Silica-Based Composite Sorbents for Heavy Metal Ions Removal from Aqueous Solutions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Synthesis of the Silica Composites
- ISs (5.0 g) were suspended in 12 mL of 1 M PEI, followed by the gradual addition of 6 mL of either PAA or PMAA at the same concentration under energetic stirring conditions until the solution became transparent;
- Crosslinking with GA at two different molar ratios (r), namely, a weak degree, r = [—CHO]:[—NH2] = 1:10, and a strong degree, r = [—CHO]:[—NH2] = 1:1. Based on the content of the precipitated PEI, the volume of GA (2.5% w/v) required for the crosslinking of each sample was calculated;
- Extraction of the non-crosslinked polyelectrolyte chains from the silica composite microparticles was carried out with a strong basic (1 M NaOH) or acidic (1 M HCl) treatment to ensure the flexibility of the organic shell.
2.3. Batch Sorption and Desorption Studies
2.4. Adsorption Data Modeling
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Adsorption Isotherms
3.2. Influence of Contact Time and Kinetics
3.3. Sorbent Regeneration/Reusability
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chai, W.S.; Cheun, J.Y.; Kumar, P.S.; Mubashir, M.; Majeed, Z.; Banat, F.; Ho, S.H.; Show, P.L. A Review on Conventional and Novel Materials towards Heavy Metal Adsorption in Wastewater Treatment Application. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 296, 126589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hama Aziz, K.H.; Mustafa, F.S.; Omer, K.M.; Hama, S.; Hamarawf, R.F.; Rahman, K.O. Heavy Metal Pollution in the Aquatic Environment: Efficient and Low-Cost Removal Approaches to Eliminate Their Toxicity: A Review. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 17595–17610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajendran, S.; Priya, A.K.; Senthil Kumar, P.; Hoang, T.K.A.; Sekar, K.; Chong, K.Y.; Khoo, K.S.; Ng, H.S.; Show, P.L. A Critical and Recent Developments on Adsorption Technique for Removal of Heavy Metals from Wastewater—A Review. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 135146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, M.; Lee, I.; Sharma, S.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, V.; Kim, H. Simultaneous Removal of Heavy Metals and Ciprofloxacin Micropollutants from Wastewater Using Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid-Functionalized β-Cyclodextrin-Chitosan Adsorbent. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 34624–34634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadaki, E.S.; Chatzimitakos, T.; Athanasiadis, V.; Kalompatsios, D.; Bozinou, E.; Mitlianga, P.; Lalas, S.I. Assessment of Humic and Fulvic Acid Sorbing Potential for Heavy Metals in Water. Foundations 2023, 3, 788–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Kant, R.; Sharma, A.K.; Sharma, A.K. Exploring the Impact of Heavy Metals Toxicity in the Aquatic Ecosystem. Int. J. Energy Water Resour. 2024, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ATSDR. 2022. Available online: https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/SPL/#2022spl (accessed on 28 August 2024).
- Wang, X.; Tian, C.; Sun, F.; Wu, S.; Jiang, Q.; Ji, K.; Li, R. Synthesis of a Novel Guar Gum-Bentonite Composite for Effective Removal of Pb(II) Species from Wastewater: Studies on Isotherms, Kinetics, Thermodynamic and Adsorption Mechanisms. Desalin. Water Treat. 2024, 319, 100424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.T.; Yang, W.J.; Huang, H.C.; Tang, S.C.; Ko, J.L. Exposure to Nickel Chloride Induces Epigenetic Modification on Detoxification Enzyme Glutathione S-Transferase M2. Environ. Toxicol. 2024, 39, 1729–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC. 2023. Available online: https://monographs.iarc.who.int/list-of-classifications (accessed on 28 August 2024).
- Barjoveanu, G.; Teodosiu, C.; Morosanu, I.; Ciobanu, R.; Bucatariu, F.; Mihai, M. Life Cycle Assessment as Support Tool for Development of Novel Polyelectrolyte Materials Used for Wastewater Treatment. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellaoui, L.; Abdulaziz, F.; Chebaane, S.; Manai, L.; Azhary, A.; Alsehli, A.H.; Alsowayigh, M.M.; Piscitelli, A.; Erto, A. Adsorption of Pharmaceutical Pollutants on Activated Carbon: Physicochemical Assessment of the Adsorption Mechanism via Advanced Modelling. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 389, 122929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalfa, L.; Sdiri, A.; Bagane, M.; Cervera, M.L. A Calcined Clay Fixed Bed Adsorption Studies for the Removal of Heavy Metals from Aqueous Solutions. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 123935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smiljanić, D.; de Gennaro, B.; Izzo, F.; Langella, A.; Daković, A.; Germinario, C.; Rottinghaus, G.E.; Spasojević, M.; Mercurio, M. Removal of Emerging Contaminants from Water by Zeolite-Rich Composites: A First Approach Aiming at Diclofenac and Ketoprofen. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2020, 298, 110057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Sireesha, S.; Sreedhar, I.; Patel, C.M.; Anitha, K.L. Latest Trends in Heavy Metal Removal from Wastewater by Biochar Based Sorbents. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 38, 101561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morosanu, I.; Teodosiu, C.; Tofan, L.; Fighir, D.; Paduraru, C. Valorization of Rapeseed Waste Biomass in Sorption Processes for Wastewater Treatment. In Environmental Issues and Sustainable Development; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Natale, F.; Gargiulo, V.; Alfè, M. Adsorption of Heavy Metals on Silica-Supported Hydrophilic Carbonaceous Nanoparticles (SHNPs). J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Credico, B.; Manzini, E.; Viganò, L.; Canevali, C.; D’Arienzo, M.; Mostoni, S.; Nisticò, R.; Scotti, R. Silica Nanoparticles Self-Assembly Process in Polymer Composites: Towards Advanced Materials. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 26165–26181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucatariu, F.; Teodosiu, C.; Morosanu, I.; Fighir, D.; Ciobanu, R.; Petrila, L.M.; Mihai, M. An Overview on Composite Sorbents Based on Polyelectrolytes Used in Advanced Wastewater Treatment. Polymers 2021, 13, 3963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenova, A.; Giles, L.W.; Vidallon, M.L.P.; Follink, B.; Brown, P.L.; Tabor, R.F. The Structure of Colloidal Polyethylenimine–Silica Nanocomposite Microparticles. Particuology 2023, 76, 86–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawed, A.; Saxena, V.; Pandey, L.M. Engineered Nanomaterials and Their Surface Functionalization for the Removal of Heavy Metals: A Review. J. Water Process. Eng. 2020, 33, 101009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.; Chejanovsky, I.; Suckeveriene, R.Y. Grafting of Poly(Ethylene Imine) to Silica Nanoparticles for Odor Removal from Recycled Materials. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, X.; Yang, A.; Zhao, T.; Liu, F. Polyethyleneimine-Modified Amorphous Silica for the Selective Adsorption of CO2/N2 at High Temperatures. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 35389–35397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucatariu, F.; Schwarz, D.; Zaharia, M.; Steinbach, C.; Ghiorghita, C.A.; Schwarz, S.; Mihai, M. Nanostructured Polymer Composites for Selective Heavy Metal Ion Sorption. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 603, 125211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morosanu, I.; Paduraru, C.; Bucatariu, F.; Fighir, D.; Mihai, M.; Teodosiu, C. Shaping Polyelectrolyte Composites for Heavy Metals Adsorption from Wastewater: Experimental Assessment and Equilibrium Studies. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 321, 115999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitsou, I.; Tsetsekou, A. A Water-Based Synthesis of Hybrid Silica/Hyperbranched Poly(Ethylene Imine) Nanopowder for Heavy Metal Sorption from Aqueous Solutions. J. Nanomater. 2019, 2019, 730317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qhubu, M.C.; Nomngongo, P.N.; Pakade, V.E. Exploring the Iron Oxide Functionalized Biobased Carbon-Silica-Polyethyleneimine Composites for Hexavalent Chromium Removal from Dilute Aqueous Solutions. Water 2021, 13, 3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.K.; Lee, S.C.; Jang, H.Y.; Kim, S.B. Synthesis of Poly(Ethyleneimine)-Functionalized Mesoporous Silica Gel with Dual Loading of Host Ion and Crosslinking for Enhanced Heavy Metal Removal in Multinary Solutions. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 311, 110698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da’na, E. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials Adsorption of Heavy Metals on Functionalized-Mesoporous Silica: A Review. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2017, 308, 57–63. [Google Scholar]
- Barjoveanu, G.; Teodosiu, C.; Bucatariu, F.; Mihai, M. Prospective Life Cycle Assessment for Sustainable Synthesis Design of Organic/Inorganic Composites for Water Treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 272, 122672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, A.; Wang, W.; Duo, T.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Liu, R. High-Performance Polyethyleneimine/Sodium Silicate Material: One-Step Strategy at Ambient Temperature and Application in Removing Heavy Metal Ion. J. Mater. Sci. 2022, 57, 4221–4238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.; Lee, S.; Park, J.O.; Park, J.A.; Cho, S.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Choi, J.W. Chromium Removal from Aqueous Solution by a PEI-Silica Nanocomposite. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fighir, D.; Paduraru, C.; Ciobanu, R.; Bucatariu, F.; Plavan, O.; Gherghel, A.; Barjoveanu, G.; Mihai, M.; Teodosiu, C. Removal of Diclofenac and Heavy Metal Ions from Aqueous Media Using Composite Sorbents in Dynamic Conditions. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucatariu, F.; Ghiorghita, C.A.; Zaharia, M.M.; Schwarz, S.; Simon, F.; Mihai, M. Removal and Separation of Heavy Metal Ions from Multicomponent Simulated Waters Using Silica/Polyethyleneimine Composite Microparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 37585–37596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Guo, X. Adsorption Isotherm Models: Classification, Physical Meaning, Application and Solving Method. Chemosphere 2020, 258, 127279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Guo, X. Adsorption Kinetic Models: Physical Meanings, Applications, and Solving Methods. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 390, 122156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serafin, J.; Dziejarski, B. Application of Isotherms Models and Error Functions in Activated Carbon CO2 Sorption Processes. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2023, 354, 112513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akpa, O.M.; Unuabonah, E.I. Small-Sample Corrected Akaike Information Criterion: An Appropriate Statistical Tool for Ranking of Adsorption Isotherm Models. Desalination 2011, 272, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajahmundry, G.K.; Garlapati, C.; Kumar, P.S.; Alwi, R.S.; Vo, D.V.N. Statistical Analysis of Adsorption Isotherm Models and Its Appropriate Selection. Chemosphere 2021, 276, 130176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghouti, M.A.; Da’ana, D.A. Guidelines for the Use and Interpretation of Adsorption Isotherm Models: A Review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- G.D. 352/2005. Available online: https://legislatie.just.ro/Public/DetaliiDocument/61585 (accessed on 28 August 2024).


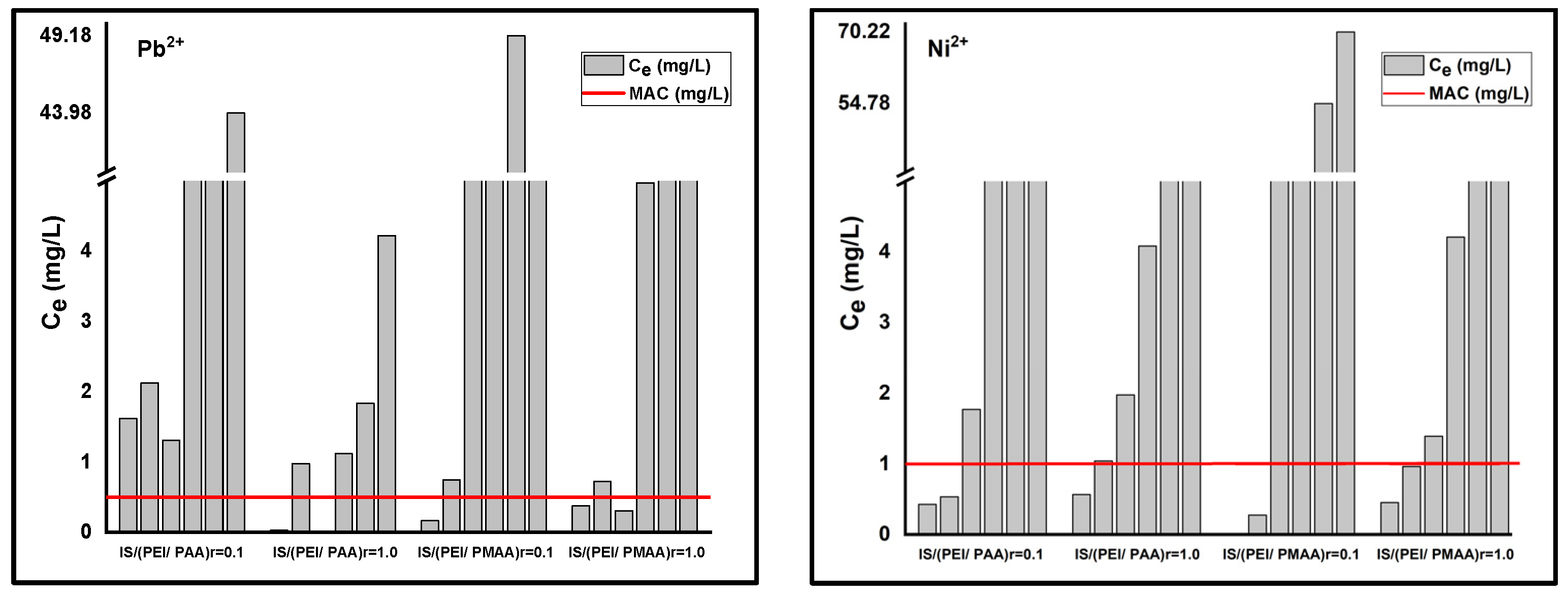
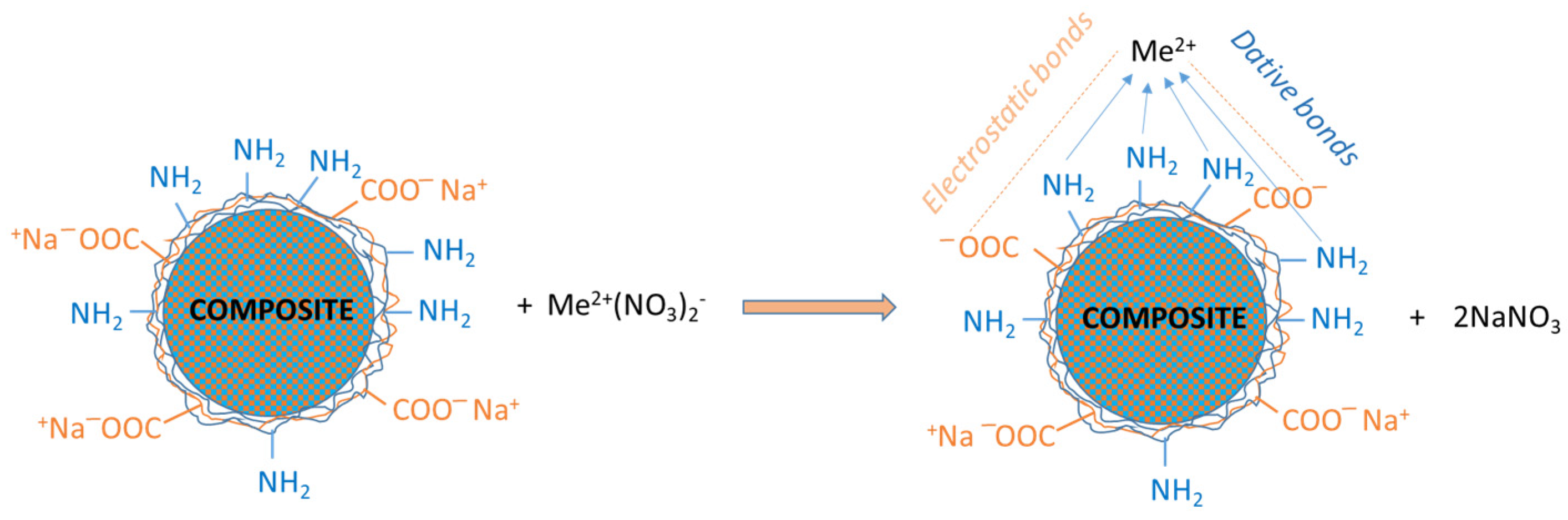
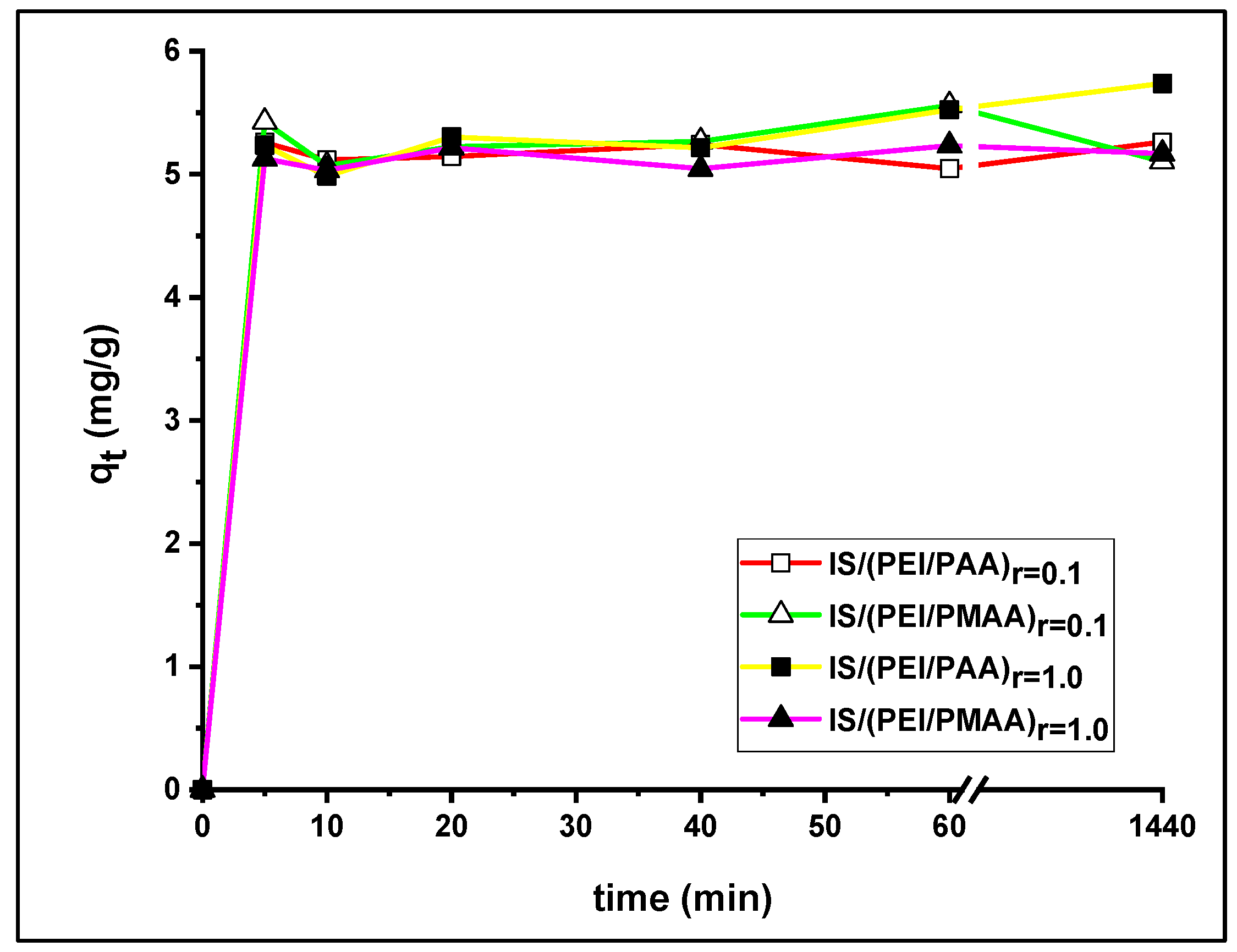
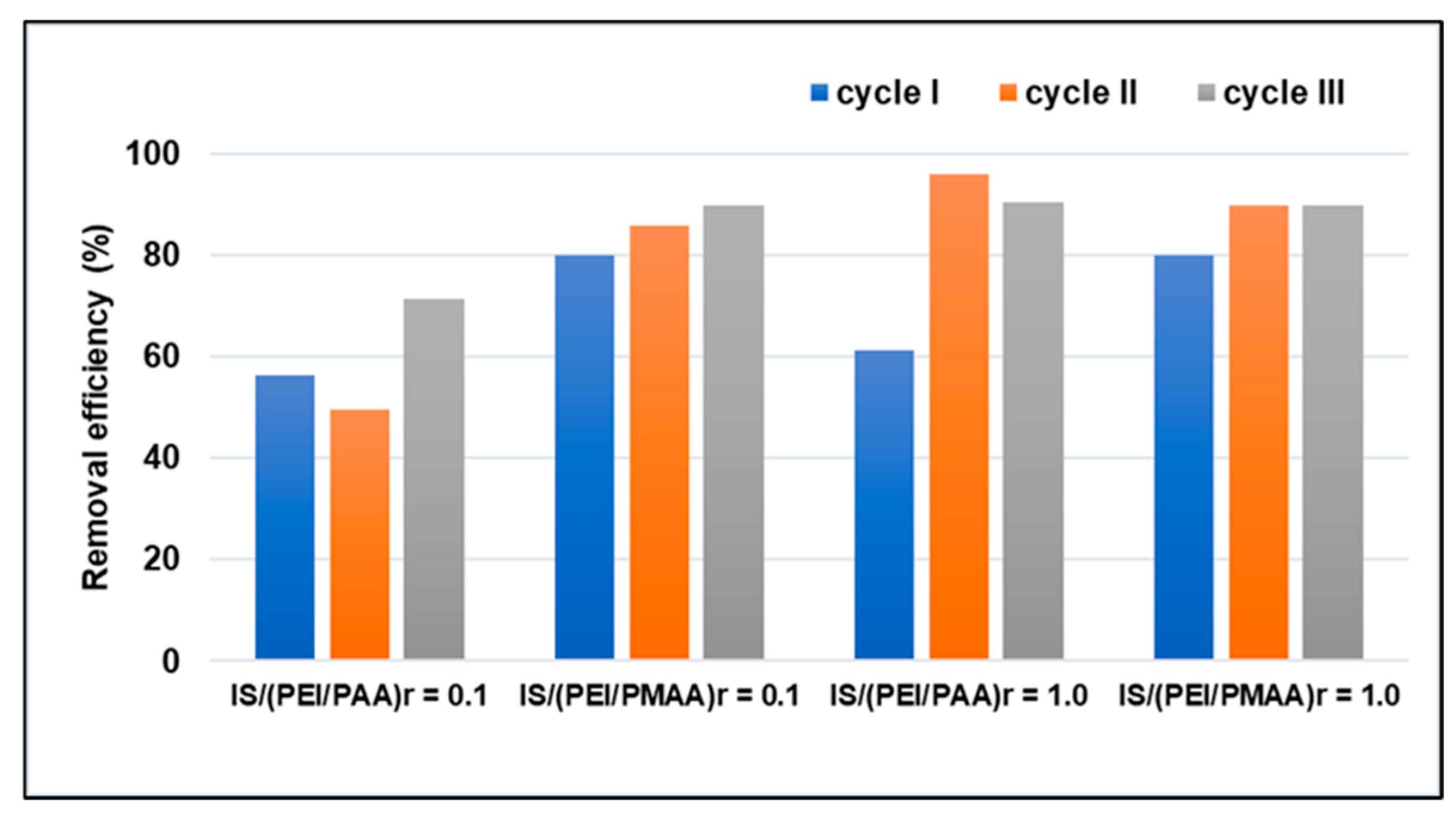
| Composite Sorbent | Crosslinking Degree (r) | Amount of Composites (mg) | Contact Time (h) | Ci Pb2+ (mg/L) | Ci Ni2+ (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IS/(PEI/PAA) | r = 0.1 | 100 | 3 | 5; 10; 20; 50; 75; 100 | 1; 2; 5; 13; 19; 26 |
| r = 1.0 | |||||
| IS/(PEI/PMAA) | r = 0.1 | ||||
| r = 1.0 |
| Model | Equation | Equation No. |
|---|---|---|
| Isotherm models | ||
| Langmuir | (3) | |
| Freundlich | (4) | |
| Sips | (5) | |
| Toth | (6) | |
| Kinetic models | ||
| Pseudo-first-order | (7) | |
| Pseudo-second-order | (8) | |
| Error functions | ||
| Sum of the square error (SSE) | (9) | |
| Chi-square test (χ2) | (10) | |
| Derivative of hybrid fractional error function (HYBRID) | (11) | |
| Average relative error (ARE) | (12) | |
| Akaike information criterion (AIC) | (13) | |
| Isotherm Model | Parameters | Pb2+ | Ni2+ | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IS/(PEI/PAA)r=0.1 | IS/(PEI/PAA)r=1.0 | IS/(PEI/PMAA)r=0.1 | IS/(PEI/PMAA)r=1.0 | IS/(PEI/PAA)r=0.1 | IS/(PEI/PAA)r=1.0 | IS/(PEI/PMAA)r=0.1 | IS/(PEI/PMAA)r=1.0 | ||
| Langmuir | qm,L (mg/g) | 7.050 | 22.08 | 7.161 | 9.156 | 0.518 | 30.122 | 21.77 | 12.638 |
| KL (L/mg) | 0.043 | 0.195 | 0.076 | 0.188 | 0.613 | 0.076 | 0.008 | 0.017 | |
| SSE | 0.096 | 10.45 | 3.54 | 3.36 | 0.04 | 12.21 | 0.12 | 0.01 | |
| χ2 | 0.07 | 8.44 | 1.62 | 1.34 | 0.10 | 3.56 | 0.12 | 0.04 | |
| HYBRID | 2.34 | 301.74 | 36.27 | 17.64 | 8.52 | 109.34 | 10.52 | 3.73 | |
| ARE | 8.60 | 81.53 | 41.94 | 24.47 | 22.29 | 61.18 | 22.79 | 12.27 | |
| AIC | 26.37 | −2.24 | 4.73 | 5.05 | 31.48 | −2.69 | 25.23 | 38.42 | |
| Freundlich | KF | 0.422 | 2.006 | 1.00 | 1.713 | 0.185 | 1.384 | 0.177 | 0.211 |
| 1/nF | 0.642 | 1.142 | 0.452 | 0.733 | 0.359 | 1.287 | 1.00 | 0.958 | |
| SSE | 0.336 | 19.98 | 5.15 | 3.28 | 0.03 | 18.28 | 0.15 | 0.02 | |
| χ2 | 0.185 | 4.63 | 1.39 | 1.39 | 0.11 | 4.28 | 0.13 | 0.04 | |
| HYBRID | 6.87 | 67.29 | 13.46 | 24.28 | 14.35 | 48.49 | 6.40 | 3.81 | |
| ARE | 14.98 | 52.48 | 24.01 | 31.15 | 26.35 | 42.66 | 18.80 | 12.66 | |
| AIC | 18.86 | −5.48 | 2.49 | 5.20 | 32.54 | −5.11 | 23.81 | 37.36 | |
| Sips | qm,S | 7.45 | 7.31 | 3.01 | 10.01 | 0.31 | 5.03 | 2.384 | 4.63 |
| Ks | 0.045 | 9.98 | 15.97 | 0.146 | 1.587 | 13,625 | 0.07 | 0.05 | |
| nS | 0.95 | 202.38 | 100.21 | 0.98 | 1.66 | 9.93 | 1.52 | 1.13 | |
| SSE | 0.08 | 11.40 | 15.55 | 3.48 | 0.03 | 1.49 | 0.04 | 0.02 | |
| χ2 | 0.07 | 2.22 | 5.49 | 1.38 | 0.06 | 0.39 | 0.03 | 0.03 | |
| HYBRID | 3.52 | 64.72 | 123.48 | 21.80 | 5.27 | 34.90 | 1.71 | 3.42 | |
| ARE | 9.49 | 34.70 | 70.76 | 20.80 | 14.49 | 21.74 | 7.17 | 9.45 | |
| AIC | 27.94 | −2.70 | −3.87 | 5.10 | 34.43 | 10.18 | 32.58 | 37.68 | |
| Toth | qm,T | 8.30 | 22.62 | 320.03 | 9.27 | 0.44 | 6.22 | 1.63 | 3.59 |
| KT | 0.04 | 0.1 | 0.578 | 0.16 | 0.55 | 0.368 | 0.12 | 0.06 | |
| nT | 0.82 | 100.14 | 0.125 | 1.05 | 3.16 | 4.77 | 31.55 | 1.97 | |
| SSE | 0.08 | 17.84 | 4.71 | 3.54 | 0.05 | 11.50 | 0.04 | 0.01 | |
| χ2 | 0.07 | 4.80 | 1.39 | 1.38 | 0.10 | 3.44 | 0.08 | 0.04 | |
| HYBRID | 3.51 | 161.80 | 21.23 | 21.81 | 9.64 | 150.41 | 16.50 | 4.61 | |
| ARE | 9.51 | 64.58 | 27.54 | 27.72 | 17.71 | 61.06 | 22.01 | 11.86 | |
| AIC | 27.76 | −4.94 | 3.28 | 5.01 | 31.06 | −2.06 | 31.41 | 38.14 | |
| Experimental | qexp (mg/g) | 4.98 | 9.63 | 5.52 | 8.03 | 0.63 | 2.62 | 1.63 | 1.72 |
| Model | Parameters | Pb2+ | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IS/(PEI/PAA) r=0.1 | IS/(PEI/PAA) r=1.0 | IS/(PEI/PMAA) r=0.1 | IS/(PEI/PMAA) r=1.0 | ||
| PFO | k1 (1/min) | 3.88 × 105 | 0.74 | 26.96 | 1.19 |
| qe,1 (mg/g) | 51.44 | 53.45 | 52.63 | 51.39 | |
| SSE | 4.69 | 33.20 | 17.87 | 3.62 | |
| χ2 | 0.09 | 0.61 | 0.33 | 0.07 | |
| HYBRID | 0.04 | 0.28 | 0.15 | 0.03 | |
| ARE | 1.46 | 3.47 | 2.68 | 1.31 | |
| AIC | 3.043 | −8.69 | −4.98 | 4.58 | |
| PSO | k2 (g/(mg⋅min)) | 1.00 × 1030 | 0.04 | 1.00 × 1030 | 0.30 |
| qe,2 (mg/g) | 51.76 | 54.64 | 52.69 | 51.57 | |
| SSE | 3.99 | 22.87 | 17.81 | 3.32 | |
| χ2 | 0.08 | 0.43 | 0.33 | 0.06 | |
| HYBRID | 0.04 | 0.20 | 0.15 | 0.03 | |
| ARE | 1.47 | 3.34 | 2.70 | 1.3 | |
| AIC | 4.00 | −6.46 | −4.96 | 5.10 | |
| Experimental | qexp (mg/g) | 52.62 | 57.38 | 52.7 | 51.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ciobanu, R.; Bucatariu, F.; Mihai, M.; Teodosiu, C. Silica-Based Composite Sorbents for Heavy Metal Ions Removal from Aqueous Solutions. Polymers 2024, 16, 3048. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16213048
Ciobanu R, Bucatariu F, Mihai M, Teodosiu C. Silica-Based Composite Sorbents for Heavy Metal Ions Removal from Aqueous Solutions. Polymers. 2024; 16(21):3048. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16213048
Chicago/Turabian StyleCiobanu, Ramona, Florin Bucatariu, Marcela Mihai, and Carmen Teodosiu. 2024. "Silica-Based Composite Sorbents for Heavy Metal Ions Removal from Aqueous Solutions" Polymers 16, no. 21: 3048. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16213048
APA StyleCiobanu, R., Bucatariu, F., Mihai, M., & Teodosiu, C. (2024). Silica-Based Composite Sorbents for Heavy Metal Ions Removal from Aqueous Solutions. Polymers, 16(21), 3048. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16213048








