The Development and Performance of Knitted Cool Fabric Based on Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Materials
2.2. Fabric Structure Design and Preparation
2.3. Fabric Property Test
2.3.1. Air Permeability
2.3.2. Moisture Permeability
2.3.3. Moisture Absorption and Humidity Conduction
2.3.4. Thermal Property
2.3.5. Contact Cool Feeling Property
3. Results and Discussion
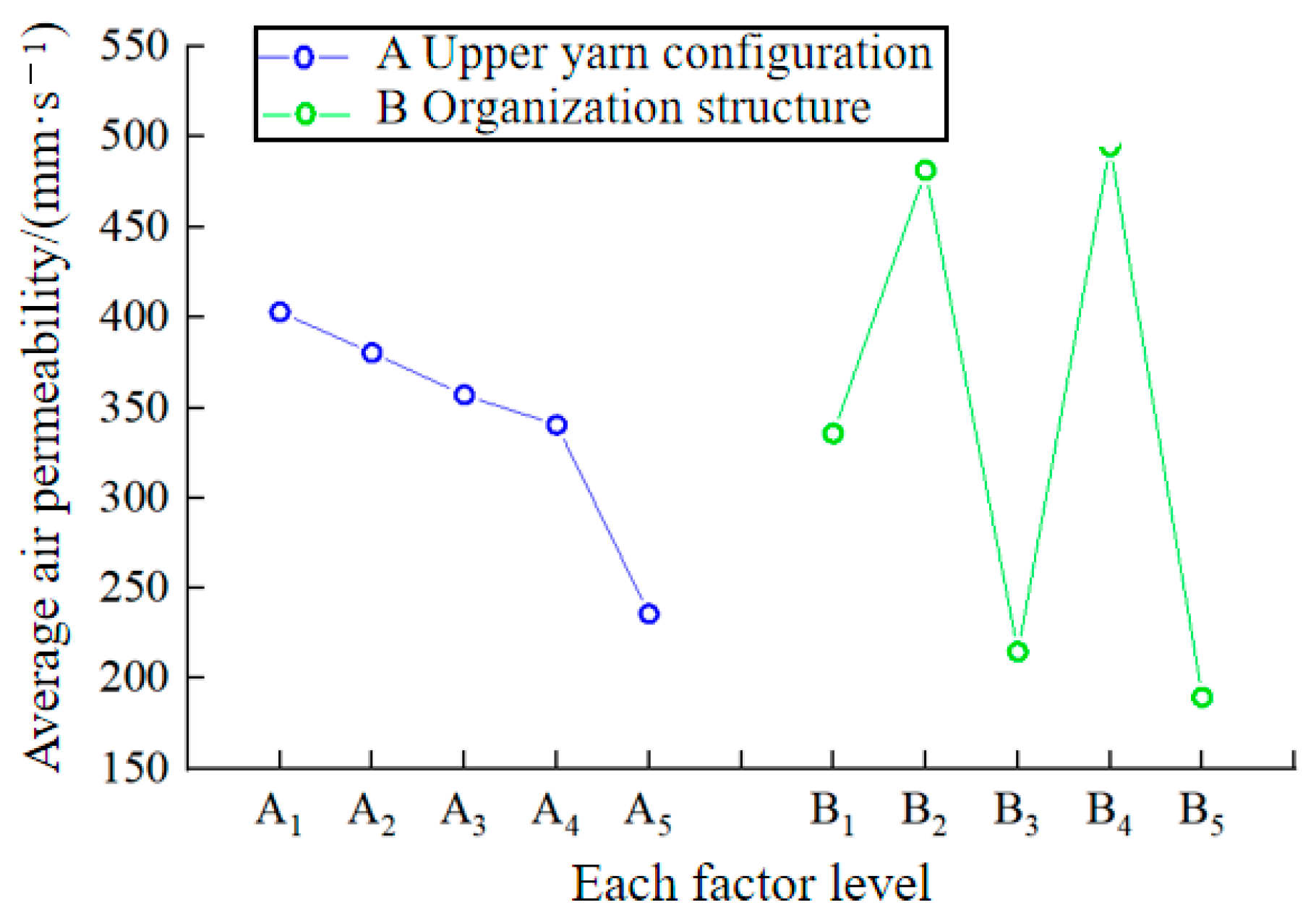
3.1. Air Permeability
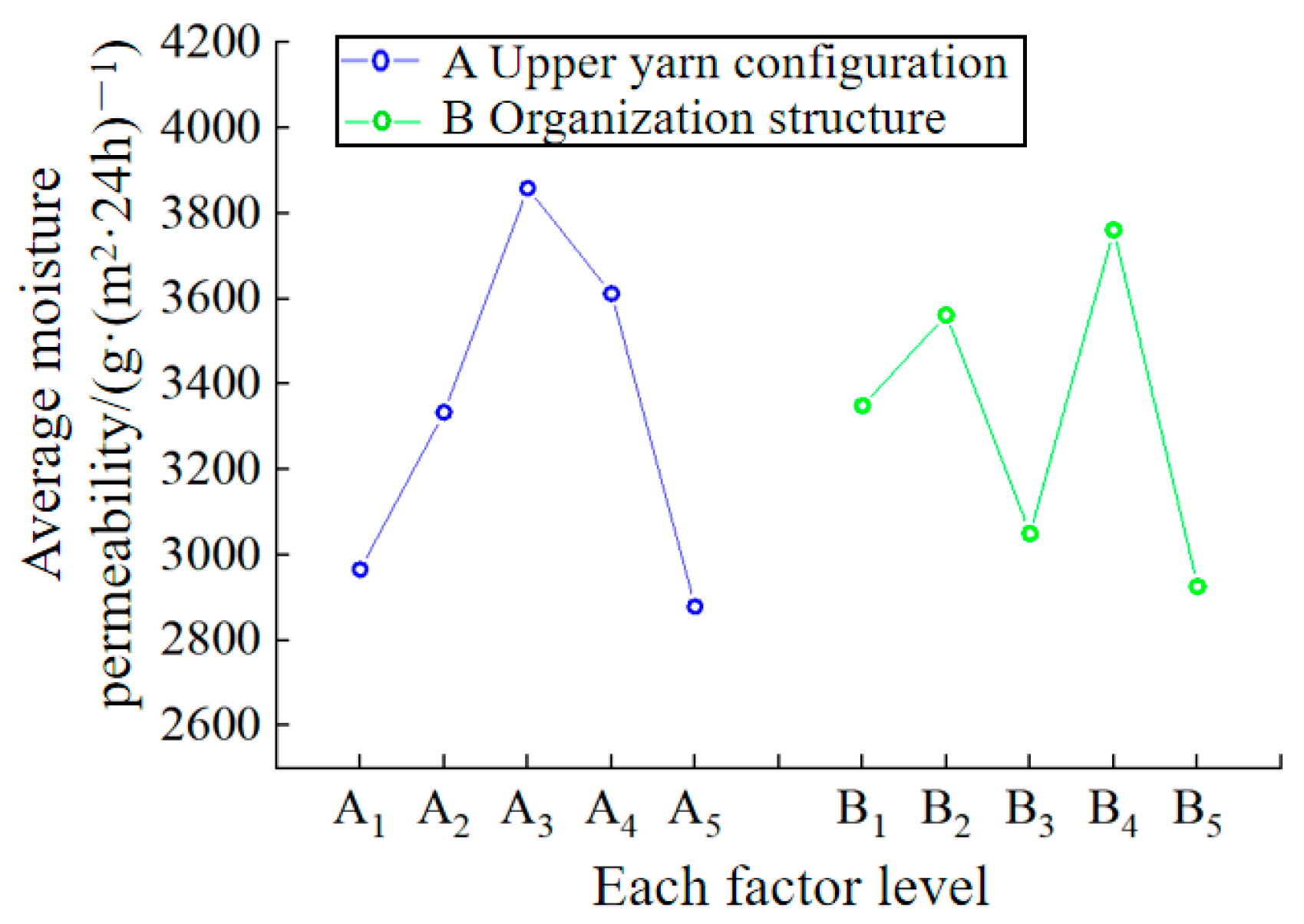
3.2. Moisture Permeability
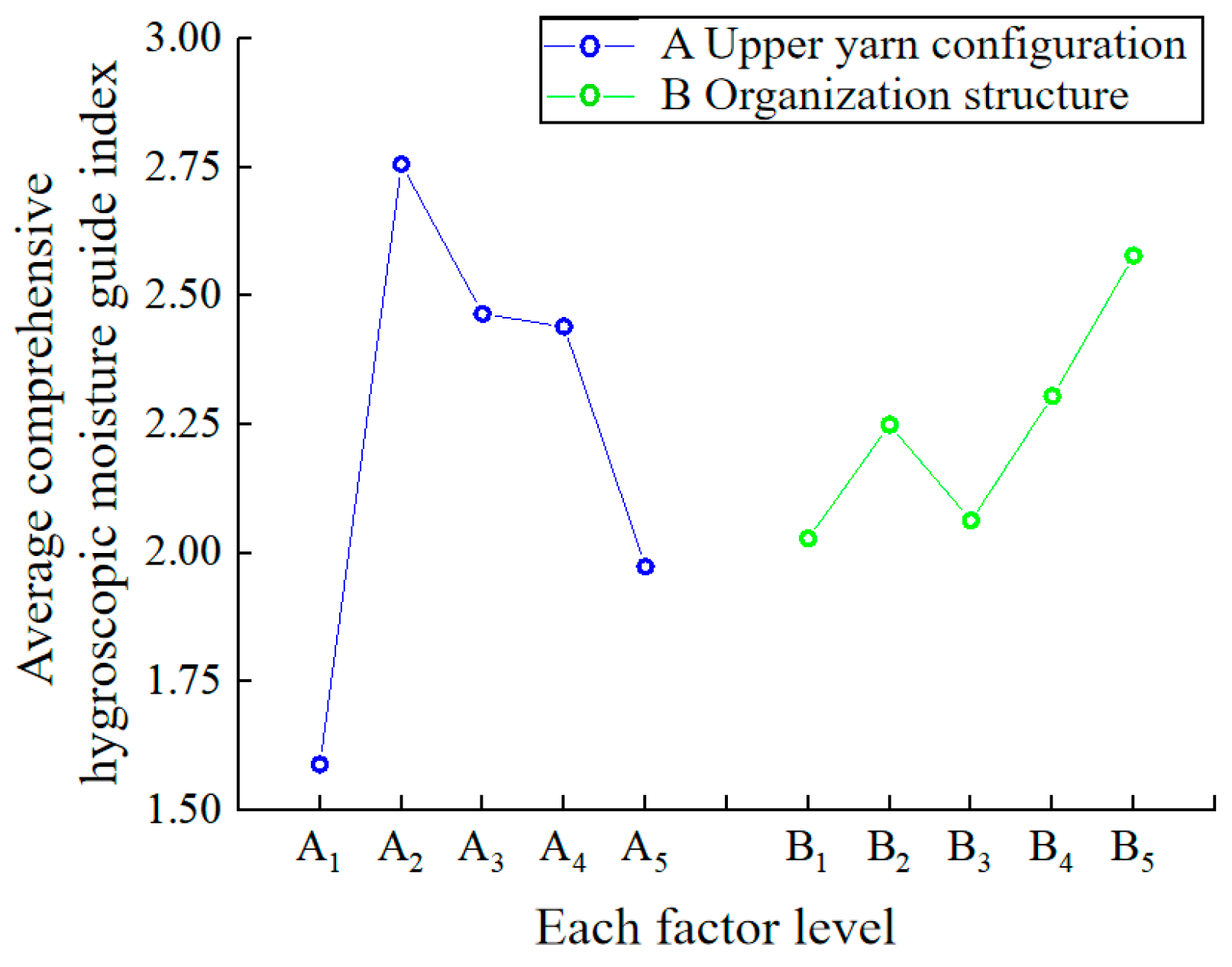
3.3. Moisture Absorption and Humidity Conduction
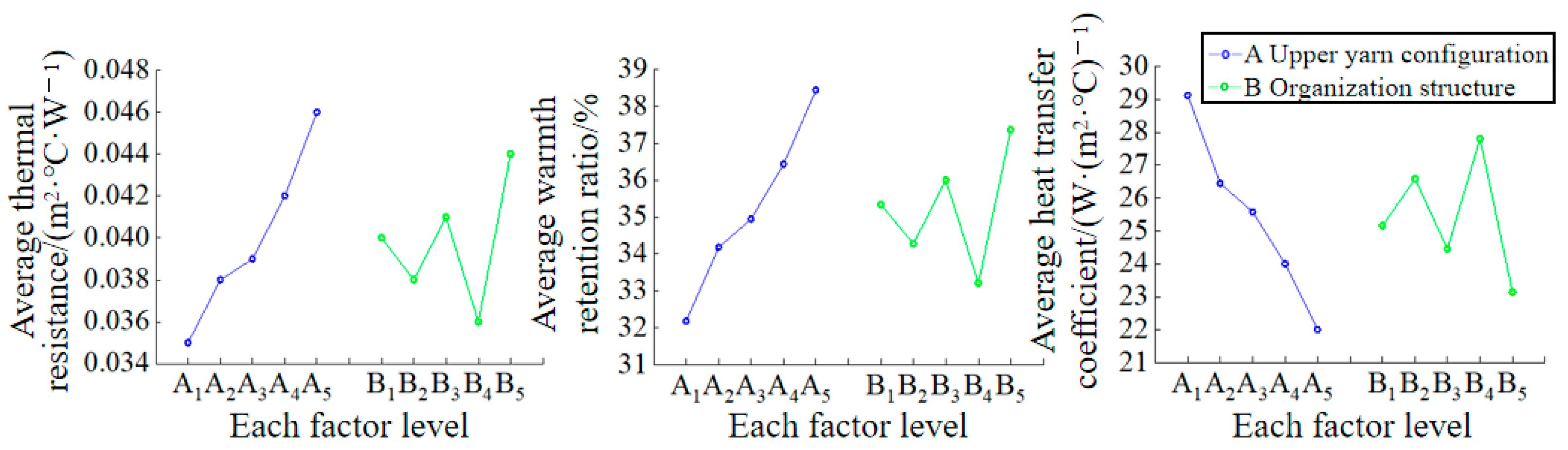
3.4. Thermal Property
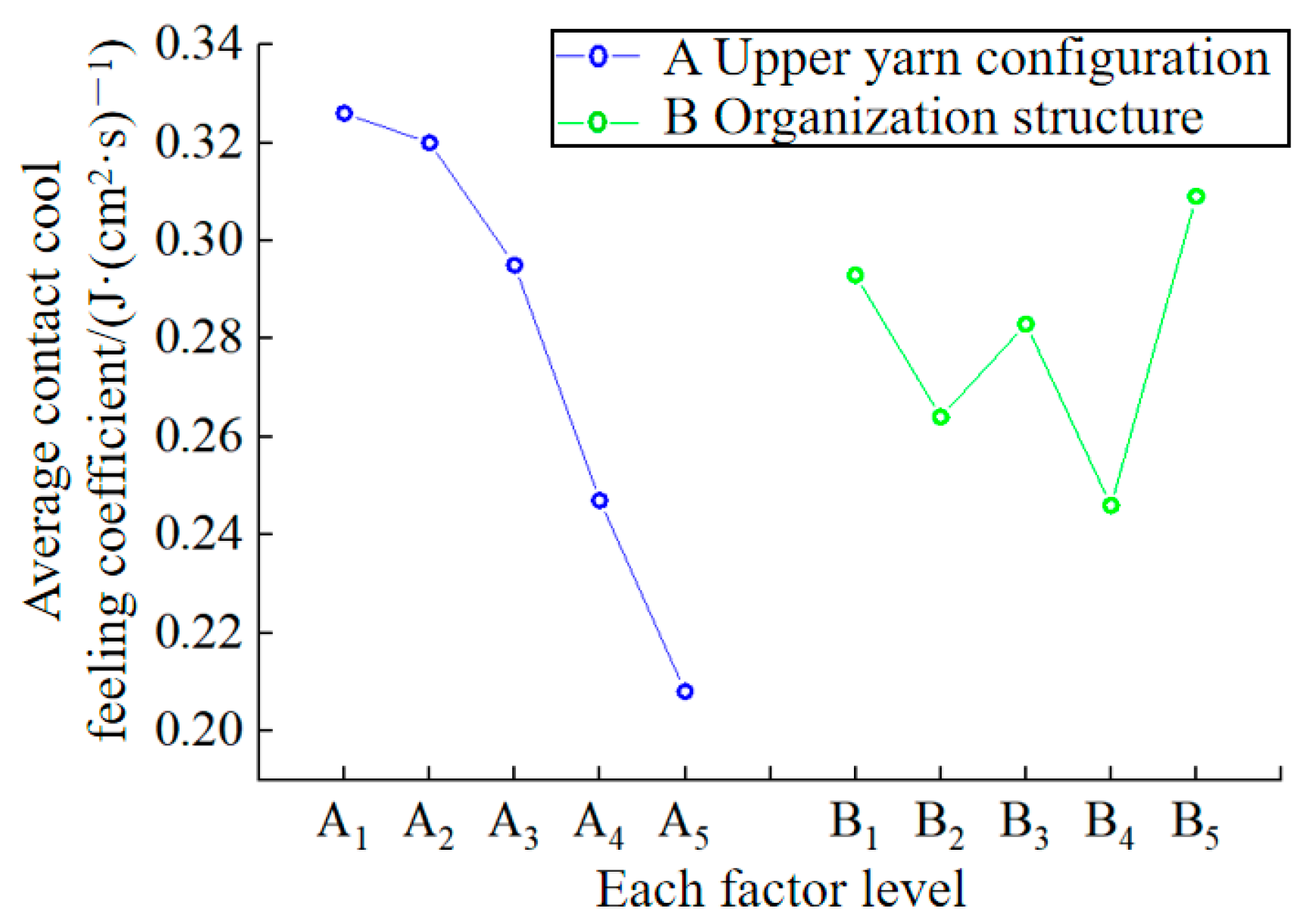
3.5. Contact Cool Feeling Property
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ji, B.L.; Wang, B.J.; Mao, Z.P. Key technologies supporting low-carbon emissions in dyeing and finishing of textiles. J. Text. Res. 2022, 43, 113–121. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, P.P. Research on the cool-feeling fabrics. China Fiber Insp. 2019, 36, 122–124. [Google Scholar]
- Bhuiyan, M.A.R.; Wang, L.; Shaid, A.; Jahan, I.; Shanks, R.A. Silica aerogel-integrated nonwoven protective fabrics for chemical and thermal protection and thermophysiological wear comfort. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 2405–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, A.S.; Zhang, P. Fundamentals, materials and strategies for personal thermal management by next-generation textiles. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2021, 142, 106249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.N.; Hu, J.Y.; Zhang, M.N.; Xiang, Y.Z.; Wu, J.W.; Su, M.Y.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Shen, M.; Hong, P.; Huang, Z.L.; et al. Cooling textiles for personal thermal management. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2022, 67, 1167–1179. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J. Innovative development and future trend of functional home textiles. China Text. Lead. 2020, 39, 28–35. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.H.; Liu, Y.; Jia, Y.H.; Bai, Z.H.; Liu, L.; Zhang, R.Y.; Du, L.X. Research status and progress of cool functional textiles. Wool Text. J. 2023, 51, 135–141. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.Y.; Zhang, X.Q. Research progress on development of cool-feeling fibers and its detection method. Synth. Fiber China 2021, 50, 45–48. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Yu, X.; Wang, X.G.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, P.; Liu, X. Effect of jade nanoparticle content and twist of cool-touch polyester filaments on comfort performance of knitted fabrics. Text. Res. J. 2020, 90, 2385–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.S.; Chen, H.H.; Guan, F.W.; Kun, H. Application and development prospect of jade fiber in summer knitted garment. Front. Art Res. 2022, 4, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, P.F.; Zhang, Y.X.; Sheng, C.H.; Zhang, X.Q. The development of cool functional woven fabric made of mica fiber and coolmax fiber. Synth. Fiber China 2020, 49, 28–30+51. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.Y. Study on Test and Evaluation for Absorption and Quick-Drying Properties of Shaped Fibers and the Fabric. Ph.D. Thesis, Donghua University, Shanghai, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Q.E.; Zhou, T.; Wang, M.; Li, L.; Chen, N. Structure evolution and performance of poly (vinyl alcohol) fibers with controllable cross-section fabricated using a combination of melt-spinning and stretching. Polym. Test. 2023, 117, 107867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yu, X.; Wang, X.G.; Liu, X.; Zhang, P. Thermal comfort properties of cool-touch nylon and common nylon knitted fabrics with different fibre fineness and cross-section. Ind. Textila 2021, 72, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.H.; Wu, H.; Shen, L.P.; Ling, Z.C. Effect of fabric weave structure on properties of graphene/wool worsted shirt fabric. Synth. Fiber China 2020, 49, 34–37. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, W.L.; Zhu, B.L.; Xu, R.C. Research of Outlast modified acrylic fiber blended fabric temperature-adjusting property. Cotton Text. Technol. 2012, 40, 26–28. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, J.; Xie, T.; Chen, L.Q.; Li, Z.; Guo, N.; Fu, S.; Zhang, P. Effect of knitting structure and polyethylene content on thermal-wet comfort and cooling properties of polyethylene/polyester fabrics. Fibers Polym. 2022, 23, 3297–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.H.; Li, Y.X. Development and practice of a cool cotton fabric. China Text. Lead. 2021, 40, 53–55. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G. Development and Performance Research of Cool Nylon Filament Knitted Products. Ph.D. Thesis, Donghua University, Shanghai, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.P. Performance Research and Comprehensive Evaluation of Jade Fiber Summer Sports Knitted Fabrics. Ph.D. Thesis, Zhejiang Sci-Tech University, Hangzhou, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bait, S.H.; Shrivastava, N.; Behera, J.; Ramakrishnan, V.; Dayal, A.; Jadhav, G. Development of sportswear with enhanced moisture management properties using cotton and regenerated cellulosic fibres. Indian J. Fibre Text. Res. 2019, 44, 24–30. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, T.; Qian, J.; Zhang, P.H. Application and prospect of the cool feeling polyethylene fiber in cool textiles. Tech. Text. 2021, 39, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Alberghini, M.; Hong, S.; Lozano, L.M.; Korolovych, V.; Huang, Y.; Signorato, F.; Zandavi, S.H.; Fucetola, C.; Uluturk, I.; Tolstorukov, M.Y.; et al. Sustainable polyethylene fabrics with engineered moisture transport for passive cooling. Nat. Sustain. 2021, 4, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.X. Study on the Technology and Performance of Viscose/UHMWPE Yarn Bed Fabric. Ph.D. Thesis, Soochow University, Suzhou, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.Y.; Wang, Y.P. Modern Clothing Materials Science; China Textile Press: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Yuxiu, B.; Hong, X.; Yueping, W.; Chao, S.; Weijing, Y. Influence of fabric parameters on thermal conductivity of UHMWPE interwoven fabric. Wool Text. J. 2020, 48, 14–17. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.S. Research on Cool Feeling Fabric. Ph.D. Thesis, Zhongyuan University of Technology, Zhengzhou, Chian, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Song, G.L. Review of the circular seamless underwear knitting machines on the 2016 china international textile machinery exhibition-ITMA Asia. Knitt. Ind. 2013, 41, 9–10. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, H.; Shao, X.H. Equipment and process of producing seamless underwear. Prog. Text. Sci. Technol. 2007, 14, 88–90. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, A. Development of Knitted Woolen Sports Fabric Based on Plasma Technology. Ph.D. Thesis, Jiangnan University, Wuxi, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Mavruz, S.; Ogulata, R.T. Investigation and statistical prediction of air permeability of cotton knitted fabrics. Tekst. Konfeksiyon 2009, 19, 29–38. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, X.A. Comparison of two calculation methods for textile air-permeability. Knitt. Ind. 2013, 41, 66–67. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 5453-1997; Textiles—Determination of the Permeability of Fabrics to Air. National Standard of the China: Beijing, China, 1997.
- Huang, J.H.; Qian, X.M. Comparison of test methods for measuring water vapor permeability of fabrics. Text. Res. J. 2008, 78, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 12704.1-2009; Textiles—Test Method for Water-Vapor Transmission of Fabrics—Part 1: Desiccant Method. National Standard of the China: Beijing, China, 2009.
- Zhao, K.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Yu, D. Moisture absorption, perspiration and thermal conductive polyester fabric prepared by thiol-ene click chemistry with reduced graphene oxide finishing agent. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 14262–14273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 21655.2-2009; Textiles—Evaluation of Absorption and Quick-Drying Part 2: Method for Moisture Management Tests. National Standard of the China: Beijing, China, 2009.
- Afzal, A.; Ahmad, S.; Rasheed, A.; Ahmad, F.; Iftikhar, F.; Nawab, Y. Influence of fabric parameters on thermal comfort performance of double layer knitted interlock fabrics. Autex Res. J. 2017, 17, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 11048-2008; Textiles—Physiological Effects—Measurement of Thermal and Water-Vapor Resistance under Steady-State Conditions. National Standard of the China: Beijing, China, 2008.
- Ni, Q.M. Study on the Preparation and Evaluation of the Cool-Feel Knitted Fabric. Ph.D. Thesis, Soochow University, Suzhou, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 35263-2017; Textiles—Testing and Evaluation for Instant Contact Cool Feeling. National Standard of the China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Muraliene, L.; Mikucioniene, D. Influence of structure and stretch on air permeability of compression knits. Int. J. Cloth. Sci. Technol. 2020, 32, 825–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.Y. Discussion on the test methods and influencing factors of moisture permeability of textile fabrics. Text. Test. Stand. 2023, 9, 4–8. [Google Scholar]
- Manohari, B.G.; Kannappan, J.; Kandhavadivu, P.; Ramachandran, T.; Liu, C. Liquid moisture transmission behavior of microfiber blended knitted fabrics. Melliand China 2011, 39, 38–40. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.F.; Wang, W.A.; Jing, Z.Y.; Jiang, X.T.; Xin, H. Research status and progress of unidirectional water-transport fabrics. Wool Text. J. 2022, 50, 108–115. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, C.Y.; Cui, Y.Z.; Jiang, F.Q.; Fu, C.L. The influence of fabric structure on moisture absorbency and sweat transport. Shanghai Text. Sci. Technol. 2011, 39, 20–22. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, J.; Xie, T.; Zhang, P.H.; Fu, S.J. Thermal and moisture comfort performance of polyethylene knitted fabric. J. Text. Res. 2022, 43, 60–66. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.M.; Wang, S.H.; Li, Y.Q.; Jin, X.; Ma, L.; Tian, W.; Zhu, C. Evaluation model of fabric transient cooling sensation based on multiple stepwise regression analysis. J. Eng. Fibers Fabr. 2023, 18, 15589250221144014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

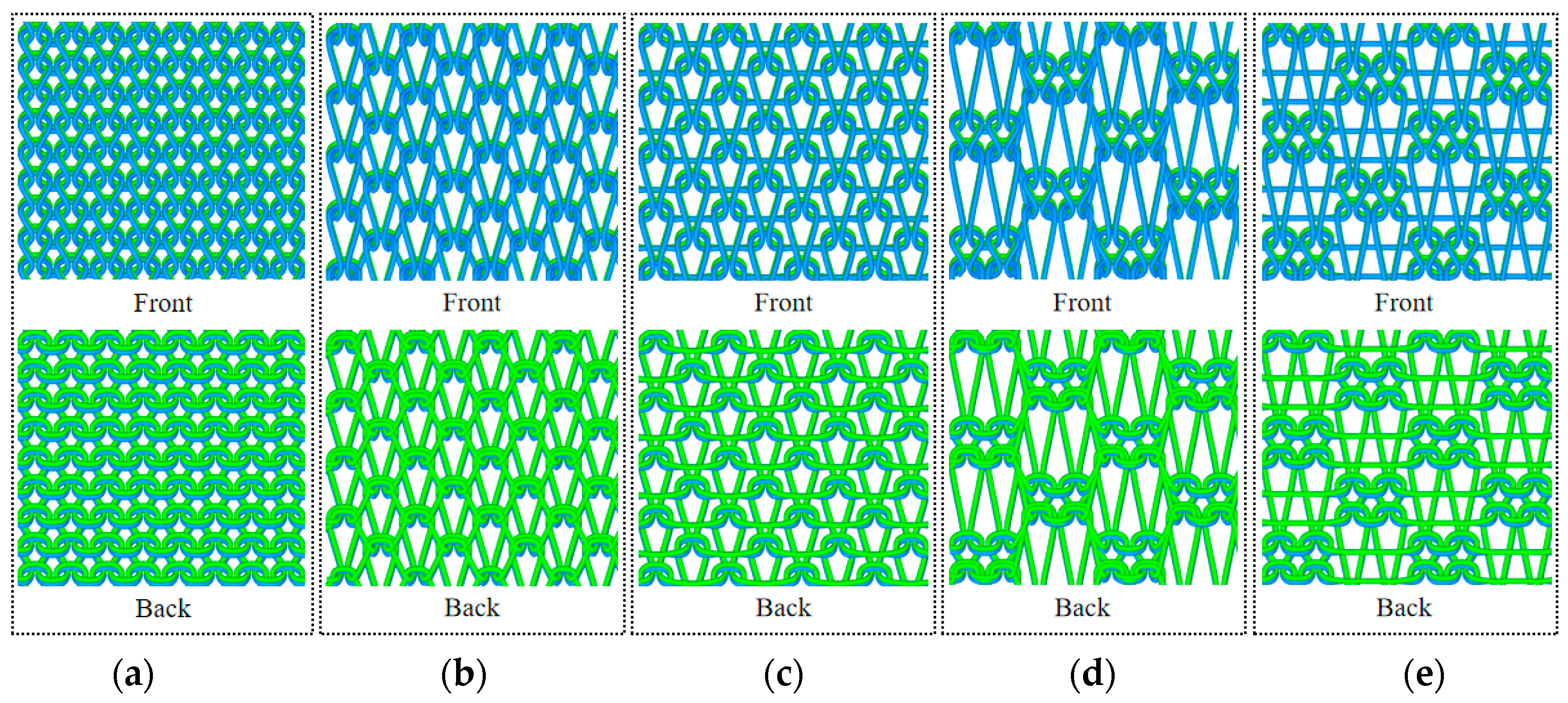
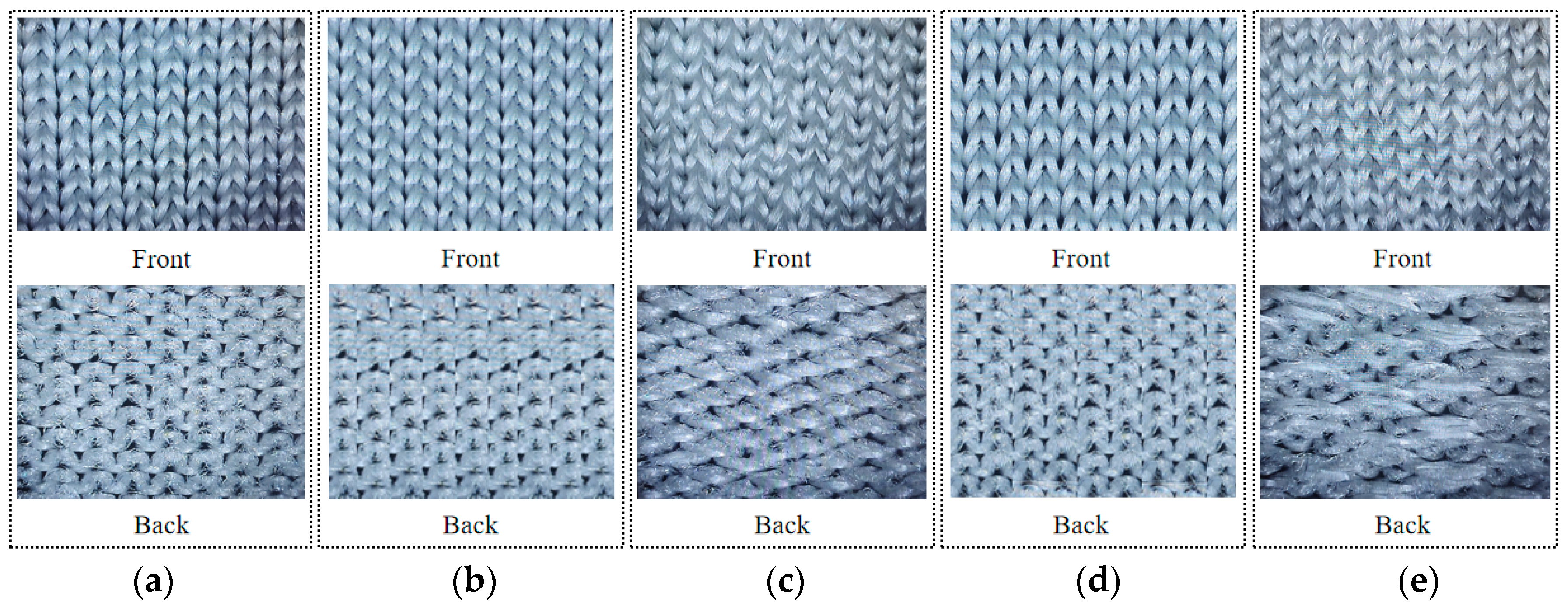
| Fibre Type | Thermal Conductivity/(W·(m·°C)−1) | Fibre Type | Thermal Conductivity/(W·(m·°C)−1) | Fibre Type | Thermal Conductivity/(W·(m·°C)−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| silk | 0.050~0.055 | viscose fibre | 0.055~0.071 | polypropylene | 0.221~0.302 |
| cotton | 0.071~0.073 | acetate fibre | 0.05 | polyvinyl chloride | 0.042 |
| wool | 0.052~0.055 | polyester | 0.084 | water (non-fiber) | 0.697 |
| polyamide | 0.244~0.337 | acrylic | 0.051 | air (non-fiber) | 0.026 |
| Factor | A: Upper Yarn Configuration (Upper Yarn Feeding Method) | B: Organizational Structure | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Level | |||
| 1 | 8U0N (8 roads UHMWPE + 0 road polyamide) | a (flat needle plating organization) | |
| 2 | 6U2N (6 roads UHMWPE + 2 roads polyamide) | b (single needle single column set circle add yarn organization) | |
| 3 | 4U4N (4 roads UHMWPE + 4 roads polyamide) | c (1 separate 1 float wire organization) | |
| 4 | 2U6N (2 roads UHMWPE + 6 roads polyamide) | d (double needle and double column set circle to add yarn organization) | |
| 5 | 0U8N (0 road UHMWPE + 8 roads polyamide) | e (2 separate 2 float wire organization) | |
| Sample Number | A: Upper Yarn Configuration | B: Organizational Structure | Mass per Unit Area /(g·m−2) | Course Density /(wale·cm−1) | Wale Density /(course·cm−1) | Thickness /mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1# | A1: 8U0N | B1: a | 211 | 17 | 25 | 0.9 |
| 2# | A1: 8U0N | B2: b | 196 | 17 | 26 | 0.93 |
| 3# | A1: 8U0N | B3: c | 250 | 17 | 24 | 0.96 |
| 4# | A1: 8U0N | B4: d | 187 | 17 | 26 | 0.93 |
| 5# | A1: 8U0N | B5: e | 289 | 17 | 26 | 1.1 |
| 6# | A2: 6U2N | B1: a | 211 | 17 | 24 | 0.92 |
| 7# | A2: 6U2N | B2: b | 197 | 17 | 26 | 0.95 |
| 8# | A2: 6U2N | B3: c | 254 | 17 | 25 | 0.99 |
| 9# | A2: 6U2N | B4: d | 195 | 17 | 26 | 0.95 |
| 10# | A2: 6U2N | B5: e | 292 | 17 | 25 | 1.11 |
| 11# | A3: 4U4N | B1: a | 219 | 17 | 26 | 0.95 |
| 12# | A3: 4U4N | B2: b | 198 | 17 | 27 | 0.96 |
| 13# | A3: 4U4N | B3: c | 266 | 17 | 25 | 1.01 |
| 14# | A3: 4U4N | B4: d | 198 | 17 | 26 | 0.96 |
| 15# | A3: 4U4N | B5: e | 294 | 17 | 26 | 1.11 |
| 16# | A4: 2U6N | B1: a | 220 | 17 | 26 | 0.96 |
| 17# | A4: 2U6N | B2: b | 200 | 17 | 26 | 0.96 |
| 18# | A4: 2U6N | B3: c | 267 | 18 | 23 | 1.01 |
| 19# | A4: 2U6N | B4: d | 199 | 17 | 26 | 0.97 |
| 20# | A4: 2U6N | B5: e | 295 | 18 | 27 | 1.12 |
| 21# | A5: 0U8N | B1: a | 237 | 17 | 26 | 0.97 |
| 22# | A5: 0U8N | B2: b | 216 | 17 | 28 | 0.97 |
| 23# | A5: 0U8N | B3: c | 283 | 17 | 26 | 1.01 |
| 24# | A5: 0U8N | B4: d | 216 | 17 | 29 | 0.98 |
| 25# | A5: 0U8N | B5: e | 308 | 19 | 27 | 1.14 |
| Sample Number | Q /(mm·s−1) | WVT /(g·(m2·24 h)−1) | T1 /s | T2 /s | A1 /(%·s−1) | A2 /(%·s−1) | O | Rt /(m2·°C·W−1) | Wt | Kt /(W·(m2·°C)−1) | qmax /(J·(cm2·s)−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1# | 445.24 | 2942.756 | 6.7 | 5.2 | 43.2 | 48.6 | 100.31 | 0.0372 | 33.84 | 26.81 | 0.340 |
| 2# | 533.61 | 3036.042 | 7.2 | 15.6 | 45.0 | 59.7 | 100.72 | 0.0303 | 29.37 | 32.98 | 0.319 |
| 3# | 260.32 | 2825.795 | 6.1 | 3.6 | 38.3 | 39.0 | 111.44 | 0.0377 | 34.13 | 26.46 | 0.324 |
| 4# | 557.20 | 3265.018 | 6.1 | 7.8 | 42.0 | 45.1 | 169.60 | 0.0303 | 29.36 | 33.00 | 0.300 |
| 5# | 218.96 | 2756.184 | 5.6 | 19.0 | 48.3 | 857.0 | 194.61 | 0.0379 | 34.23 | 26.35 | 0.346 |
| 6# | 364.72 | 3431.095 | 4.6 | 11.8 | 73.6 | 141.2 | 121.50 | 0.0378 | 34.17 | 26.42 | 0.327 |
| 7# | 530.20 | 3451.590 | 2.1 | 2.1 | 73.6 | 80.9 | 240.39 | 0.0377 | 34.14 | 26.46 | 0.318 |
| 8# | 246.42 | 3061.484 | 5.2 | 5.2 | 38.0 | 41.7 | 255.30 | 0.0395 | 35.15 | 25.30 | 0.322 |
| 9# | 549.33 | 3756.890 | 5.2 | 11.3 | 55.5 | 109.7 | 285.30 | 0.0345 | 32.14 | 28.95 | 0.296 |
| 10# | 210.84 | 2968.198 | 3.1 | 2.6 | 90.8 | 103.0 | 372.81 | 0.0398 | 35.32 | 25.11 | 0.338 |
| 11# | 336.66 | 3926.148 | 2.6 | 4.1 | 59.2 | 56.9 | −117.59 | 0.0392 | 35.03 | 25.44 | 0.325 |
| 12# | 525.78 | 4096.113 | 2.6 | 3.6 | 55.7 | 57.1 | −48.91 | 0.0383 | 34.47 | 26.07 | 0.254 |
| 13# | 208.80 | 3578.799 | 3.6 | 5.1 | 52.5 | 63.5 | 19.94 | 0.0399 | 35.38 | 25.05 | 0.318 |
| 14# | 527.52 | 4443.816 | 2.6 | 4.1 | 57.6 | 66.3 | 118.28 | 0.0359 | 33.01 | 27.83 | 0.240 |
| 15# | 186.22 | 3248.057 | 4.1 | 2.6 | 51.6 | 55.9 | 186.02 | 0.0425 | 36.85 | 23.50 | 0.336 |
| 16# | 299.32 | 3816.254 | 3.1 | 4.1 | 62.8 | 54.8 | −120.16 | 0.0401 | 35.54 | 24.88 | 0.260 |
| 17# | 512.10 | 3875.618 | 2.6 | 5.1 | 58.0 | 63.6 | 32.72 | 0.0399 | 35.40 | 25.03 | 0.229 |
| 18# | 201.50 | 3256.537 | 2.6 | 7.5 | 49.8 | 57.3 | 28.01 | 0.0415 | 36.31 | 24.05 | 0.238 |
| 19# | 513.72 | 3962.898 | 2.6 | 4.1 | 58.7 | 72.2 | 142.86 | 0.0395 | 35.18 | 25.27 | 0.207 |
| 20# | 175.62 | 3146.290 | 4.6 | 5.2 | 54.7 | 59.2 | 140.25 | 0.0480 | 39.74 | 20.79 | 0.300 |
| 21# | 232.96 | 2628.975 | 5.2 | 7.2 | 62.9 | 59.6 | −209.31 | 0.0448 | 38.11 | 22.27 | 0.215 |
| 22# | 305.86 | 3349.823 | 2.6 | 12.3 | 54.2 | 111.1 | −111.38 | 0.0446 | 37.99 | 22.38 | 0.202 |
| 23# | 156.42 | 2527.208 | 3.1 | 7.2 | 51.1 | 65.5 | 9.89 | 0.0466 | 39.03 | 21.42 | 0.211 |
| 24# | 326.74 | 3375.265 | 3.6 | 5.7 | 51.8 | 63.2 | 46.72 | 0.0416 | 36.37 | 23.99 | 0.186 |
| 25# | 156.38 | 2510.247 | 4.6 | 5.7 | 44.0 | 56.0 | 141.31 | 0.0500 | 40.71 | 19.97 | 0.224 |
| Sample Number | Q /(mm·s−1) | WVT /(g·(m2·24 h)−1) | T1 /s | T2 /s | A1 /(%·s−1) | A2 /(%·s−1) | O | Kt /(W·(m2·°C)−1) | qmax /(J·(cm2·s)−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1# | 13.683 | 47.192 | 0.122 | 0.255 | 0.158 | 0.265 | 0.383 | 0.557 | 0.007 |
| 2# | 14.763 | 37.598 | 0.158 | 0.255 | 0.187 | 0.367 | 0.315 | 0.191 | 0.005 |
| 3# | 15.049 | 44.281 | 0.071 | 0.187 | 0.255 | 0.332 | 0.389 | 0.361 | 0.004 |
| 4# | 20.141 | 5.553 | 0.187 | 0.122 | 0.212 | 0.308 | 0.828 | 0.082 | 0.007 |
| 5# | 10.556 | 38.825 | 0.158 | 0.212 | 0.381 | 1.340 | 0.587 | 0.164 | 0.003 |
| 6# | 6.950 | 22.351 | 0.187 | 0.255 | 0.292 | 0.552 | 0.433 | 0.131 | 0.005 |
| 7# | 14.370 | 15.265 | 0.187 | 0.100 | 0.122 | 0.308 | 0.429 | 0.115 | 0.003 |
| 8# | 12.469 | 4.151 | 0.158 | 0.187 | 0.122 | 0.430 | 0.446 | 0.433 | 0.004 |
| 9# | 13.983 | 25.552 | 0.173 | 0.224 | 0.122 | 0.367 | 0.819 | 0.957 | 0.005 |
| 10# | 5.752 | 45.133 | 0.158 | 0.187 | 0.122 | 0.453 | 0.617 | 0.085 | 0.004 |
| 11# | 8.094 | 23.394 | 0.158 | 0.122 | 0.235 | 0.354 | 0.888 | 0.185 | 0.003 |
| 12# | 20.588 | 23.246 | 0.122 | 0.158 | 0.339 | 0.400 | 0.450 | 0.070 | 0.004 |
| 13# | 3.816 | 27.531 | 0.212 | 0.122 | 0.245 | 0.604 | 0.471 | 0.082 | 0.002 |
| 14# | 7.540 | 11.778 | 0.122 | 0.187 | 0.339 | 0.474 | 0.336 | 0.233 | 0.002 |
| 15# | 8.912 | 13.718 | 0.122 | 0.224 | 0.418 | 0.339 | 0.386 | 0.098 | 0.003 |
| 16# | 7.837 | 15.625 | 0.122 | 0.122 | 0.245 | 0.510 | 0.664 | 0.174 | 0.002 |
| 17# | 13.012 | 6.276 | 0.122 | 0.071 | 0.274 | 0.406 | 0.435 | 0.151 | 0.002 |
| 18# | 8.430 | 17.190 | 0.187 | 0.122 | 0.418 | 0.675 | 0.375 | 0.131 | 0.002 |
| 19# | 9.816 | 7.163 | 0.122 | 0.173 | 0.187 | 0.608 | 0.361 | 0.069 | 0.004 |
| 20# | 8.844 | 25.152 | 0.187 | 0.187 | 0.339 | 0.561 | 0.522 | 0.053 | 0.002 |
| 21# | 8.967 | 25.215 | 0.235 | 0.122 | 0.381 | 0.524 | 0.486 | 0.052 | 0.004 |
| 22# | 9.618 | 9.457 | 0.212 | 0.255 | 0.308 | 0.604 | 0.622 | 0.017 | 0.003 |
| 23# | 5.752 | 22.961 | 0.100 | 0.141 | 0.255 | 0.367 | 0.434 | 0.062 | 0.003 |
| 24# | 5.044 | 7.084 | 0.212 | 0.122 | 0.381 | 0.583 | 0.542 | 0.053 | 0.001 |
| 25# | 8.932 | 12.139 | 0.071 | 0.122 | 0.339 | 0.604 | 0.485 | 0.111 | 0.004 |
| Factor | R | The Best Level of Factors | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 403.066 | 380.302 | 356.996 | 340.452 | 235.672 | 167.394 | A1 |
| B | 335.780 | 481.510 | 214.692 | 494.902 | 189.604 | 305.298 | B4 |
| Fabric Specification Parameters | Mass per Unit Area | Thickness | PU |
|---|---|---|---|
| Correlation coefficient r | −0.978 | −0.847 | 0.439 |
| Significant difference p value | 0.000 *** | 0.000 *** | 0.028 ** |
| Factor | R | The Best Level of Factors | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 2965.159 | 3333.851 | 3858.587 | 3611.519 | 2878.304 | 980.283 | A3 |
| B | 3349.046 | 3561.837 | 3049.965 | 3760.777 | 2925.795 | 834.982 | B4 |
| Fabric Specification Parameters | Mass per Unit Area | Thickness | PU | Air Permeability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Correlation coefficient r | −0.576 | −0.388 | −0.063 | 0.58 |
| Significant difference p value | 0.003 *** | 0.056 * | 0.766 | 0.002 *** |
| T1 | T2 | A1 | A2 | O | C | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | A | B | A | B | A | B | A | B | A | B | |
| 0.169 | 0.541 | 0.518 | 0.741 | 0.102 | 0.423 | 0.209 | 0.041 | 0.592 | 0.282 | 1.589 | 2.028 | |
| 0.620 | 0.741 | 0.734 | 0.666 | 0.536 | 0.366 | 0.069 | 0.043 | 0.798 | 0.433 | 2.756 | 2.249 | |
| 0.804 | 0.604 | 0.893 | 0.786 | 0.328 | 0.150 | 0.026 | 0.018 | 0.414 | 0.505 | 2.465 | 2.063 | |
| 0.804 | 0.624 | 0.817 | 0.734 | 0.356 | 0.286 | 0.027 | 0.039 | 0.436 | 0.622 | 2.440 | 2.305 | |
| 0.663 | 0.549 | 0.673 | 0.709 | 0.280 | 0.377 | 0.039 | 0.229 | 0.317 | 0.715 | 1.973 | 2.578 | |
| The best level of factors | A2 | B5 | ||||||||||
| Fabric Specification Parameters | Mass per Unit Area | Thickness | PU | Air Permeability | Moisture Permeability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Correlation coefficient r | 0.035 | 0.184 | −0.161 | 0.019 | 0.595 |
| Significant difference p value | 0.868 | 0.378 | 0.443 | 0.927 | 0.002 *** |
| Rt/(m2·°C·W−1) | Wt | Kt/(W·(m2·°C)−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | A | B | A | B | |
| 0.035 | 0.040 | 32.186 | 35.338 | 29.120 | 25.164 | |
| 0.038 | 0.038 | 34.184 | 34.274 | 26.448 | 26.584 | |
| 0.039 | 0.041 | 34.948 | 36.000 | 25.578 | 24.456 | |
| 0.042 | 0.036 | 36.434 | 33.212 | 24.004 | 27.808 | |
| 0.046 | 0.044 | 38.442 | 37.370 | 22.006 | 23.144 | |
| R | 0.011 | 0.007 | 6.256 | 4.158 | 7.114 | 4.664 |
| The best level of factors | For the thermal conductivity of the sample, the smaller the value of thermal resistance and warmth retention ratio, the larger the value of heat transfer coefficient, the better the thermal conductivity. Therefore, the best factor level of the thermal properties of the sample is A1B4 | |||||
| Fabric Specifications and Performance Indicators | Mass per Unit Area | Thickness | PU | Air Permeability | Moisture Permeability | C | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rt | Correlation coefficient r | 0.733 | 0.761 | −0.848 | −0.805 | −0.295 | 0.088 |
| Significant difference p value | 0.000 *** | 0.000 *** | 0.000 *** | 0.000 *** | 0.152 | 0.677 | |
| Wt | Correlation coefficient r | 0.721 | 0.754 | −0.855 | −0.793 | −0.285 | 0.103 |
| Significant difference p value | 0.000 *** | 0.000 *** | 0.000 *** | 0.000 *** | 0.167 | 0.624 | |
| Kt | Correlation coefficient r | −0.726 | −0.755 | 0.853 | 0.797 | 0.290 | −0.096 |
| Significant difference p value | 0.000 *** | 0.000 *** | 0.000 *** | 0.000 *** | 0.160 | 0.649 | |
| Factor | R | The Best Level of Factors | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0.326 | 0.32 | 0.295 | 0.247 | 0.208 | 0.118 | A1 |
| B | 0.293 | 0.264 | 0.283 | 0.246 | 0.309 | 0.063 | B5 |
| Fabric Specification | Mass per Unit Area | Thickness | PU | Air Permeability | Moisture Permeability | C | Heat Transfer Coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Correlation coefficient r | 0.146 | −0.164 | 0.816 | −0.007 | −0.199 | 0.012 | 0.476 |
| Significant difference p value | 0.485 | 0.434 | 0.000 *** | 0.974 | 0.340 | 0.956 | 0.016 ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Dong, Z.; He, H.; Cong, H. The Development and Performance of Knitted Cool Fabric Based on Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene. Polymers 2024, 16, 325. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16030325
Zhao Y, Dong Z, He H, Cong H. The Development and Performance of Knitted Cool Fabric Based on Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene. Polymers. 2024; 16(3):325. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16030325
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yajie, Zhijia Dong, Haijun He, and Honglian Cong. 2024. "The Development and Performance of Knitted Cool Fabric Based on Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene" Polymers 16, no. 3: 325. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16030325
APA StyleZhao, Y., Dong, Z., He, H., & Cong, H. (2024). The Development and Performance of Knitted Cool Fabric Based on Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene. Polymers, 16(3), 325. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16030325







