Synthesis of Some Eco-Friendly Materials for Gold Recovery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Adsorbent Synthesis
2.2. Adsorbent Testing for Au(III) Recovery
2.3. Selected Adsorbent Characterization, CE-Cys
2.4. Au(III) Recovery Mechanism by Adsorption onto CE-Cys Material
2.4.1. Kinetic Studies
2.4.2. The Influence of the S:L Ratio on the Efficiency of the Adsorption Process
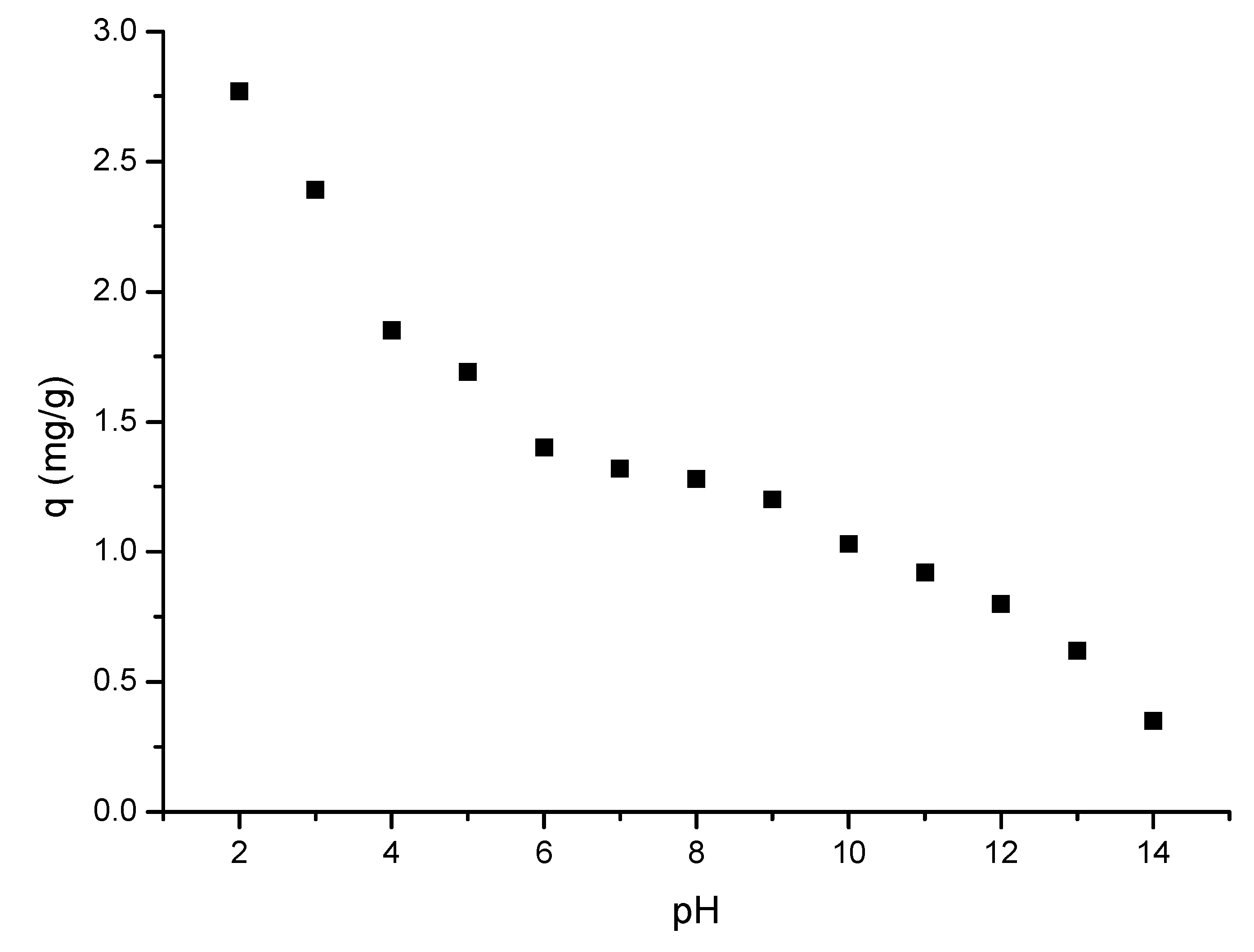
2.4.3. pH Influence
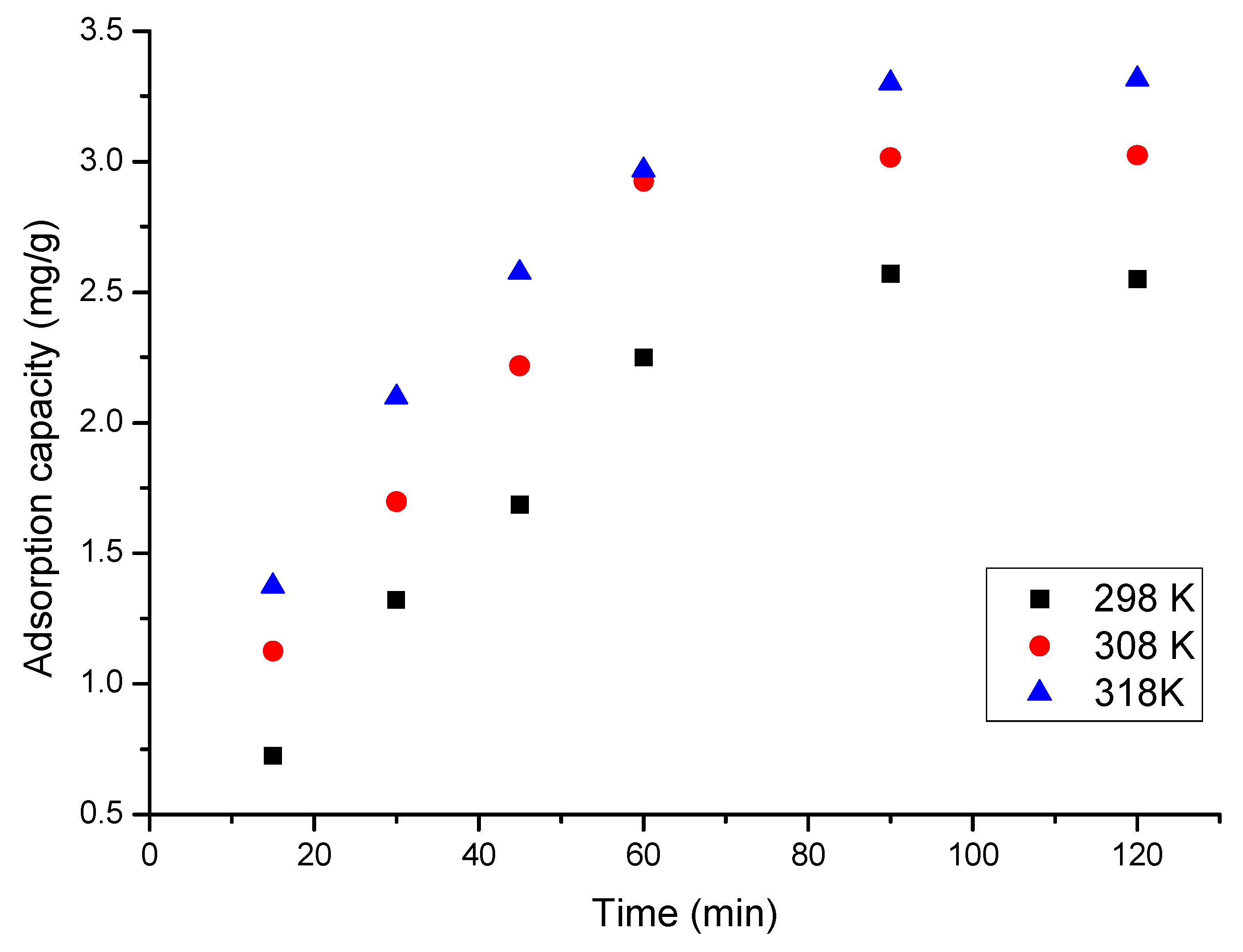
2.4.4. Contact Time and Temperature
2.4.5. Thermodynamic Studies
2.4.6. Equilibrium Studies
2.4.7. CE-Cys Material Reuse Studies
3. Results and Discussion
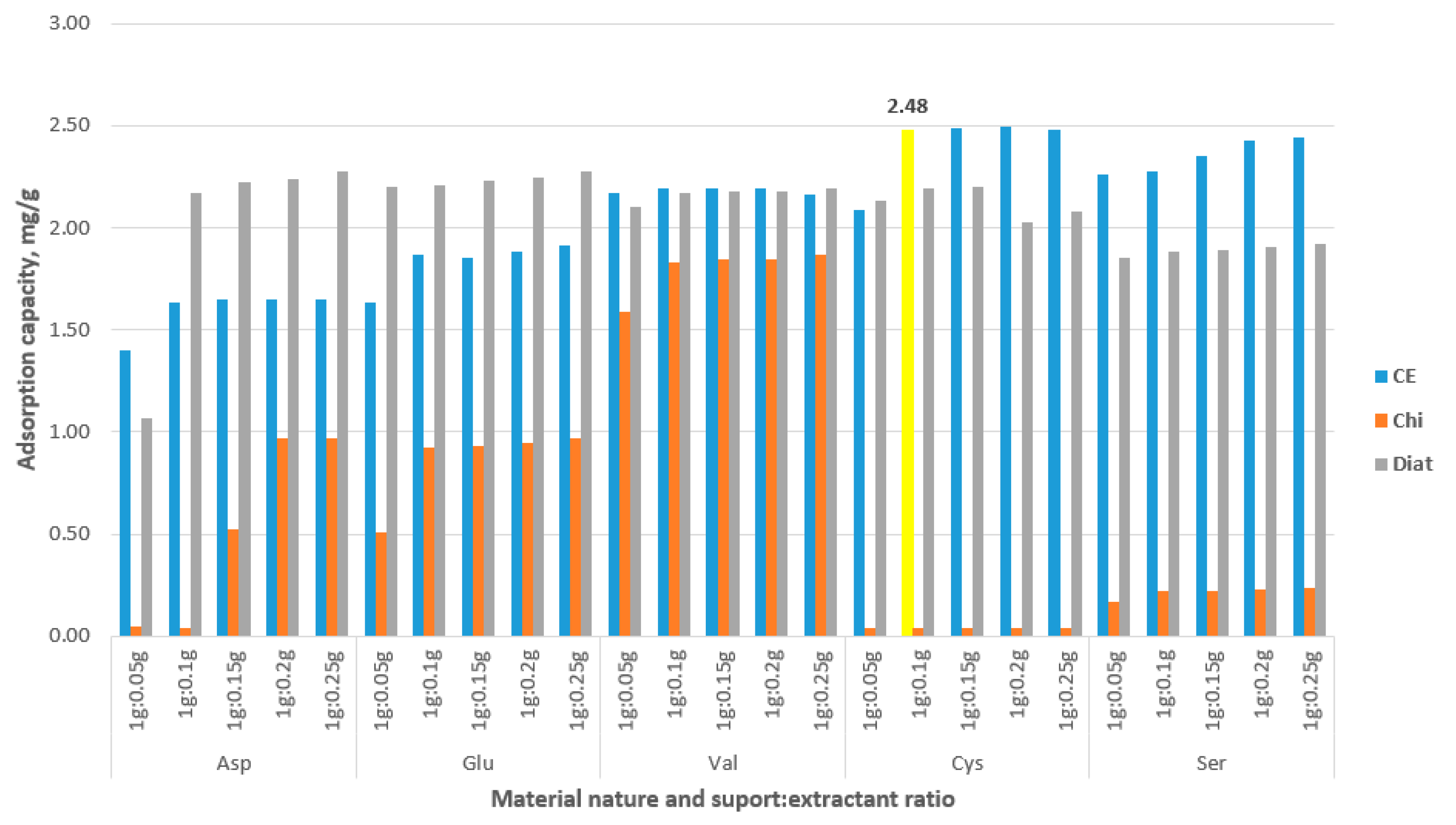
3.1. Testing as an Adsorbent for Gold Recovery
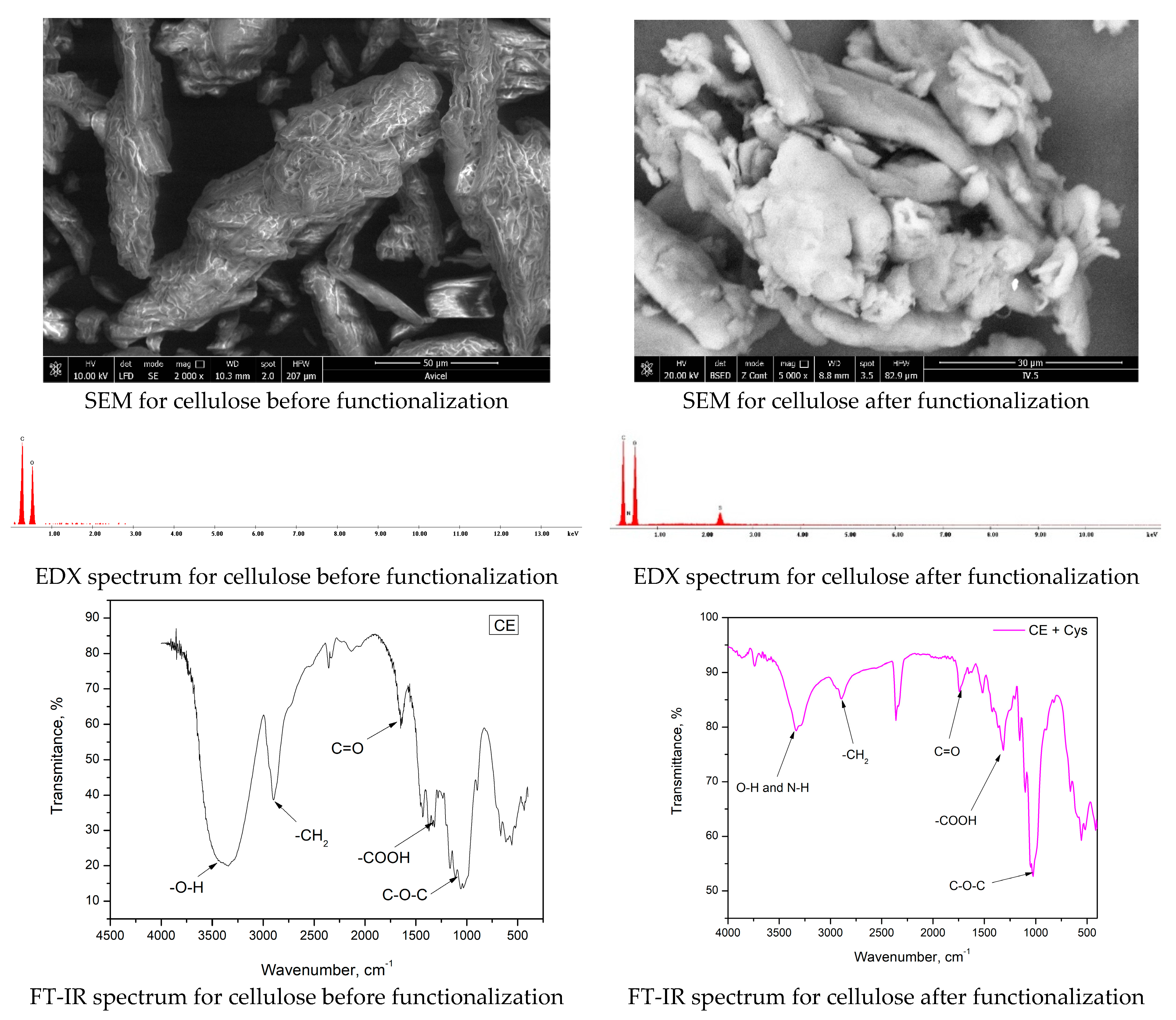
3.2. Characterization of New Synthesized CE-Cys Adsorbent Material
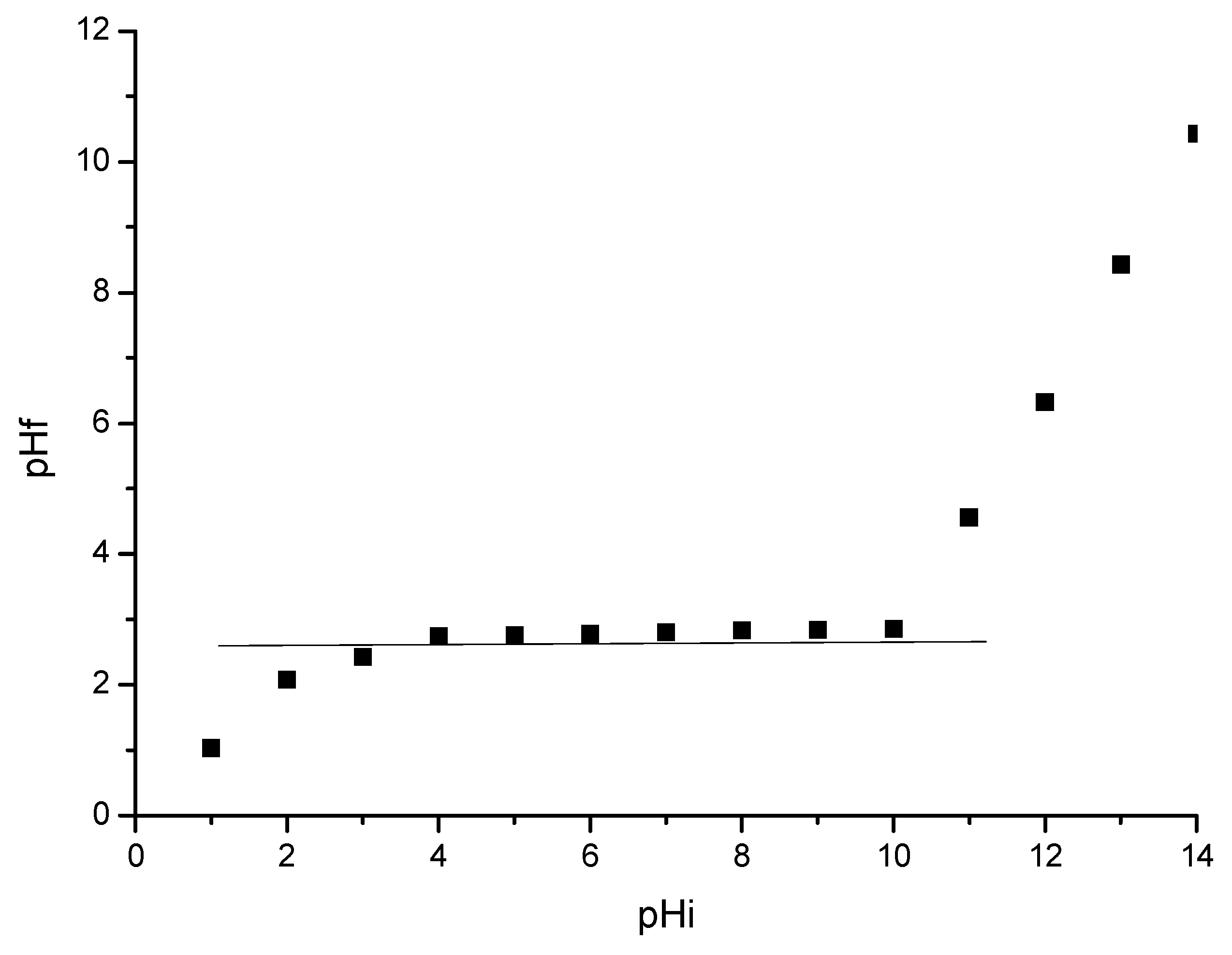
3.3. Determination of Material pHpZc
3.4. Au(III) Recovery Mechanism by Adsorption onto CE-Cys Material
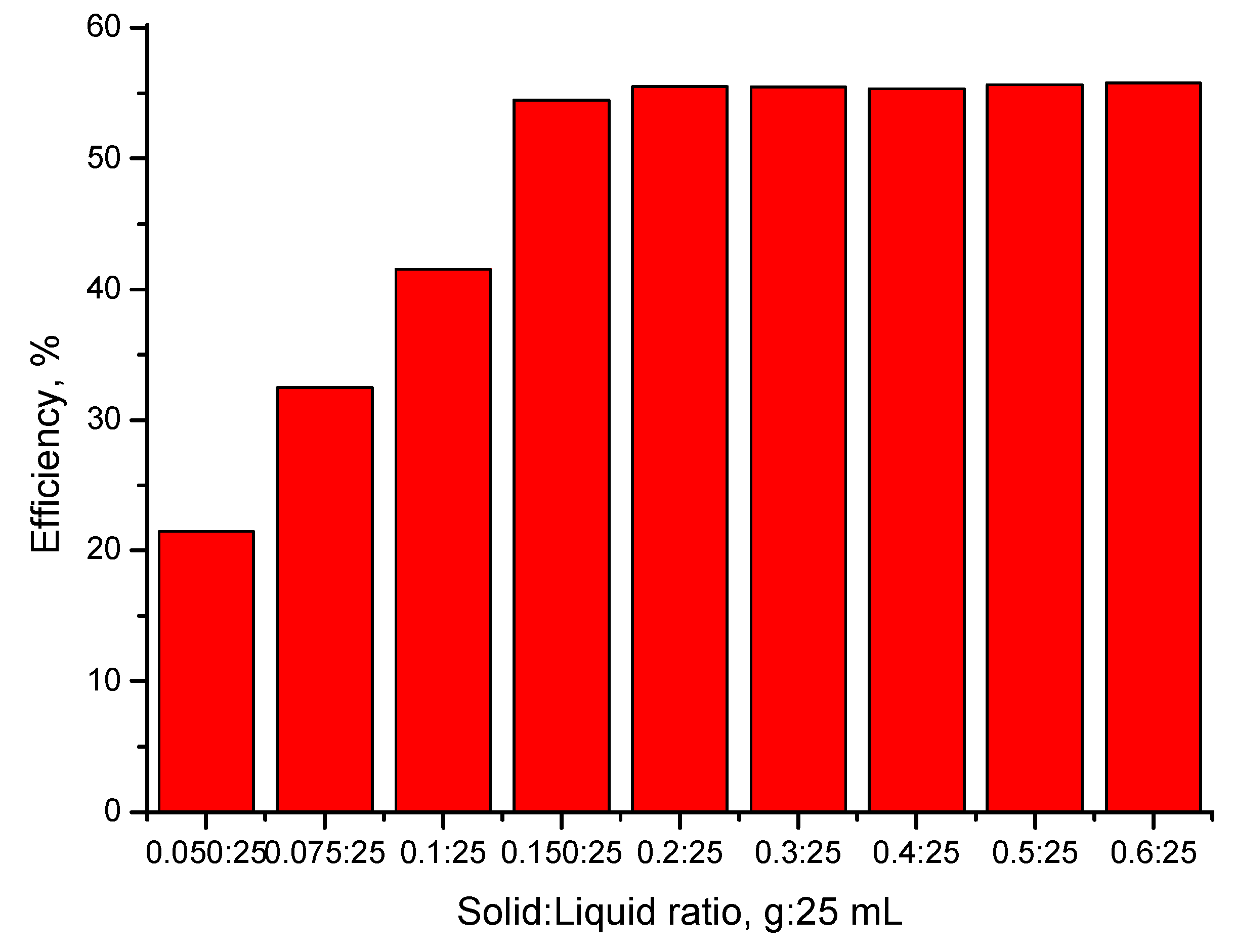
3.4.1. The Influence of the S:L Ratio on the Efficiency of the Adsorption Process
3.4.2. pH Influence
3.4.3. Contact Time and Temperature Influence
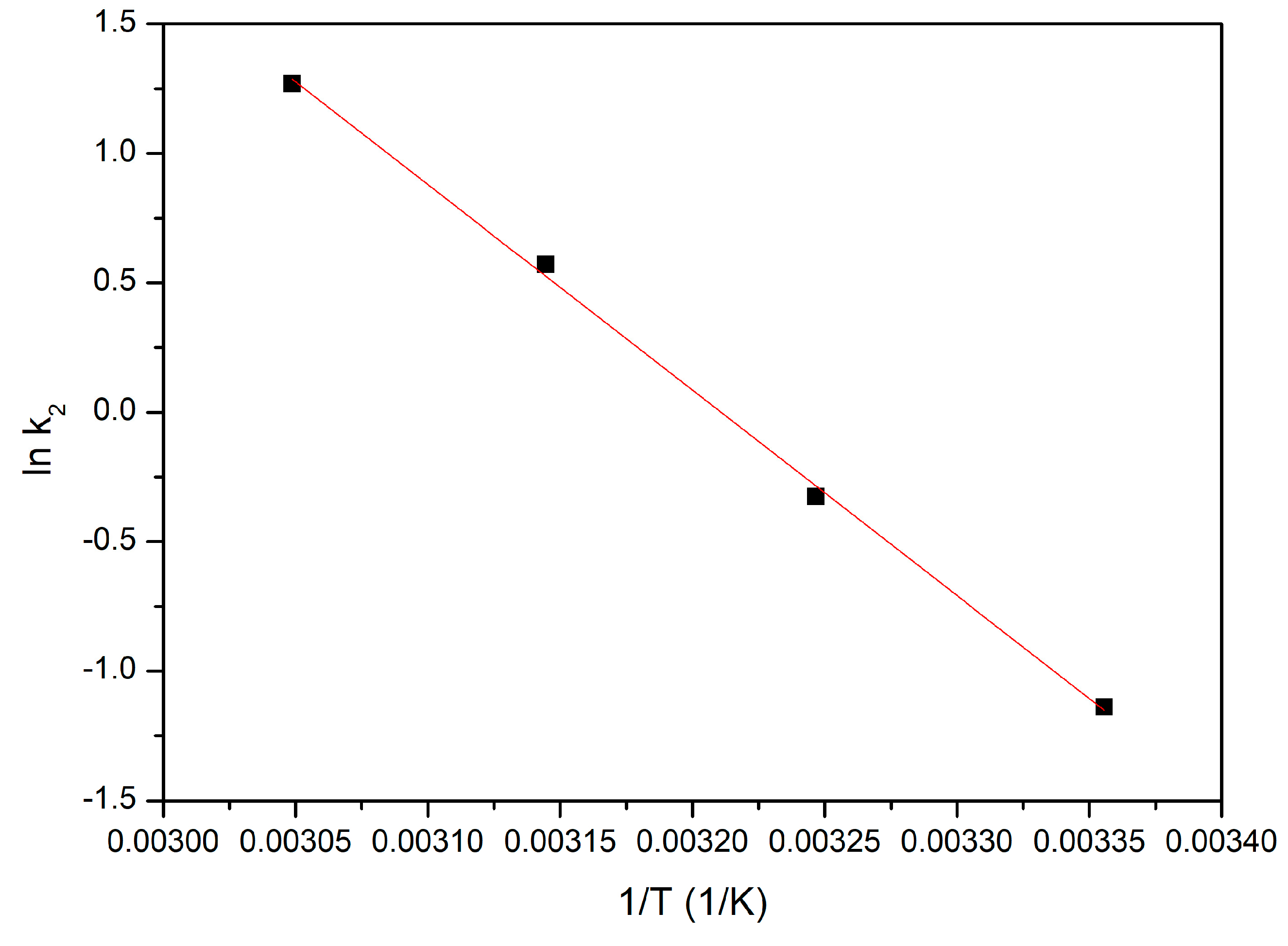
3.4.4. Kinetic Studies
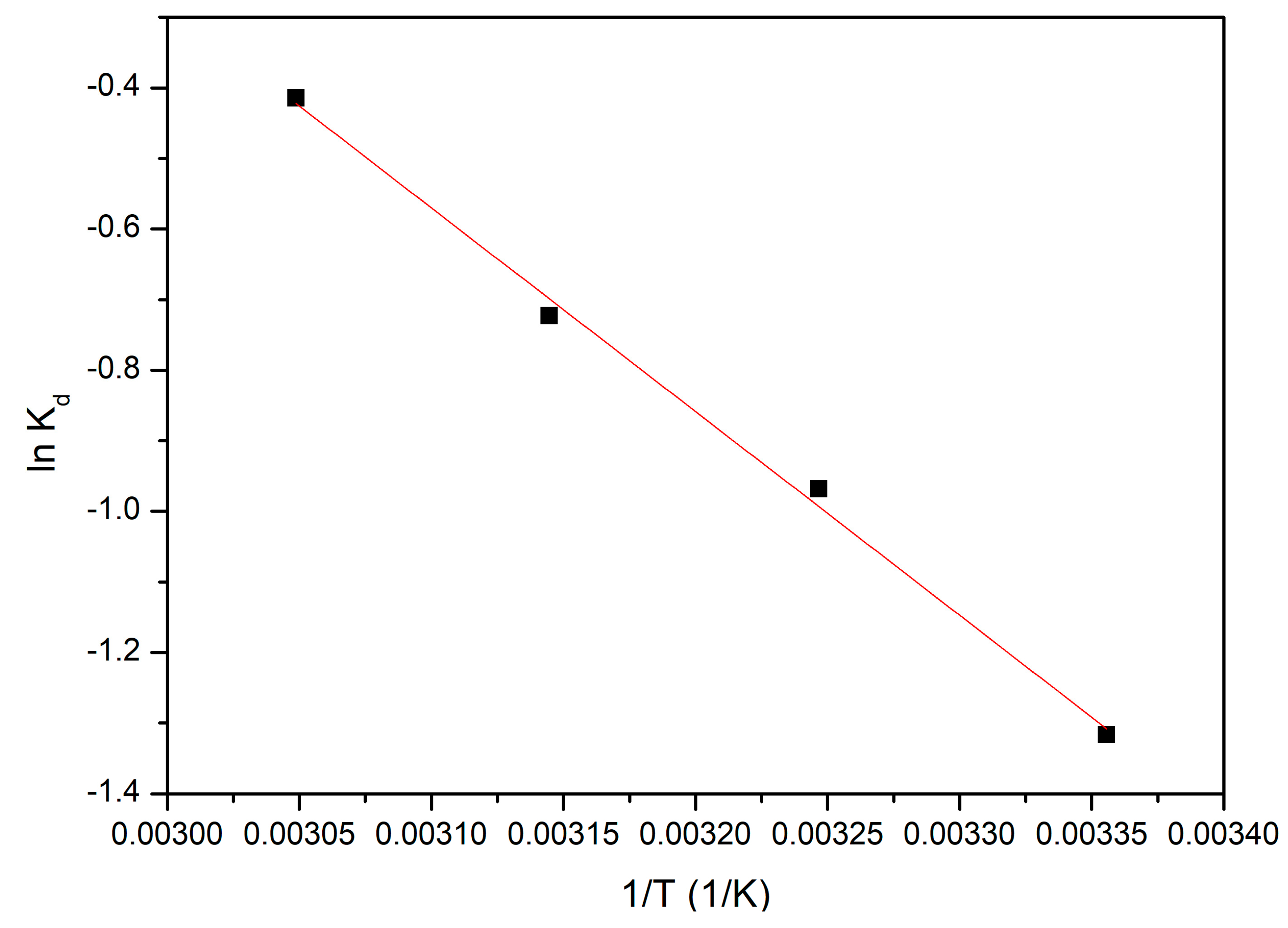
3.4.5. Thermodynamic Studies
3.4.6. Activation Energy
3.4.7. Equilibrium Studies
3.4.8. CE-Cys Material Reuse Studies
- -
- With the increase in the number of sorption/desorption cycles, the volume of Au(III) solution passed through the material with adsorbent properties decreases;
- -
- For each adsorption cycle, it was observed that, with the increase in the volume sequence of the added Au(III) solution, the residual concentration of Au(III) ions decreases and the retention efficiency increases until the column breakthrough when the desorption is necessary;
- -
- For each desorption cycle performed, it was observed that the degree of desorption decreases (Figure 12). The maximum number of adsorption/desorption cycles is 5.
4. Conclusions
- -
- The optimal S:L ratio is 0.1 g of adsorbent material:25 mL of gold solution;
- -
- The optimal pH < 4;
- -
- With the increasing contact time, the adsorption capacity increases, reaching equilibrium after 90 min;
- -
- With the temperature increase, an insignificant difference in adsorption capacity was observed;
- -
- The studied adsorption process is accurately shown by the pseudo-second-order kinetic model;
- -
- Since the activation energy calculated for the studied adsorption process is lower than 8 kJ mol−1, gold adsorption is a physical process;
- -
- The adsorption data were better modelled by the Sips isotherm;
- -
- The studied material was able to be reused for five adsorption/desorption cycles.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Monier, M.; Abdel-Latif, D.A. Fabrication of Au(III) ion-imprinted polymer based on thiol-modified chitosan. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 105, 777–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Zhou, L.; Wang, W.; Yu, G.; Deng, S. Adsorptive recovery of Au(III) from aqueous solution using crosslinked polyethyleneimine resins. Chemosphere 2020, 2411, 125122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Xu, W.; Li, H.; Zhou, S.; Mo, X.; Zhang, P.; Tang, K. Highly Efficient Adsorption of Au(III) from Water by a Novel Metal–Organic Framework Constructed with Sulfur-Containing Ligands and Zn(II). Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 17972–17979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Xu, X.; Ao, J.; Ma, L.; Ye, F.; Wang, Z.; Xu, L.; Zhao, X.; Ma, H. Selective Adsorption, Reduction, and Separation of Au(III) from Aqueous Solution with Amine-Type Non-Woven Fabric Adsorbents. Materials 2020, 13, 2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.S.; Hong, Y.; Dogan, N.A.; Yavuz, C.T. Gold Recovery from E-Waste by Porous Porphyrin–Phenazine Network Polymers. Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 5343–5349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Peng, L.; Dong, Z.; Yan, J.; Wang, C.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, L. Highly efficient and selective recovery of Au(III) by cellulose microspheres bearing nucleobase and their applications in gold slag treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 3144, 123669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birtane, H.; Urucu, O.A.; Yıldız, N.; Çiğil, A.B.; Kahraman, M.V. Statistical optimization and selective uptake of Au(III) from aqueous solution using carbon nanotube-cellulose based adsorbent. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 300, 103144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L. Engineering of UiO-66-NH2 as selective and reusable adsorbent to enhance the removal of Au(III) from water: Kinetics, isotherm and thermodynamics. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 6011, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakili, M.; Deng, S.; Li, T.; Wang, W.; Wang, W.; Yu, G. Novel crosslinked chitosan for enhanced adsorption of hexavalent chromium in acidic solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 3477, 782–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, F.; Qin, X. Adsorption of diclofenac onto goethite: Adsorption kinetics and effects of pH. Chemosphere 2017, 1800, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Sui, J.; Li, J.; Tang, Y.; Cai, W. Efficient removal of heavy metal ions by thiol-functionalized superparamagnetic carbon nanotubes. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 2100, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, A.D.; Dubey, S.P.; Hokkanen, S.; Fallah, R.N.; Sillanpää, M. Recovery of gold from aqueous solutions by taurine modified cellulose: An adsorptive–reduction pathway. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 2555, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amen, R.; Elsayed, I.; Schueneman, G.T.; Hassan, E.B. Self-Assembled Aminated and TEMPO Cellulose Nanofibers (Am/TEMPO-CNF) Aerogel for Adsorptive Removal of Oxytetracycline and Chloramphenicol Antibiotics from Water. Gels 2024, 10, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Zhang, B.; Peng, J. Selective recovery of Au(III) from aqueous solutions by nanosilica grafted with cationic polymer: Kinetics and isotherm. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 80, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, M.A.; Elnagar, M.M.; Kenawy, I.M.; Ismail, M.A. Synthesis and application of hydrazono-imidazoline modified cellulose for selective separation of precious metals from geological samples. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 237, 116177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, F.B.; Rahman, I.M.M.; Nakakubo, K.; Endo, M.; Nagai, K.; Mashio, A.S.; Taniguchi, T.; Nishimura, T.; Maeda, K.; Hasegawa, H. Highly selective and straightforward recovery of gold and platinum from acidic waste effluents using cellulose-based bio-adsorbent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 410, 124569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boccia, A.C.; Neagu, M.; Pulvirenti, A. Bio-Based Aerogels for the Removal of Heavy Metal Ions and Oils from Water: Novel Solutions for Environmental Remediation. Gels 2024, 10, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vassalini, I.; Maddaloni, M.; Depedro, M.; De Villi, A.; Ferroni, M.; Alessandri, I. From Water for Water: PEDOT:PSS-Chitosan Beads for Sustainable Dyes Adsorption. Gels 2024, 10, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatsenko, E.A.; Trofimov, S.V.; Goltsman, B.M.; Li, W.; Smoliy, V.A.; Ryabova, A.V.; Klimova, L.V.; Izvarin, A.I. Study on the Curing and Foaming of Surfactant-Modified Geopolymer Gels Based on Ash and Slag Waste from Coal Combustion. Gels 2024, 10, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Mao, Y.; Song, Z.; Yang, Y.; Yan, X.; Kang, H.; Liu, Y.; Gu, D.; Zhang, X.; Yan, X. Selective adsorption and mechanism of Au (III) onto thiourea functionalized cuprous oxide. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwandira, W.; Nakashima, K.; Togo, Y.; Sato, T.; Kawasaki, S. Cellulose-metallothionein biosorbent for removal of Pb(II) and Zn(II) from polluted water. Chemosphere 2020, 246, 125733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Wu, L.; Han, X.; Yao, L.; Zhao, S.; Sun, J.; Xu, Y.; Li, J.; Xiong, C. Green chemical synthesis of new chelating fiber and its mechanism for recovery gold from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 378, 120674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Biswas, B.; Hassan, M.; Naidu, R. Green Adsorbents for Environmental Remediation: Synthesis Methods, Ecotoxicity, and Reusability Prospects. Processes 2024, 12, 1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.J.; Li, E.Z.; Li, Y.Z.; Li, J.F.; Du, Z.P.; Cheng, F.Q. Enhanced Removal of Dissolved Humic Acid from Water Using Eco-Friendly Phenylalanine-Modified-Chitosan Fe3O4 Magnetic Nanoparticles. Chemistryselect 2020, 5, 4285–4291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullaimalar, A.; Thanigaiselvan, R.; Karuppaiyan, J.; Kiruthika, S.; Jeyalakshmi, R.; Albeshr, M.F. An efficient eco-friendly adsorbent material based on waste copper slag-biomass ash geopolymer: Dye sorption capacity and sustainable properties. Environ. Geochem. Health 2024, 46, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.-T.; Lee, J.-W.; An, H.-E.; Cho, S.-H.; Jeong, S. Efficient Fluoride Wastewater Treatment Using Eco-Friendly Synthesized AlOOH. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekry, M.; Elmesallamy, S.M.; El-Rahman, N.R.A.; Bekhit, M.; Elsaied, H.A. Eco-friendly adsorbents based on abietic acid, boswellic acid, and chitosan/magnetite for removing waste oil from the surface of the water. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 64633–64646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kang, T.; Kim, H.; Shin, H.J.; Oh, S.G. Preparation of PVA/PAA nanofibers containing thiol-modified silica particles by electrospinning as an eco-friendly Cu (II) adsorbent. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 77, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Liang, Y.N.; Hu, X. An eco-friendly approach for heavy metal adsorbent regeneration using CO2-responsive molecular octopus. Chemosphere 2017, 185, 1157–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, N.; Abarca, R.L.; Linares-Flores, C. Two Fascinating Polysaccharides: Chitosan and Starch. Some Prominent Characterizations for Applying as Eco-Friendly Food Packaging and Pollutant Remover in Aqueous Medium. Progress in Recent Years: A Review. Polymers 2021, 13, 1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Fang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Mei, D.; Ma, F.; Meng, Y.; Dong, H.; Zhang, C. Synthesis of amino acid modified MIL-101 and efficient uranium adsorption from water. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 349, 118095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Wang, Z.; Xia, C.; Wang, X.; He, H.; Nie, Z.; Wang, S.; Li, W. Regulating the Interface Polarity Distribution of Zr-Based MOFs by Amino Acid-Like Ligand Functionalization Enables Efficient Recovery of Gold. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 349, 118095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Zhang, M.; Dong, Z.; Qi, W.; Zhai, M.; Zhao, L. Efficient and selective adsorption of Pd(II) by amino acid-functionalized cellulose microspheres and their applications in palladium recovery from PCBs leaching solution. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 301, 122037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Mattocks, J.A.; Seidel, J.A.; Cotruvo, J.A.; Park, D.M. Protein-based approach for high-purity Sc, Y, and grouped lanthanide separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 333, 125919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L. A method for preparing silica-containing iron(III) oxide adsorbents for arsenic removal. Water Res. 2003, 37, 4351–4358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortina, J.L.; Miralles, N.; Sastre, A.M.; Aguilar, M. Solid-liquid extraction studies of divalent metals with impregnated resins containing mixtures of organophosphorus extractants. React. Funct. Polym. 1997, 32, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortina, J.L.; Warshawsky, A.; Miralles, N.; Aguilar, M.; Sastre, A.M. Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Liquid Effluents by Solvent-Impregnated Resins. In Hydrometallurgy ’94, Proceedings of the International Symposium ‘Hydrometallurgy ’94′, Cambridge, UK, 11–15 July 1994; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1994; pp. 725–739. [Google Scholar]
- An, B.; Steinwinder, T.R.; Zhao, D. Selective removal of arsenate from drinking water using a polymeric ligand exchanger. Water Res. 2005, 39, 4993–5004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belkhouche, N.-E.; Didi, M.A. Extraction of Bi(III) from nitrate medium by D2EHPA impregnated onto Amberlite XAD-1180. Hydrometallurgy 2010, 103, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabani, M.; Amrane, A.; Bensmaili, A. Kinetics of nitrates adsorption on Amberlite IRA 400 resin. Desalination 2007, 206, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanda, M.; O’Driscoll, K.F.; Rempel, G.L. Ligand exchange sorption of arsenate and arsenite anions by chelating resins in ferric ion form: II. Iminodiacetic chelating resin Chelex 100. React. Polym. Ion Exch. Sorbents 1988, 8, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A.; Hosseini, M.S.; Sarw-Ghadi, M.; Zowghi, S.; Hosseini, E.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, H. Kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamic study of Cr(VI) sorption into toluidine blue o-impregnated XAD-7 resin beads and its application for the treatment of wastewaters containing Cr(VI). Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 160, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, S.; Shah, K.H.; Naeem, A.; Waseem, M.; Tahir, M. Chromium (III) removal by weak acid exchanger Amberlite IRC-50 (Na). J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 160, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Jyo, A. REMOVAL of ARSENIC(V) by ZIRCONIUM(IV)-LOADED PHOSPHORIC ACID CHELATING RESIN. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2001, 36, 3175–3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, L.; Wan, Y.; Wang, X.; Liang, Q.; Li, Z.; Xu, S. Efficient visible light photocatalytic activitiy of tetranitro substituted cobalt phthalocyanines–attapulgite hybrid materials fabricated by ultrasonic impregnation method. Optik 2016, 127, 4127–4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barathi, M.; Kumar, A.S.K.; Rajesh, N. A novel ultrasonication method in the preparation of zirconium impregnated cellulose for effective fluoride adsorption. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2014, 21, 1090–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawant, S.S.; Anil, A.C.; Krishnamurthy, V.; Gaonkar, C.; Kolwalkar, J.; Khandeparker, L.; Desai, D.; Mahulkar, A.V.; Ranade, V.V.; Pandit, A.B. Effect of hydrodynamic cavitation on zooplankton: A tool for disinfection. Biochem. Eng. J. 2008, 42, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iskalieva, A.; Yimmou, B.M.; Gogate, P.R.; Horvath, M.; Horvath, P.G.; Csoka, L. Cavitation assisted delignification of wheat straw: A review. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2012, 19, 984–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Ma, G.; Ye, X.; Kakuda, Y.; Meng, R. Stability of all-trans-β-carotene under ultrasound treatment in a model system: Effects of different factors, kinetics and newly formed compounds. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2010, 17, 654–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittmann, B.; Haupert, F.; Schlarb, A.K. Ultrasonic dispersion of inorganic nanoparticles in epoxy resin. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2009, 16, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnside, S.D.; Giannelis, E.P. Synthesis and properties of new poly(dimethylsiloxane) nanocomposites. Chem. Mater. 1995, 7, 1597–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.S.; Bernet, N.; de la Roche, S.; Hahn, H.T. Processing of Iron Oxide-epoxy Vinyl Ester Nanocomposites. J. Compos. Mater. 2003, 37, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, R.D.; Malhotra, V.M. Rupture of nanoparticle agglomerates and formulation of Al2O3-epoxy nanocomposites using ultrasonic cavitation approach: Effects on the structural and mechanical properties. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2006, 46, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahfuz, H.; Uddin, M.F.; Rangari, V.K.; Saha, M.C.; Zainuddin, S.; Jeelani, S. High Strain Rate Response of Sandwich Composites with Nanophased Cores. Appl. Compos. Mater. 2005, 12, 193–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Wang, Q. Preparation of conductive polyaniline/nanosilica particle composites through ultrasonic irradiation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 87, 1811–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borah, D.; Satokawa, S.; Kato, S.; Kojima, T. Surface-modified carbon black for As(V) removal. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 319, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borah, D.; Satokawa, S.; Kato, S.; Kojima, T. Sorption of As(V) from aqueous solution using acid modified carbon black. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 162, 1269–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhalara, P.D.; Punetha, D.; Balasubramanian, K. A review of potential remediation techniques for uranium(VI) ion retrieval from contaminated aqueous environment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1621–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagergren, S. About the theory of so-called adsorption of soluble substabces. Kungl. Sven. Vetenskapsakademiens Handl. 1898, 24, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, Y.S. Review of second-order models for adsorption systems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 136, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. A Comparison of Chemisorption Kinetic Models Applied to Pollutant Removal on Various Sorbents. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 1998, 76, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; Mckay, G. The kinetics of sorption of basic dyes from aqueous solution by sphagnum moss peat. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 1998, 76, 822–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daminescu, D.; Duteanu, N.; Ciopec, M.; Negrea, A.; Negrea, P.; Nemes, N.S.; Pascu, B.; Ianasi, C.; Cotet, L. Adsorption of Scandium Ions by Amberlite XAD7HP Polymeric Adsorbent Loaded with Tri-n-Octylphosphine Oxide. Molecules 2024, 29, 822–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkins, P.; Paula, D.J. Atkins’ Physical Chemistry; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2005; p. 1008. [Google Scholar]
- Freundlich, H.M.F. Over the adsorption in solution. J. Phys. Chem. 1906, 57, 385–470. [Google Scholar]
- Gautam, R.K.; Chattopadhyaya, M.C.; Sharma, S.K. Biosorption of Heavy Metals: Recent Trends and Challenges. In Wastewater Reuse and Management; Sharma, S.K., Sanghi, R., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 305–322. [Google Scholar]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sert, Ş.; Kütahyali, C.; İnan, S.; Talip, Z.; Çetinkaya, B.; Eral, M. Biosorption of lanthanum and cerium from aqueous solutions by Platanus orientalis leaf powder. Hydrometallurgy 2008, 90, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihăilescu, M.; Negrea, A.; Ciopec, M.; Davidescu, C.M.; Negrea, P.; Duţeanu, N.; Rusu, G. Gold (III) adsorption from dilute waste solutions onto Amberlite XAD7 resin modified with L-glutamic acid. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohaimy, M.I.H.; Isa, M.I.N. Proton-Conducting Biopolymer Electrolytes Based on Carboxymethyl Cellulose Doped with Ammonium Formate. Polymers 2022, 14, 3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Xiao, X.; Yang, Y.; Zou, T.; Xing, X.; Zhao, R.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y. L-Aspartic Acid Capped CdS Quantum Dots as a High Performance Fluorescence Assay for Sliver Ions (I) Detection. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komal; Gupta, K.; Kaur, S.; Kaur, J.; Kaushik, A.; Singhal, S. A comparative analysis of source based distinctly functionalized nanostructured cellulose for the adsorptive removal of toxic colorants. Cellulose 2019, 26, 1703–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Jeong, D.; Park, K.H.; Yu, J.-H.; Jung, S. Efficient Adsorption on Benzoyl and Stearoyl Cellulose to Remove Phenanthrene and Pyrene from Aqueous Solution. Polymers 2018, 10, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daltro, P.; Cerqueira, D.; Molina de Olyveira, G.; Basmaji, P.; Carlos, G. Hydrogel and bacterial cellulose mats behavior with calcium phosphate deposition. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2016, 4, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Chassary, P.; Vincent, T.; Sanchez Marcano, J.; Macaskie, L.E.; Guibal, E. Palladium and platinum recovery from bicomponent mixtures using chitosan derivatives. Hydrometallurgy 2005, 76, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, K.; Ramesh, A.; Maki, T.; Hasegawa, H.; Ueda, K. Adsorption of platinum (IV), palladium (II) and gold (III) from aqueous solutions onto l-lysine modified crosslinked chitosan resin. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 146, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodeiro, P.; Sillanpää, M. Gold recovery from artificial seawater using synthetic materials and seaweed biomass to induce gold nanoparticles formation in batch and column experiments. Mar. Chem. 2013, 152, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guibal, E.; Von Offenberg Sweeney, N.; Vincent, T.; Tobin, J.M. Sulfur derivatives of chitosan for palladium sorption. React. Funct. Polym. 2002, 50, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döker, S.; Malcı, S.; Doğan, M.; Salih, B. New poly(N-(hydroxymethyl)methacrylamide–1-allyl-2-thiourea) hydrogels prepared by radiation-induced polymerisation: Selective adsorption, recovery and pre-concentration of Pt(II) and Pd(II). Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 553, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.-W.; Liao, X.-P.; Liu, X.; Shi, B. Recovery of platinum(IV) and palladium(II) by bayberry tannin immobilized collagen fiber membrane from water solution. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 278, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavaklı, C.; Malcı, S.; Tuncel, S.A.; Salih, B. Selective adsorption and recovery of precious metal ions from geological samples by 1,5,9,13-tetrathiacyclohexadecane-3,11-diol anchored poly(p-CMS-DVB) microbeads. React. Funct. Polym. 2006, 66, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vences-Alvarez, E.; Razo-Flores, E.; Lázaro, I.; Briones-Gallardo, R.; Velasco-Martínez, G.; Rangel-Mendez, R. Gold recovery from very dilute solutions from a mine in closing process: Adsorption-desorption onto carbon materials. J. Mol. Liquids 2017, 240, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, H.S. THE ACTIVATION ENERGY of ADSORPTION PROCESSES. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1931, 53, 578–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tassist, A.; Lounici, H.; Abdi, N.; Mameri, N. Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies on aluminum biosorption by a mycelial biomass (Streptomyces rimosus). J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 183, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Bai, H.; Tarasov, V.V. Calixarene-functionalized graphene oxide composites for adsorption of neodymium ions from the aqueous phase. R. Soc. Chem. Adv. 2016, 6, 30384–30394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Pseudo-first-order | ||||
| Temperature (K) | qe,exp (mg g−1) | k1 (min−1) | qe,calc (mg g−1) | R2 |
| 298 | 2.60 | 0.0093 | 2.51 | 0.9055 |
| 308 | 3.01 | 0.0109 | 2.73 | 0.9106 |
| 318 | 3.30 | 0.0133 | 3.0 | 0.9275 |
| 328 | 3.57 | 0.0167 | 3.56 | 0.9771 |
| Pseudo-second-order | ||||
| Temperature (K) | qe,exp (mg g−1) | k2 (g mg−1·min−1) | qe,calc (mg g−1) | R2 |
| 298 | 2.60 | 0.32 | 2.01 | 0.9908 |
| 308 | 3.01 | 0.72 | 2.77 | 0.9905 |
| 318 | 3.30 | 1.77 | 3.41 | 0.9937 |
| 328 | 3.57 | 3.55 | 4.33 | 0.9955 |
| Intraparticle diffusion model (IPD) | ||||
| Temperature (K) | Kdiff (mg·g−1 min−1/2) | C | R2 | |
| 298 | 0.030 | 0.038 | 0.9057 | |
| 308 | 0.050 | 0.057 | 0.9000 | |
| 318 | 0.064 | 0.102 | 0.8663 | |
| 328 | 0.079 | 0.110 | 0.8864 | |
| ΔH0 (kJ/mol) | ΔS0 (J/mol·K) | ΔG0 (kJ/mol) | R2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24.00 | 69.6 | 298 K | 308 K | 318 K | 328K | 0.9969 |
| −20.7 | −21.4 | −22.1 | −22.8 | |||
| Langmuir isotherm | |||
| qm,exp (mg/g) | KL (L/mg) | qL (mg/g) | R2 |
| 12.2 | 0.0311 | 23.2 | 0.9715 |
| Freundlich isotherm | |||
| KF (mg/g) | 1/nF | R2 | |
| 1.26 | 0.48 | 0.9693 | |
| Sips isotherm | |||
| KS | qS (mg/g) | 1/nS | R2 |
| 0.03 | 16.9 | 0.23 | 0.9804 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Babău, T.; Ciopec, M.; Duteanu, N.; Negrea, A.; Negrea, P.; Nemeş, N.S.; Pascu, B.; Mihăilescu, M.; Ianasi, C. Synthesis of Some Eco-Friendly Materials for Gold Recovery. Polymers 2024, 16, 2512. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16172512
Babău T, Ciopec M, Duteanu N, Negrea A, Negrea P, Nemeş NS, Pascu B, Mihăilescu M, Ianasi C. Synthesis of Some Eco-Friendly Materials for Gold Recovery. Polymers. 2024; 16(17):2512. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16172512
Chicago/Turabian StyleBabău, Theodora, Mihaela Ciopec, Narcis Duteanu, Adina Negrea, Petru Negrea, Nicoleta Sorina Nemeş, Bogdan Pascu, Maria Mihăilescu, and Catalin Ianasi. 2024. "Synthesis of Some Eco-Friendly Materials for Gold Recovery" Polymers 16, no. 17: 2512. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16172512
APA StyleBabău, T., Ciopec, M., Duteanu, N., Negrea, A., Negrea, P., Nemeş, N. S., Pascu, B., Mihăilescu, M., & Ianasi, C. (2024). Synthesis of Some Eco-Friendly Materials for Gold Recovery. Polymers, 16(17), 2512. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16172512









