The Design of Hyperbranched Polymer Biguanide Molecules with a Four-Arm Branched Core Structure Enhances Antibacterial Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
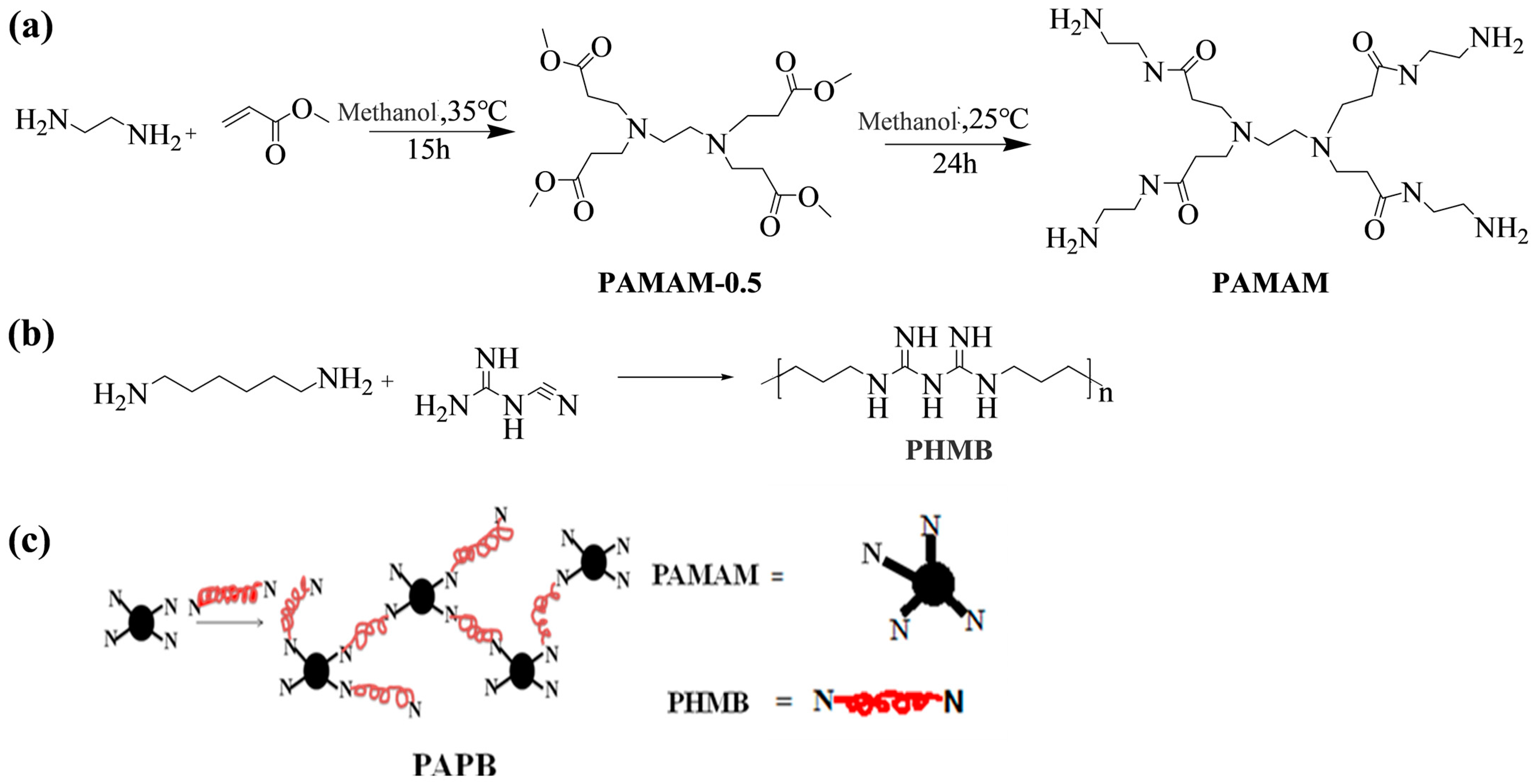
2.2. Synthesis of Polyhexamethylene Biguanide Salt PAPB with Four-Arm Branched Nucleus
2.3. Characterizations
3. Results and Discussion
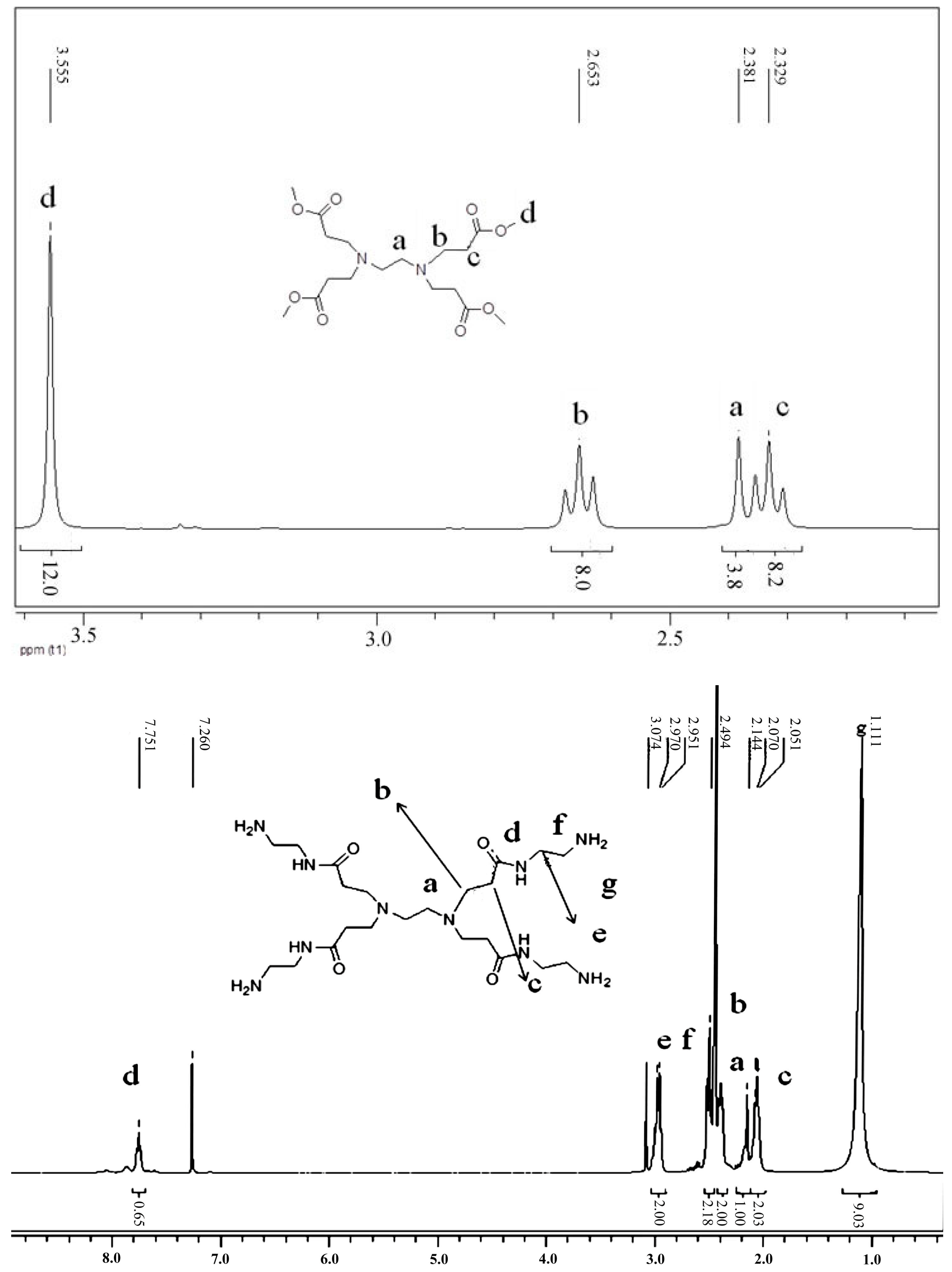
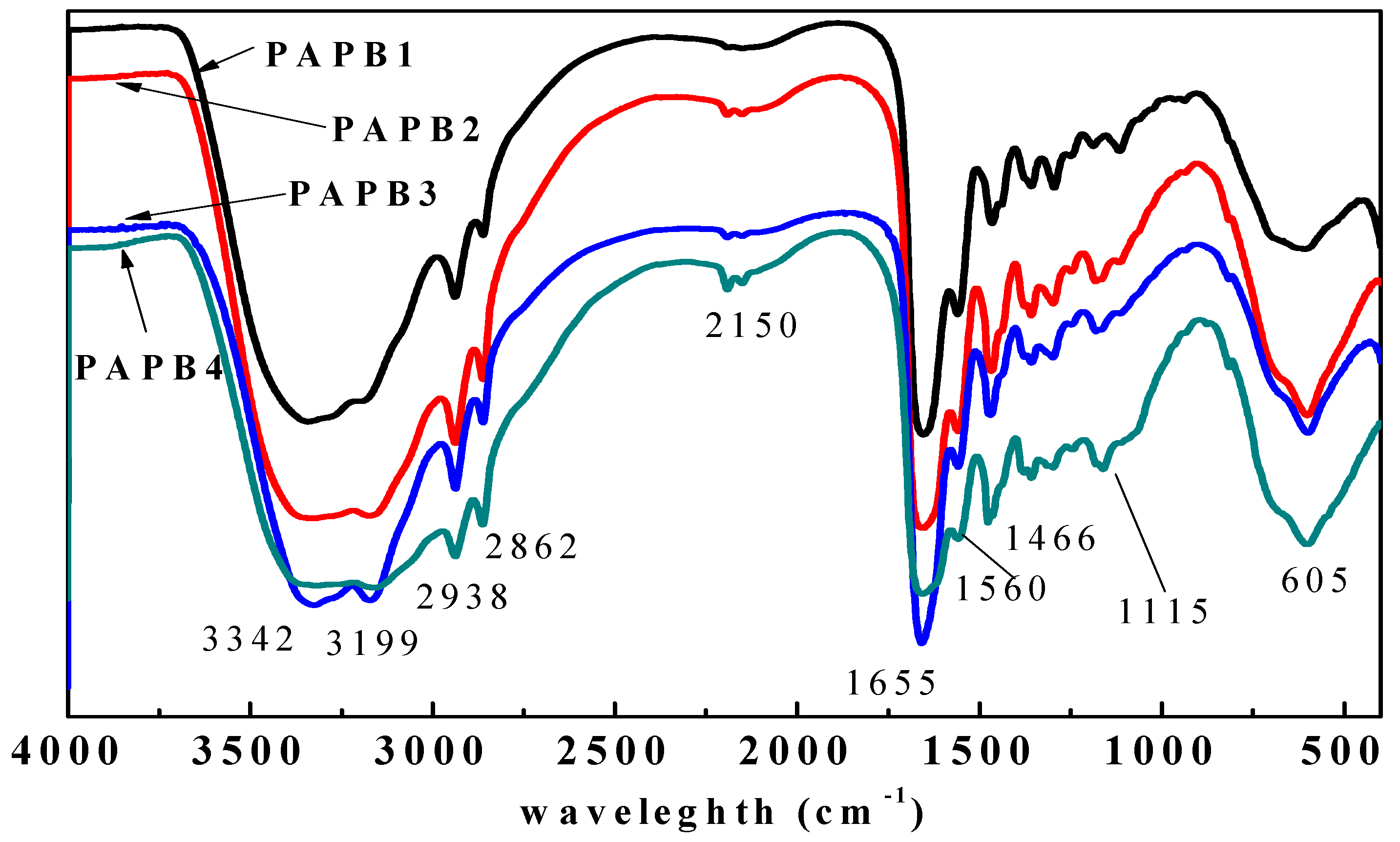
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Hyperbranched Polymerized Biguanides with PAMAM Structure
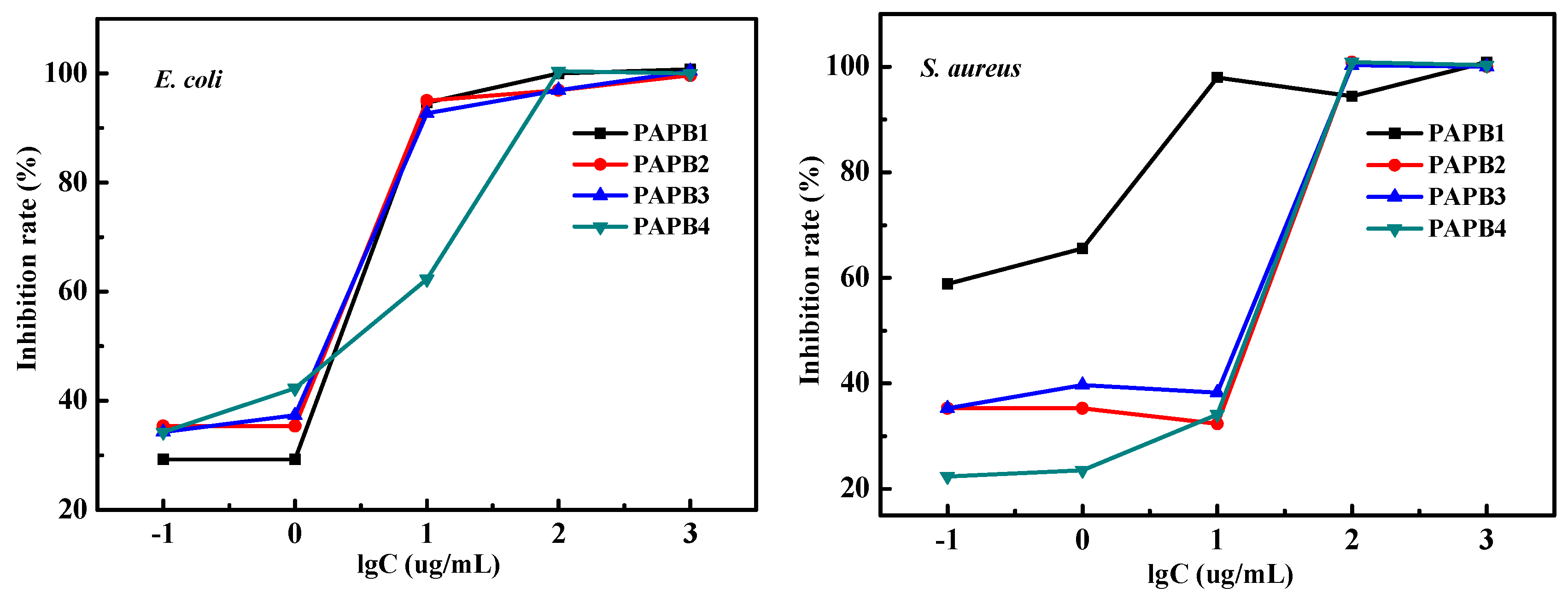
3.2. Antibacterial Property
3.3. Analysis of Antibacterial Mechanism
3.4. Toxic Effect of PAPB on 3T3 Cell
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zaman, S.; Ullah, A.; Shafaqat, A. Structural modeling and topological characterization of three kinds of dendrimer networks. Eur. Phys. J. E 2023, 46, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, T.; Frey, H. Hyperbranched polymer architectures: From Flory’s AB(f-1) polycondensates to controlled structures. Polymer 2020, 211, 123113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Arcy, R.; Burke, J.; Tirelli, N. Branched polyesters: Preparative strategies and applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107, 60–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zheng, L.; Peng, C.; Shen, M.; Shi, X.; Zhang, G. Folic acid-modified dendrimer-entrapped gold nanoparticles as nanoprobes for targeted CT imaging of human lung adencarcinoma. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grodzicka, M.; Pena-Gonzalez, C.E.; Ortega, P.; Michlewska, S.; Lozano, R.; Bryszewska, M.; de la Mata, F.J.; Ionov, M. Heterofunctionalized polyphenolic dendrimers decorated with caffeic acid: Synthesis, characterization and antioxidant activity. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2022, 33, e00497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jikei, M.; Kakimoto, M. Hyperbranched polymers: A promising new class of materials. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2001, 26, 1233–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Z.; Cooper, S.L. Recent Advances in Antimicrobial Dendrimers. Adv. Mater. 2000, 12, 843–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Z.; Beck-Tan, N.C.; Dhurjati, P.; van Dyk, T.K.; LaRossa, R.A.; Cooper, S.L. Quaternary ammonium functionalized poly(propylene imine) dendrimers as effective antimicrobials: Structure−activity studies. Biomacromolecules 2000, 1, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomalia, D.A.; Baker, H.; Dewald, J.; Hall, M.; Kallos, G.; Martin, S.; Roeck, J.; Ryder, J.; Smith, P. A new class of polymers: Starburst-dendritic macromolecules. Polym. J. 1985, 17, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfand, R.; Tomalia, D.A. Poly(amidoamine) (PAMAM) dendrimers: From biomimicry to drug delivery and biomedical applications. Drug Discov. Today 2001, 6, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J.R., Jr. Dendrimer-based nanoparticles for cancer therapy. Hematology 2009, 2009, 708–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolhe, P.; Khandare, J.; Pillai, O.; Kannan, S.; Lieh-Lai, M.; Kannan, R.M. Preparation, cellular transport, and activity of polyamidoamine-based dendritic nanodevices with a high drug payload. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 660–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomlinson, R.; Heller, J.; Brocchini, S.; Duncan, R. Polyacetal−doxorubicin conjugates designed for pH-dependent degradation. Bioconjugate Chem. 2003, 14, 1096–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hélin, V.; Gottikh, M.; Mishal, Z.; Subra, F.; Malvy, C.; Lavignon, M. Uptake and intracellular distribution of oligonucleotides vectorized by a PAMAM dendrimer. Nucleosides Nucleotides 1999, 18, 1721–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, H.; Juliano, R.L. Enhanced delivery of antisense oligonucleotides with fluorophore-conjugated PAMAM dendrimers. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 4225–4231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Wangoo, N.; Gondil, V.S.; Pandey, S.K.; Lalhall, A.; Sharma, R.K.; Chhibber, S. Glycolic acid functionalized silver nanoparticles: A novel approach towards generation of effective antibacterial agent against skin infections. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 60, 102074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaręba, M.; Chmiel-Szukiewicz, E.; Uram, Ł.; Noga, J.; Rzepna, M.; Wołowiec, S. A novel PAMAM G3 dendrimer-based foam with polyether polyol and castor oil components as drug delivery system into cancer and normal cells. Materials 2024, 17, 3905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesniak, W.G.; Kariapper, M.S.T.; Nair, B.M.; Tan, W.; Hutson, A.; Balogh, L.P.; Khan, M.K. Synthesis and characterization of PAMAM dendrimer-based multifunctional nanodevices for targeting αvβ3 integrins. Bioconjugate Chem. 2007, 18, 1148–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, C.J.; Aljayyoussi, G.; Mansour, O.; Griffiths, P.; Gumbleton, M. Endocytic Uptake, Transport and macromolecular interactions of anionic PAMAM dendrimers within lung tissue. Pharm. Res. 2017, 34, 2517–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uehara, T.; Ishii, D.; Uemura, T.; Suzuki, H.; Kanei, T.; Takagi, K.; Takama, M.; Murakami, M.; Akizawa, H.; Arano, Y. γ-Glutamyl PAMAM dendrimer as versatile precursor for dendrimer-based targeting devices. Bioconjugate Chem. 2010, 21, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatemi, S.M.; Fatemi, S.J.; Abbasi, Z. PAMAM dendrimer-based macromolecules and their potential applications: Recent advances in theoretical studies. Polym. Bull. 2020, 77, 6671–6691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Wang, B.; Liang, L.; Liu, B.J.P.K. Polyhexamethylene biguanide functionalized hyperbranched polymers enhance their antimicrobial activities. Polym. Korea 2017, 41, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Liu, B.; Peng, G.; Meng, X.; Jiang, Z.; Chen, H. Synthesis and antimicrobial properties of a guanidine-based oligomer grafted with a reactive cationic surfactant through Michael addition. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 130, 3489–3497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, P.; Moore, L.E. Cationic Antiseptics: Diversity of Action under a Common Epithet. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2005, 99, 703–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| PHMB | PAMAM | PAPB1 | PAPB2 | PAPB3 | PAPB4 | DPB1 [22] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibition zone (cm) | 4 | 1 | 5.9 | 5 | 4 | 3.6 | 6.8 |
| MIC (ppm) | 128 | 256 | 32 | 64 | 128 | 128 | 64 |
| Antibacterial rate (%) | 96.8 | 92.4 | 98.6 | 99.0 | 98.9 | 98.7 | 70.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, B.; Meng, X. The Design of Hyperbranched Polymer Biguanide Molecules with a Four-Arm Branched Core Structure Enhances Antibacterial Properties. Polymers 2024, 16, 3481. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16243481
Wang B, Meng X. The Design of Hyperbranched Polymer Biguanide Molecules with a Four-Arm Branched Core Structure Enhances Antibacterial Properties. Polymers. 2024; 16(24):3481. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16243481
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Bin, and Xu Meng. 2024. "The Design of Hyperbranched Polymer Biguanide Molecules with a Four-Arm Branched Core Structure Enhances Antibacterial Properties" Polymers 16, no. 24: 3481. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16243481
APA StyleWang, B., & Meng, X. (2024). The Design of Hyperbranched Polymer Biguanide Molecules with a Four-Arm Branched Core Structure Enhances Antibacterial Properties. Polymers, 16(24), 3481. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16243481





