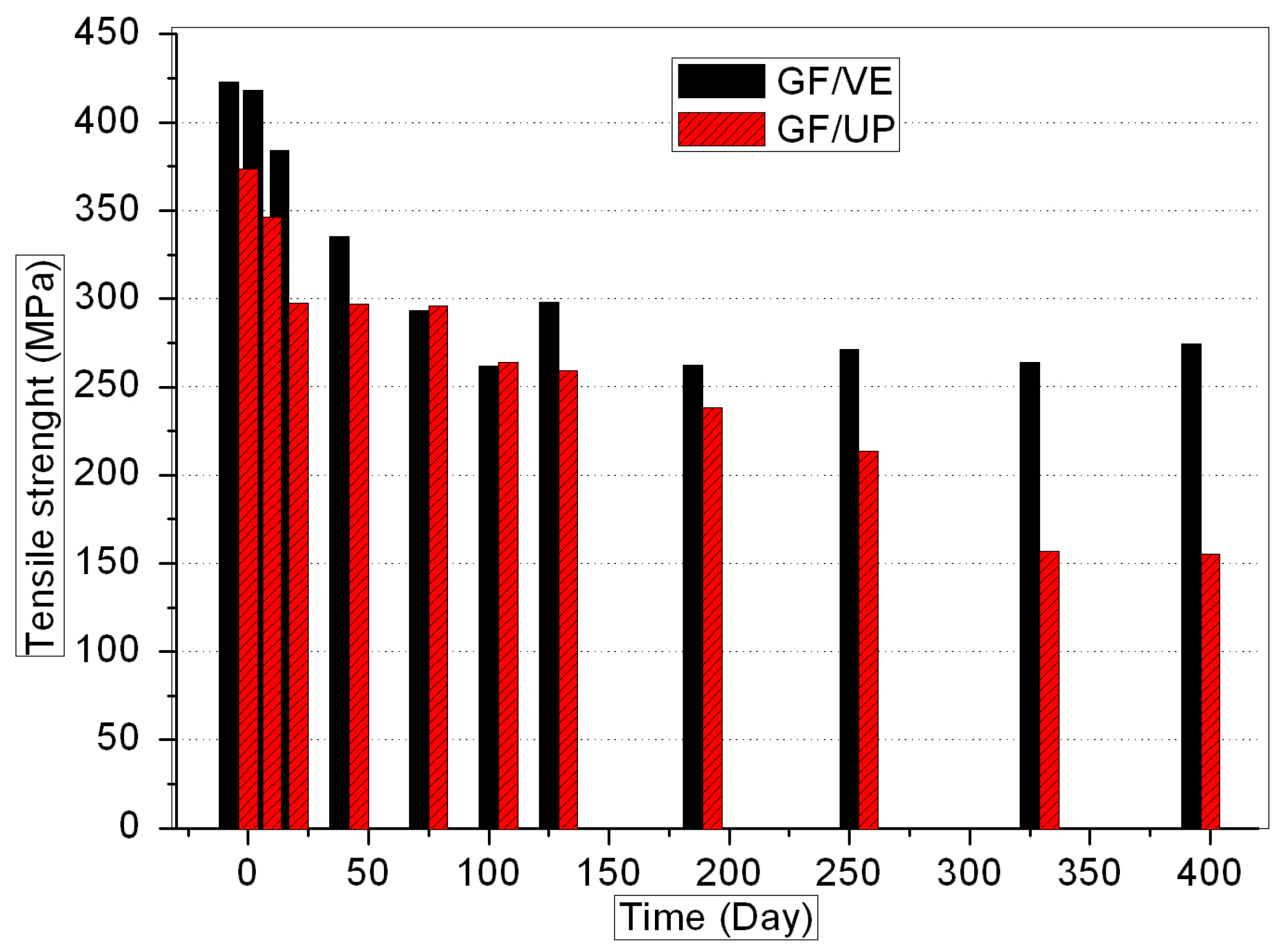
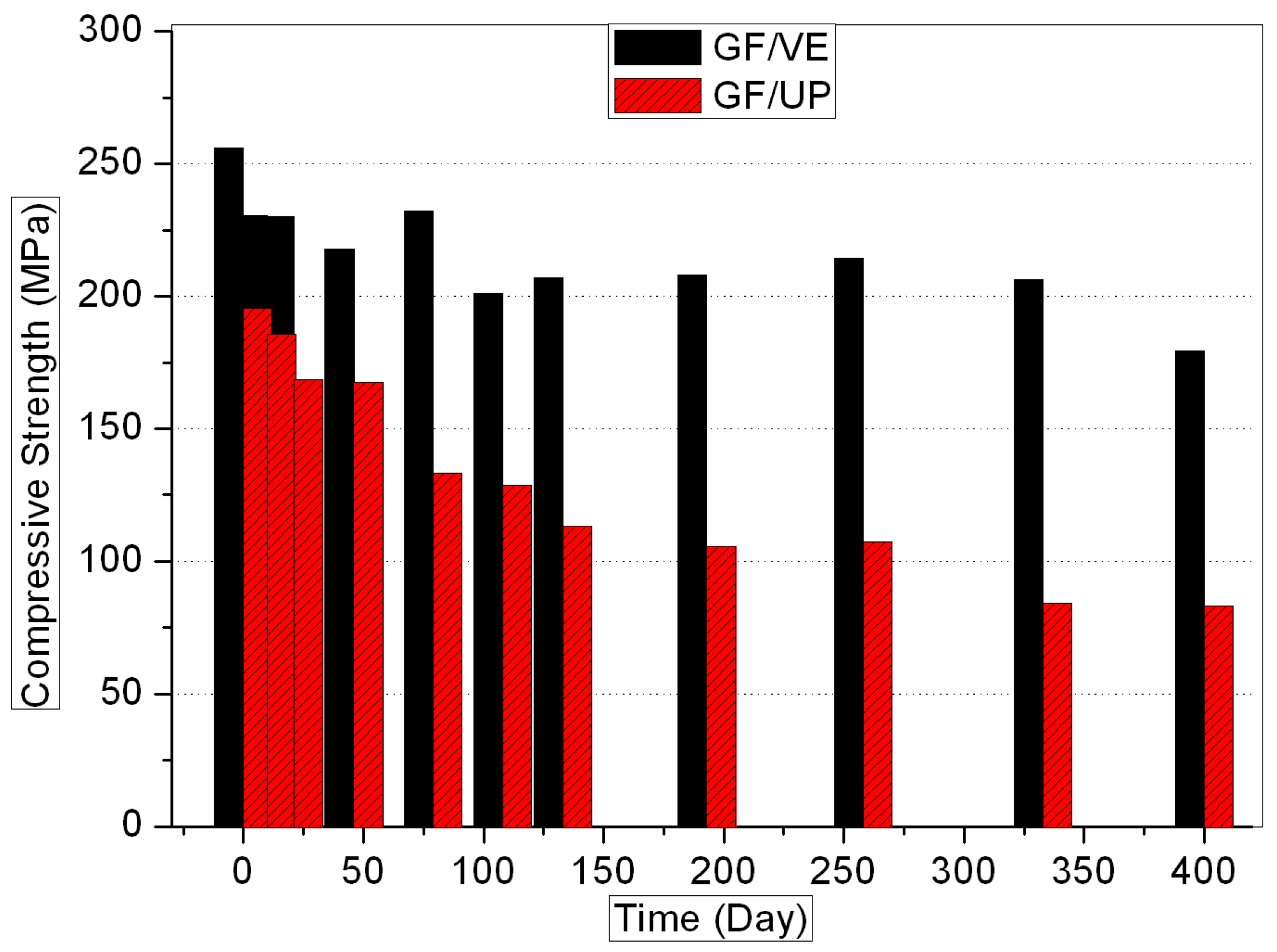
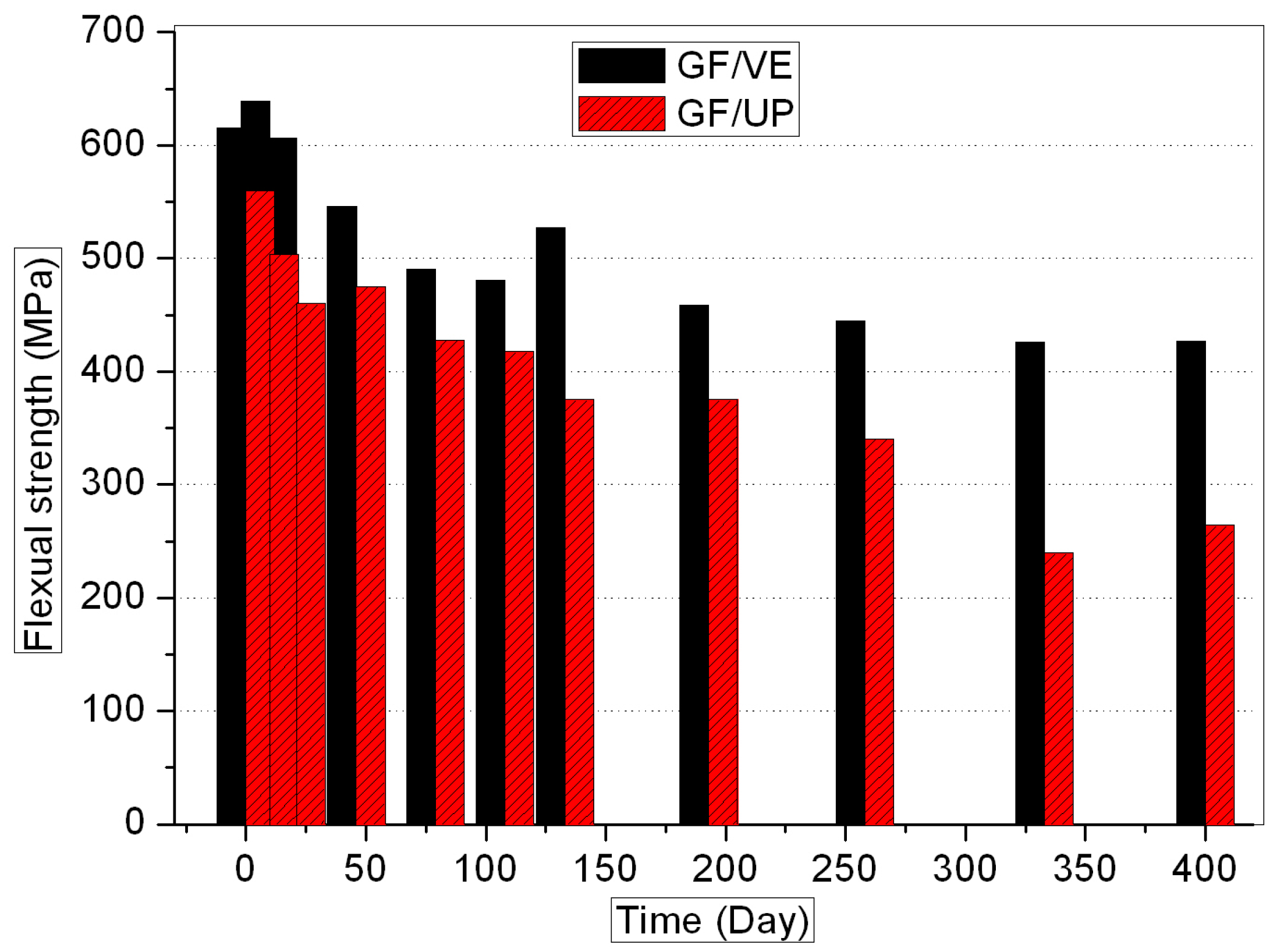
3.1. Mechanical Properties
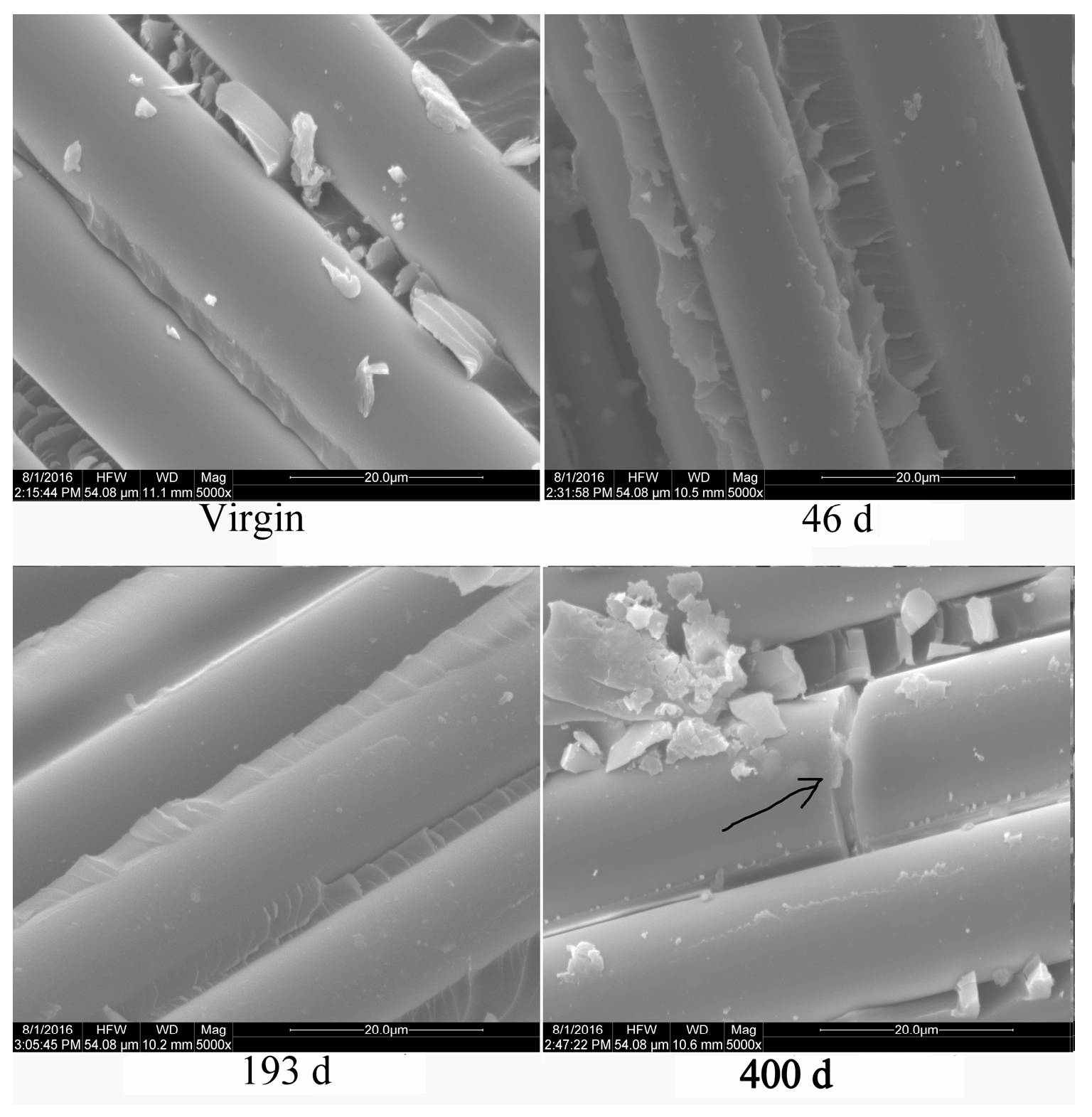
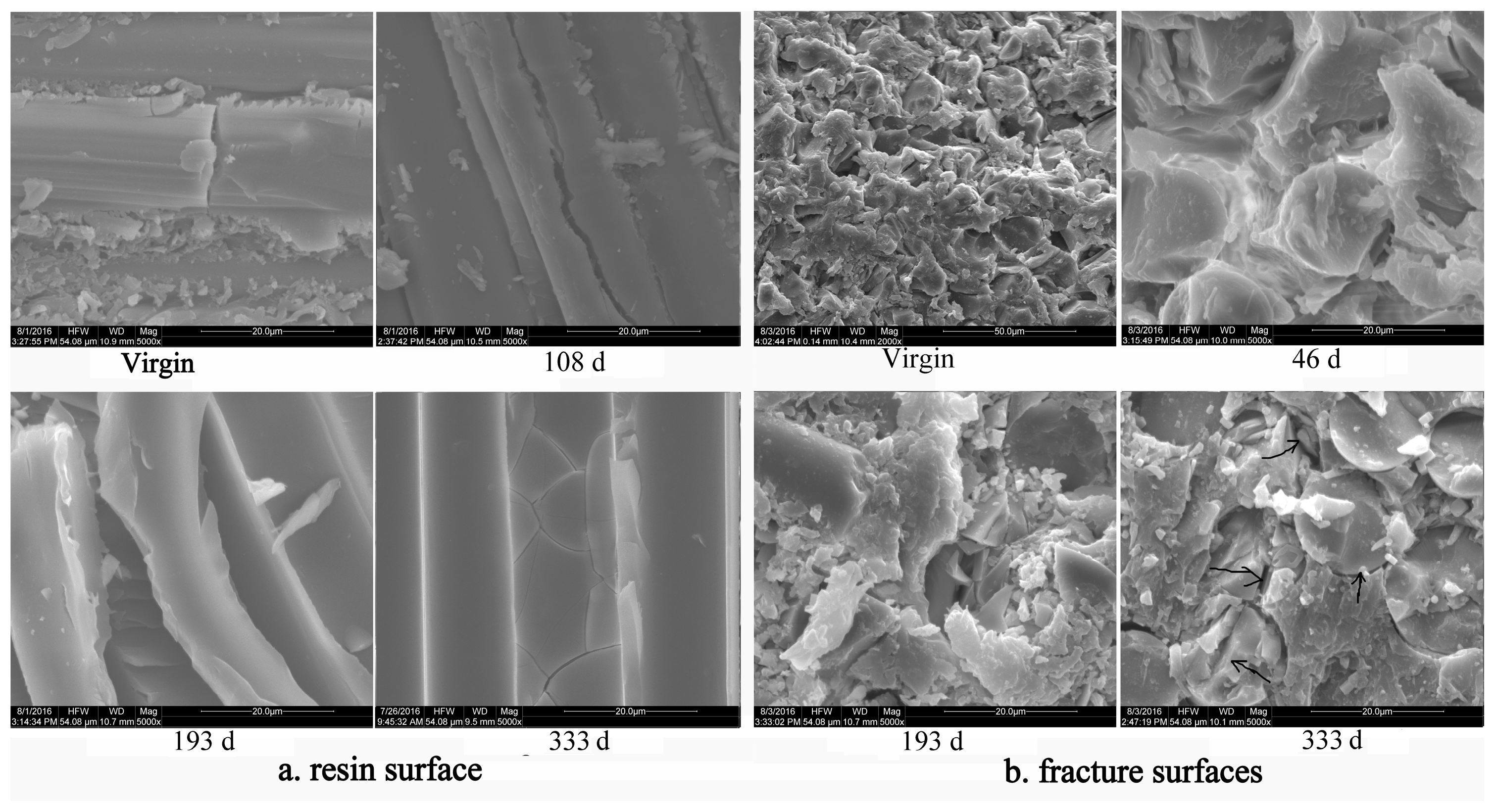
3.2. Appearance and Failure Surface Morphology Observation
3.3. Thermal Properties
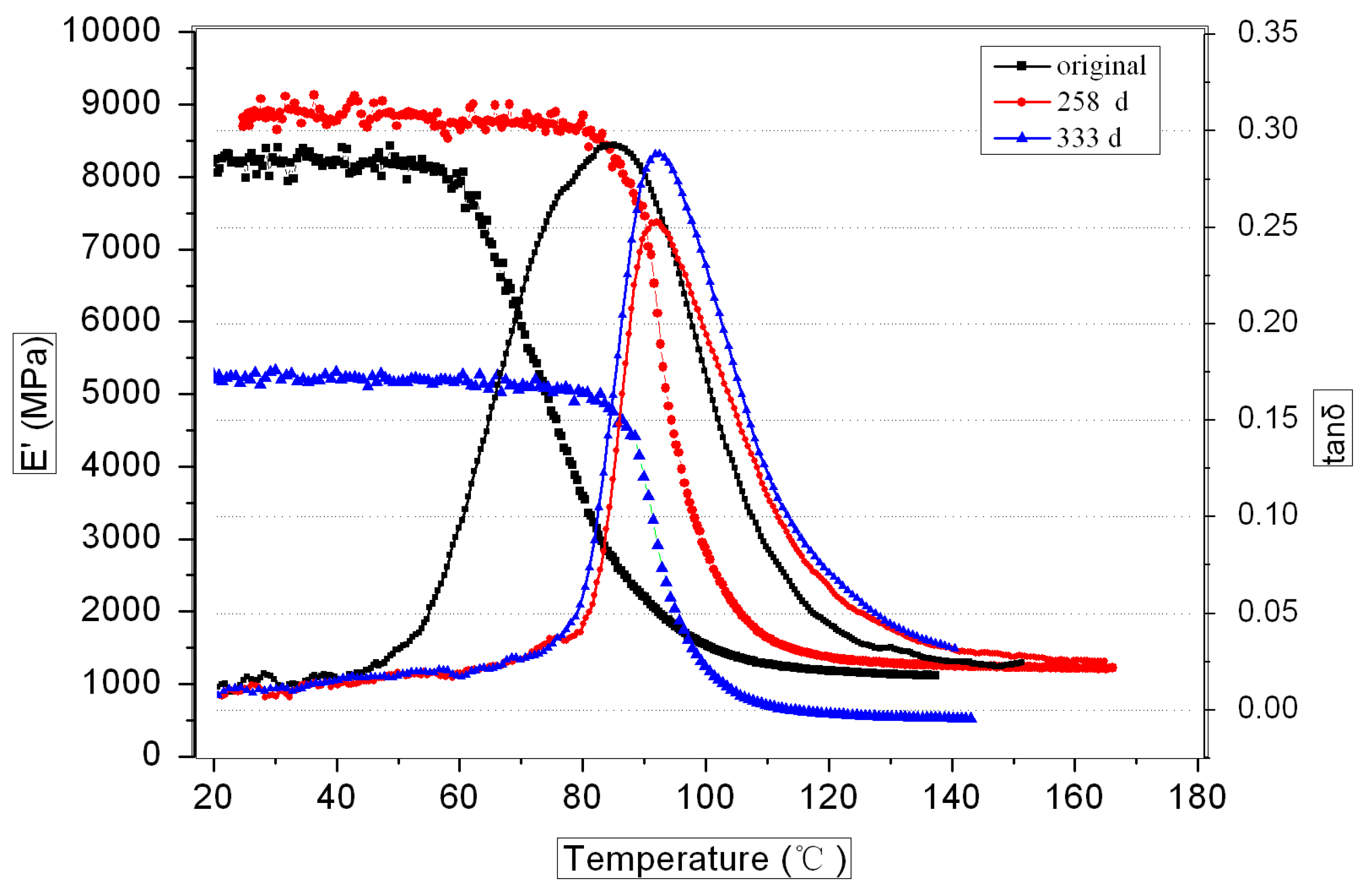
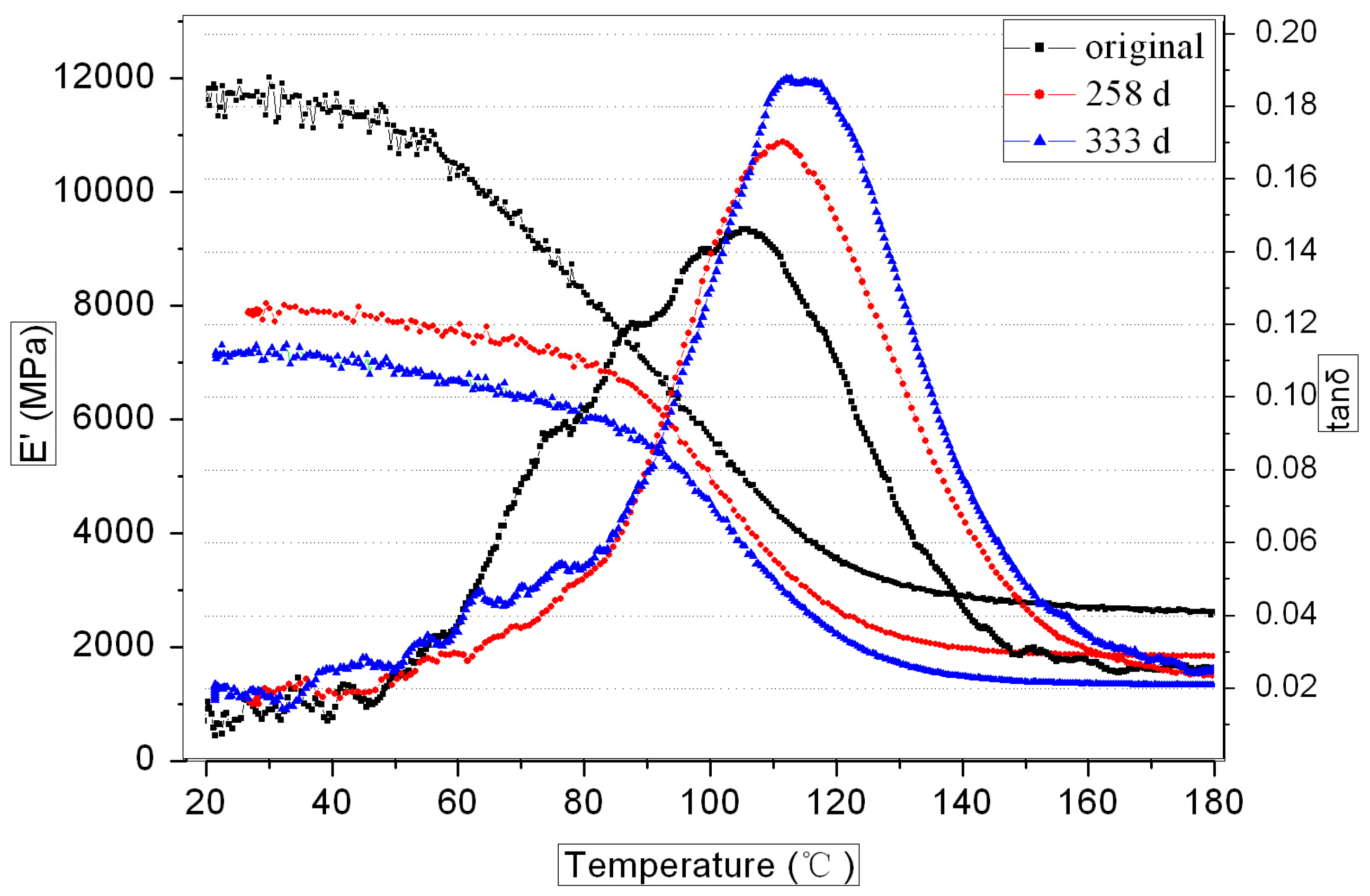
3.3.1. DMA Analysis
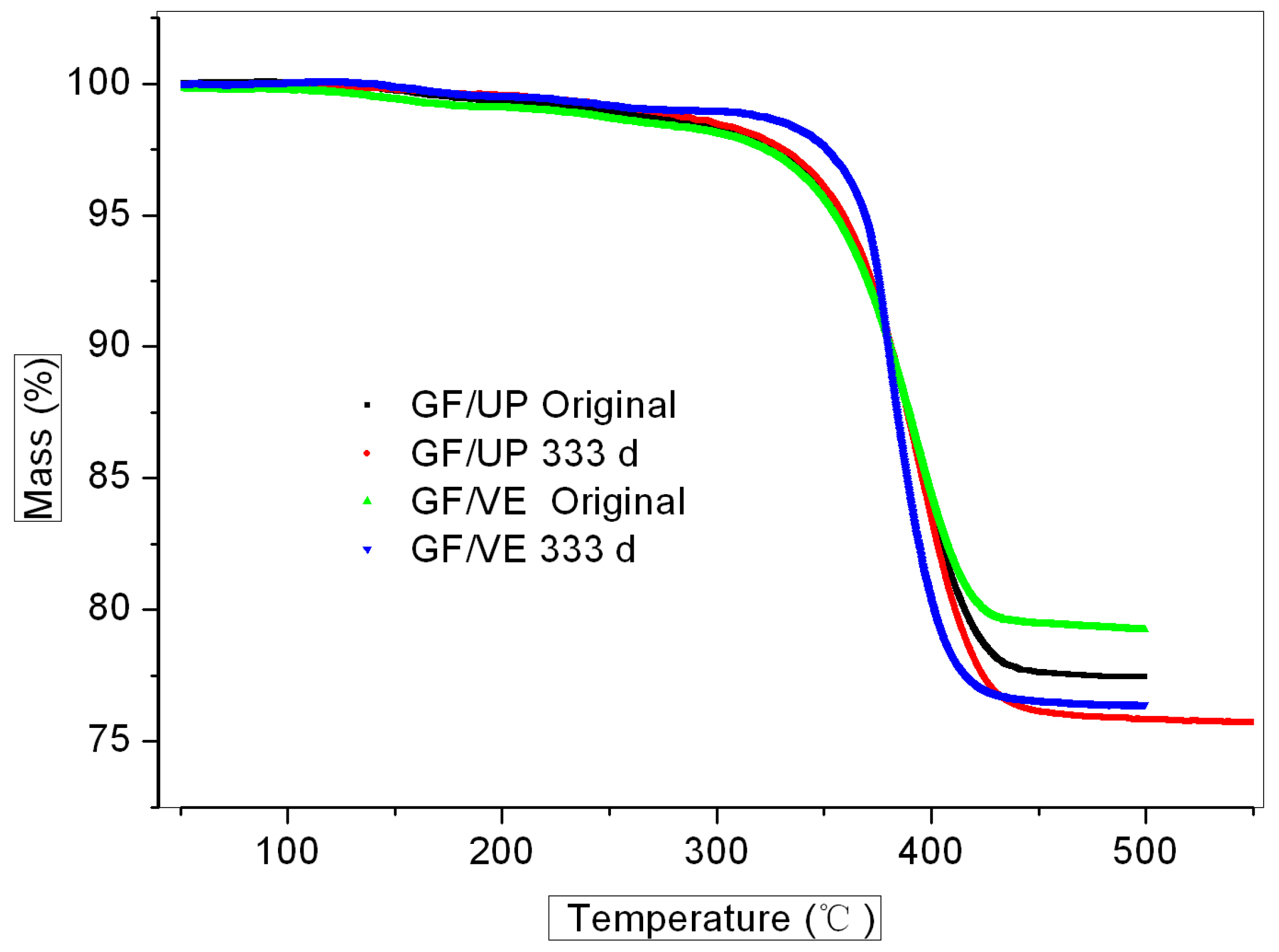
3.3.2. TGA Analysis
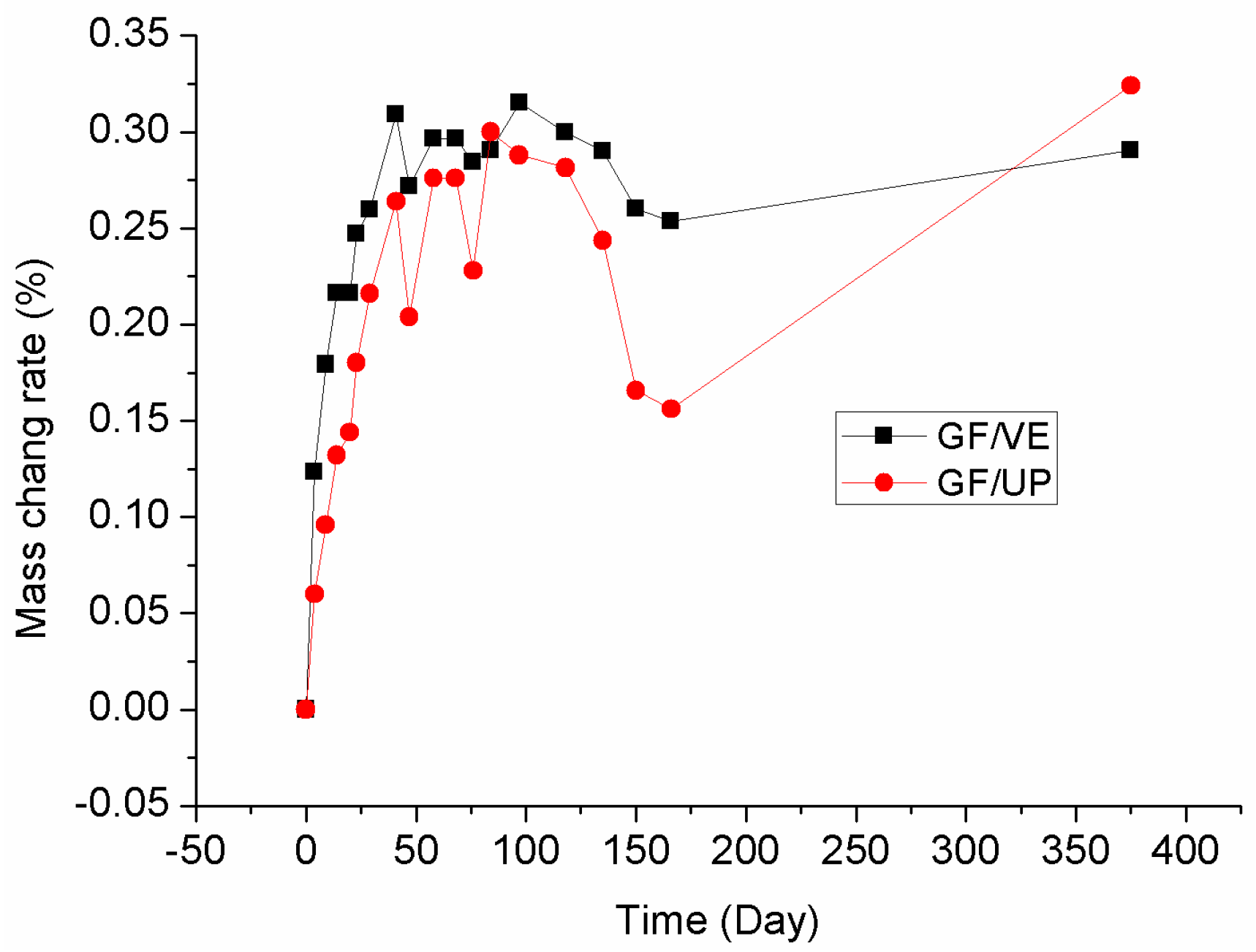
3.4. Mass Change Rate
4. Discussion
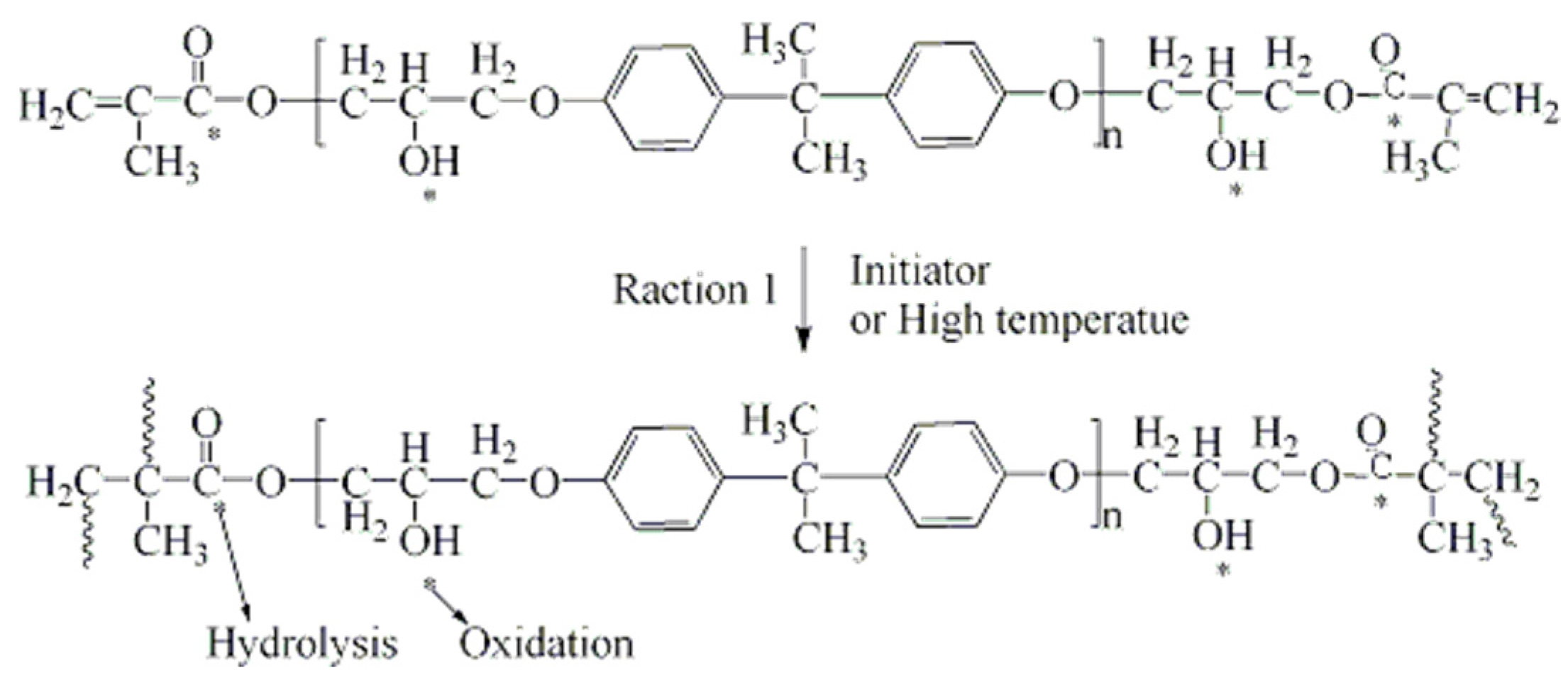
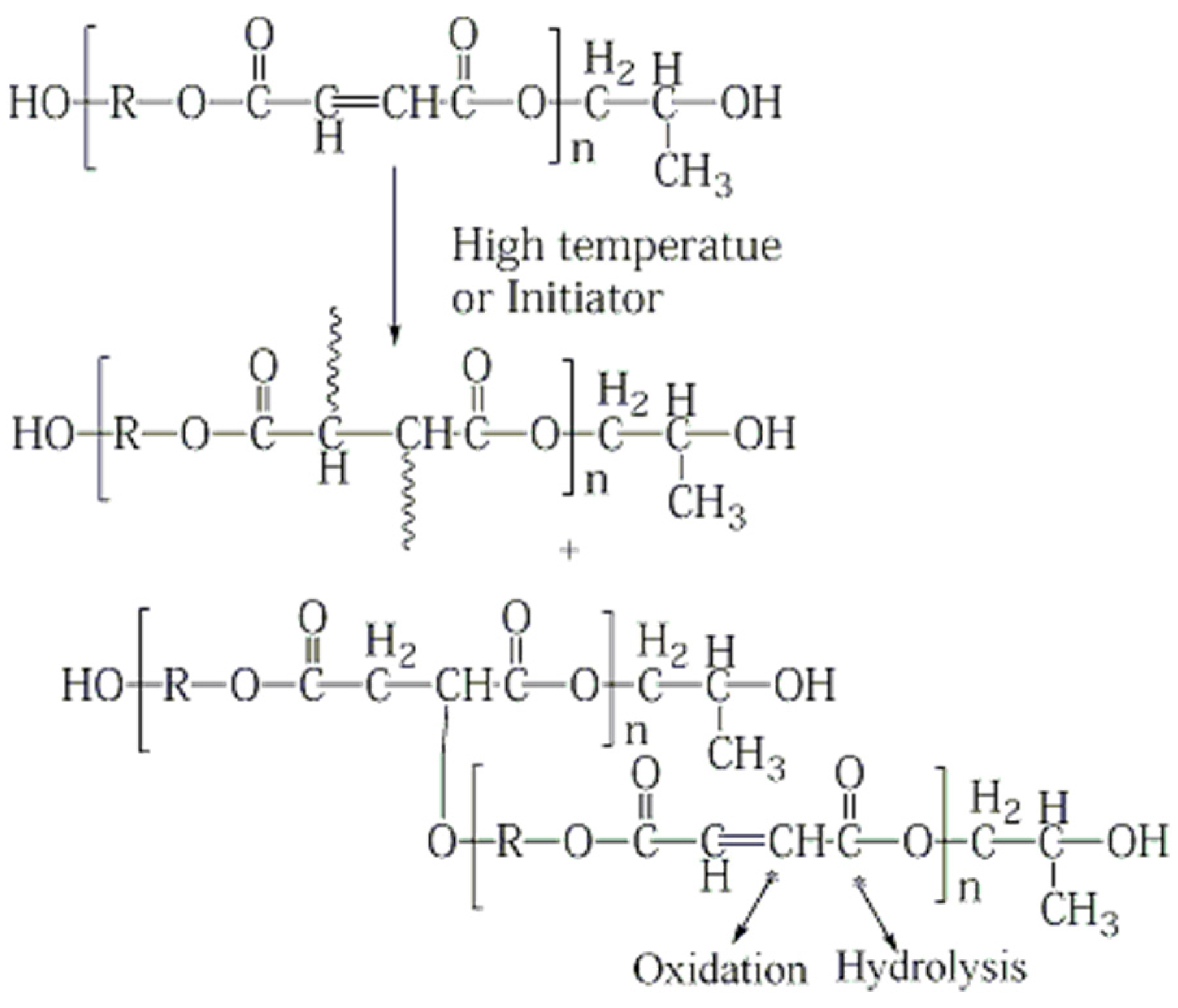
4.1. Changes of the Matrix Resin
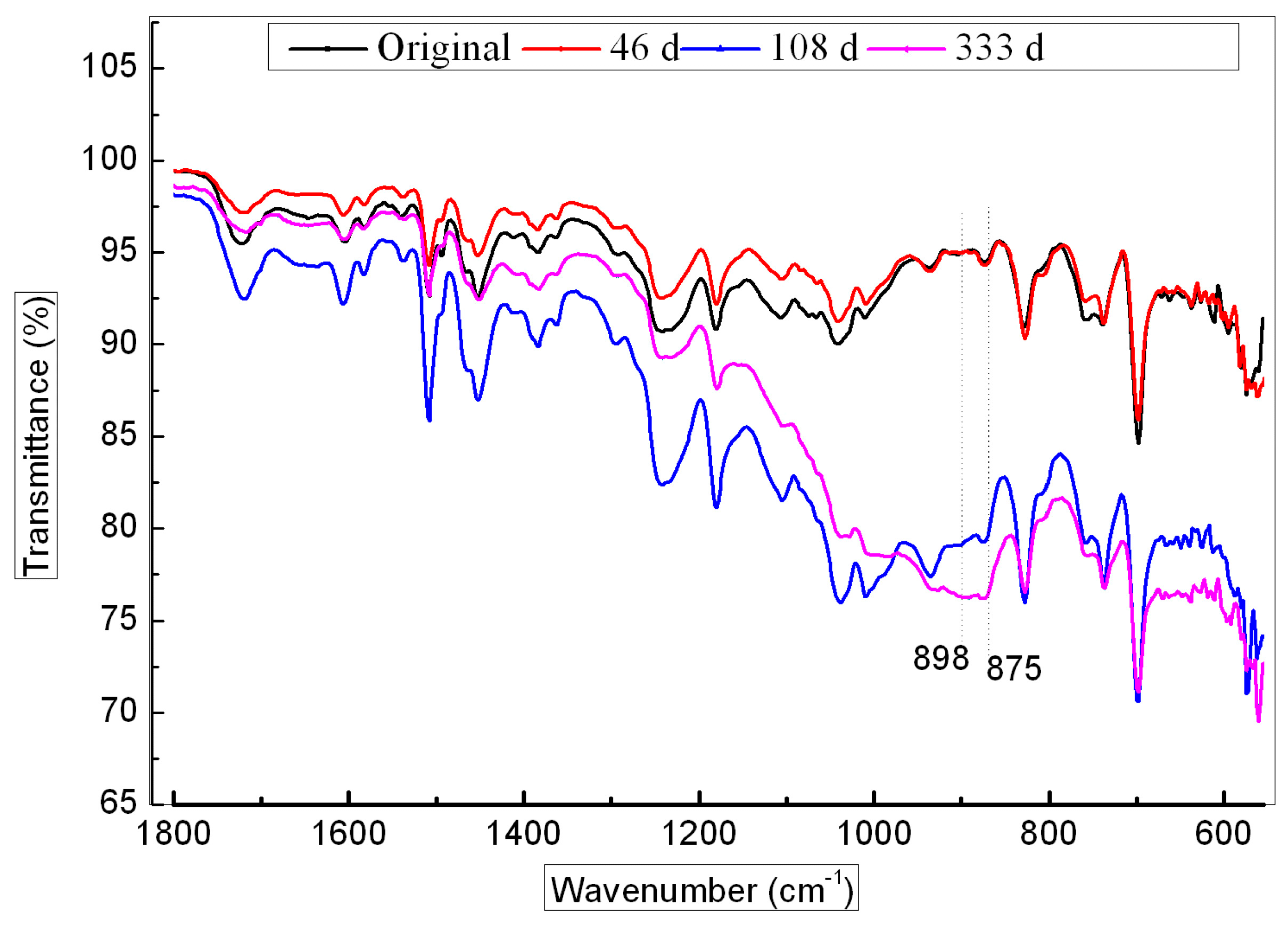
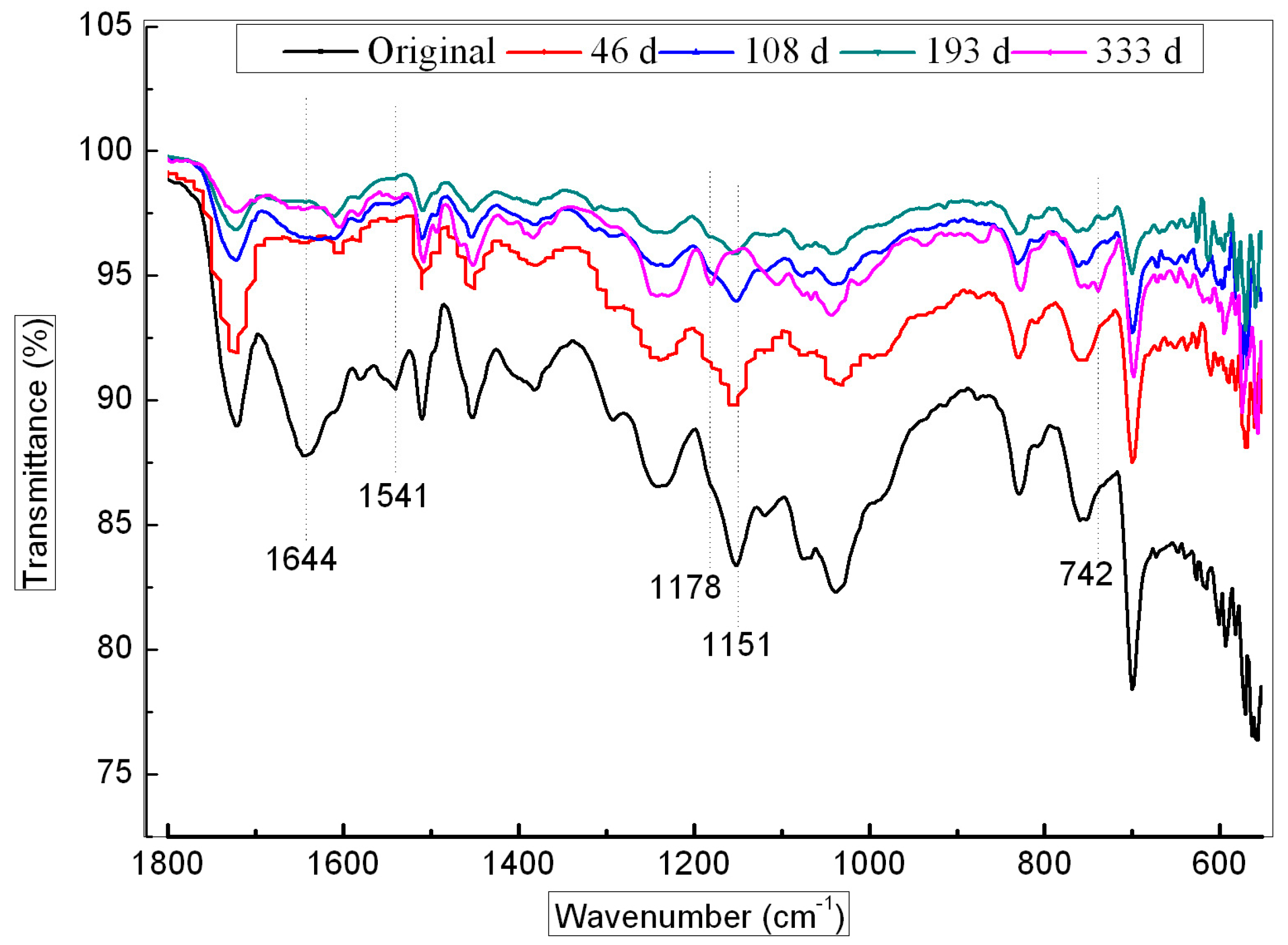
ATR-FTIR Analysis
4.2. Changes of the Glass Fiber
4.2.1. Appearance Observation
4.2.2. XPS Analysis
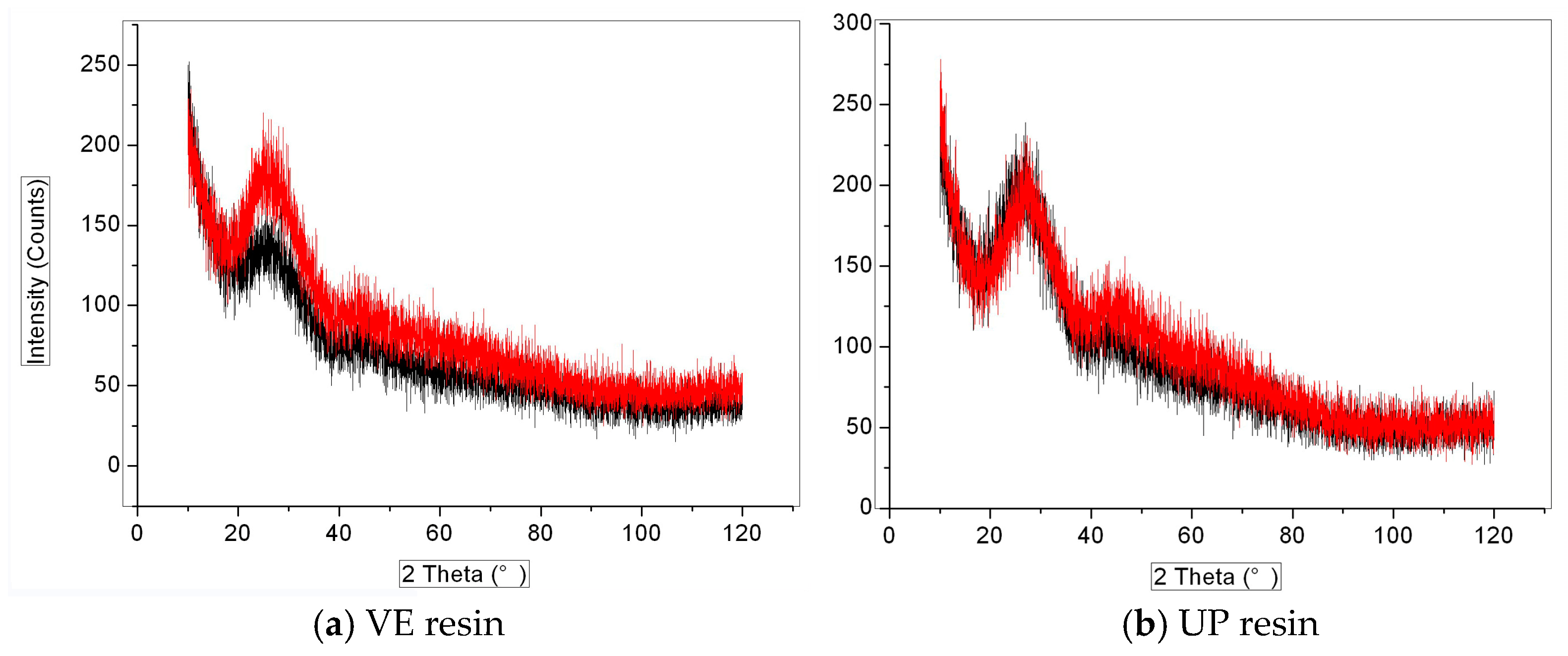
4.2.3. XRD Analysis
4.2.4. Microstructure Observation
Summary of Deterioration Reason for Glass Fiber
4.3. Changes of the Interface
5. Conclusions
- The hygrothermal environment causes performance decline, both in GF/VE and GF/UP composites. The hygrothermal environment has a stronger effect on GF/UP than on GF/VE.
- High temperature, when combined with water, has significant effects on the matrix resin and reinforcing fiber of the GF/UP composites system, despite the fiber being wrapped and bonded by the matrix resin. However, this environment mainly affects the basic resin of the GF/VE composites system, and basically does not affect the fiber. The degeneration mechanism of E-glass fiber should be investigated further.
- Analysis of the results for SEM, ATR-FTIR, DMA, TGA and mechanical properties, indicate that the degradation of the matrix resin and glass fiber are mutually promoted. The cooperating effects of heat and humidity cause the degradation of the composite system, both in the resin and the interface.
- On the one hand, the carbolic acid obtained from the hydrolysis of the resin erodes the glass fiber and accelerates its degradation. On the other hand, the product from the glass fiber corrosion promotes hydrolysis and accelerates the degradation of the resin.
- The interaction between the basic resin and reinforced fiber should be further researched. Aging mechanism and failure mode of the fiber, along with the interface between the fiber and the matrix in the aforementioned two systems, should be the primary preoccupation of further study and research.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, Q.; Jia, Z.; Li, X.; Ye, Z. Surface degradation of unsaturated polyester resin in Xe artificial weathering environment. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 4457–4460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrieta, J.S.; Richaud, E.; Fayolle, B.; Nizeyimana, F. Thermal oxidation of vinyl ester and unsaturated polyester resins. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2016, 129, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandebauer, A.; Tondi, G.; Zaske, O.C.; Goodman, S.H. Unsaturated polyester and Vinyl Ester. In Handbook of Thermoset Plastic, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 6, pp. 111–172. [Google Scholar]
- Benmokrane, B.; Ali, A.H.; Mohamed, H.M.; ElSafty, A.; Manalo, A. Laboratory assessment and durability performance of vinyl-ester, polyester, and epoxy glass-FRP bars for concrete structures. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 114, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, F.R. Unsaturated Polyester Resins. In Brydson’s Plastics Materials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 743–772. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, K.G.; Yang, L.S. Unsaturated Polyesters: Preparation, Properties and Applications of Unsaturated Polyesters. In Modern Polyesters: Chemistry and Technology of Polyesters and Copolyesters; Scheirs, J., Long, T.E., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Sun, Y.; Xie, K.; LI, H.; Duan, J.; Wang, X.; Shao, M. Long term aging and failure behaviors of carbon fiber reinforced polymer composites in simulated marine environments. Acta Mater. Compos. Sin. 2022, 39, 1353–1362. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, X.-L.; Xian, G.; Wu, G.; Singh Raman, R.K.; Al-Saadi, S. Durability study on interlaminar shear behaviour of basalt-, glass- and carbon-fibre reinforced polymer (B/G/CFRP) bars in seawater sea sand concrete environment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 156, 985–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Guo, S.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, C.; Zhu, D. A review on durability of fiber reinforced polymer (FRP) bars reinforced seawater sea sand concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 256, 119484–119500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, M.; Rizvi, M.J.; Grove, S.M.; Le, H.R. Effects of hygrothermal stress on the failure of CFRP composites. Compos. Struct. 2015, 133, 1024–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jefferson, G.D.; Farah, B.; Hempowicz, M.L.; Hsiao, K.-T. Influence of hygrothermal aging on carbon nanofiber enhanced polyester material systems. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 78, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Su, Q.; Zhu, J.; Song, X. The Aging Behavior and Life Prediction of CFRP Rods under a Hygrothermal Environment. Polymers 2023, 15, 2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghabezi, P.; Farahani, M.; Hosseini Fakhr, M. Experimental investigation of nano-alumina effect on the filling time in VARTM process. J. Fundam. Appl. Sci. 2016, 8, 925–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ghabezi, P.; Farahani, M.; Fakhr, M.H.; Abroshan, H. Investigation of Mechanical Behavior of Alfa and Gamma Nano-Alumina Epoxy Composite Made By Vartm. Int. J. Adv. Biotechnol. Res. (IJBR) 2016, 7, 731–736. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Liu, H.; Li, Y. Study on Mechanical Properties of Carbon Nanotube Reinforced Composites. Polymers 2023, 15, 3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouzakis, D.E.; Zoga, H.; Galiotis, C. Accelerated environmental ageing study of polyester/glass fiber reinforced composites (GFRPCs). Compos. Part B Eng. 2008, 39, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral-Fonseca, S.; Correia, J.R.; Rodrigues, M.P.; Branco, F.A. Artificial Accelerated Ageing of GFRP Pultruded Profiles Made of Polyester and Vinylester Resins: Characterisation of Physical–Chemical and Mechanical Damage. Strain 2011, 48, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Mella, Y.; López-Morán, T.; López-Quintela, M.A.; Lazzari, M. Durability of an industrial epoxy vinyl ester resin used for the fabrication of a contemporary art sculpture. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2014, 107, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Liu, W.; Fang, Y.; Huo, R. Influence of hygrothermal aging on the durability and interfacial performance of pultruded glass fiber-reinforced polymer composites. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 54, 2102–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Kolstein, H.; Bijlaard, F.S.K. Moisture diffusion in glass–fiber-reinforced polymer composite bridge under hot/wet environment. Compos. Part B Eng. 2013, 45, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakal, H.; Zhang, Z.; Richardson, M. Effect of water absorption on the mechanical properties of hemp fibre reinforced unsaturated polyester composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2007, 67, 1674–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errajhi, O.A.Z.; Osborne, J.R.F.; Richardson, M.O.W.; Dhakal, H.N. Water absorption characteristics of aluminised E-glass fibre reinforced unsaturated polyester composites. Compos. Struct. 2005, 71, 333–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeşil, Ö.; Asi, O. Investigation of the Water Absorption Properties of pultruded Hybrid Composite Profiles. J. Eng. Sci. 2019, 2, 48–56. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Liu, W.; Huang, Y.; Huo, R. Effects of Corrosion Depths on Flexural Properties of Glass Fiber/Unsaturated Polyester Composites in Salt Spray Environment. Acta Mater. Cmoposite Sin. 2016, 33, 1223–1233. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, R.; Li, C.; Xian, G. Water absorption and long-term thermal and mechanical properties of carbon/glass hybrid rod for bridge cable. Eng. Struct. 2023, 274, 115176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visco, A.; Brancato, V.; Campo, N. Degradation effects in polyester and vinyl ester resins induced by accelerated aging in seawater. J. Compos. Mater. 2012, 46, 2025–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benmokrane, B.; Elgabbas, F.; Ahmed, E.A.; Cousin, P. Characterization and Comparative Durability Study of Glass/Vinylester, Basalt/Vinylester, and Basalt/Epoxy FRP Bars. J. Compos. Constr. 2015, 19, 04015008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Suo, Y.; Jia, P.; Huang, F. Dispersion of Mechanical Properties of High-Strength Glass Fibre Composites in Hygrothermal Environment. Polymers 2022, 14, 3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuentes, C.A.; Ting, K.W.; Dupont-Gillain, C.; Steensma, M.; Talma, A.G.; Zuijderduin, R.; Van Vuure, A.W. Effect of humidity during manufacturing on the interfacial strength of non-pre-dried flax fibre/unsaturated polyester composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2016, 84, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautier, L.; Mortaigne, B.; Bellenger, V. Interface damage study of hydrothermally aged glass fibre-reinforced polyester composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 1999, 59, 2329–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 2574-1989; Test Method for Resistance of Glass Fiber Reinforced Plastics to Damp Heat. China Standards Press: Beijing, China, 1989.






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, D.; Sun, Y.; Duan, J.; Xie, K.; Li, J.; An, Q.; Wang, X. Hygrothermal Effect on GF/VE and GF/UP Composites: Durability Performance and Laboratory Assessment. Polymers 2024, 16, 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16050632
Wang D, Sun Y, Duan J, Xie K, Li J, An Q, Wang X. Hygrothermal Effect on GF/VE and GF/UP Composites: Durability Performance and Laboratory Assessment. Polymers. 2024; 16(5):632. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16050632
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Dengxia, Yan Sun, Jian Duan, Keyong Xie, Jikai Li, Qi An, and Xinbo Wang. 2024. "Hygrothermal Effect on GF/VE and GF/UP Composites: Durability Performance and Laboratory Assessment" Polymers 16, no. 5: 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16050632
APA StyleWang, D., Sun, Y., Duan, J., Xie, K., Li, J., An, Q., & Wang, X. (2024). Hygrothermal Effect on GF/VE and GF/UP Composites: Durability Performance and Laboratory Assessment. Polymers, 16(5), 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16050632




