PVC/CNT Electrospun Composites: Morphology and Thermal and Impedance Behavior
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Solution Preparation
2.3. Preparation of Electrospun Membranes
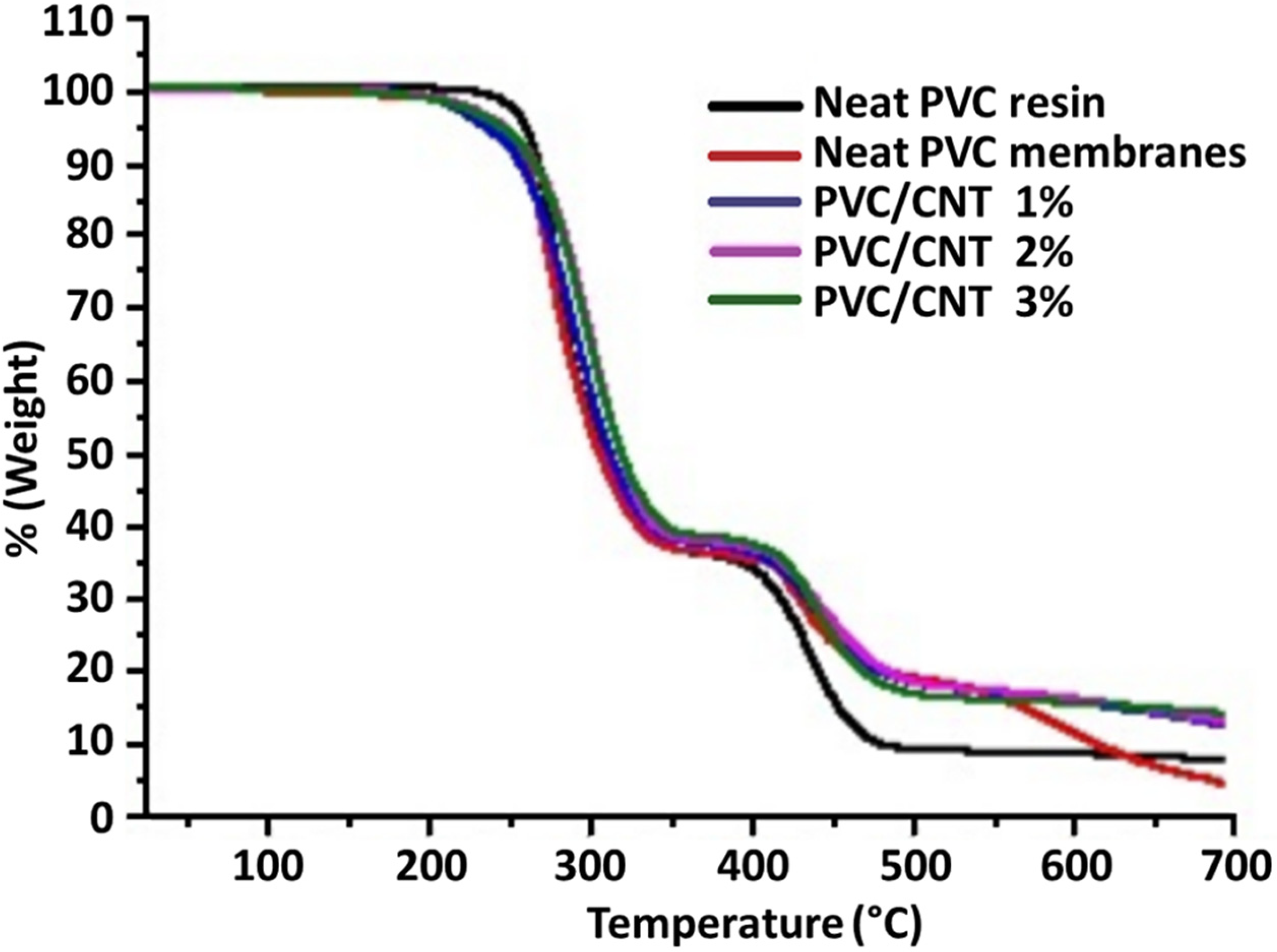
2.4. Thermal Characterization
2.5. X-ray Diffractometry (XDR)
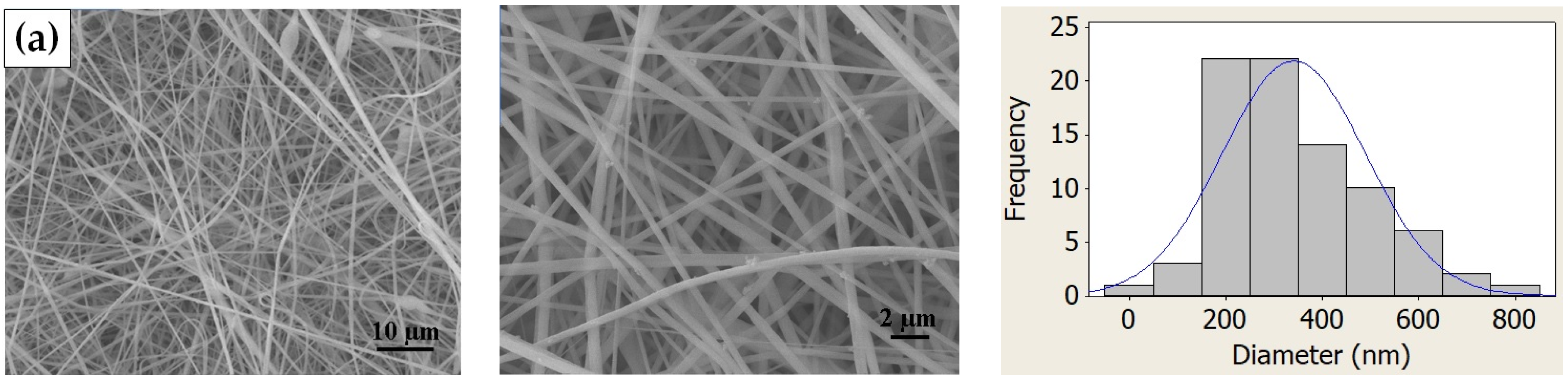
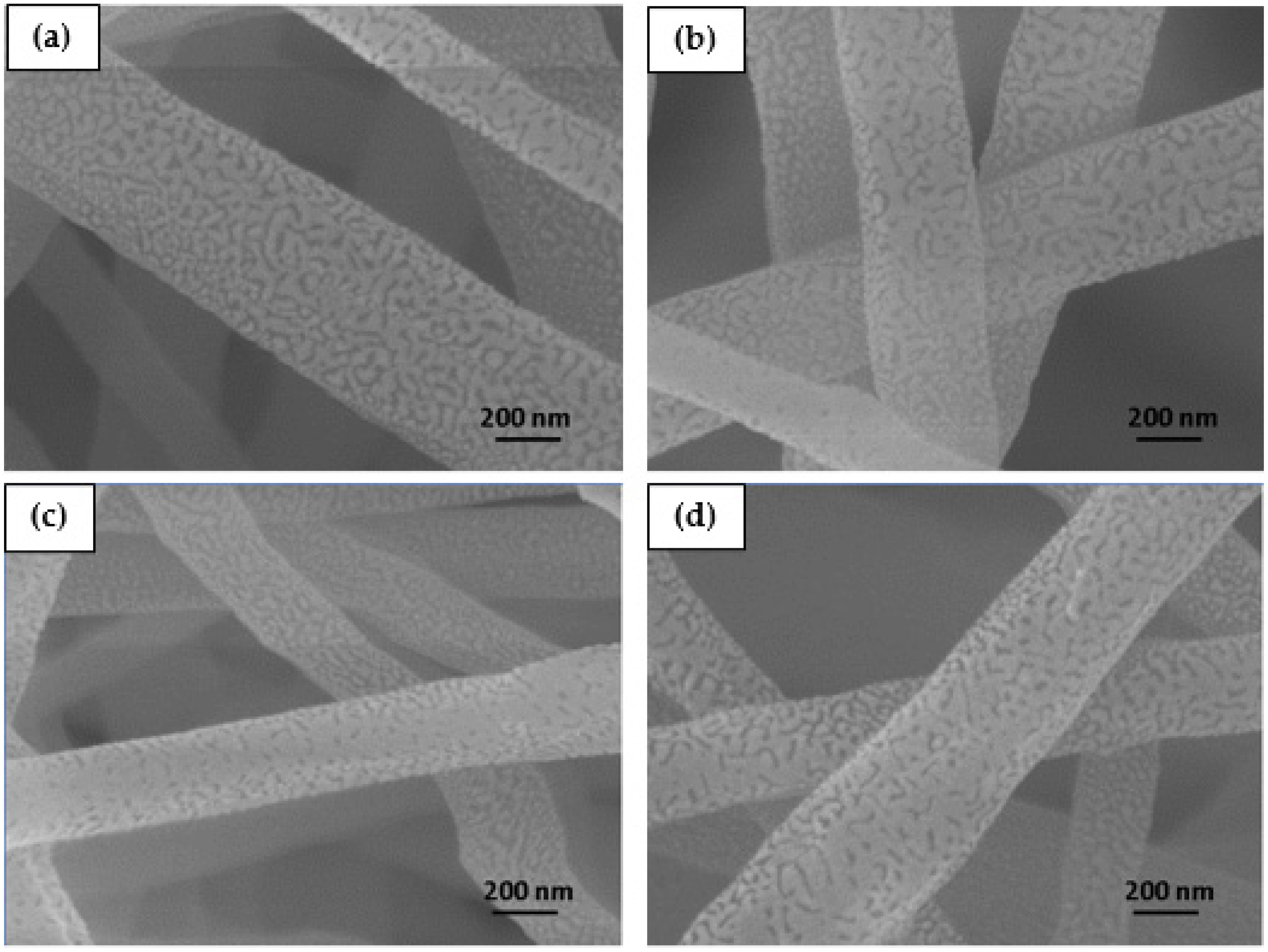
2.6. Morphological Characterization
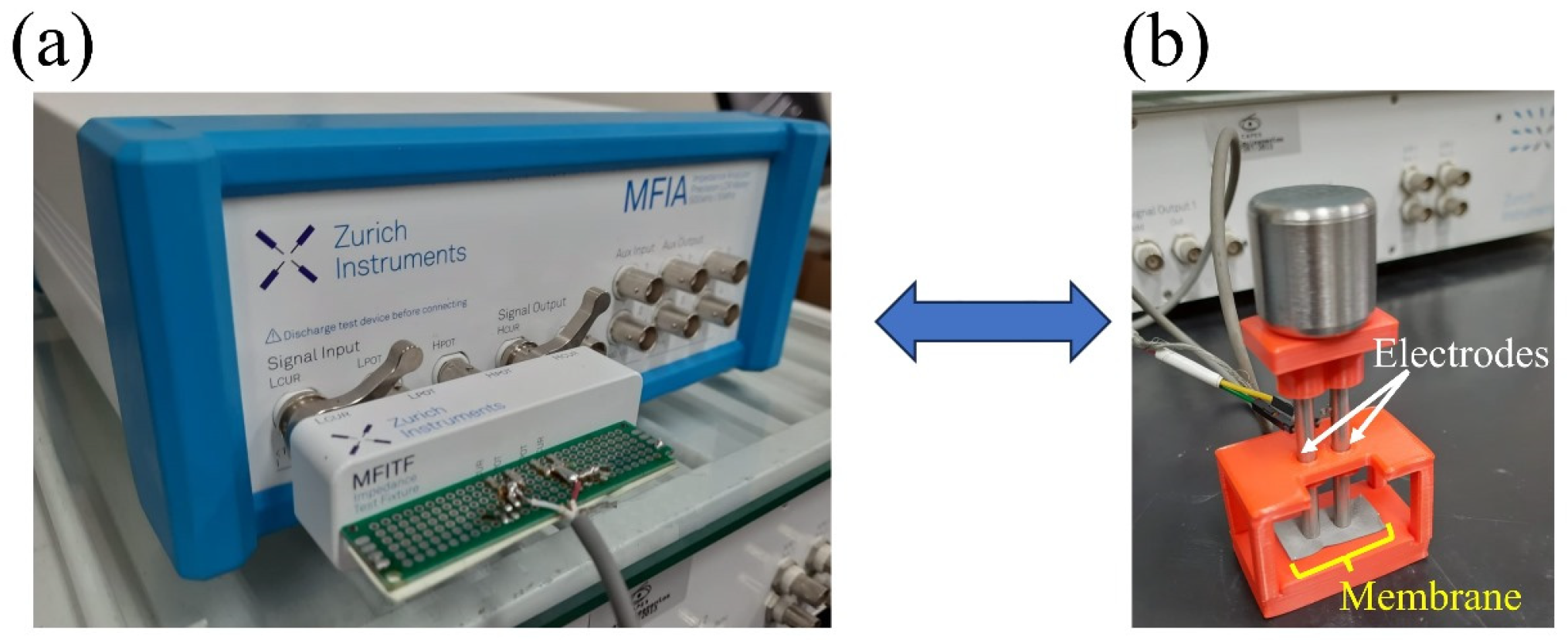
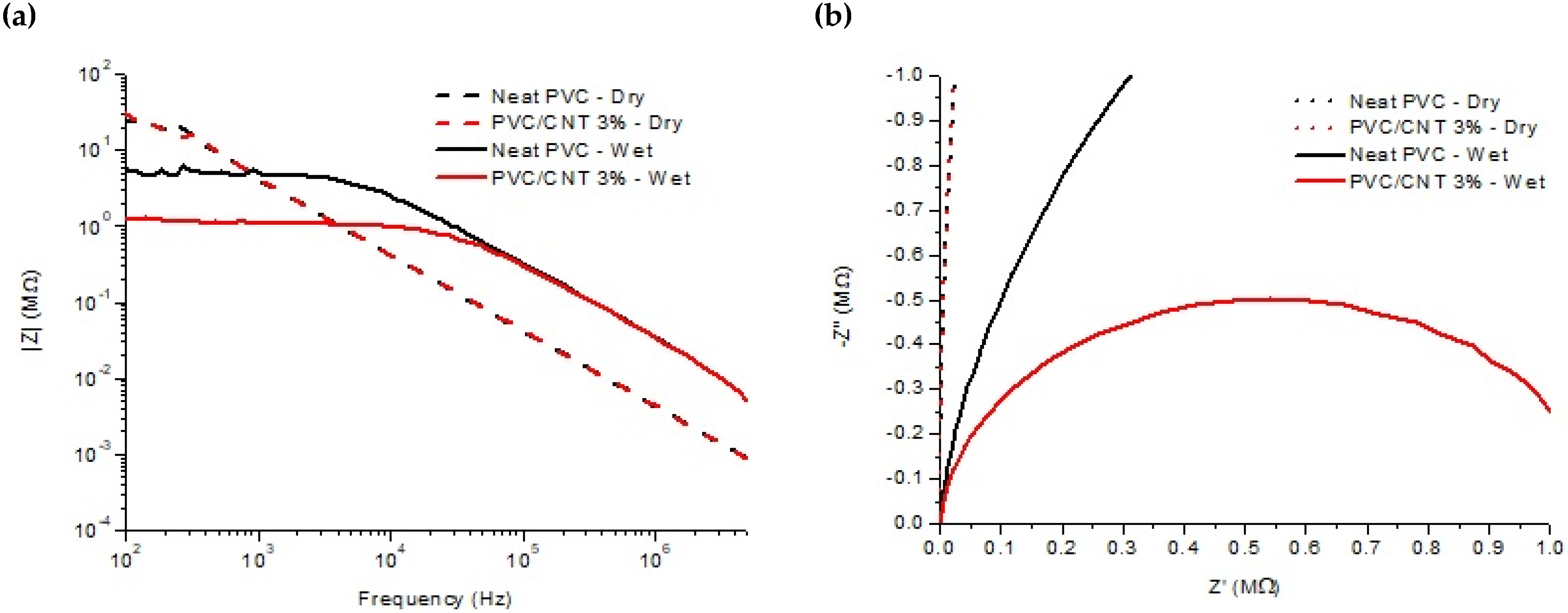
2.7. Electrical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS)
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sakamoto, H.; Fujiwara, I.; Takamura, E.; Suye, S. Nanofiber-Guided Orientation of Electrospun Carbon Nanotubes and Fabrication of Aligned CNT Electrodes for Biodevice Applications. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 245, 122745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Wang, B.; Wang, W.; Yang, H.; Wan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Guan, L.; Yao, Y.; Teng, X.; Meng, C. Structural Design of Electrospun Nanofibers for Electrochemical Energy Storage and Conversion. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 935, 167920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.-H.; Wang, M.-Q.; Yuan, J.-X.; Hao, C.-C.; Li, C.-J.; Long, Y.-Z.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospun Aligned Nanofibers: A Review. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 104193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharafkhani, S.; Kokabi, M. High Performance Flexible Actuator: PVDF Nanofibers Incorporated with Axially Aligned Carbon Nanotubes. Compos. B Eng. 2021, 222, 109060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElMessiry, M.; Fadel, N. The Tensile Properties of Electrospun Poly Vinyl Chloride and Cellulose Acetate (PVC/CA) Bi-Component Polymers Nanofibers. Alex. Eng. J. 2019, 58, 885–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Es-Saheb, M.; Elzatahry, A.A.; Sherif, E.-S.M.; Alkaraki, A.S.; Kenawy, E.-R. A Novel Electrospinning Application for Polyvinyl Chloride Nanofiber Coating Deposition as a Corrosion Inhibitor for Aluminum, Steel, and Brass in Chloride Solutions. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2012, 7, 5962–5976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiscan, O.; Dumitru, I.; Tura, V.; Stancu, A. PVC/Fe Electrospun Nanofibers for High Frequency Applications. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 2322–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, F.G.; Pirayandeh, S.; Mohammadi, T.; Tofighy, M.A. Nanocomposite of PVC with CNT. In Poly(Vinyl Chloride) Based Composites and Nanocomposites. Engineering Materials; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 241–260. [Google Scholar]
- Quoc Pham, L.; Uspenskaya, M.V.; Olekhnovich, R.O.; Olvera Bernal, R.A. A Review on Electrospun Pvc Nanofibers: Fabrication, Properties, and Application. Fibers 2021, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namsaeng, J.; Punyodom, W.; Worajittiphon, P. Synergistic Effect of Welding Electrospun Fibers and MWCNT Reinforcement on Strength Enhancement of PAN–PVC Non-Woven Mats for Water Filtration. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2019, 193, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkasaby, M.A.; Utkarsh, U.; Syed, N.A.; Rizvi, G.; Mohany, A.; Pop-Iliev, R. Evaluation of Electro-Spun Polymeric Nanofibers for Sound Absorption Applications. In Proceedings of the AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing: Long Island, NY, USA, 2020; Volume 2205. [Google Scholar]
- Iribarren, A.; Rivero, P.J.; Berlanga, C.; Larumbe, S.; Miguel, A.; Palacio, J.F.; Rodriguez, R. Multifunctional Protective PVC-ZnO Nanocomposite Coatings Deposited on Aluminum Alloys by Electrospinning. Coatings 2019, 9, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; Qing, X. A Flexible Capacitive Sensor Based on the Electrospun PVDF Nanofiber Membrane with Carbon Nanotubes. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2019, 299, 111579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dror, Y.; Salalha, W.; Khalfin, R.L.; Cohen, Y.; Yarin, A.L.; Zussman, E. Carbon Nanotubes Embedded in Oriented Polymer Nanofibers by Electrospinning. Langmuir 2003, 19, 7012–7020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliahmad, N.; Biswas, P.K.; Wable, V.; Hernandez, I.; Siegel, A.; Dalir, H.; Agarwal, M. Electrospun Thermosetting Carbon Nanotube–Epoxy Nanofibers. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 3, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amalia, R.; Noviyanto, A.; Rahma, L.A.; Merita; Labanni, A.; Fahroji, M.; Purwajanti, S.; Hapidin, D.A.; Zulfi, A. PVC Waste-Derived Nanofiber: Simple Fabrication with High Potential Performance for PM Removal in Air Filtration. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2024, 40, e00928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Fu, Z.; Zhou, H. Experimental Study of the Effect of Humidity on Air Filter Material Performance. Energies 2023, 16, 3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.-J.; Lee, S.; Kim, B.; Kim, J.-H.; So, J.-H.; Koo, H.-J. Impedance Study on Humidity Dependent Conductivity of Polymer Composites with Conductive Nanofillers. Compos. B Eng. 2020, 202, 108412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhizhin, K.Y.; Turyshev, E.S.; Shpigun, L.K.; Gorobtsov, P.Y.; Simonenko, N.P.; Simonenko, T.L.; Kuznetsov, N.T. Poly(Vinyl Chloride)/Nanocarbon Composites for Advanced Potentiometric Membrane Sensor Design. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, W.; Wu, R.; Tang, H.; Ma, Y.; Xu, W.; Jiang, S. Electrospun MoS2-CNTs-PVA/PVA Hybrid Separator for High-Performance Li/FeS2 Batteries. Polymers 2024, 16, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, N.A.; Shoparwe, N.F.; Yusoff, A.H.; Sulaiman, A.Z.; Ahmad, A.L.; Azmi, N.A. Fabrication and Characterisation of MWCNT/Polyvinyl (PVC) Polymer Inclusion Membrane for Zinc (II) Ion Removal from Aqueous Solution. Membranes 2022, 12, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Xu, W.; Ding, Y.; Agarwal, S.; Greiner, A.; Duan, G. A Review of Smart Electrospun Fibers toward Textiles. Compos. Commun. 2020, 22, 100506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardana, S.; Singh, Z.; Sharma, A.K.; Kaur, N.; Pati, P.K.; Mahajan, A. Self-Powered Biocompatible Humidity Sensor Based on an Electrospun Anisotropic Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Non-Invasive Diagnostic Applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 371, 132507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazinani, S.; Ajji, A.; Dubois, C. Fundamental Study of Crystallization, Orientation, and Electrical Conductivity of Electrospun PET/Carbon Nanotube Nanofibers. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 2010, 48, 2052–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, L.Q.; Uspenskaya, M. V Morphalogy PVC Nanofiber, Produced by Electrospinning Method. In International Multidisciplinary Scientific GeoConference Surveying Geology and Mining Ecology Management; SGEM: Sofia, Bulgaria, 2019; Volume 19, pp. 289–295. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Ding, B.; Yang, J.; Yu, J.; Sun, G. Subtle Regulation of the Micro-and Nanostructures of Electrospun Polystyrene Fibers and Their Application in Oil Absorption. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Chang, Z.; Zhu, M.; Mo, X.; Chen, D. Electrospun Carbon Nanotube Composite Nanofibres with Uniaxially Aligned Arrays. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 115611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q. Roles of Carbon Nanotubes in Novel Energy Storage Devices. Carbon 2017, 122, 462–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.; Kumar, R.; Barakat, M.A.; Lee, M. Synthesis of PVC/CNT Nanocomposite Fibers Using a Simple Deposition Technique for the Application of Alizarin Red S (ARS) Removal. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 14393–14399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ero-Phillips, O.; Jenkins, M.; Stamboulis, A. Tailoring Crystallinity of Electrospun Plla Fibres by Control of Electrospinning Parameters. Polymers 2012, 4, 1331–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bognitzki, M.; Czado, W.; Frese, T.; Schaper, A.; Hellwig, M.; Steinhart, M.; Greiner, A.; Wendorff, J.H. Nanostructured Fibers via Electrospinning. Adv. Mater. 2001, 13, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaszewska, J.; Sterzyński, T.; Woźniak-Braszak, A.; Banaszak, M. Review of Recent Developments of Glass Transition in PVC Nanocomposites. Polymers 2021, 13, 4336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.C.; Gilbert, M. Characterisation and Properties of Oriented PVC Fibres. Polymers 2004, 45, 7293–7301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedri, A.; Zaabat, M.; Boudine, B.; Hafdallah, A. Synthesis, Characterization, Structural, and Optical Properties of Polyvinyl Chloride/Zinc Oxide Nanocomposite Films for Photocatalysis Application. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2020, 30, 4884–4894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callister, W.D., Jr.; Rethwish, D.G. Materials Science and Engineering an Introduction; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Helal, A.I.; Vshivkov, S.A.; Zaki, M.F.; Elkalashy, S.I.; Soliman, T.S. Effect of Carbon Nano Tube in the Structural and Physical Properties of Polyvinyl Chloride Films. Phys. Scr. 2021, 96, 085804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nofal, M.M.; Aziz, S.B.; Ghareeb, H.O.; Hadi, J.M.; Dannoun, E.M.A.; Al-Saeedi, S.I. Impedance and Dielectric Properties of PVC:NH4I Solid Polymer Electrolytes (SPEs): Steps toward the Fabrication of SPEs with High Resistivity. Materials 2022, 15, 2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Carlberg, B.; Lu, X.; Cheng, Z.; Liu, J.; Shangguan, D. Investigation of Dielectric Strength of Electrospun Nanofiber Based Thermal Interface Material. In Proceedings of the 2007 International Symposium on High Density Packaging and Microsystem Integration, Shanghai, China, 26–28 June 2007; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Al Naim, A.F.; AlFannakh, H.; Arafat, S.; Ibrahim, S.S. Characterization of PVC/MWCNTs Nanocomposite: Solvent Blend. Sci. Eng. Compos. Mater. 2020, 27, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mkhabela, V.J.; Mishra, A.K.; Mbianda, X.Y. Thermal and Mechanical Properties of Phosphorylated Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube/Polyvinyl Chloride Composites. Carbon 2011, 49, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljaafari, A.; Abu-Abdeen, M.; Aljaafari, M. Mechanical and Electrical Properties of Poly(Vinyl Chloride) Loaded with Carbon Nanotubes and Carbon Nanopowder. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2012, 25, 679–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

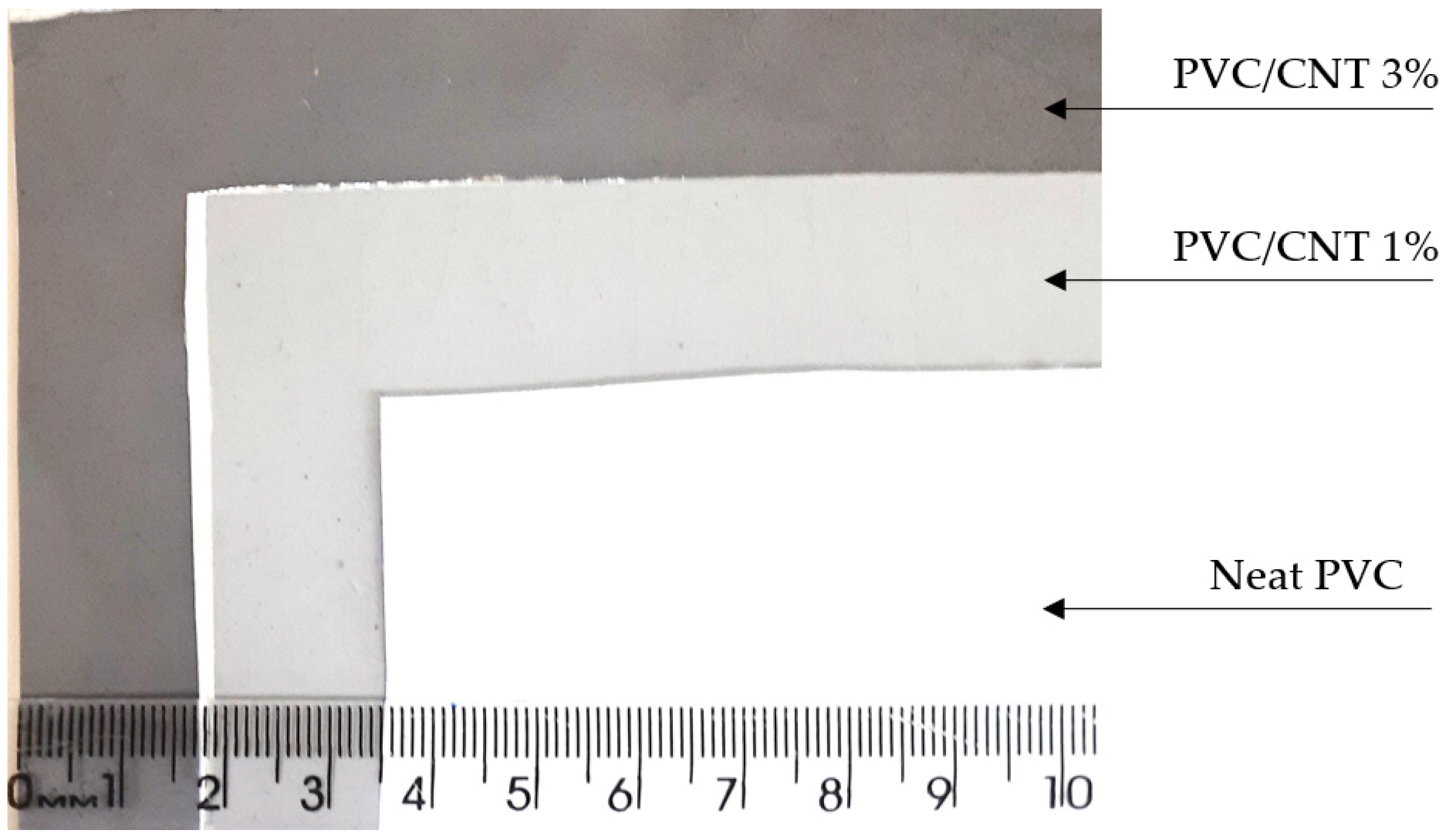






| Name | PVC (g) | CNTs (g) | Triton X-100 (g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neat PVC | 3.6 | - | - |
| PVC/CNT 1% | 3.6 | 0.036 | 0.118 |
| PVC/CNT 2% | 3.6 | 0.072 | 0.118 |
| PVC/CNT 3% | 3.6 | 0.108 | 0.119 |
| Variables | Values |
|---|---|
| Flow rate | 3 mL/h |
| Work distance | 15 cm |
| Collector rotation | 160 rpm |
| Syringe | 10 mL |
| Needle | Ø0.7 × 30 mm |
| Temperature | 23 °C |
| Humidity | 42–55% |
| Name | 1st Heating (°C) | 2nd Heating (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| Neat PVC resin | 82 | 82 |
| Neat PVC membrane | 79 | 75 |
| PVC/CNT 1% | 74 | 66 |
| PVC/CNT 2% | 71 | 62 |
| PVC/CNT 3% | 62 | 61 |
| Properties | Results | Literature | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Morphological |
|
| [24] |
| [25] | ||
| [4] | ||
|
| [24] | |
| [4] | ||
|
| [26] | |
|
| [33,34,36] | |
| Thermal |
|
| [29] |
| [39] | ||
|
| [32] | |
| [40] | ||
| [40] | ||
| Impedance spectra |
|
| [18] |
| |||
| [41] | ||
| [37] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Briesemeister, M.; Gómez-Sánchez, J.A.; Bertemes-Filho, P.; Pezzin, S.H. PVC/CNT Electrospun Composites: Morphology and Thermal and Impedance Behavior. Polymers 2024, 16, 2867. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16202867
Briesemeister M, Gómez-Sánchez JA, Bertemes-Filho P, Pezzin SH. PVC/CNT Electrospun Composites: Morphology and Thermal and Impedance Behavior. Polymers. 2024; 16(20):2867. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16202867
Chicago/Turabian StyleBriesemeister, Marcio, John A. Gómez-Sánchez, Pedro Bertemes-Filho, and Sérgio Henrique Pezzin. 2024. "PVC/CNT Electrospun Composites: Morphology and Thermal and Impedance Behavior" Polymers 16, no. 20: 2867. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16202867
APA StyleBriesemeister, M., Gómez-Sánchez, J. A., Bertemes-Filho, P., & Pezzin, S. H. (2024). PVC/CNT Electrospun Composites: Morphology and Thermal and Impedance Behavior. Polymers, 16(20), 2867. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16202867








