Mechanical Properties and Degradation Rate of Poly(Sorbitol Adipate-Co-Dioladipate) Copolymers Obtained with a Catalyst-Free Melt Polycondensation Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
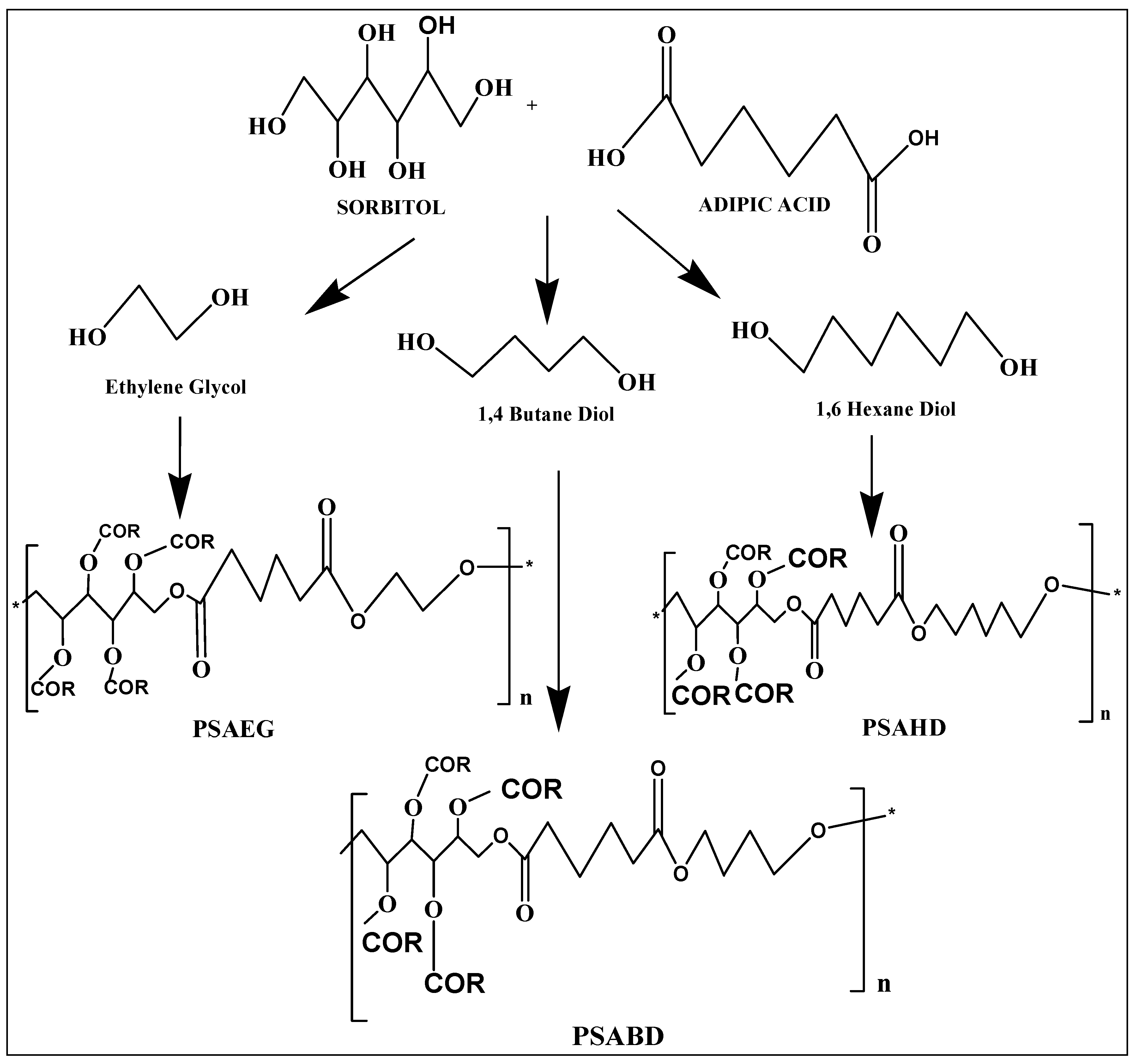
2.2. Synthesis of Copolymer Samples
2.3. Characterization
2.3.1. Solubility Test
2.3.2. Analysis by Use of FTIR Spectrometry (Fourier-Transform Infrared)
2.3.3. Spectroscopic Analysis Using Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
2.3.4. Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-MASS) Analysis
2.3.5. Thermal Analysis
2.3.6. In Vitro Degradation of Polymers
2.3.7. Polymer Sol Concentrations and Swelling Properties in DMSO and Water
2.3.8. Mechanical Properties
2.3.9. Scanning Electron Microscope
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Solubility Studies
3.2. Analysis Using Fourier-Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectrometry
3.3. Spectroscopic Analysis of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR)
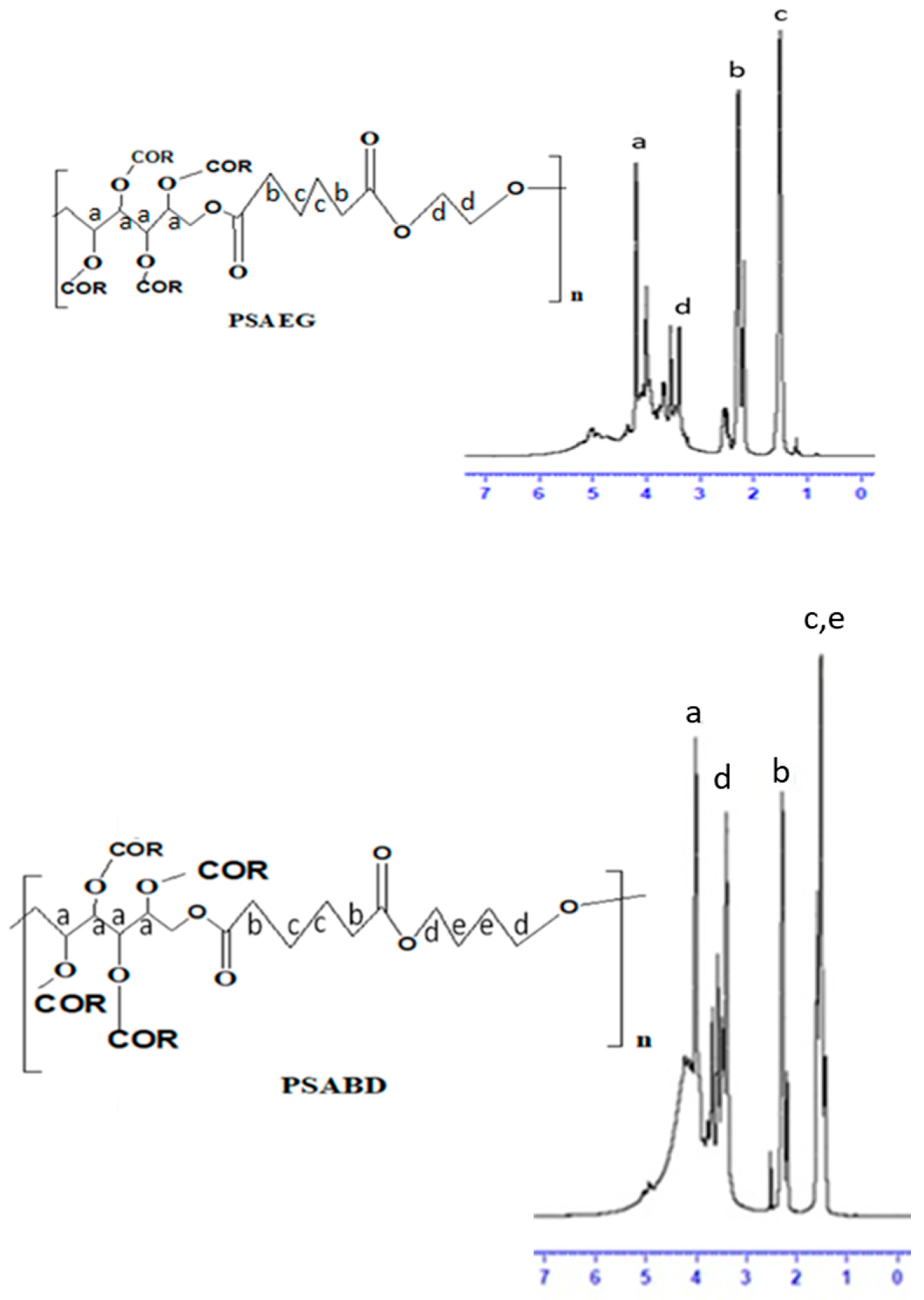
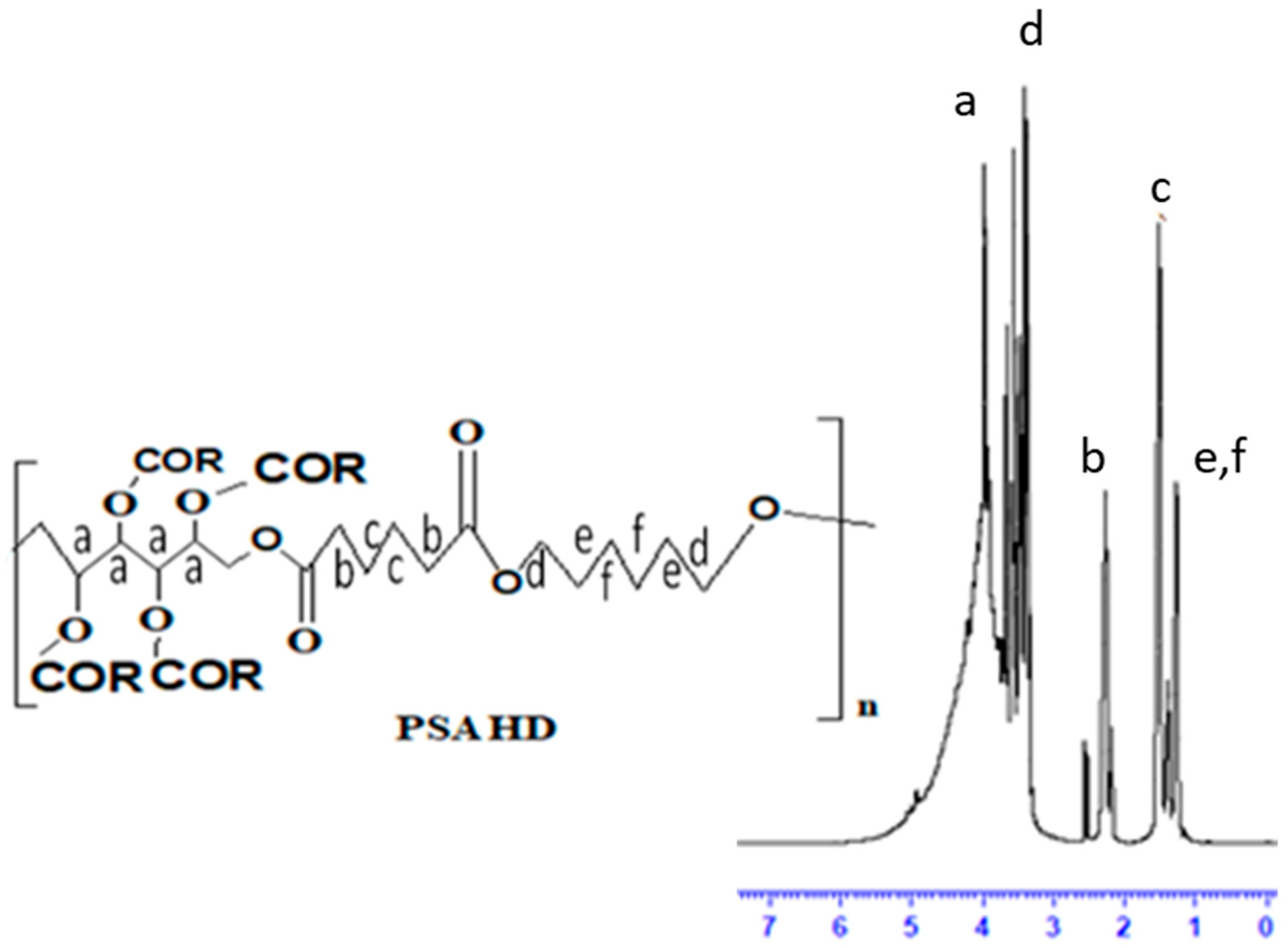
3.3.1. 1H NMR Analysis
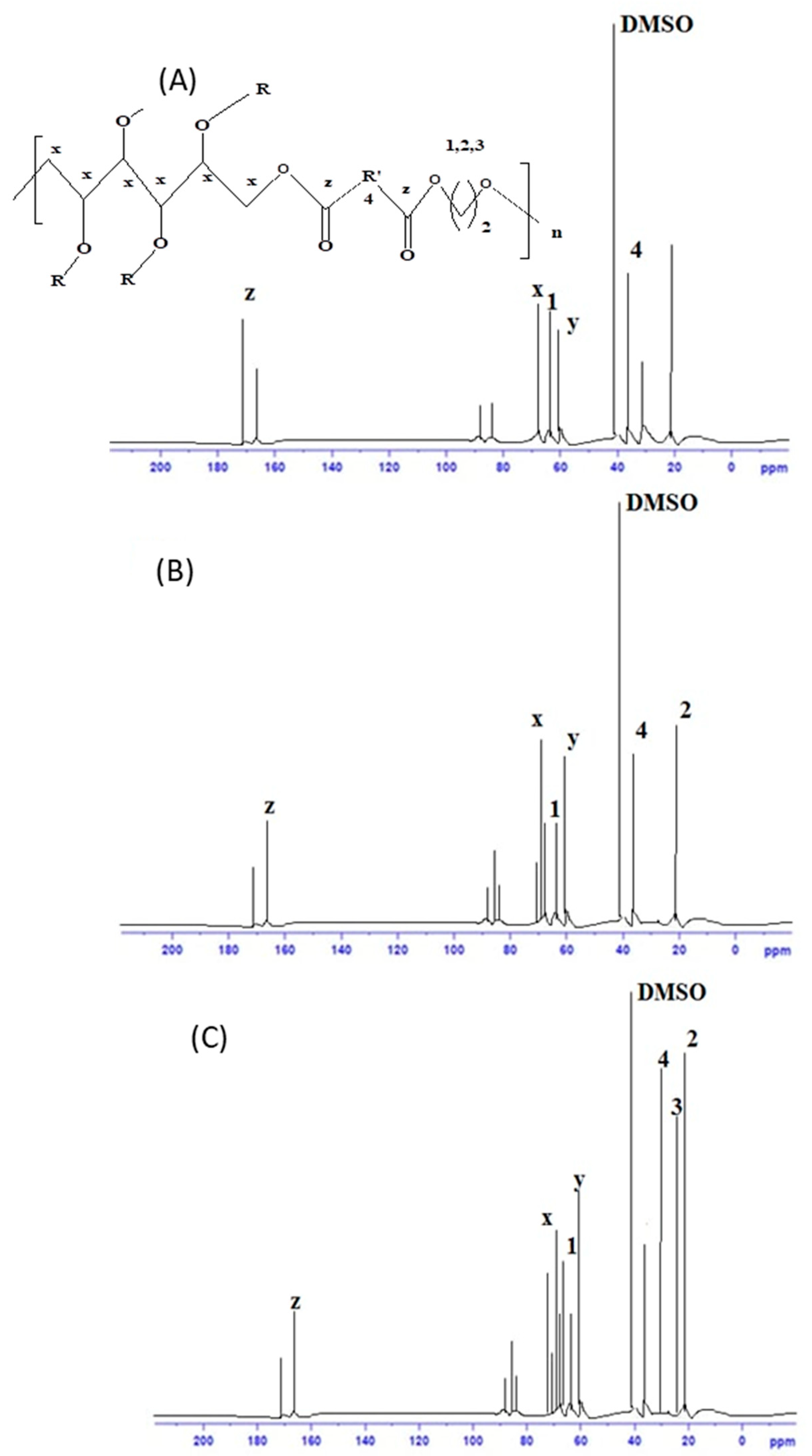
3.3.2. 13C NMR Analysis
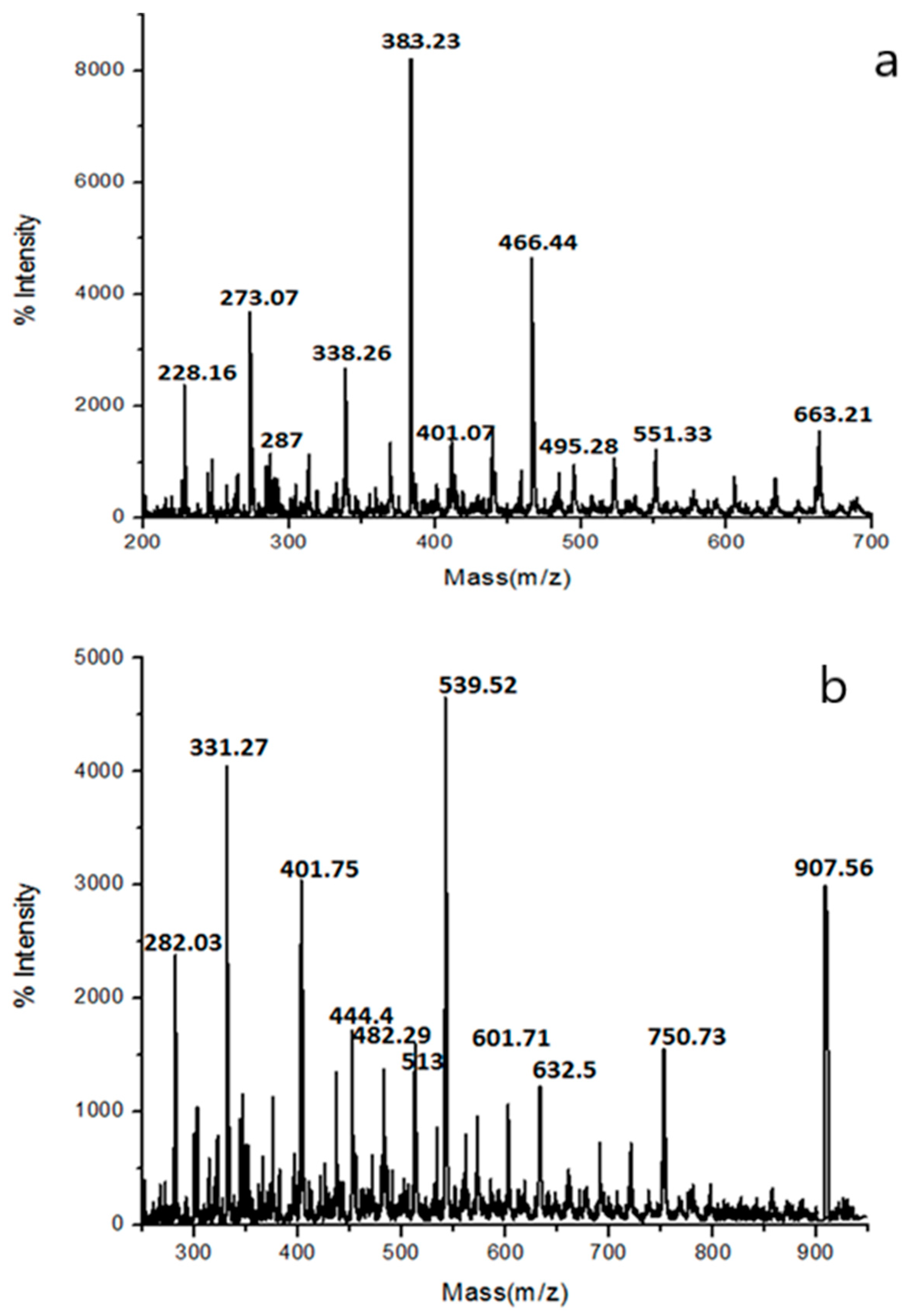
3.3.3. Molecular Weight and Structural Composition Analysis by MALDI-MASS Spectroscopy
3.4. Thermal Analysis
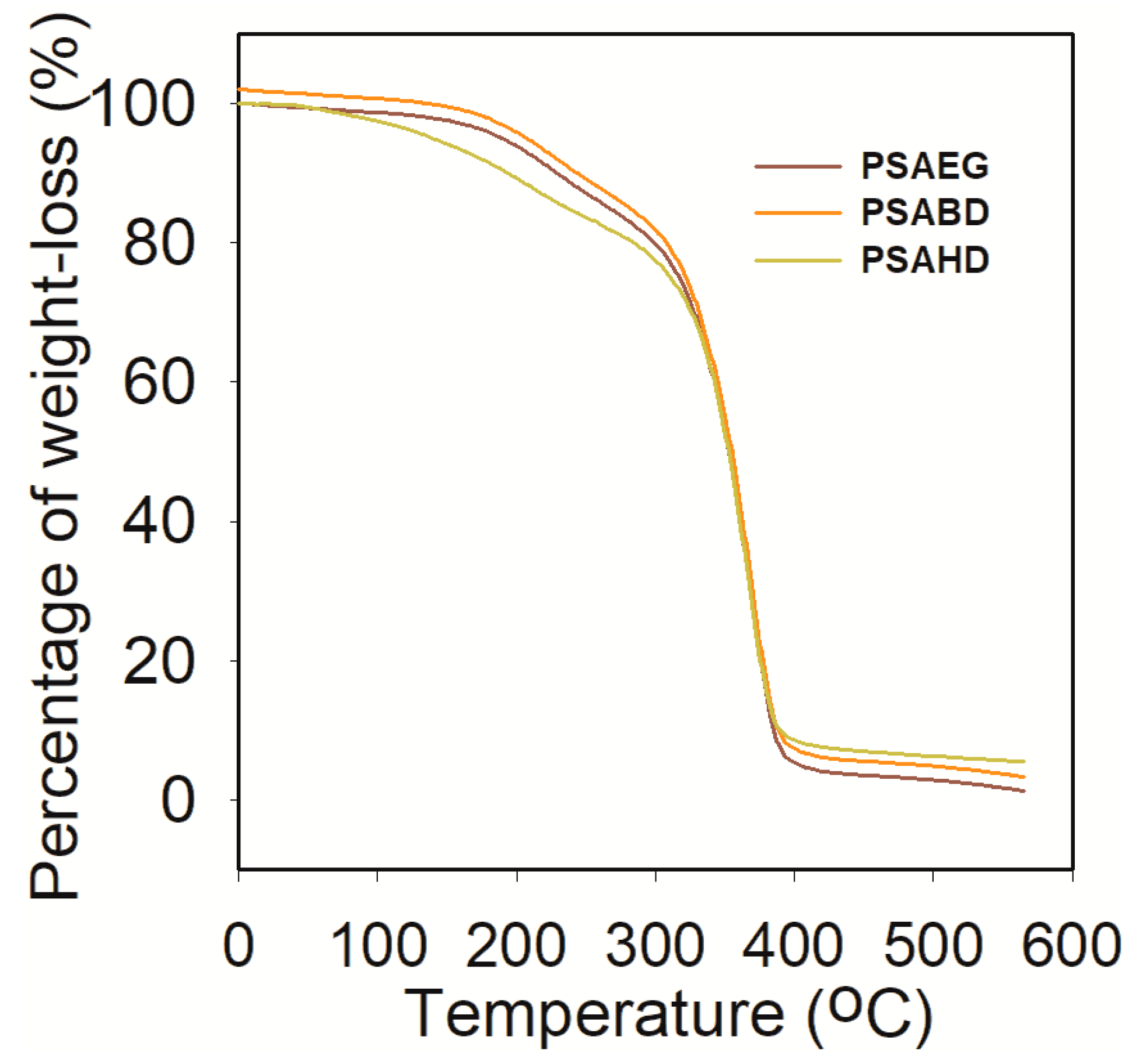
3.4.1. Thermo gravimetric Analysis
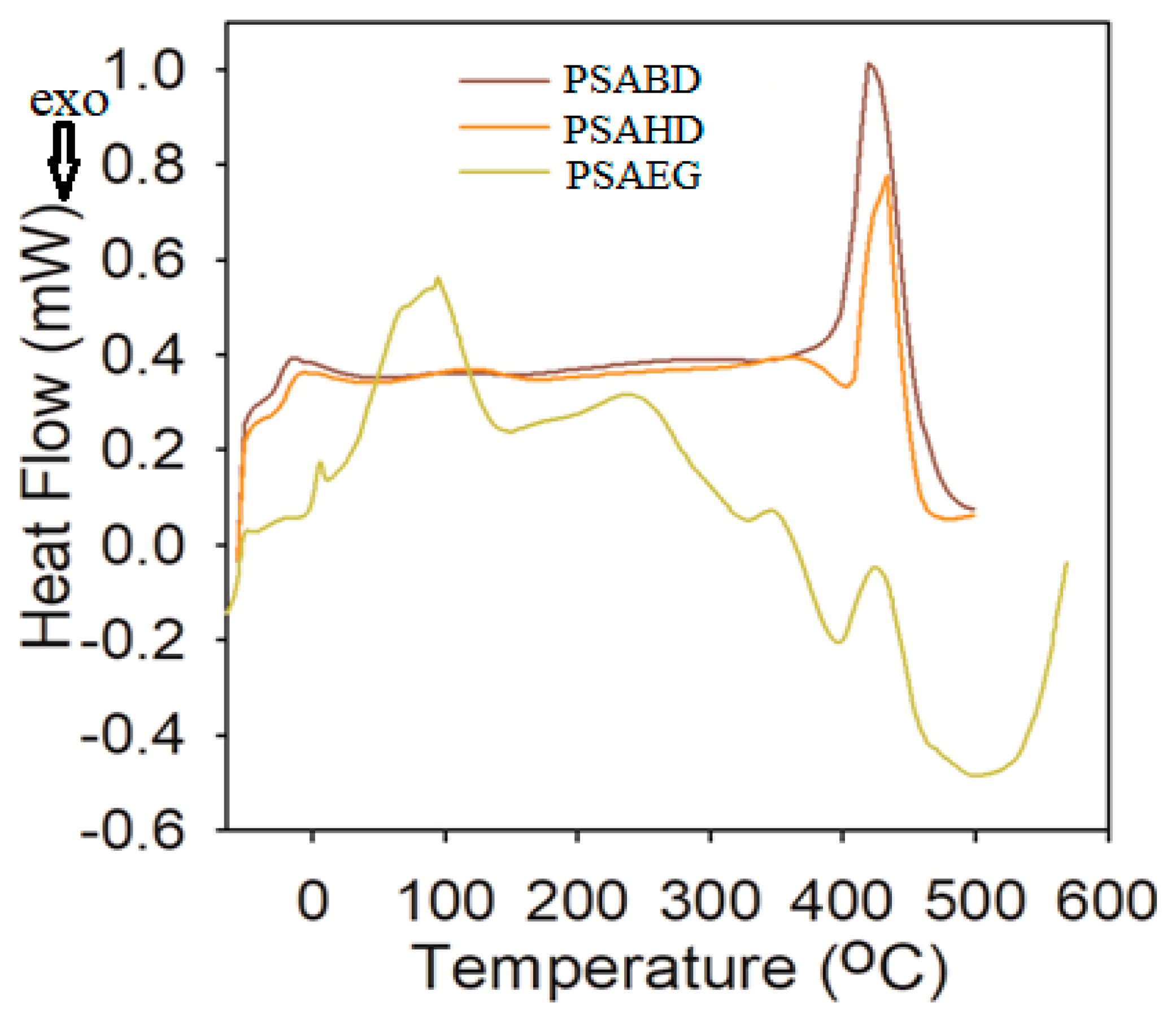
3.4.2. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
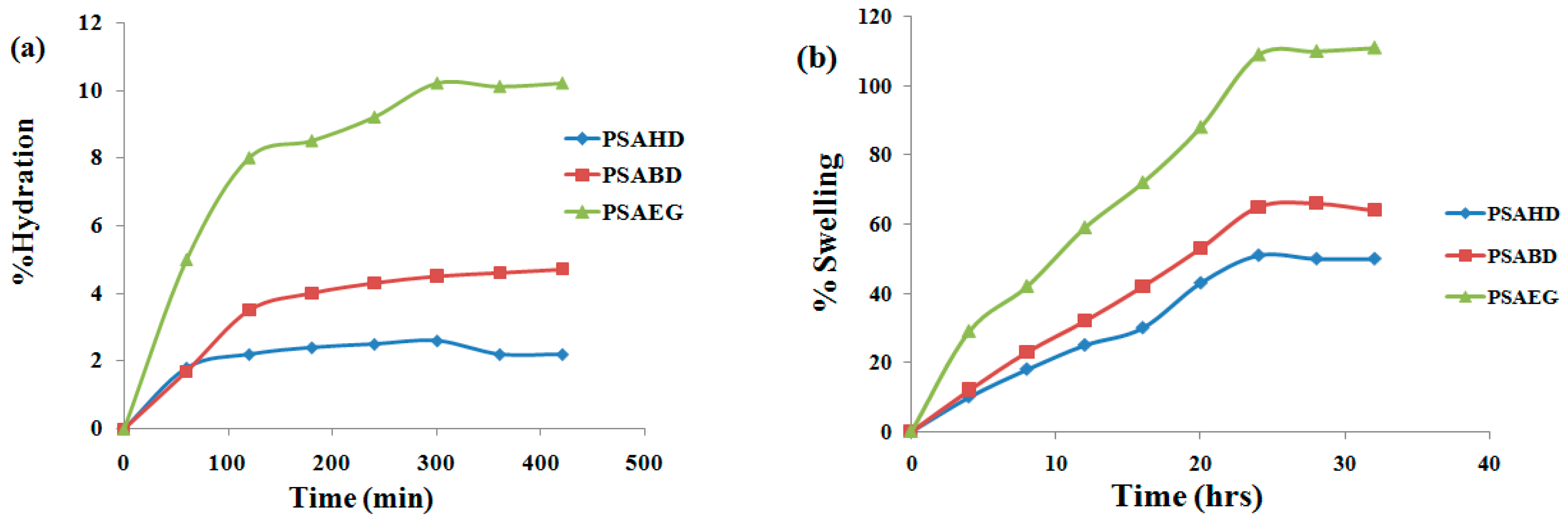
3.5. Swelling Studies of Elastomers in Water and DMSO
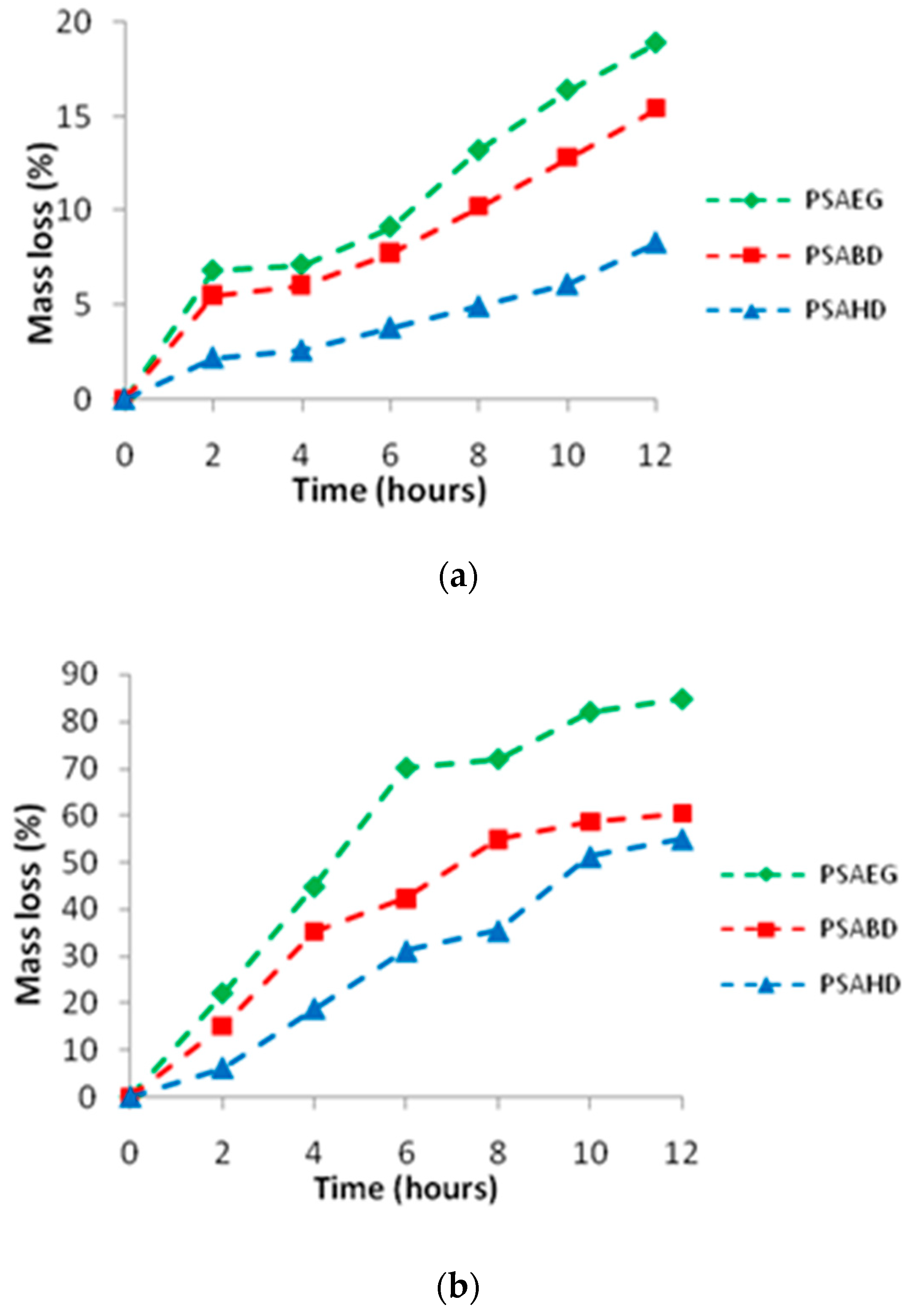
3.6. In Vitro Degradation of Copolymers
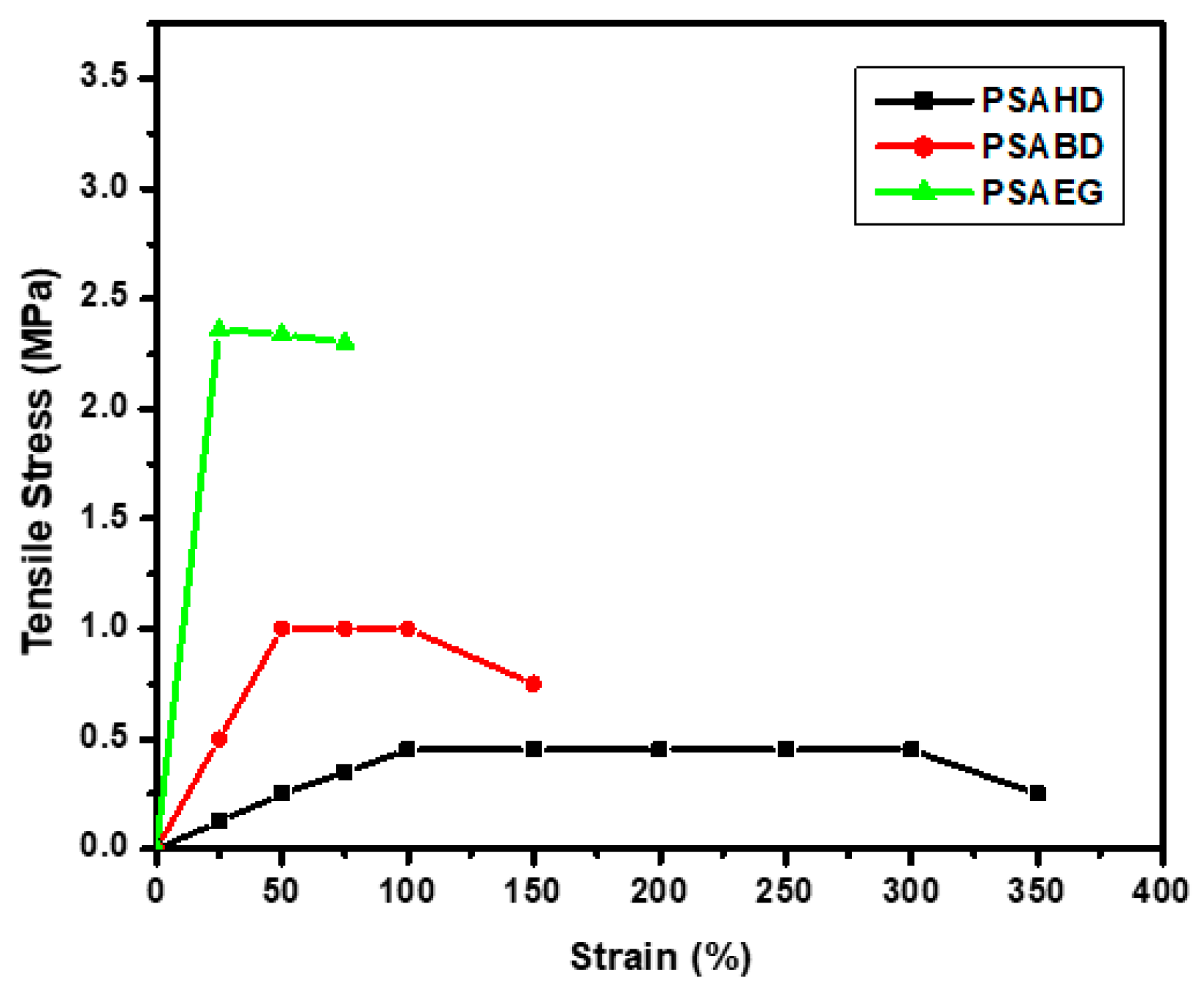
3.7. Mechanical Properties
3.8. Scanning Electron Microscopy
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Geyer, R.; Jambeck, J.R.; Law, K.L. Production, use, and fate of all plastics ever made. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1700782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ghoul, Y.; Alminderej, F.M.; Alsubaie, F.M.; Alrasheed, R.; Almousa, N.H. Recent Advances in Functional Polymer Materials for Energy, Water, and Biomedical Applications: A Review. Polymers 2021, 13, 4327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Ma, P.X. Synthetic biodegradable functional polymers for tissue engineering: A brief review. Sci. China Chem. 2014, 57, 490–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laycock, B.; Pratt, S.; Halley, P. A perspective on biodegradable polymer biocomposites—From processing to degradation. Funct. Compos. Mater. 2023, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.C.; Tse, H.F.; Fok, L. Plastic waste in the marine environment: A review of sources, occurrence and effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566–567, 333–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miloloža, M.; KučićGrgić, D.; Bolanča, T.; Ukić, Š.; Cvetnić, M.; OcelićBulatović, V.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Kušić, H. Ecotoxicological Assessment of Microplastics in Freshwater Sources—A Review. Water 2021, 13, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanase, L.I.; Salhi, S.; Cucoveica, O.; Ponjavic, M.; Nikodinovic-Runic, J.; Delaite, C. Biodegradability Assessment of Polyester Copolymers Based on Poly(ethylene adipate) and Poly(ε-caprolactone). Polymers 2022, 14, 3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivito, F.; Jagdale, P.; Oza, G. Synthesis and Biodegradation Test of a New Polyether Polyurethane Foam Produced from PEG 400, L-Lysine Ethyl Ester Diisocyanate (L-LDI) and Bis-hydroxymethyl Furan (BHMF). Toxics 2023, 11, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, L.; Dai, H. A Highly Hydrophilic and Biodegradable Novel Poly(amide-imide) for Biomedical Applications. Polymers 2016, 8, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damodaran, V.B.; Bhatnagar, D.; Murthy, N.S. Biomedical Polymers: Processing. In Biomedical Polymers; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 55–71. [Google Scholar]
- Morganti, P.; Febo, P.; Cardillo, M.; Donnarumma, G.; Baroni, A. Chitin nanofibril and nanolignin: Natural polymers of biomedical interest. J. Clin. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2017, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samir, A.; Ashour, F.H.; Hakim, A.A.A.; Bassyouni, M. Recent advances in biodegradable polymers for sustainable applications. Npj Mater. Degrad. 2022, 6, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rydz, J.; Zawidlak-Węgrzyńska, B.; Christova, D. Degradable polymers. In Encyclopedia of Biomedical Polymers and Polymeric Biomaterials; Mishra, M.K., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Ratón, FL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kavimani, V.; Jaisankar, V. Synthesis and characterization of sorbitol based copolyesters for biomedical applications. J. Phys. Sci. Appl. 2014, 4, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, Y.; Ma, J.; Bei, J.; Wang, S. Surface Modification of Aliphatic Polyester to Enhance Biocompatibility. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salhi, S.; Mahfoudh, J.; Abid, S.; Atanase, L.I.; Popa, M.; Delaite, C. Random poly(ε-caprolactone-L-alanine) by direct melt copolymerization. Polym. Int. 2020, 69, 1161–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortman, D.J.; Brutman, J.P.; De Hoe, G.X.; Snyder, R.L.; Dichtel, W.R.; Hillmyer, M.A. Approaches to sustainable and continually recyclable cross-linked polymers. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 11145–11159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, K.; Sánchez-Leija, R.J.; Gross, R.A.; Linhardt, R.J. Review on the Impact of Polyols on the Properties of Bio-Based Polyesters. Polymers 2020, 12, 2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavimani, V.; Jaisankar, V. Design, Synthesis and Characterization of Biodegradable Sorbitol Elastomers with Tunable Mechanical and Degradation Properties. Indian J. Adv. Chem. Sci. 2015, 3, 192–197. [Google Scholar]
- Pasupuleti, S.; Madras, G. Synthesis and degradation of sorbitol-based polymers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 121, 2861–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tham, W.H.; Wahit, M.U.; Kadir, M.R.A.; Wong, T.W. Biodegradable hydroxyapatite/poly (sorbitol sebacate malate) composites: Mechanical and thermal properties. Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 2013, 35, 57–61. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, W.; Li, T.; Xiang, S.; Ma, P.; Chen, M. Influence of Glutamic Acid on the Properties of Poly(xylitol glutamate sebacate) Bioelastomer. Polymers 2013, 5, 1339–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, H.; Golitsyn, Y.; Bilal, M.H.; Mäder, K.; Reichert, D.; Kressler, J. Polymer Networks Synthesized from Poly(Sorbitol Adipate) and Functionalized Poly(Ethylene Glycol). Gels 2021, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruggeman, J.P.; de Bruin, B.J.; Bettinger, C.J.; Langer, R. Biodegradable poly(polyolsebacate) polymers. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 4726–4735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasupuleti, S.; Avadanam, A.; Madras, G. Synthesis, characterization, and degradation of biodegradable poly (mannitol citric dicarboxylate) copolyesters. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2011, 51, 2035–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, M.A.R.; Schubert, U.S. Evaluation of a new multiple-layer spotting technique for matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry of synthetic polymers. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2003, 17, 713–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustini, L.; Noordover, B.A.J.; Gehrels, C.; Dietz, C.; Koning, C.E. Enzymatic synthesis and preliminary evaluation as coating of sorbitol-based, hydroxy-functional polyesters with controlled molecular weights. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 67, 459–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piątek-Hnat, M. Influence of the addition of citric acid on the physico-chemical properties of poly(sorbitol sebacate-co- butylene sebacate). Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2018, 9, 1092–1094. [Google Scholar]
- Nijst, C.L.; Bruggeman, J.P.; Karp, J.M.; Ferreira, L.; Zumbuehl, A.; Bettinger, C.J.; Langer, R. Synthesis and characterization of photocurable elastomers from poly(glycerol-co-sebacate). Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 3067–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepa, K.; Jaisankar, V. Synthesis and characterisation of antihyperglycemic drug delivery applications of certain xylitol based copolyester. Trends Biomater. Artif. Organs. 2018, 32, 105–110. [Google Scholar]
- Barrett, D.G.; Luo, W.; Yousaf, M.N. Aliphatic polyester elastomers derived from erythritol and α, ω-diacids. Polym. Chem. 2010, 1, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piątek-Hnat, M.; Bomba, K.; Pęksiński, J. Structure and Properties of Biodegradable Poly (Xylitol Sebacate-Co-Butylene Sebacate) Copolyester. Molecules 2020, 25, 1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Z.; Cao, H.; Gao, J.; Shin, P.H.; Day, B.W.; Wang, Y. A functionalizable polyester with free hydroxyl groups and tunable physiochemical and biological properties. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 3129–3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Huang, W.; Cook, W.D.; Chen, Q. A comparative study on poly(xylitol sebacate) and poly(glycerol sebacate): Mechanical properties, biodegradation and cytocompatibility. Biomed. Mater. 2013, 8, 035006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Chen, Y.; Chao, C.A.; Wu, Y.L.; Wang, Y. Control the Mechanical Properties and Degradation of Poly(Glycerol Sebacate) by Substitution of the Hydroxyl Groups with Palmitates. Macromol. Biosci. 2020, 20, e2000101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risley, B.B.; Ding, X.; Chen, Y.; Miller, P.G.; Wang, Y. Citrate CrosslinkedPoly(Glycerol Sebacate) with Tunable Elastomeric Properties. Macromol. Biosci. 2021, 21, e2000301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hong, A.T.; Naskar, N.; Chung, H.J. Criteria for Quick and Consistent Synthesis of Poly(glycerol sebacate) for Tailored Mechanical Properties. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 1525–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruggeman, J.P.; Bettinger, C.J.; Langer, R. Biodegradable xylitol-based elastomers: In vivo behavior and biocompatibility. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2010, 95, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample | DMSO | 1,4 Dioxane | Acetone | CHCl3 | Ethanol | Methanol | Water |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSAEG | +++ | +++ | ++ | +++ | −−− | −−− | −−− |
| PSABD | +++ | +++ | ++ | +++ | −−− | −−− | −−− |
| PSAHD | +++ | +++ | ++ | +++ | −−− | −−− | −−− |
| Samples | Composition | m/z | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Experimental | Theoretical | ||
| PSAEG | P(A1EG1)-2Na | 226.16 | 228.16 |
| P(A1EG1)-4Na | 272.16 | 273.07 | |
| P(A1EG2)-2Na | 288.23 | 287.00 | |
| P(A1EG2)-4Na | 334.23 | 338.26 | |
| P(S1A1EG1)-Na | 385.3 | 383.23 | |
| P(A2EG2)-2Na | 406.32 | 401.07 | |
| P(S1A1EG2)-2Na | 470.37 | 466.44 | |
| PSAHD | P(A1HD1)-2Na | 282.03 | 282.29 |
| P(A1HD1)-4Na | 331.27 | 328.29 | |
| P(S1A1HD1)-Na | 444.4 | 441.46 | |
| P(S1A1HD1)-4Na | 513.39 | 510.46 | |
| P(S1A2HD)-4Na | 632.5 | 628.55 | |
| P(S1A2HD2)-4Na | 750.73 | 746.75 | |
| P(S2A2HD2)-Na | 907.56 | 911.04 | |
| Sample | Td under Nitrogen Atmosphere (°C) | Residual Sample at 594.9 °C (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tonset (°C) | T25% (°C) | T50% (°C) | T75% (°C) | Tmax (°C) | ||
| PSAEG | 34.8 | 310.7 | 381.3 | 406.1 | 402.5 | 0.97 |
| PSABD | 34.8 | 313.8 | 382.7 | 406.1 | 403.4 | 2.74 |
| PSAHD | 34.8 | 314.7 | 382.0 | 406.1 | 399.4 | 5.21 |
| Sample | Tg (°C) |
|---|---|
| PSAEG | −59.2 |
| PSABD | −28.4 |
| PSAHD | −23.7 |
| Sample | Sol Content (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Water | DMSO | |
| PSAEG | 12.0 | 11.2 |
| PSABD | 10.9 | 5.8 |
| PSAHD | 6.8 | 2.51 |
| Sample | Young’s Modulus (MPa) | Tensile Stress (MPa) | Cross-Link Density n × 103 (mol/m3) | Elongation at Break (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSAEG | 3.44 ± 0.03 | 2.36 ± 0.02 | 22.23 ± 0.03 | 62 ± 2 |
| PSABD | 0.25 ± 0.01 | 1.05 ± 0.02 | 13.1 ± 0.02 | 142 ± 3 |
| PSAHD | 0.09 ± 0.01 | 0.46 ± 0.01 | 11.4 ± 0.02 | 308 ± 5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kavimani, V.; Lakkaboyana, S.K.; Trilaksana, H.; Atanase, L.I. Mechanical Properties and Degradation Rate of Poly(Sorbitol Adipate-Co-Dioladipate) Copolymers Obtained with a Catalyst-Free Melt Polycondensation Method. Polymers 2024, 16, 499. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16040499
Kavimani V, Lakkaboyana SK, Trilaksana H, Atanase LI. Mechanical Properties and Degradation Rate of Poly(Sorbitol Adipate-Co-Dioladipate) Copolymers Obtained with a Catalyst-Free Melt Polycondensation Method. Polymers. 2024; 16(4):499. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16040499
Chicago/Turabian StyleKavimani, V., Sivarama Krishna Lakkaboyana, Herri Trilaksana, and Leonard I. Atanase. 2024. "Mechanical Properties and Degradation Rate of Poly(Sorbitol Adipate-Co-Dioladipate) Copolymers Obtained with a Catalyst-Free Melt Polycondensation Method" Polymers 16, no. 4: 499. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16040499
APA StyleKavimani, V., Lakkaboyana, S. K., Trilaksana, H., & Atanase, L. I. (2024). Mechanical Properties and Degradation Rate of Poly(Sorbitol Adipate-Co-Dioladipate) Copolymers Obtained with a Catalyst-Free Melt Polycondensation Method. Polymers, 16(4), 499. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16040499






