Thermo-Responsive and Electroconductive Nano Au-PNiPAAm Hydrogel Nanocomposites: Influence of Synthesis Method and Nanoparticle Shape on Physicochemical Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Chemical Synthesis of Gold Nanospheres and Gold Nanorods
2.3. Synthesis of PNiPAAm Hydrogel
2.4. Synthesis of Nano Au-PNiPAAm Hydrogel Nanocomposites
2.5. Methods of Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Optical Features of Nano Au-PNiPAAm Hydrogel Nanocomposites
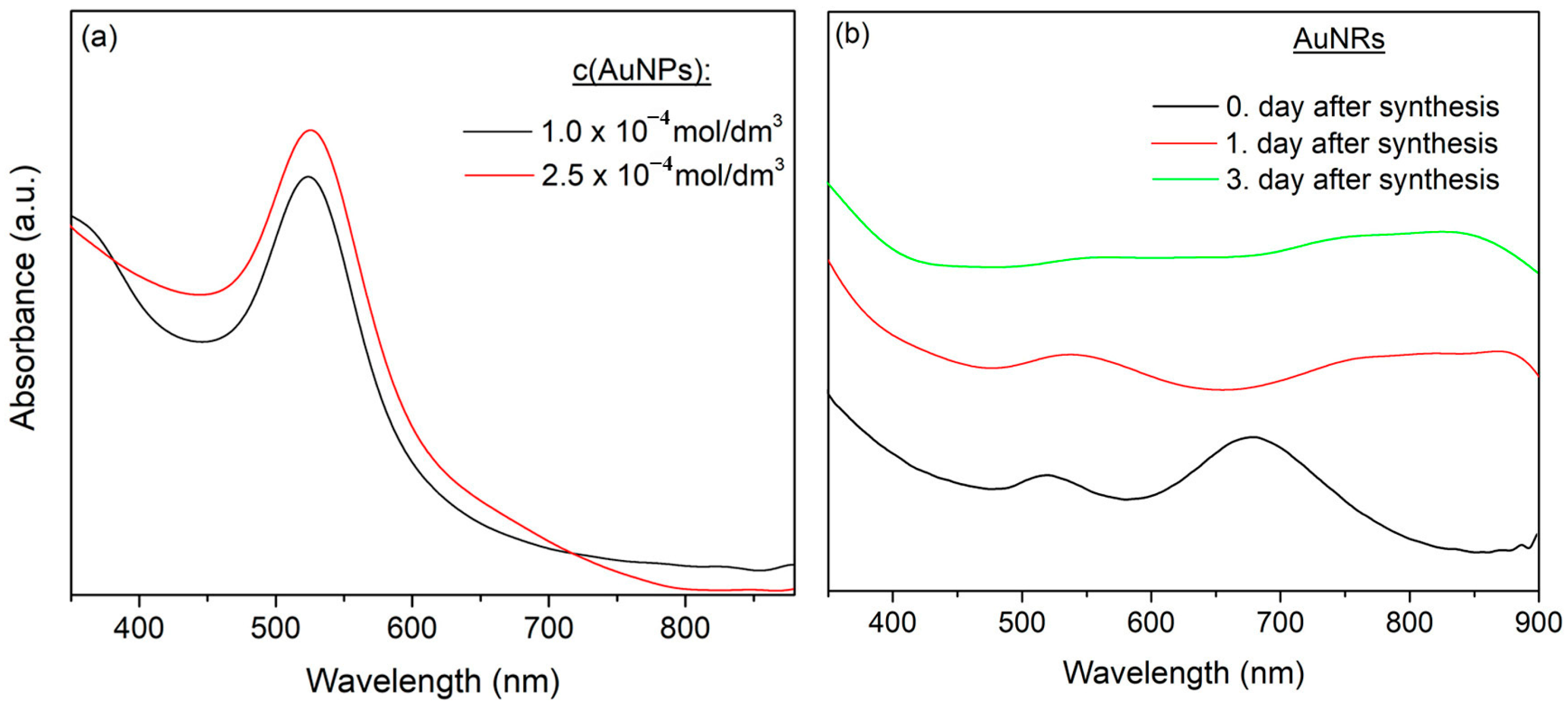
3.1.1. γ-Irradiation-Induced In Situ Synthesis—Method I
3.1.2. Chemical Method of Synthesis—Method II
3.1.3. The Efficiency of the Chosen γ-Irradiation Method for the Crosslinking Process
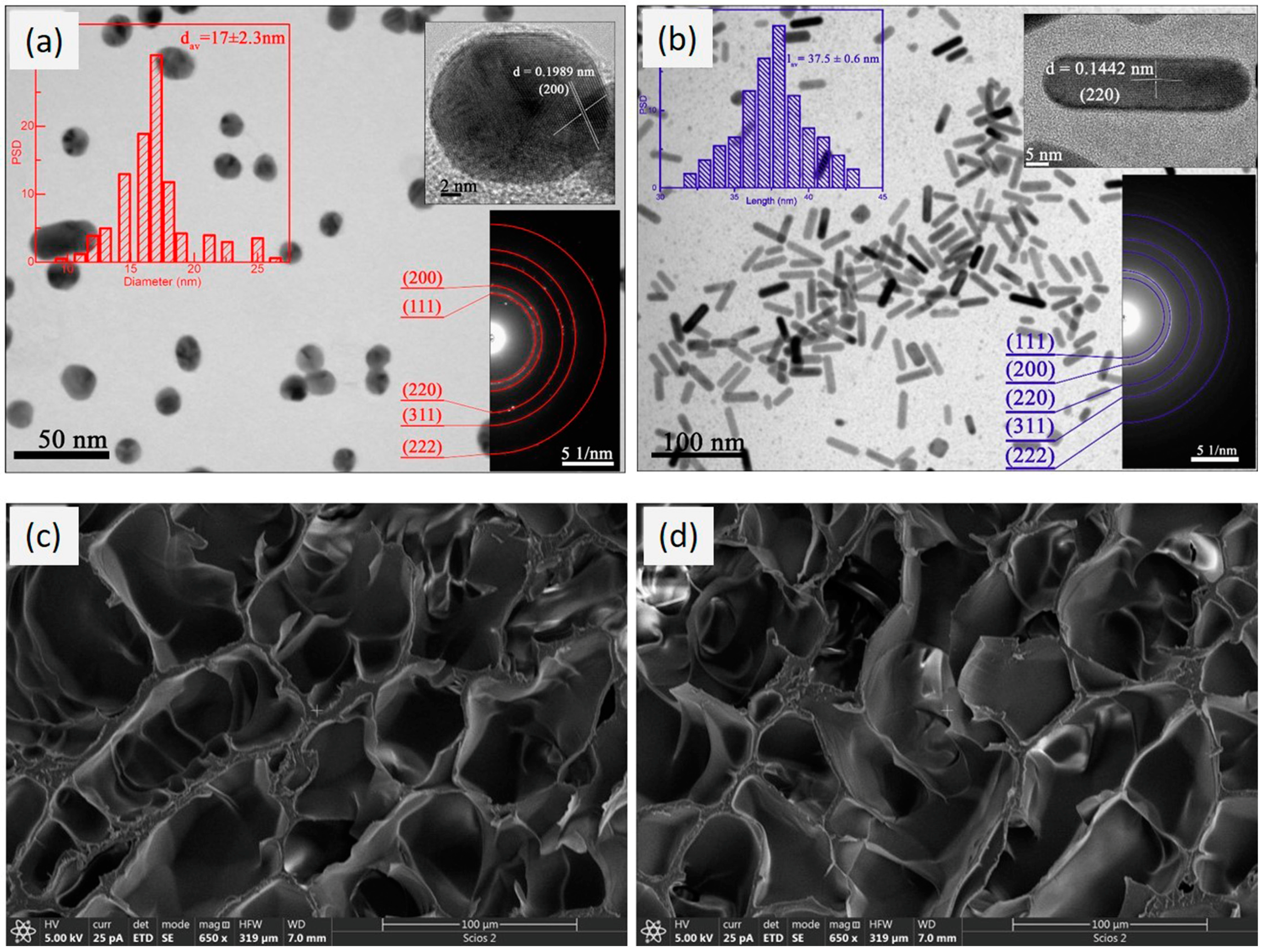
3.2. Morphological Properties of the Nanoparticles and Polymer Network
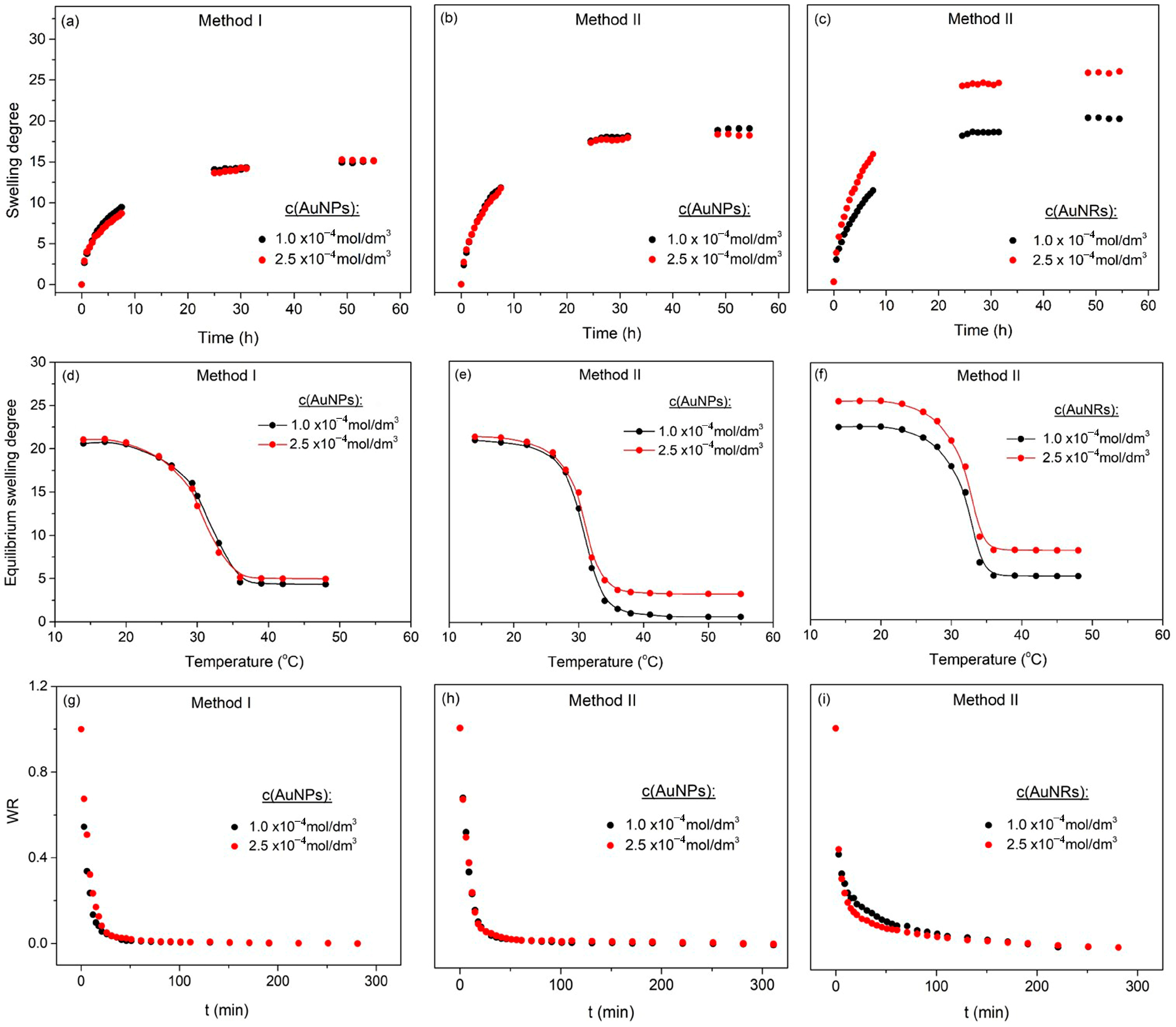
3.3. Physicochemical Characterization
3.4. XRD Analysis
3.5. FTIR Spectroscopy
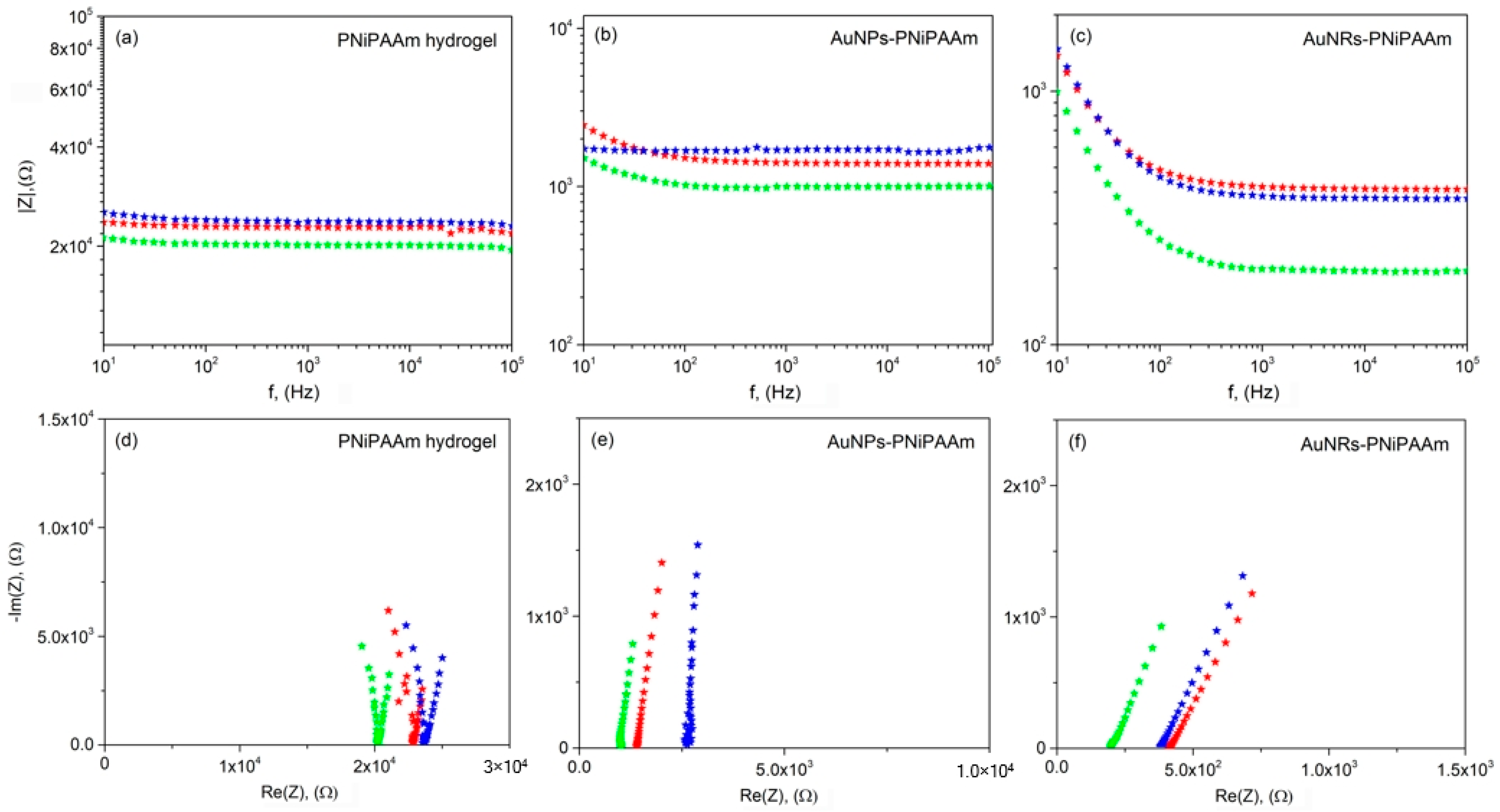
3.6. Thermo-Switchable Electrical Conductivity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spasojević, J.; Radosavljević, A.; Krstić, J.; Jovanović, D.; Spasojević, V.; Kalagasidis-Krušić, M.; Kačarević-Popović, Z. Dual responsive antibacterial Ag-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide/itaconic acid) hydrogel nanocomposites synthesized by gamma irradiation. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 69, 168–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milašinović, N.; Kalagasidis-Krušic, M.; Knežević-Jugović, Z.; Filipović, J. Hydrogels of N-isopropylacrylamide copolymers with controlled release of a model protein. Int. J. Pharmaceut. 2010, 383, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, A. Hydrogels for biomedical applications. Adv. Drug Deliver. Rev. 2002, 43, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gheysoori, P.; Paydayesh, A.; Jafari, M.; Peidayesh, H. Thermoresponsive nanocomposite hydrogels based on Gelatin/poly(N–isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAM) for controlled drug delivery. Eur. Pol. J. 2023, 186, 111846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcon, C.H.; Pennadam, S.; Alexander, C. Stimuli responsive polymers for biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2005, 34, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Liu, H.; Tang, D.; Li, Y.; Li, X.J.; Xu, F. Bioactuators based on stimulus-responsive hydrogels and their emerging biomedical applications. NPG Asia Mater. 2019, 11, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Matthews, A.; Smitherman, A.; Bulick, A.; Hahn, M.; Hou, H.; Han, A.; Grunlan, M. Thermoresponsive nanocomposite hydrogels with cell-releasing behavior. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 3175–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Armstrong, T.; Andres-Arroyo, A.; Bennett, D.; Soeriyadi, A.; Chamazketi, A.A.; Bakthavathsalam, P.; Tilley, R.D.; Gooding, J.J.; Reece, P.J. Optical tweezers-based characterisation of gold core-satellite plasmonic nano-assemblies incorporating thermo-responsive polymers. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 1680–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, X.; Du, T.; Zhu, J.; Xie, Y.; Wu, F.; Wang, Y.; Guan, M. Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide) Based Electrically Conductive Hydrogels and Their Applications. Gels 2022, 8, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, F.; Wang, L.; Chen, B.; Qiu, L.; Nie, J.; Ma, G. Bifunctional Smart Hydrogel Dressing with Strain Sensitivity and NIR-Responsive Performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2021, 13, 46938–46950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.L.; Cao, F.H.; Wang, J.L.; Yu, Z.L.; Ge, J.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Z.H.; Yu, S.H. A Highly Stimuli-Responsive Au Nanorods/Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAM) Composite Hydrogel for Smart Switch. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 24857–24863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Tan, Y.; Lao, J.; Gao, H.; Yu, J. Hydrogels for flexible electronics. ASC Nano 2023, 17, 9681–9693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, F.; Lyu, Q. A Review on Thermal Properties of Hydrogels for Electronic Devices Applications. Gels 2023, 9, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaharwar, A.; Peppas, N.A.; Khademhosseini, A. Nanocomposite Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2014, 111, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schexnailder, P.; Schmidt, G. Nanocomposite polymer hydrogels. Colloid. Polym. Sci. 2009, 287, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krklješ, A.; Nedeljković, J.; Kačarević-Popović, Z. Fabrication of Ag-PVA hydrogel nanocomposite by γ-irradiation. Polym. Bull. 2007, 58, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktürk, A.; Taygun, M.E.; Güler, F.K.; Goller, G.; Küçükbayrak, S. Fabrication of antibacterial polyvinylalcohol nanocomposite mats with soluble starch coated silver nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. A 2014, 562, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krstić, J.; Spasojević, J.; Radosavljević, A.; Perić-Grujić, A.; Djurić, M.; Kačarević-Popović, Z.; Popović, S. In Vitro Silver Ion Release Kinetics from Nanosilver/Poly(vinyl alcohol) Hydrogels Synthesized by Gamma Irradiation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 40321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spasojević, J.; Milošević, M.; Vidičević-Novaković, S.; Tasić, J.; Milovanović, P.; Djurić, M.; Ranković, D.; Kaačarević-Popović, Z.; Radosavljević, A. Multifunctional Ag-Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide/itaconic Acid) Hydrogel Nanocomposites Prepared by Gamma Irradiation for Potential Application as Topical Treatment Dressings. Polymers 2024, 16, 3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, J.; Ramnani, S.P.; Tewari, R.; Dey, G.K.; Sabharwal, S. Short aspect ratio gold nanorods prepared using gamma radiation in the presence of cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide (CTAB) as a directing agent. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2010, 79, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, A.T.; Antony, R. Green synthesis of silver doped nano metal oxides of zinc & copper for antibacterial properties, adsorption, catalytic hydrogenation & photodegradation of aromatics. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 102840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanmani, P.; Rhim, J.W. Physical, mechanical and antimicrobial properties of gelatin based active nanocomposite films containing AgNPs and nanoclay. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 35, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanović, U.; Vodnik, V.; Ahrenkiel, S.P.; Stoiljković, M.; Ćirić-Marjanović, G.; Nedeljković, J. Interfacial synthesis and characterization of gold/polyaniline nanocomposites. Synthetic Met. 2014, 195, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milikić, J.; Stamenović, U.; Vodnik, V.; Ahrenkiel, S.P.; Šljukić, B. Gold nanorod-polyaniline composites: Synthesis and evaluation as anode electrocatalysts for direct borohydride fuel cells. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 328, 135115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapiro, A. Radiation Chemistry of Polymeric Systems; Interscience Publishers: New York, NY, USA; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1962; p. 686. [Google Scholar]
- Caykara, T. Effect of maleic acid content on network structure and swelling properties of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-maleic acid) polyelectrolyte hydrogels. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 92, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safrany, A.; Wojnarovits, L. First steps in radiation-induced hydrogel synthesis: Radical formation and oligomerization in dilute aqueous N-isopropylacrylamide solutions. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2003, 67, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Panda, A.; Sabharwal, S. Reactions of N-isopropylacrylamide with some reducing and oxidizing radicals in aqueous solutions: A pulse radiolysis study. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2000, 59, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.D.; Kowandy, C.; Dupont, L.; Coqueret, X. Evidence of chitosan-mediated reduction of Au(III) to Au(0) nanoparticles under electron beam by using OH• and e−aq scavengers. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 4017–4020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henglein, A.; Meisel, D. Radiolytic Control of the Size of Colloidal Gold Nanoparticles. Langmuir 1998, 14, 7392–7396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.H.; Hai, Z.B.; Cui, C.H.; Li, H.H.; Chen, J.F.; Yu, S.H. In Situ Controlled Synthesis of Thermosensitive Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)/Au Nanocomposite Hydrogels by Gamma Radiation for Catalytic Application. Small 2012, 8, 930–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolić, N.; Spasojević, J.; Radosavljević, A.; Milošević, M.; Barudžija, T.; Rakočević, L.; Kačarević-Popović, Z. Influence of poly(vinyl alcohol)/poly(N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone) polymer matrix composition on the bonding environment and characteristics of Ag nanoparticles produced by gamma irradiation. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2023, 202, 110564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.P.; Gopalan, A.I.; Santhosh, P.; Lee, S.H.; Nho, Y.C. Gamma radiation induced distribution of gold nanoparticles into carbon nanotube-polyaniline composite. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2007, 67, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.D.; Chen, T.P.; Liu, Y.; Leong, K.C. Influence of localized surface plasmon resonance and free electrons on the optical properties of ultrathin Au films: A study of the aggregation effect. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 5124–5132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gezgin, S.Y.; Kepceoğlu, A.; Gündoğdu, Y.; Zongo, S.; Zawadzka, A.; Kiliç, H.S.; Sahraoui, B. Effect of Ar Gas Pressure on LSPR Property of Au Nanoparticles: Comparison of Experimental and Theoretical Studies. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mie, G. Contributions to the optics of turbid media, particularly of colloidal metal solutions. Ann. Phys. 1908, 25, 377–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veenas, C.L.; Nissamudeen, K.M.; Smitha, S.L.; Biju, V.; Gopchandran, K.G. Off-axis PLD: A novel technique for plasmonic engineering of silver nanoparticles. J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. 2009, 11, 114–122. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.; Clogston, J.D.; Patri, A.K.; Dobrovolskaia, M.A.; McNeil, S.E. Sterilization of Silver Nanoparticles Using Standard Gamma Irradiation Procedure Affects Particle Integrity and Biocompatibility. J. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. 2011, 2011 (Suppl. S5), 001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Clogston, J.D.; Patri, A.K.; McNeil, S.E.; Dobrovolskaia, M.A. Sterilization Case Study 2: Effects of Sterilization Techniques on Silver Nanoparticles. In Handbook of Immunological Properties of Engineered Nanomaterials, 2nd ed.; Dobrovolskaia, M.A., McNeil, S.E., Eds.; World Scientific Publishing Co., Inc.: Hackensack, NJ, USA, 2016; Chapter 5; pp. 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asnag, G.M.; Oraby, A.H.; Abdelghany, A.M. Effect of gamma-irradiation on the structural, optical and electrical properties of PEO/starch blend containing different concentrations of gold nanoparticles. Radiat. Eff. Defects Solids 2019, 174, 579–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, M.; Araby, E. Bactericidal effect of poly (acrylamid/itaconic acid)-silver nanoparticles synthesized by gamma irradiation against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2013, 171, 469–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milosavljević, N.; Milašinović, N.; Popović, I.; Filipović, J.; Kalagasidis Krušic, M. Preparation and characterization of pH-sensitive hydrogels based on chitosan, itaconic acid and methacrylic acid. Polym. Int. 2011, 60, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can, H.K.; Denizli, B.K.; Kavlak, S.; Guner, A. Preparation and swelling studies of biocompatible hydrogel systems by using gamma radiation-induced polymerization. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2005, 72, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasdelen, B.; Kayaman-Apohan, N.; Guven, O.; Baysal, B. Swelling and Diffusion Studies of Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide/itaconic acid) Copolymeric Hydrogels in Water and Aqueous Solutions of Drugs. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 91, 911–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olejniczak, M.; Piechocki, K.; Kozanecki, M.; Koynov, K.; Adamus, A.; Wach, R.A. The influence of selected NSAIDs on volume phase transition in poly(2-(2-methoxyethoxy)ethyl methacrylate) hydrogels. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 1528–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radinović, K.; Milikić, J.; Stamenović, U.; Vodnik, V.; Otoničar, M.; Škapin, S.; Šljukić, B. Tailoring gold-conducting polymer nanocomposites for sensors applications: Proof of concept for As(III) sensing in aqueous media. Synth. Met. 2021, 278, 116834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dueramae, I.; Tanaka, F.; Shinyashiki, N.; Yagihara, S.; Kita, R. UV-Crosslinked Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Interpenetrated into Chitosan Structure with Enhancement of Mechanical Properties Implemented as Anti-Fouling Materials. Gels 2024, 10, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safo, I.A.; Werheid, M.; Dosche, C.; Oezaslan, M. The role of polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) as a capping and structure-directing agent in the formation of Pt nanocubes. Nanoscale Adv. 2019, 1, 3095–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheswari, B.; Jagadeesh Babu, P.E.; Agarwal, M. Role of N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidinone on the thermoresponsive behavior of PNIPAm hydrogel and its release kinetics using dye and vitamin-B12 as model drug. J. Biomat. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2013, 25, 269–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spasojević, J.; Radosavljević, A.; Krstić, J.; Mitrić, M.; Popović, M.; Rakocević, Z.; Kalagasidis-Krušić, M.; Kačarević-Popović, Z. Structural Characteristics and Bonding Environment of Ag Nanoparticles Synthesized by Gamma Irradiation Within Thermo-Responsive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Hydrogel. Polym. Compos. 2015, 38, 1014–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaklamani, G.; Kazaryan, D.; Bowen, J.; Iacovella, F.; Anastasiadis, S.H.; Deligeorgis, G. On the electrical conductivity of alginate hydrogels. Regen. Biomater. 2018, 5, 193–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magar, H.S.; Hassan, R.Y.A.; Mulchandani, A. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS): Principles, Construction, and Biosensing Applications. Sensors 2021, 21, 6578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; Gharbi, O.; Vivier, V.; Gao, M.; Orazem, M.E. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 2021, 1, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mišković-Stanković, V.; Jevremović, I.; Jung, I.; Rhee, K.Y. Electrochemical study of corrosion behavior of graphene coatings on copper and aluminum in a chloride solution. Carbon 2014, 75, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciarleglio, G.; Toto, E.; Santonicola, M.G. Conductive and Thermo-Responsive Composite Hydrogels with Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) and Carbon Nanotubes Fabricated by Two-Step Photopolymerization. Polymers 2023, 15, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelhalim, M.A.K.; Mady, M.M.; Ghannam, M.M. Dielectric constant, electrical conductivity and relaxation time measurements of different gold nanoparticle sizes. Int. J. Phys. Sci. 2011, 6, 5487–5491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curry, F.; Lim, T.; Fontaine, N.S.; Adkins, M.D.; Zhang, H. Highly conductive thermoresponsive silver nanowire PNIPAM nanocomposite for reversible electrical switch. Soft Matter 2022, 18, 7171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| c(NPs) × 104 (mol/dm3) | SDeq | n | D × 107 (cm2/s) | Kd × 103 (1/min) | VPTT (°C) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PNiPAAm hydrogel | 0 | 12.6 ± 0.31 | 0.51 ± 0.01 | 1.5 ± 0.030 | 5.1 ± 0.15 | 30.1 ± 0.5 |
| Method I | ||||||
| AuNPs-PNiPAAm | 1.0 | 15.2 ± 0.38 | 0.59 ± 0.02 | 2.9 ± 0.033 | 11.8 ± 0.26 | 30.7 ± 0.7 |
| 2.5 | 15.1 ± 0.37 | 0.57 ± 0.01 | 3.1 ± 0.034 | 11.2 ± 0.25 | 30.9 ± 0.6 | |
| AuNRs-PNiPAAm | 1.0 | 12.9 ± 0.33 | 0.56 ± 0.01 | 2.2 ± 0.027 | 5.0 ± 0.17 | 30.1 ± 0.5 |
| 2.5 | 13.1 ± 0.32 | 0.54 ± 0.01 | 1.8 ± 0.022 | 5.9 ± 0.19 | 30.2 ± 0.5 | |
| Method II | ||||||
| AuNP-PNiPAAm | 1.0 | 19.0 ± 0.48 | 0.58 ± 0.01 | 3.14 ± 0.028 | 12.1 ± 0.25 | 31.0 ± 0.7 |
| 2.5 | 18.5 ± 0.49 | 0.61 ± 0.02 | 5.81 ± 0.039 | 10.7 ± 0.27 | 31.1 ± 0.6 | |
| AuNRs-PNiPAAm | 1.0 | 20.1 ± 0.57 | 0.64 ± 0.02 | 7.73 ± 0.049 | 11.9 ± 0.25 | 32.5 ± 0.8 |
| 2.5 | 25.8 ± 0.65 | 0.69 ± 0.02 | 8.44 ± 0.053 | 12.3 ± 0.28 | 32.6 ± 0.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Radojković, N.; Spasojević, J.; Kačarević-Popović, Z.; Stamenović, U.; Vodnik, V.; Roglić, G.; Radosavljević, A. Thermo-Responsive and Electroconductive Nano Au-PNiPAAm Hydrogel Nanocomposites: Influence of Synthesis Method and Nanoparticle Shape on Physicochemical Properties. Polymers 2024, 16, 3416. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16233416
Radojković N, Spasojević J, Kačarević-Popović Z, Stamenović U, Vodnik V, Roglić G, Radosavljević A. Thermo-Responsive and Electroconductive Nano Au-PNiPAAm Hydrogel Nanocomposites: Influence of Synthesis Method and Nanoparticle Shape on Physicochemical Properties. Polymers. 2024; 16(23):3416. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16233416
Chicago/Turabian StyleRadojković, Nikolina, Jelena Spasojević, Zorica Kačarević-Popović, Una Stamenović, Vesna Vodnik, Goran Roglić, and Aleksandra Radosavljević. 2024. "Thermo-Responsive and Electroconductive Nano Au-PNiPAAm Hydrogel Nanocomposites: Influence of Synthesis Method and Nanoparticle Shape on Physicochemical Properties" Polymers 16, no. 23: 3416. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16233416
APA StyleRadojković, N., Spasojević, J., Kačarević-Popović, Z., Stamenović, U., Vodnik, V., Roglić, G., & Radosavljević, A. (2024). Thermo-Responsive and Electroconductive Nano Au-PNiPAAm Hydrogel Nanocomposites: Influence of Synthesis Method and Nanoparticle Shape on Physicochemical Properties. Polymers, 16(23), 3416. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16233416






